Synthetic Aperture Radar Three-dimensional Imaging——From TomoSAR and Array InSAR to Microwave Vision(in English)
-
摘要:
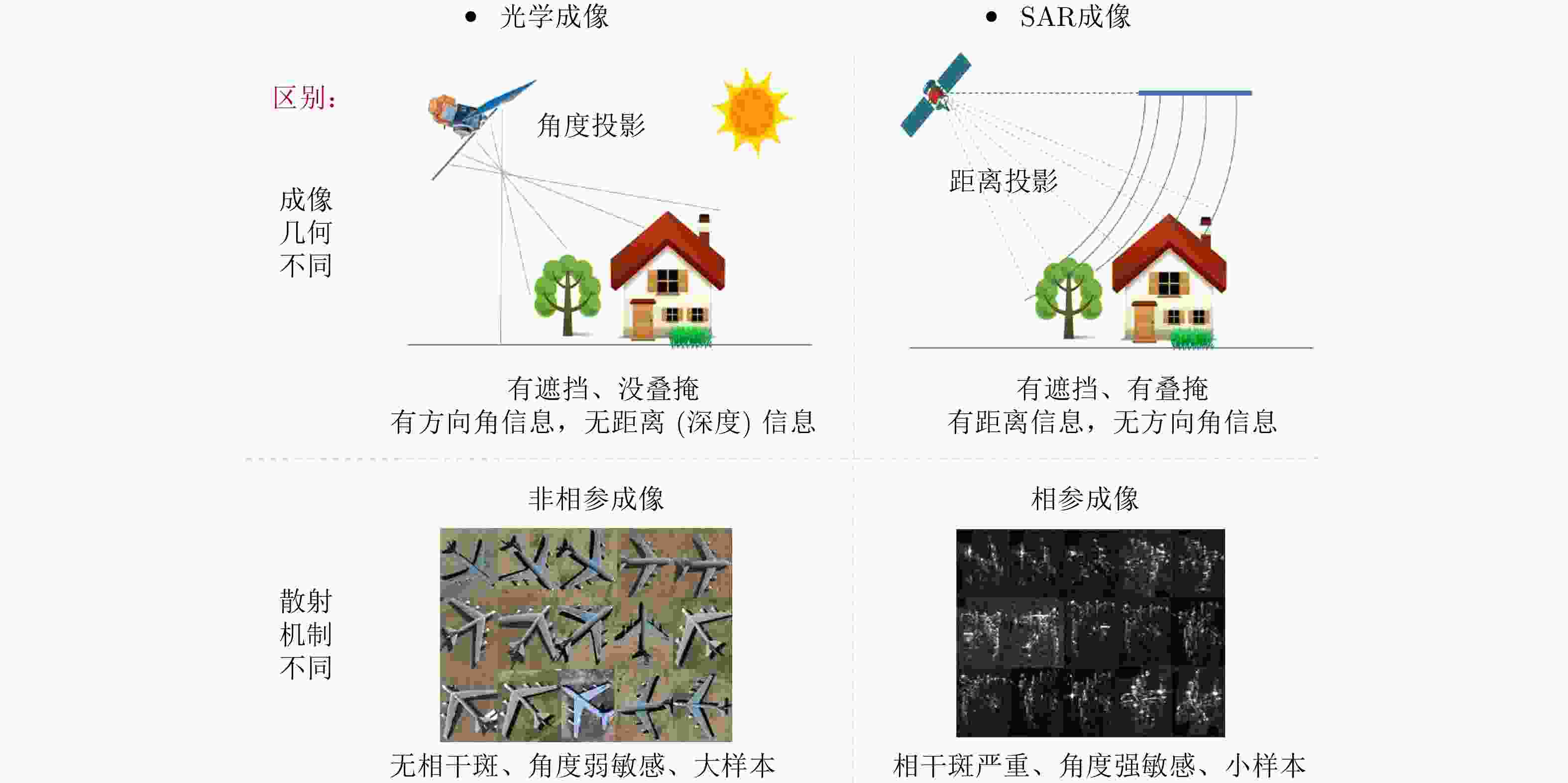
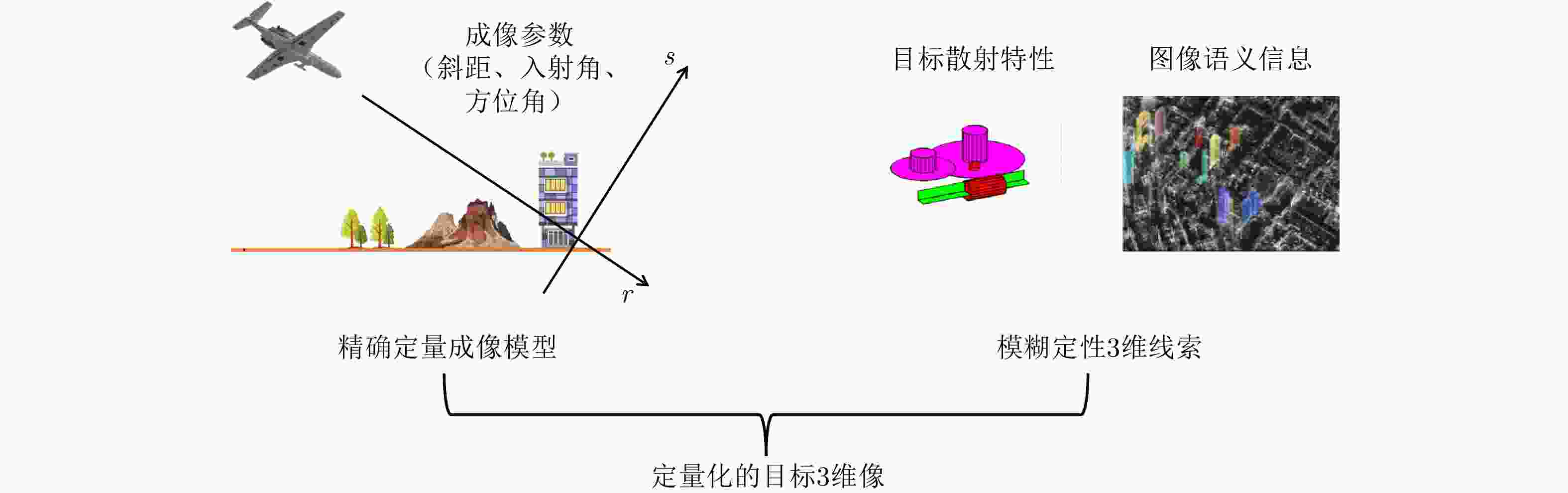
合成孔径雷达3维成像技术可以消除目标和地形在2维图像上产生的严重混叠,显著提升目标识别和3维建模能力,已经成为当前SAR发展的重要趋势。合成孔径雷达3维成像技术经过了数十年的发展,已提出多种技术体制。该文系统性回顾了SAR 3维成像技术领域的发展过程,深入分析了现有SAR 3维成像技术的特点;指出了SAR回波及图像中蕴含的未被现有技术利用的3维信息,提出“合成孔径雷达微波视觉3维成像”的新概念和新思路,将SAR成像方法与微波散射机制和图像视觉语义有机融合,形成SAR微波视觉3维成像理论与方法,实现高效能、低成本的SAR 3维成像。该文重点阐述了SAR微波视觉3维成像的概念、目标和关键科学问题,并给出了初步的技术途径,为SAR 3维成像提供了新的技术思路。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达3维成像 /
- 阵列干涉 /
- 层析SAR /
- SAR微波视觉3维成像
Abstract:Synthetic Aperture Radar three-dimensional (SAR 3D) imaging technology can eliminate severe overlap in 2D images, and improve target recognition and 3D modeling capabilities, which have become an important trend in SAR development. After decades of development of SAR 3D imaging technology, many types of 3D imaging methods have been proposed. In this study, the history of SAR 3D imaging technology is systematically reviewed and the characteristics of existing SAR 3D imaging technology are analyzed. Given that the 3D information contained in SAR echo and images is not fully used by existing techniques, a new concept of SAR microwave vision 3D imaging has been proposed for the first time. This new concept is integrated with microwave scattering mechanism and image visual semantics to realize three-dimensional reconstruction, which form the theory and method of SAR microwave vision 3D imaging and can achieve high-efficiency and low-cost SAR 3D imaging. This study also analyzes the concept, goal and key scientific problems of SAR microwave vision 3D imaging and provides a preliminary solution, which will contribute in several ways to our understanding of SAR 3D imaging and provide the basis for further research.
-
Key words:
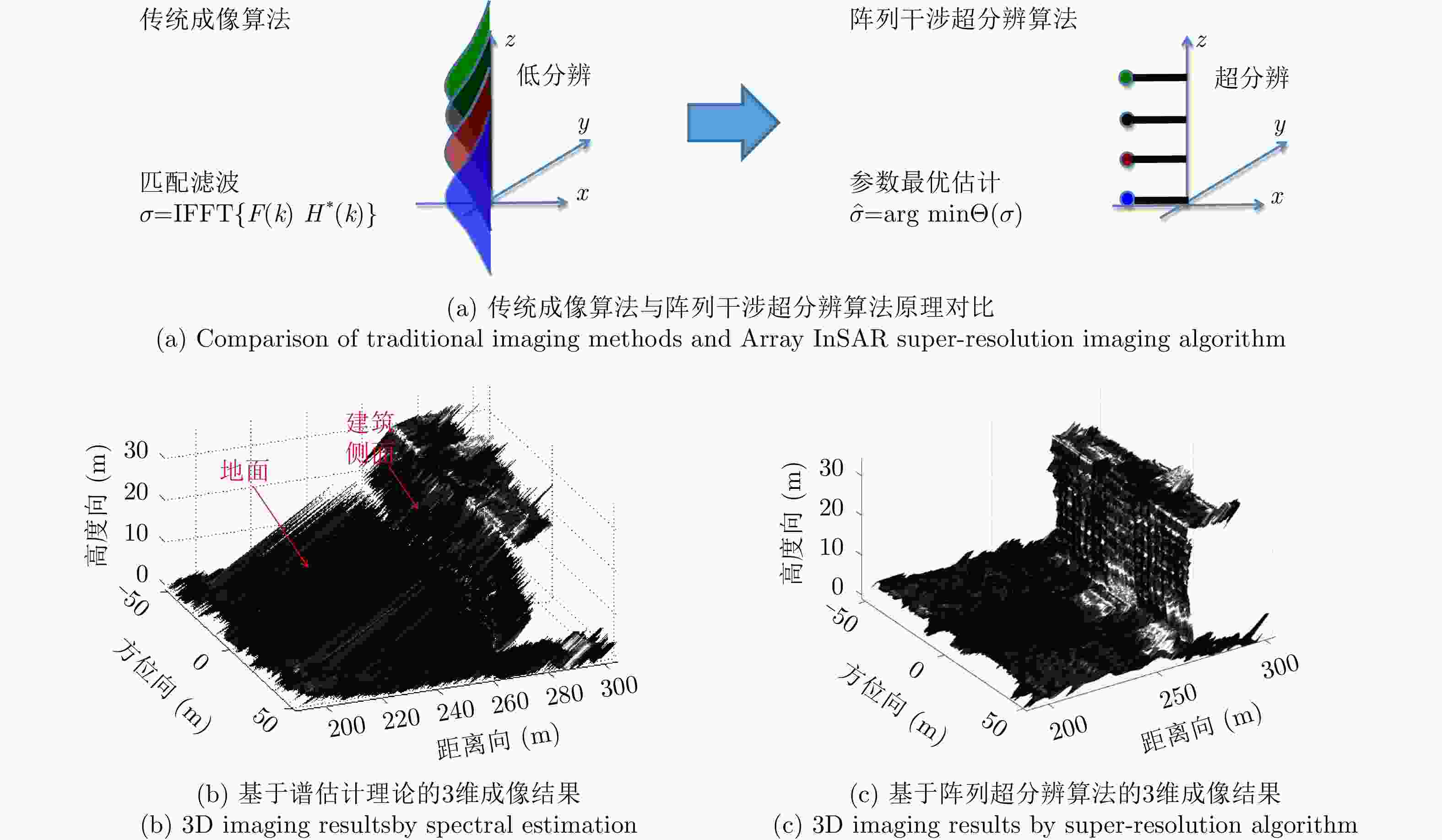
- SAR 3D imaging /
- Array InSAR /
- SAR Tomography /
- SAR microwave vision 3D imaging
-
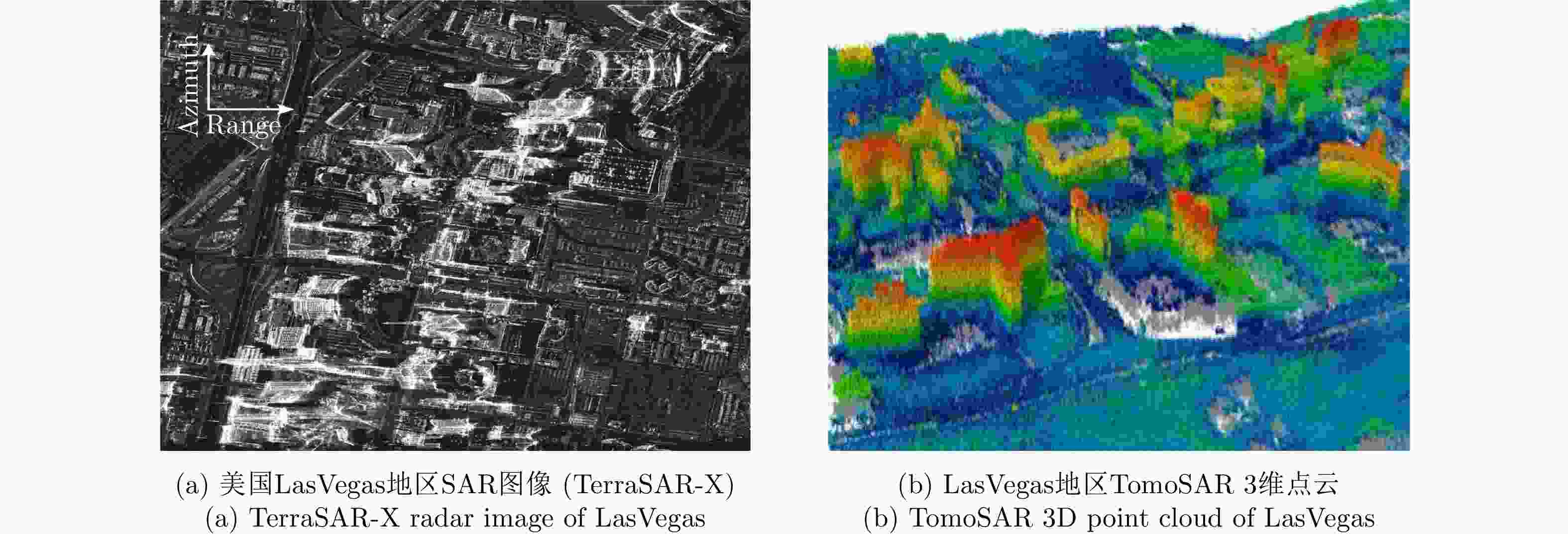
图 3 TomoSAR 3D imaging result of urban areas by DLR[12]
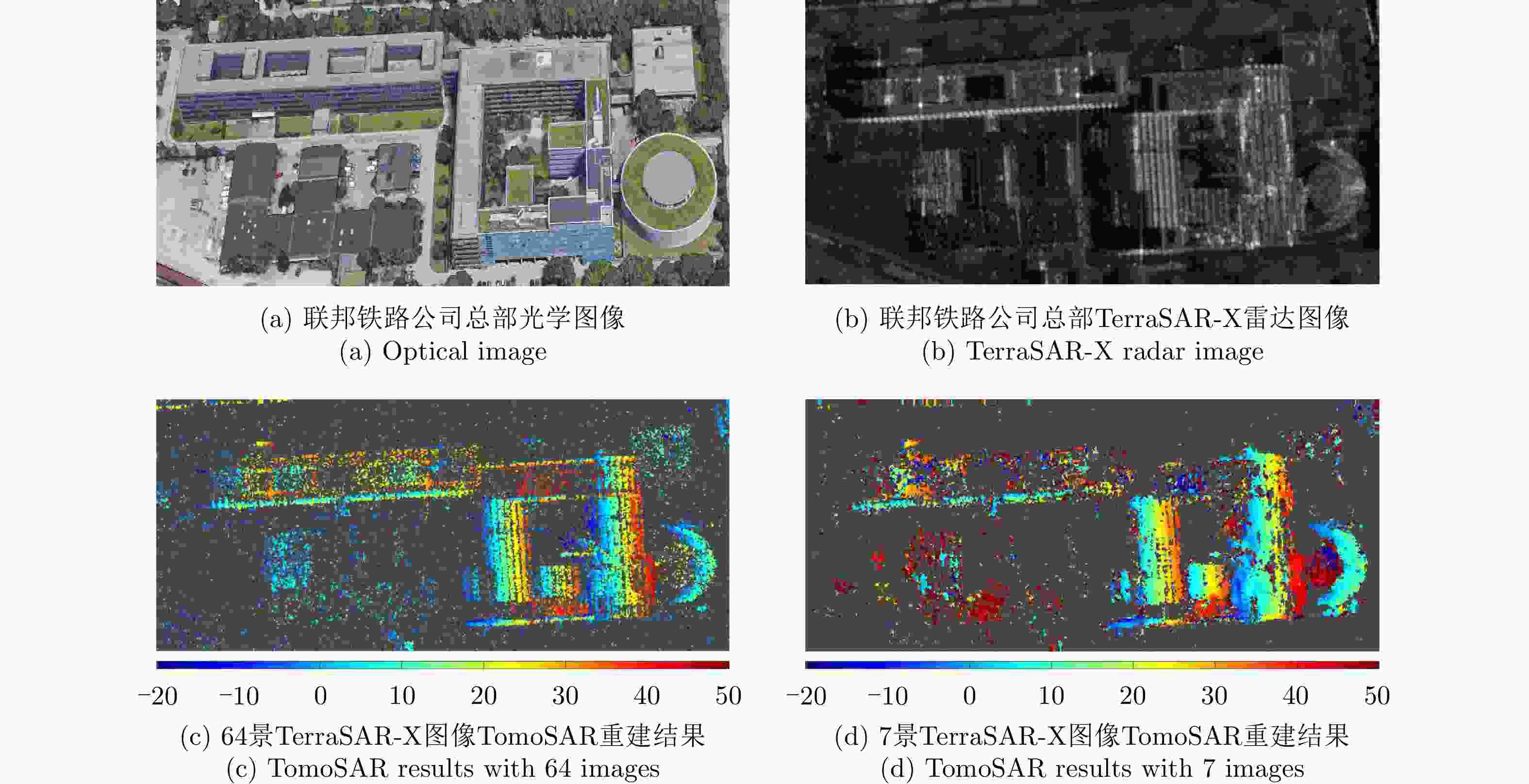
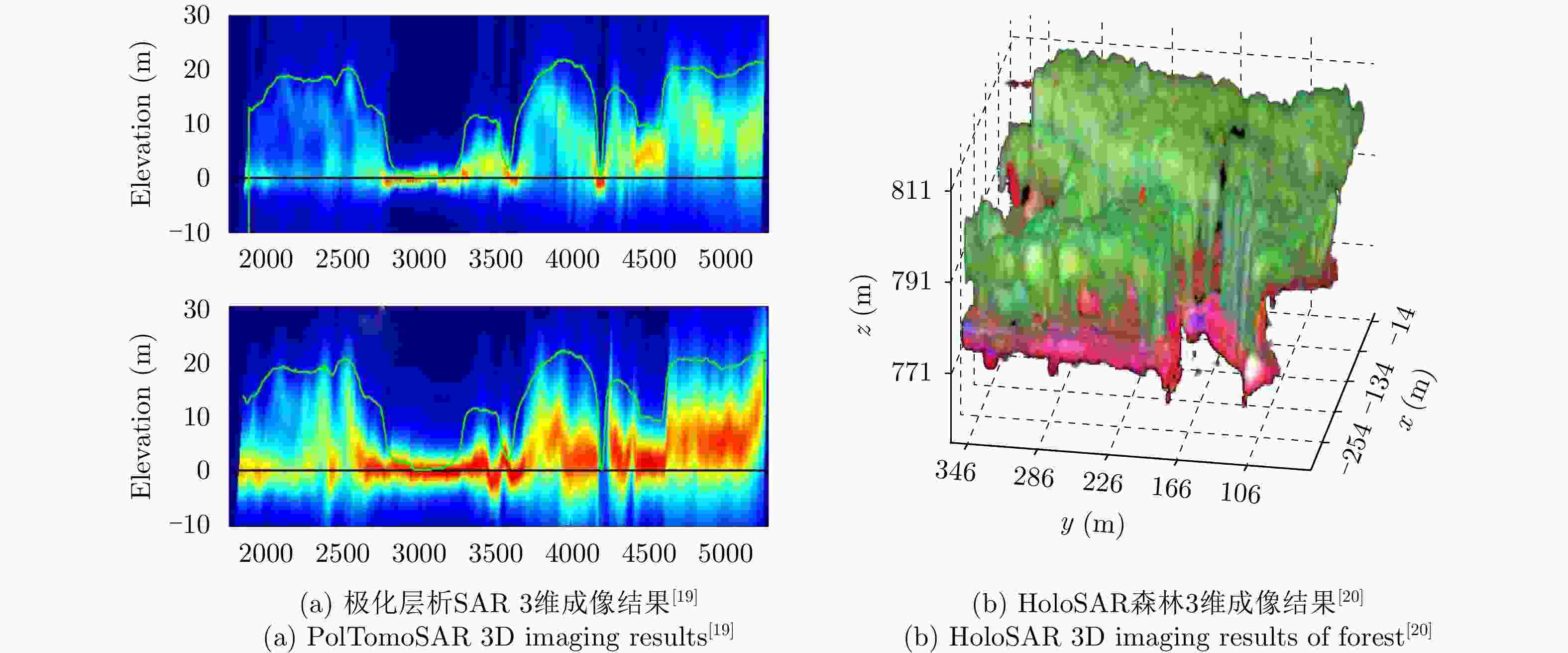
图 5 TomoSAR imaging results of the DB Headquarters in Munich[32]
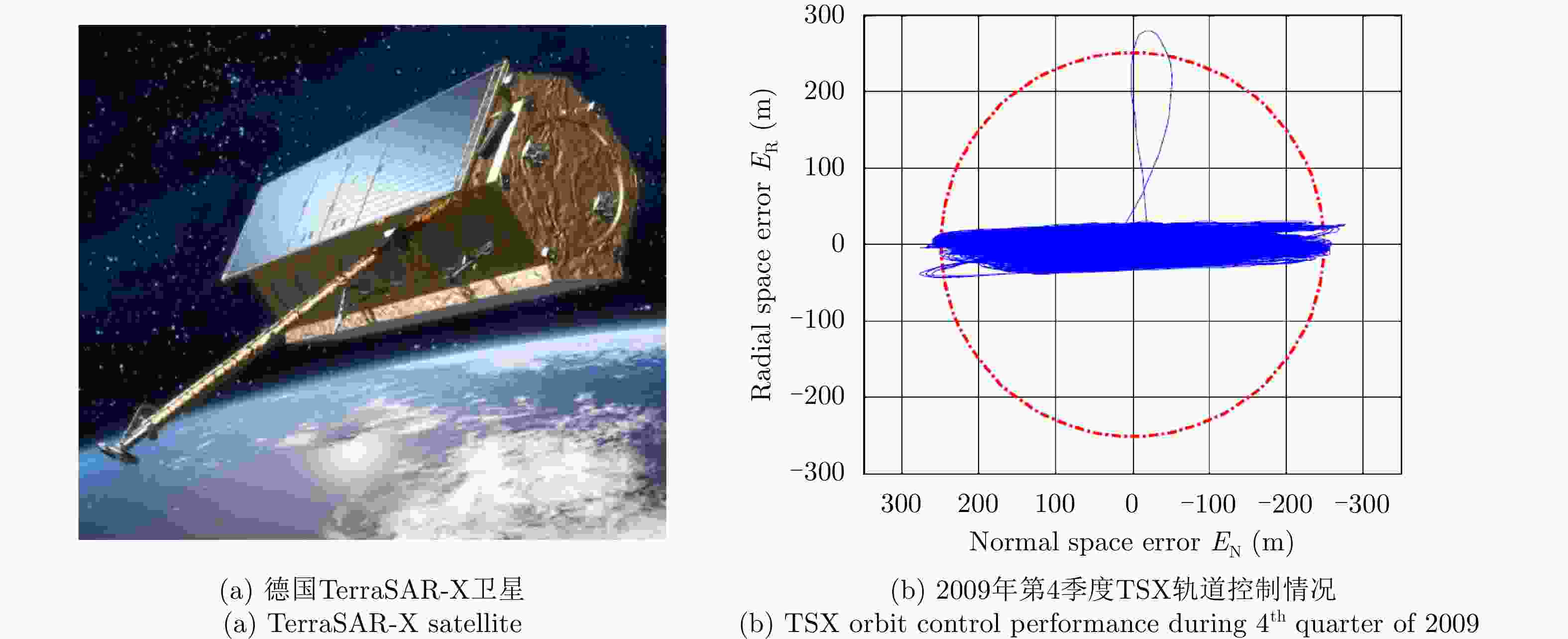
图 6 Diagram of the TSX orbit control performance[33]
表 1 SAR 微波视觉3维成像与传统成像技术的对比
Table 1. Comparison between SAR microwave vision 3D imaging and traditional 3D imaging techniques
维度 分辨机理 分辨方法 信息来源 雷达体制 1 距离维 时间分辨 脉冲压缩 频率扩展 传统雷达 2 方位维 角度分辨 合成孔径 空间扩展 2维雷达成像(SAR) 3 高度维 角度分辨 合成孔径 空间扩展 层析/阵列干涉SAR 3维成像 散射机制
视觉语义
角度分辨SAR微波视觉
3维成像方法散射机制
视觉内容
空间扩展微波视觉
3维SAR表 1 Comparison between SAR microwave vision 3D and traditional 3D imaging techniques
Dimension Resolution mechanism Processing method Source of information Radar system 1st Range Time resolution Range compression Frequency expansion Traditional radar 2nd Azimuth Angular resolution Synthetic aperture Space expansion SAR 3rd Elevation Angular resolution Synthetic aperture Space expansion TomoSAR and array InSAR Scattering mechanism visual semantics angular resolution SAR microwave vision 3D imaging Scattering mechanism Visual information space expansion Microwave vision 3D SAR -
[1] GRAHAM L C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(6): 763–768. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9516 [2] LAPRADE G L. An analytical and experimental study of stereo for radar[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering, 1963, 29(2): 294–300. [3] LEBERL F W, RAGGAM J, and KOBRICK M. On stereo viewing of SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1985, GE-23(2): 110–117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1985.289407 [4] KNAELL K. Three-dimensional SAR from curvilinear apertures[C]. Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE national Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1996. [5] SCHMITT M and ZHU Xiaoxiang. Demonstration of single-pass millimeterwave SAR tomography for forest volumes[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 202–206. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2506150 [6] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization—the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [7] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487 [8] PASQUALI P, PRATI C, ROCCA F, et al. A 3-D sar experiment with EMSL data[C]. Proceedings of International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’95, Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Firenze, Italy, 1995: 784–786. [9] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [10] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, and SERAFINO F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567 [11] FORNARO G, LOMBARDINI F, PAUCIULLO A, et al. Tomographic processing of interferometric SAR data: Developments, applications, and future research perspectives[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 41–50. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312073 [12] REALE D, FORNARO G, PAUCIULLO A, et al. Tomographic imaging and monitoring of buildings with very high resolution SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 661–665. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098845 [13] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Demonstration of super-resolution for tomographic SAR imaging in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3150–3157. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2177843 [14] ZHU Xiaoxiang, MONTAZERI S, GISINGER C, et al. Geodetic SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 18–35. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2448686 [15] WANG Yuanyuan, ZHU Xiaoxiang, and BAMLER R. An efficient tomographic inversion approach for urban mapping using meter resolution SAR image stacks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(7): 1250–1254. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2290833 [16] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 50(1): 247–258. [17] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 [18] ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646 [19] TEBALDINI S and ROCCA F. Multibaseline polarimetric SAR tomography of a boreal forest at P-and L-bands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 232–246. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2159614 [20] PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. First airborne demonstration of holographic SAR tomography with fully Polarimetric multicircular acquisitions at L-Band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6170–6196. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2582959 [21] BI Hui, ZHANG Bingchen, and HONG Wen. Lq regularization-based unobserved baselines’ data estimation method for tomographic synthetic aperture radar inversion[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(3): 035014. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.035014 [22] BI Hui, LIU Jianguo, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Baseline distribution optimization and missing data completion in wavelet-based CS-TomoSAR[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(4): 042302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-9068-y [23] WEI Lianhuan, BALZ T, and LIAO Mingsheng. Tomographic analysis of high-rise buildings using TerraSAR-X spotlight data with compressive sensing approach[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014. [24] WANG Jinfeng and PI Yiming. SAR tomography imaging via higher-order spectrum analysis[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 20(4): 748–754. [25] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [26] BARANIUK R G. Compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(4): 181–121. [27] BARANIUK R and STEEGHS P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2007: 128-133. [28] BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. SAR tomography from sparse samples[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: IV-865–IV-868. [29] BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. Three-dimensional SAR focusing from multipass signals using compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 488–499. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2054099 [30] REN X Z and SUN F. Tomography SAR imaging strategy based on block-sparse model[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2016, 47: 191–200. doi: 10.2528/PIERM16010904 [31] WEI Lianhuan, BALZ T, ZHANG Lu, et al. A novel fast approach for SAR tomography: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(6): 1377–1381. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2402124 [32] SHI Yilei, ZHU Xiaoxiang, and BAMLER R. Nonlocal compressive sensing-based SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 3015–3024. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2879382 [33] YOON Y T, EINEDER M, YAGUE-MARTINEZ N, et al. TerraSAR-X precise trajectory estimation and quality assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(6): 1859–1868. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2006983 [34] DE FLORIO S and D’AMICO S. Optimal Autonomous Orbit Control of a Remote Sensing Spacecraft[M]. AAIA. Spaceflight Mechanics 2009. Univelt, San Diego: AAIA, 2009: 949-968. [35] PITZ W and MILLER D. The TerraSAR-X satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 615–622. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037432 [36] WERMUTH M, HAUSCHILD A, MONTENBRUCK O, et al. TerraSAR-X rapid and precise orbit determination[C]. Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics, Toulouse, Frankreich, 2009. [37] CALTAGIRONE F. Status, results and perspectives of the Italian Earth Observation SAR COSMO-SkyMed[C]. Proceedings of European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2009: 330–334. [38] GIERULL C H. On a concept for an airborne downward-looking imaging radar[J]. International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 1999, 53(6): 295–304. [39] GIRET R, JEULAND H, and ENERT P. A study of a 3D-SAR concept for a millimeter wave imaging radar onboard an UAV[C]. The First European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004: 201–204. [40] NOUVEL J, JEULAND H, BONIN G, et al. A Ka band imaging radar: DRIVE on board ONERA motorglider[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 134–136. [41] NOUVEL J F. ONERA DRIVE project[C]. Proceedings of International Radar Conference "Surveillance for a Safer World", Bordeaux, France, 2009: 1–4. [42] WEIß M, PETERS O, and ENDER J. First flight trials with ARTINO[C]. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1-4. [43] KLARE J, BRENNER A, and ENDER J. Impact of platform attitude disturbances on the 3D imaging quality of the UAV ARTINO[C]. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008. [44] WEIß M and GILLES M. Initial ARTINO radar experiments[C]. Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 1–4. [45] PENG Xueming, WANG Yanping, HONG Wen, et al. Airborne downward looking sparse linear array 3-D SAR heterogeneous parallel simulation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2013, 5(10): 5304–5329. doi: 10.3390/rs5105304 [46] 彭学明, 王彦平, 谭维贤, 等. 基于跨航向稀疏阵列的机载下视 MIMO 3D-SAR三维成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720PENG Xueming, WANG Yanping, TAN Weixian, et al. Airborne downward-looking MIMO 3D-SAR imaging algorithm based on cross-track thinned array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 943–949. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00720 [47] ZHANG Fubo, LIANG Xingdong, WU Yirong, et al. 3D surface reconstruction of layover areas in continuous terrain for multi-baseline SAR interferometry using a curve model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(8): 2093–2112. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1030042 [48] LI Hang, LIANG Xingdong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. A novel 3-D reconstruction approach based on group sparsity of array InSAR[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2018, 48(8): 1051–1064. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00023 [49] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, and CHEN Longyong. MIMO SAR system using digital implemented OFDM waveforms[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 7428–7431. [50] WANG Jie, CHEN Longyong, LIANG Xingdong, et al. Implementation of the OFDM chirp waveform on MIMO SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 5218–5228. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2419271 [51] WANG Jie, LIANG Xingdong, DING Chibiao, et al. An improved OFDM chirp waveform used for MIMO SAR system[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2014, 57(6): 1–9. [52] 王杰, 丁赤飚, 梁兴东, 等. 机载同时同频MIMO-SAR系统研究概述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046WANG Jie, DING Chibiao, LIANG Xingdong, et al. Research outline of airborne MIMO-SAR system with same time-frequency coverage[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046 [53] 向茂生, 丁赤飚. 一种基于刚性和柔性基线组合的多基线测量方法[P]. 中国, CN201210512927.4, 2014. [54] SPORTOUCHE H, TUPIN F, and DENISE L. Extraction and three-dimensional reconstruction of isolated buildings in urban scenes from high-resolution optical and SAR Spaceborne images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3932–3946. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2132727 [55] XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Automatic reconstruction of building objects from multiaspect meter-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(7): 2336–2353. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.896614 [56] ZHANG Yueting, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. The characteristics of the multipath scattering and the application for geometry extraction in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(8): 4687–4699. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2406793 [57] POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [58] JACKSON J A, RIGLING B D, and MOSES R L. Canonical scattering feature models for 3D and bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 525–541. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461639 [59] JACKSON J A and MOSES R L. Synthetic aperture radar 3D feature extraction for arbitrary flight paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 2065–2084. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237579 [60] LI Yongchen, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. A complex target reconstruction characterized by canonical scattering objects[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 1278–1280. [61] XU Feng, JIN Yaqiu, and MOREIRA A. A preliminary study on SAR advanced information retrieval and scene reconstruction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1443–1447. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2590878 [62] LIU Xiaobai, ZHAO Yibiao, and ZHU Songchun. Single-view 3D scene reconstruction and parsing by attribute grammar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(3): 710–725. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2689007 [63] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 从物理智能到微波视觉[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(10): 30–44.XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science&Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. [64] 陈健堃, 彭凌霄, 仇晓兰, 等. 基于深度神经网络的SAR建筑目标3维重建方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(11): 1–20.CHEN Jiankun, PENG Lingxiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. A 3D building reconstruction method for SAR based on deep neural network[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(11): 1–20. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
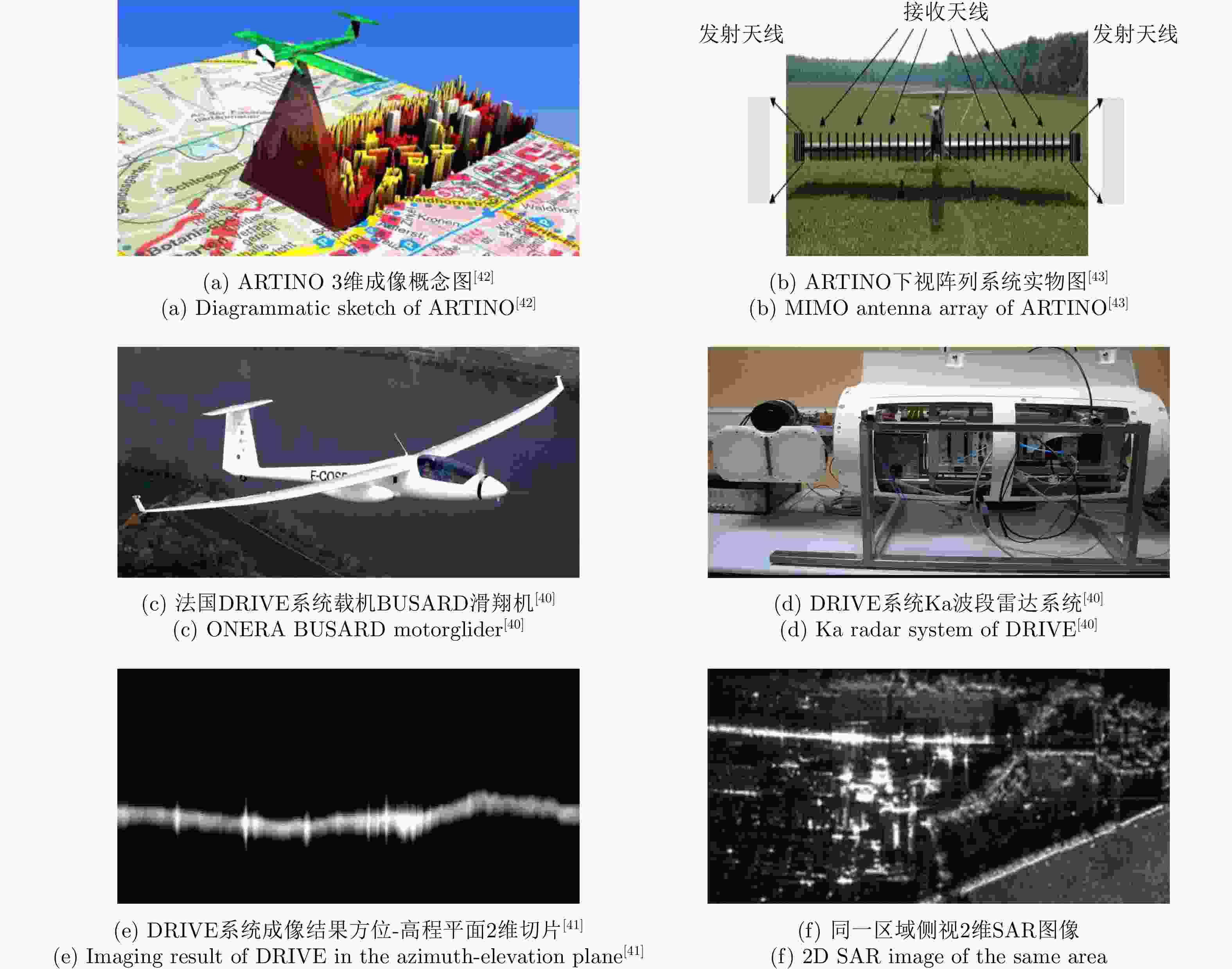
下载: