Imaging Method for Co-prime-sampling Space-borne SAR Based on 2D Sparse-signal Reconstruction
-
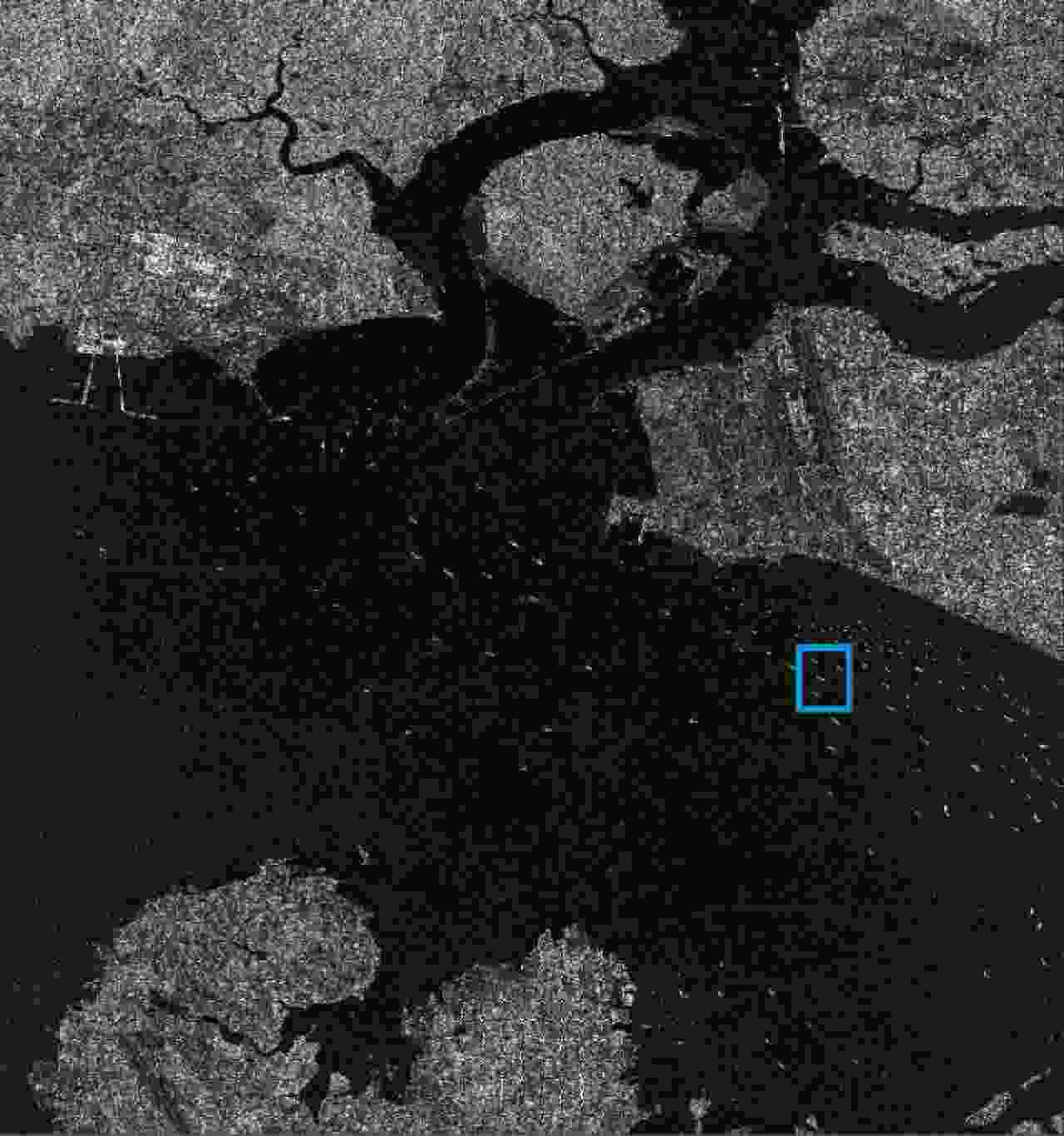
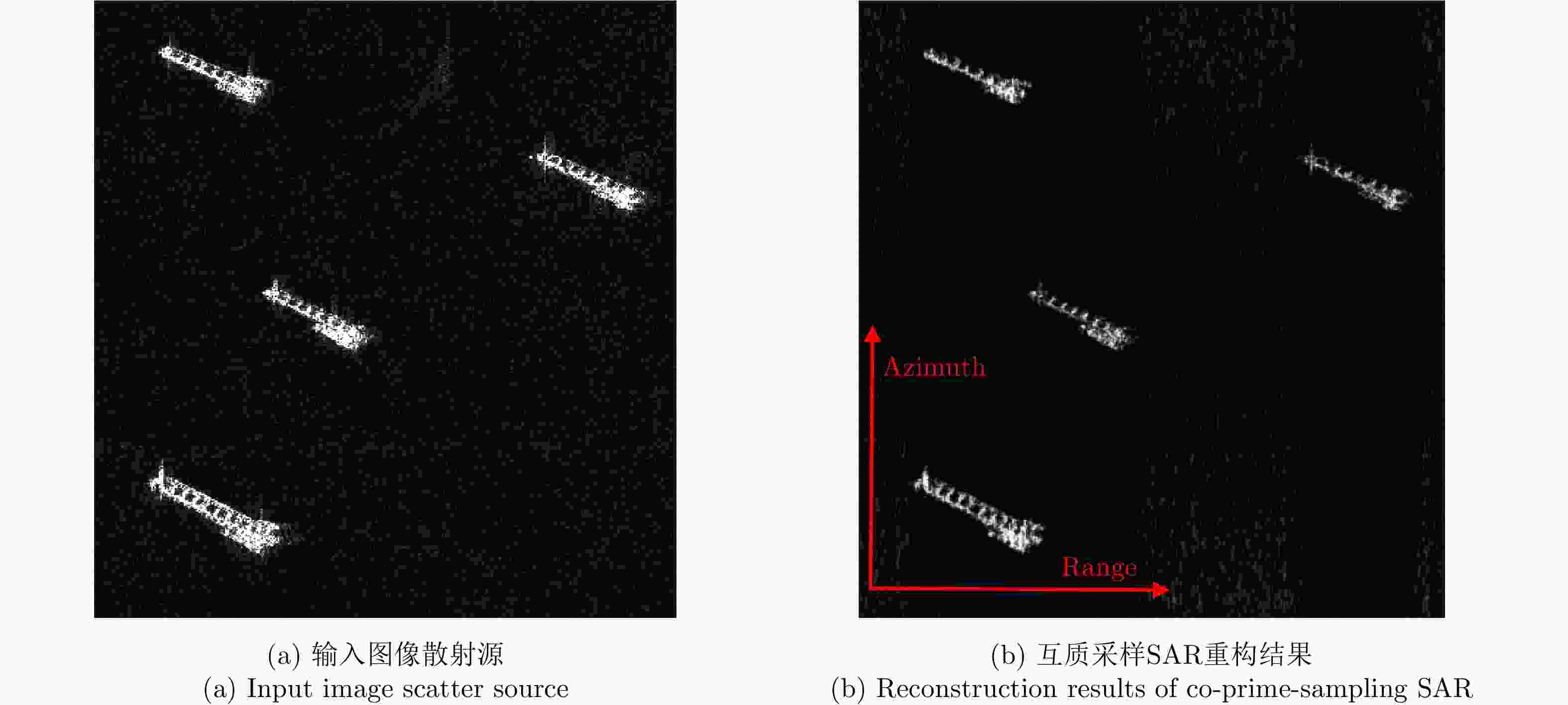
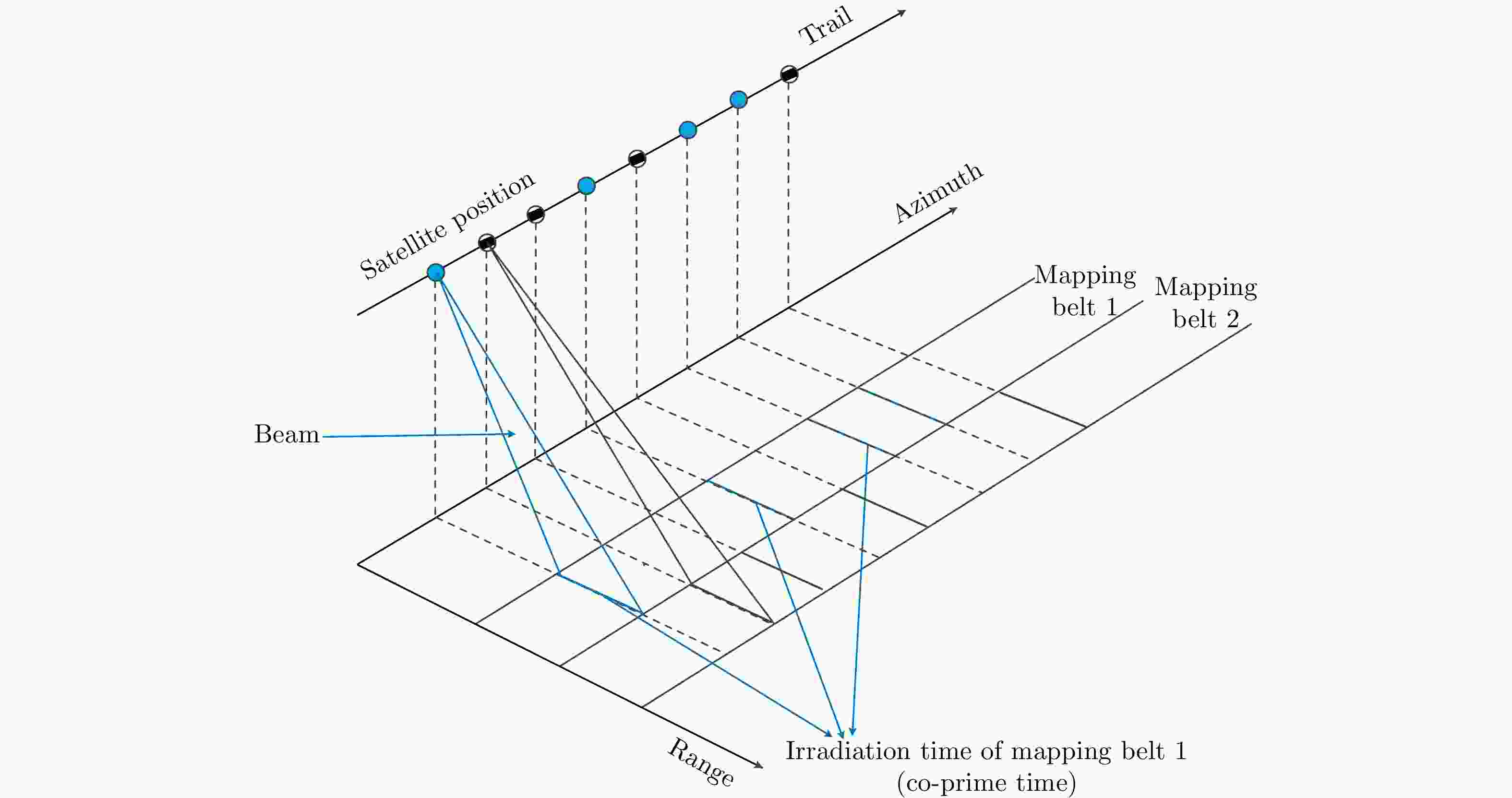
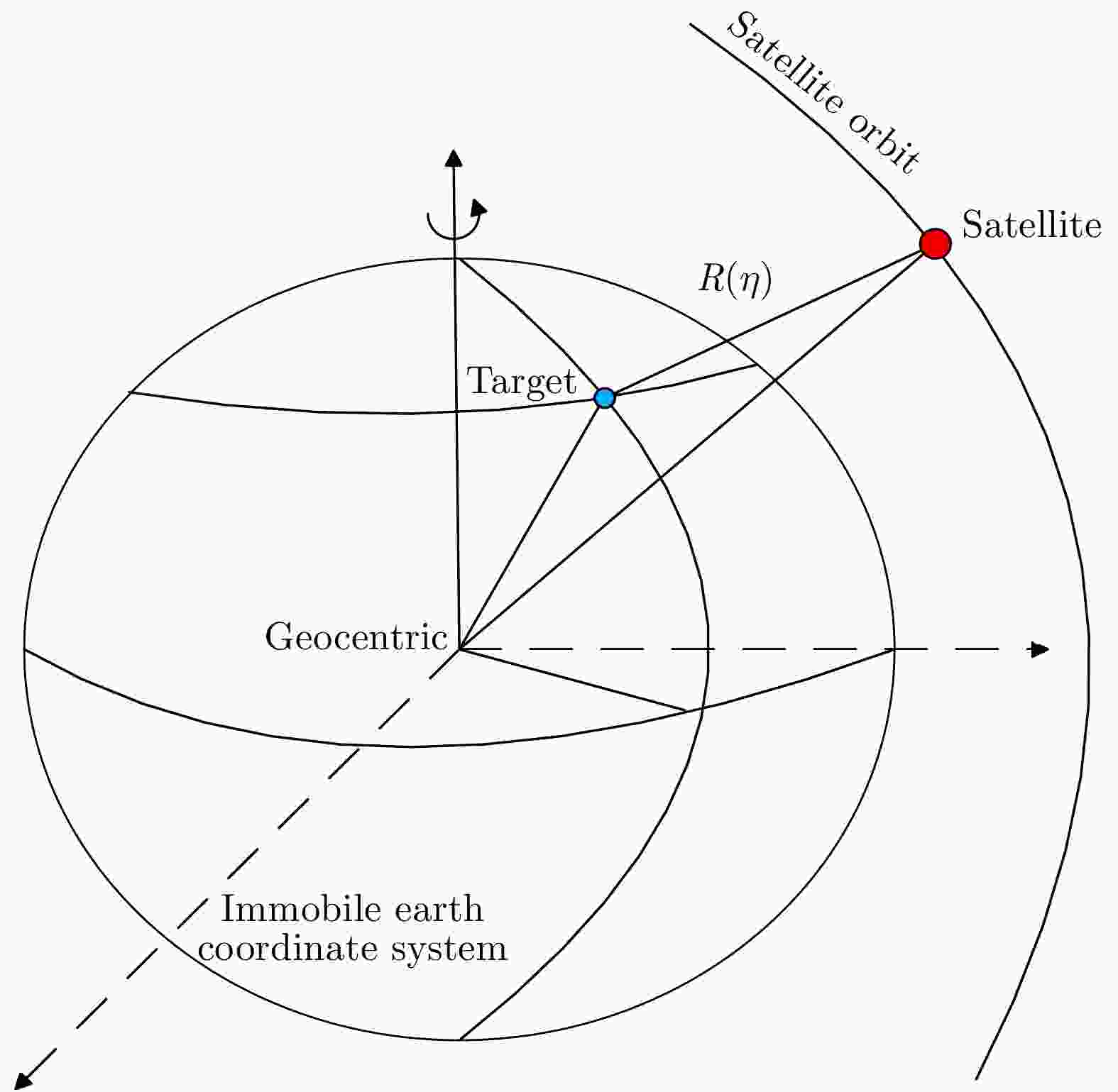
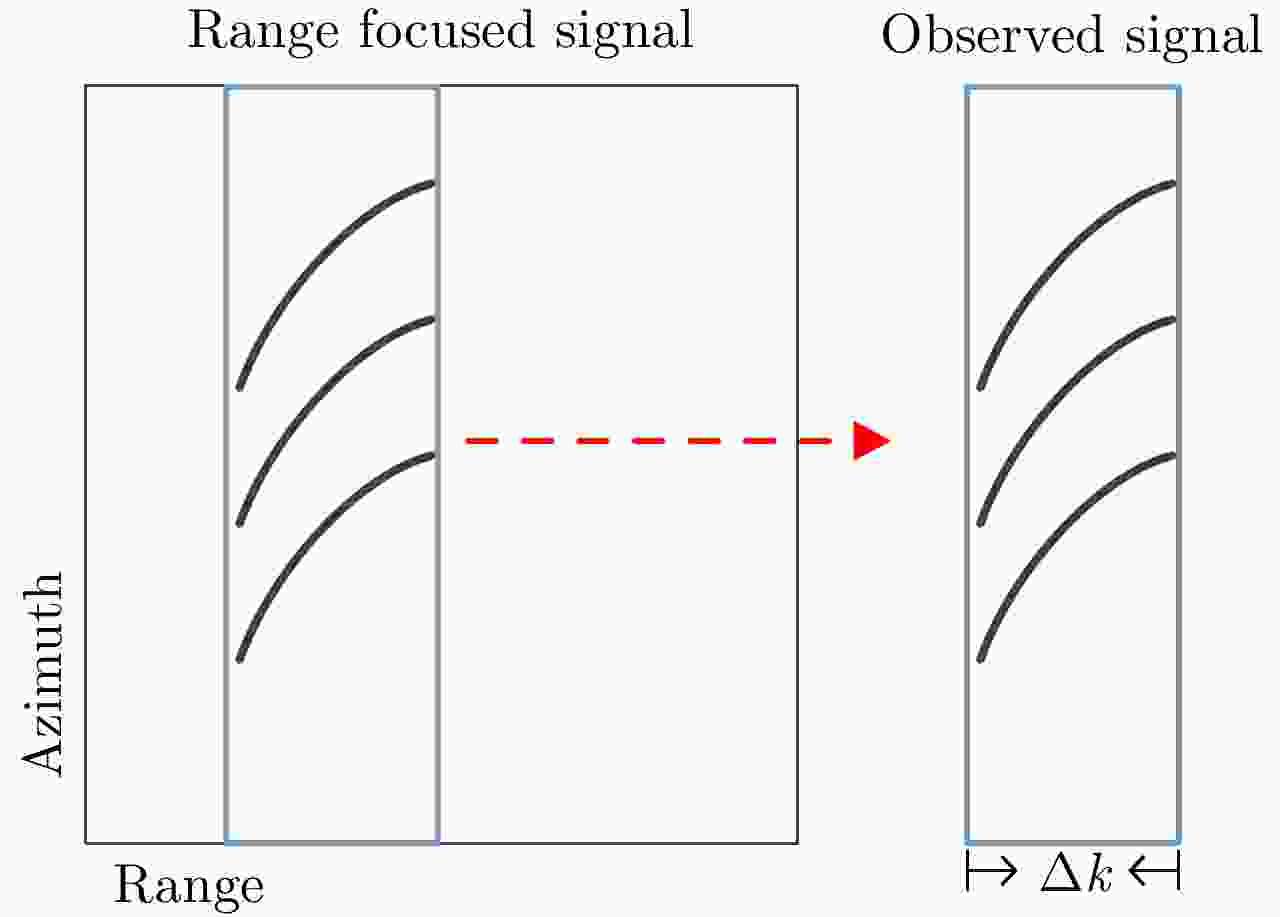
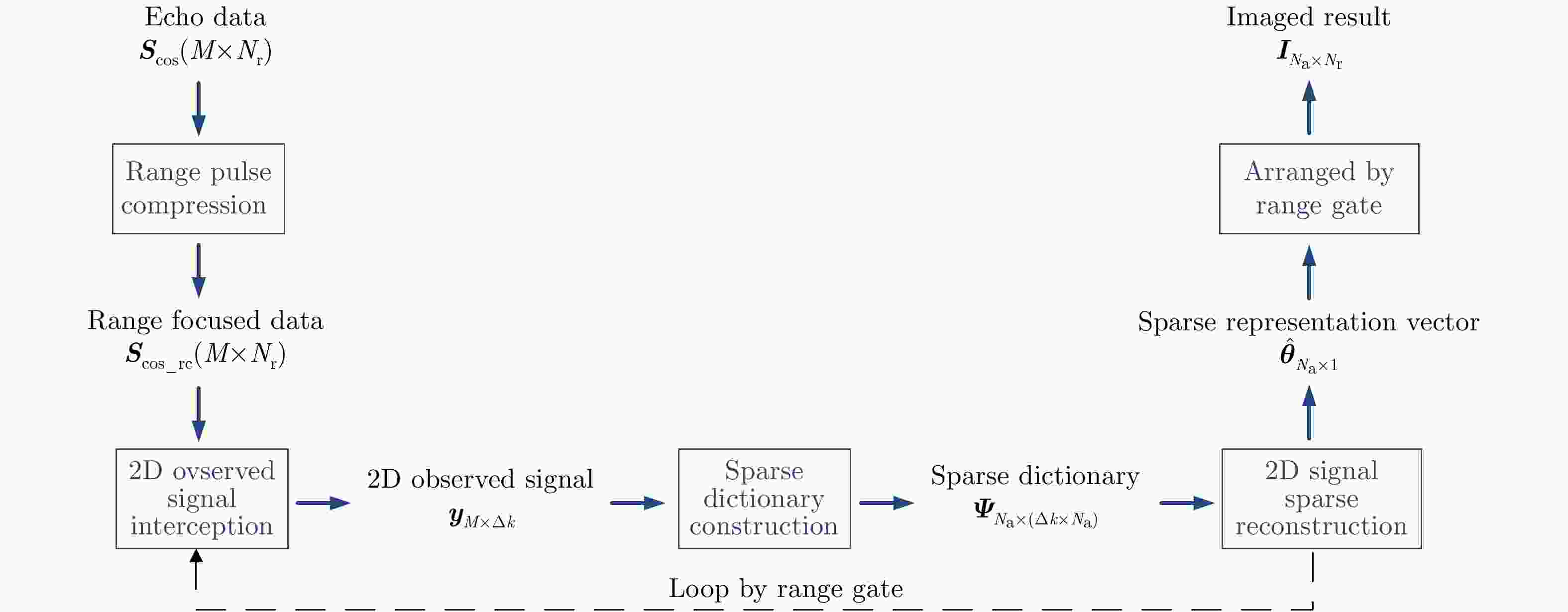
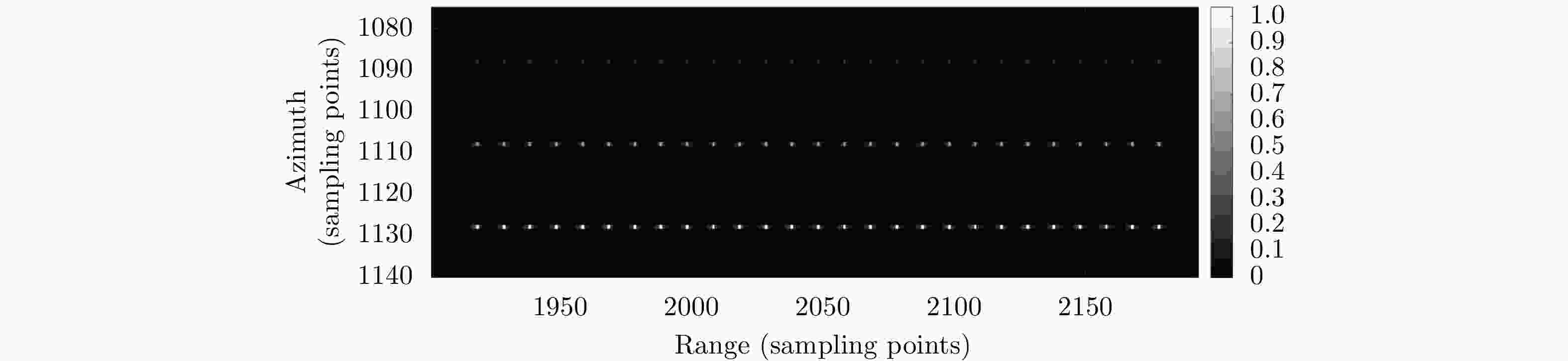
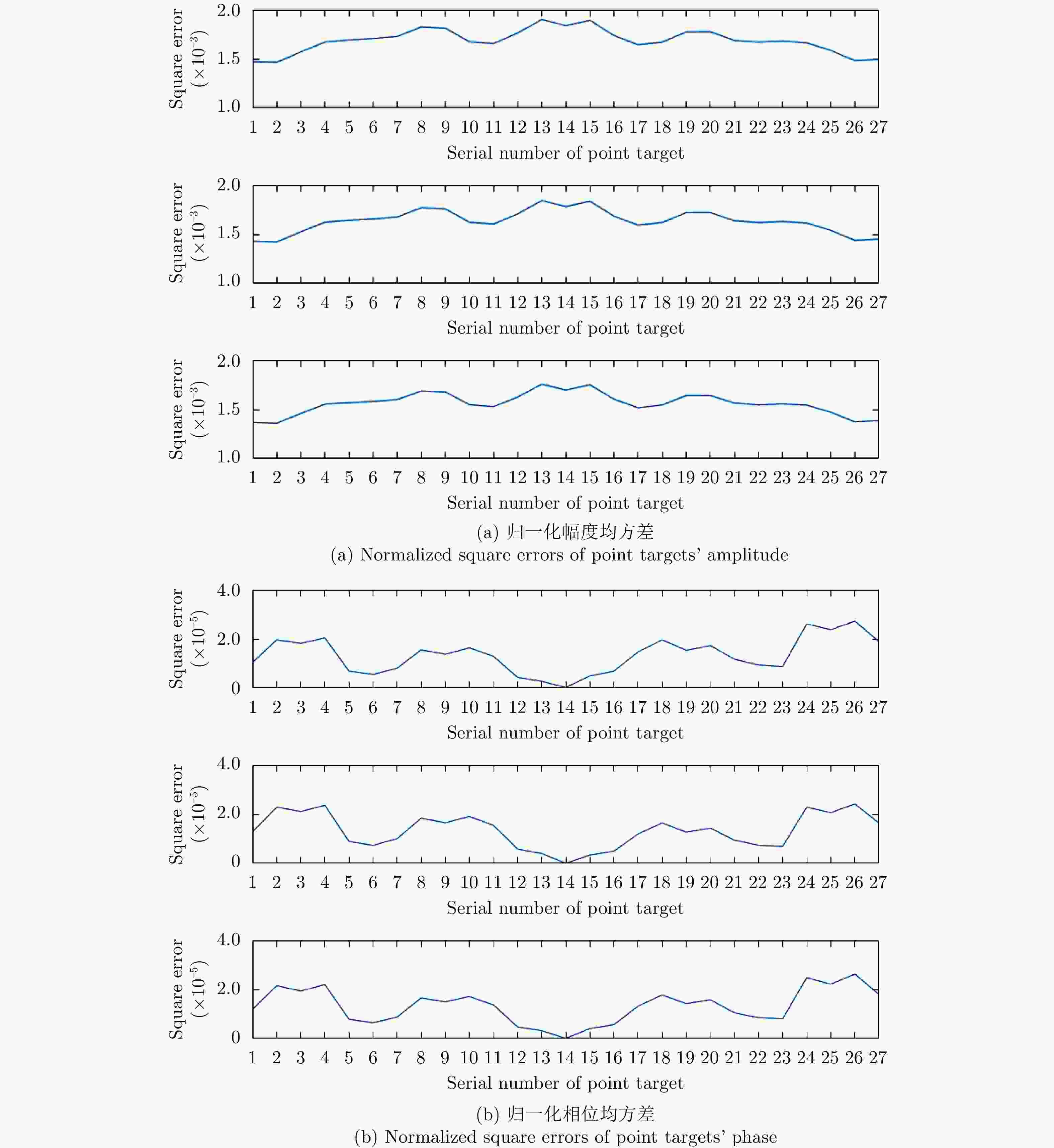
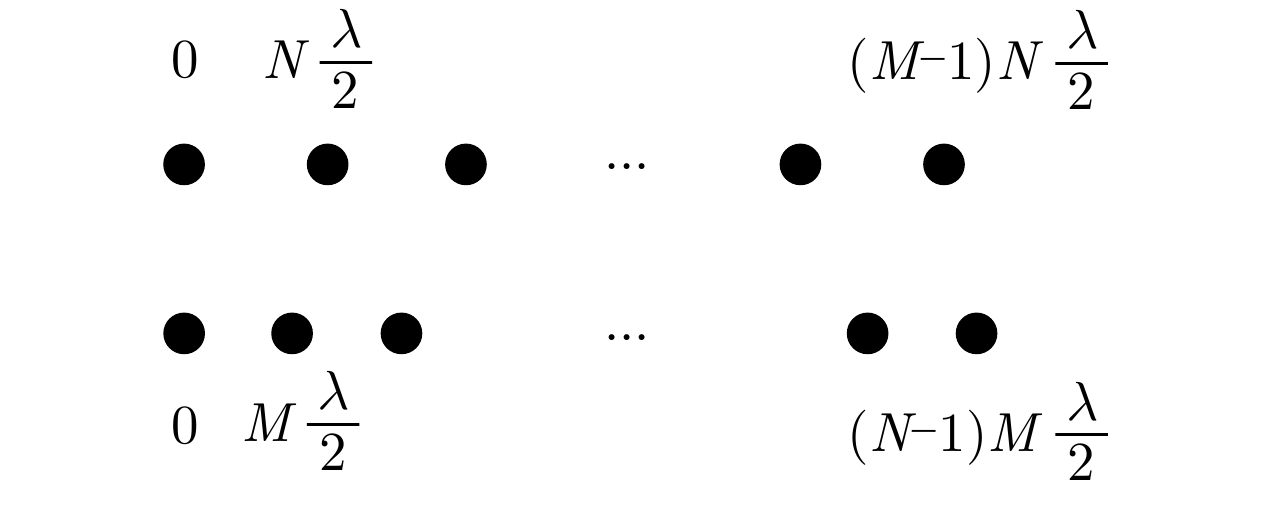
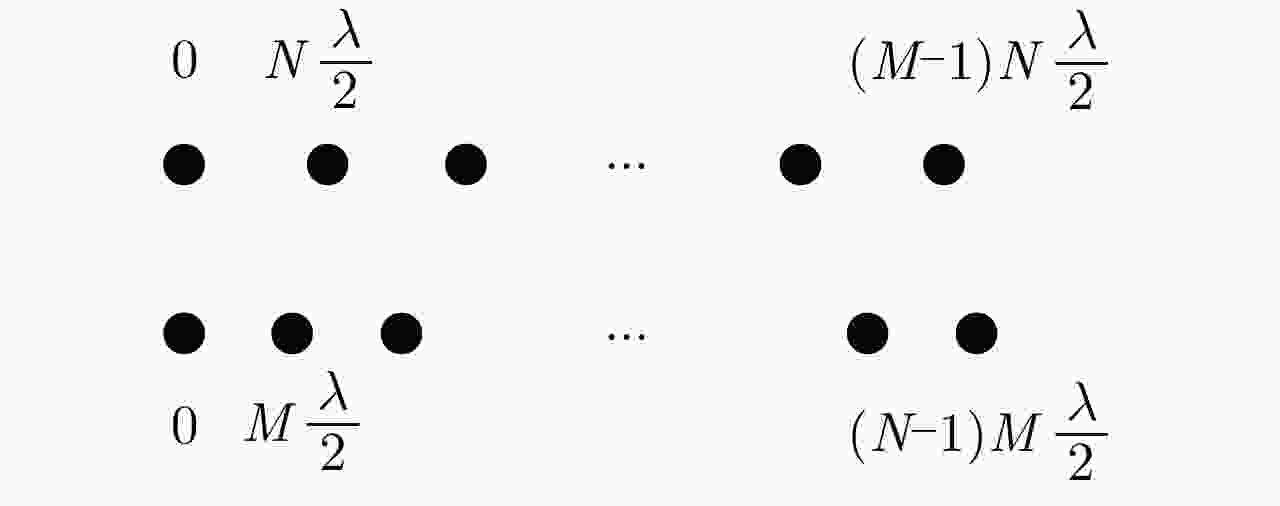
摘要: 互质采样星载SAR通过方位互质采样代替传统方位均匀采样,可有效缓解空间分辨率与有效成像宽度之间的相互制约,提升SAR系统的对地探测性能。然而,方位向互质采样使得回波信号呈现方位欠采样及非均匀采样特性,导致传统SAR成像处理方法无法实现互质采样星载SAR的有效成像处理。该文提出一种基于2维信号稀疏重构的互质采样星载SAR成像处理方法。该方法在距离向脉冲压缩后,根据各距离门的多普勒参数截取2维观测信号并构造相应的稀疏字典,然后通过改进的2维信号稀疏度自适应匹配追踪算法完成方位聚焦处理。该方法不仅可以补偿SAR回波信号的距离方位2维耦合,还可以消除成像参数随距离空变对稀疏重构造成的影响,从而实现全场景的精确重构。点目标及分布目标仿真实验结果验证了所提算法可在远低于奈奎斯特采样率的情况下实现稀疏场景的有效重构。Abstract: Co-prime-sampling space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) replaces the traditional uniform sampling by performing co-prime sampling in azimuth, which effectively alleviates the conflict between spatial resolution and effective swath width, while also improving the ground detection performance of the SAR system. However, co-prime-sampling in azimuth causes the echo signal to exhibit azimuthal under sampling and non-uniform sampling characteristics, which means the traditional SAR image-processing method can not effectively image co-prime-sampled SAR. In this paper, an imaging method based on Two-Dimensional (2D) sparse-signal reconstruction is proposed for co-prime-sampling space-borne SAR. Using this method, after range-pulse compression, the 2D observed signal is intercepted and a corresponding sparse dictionary consisting of 2D atoms is constructed according to the Doppler parameters of each range gate. Then, azimuth-focus processing is completed by the improved 2D-signal sparsity adaptive matching pursuit algorithm. The proposed method not only compensates for the 2D coupling between the range and azimuth, but also eliminates the influence of space-varying imaging parameters on sparse reconstruction to achieve accurate reconstruction of the entire scene. The simulation results of the point targets and distribution targets verify that the proposed method can effectively reconstruct sparse scenes at a rate much lower than the Nyquist sampling rate.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Co-prime-sampling /
- Sparse recovery /
- Doppler parameters
-
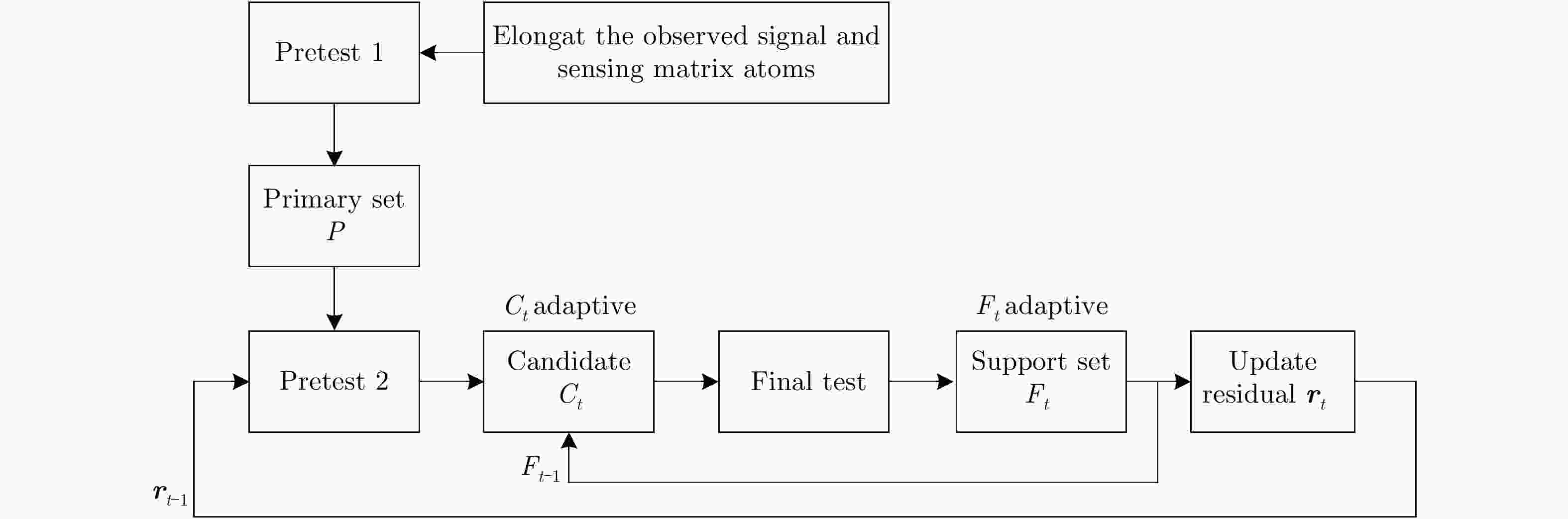
表 1 改进的SAMP算法
Table 1. The modified 2D SAMP algorithm
输入:感知矩阵${{ A}} = {{\varPhi \varPsi }}$,观测信号${{y}}$,步长$l$;
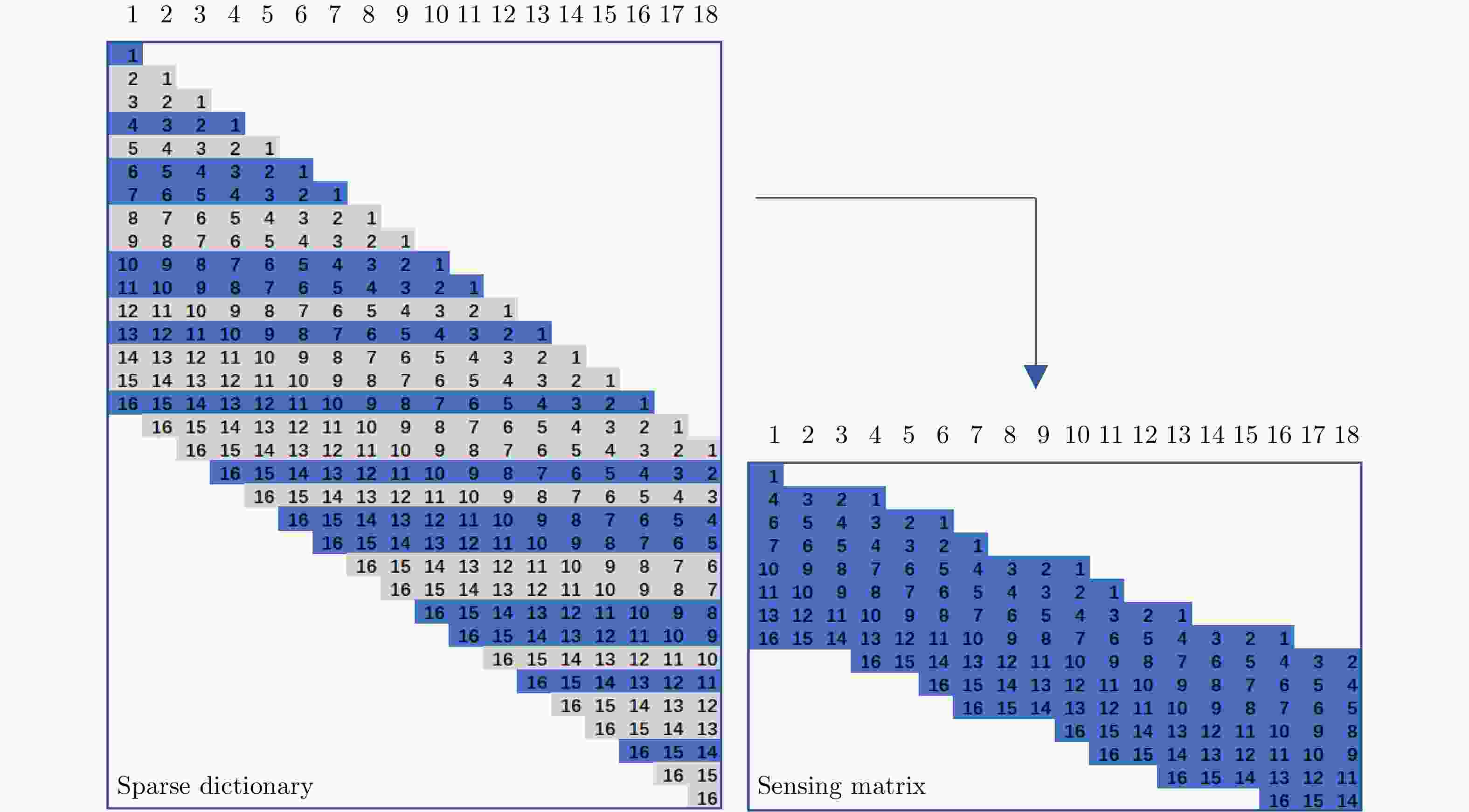
输出:输入观测信号的1维稀疏表示向量估计${{\hat{ \theta }}_{N \times 1}}$;拉长:将观测信号${{y}}$和感知矩阵$ {{ A}}$中所有原子均拉长为一个1维列向量;
初始化:${{{r}}_0} = {{y}}$, ${{\varLambda }_0} = \varnothing $, ${L_y} = l$, ${L_r} = l$, $t = 1$, ${{\hat{ \theta }}_{N \times 1}} = \left[ {0,0, ··· ,0} \right]_{_{1 \times N}}^{\rm{T}}$;预测试1:选择感知矩阵$ {{ A}}$中有效回波位置正确的原子加入初选集$P$; 重复下述循环: 预测试2:$S_{yt}^{} = {\rm{Max}}\left\{ {\left| {{{ A}}_P^{\rm{H}}{{y}}} \right|,{L_y}} \right\}$, $S_{rt}^{} = {\rm{Max}}\left\{ {\left| {{{ A}}_P^{\rm{H}}{{{r}}_{t - 1}}} \right|,{L_r}} \right\}$, ${C_t} = {{\varLambda }_{t - 1}} \cup {S_{yt}} \cup {S_{rt}}$; 最终测试:${F_t} = {\rm{Max}}\left\{ {\left| {{{\left( {{{A}}_{{C_t}}^{\rm{H}}{{{A}}_{{C_t}}}} \right)}^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}{{A}}_{{C_t}}^{\rm{H}}{{y}}} \right|,{L_y}} \right\}$; 计算:${{{r}}_{{\rm{new}}}} = {{y}} - {{{A}}_{{F_t}}}{\left( {{{A}}_{{F_t}}^{\rm{H}}{{{A}}_{{F_t}}}} \right)^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}{{A}}_{{F_t}}^{\rm{H}}{{y}}$, ${\rm{rat}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{0}}} = \;\;{{\left( {{{\left\| {{{{r}}_0}} \right\|}_2} - {{\left\| {{{{r}}_{{\rm{new}}}}} \right\|}_2}} \right)} / {{{\left\| {{{{r}}_0}} \right\|}_2}}}$, ${\rm{rat}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{1}}} = \;{{\left( {{{\left\| {{{{r}}_{t - 1}}} \right\|}_2} - {{\left\| {{{{r}}_{{\rm{new}}}}} \right\|}_2}} \right)} / {{{\left\| {{{{r}}_0}} \right\|}_2}}}$; 判断:if ${\rm{rat}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{0}}} > 1 - {\varepsilon _0}$: ${F_{{\rm{final}}}} = {F_t}$, quit; else: if ${\rm{rat}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{1}}} < 0$: ${L_y} = {L_y} + l$, ${L_r} = {L_r} + l$; else: ${L_y} = {L_y} + l$, ${L_r} = l$, ${{\varLambda }_t} = {F_t}$, ${{{r}}_t} = {{{r}}_{{\rm{new}}}}$, $t = t + 1$, if ${\rm{rat}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{1}}} > {\varepsilon _1}$: ${F_{{\rm{final}}}} = {F_t}$; else: quit; 结束循环条件:$t = M$;
输出:${{\hat{ \theta }}_{N \times 1}} = {{{A}}_{{F_{{\rm{final}}}}}}{\left( {{{A}}_{{F_{{\rm{final}}}}}^{\rm{H}}{{{A}}_{{F_{{\rm{final}}}}}}} \right)^{{\rm{ - 1}}}}{{A}}_{{F_{{\rm{final}}}}}^{\rm{H}}{{y}}$表 2 SAR成像仿真参数
Table 2. SAR imaging simulation parameters
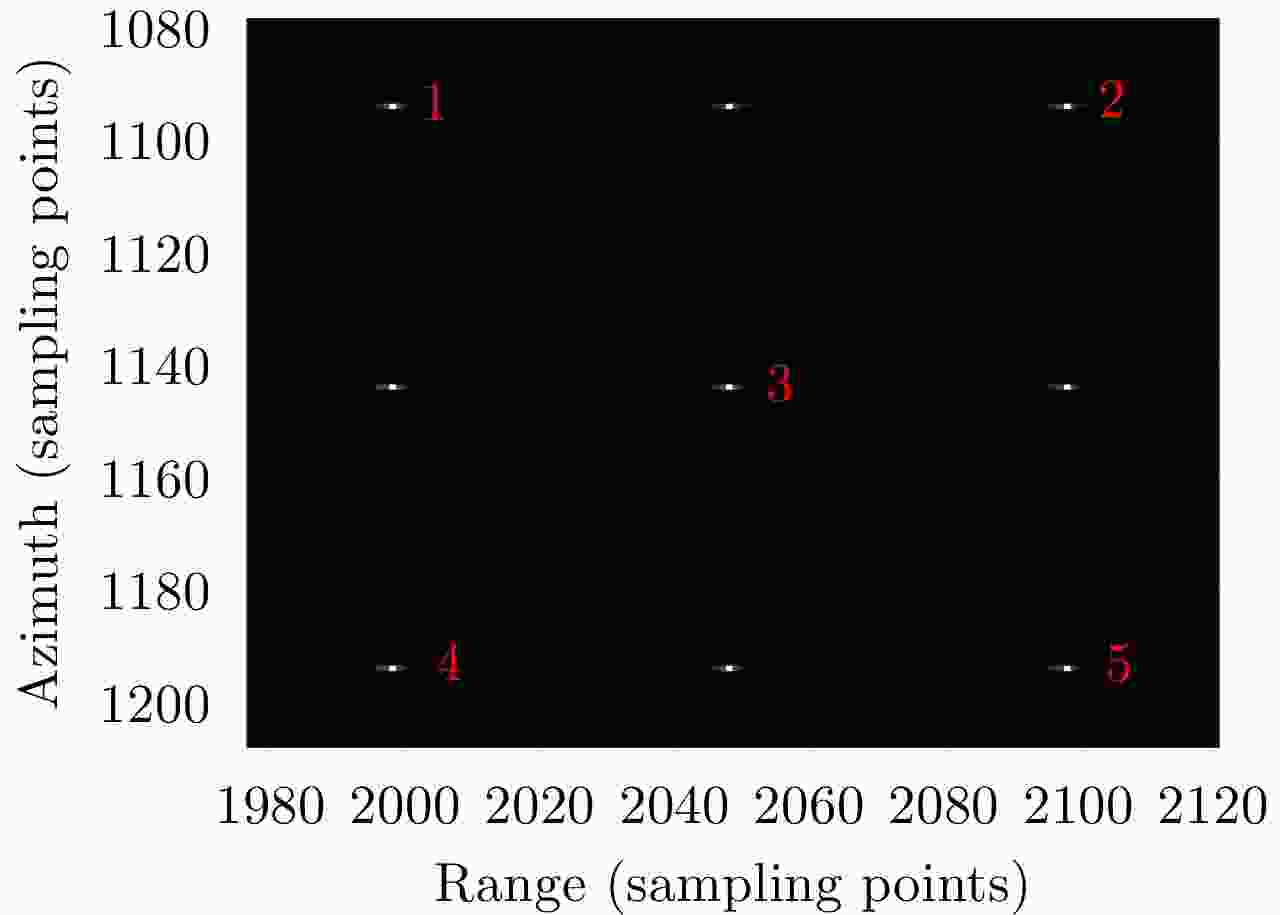
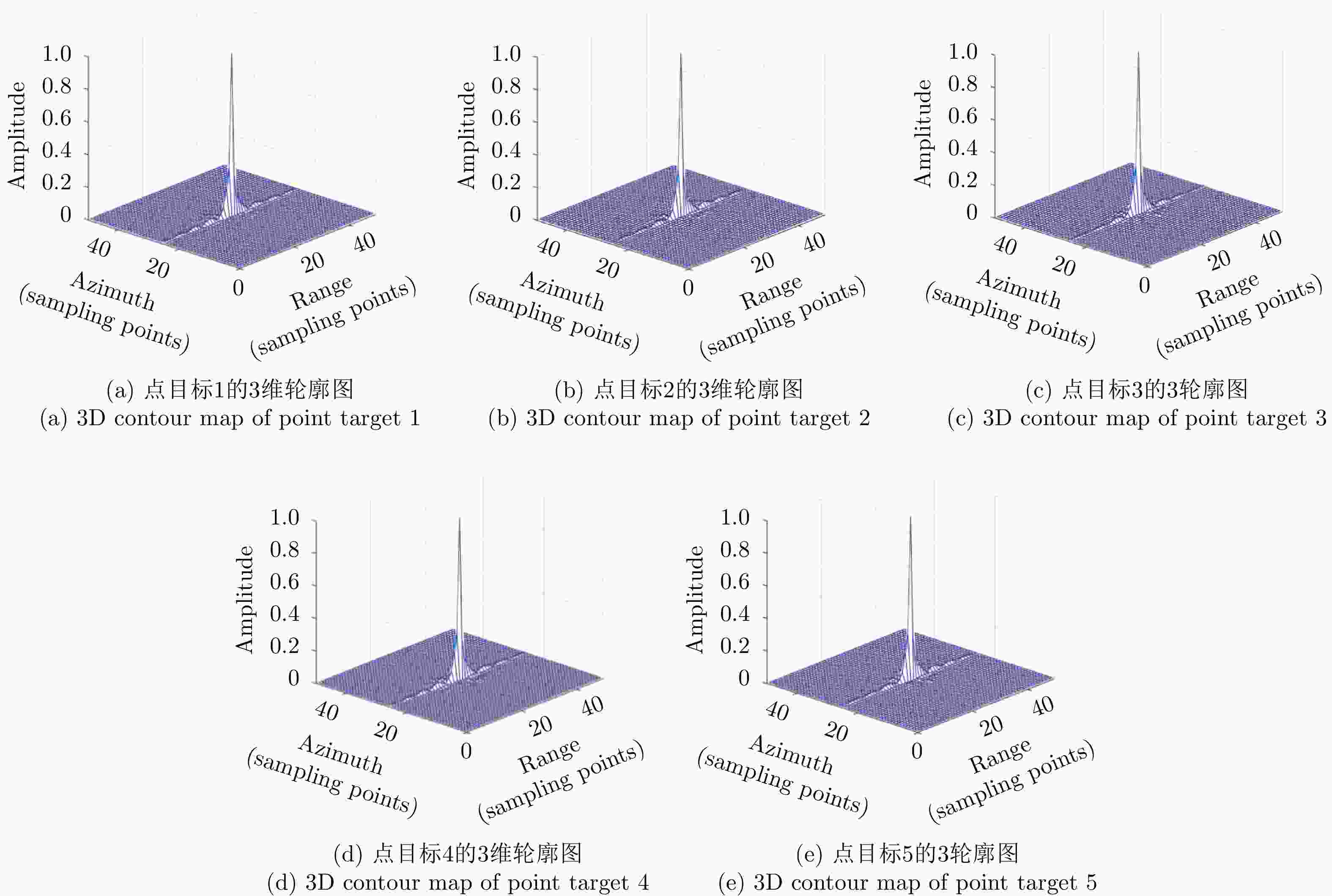
参数 值 轨道高度 (km) 800 发射信号载频 (GHz) 10 发射信号脉宽 (μs) 30 发射信号带宽 (MHz) 60 距离向采样率 (MHz) 72 方位向天线长度 (m) 9 脉冲重复频率 (Hz) 2000 -
[1] 李春升, 杨威, 王鹏波. 星载SAR成像处理算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071 [2] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [3] 赵耀, 邓云凯, 王宇, 等. 原始数据压缩对方位向多通道SAR系统影响研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 397–407. doi: 10.12000/JR17030ZHAO Yao, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. Study of effect of raw data compression on azimuth multi-channel SAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 397–407. doi: 10.12000/JR17030 [4] 罗绣莲, 徐伟, 郭磊. 捷变PRF技术在斜视聚束SAR中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 70–77. doi: 10.12000/JR14149LUO Xiulian, XU Wei, and GUO Lei. The application of PRF variation to squint spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 70–77. doi: 10.12000/JR14149 [5] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [6] ENDER J H G. On compressive sensing applied to radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(5): 1402–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.11.009 [7] VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 573–586. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2089682 [8] VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Theory of sparse coprime sensing in multiple dimensions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(8): 3592–3608. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2011.2135348 [9] ZHANG Y D, AMIN M G, and HIMED B. Sparsity-based DOA estimation using co-prime arrays[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638403. [10] TAN Zhao, ELDAR Y C, and NEHORAI A. Direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays: A super resolution viewpoint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5565–5576. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354316 [11] YU Lei, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Wei. Adaptive beamforming based on nonuniform linear arrays with enhanced degrees of freedom[C]. TENCON 2015- 2015 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Macao, China, 2015. doi: 10.1109/TENCON.2015.7373099. [12] QIN Si, ZHANG Y D, and AMIN M G. Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(6): 1377–1390. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2393838 [13] SUN Fenggang, GAO Bin, CHEN Lizhen, et al. A low-complexity ESPRIT-based DOA estimation method for co-prime linear arrays[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(9): 1367. doi: 10.3390/s16091367 [14] 王龙刚, 李廉林. 基于互质阵列雷达技术的近距离目标探测方法(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 244–253. doi: 10.12000/JR16022WANG Longgang and LI Lianlin. Short-range radar detection with (M, N)-coprime array configurations[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 244–253. doi: 10.12000/JR16022 [15] SUN Fenggang, LAN Peng, and ZHANG Guowei. Reduced dimension based two-dimensional DOA estimation with full DOFs for generalized co-prime planar arrays[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(6): 1725. doi: 10.3390/s18061725 [16] RAZA A, LIU Wei, and SHEN Qing. Thinned coprime array for second-order difference co-array generation with reduced mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(8): 2052–2065. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2901380 [17] DI MARTINO G and IODICE A. Orthogonal coprime synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 432–440. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2608140 [18] TAO Yu, ZHANG Gong, and LI Daren. Coprime sampling with deterministic digital filters in compressive sensing radar[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059224. [19] SHI Hongyin and JIA Baojing. SAR imaging method based on coprime sampling and nested sparse sampling[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 26(6): 1222–1228. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2015.00134 [20] CAFFORIO C, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. SAR data focusing using seismic migration techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1991, 27(2): 194–207. doi: 10.1109/7.78293 [21] MITTERMAYER J, MOREIRA A, and LOFFELD O. Spotlight SAR data processing using the frequency scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2198–2214. doi: 10.1109/36.789617 [22] SUN Xiaobing, YEO T S, and ZHANG Chengbo, et al. Time-varying step-transform algorithm for high squint SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(6): 2668–2677. doi: 10.1109/36.803414 [23] WANG Pengbo, LIU Wei, CHEN Jie, et al. A high-order imaging algorithm for high-resolution spaceborne SAR based on a modified equivalent squint range model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1225–1235. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2336241 [24] DO T T, GAN Lu, NGUYEN N, et al. Sparsity adaptive matching pursuit algorithm for practical compressed sensing[C]. The 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, 2008. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2008.5074472. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: