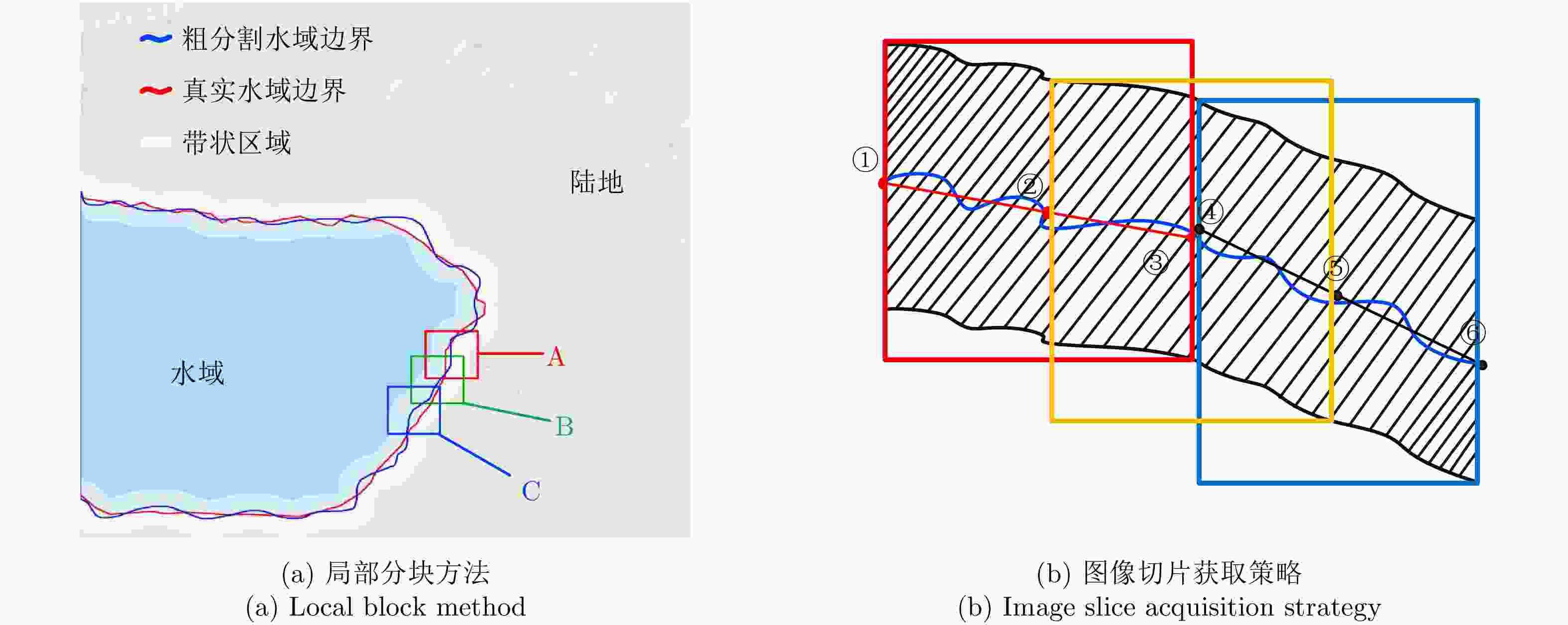
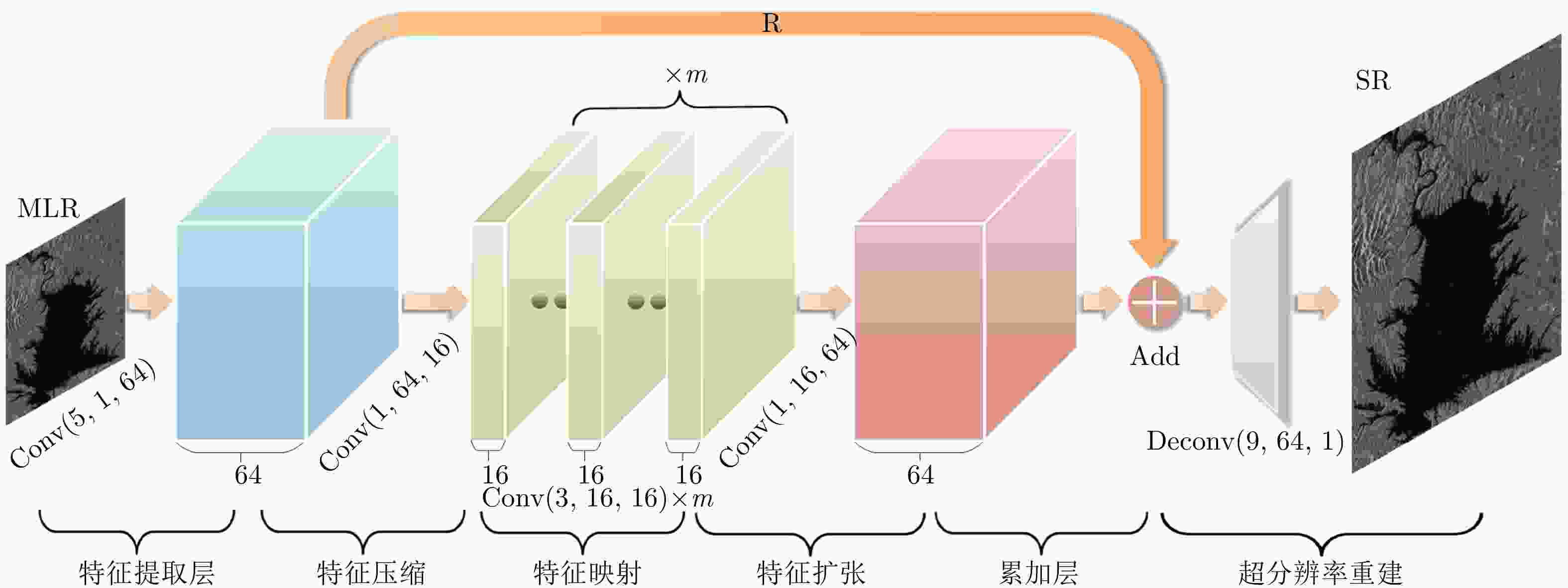
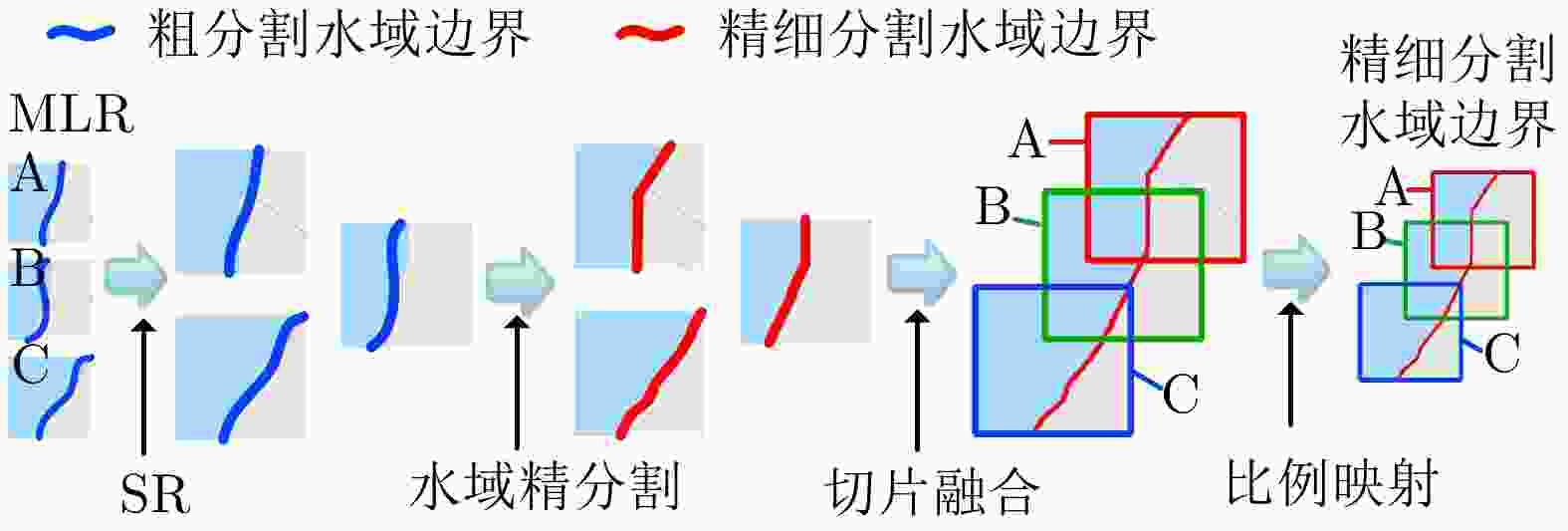
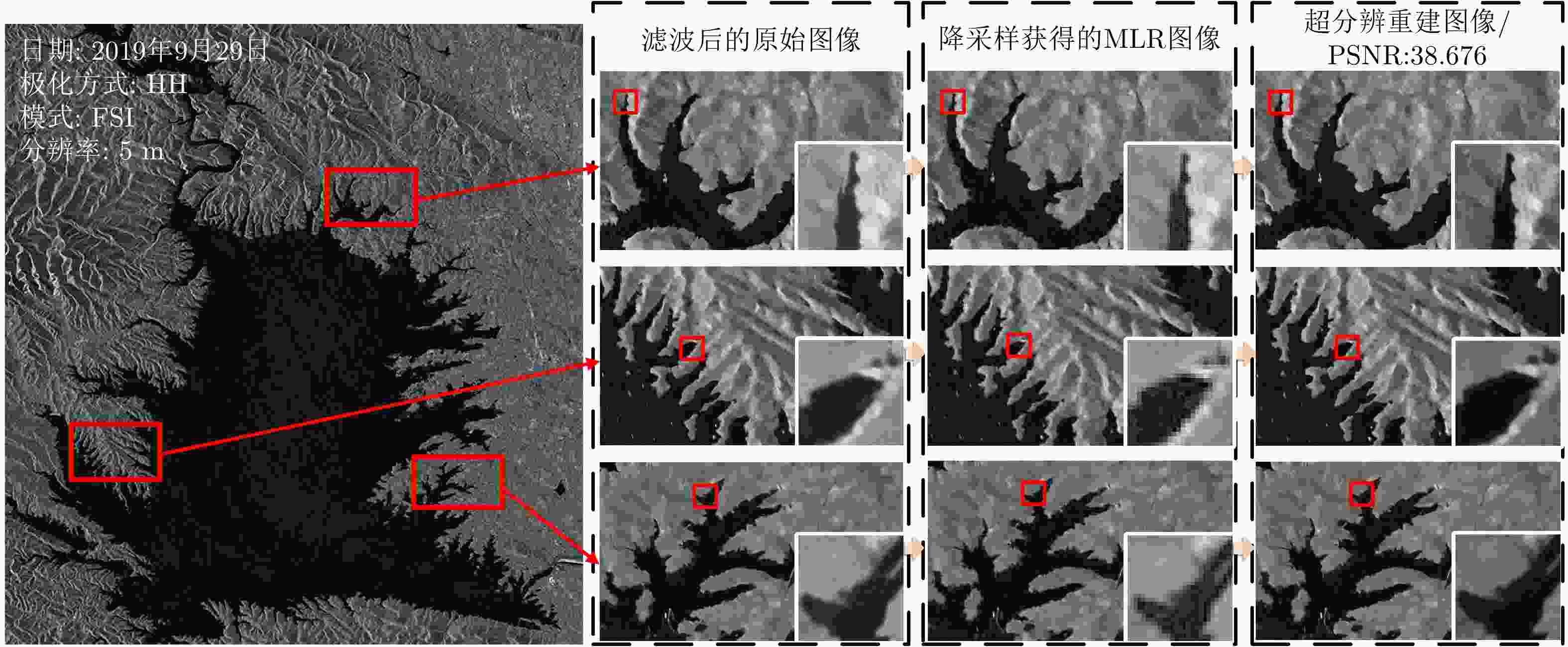
High-precision Water Segmentation from Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Based on Local Super-resolution Restoration Technology
-
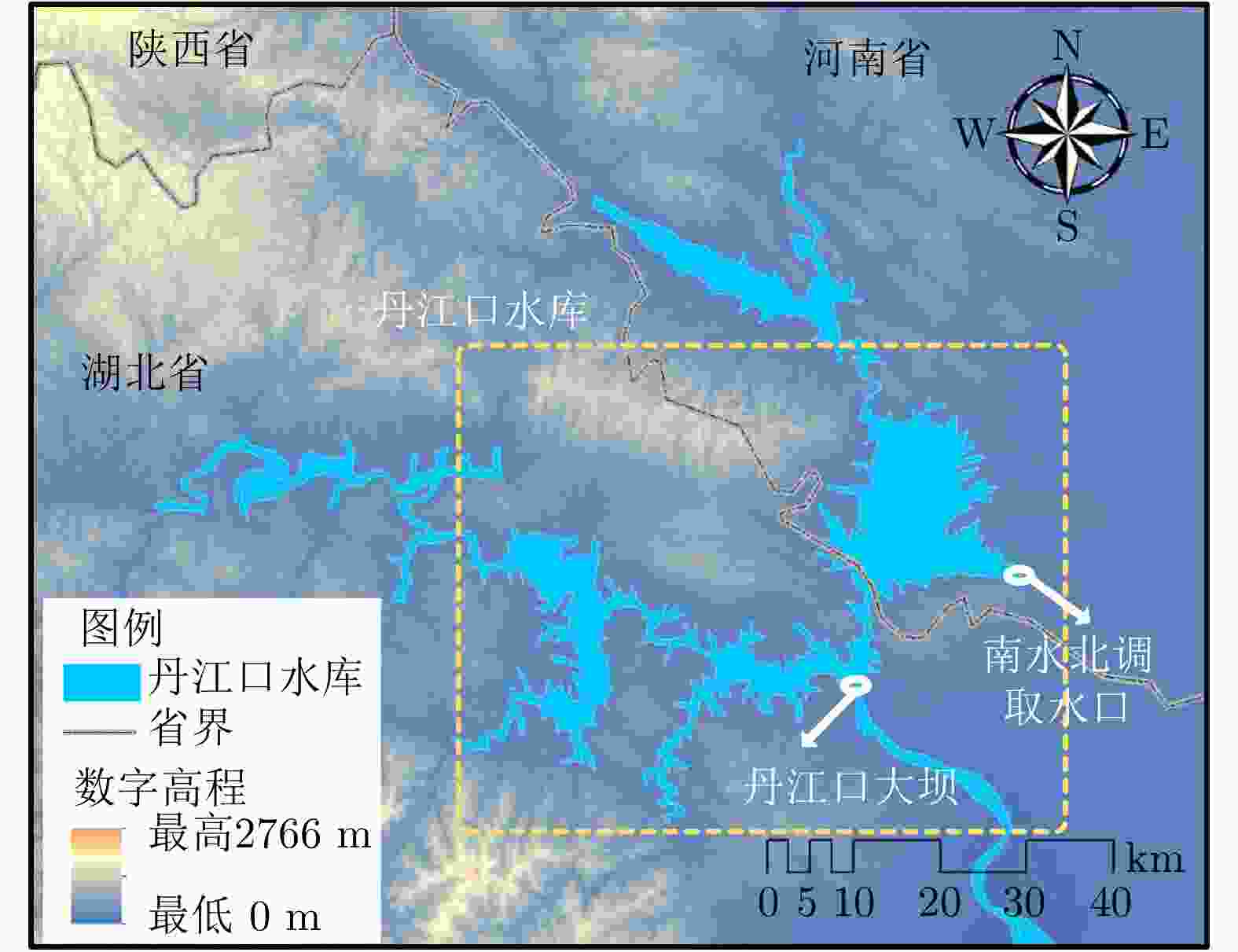
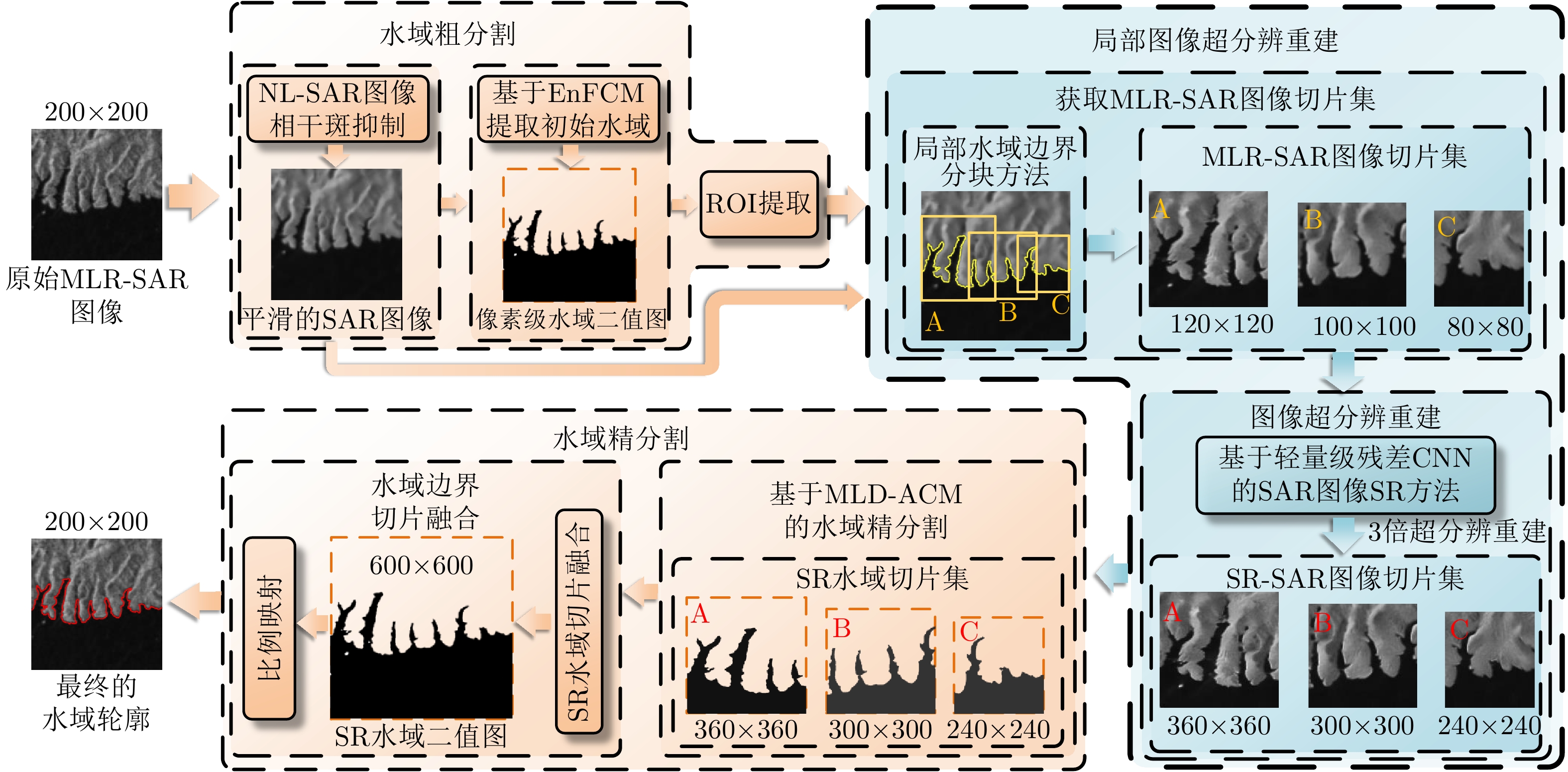
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像水域分割在水资源调查、灾害监测等领域具有重要意义。针对中低分辨率星载SAR图像水域提取精度不足的难题,该文融合基于轻量级残差卷积神经网络(CNN)的图像超分辨率重建技术和传统SAR图像水域分割技术的优点,提出了一种基于局部超分辨重建的SAR图像水域分割方法,显著提升了SAR图像水域分割的精度。为了验证上述方法的有效性,该文以南水北调中线工程水源地丹江口水库为应用对象,基于国产高分三号(GF-3)卫星的8 m分辨率标准条带(SS)模式图像和欧空局Sentinel-1卫星20 m分辨率干涉宽幅(IW)模式图像,开展了水域分割的实验验证和精度评估工作。实验结果表明,该文所提方法可在中低分辨率SAR图像中获取更精确的水域分割结果,其水域分割性能较传统方法有大幅提升。Abstract: The extraction of water from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is of great significance in water resources investigation and monitoring disasters. To deal with the problems of the insufficient accuracy of water boundaries extracted from middle-low resolution SAR images. This paper proposes a high-precision water boundaries extraction method based on a local super-resolution restoration technology that combines the advantages of the super-resolution restoration technology based on the lightweight residual Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and the traditional SAR images water extraction methods. The proposed method can significantly improve the accuracy of water segmentation results by using SAR images. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, as a study area, we selected the Danjiangkou Reservoir, the water source of the middle route of a south-to-north water diversion project. Further, we conducted experiments on the multi-mode SAR dataset and evaluated its accuracy. This dataset included one Standard Strip-map (SS) mode image obtained by the Chinese GaoFen-3 (GF-3) satellite with a resolution of 8 m and one Interferometric Wide-swath (IW) mode SAR image obtained by Sentinel-1 satellite with a resolution of 20 m. The experimental results showed that the water segmentation results from the middle–low resolution SAR images of the proposed method were more precise, and the overall water segmentation performance was superior to that of the traditional methods.
-
表 1 LRSR网络卷积与反卷积参数设置
Table 1. Convolution and deconvolution parameters of the LRSR
数据处理层[卷积数目:深度× (${I_i}$×${O_i}$),
卷积核大小:(${F_i}$×${F_i}$)]padding stride 特征提取层 [(1×64), (5×5)] 0 1 特征压缩层 [(64×16), (1×1)] 0 1 特征映射层 [m×(16×16), (3×3)] 1 1 特征扩张层 [(1×64), (1×1)] 0 1 超分辨重建层 [(64×1), (9×9)] 4 k 表 2 LRSR网络训练参数
Table 2. Convolution and deconvolution parameters of the LRSR
卷积学
习率卷积偏置
学习率反卷积
学习率反卷积偏置
学习率权值衰减 最大迭代
次数10–3 10–4 10–4 2 × 10–4 10–4 10–7 表 3 LRSR网络MSE损失训练结果
Table 3. LRSR training results of MSE loss
k m 4 5 6 7 8 2 0.01767 0.01725 0.01754 0.01847 0.01894 3 0.09077 0.08939 0.08856 0.08866 0.08978 4 0.25842 0.25220 0.25034 0.25639 0.25464 表 4 实验使用的SAR图像详细参数
Table 4. Detailed parameters of experimental SAR data
SAR图像1 SAR图像2 卫星 Sentinel-1 GF-3 成像模式 干涉宽测绘带(Interferometric Wide-swath, IW) 标准条带 (Stand Stripmap, SS) 成像日期 2019年2月8日 2017年7月14日 标称分辨率 20 m 8 m 图像尺寸 3824×2255像素 7428×5221像素 极化方式 VV HH 表 5 对比试验方法
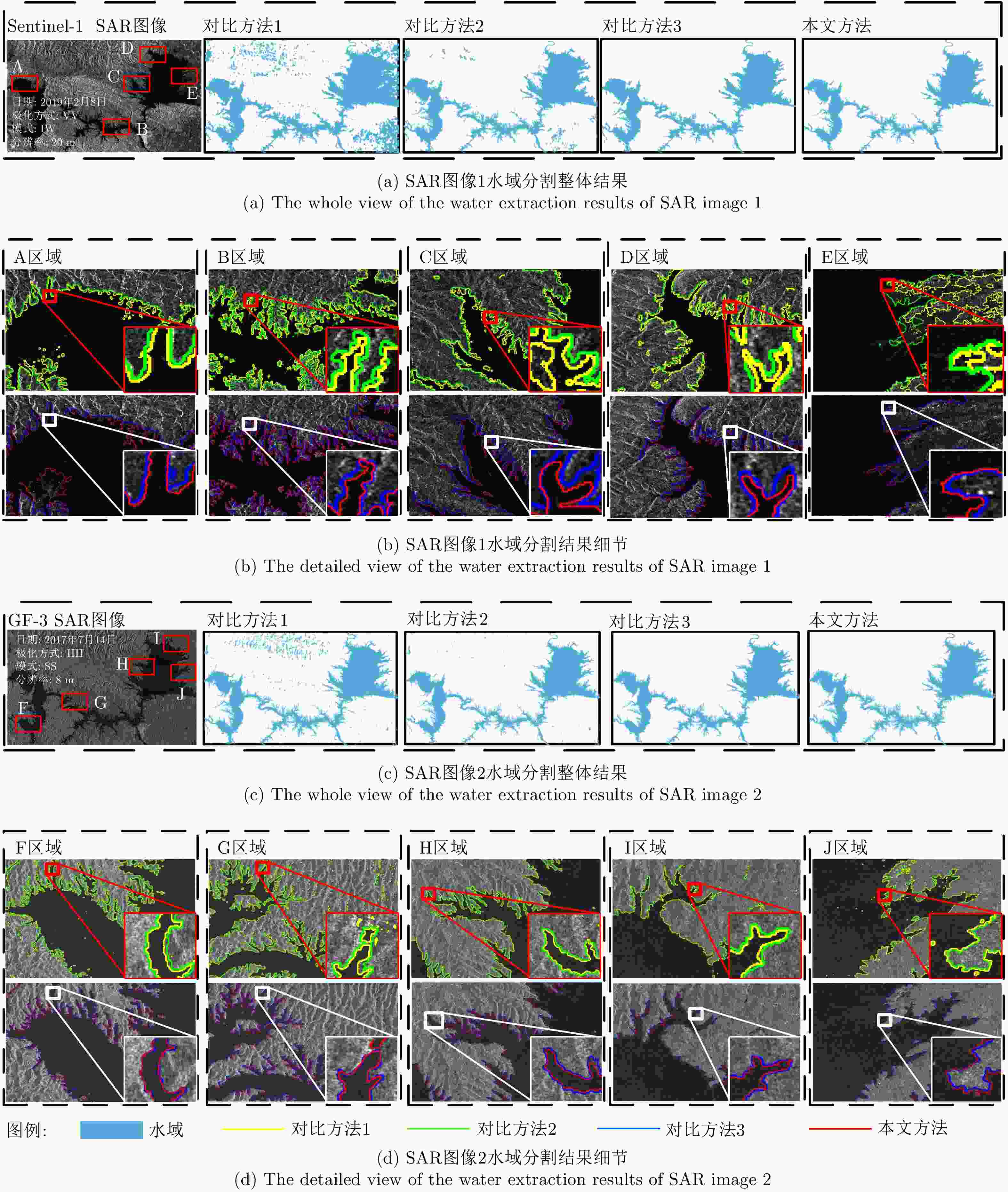
Table 5. Comparison test methods
对比方法 方法详情 方法1 水域粗分割(FCM聚类)+ACM精细分割 方法2 水域粗分割(相干斑滤波+FCM聚类+ROI提取)+ACM精细分割 方法3 水域粗分割(相干斑滤波+FCM聚类+ROI提取)+水域边界局部分块法+ACM精细分割 本文方法 水域粗分割(相干斑滤波+FCM聚类+ROI提取)+水域边界局部分块法+图像超分辨重建+ACM精细分割 表 6 定量分析结果
Table 6. Results of quantitative analysis
SAR图像编号 对比方法1 对比方法2 对比方法3 本文方法 虚警率(%) 准确率(%) 轮廓平均偏
移像素(个)虚警率(%) 准确率(%) 轮廓平均偏移
像素(个)虚警率(%) 准确率(%) 轮廓平均偏移
像素(个)虚警率(%) 准确率(%) 轮廓平均偏
移像素(个)1 20.43 85.23 2.1714 10.59 91.06 1.5411 0.68 98.69 0.7957 0.014 99.65 0.1543 2 9.27 90.15 1.6228 3.28 92.43 1.3652 0.91 98.83 0.7468 0.034 99.72 0.1403 -
[1] 牛世林, 郭拯危, 李宁, 等. 星载SAR水域分割研究进展与趋势分析[J]. 聊城大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 118(2): 75–89.NIU Shilin, GUO Zhengwei, LI Ning, et al. Research progress and trend analysis of water extraction by spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Liaocheng University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 118(2): 75–89. [2] LI Ning, NIU Shilin, GUO Zhengwei, et al. Dynamic waterline mapping of inland great lakes using time-series SAR data from GF-3 and S-1A satellites: A case study of DJK reservoir, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(11): 4297–4314. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2952902 [3] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [4] GUO Yaru and ZHANG Jixian. A new 2D OTSU for water extraction from SAR image[J]. ISPRS - International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2017, XLII-2/W7: 733–736. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-2-W7-733-2017 [5] LI Ning, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Waterline mapping and change detection of Tangjiashan dammed lake after Wenchuan earthquake from multitemporal high-resolution airborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(8): 3200–3209. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2345417 [6] 冷英, 刘忠玲, 张衡, 等. 一种改进的ACM算法及其在鄱阳湖水域监测中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1064–1070. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160870LENG Ying, LIU Zhongling, ZHANG Heng, et al. Improved ACM algorithm for Poyang lake monitoring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1064–1070. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160870 [7] 冷英, 李宁. 一种改进的变化检测方法及其在洪水监测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139LENG Ying and LI Ning. Improved change detection method for flood monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139 [8] 张金松, 邢孟道, 孙光才. 一种基于密集深度分离卷积的SAR图像水域分割算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 400–412. doi: 10.12000/JR19008ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and SUN Guangcai. A water segmentation algorithm for SAR image based on dense depthwise separable convolution[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 400–412. doi: 10.12000/JR19008 [9] SZILAGYI L, BENYÓ Z, SZILAGYI S M, et al. MR brain image segmentation using an enhanced fuzzy C-means algorithm[C]. The 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 2015, 1: 724–726. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2003.1279866. [10] CHEN Jiaqi, WANG Qingwei, WANG Jian, et al. Change detection of water index in danjiangkou reservoir using mixed log-normal distribution based active contour model[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 95430–95442. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929178 [11] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [12] DONG Chao, LOY C C, and TANG Xiaoou. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV’16), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 391–407. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_25. [13] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’16), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646–1654. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.182. [14] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.19. [15] LIM B, SON S H, KIM H W, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1132–1140. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.151. [16] FENG Hongxiao, HOU Biao, and GONG Maoguo. SAR Image despeckling based on local homogeneous-region segmentation by using pixel-relativity measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(7): 2724–2737. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2107915 [17] ZEILER M D and FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 818–833. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53. [18] 郭玥秀, 杨伟, 刘琦, 等. 残差网络研究综述[J/OL]. 计算机应用研究: 1–8. http://kreader.cnki.net/Kreader/CatalogViewPage.aspx?dbCode=CJFQ&filename=JSYJ20190606001&tablename=CAPJLAST&compose=&first=1&uid=, 2019.GUO Yuexiu, YANG Wei, LIU Qi, et al. Survey of residual network[J/OL]. Application Research of Computers: 1–8. http://kreader.cnki.net/Kreader/CatalogViewPage.aspx?dbCode=CJFQ&filename=JSYJ20190606001&tablename=CAPJLAST&compose=&first=1&uid=, 2019. [19] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xingyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.123. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: