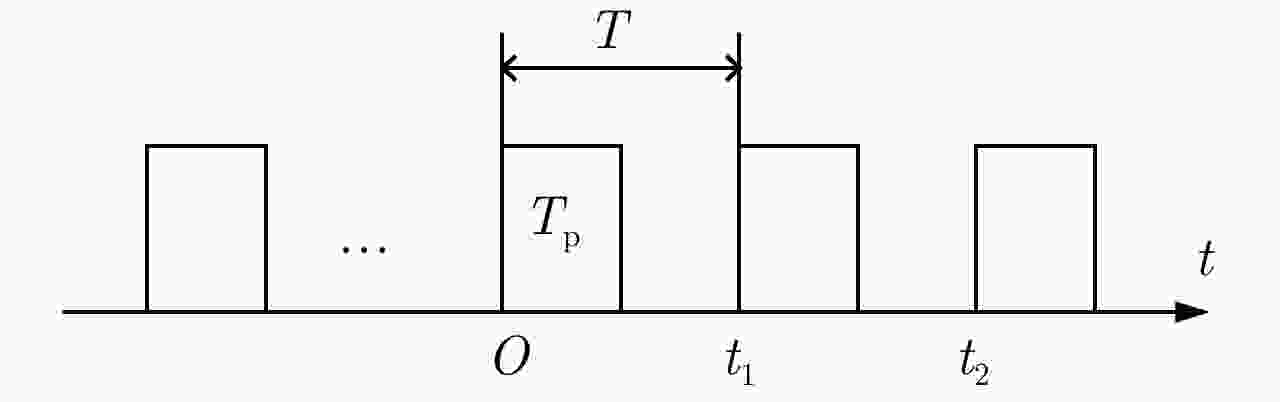
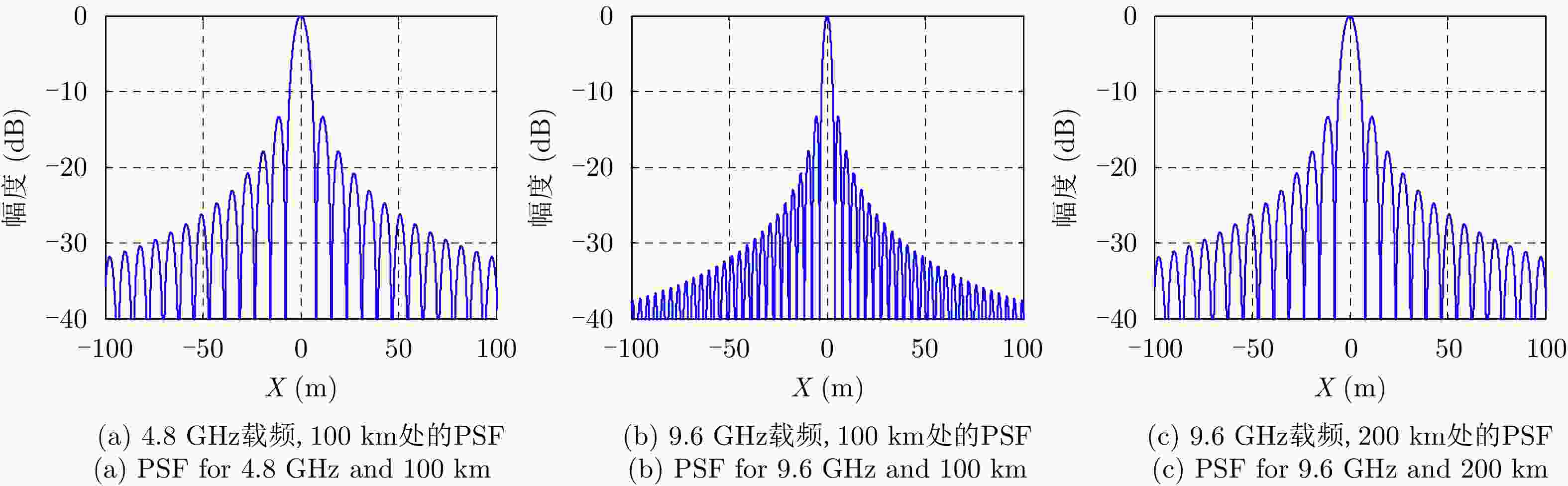
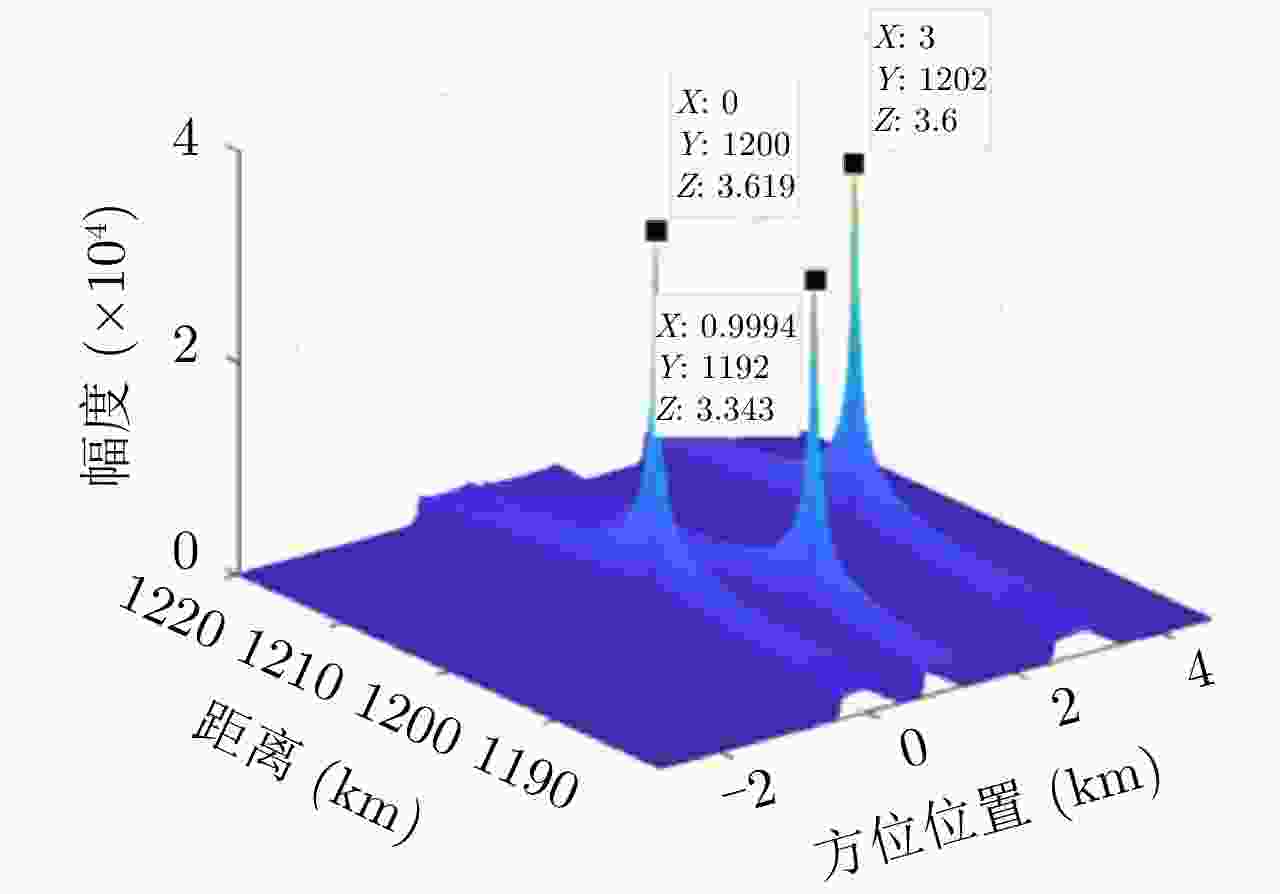
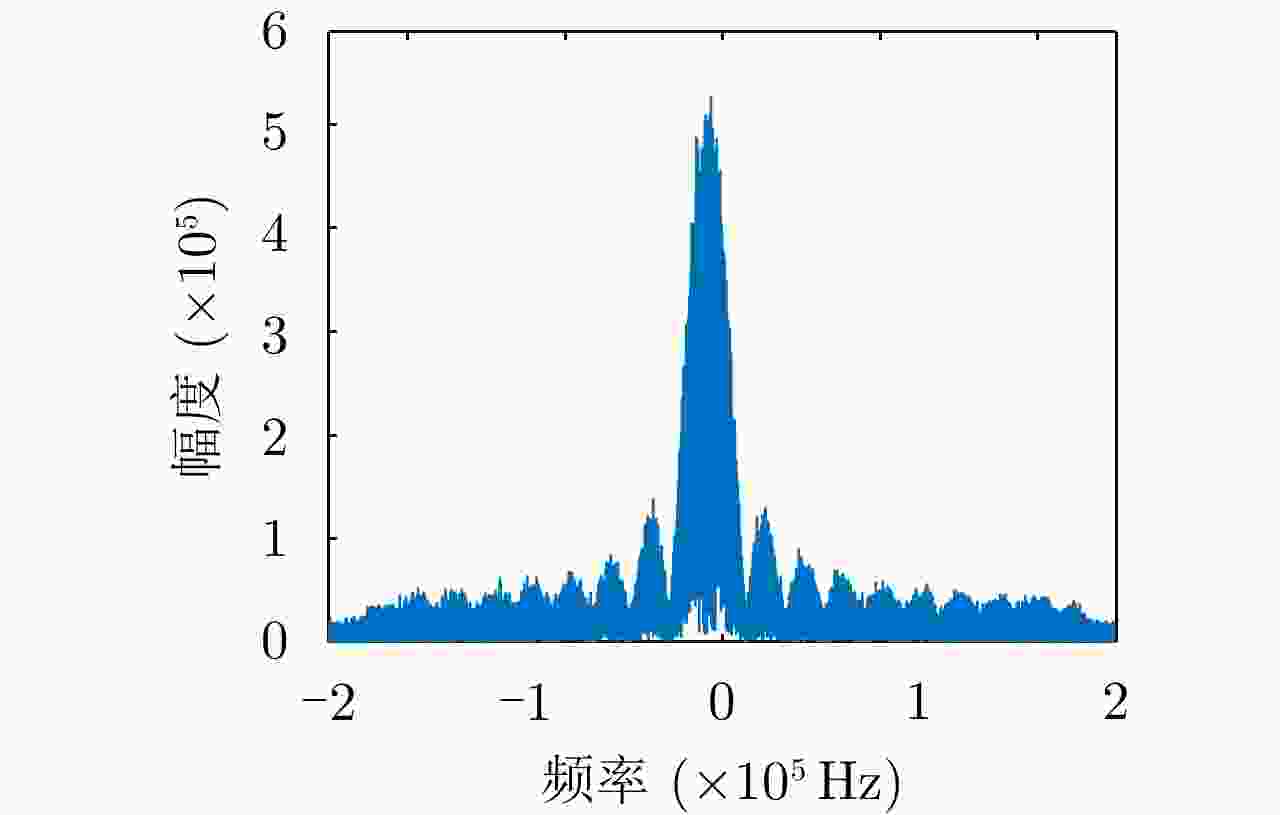
Passive Localization Algorithm for Radiation Source Based on Long Synthetic Aperture
-
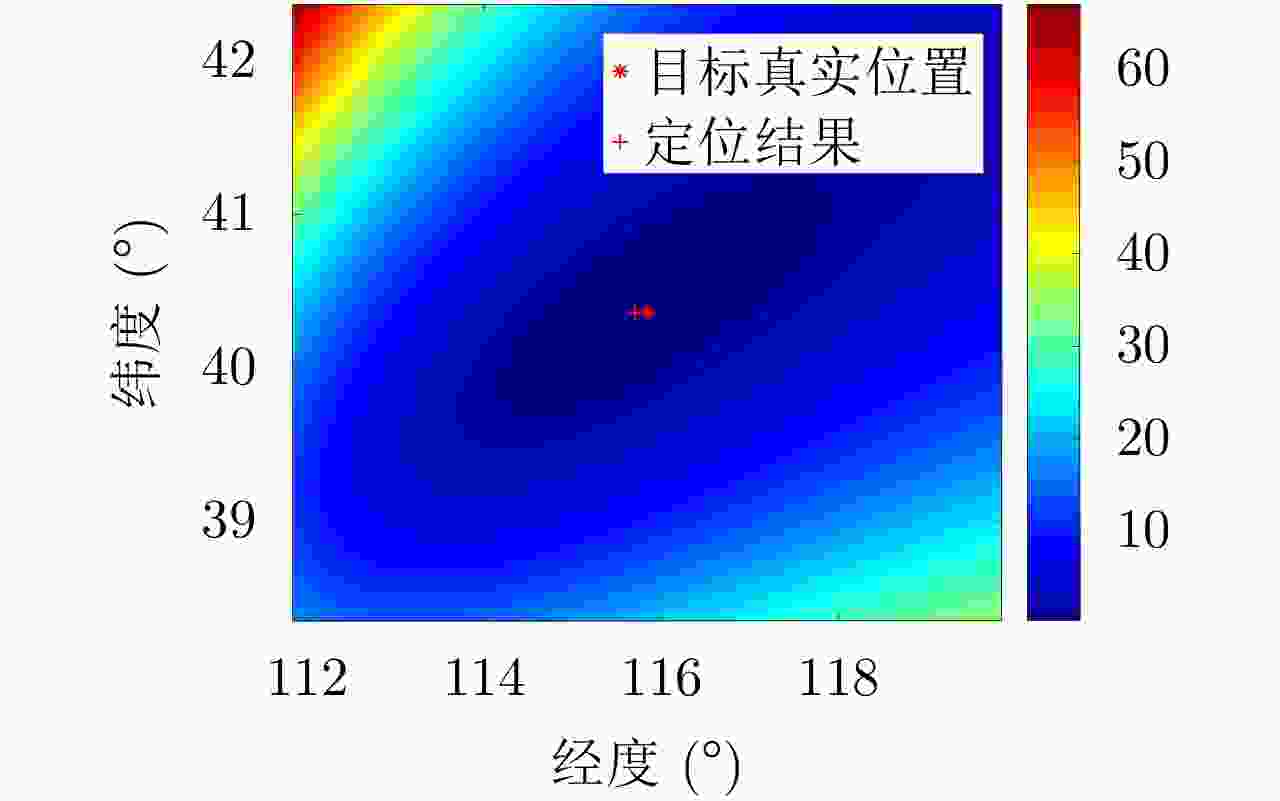
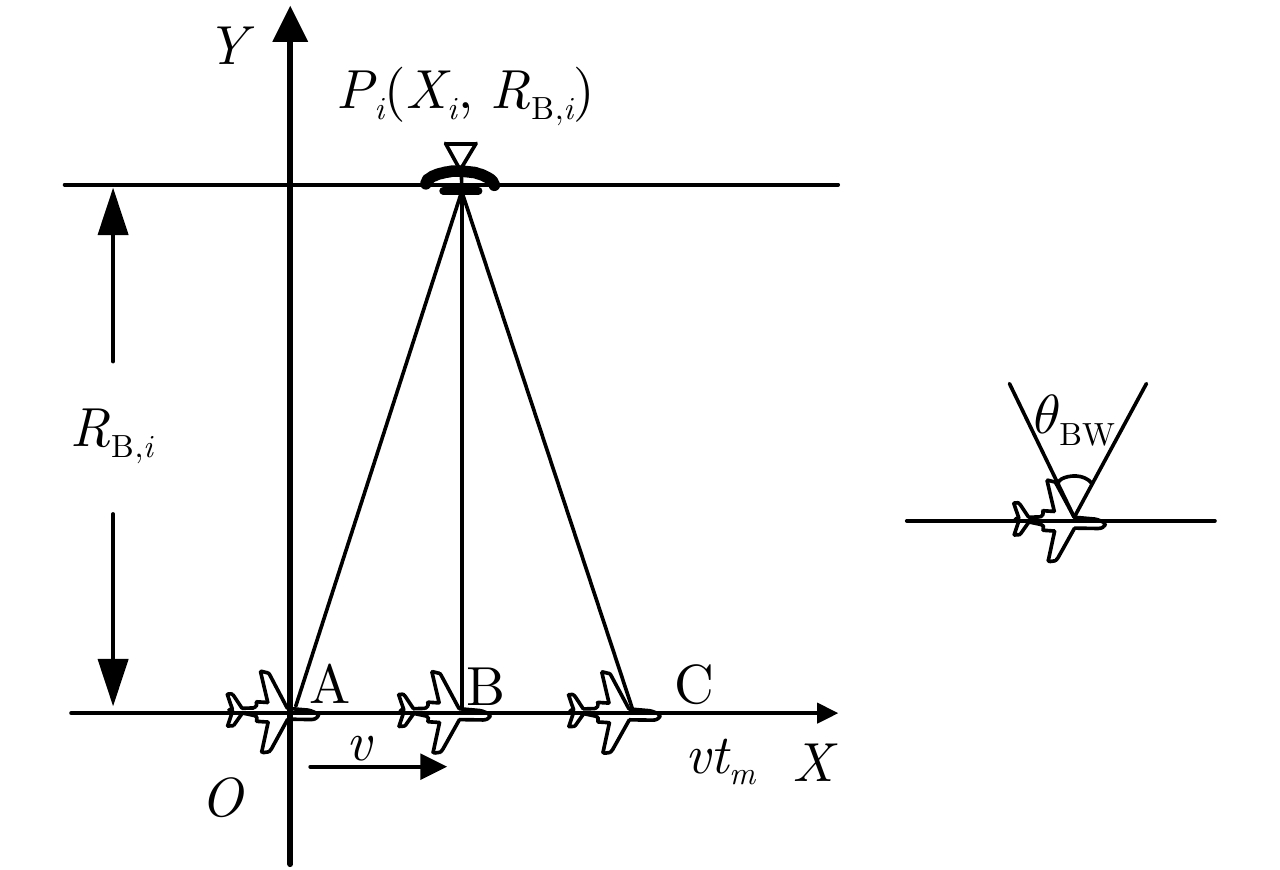
摘要: 考虑到单平台测角的定位精度随目标的距离增加而下降、远距离处的方位定位精度有待提高的问题,该文提出了一种基于长合成孔径的辐射源定位算法。该算法将合成孔径成像的概念引入到辐射源无源定位中,通过平台的移动形成长的虚拟孔径,以合成孔径雷达的方式处理数据,获得很高的方位定位精度。对于单频辐射源,接收信号在方位上等效为线性调频信号,其调频率与辐射源的距离成反比,通过距离搜索和方位聚焦的方法在距离-方位域完成信号聚焦,直接获得辐射源2维成像定位结果。针对宽波束侦察的特点,分析了低采样率下调频率距离-方位的耦合关系,并提出了信号角度估计和2维成像定位的方法。理论推导和实测数据处理结果验证了该定位算法的有效性。Abstract: When the direction-of-arrival estimation is made by a single platform, the localization accuracy decreases with increases in the distance from the radiation source, which means the localization accuracy of the azimuth of the radiation source at long distances must be improved. To address this problem, we propose a radiation-source localization algorithm based on a long synthetic aperture. This algorithm introduces the use of synthetic aperture imaging to the passive localization of radiation sources. A long virtual aperture is obtained by movement of the platform, and received data is processed in the form of synthetic aperture radar to obtain high azimuth localization accuracy. For a single-frequency radiation source, the received signal is equivalent to a linear frequency-modulation signal in the azimuth domain, and its chirp rate is inversely proportional to the distance from the radiation source. A range search and azimuth-focusing method are used to perform signal focusing in the range–azimuth domain, and the localization of the radiation source is obtained directly by two-dimensional imaging. Moreover, with respect to the characteristics of wide-beam reconnaissance, we analyzed the range–azimuth coupling relationship of the chirp rate at a low sampling frequency. On this basis, methods for direction-of-arrival estimation and two-dimensional imaging localization are proposed. Our theoretical derivation and experimental data processing results verify the validity of this algorithm.
-
表 1 定位误差对比(km)
Table 1. Comparison of localization errors (km)
测角定位误差 合成孔径定位误差 27.477 6.214 23.450 8.262 14.009 3.163 34.906 7.276 -
[1] 赵国庆. 雷达对抗原理[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 1999.ZHAO Guoqing. Principle of Radar Countermeasure[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 1999. [2] 杨小牛, 楼才义, 徐建良. 软件无线电原理与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2001.YANG Xiaoniu, LOU Caiyi, and XU Jianliang. Software Radio Principles and Applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2001. [3] 胡来招. 雷达侦察接收机设计[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2000.HU Laizhao. Design for Radar Reconnaissance Receivers[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2000. [4] 胡来招. 关于定点侦察的思考[J]. 通信对抗, 2009, (4): 3–5, 9.HU Laizhao. Considerations on position-based reconnaissance[J]. Communication Countermeasures, 2009, (4): 3–5, 9. [5] ZHOU Longjian, ZHU Weiqiang, LUO Jingqing, et al. Direct positioning maximum likelihood estimator using TDOA and FDOA for coherent short-pulse radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1505–1511. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0437 [6] ZHANG Huichuan, SUN Zhengbo, PENG Huafeng, et al. A DTO and DFO estimation algorithm of broadband frequency-hopping pulse signal[C]. The 2012 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Changchun, China, 2012: 188–192. doi: 10.1109/ICCSNT.2012.6525918. [7] 张杰, 蒋建中, 郭军利. 基于约束加权最小二乘的多站无源定位[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(1): 119–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.01.017ZHANG Jie, JIANG Jianzhong, and GUO Junli. Multi-station passive localization based on CWLS algorithm[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(1): 119–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.01.017 [8] 秦兆涛, 王俊, 魏少明, 等. 基于目标高度先验信息的多站时差无源定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2219–2226. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171231QIN Zhaotao, WANG Jun, WEI Shaoming, et al. Passive localization using TDOA measurements from multiple sensors based on priori knowledge of target altitude[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2219–2226. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171231 [9] 房嘉奇, 冯大政, 李进. 稳健收敛的时差频差定位技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 798–803. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140560FANG Jiaqi, FENG Dazheng, and LI Jin. A robustly convergent algorithm for source localization using time difference of arrival and frequency difference of arrival[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 798–803. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140560 [10] 陆安南, 杨小牛. 最小相位误差单星无源定位法[J]. 上海航天, 2007, 24(3): 6–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2007.03.002LU Annan and YANG Xiaoniu. Passive location with minimizing phase difference error by single satellite[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2007, 24(3): 6–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1630.2007.03.002 [11] 莫成坤, 陈树新, 吴昊, 等. 基于角度信息的递推最小二乘无源定位算法[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2014, 22(9): 2863–2866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2014.09.046MO Chengkun, CHEN Shuxin, WU Hao, et al. Recursion least-squares passive location algorithm based on angle information[J]. Computer Measurement &Control, 2014, 22(9): 2863–2866. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4598.2014.09.046 [12] 游屈波, 吴耀云, 胡飞, 等. 基于机载单站双航段联合估计的纯方位定位跟踪算法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2019, 34(5): 28–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2019.05.007YOU Qubo, WU Yaoyun, HU Fei, et al. Bearing-only target location and tracking algorithm based on joint estimation with two flight segments of single observer[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2019, 34(5): 28–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2019.05.007 [13] 李腾, 郭福成, 姜文利. 星载干涉仪无源定位新方法及其误差分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032LI Teng, GUO Fucheng, and JIANG Wenli. A novel method for satellite-borne passive localization using interferometer and its error analysis[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032 [14] 石荣, 阎剑, 张聪. 干涉仪相位差测量精度及其影响因素分析[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2013, 29(2): 35–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2013.02.011SHI Rong, YAN Jian, and ZHANG Cong. Analysis on precision and infection factors about phase difference measurement for interferometer[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2013, 29(2): 35–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2013.02.011 [15] 王克让, 李娟慧, 朱晓丹, 等. 提高相位干涉仪测角精度新方法[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2017, 33(4): 7–10. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2017.04.003WANG Kerang, LI Juanhui, ZHU Xiaodan, et al. A novel improving angle accuracy method for phase interferometer[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2017, 33(4): 7–10. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2017.04.003 [16] 戴幻尧, 申绪涧, 乔会东, 等. 基于极化误差的干涉仪测角性能建模与仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2013, 30(10): 237–240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2013.10.054DAI Huanyao, SHEN Xujian, QIAO Huidong, et al. Interferometer angle measurement performance modeling and simulation based on polarization error[J]. Computer Simulation, 2013, 30(10): 237–240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2013.10.054 [17] 郑坤, 汪兵. 同时同频多源信号对干涉仪测角的影响分析[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2018, 33(6): 1–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2018.06.001ZHENG Kun and WANG Bing. Influences analysis on interferometer direction-finding of simultaneous multiple source signals under common-frequency[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2018, 33(6): 1–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2018.06.001 [18] 许志伟, 王运锋, 张小琴. 基于只测向的机载单站定位技术[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 54(2): 293–297.XU Zhiwei, WANG Yunfeng, and ZHANG Xiaoqin. Airborne single-station passive location technology only based on bearing method[J]. Journal of Sichuan University:Natural Science Edition, 2017, 54(2): 293–297. [19] 张敏, 冯道旺, 郭福成. 基于多普勒变化率的单星无源定位[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2009, 25(5): 11–13, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2009.05.004ZHANG Min, FENG Daowang, and GUO Fucheng. Passive localization by a single satellite based on Doppler rate-of-change[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2009, 25(5): 11–13, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2009.05.004 [20] 曹东波, 张敏, 姜文利. 单星多普勒变化率无源定位精度分析[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2010, 26(4): 1–4, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.04.001CAO Dongbo, ZHANG Min, and JIANG Wenli. Accuracy analysis for passive localization of a single satellite based on Doppler rate-of-change[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2010, 26(4): 1–4, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.04.001 [21] 谈欣荣, 高宪军, 李宝珠, 等. 一种基于多普勒频率变化率单站无源定位的改进跟踪滤波算法[J]. 电子设计工程, 2014, 22(8): 77–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2014.08.024TAN Xinrong, GAO Xianjun, LI Baozhu, et al. An improved tracking filter algorithm of single observer passive localization based on Doppler changing rate[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2014, 22(8): 77–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2014.08.024 [22] 李华, 郭福成. 等高程运动假设的单星角度融合多普勒变化率跟踪方法[J]. 空间电子技术, 2018, 15(4): 41–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2018.04.009LI Hua and GUO Fucheng. A fusion of angle and Doppler rate-of-changing based tracking method forconstant altitude moving target by single satellite[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2018, 15(4): 41–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2018.04.009 [23] WALTER W G. Synthetic Aperture Radar and Electronic Warfare[M]. New York: Artech House, 1993. [24] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005. [25] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Norwood, UK: Artech House, Inc., 2005. [26] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Beam steering SAR data processing by a generalized PFA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4366–4377. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2237407 [27] SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A unified focusing algorithm for several modes of SAR based on FrFT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3139–3155. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2212280 [28] YANG Jun, SUN Guangcai, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A subaperture imaging scheme for wide azimuth beam airborne SAR based on modified RMA with motion compensation[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 608–611. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946496. [29] LIU Baochang, WANG Tong, and BAO Zheng. Slant-range velocity estimation based on Small-FM-Rate chirp[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 88(10): 2472–2482. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.04.013 [30] WU Yufeng, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. An improved SAC algorithm based on the range-keystone transform for Doppler rate estimation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 741–745. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2220753 [31] 孙光才, 周峰, 邢孟道, 等. 虚假场景SAR欺骗式干扰技术及实时性分析[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2009, 36(5): 813–818, 866.SUN Guangcai, ZHOU Feng, XING Mengdao, et al. Deception-jamming technology against the SAR based on the deceptive scene and real-time analyses[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2009, 36(5): 813–818, 866. [32] 刘亚波, 刘霖, 童智勇, 等. S波段高分辨宽幅SAR辐射定标及误差分析方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1946–1951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180983LIU Yabo, LIU Lin, TONG Zhiyong, et al. A radiometric calibration and error analysis method for HWRS SAR at S-band[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1946–1951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180983 [33] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, Lin Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 [34] BORN M and WOLF E. Principles of Optics[M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1959. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: