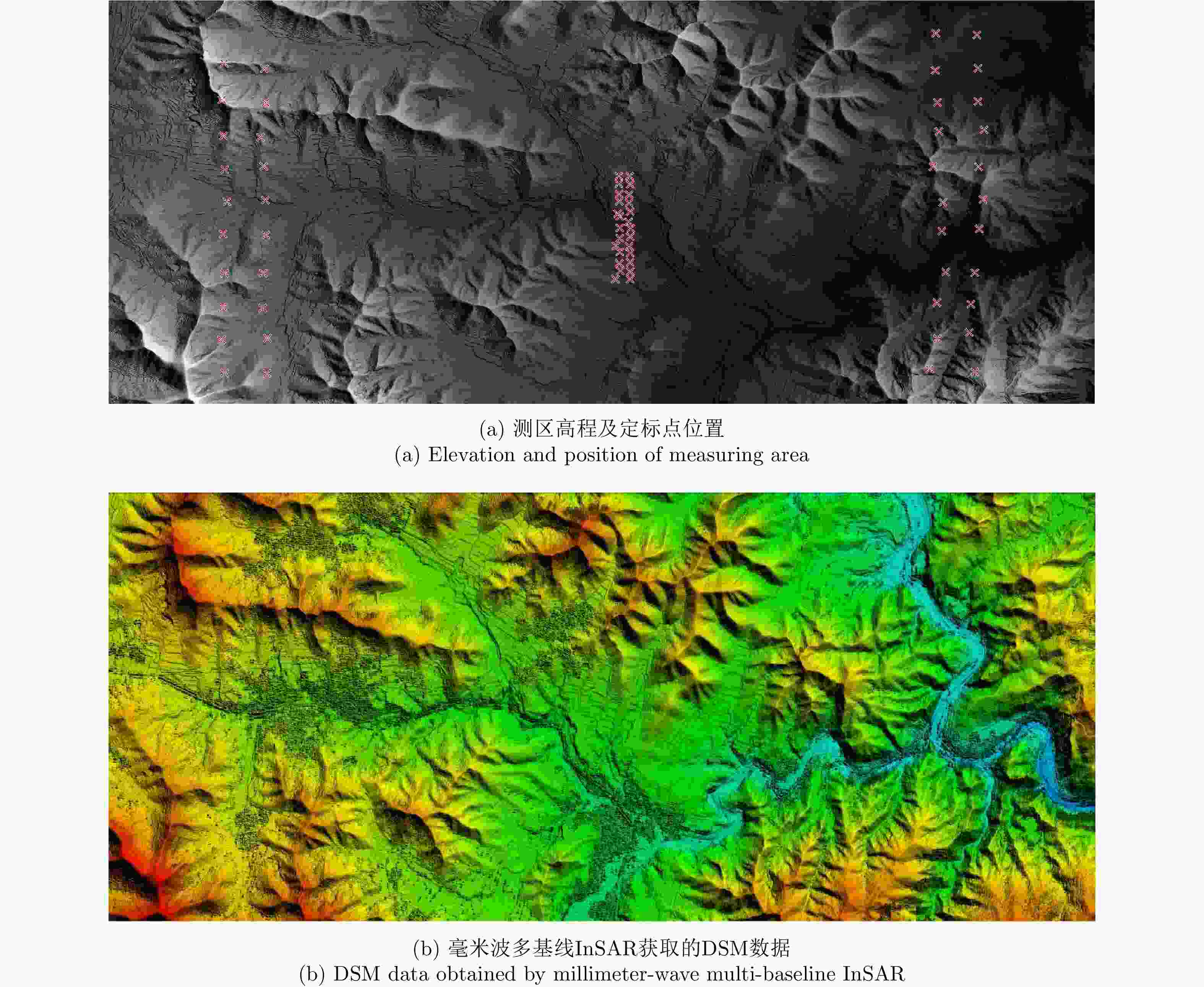
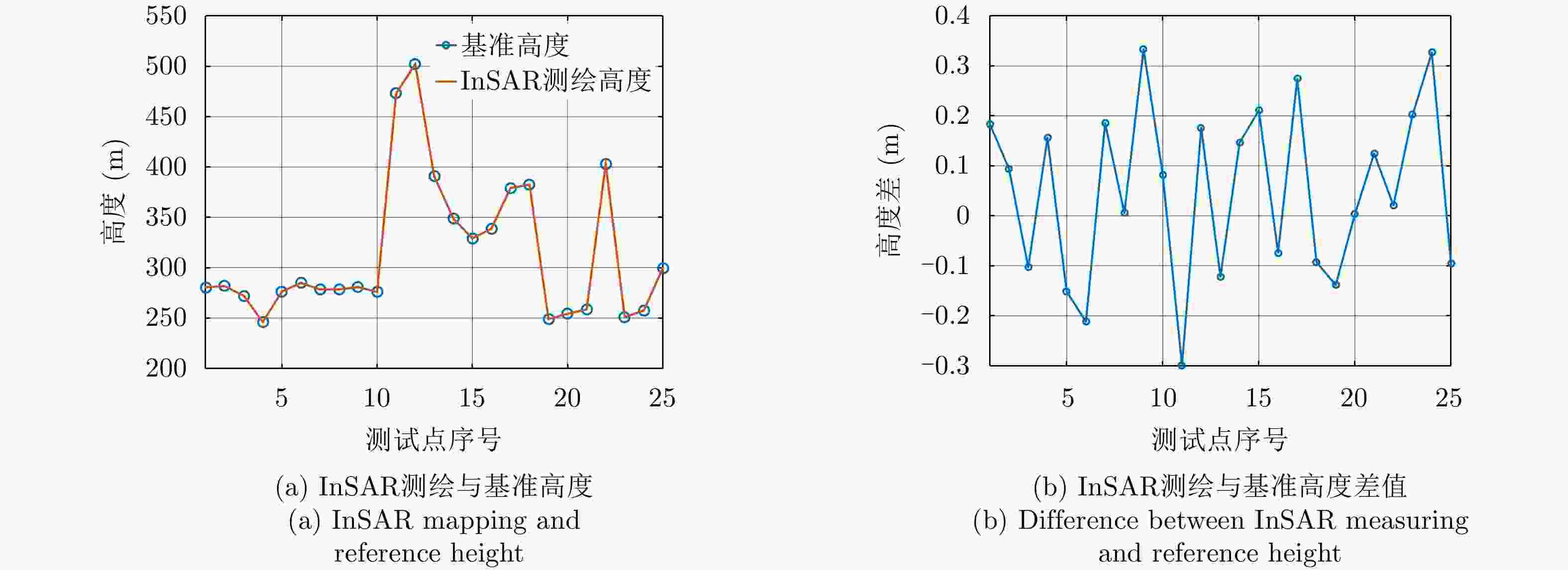
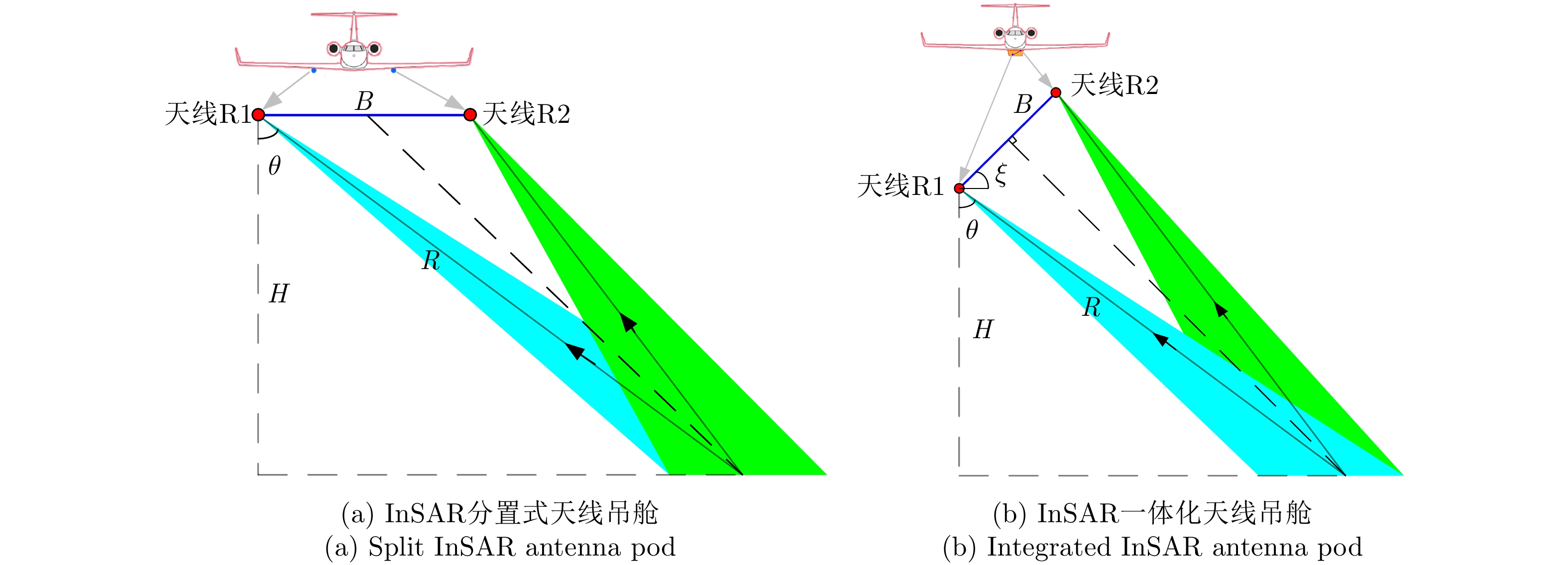
-
摘要:
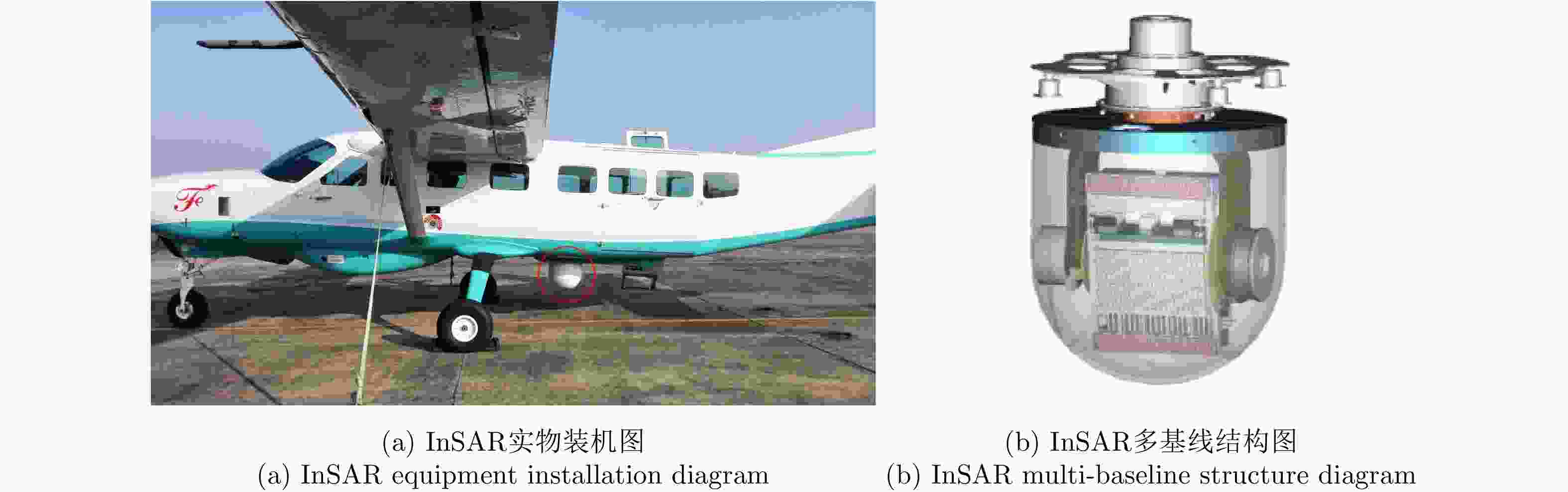
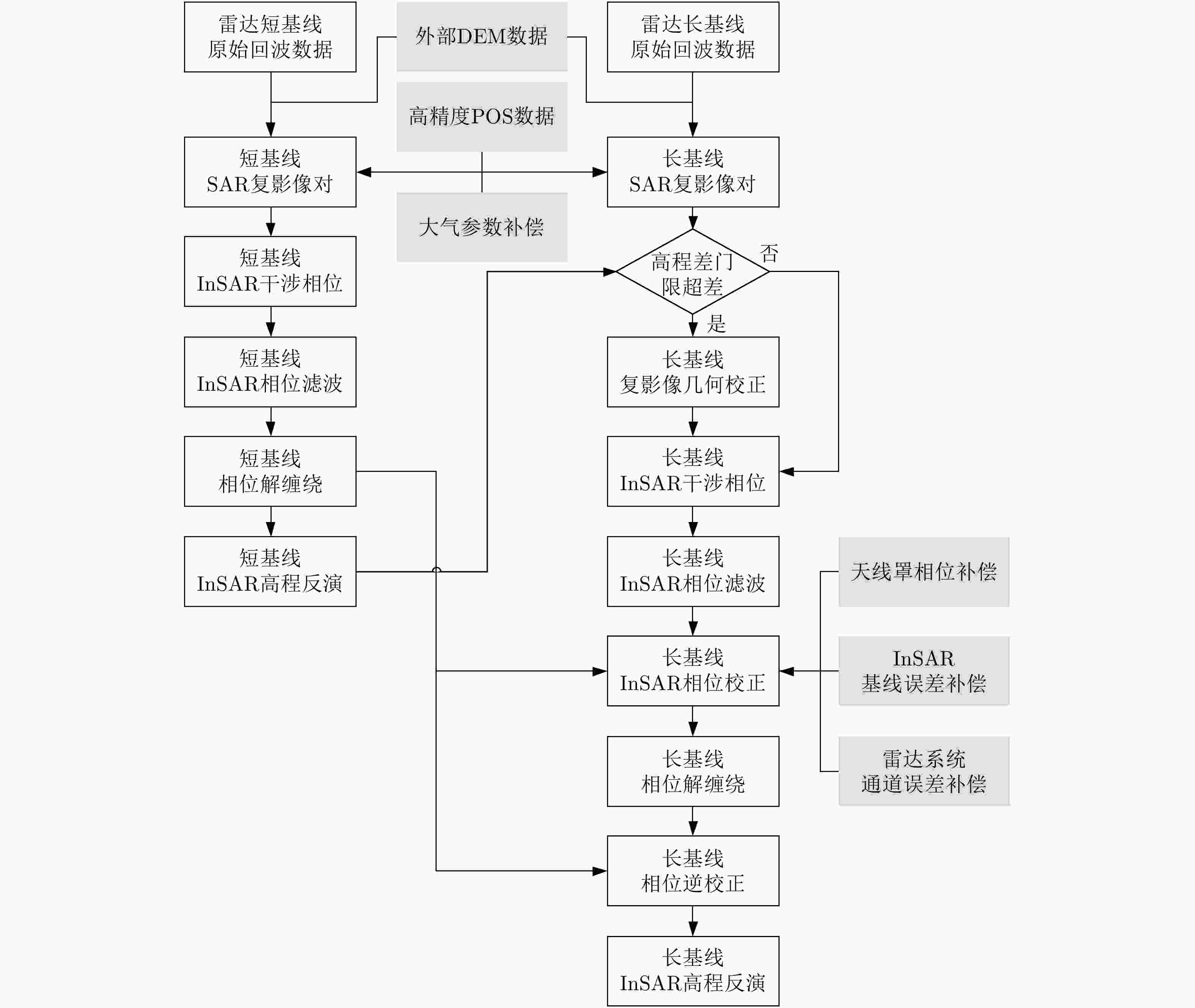
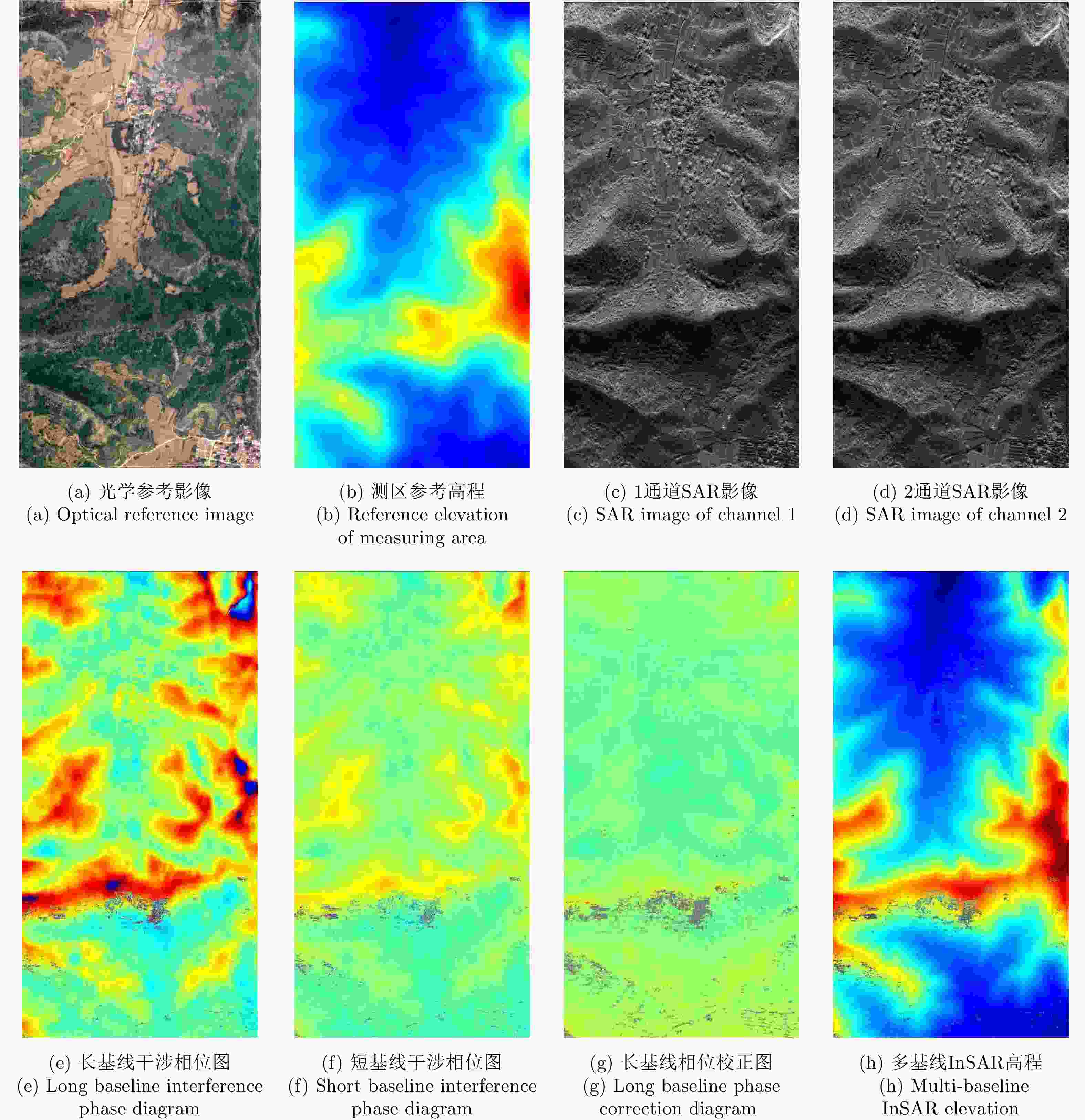
机载毫米波InSAR具备不受光照限制、测绘幅宽大、测绘精度高的特点,近年来随着其技术的不断发展和完善,逐渐成为一种被广泛关注的测绘手段。在针对小型飞行平台的高精度毫米波InSAR系统设计中,InSAR基线构型、多基线配置、外部数字高程模型(DEM)参考及InSAR处理流程是系统设计的核心。该文分析了机载毫米波InSAR系统中基线参数对干涉高程测量的影响,提出基于一体化天线吊舱的毫米波多基线InSAR系统设计思路,在此基础上提出基于时域成像算法的毫米波多基线InSAR测高处理流程。最后,实测数据实验验证了该文给出的机载毫米波多基线InSAR系统及其干涉数据处理方法在大比例尺测绘任务中的可行性和有效性。
Abstract:The characteristics of airborne millimeter-wave Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) include unrestricted light, large surveying width, and high mapping precision. In recent years, with the continuous development and improvement of the technology of airborne millimeter-wave InSAR, it has gradually become a widely used mapping method. The core of the system design of a high-precision millimeter-wave InSAR system designed for small aircraft platforms comprises InSAR baseline configuration, multi-baseline configuration, the external Digital Elevation Model (DEM), and InSAR processing flow. In this study, interferometric elevation measurements influenced by different baseline parameters of an airborne millimeter-wave InSAR system are analyzed. A design scheme of the millimeter-wave multi-baseline InSAR system based on integrated antenna pod is provided. Then, a time-domain imaging algorithm-based millimeter-wave multi-baseline InSAR elevation measurement process is proposed. Finally, real measured data experiments are used to illustrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed millimeter-wave multi-baseline InSAR system and the interference data processing method for large-scale mapping missions.
-
表 1 不同基线配置对InSAR高程测量精度影响对比
Table 1. Comparison of effects of different baseline configurations on InSAR elevation measurement accuracy
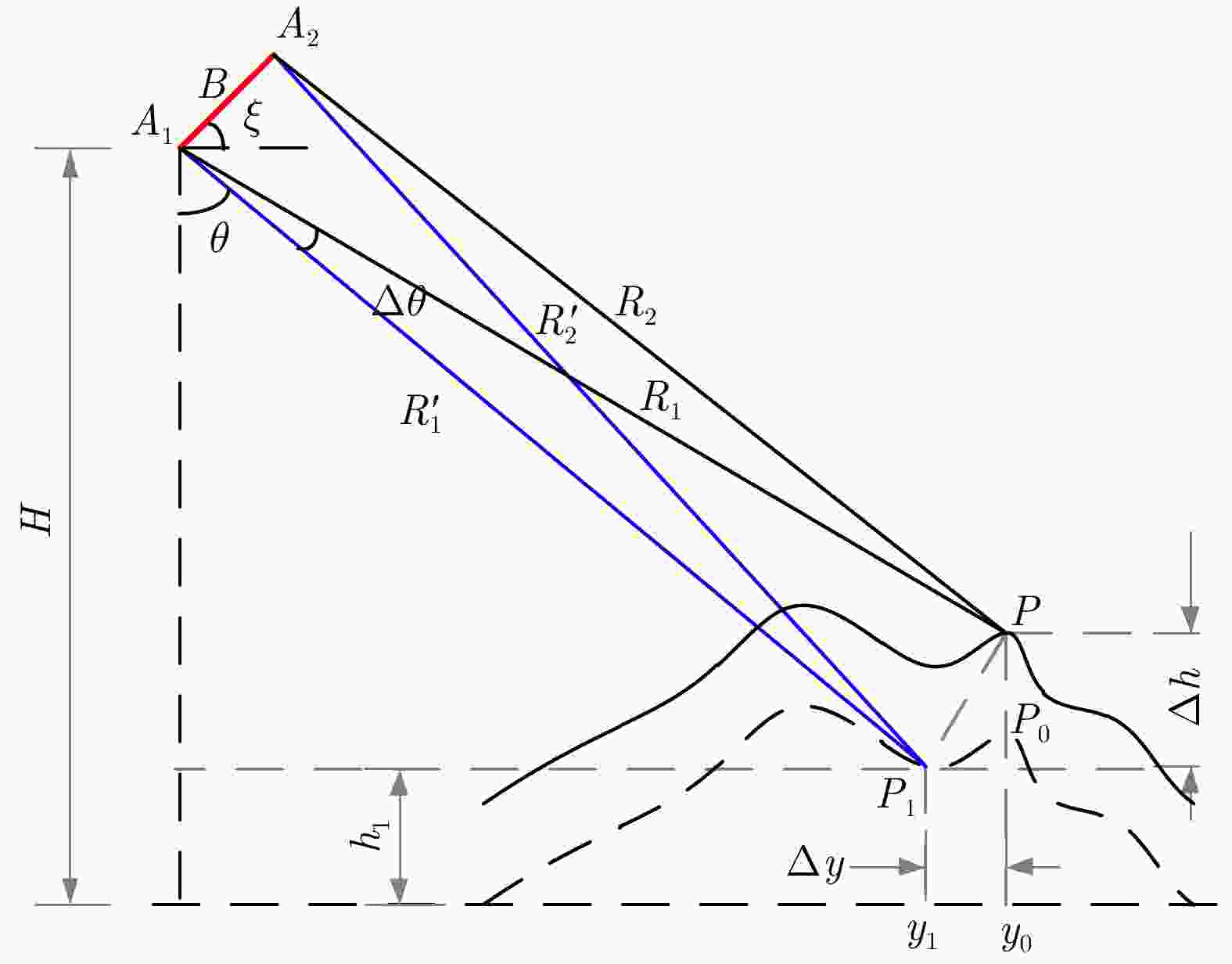
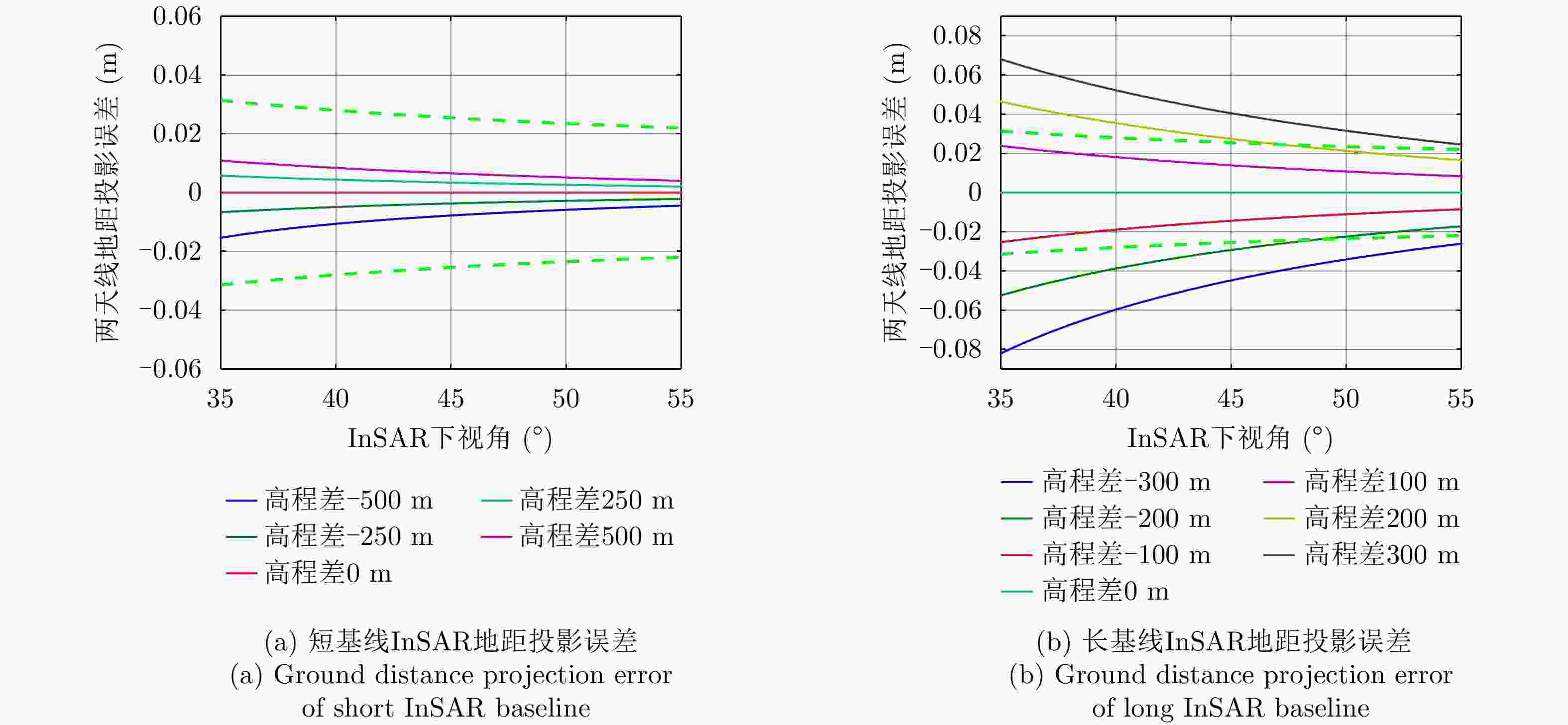
飞行高度(m) 基线误差(mm) 基线长度(m) 基线倾角(°) 下视角(°) 雷达斜距(km) 高程误差(m) 3000 0.1 1.8 45 30 3.46 0.03 45 4.24 0 60 6.00 0.08 0.3 45 30 3.46 0.15 45 4.24 0 60 6.00 0.46 表 2 InSAR不同基线长度对应的模糊高程
Table 2. Fuzzy elevation corresponding to different baseline lengths
基线长度(m) 下视角(°) 基线倾角(°) 雷达斜距(m) 模糊高程(m) 0.30 35 45 5200 61 0.30 55 45 8800 125 0.03 35 45 5200 611 0.03 55 45 8800 1247 表 3 毫米波多基线InSAR系统参数
Table 3. Parameters of millimeter-wave multi-baseline InSAR system
参数 数值 中心频率 35 GHz 长基线长度 0.31 m 短基线长度 0.03 m 基线倾角 45° 飞行高度 3000 m 信号带宽 900 MHz 雷达下视角 38°~52° 平均飞行速度 240 km/h -
[1] RODRIGUEZ E and MARTIN J M. Theory and design of interferometric synthetic aperture radars[J]. IEE Proceedings F Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(2): 147–159. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0018 [2] 钟雪莲, 向茂生, 郭华东, 等. 机载重轨干涉合成孔径雷达的发展[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(3): 367–381. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13005ZHONG Xuelian, XIANG Maosheng, GUO Huadong, et al. Current development in airborne repeat-pass interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(3): 367–381. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13005 [3] LI Huimin, WANG Yong, and LUO Xuelian. Tree height estimation at plateau mountains, northwestern Sichuan, China using dual Pol-InSAR data[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 4698–4701. DOI: 10.1109/igarss.2016.7730226. [4] ZHANG Yilong, MIAO Wei, LIN Zhenhui, et al. Millimeter-wave InSAR image reconstruction approach by total variation regularized matrix completion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1053. doi: 10.3390/rs10071053 [5] BRENNER A R and ROESSING L. Radar imaging of urban areas by means of very high-resolution SAR and interferometric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 2971–2982. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2008.920911 [6] VAN ZYL J J. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM): A breakthrough in remote sensing of topography[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2001, 48(5/12): 559–565. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(01)00020-0 [7] KRIEGER G, MOREIRA A, FIEDLER H, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3317–3341. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900693 [8] MOREIRA A, KRIEGER G, HAJNSEK I, et al. TanDEM-X: A TerraSAR-X add-on satellite for single-pass SAR interferometry[C]. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 1000–1003. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2004.1368578. [9] YAGUE-MARTINEZ N, PRATS-IRAOLA P, WOLLSTADT S, et al. The 2-look TOPS mode: Design and demonstration with TerraSAR-X[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 7682–7703. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2915797 [10] KRAUS T, KRIEGER G, BACHMANN M, et al. Spaceborne demonstration of distributed SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(11): 1731–1735. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2019.2907371 [11] GONZALEZ J H, BACHMANN M, KRIEGER G, et al. Development of the TanDEM-X calibration concept: Analysis of systematic errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 716–726. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2009.2034980 [12] LEE S K, FATOYINBO T E, LAGOMASINO D, et al. Multibaseline TanDEM-X mangrove height estimation: The selection of the vertical wavenumber[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(10): 3434–3442. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2018.2835647 [13] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [14] SAUER S, FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, et al. Polarimetric dual-baseline InSAR building height estimation at L-band[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 408–412. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2009.2014571 [15] LIANG Cunren, LIU Zhen, FIELDING E J, et al. InSAR time series analysis of L-band wide-swath SAR data acquired by ALOS-2[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4492–4506. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2018.2821150 [16] BRENNER A R and ENDER J H G. Demonstration of advanced reconnaissance techniques with the airborne SAR/GMTI sensor PAMIR[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 152–162. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20050044 [17] LAZECKY M, HLAVACOVA I, BAKON M, et al. Bridge displacements monitoring using space-borne X-Band SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(1): 205–210. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2016.2587778 [18] MALLIOT H A. DTEMS interferometric SAR design and method of baseline tilt determination[C]. 1996 IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference. Proceedings, Aspen, USA, 1996: 107–127. DOI: 10.1109/aero.1996.499406. [19] XIANG Maosheng, WU Yirong, LI Shaoen, et al. Introduction on an experimental airborne InSAR system[C]. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, South Korea, 2005: 4809-4812. DOI: 10.1109/igarss.2005.1526749. [20] MAGNARD C, FRIOUD M, SMALL D, et al. Processing of MEMPHIS Ka-band multibaseline interferometric SAR data: From raw data to digital surface models[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(7): 2927–2941. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2014.2315896 [21] OUCHI K, YOSHIDA T, and YANG Chansu. A theory of multiaperture along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1565–1569. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2019.2906104 [22] 陈国忠, 赵迪, 王晓鹏, 等. 干涉SAR多基线分析与设计[J]. 上海航天, 2016, 33(6): 26–30.CHEN Guozhong, ZHAO Di, WANG Xiaopeng, et al. Multi-baseline analysis and design of interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2016, 33(6): 26–30. [23] MAGNARD C, FRIOUD M, SMALL D, et al. Analysis of a maximum likelihood phase estimation method for airborne multibaseline SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1072–1085. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2015.2487685 [24] FERRAIUOLO G, MEGLIO F, PASCAZIO V, et al. DEM reconstruction accuracy in multichannel SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 191–201. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2008.2002644 [25] 匡辉, 杨威, 王鹏波, 等. 多方位角多基线星载SAR三维成像方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 685–695. doi: 10.12000/JR18073KUANG Hui, YANG Wei, WANG Pengbo, et al. Three-dimensional imaging algorithm for multi-azimuth-angle multi-baseline spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 685–695. doi: 10.12000/JR18073 [26] 潘舟浩, 刘波, 张清娟, 等. 三基线毫米波InSAR的相位解缠及高程反演[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2013, 32(5): 474–480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00474PAN Zhouhao, LIU Bo, ZHANG Qingjuan, et al. Millimeter-wave InSAR phase unwrapping and DEM reconstruction based on three-baseline[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2013, 32(5): 474–480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00474 [27] 潘舟浩, 李道京, 刘波, 等. 基于BP算法和时变基线的机载InSAR数据处理方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(7): 1585–1591. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00715PAN Zhouhao, LI Daojing, LIU Bo, et al. Processing of the airborne InSAR data based on the BP algorithm and the time-varying baseline[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(7): 1585–1591. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00715 [28] DOERRY A W and BICKEL D L. A comparison of interferometric SAR antenna options[C]. The SPIE: Radar Sensor Technology XVII, Baltimore, USA, 2013: 87141F. DOI: 10.1117/12.2015325. [29] 李浩林, 陈露露, 张磊, 等. 快速分解后向投影SAR成像的自聚焦算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 938–945. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00011LI Haolin, CHEN Lulu, ZHANG Lei, et al. Study of autofocus method for SAR imagery created by fast factorized backprojection[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 938–945. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00011 [30] XIE Pengfei, ZHANG Man, ZHANG Lei, et al. Residual motion error correction with backprojection multisquint algorithm for airborne synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19: 2342. doi: 10.3390/s19102342 [31] ROGAN A and CARANDE R. InSAR processing using a GPGPU[C]. SPIE: Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVIII, Orlando, USA, 2011: 80510O. DOI: 10.1117/12.889917. [32] MENG Dadi, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. Precise focusing of airborne SAR data with wide apertures large trajectory deviations: A chirp modulated back-projection approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5): 2510–2519. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2361134 [33] WEI Shunjun, GUO Liwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, et al. Millimeter-wave interferometric synthetic aperture radar imaging via ground projection[C]. 2014 IEEE 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2014: 334–339. DOI: 10.1109/cse.2014.89. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: