Overview of Techniques for Improving High-resolution Spaceborne SAR Imaging and Image Quality
-
摘要:
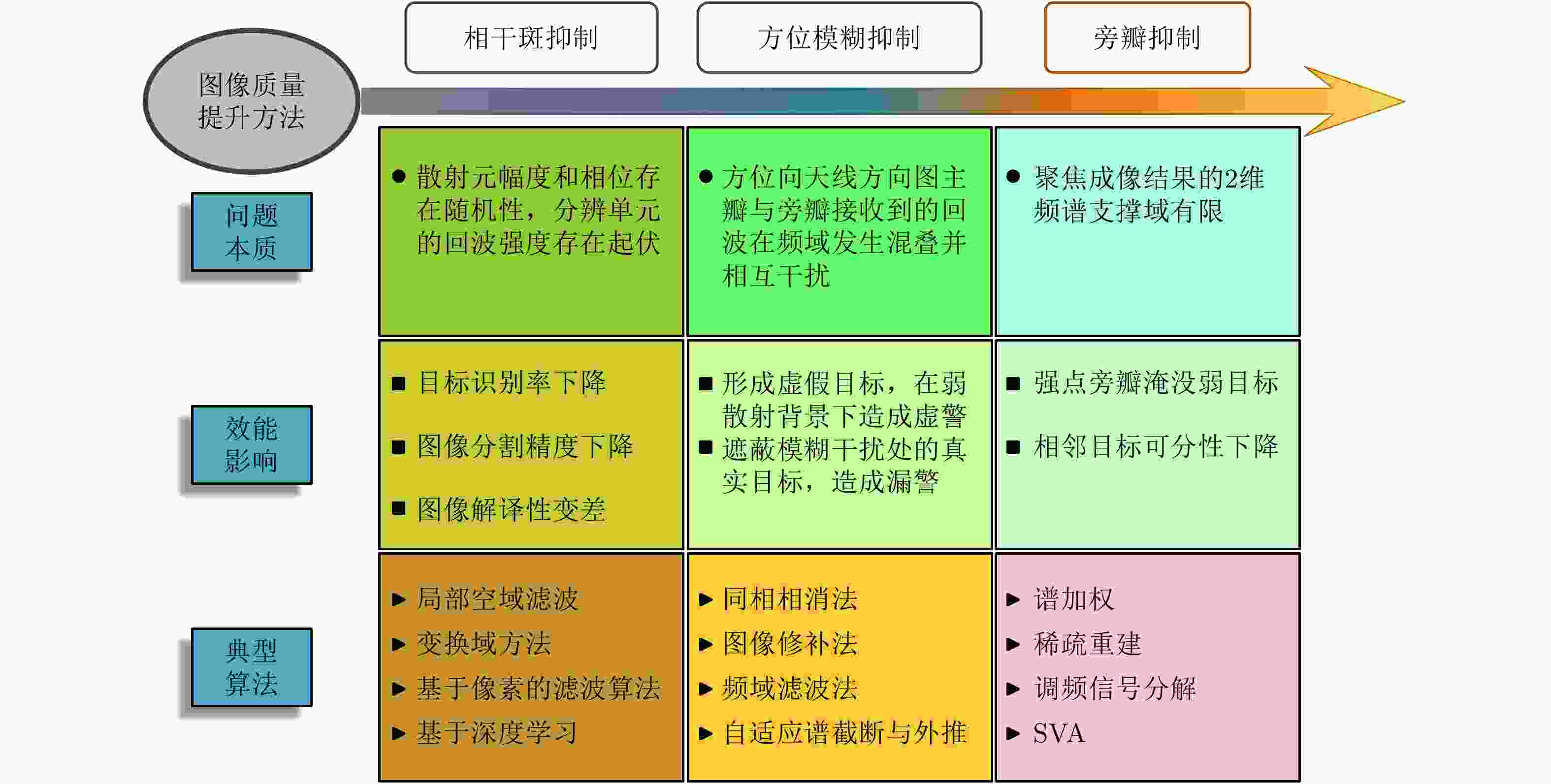
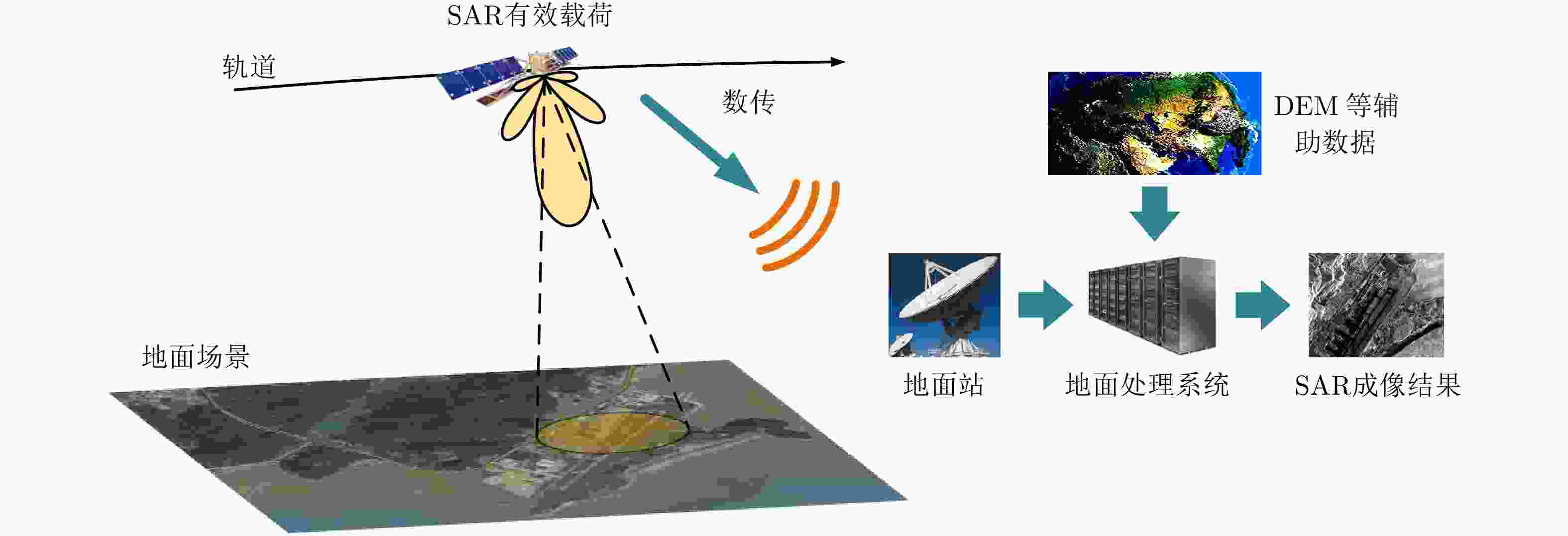
作为一种重要的空间遥感信息获取工具,星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)具备高分辨率宽测绘、多方位信息获取、高时相对地观测、3维地形测绘等多种工作体制和模式。对于任何星载SAR系统,获取高质量的图像始终是提升SAR应用效能的前提。该文基于“观测在天,成像在地”的理念,分析了卫星轨道、平台姿态、有效载荷、地面处理等环节中星载SAR成像和图像质量的影响因素;阐释了中央电子设备幅相补偿与动态调整、天线方向图预估等高精度数据获取技术;给出了基于改进运动模型的星载SAR成像补偿和对流层传播效应补偿方法,能够实现优于0.3 m分辨率的成像;总结和对比了相干斑噪声抑制、方位模糊抑制和旁瓣抑制等SAR图像处理技术,可以使得等效视数优于25、方位模糊和旁瓣抑制优于20 dB。
Abstract:As an important tool for acquiring remote sensing information, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) has various modes, including high-resolution wide-swath, multi-angle information acquisition, high temporal observation, and three-dimensional topographic mapping. For any spaceborne SAR system, obtaining high-quality images is a prerequisite for improving the performance of SAR applications. In this paper, we analyze the factors affecting spaceborne SAR imaging and image quality with respect to orbit, platform, payload, and signal processing. We describe high-precision data acquisition techniques, including amplitude-phase compensation, the dynamic adjustment of the central electronic equipment, and antenna pattern estimation. We then present imaging compensation methods based on the improved motion model and tropospheric delay correction, which can achieve resolutions better than 0.3 m. Lastly, we summarize and compare SAR image processing techniques such as speckle noise suppression, azimuth ambiguity suppression, and sidelobe suppression, whereby the equivalent number of looks can be increased to more than 25 and the azimuth ambiguity and sidelobes can both be suppressed by 20 dB.
-
表 1 实时定轨和事后定轨比较
Table 1. Comparison between real-time and precise orbit determination
输入数据类型 数据时效性 定轨精度 实时定轨 广播星历+双频伪距
载波观测数据实时 米级 事后定轨 IGS最终产品+双频伪距
载波观测数据12–18天 厘米级 表 2 通道误差补偿前后脉冲压缩性能
Table 2. Performance of pulse compression before and after compensating for channel error
幅相误差 分辨率(m) 展宽系数 峰值旁瓣比(dB) 积分旁瓣比(dB) 无补偿 0.2392 1.0800 –6.41 –5.85 补偿 0.2232 1.0077 –13.25 –9.97 表 3 仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 轨道倾角 98.06° 波束宽度(方位向) 0.305° 轨道高度 680 km 斜视角 ±6.21° 偏心率 0.001 信号带宽 1.0 GHz 观测视角 35° 脉冲宽度 40 μs 波长 0.03 m 脉冲重复频率 4000 Hz 表 4 停走误差补偿前后成像质量评估结果
Table 4. Imaging quality evaluation of point target before and after compensating for stop-go error
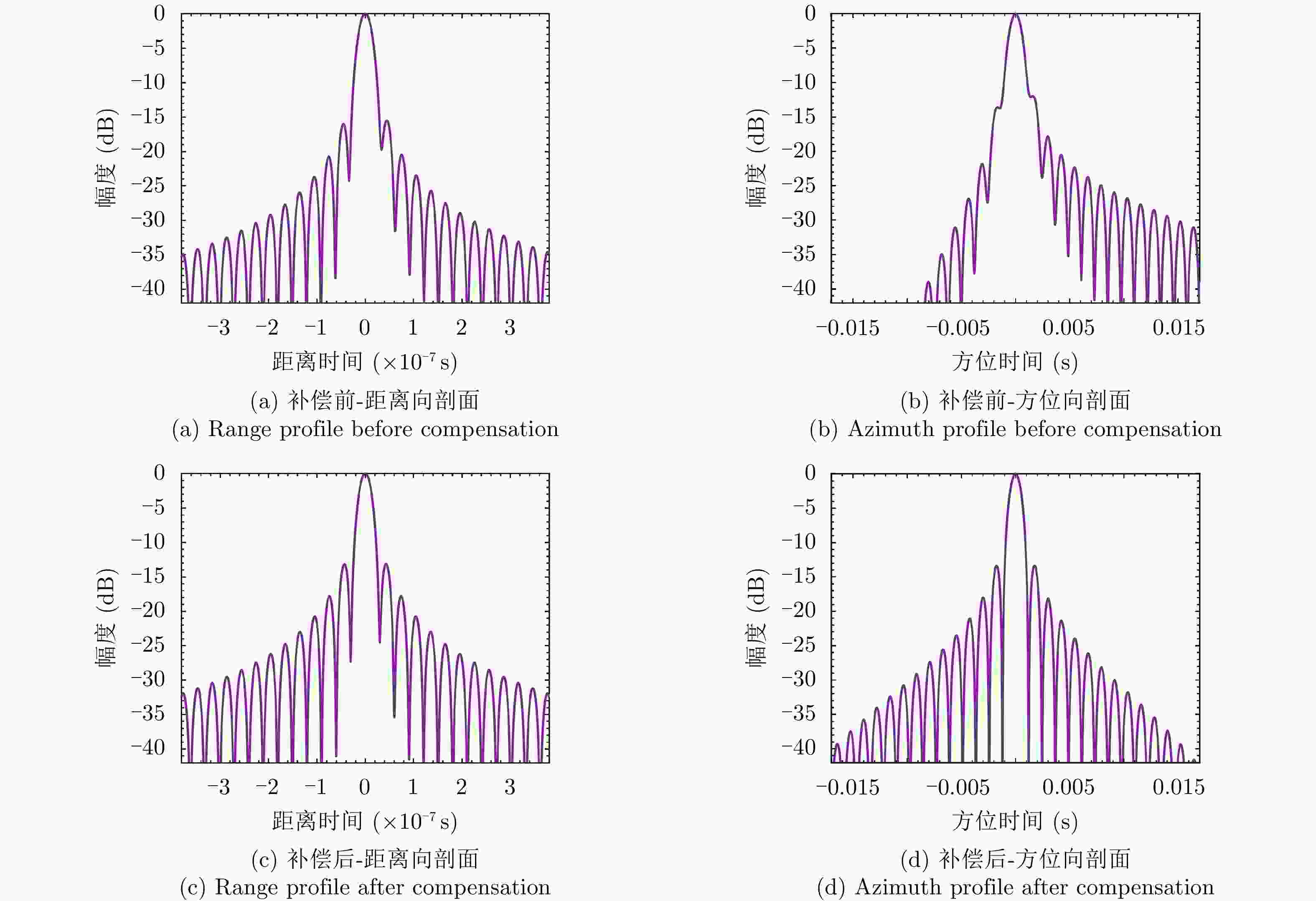
分辨率(m) 峰值旁瓣比(dB) 积分旁瓣比(dB) 距离向 补偿前 0.1444 –15.42 –12.51 补偿后 0.1342 –13.13 –9.80 方位向 补偿前 0.2420 –11.98 –9.79 补偿后 0.2170 –13.32 –10.41 表 5 不同视角下目标对流层延迟补偿前后对比
Table 5. Evaluation results before and after tropospheric delay compensation with different looking angles
视角(°) 对流层延迟补偿前方位向性能 对流层延迟补偿后方位向性能 分辨率(m) PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 分辨率(m) PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 15 0.272 –12.448 –9.213 0.270 –13.246 –10.150 35 0.272 –12.033 –8.938 0.269 –13.223 –10.319 55 0.294 –8.579 –5.860 0.275 –13.240 –10.069 -
[1] WANG Pengbo, LIU Wei, CHEN Jie, et al. A high-order imaging algorithm for high-resolution spaceborne sar based on a modified equivalent squint range model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1225–1235. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2336241 [2] CHEN Jie, KUANG Hui, YANG Wei, et al. A novel imaging algorithm for focusing high-resolution spaceborne SAR data in squinted sliding-spotlight mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1577–1581. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2598066 [3] 赵团, 邓云凯, 王宇, 等. 基于扇贝效应校正的改进滑动Mosaic全孔径成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 548–557. doi: 10.12000/JR16014ZHAO Tuan, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. Processing sliding mosaic mode data with modified full-aperture imaging algorithm integrating scalloping correction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 548–557. doi: 10.12000/JR16014 [4] TOWNSEND W. An initial assessment of the performance achieved by the Seasat-1 radar altimeter[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1980, 5(2): 80–92. doi: 10.1109/JOE.1980.1145459 [5] 李春升, 王伟杰, 王鹏波, 等. 星载SAR技术的现状与发展趋势[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 229–240.LI Chunsheng, WANG Weijie, WANG Pengbo, et al. Current situation and development trends of spaceborne SAR technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 229–240. [6] PITZ W and MILLER D. The TerraSAR-X satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 615–622. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037432 [7] DE ZAN F and GUARNIERI A M. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(9): 2352–2360. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.873853 [8] 魏钟铨. 合成孔径雷达卫星[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.WEI Zhongquan. Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. [9] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991. [10] PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, et al. On the processing of very high resolution spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6003–6016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2294353 [11] 万丽华, 魏立龙, 王磊. 基于全球台站的GNSS卫星精密定轨策略分析[J]. 测绘地理信息, 2019, 44(4): 53–58. doi: 10.14188/j.2095-6045.2017331WAN Lihua, WEI Lilong, and WANG Lei. On the strategies of precise orbit determination of GNSS from global stations[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2019, 44(4): 53–58. doi: 10.14188/j.2095-6045.2017331 [12] 丁赤飚, 刘佳音, 雷斌, 等. 高分三号SAR卫星系统级几何定位精度初探[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024DING Chibiao, LIU Jiayin, LEI Bin, et al. Preliminary exploration of systematic geolocation accuracy of GF-3 SAR satellite system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 11–16. doi: 10.12000/JR17024 [13] 秦显平. 星载GPS低轨卫星定轨理论及方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 解放军信息工程大学, 2009.QIN Xianping. Research on precision orbit determination theory and method of low earth orbiter based on GPS technique[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], PLA Information Engineering University, 2009. [14] 崔仁洁. 卫星姿态控制一体化仿真系统设计与研究[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2017.CUI Renjie. Design and research of the integrated simulation platform for satellites attitude control system[D].[Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2017. [15] LI Zhou, LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, et al. Effects of receiver saturation on image formation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 535–538. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049183. [16] SMITH A M. A new approach to range-Doppler SAR processing[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1991, 12(2): 235–251. doi: 10.1080/01431169108929650 [17] JIN M Y, CHENG F, and CHEN Ming. Chirp scaling algorithms for SAR processing[C]. 1993 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 1993: 1169–1172. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1993.322129. [18] LIU Yan, XING Mengdao, SUN Guangcai, et al. Echo model analyses and imaging algorithm for high-resolution SAR on high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(3): 933–950. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2011.2162243 [19] WU Yuan, SUN Guangcai, YANG Chun, et al. Processing of very high resolution spaceborne sliding spotlight SAR data using velocity scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1505–1518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2481923 [20] YU Ze, WANG Shusen, and LI Zhou. An imaging compensation algorithm for spaceborne high-resolution SAR based on a continuous tangent motion model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(3): 223. doi: 10.3390/rs8030223 [21] 胡程, 董锡超, 李元昊. 大气层效应对地球同步轨道SAR系统性能影响研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 412–424. doi: 10.12000/JR18032HU Cheng, DONG Xichao, and LI Yuanhao. Atmospheric effects on the performance of geosynchronous orbit SAR systems[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 412–424. doi: 10.12000/JR18032 [22] YU Ze, LI Zhou, and WANG Shusen. An imaging compensation algorithm for correcting the impact of tropospheric delay on spaceborne high-resolution SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4825–4836. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2015.2411261 [23] 郭小洋, 李洋, 林赟, 等. 基于CSAR成像的相干斑统计模型研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 708–714. doi: 10.12000/JR15039GUO Xiaoyang, LI Yang, LIN Yun, et al. Statistical models of speckle for circular SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 708–714. doi: 10.12000/JR15039 [24] KUAN D T, SAWCHUK A A, STRAND T C, et al. Adaptive noise smoothing filter for images with signal-dependent noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1985, PAMI-7(2): 165–177. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1985.4767641 [25] ARGENTI F and ALPARONE L. Speckle removal from SAR images in the undecimated wavelet domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2363–2374. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2002.805083 [26] YU Yongjian and ACTON S T. Speckle reducing anisotropic diffusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(11): 1260–1270. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2002.804276 [27] DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L, and TUPIN F. Iterative weighted maximum likelihood denoising with probabilistic patch-based weights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(12): 2661–2672. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2029593 [28] PARRILLI S, PODERICO M, ANGELINO C V, et al. A nonlocal SAR image denoising algorithm based on LLMMSE wavelet shrinkage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(2): 606–616. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2011.2161586 [29] WANG Puyang, ZHANG He, and PATEL V M. SAR image despeckling using a convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(12): 1763–1767. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2758203 [30] ZHANG Qian, YUAN Qiangqiang, LI Jie, et al. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 196. doi: 10.3390/rs10020196 [31] WANG Puyang, ZHANG He, and VISHAL M P. Generative adversarial network-based restoration of speckled SAR images[C]. 2017 IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, Curacao, Netherlands, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CAMSAP.2017.8313133. [32] YU Ze, WANG Wenqi, LI Chunsheng, et al. Speckle noise suppression in SAR images using a three-step algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3643. doi: 10.3390/s18113643 [33] 肖鹏, 吴有明, 于泽, 等. 一种基于压缩感知恢复算法的SAR图像方位模糊抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(1): 35–41. doi: 10.12000/JR16004XIAO Peng, WU Youming, YU Ze, et al. Azimuth ambiguity suppression in SAR images based on compressive sensing recovery algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(1): 35–41. doi: 10.12000/JR16004 [34] MOREIRA A. Suppressing the azimuth ambiguities in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1993, 31(4): 885–895. doi: 10.1109/36.239912 [35] CHEN Jie, IQBAL M, YANG Wei, et al. Mitigation of azimuth ambiguities in spaceborne stripmap SAR images using selective restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4038–4045. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2279109 [36] GUARNIERI A M. Adaptive removal of azimuth ambiguities in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 625–633. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2004.842476 [37] WU Youming, YU Ze, XIAO Peng, et al. Suppression of azimuth ambiguities in spaceborne SAR images using spectral selection and extrapolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6134–6147. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2832193 [38] 陶一凡. SAR图像旁瓣抑制和目标识别方法的研究及实现[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江工业大学, 2017.TAO Yifan. Research and implement on methods of SAR image sidelobe suppression and target recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University of Technology, 2017. [39] ZHU Xiaoxiang, HE Feng, YE Fan, et al. Sidelobe suppression with resolution maintenance for SAR images via sparse representation[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1589. doi: 10.3390/s18051589 [40] VARSHNEY L R and THOMAS D. Sidelobe reduction for matched filter range processing[C]. Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Radar Conference, Huntsville, USA, 2003: 446–451. doi: 10.1109/NRC.2003.1203439. [41] JIN Guodong, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. An advanced nonlinear frequency modulation waveform for radar imaging with low sidelobe[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6155–6168. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904627 [42] SMITH B H. Generalization of spatially variant apodization to noninteger Nyquist sampling rates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2000, 9(6): 1088–1093. doi: 10.1109/83.846250 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: