-
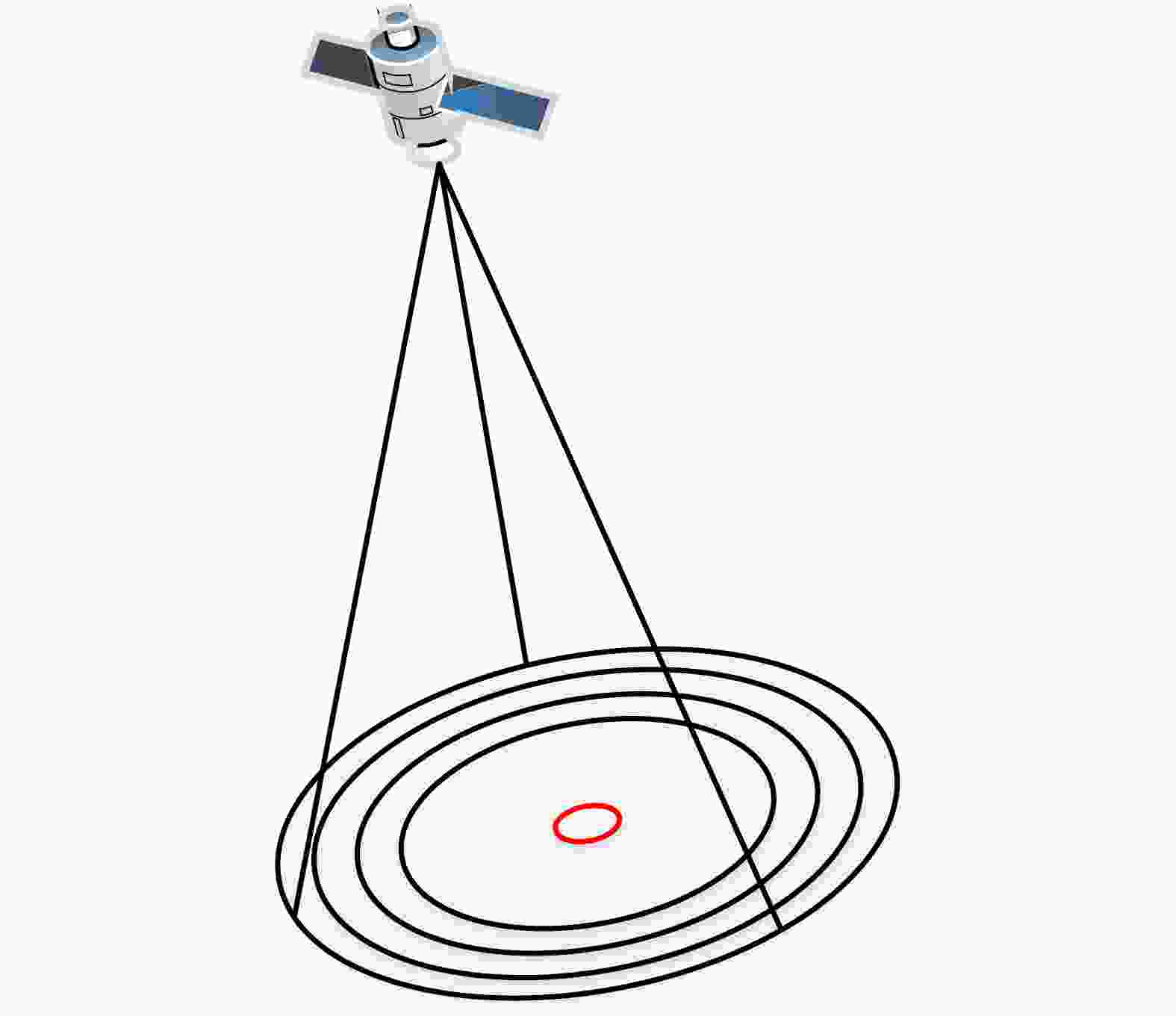
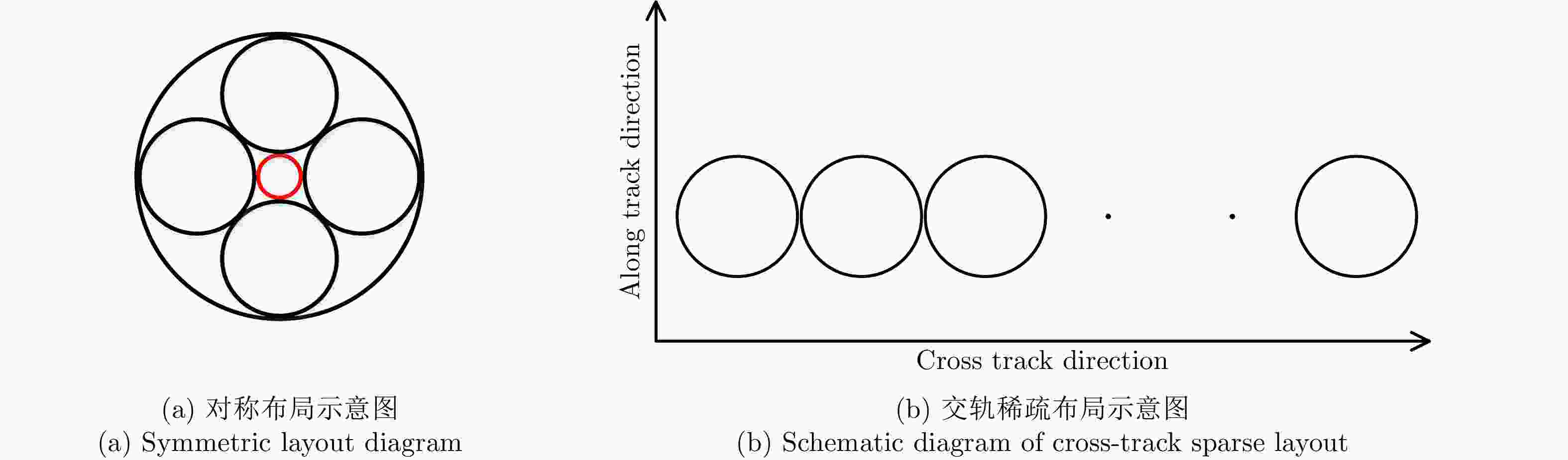
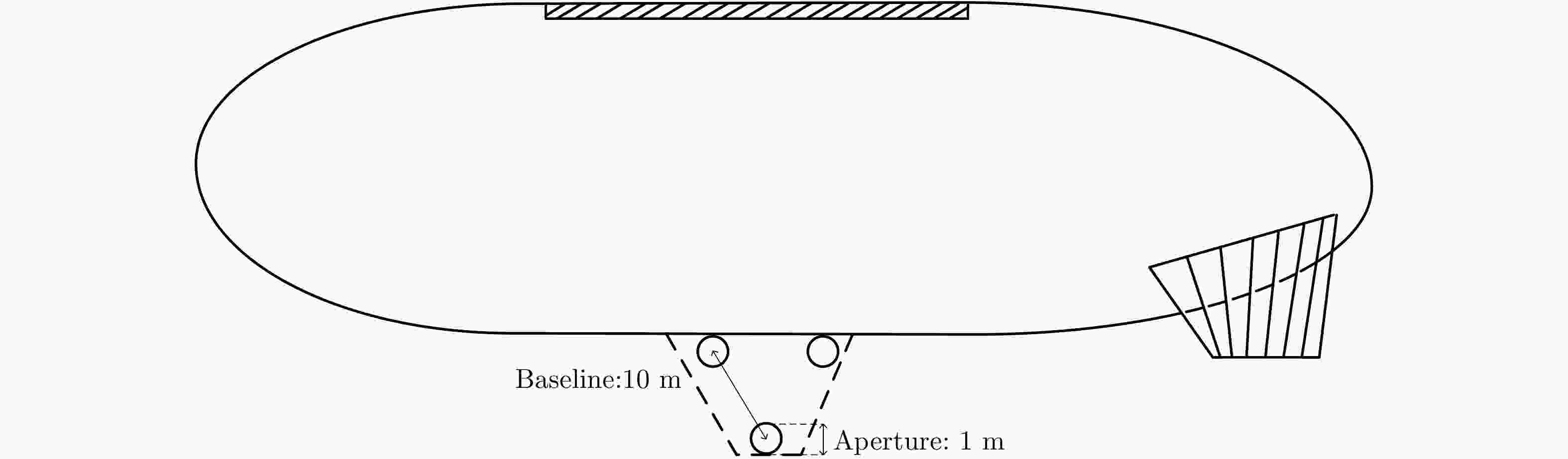
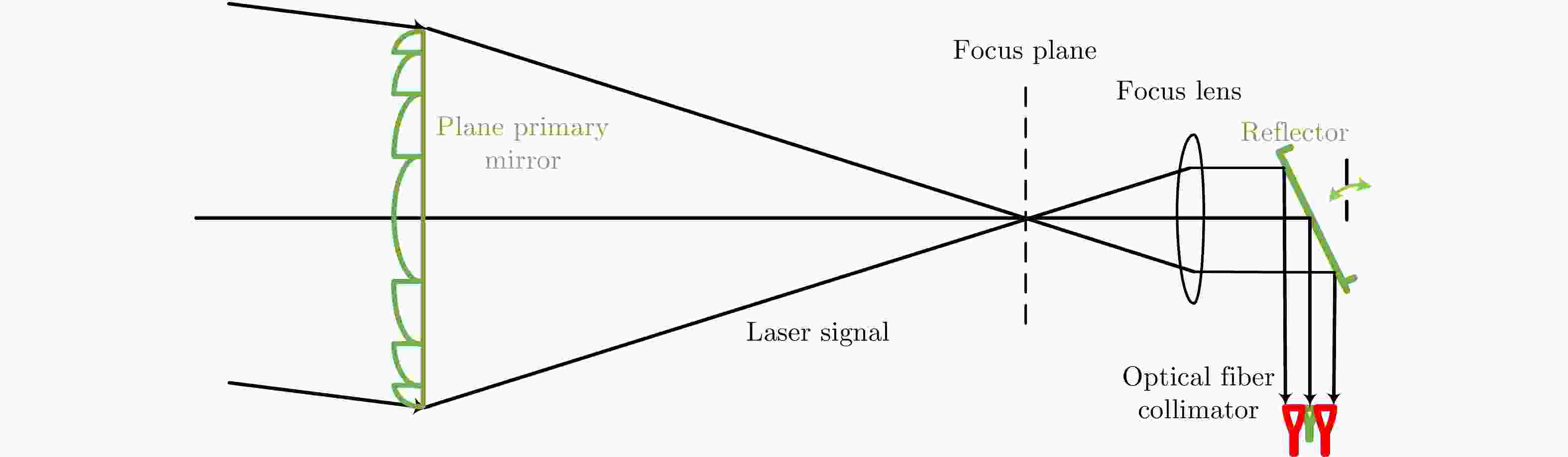
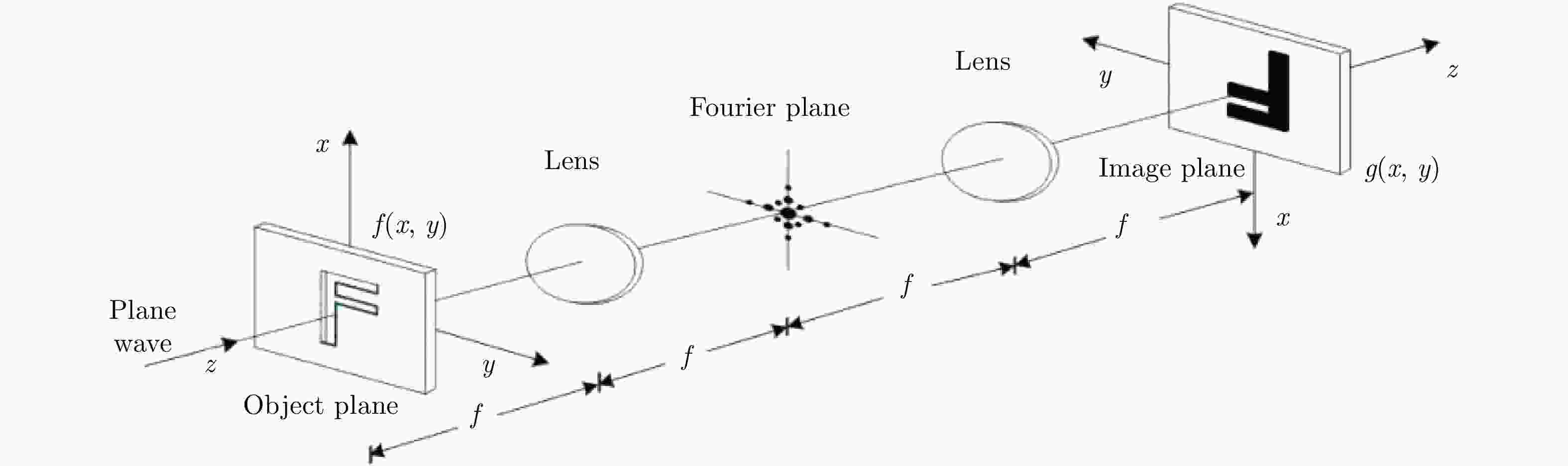
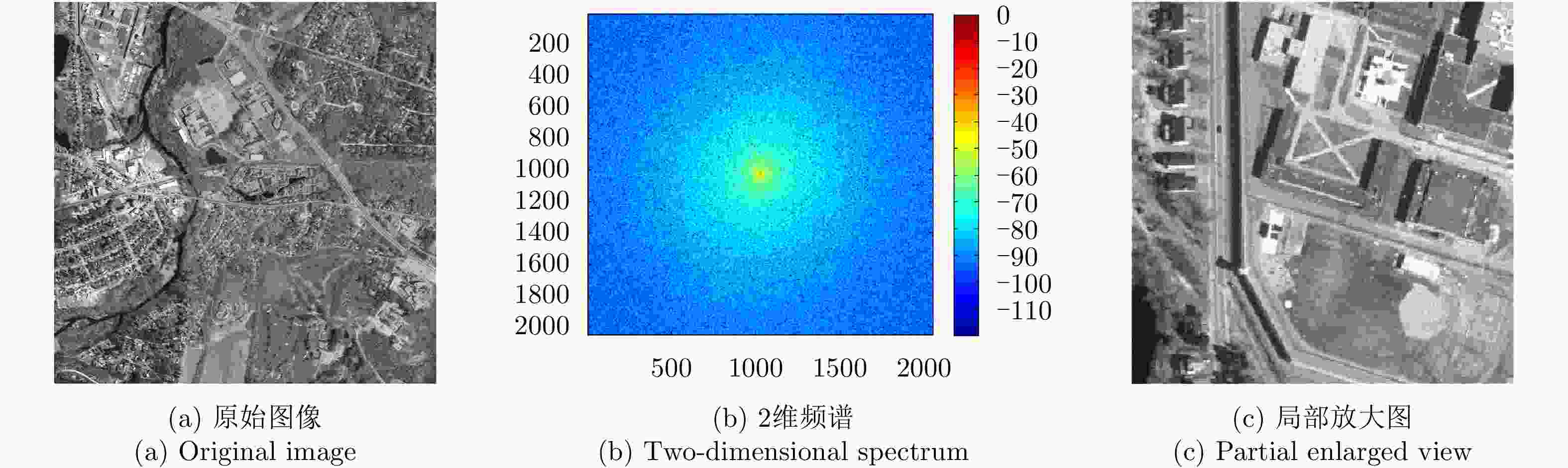
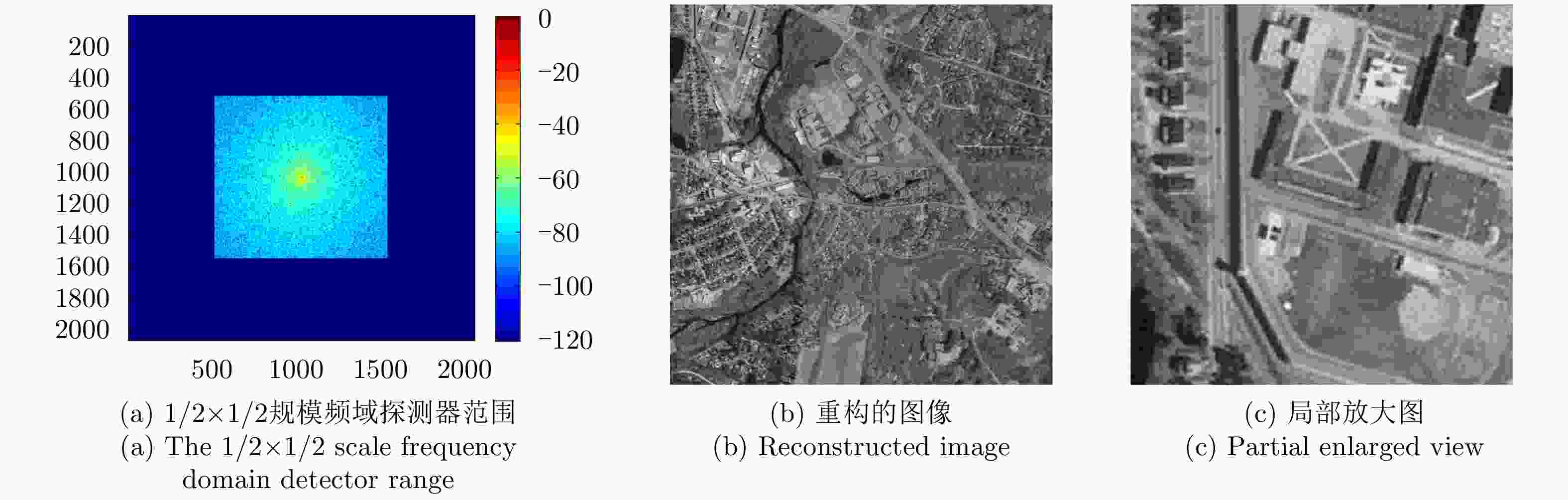
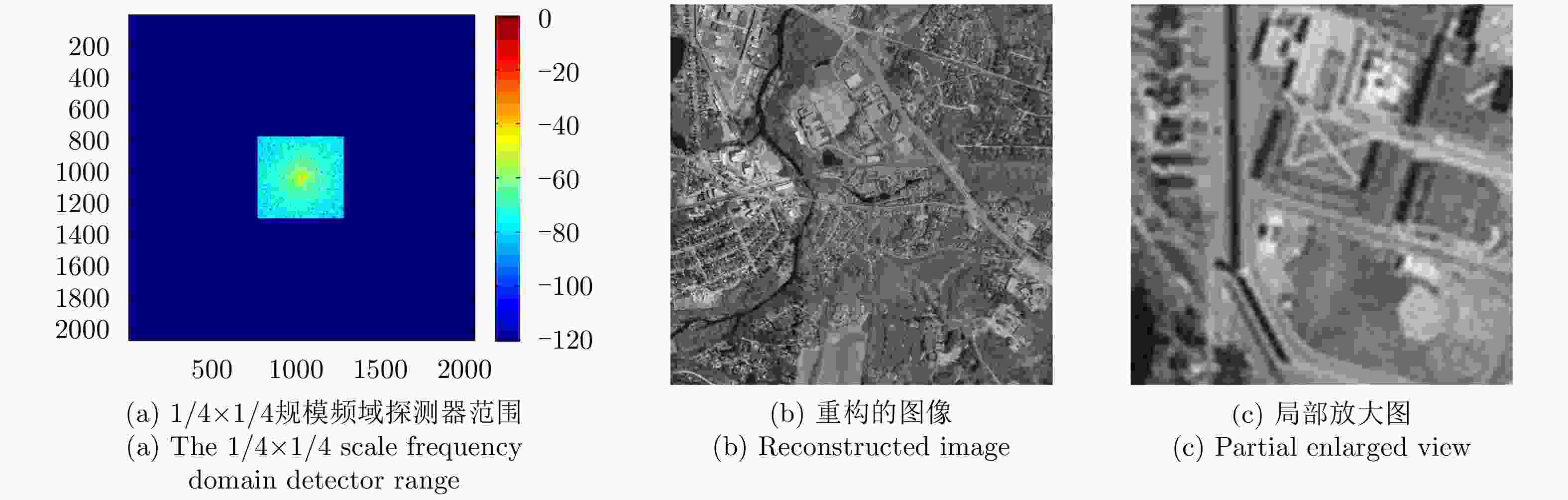
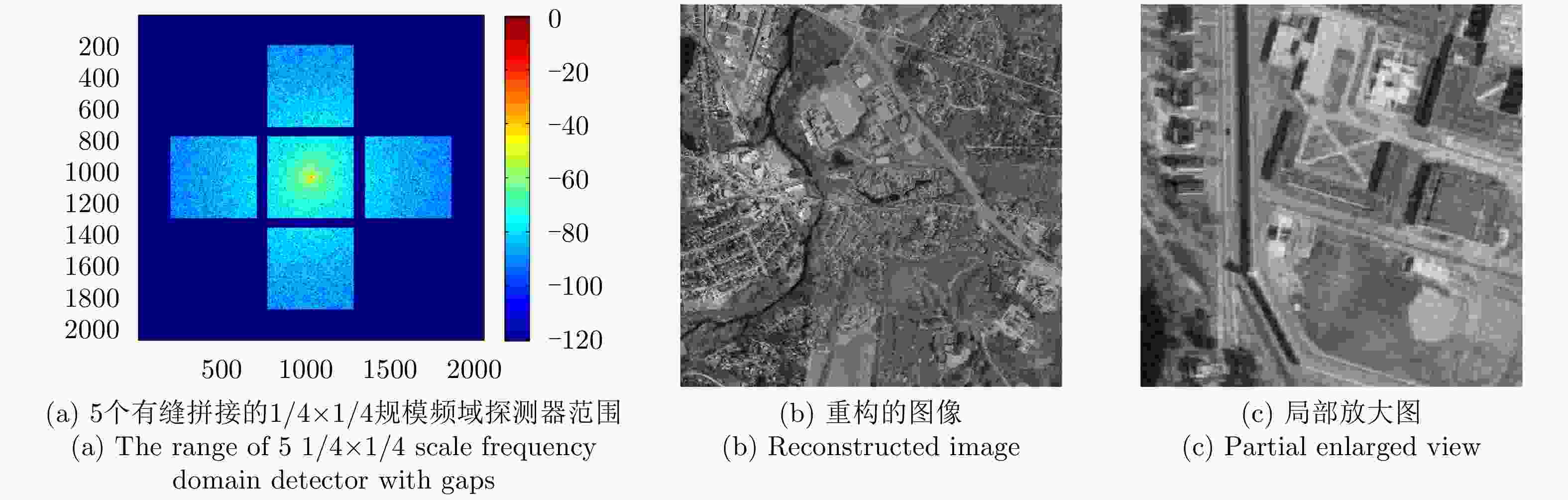
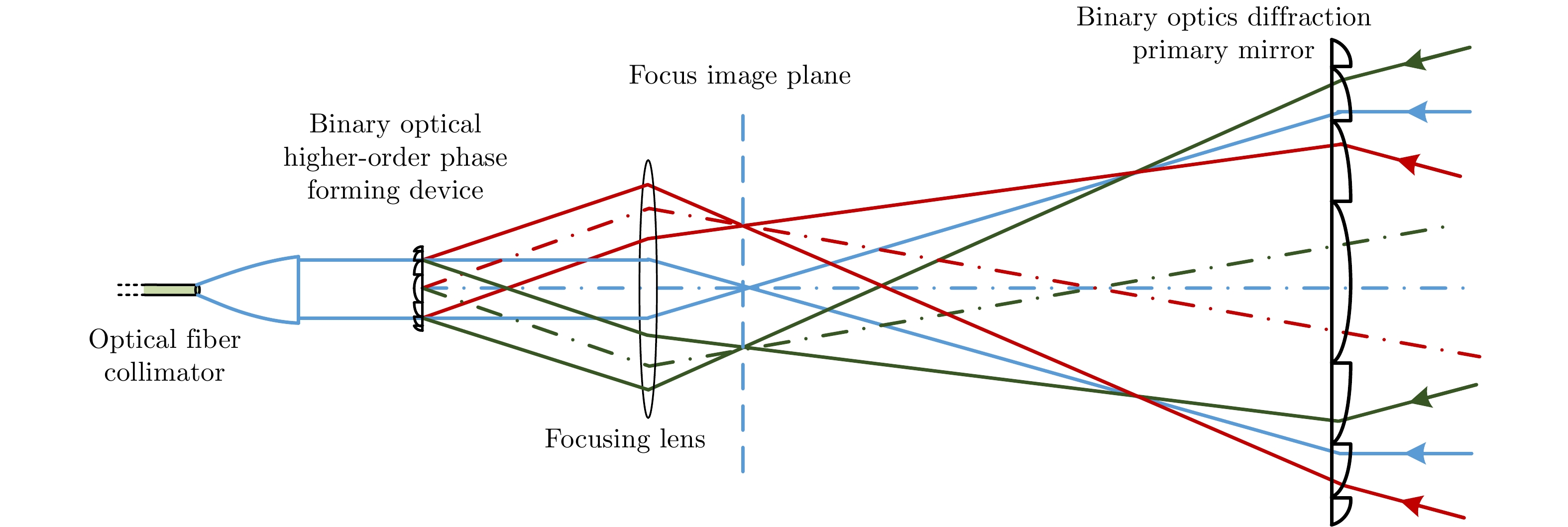
摘要: 近年来衍射光学系统得到了快速发展,衍射器件(如二元光学器件和膜基透镜)相当于微波天线的固定移相器,微波相控阵天线成熟的理论和方法应可用于其性能分析。激光SAR和激光通信都具有单色且波长较长的特点,特别适合采用非成像衍射光学系统,通过衍射器件实现信号波前控制,减小焦距并有利于系统的轻量化。基于衍射光学系统,研究激光SAR和激光通信技术具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。该文给出了衍射光学系统的相控阵解释,介绍了基于衍射光学系统已开展的机载激光SAR和星载激光SAR研究工作。提出了艇载1 m衍射口径激光通信和干涉定位系统概念并分析了其性能,该系统在10 m短基线下,其作用距离将达到4×108 km,对应的定位精度在6 km量级,可用于深空探测。该文同时探讨了稀疏采样激光成像问题,在激光照射目标条件下,提出用傅里叶透镜将激光图像信号变换到频域,在低频区域利用小规模探测器实施稀疏采样,等效进行2维低通滤波处理,再用计算机重构目标图像的设想,给出了一些初步的仿真结果。Abstract: In recent years, the diffractive optical systems have developed rapidly. Diffractive devices such as binary optical device and membrane-based lens are equivalent to fixed phase shifters of microwave antennas. Thus, the mature theories and methods of a microwave phased-array antenna could be used for diffractive devices’ performance analysis. Both laser Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and laser communication feature a single color and long wavelength, and they are specifically suitable for non-imaging diffractive optical systems. A signal wave front control realized by a diffraction device reduces the focal length and the weight of a system. Research on laser SAR and laser communication technology has important theoretical significance and application value for diffractive optical system. In this paper, we provide a phased-array interpretation of a diffractive optical system and introduce research that has been conducted on airborne and spaceborne laser SAR with respect to diffractive optical systems. We propose the concept of shipborne 1 m diffraction aperture laser communication and an interferometric positioning system and analyze its performance. The results indicated that, using a 10 m short baseline, this system can reach 400 million km with a corresponding positioning accuracy of 6 km that is suitable for use during deep space probes. We also discuss the sparse-sampling laser-imaging problem using a laser to illuminate the target, transforming the laser image signal into the frequency domain with Fourier lens, using the small-scale detector to perform sparse sampling in the low-frequency domain, and reconstructing the target image using a computer. Some preliminary simulation results are provided.
-
表 1 激光通信系统参数
Table 1. Parameters of laser telecommunication system
下行参数 数值 上行参数 数值 波长 1.064 μm 波长 1.064 μm 带宽 15 kHz 带宽 15 kHz 探测器发射望远镜口径 0.1 m 艇载发射望远镜口径 1.0 m 艇载接收望远镜口径 1.0 m 探测器接收望远镜口径 0.1 m 探测器激光发射功率 10 W 艇载激光发射功率 15 W 探测器发射光学系统传输效率 0.9 艇载发射光学系统传输效率 0.7 艇载接收光学系统传输效率 0.8 探测器接收光学系统传输效率 0.9 光电探测器量子效率 0.5 光电探测器量子效率 0.5 外差探测效率 0.5 外差探测效率 0.5 光学系统的其他损耗 0.3 光学系统的其他损耗 0.3 电子学噪声系数 2 dB 电子学噪声系数 2 dB 下行数据信噪比 6 dB 上行数据信噪比 6 dB 作用距离 4.08×108 km 作用距离 4.32×108 km -
[1] 焦建超, 苏云, 王保华, 等. 地球静止轨道膜基衍射光学成像系统的发展与应用[J]. 国际太空, 2016(6): 49–55.JIAO Jianchao, SU Yun, WANG Baohua, et al. Development and application of GEO membrane based diffraction optical imaging system[J]. Space International, 2016(6): 49–55. [2] 刘韬, 周润松. 国外地球静止轨道高分辨率光学成像系统发展综述[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(4): 91–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.04.015LIU Tao and ZHOU Runsong. Development overview on GEO high resolution optical imaging system[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(4): 91–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.04.015 [3] 李道京, 胡烜. 合成孔径激光雷达光学系统和作用距离分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 263–274. doi: 10.12000/JR18017LI Daojing and HU Xuan. Optical system and detection range analysis of synthetic aperture ladar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 263–274. doi: 10.12000/JR18017 [4] ZHU Jinyi and XIE Yongjun. Large aperture diffractive telescope design for space-based lidar receivers[C]. The SPIE 9795, Selected Papers of the Photoelectronic Technology Committee Conferences Held June–July 2015, Harbin, China, 2015. [5] 胡烜, 李道京. 10 m衍射口径天基合成孔径激光雷达系统[J]. 中国激光, 2018, 45(12): 1210002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.1210002HU Xuan and LI Daojing. Space-based synthetic aperture LiDAR system with 10 m diffractive aperture[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(12): 1210002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.1210002 [6] 周程灏, 王治乐, 朱峰. 大口径光学合成孔径成像技术发展现状[J]. 中国光学, 2017, 10(1): 25–38. doi: 10.3788/co.20171001.0025ZHOU Chenghao, WANG Zhile, and ZHU Feng. Review on optical synthetic aperture imaging technique[J]. Chinese Optical, 2017, 10(1): 25–38. doi: 10.3788/co.20171001.0025 [7] 李道京, 侯颖妮, 滕秀敏, 等. 稀疏阵列天线雷达技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.LI Daojing, HOU Yingni, TENG Xiumin, et al. Sparse Array Antenna Radar Technology and Its Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [8] 李烈辰, 李道京. 基于压缩感知的连续场景稀疏阵列SAR三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645LI Liechen and LI Daojing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 [9] 田鹤, 李道京. 稀疏重航过阵列SAR运动误差补偿和三维成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 717–729. doi: 10.12000/JR18101TIAN He and LI Daojing. Motion compensation and 3-D imaging algorithm in sparse flight based airborne array SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 717–729. doi: 10.12000/JR18101 [10] 郝万宏, 李海涛, 黄磊, 等. 建设中的深空测控网甚长基线干涉测量系统[J]. 飞行器测控学报, 2012, 31(S1): 34–37.HAO Wanhong, LI Haitao, HUANG Lei, et al. Development of a VLBI system for China’s deep space network[J]. Journal of spacecraft TT &C technology, 2012, 31(S1): 34–37. [11] 朱新颖, 李春来, 张洪波. 深空探测VLBI技术综述及我国的现状和发展[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(8): 1893–1899. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2010.08.001ZHU Xinying, LI Chunlai, and ZHANG Hongbo. A survey of VLBI technique for deep space exploration and trend in China current situation and development[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(8): 1893–1899. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2010.08.001 [12] 彭祥龙. 国外毫米波电扫描技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2009, 49(1): 85–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893X.2009.01.019PENG Xianglong. Electronically controlled millimeter wave beam steering technologies[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2009, 49(1): 85–91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893X.2009.01.019 [13] 李海涛. 深空测控通信系统设计原理与方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.LI Haitao. Principles and Design Methods of Deep Space TT&C System[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015. [14] 高铎瑞, 李天伦, 孙悦, 等. 空间激光通信最新进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国光学, 2018, 11(6): 901–913. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181106.0901GAO Duorui, LI Tianlun, SUN Yue, et al. Latest developments and trends of space laser communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(6): 901–913. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181106.0901 [15] LI Luchang. 傅里叶光学基础总结[EB/OL]. https://blog.csdn.net/u013701860/article/details/77546546, 2017.LI Luchang. Summary of Fourier optical foundation[EB/OL]. https://blog.csdn.net/u013701860/article/details/77546546, 2017. [16] ZHENG Guoan, HORSTMEYER R, and YANG C. Wide-field, high-resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(9): 739–745. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.187 [17] 孙佳嵩, 张玉珍, 陈钱, 等. 傅里叶叠层显微成像技术: 理论、发展和应用[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(10): 1011005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.1011005SUN Jiasong, ZHANG Yuzhen, CHEN Qian, et al. Fourier ptychographic microscopy: Theory, advances, and applications[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(10): 1011005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.1011005 [18] 赵明, 王希明, 张晓慧, 等. 宏观傅里叶叠层超分辨率成像实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(12): 121101.ZHAO Ming, WANG Ximing, ZHANG Xiaohui, et al. Experimental research on macroscopic Fourier ptychography super-resolution imaging[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(12): 121101. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: