-
摘要:
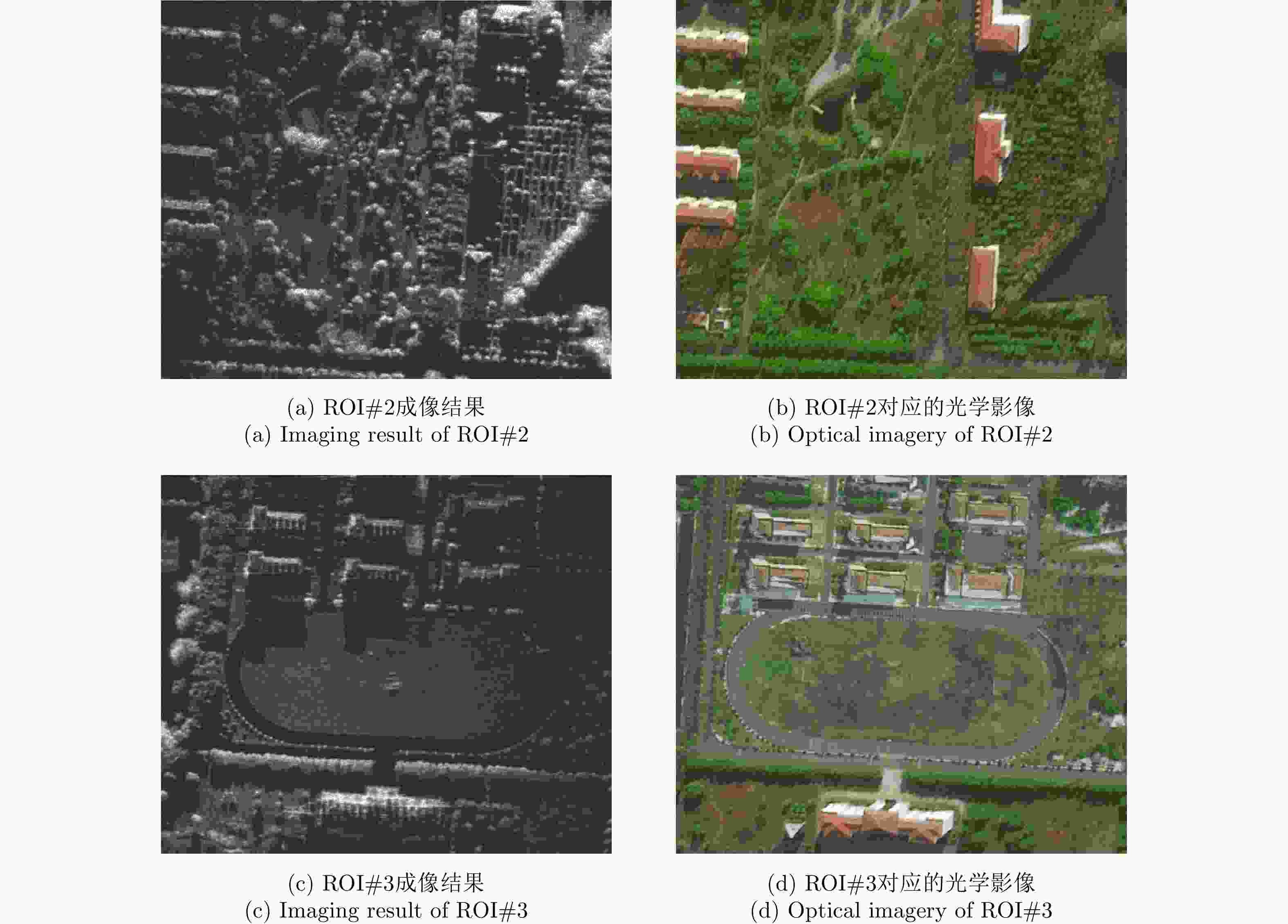
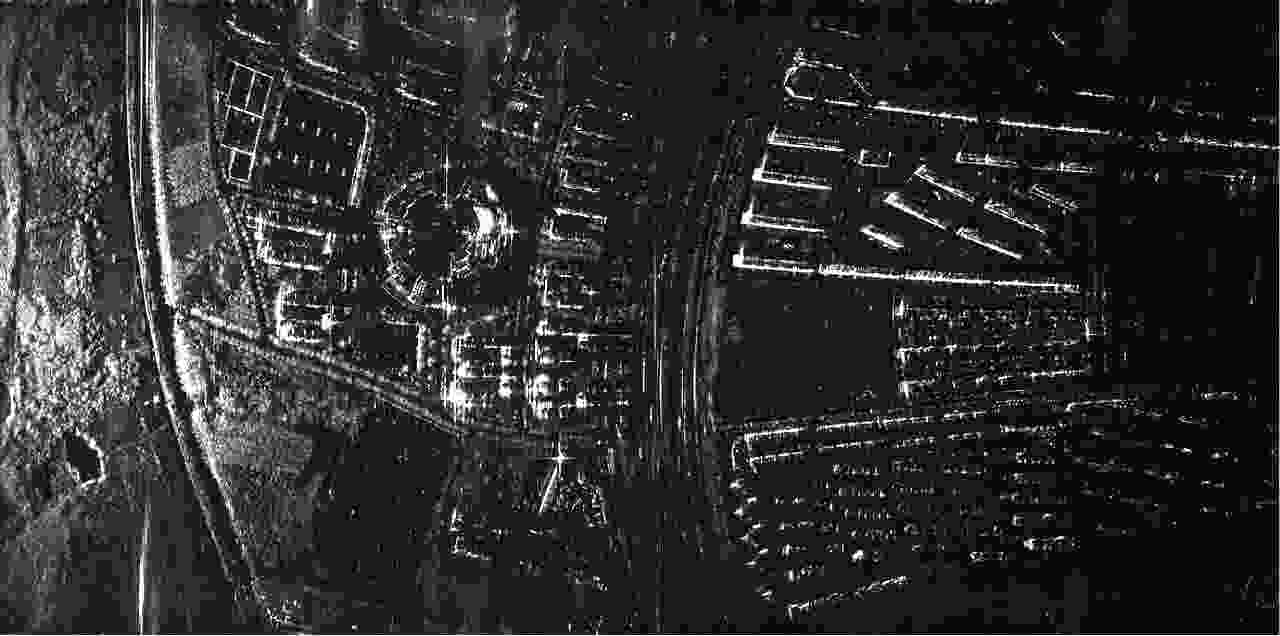
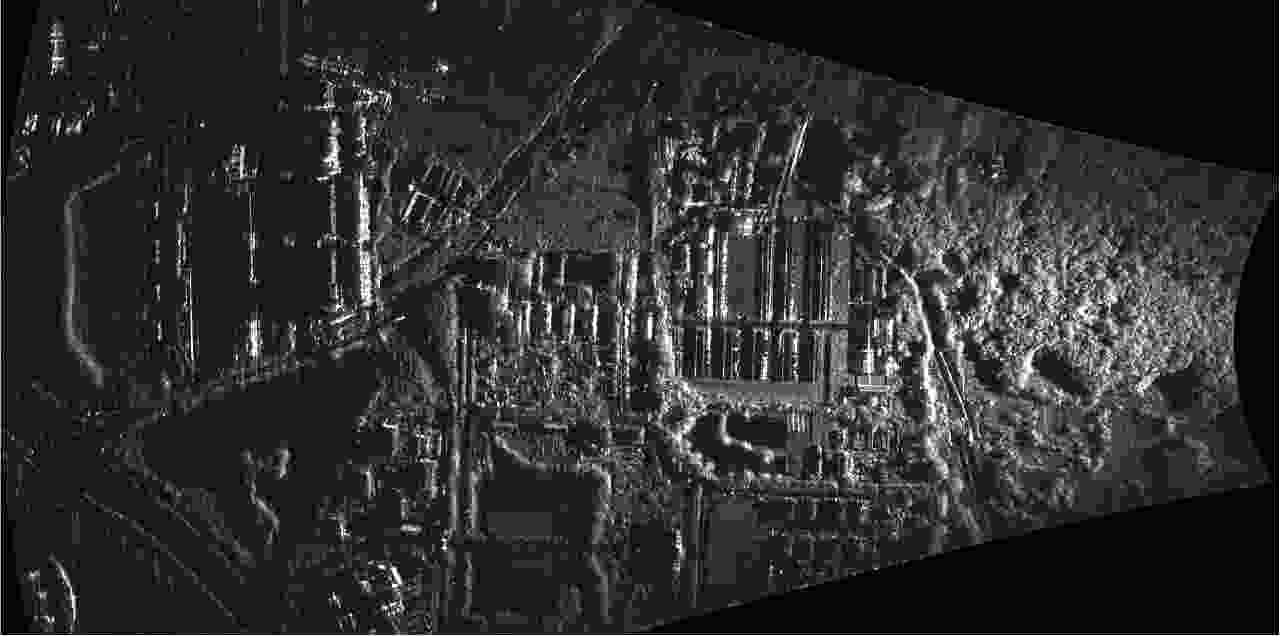
微型合成孔径雷达(MiniSAR)有效突破了时间与空间的限制,具备轻量化、低功耗、高灵活度等优势,能够满足感兴趣区域(ROI)的高分辨成像需求。然而,MiniSAR成像信号处理依然面临若干技术难题,例如复杂航迹条件下对地面目标的高分辨成像,非合作动目标的重聚焦,数据处理的效率与实时性等。据此,该文提出了一系列成像信号处理技术及其对应的现场可编辑门阵列(FPGA)硬件设计架构,从而实现了MiniSAR高分辨率成像与实时性处理。最后,基于多组聚束/条带式MiniSAR试验结果,验证了该文方法的有效性和可靠性。
Abstract:Miniature Synthetic Aperture Radar (MiniSAR) has been making breakthroughs to effectively overcome the limitations of time and space, and has exhibited superiority with respect to light weight and low-power consumption as well as high flexibility to achieve high-resolution imaging for the Region Of Interest (ROI). However, imaging signal processing for MiniSAR systems still face several technical challenges such as high-resolution imaging of ground targets under complicated trajectories, refocusing of non-cooperative moving targets, and efficient and real-time processing of echo data. In this paper, a series of imaging signal processing and associated hardware designs using Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) architecture have been proposed to realize MiniSAR ultra-high-resolution imaging and real-time processing. Additionally, experimental results utilizing considerable spotlight and stripmap MiniSAR data have been presented to demonstrate the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed technology.
-
表 1 资源利用率
Table 1. Resource utilization
资源 已用资源 可用资源 利用率(%) Slice Registers 355480 866400 41 Slice LUTs 273549 433200 63 Block RAM/FIFO 501 1470 34 DSP48E1s 1204 3600 33 表 2 主要的系统参数
Table 2. Main system parameters
系统参数 数值 带宽(GHz) 1.8 载频(GHz) 9.7 飞行速度(m/s) 5 脉冲宽度(ms) 4 数据采样率(MHz) 50 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 250 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] ZHANG Ying and ZHU Daiyin. Height retrieval in postprocessing-based VideoSAR image sequence using shadow information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(19): 8108–8116. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2865112 [3] 王岩飞, 刘畅, 詹学丽, 等. 无人机载合成孔径雷达系统技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089WANG Yanfei, LIU Chang, ZHAN Xueli, et al. Technology and applications of UAV synthetic aperture radar system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 333–349. doi: 10.12000/JR16089 [4] 丁满来, 丁赤飚, 唐跞, 等. 一种W波段无人机微型SAR系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 1939–1945. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180946DING Manlai, DING Chibiao, TANG Li, et al. A W band Mini-SAR system for unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 1939–1945. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180946 [5] ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, ZHAO Lifan, et al. Quasi-polar-based FFBP algorithm for miniature UAV SAR imaging without navigational data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7053–7065. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2739133 [6] CASALINI E, FRIOUD M, SMALL D, et al. Refocusing FMCW SAR moving target data in the wavenumber domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3436–3449. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2884830 [7] ZHAO Lifan, WANG Lu, BI Guoan, et al. An autofocus technique for high-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6392–6403. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2296497 [8] VEHMAS R, JYLHÄ J, VÄILÄ M, et al. Data-driven motion compensation techniques for noncooperative ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 295–314. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756518 [9] ZHU Daiyin, YE Shaohua, and ZHU Zhaoda. Polar format agorithm using chirp scaling for spotlight SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(4): 1433–1448. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4667720 [10] MARTORELLA M, GIUSTI E, BERIZZI F, et al. ISAR based techniques for refocusing non-cooperative targets in SAR images[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 332–340. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0310 [11] ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562 [12] 俞翔, 朱岱寅. 一种改进型全局最小熵ISAR距离对准算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2012, 27(5): 535–540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.05.003YU Xiang and ZHU Daiyin. Improved global minimum entropy range alignment algorithm for ISAR[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2012, 27(5): 535–540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.05.003 [13] ZHU Daiyin, JIANG Rui, MAO Xinhua, et al. Multi-subaperture PGA for SAR autofocusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 468–488. doi: 10.1109/taes.2013.6404115 [14] 郭江哲, 朱岱寅, 毛新华. 一种SAR两维自聚焦算法的FPGA实现[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 444–452. doi: 10.12000/JR15092GUO Jiangzhe, ZHU Daiyin, and MAO Xinhua. FPGA implementation of a SAR two-dimensional autofocus approach[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 444–452. doi: 10.12000/JR15092 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: