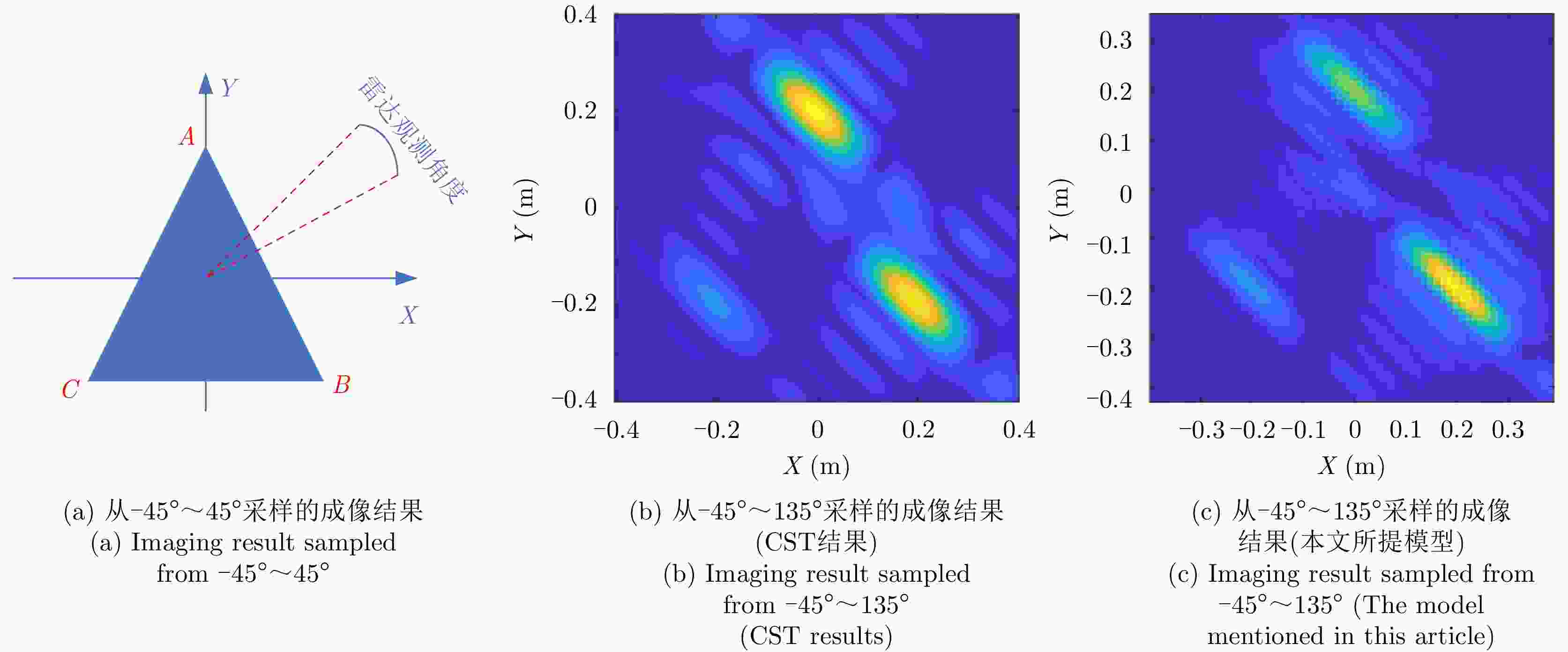
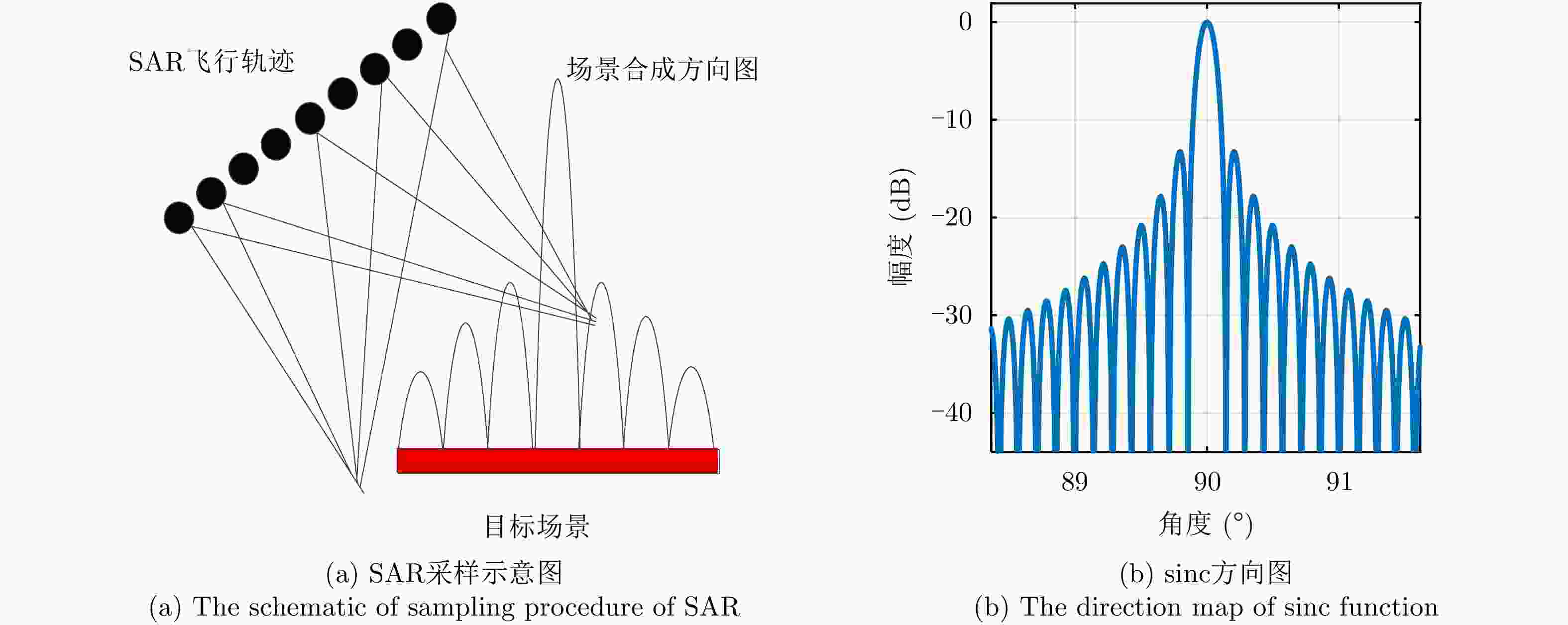
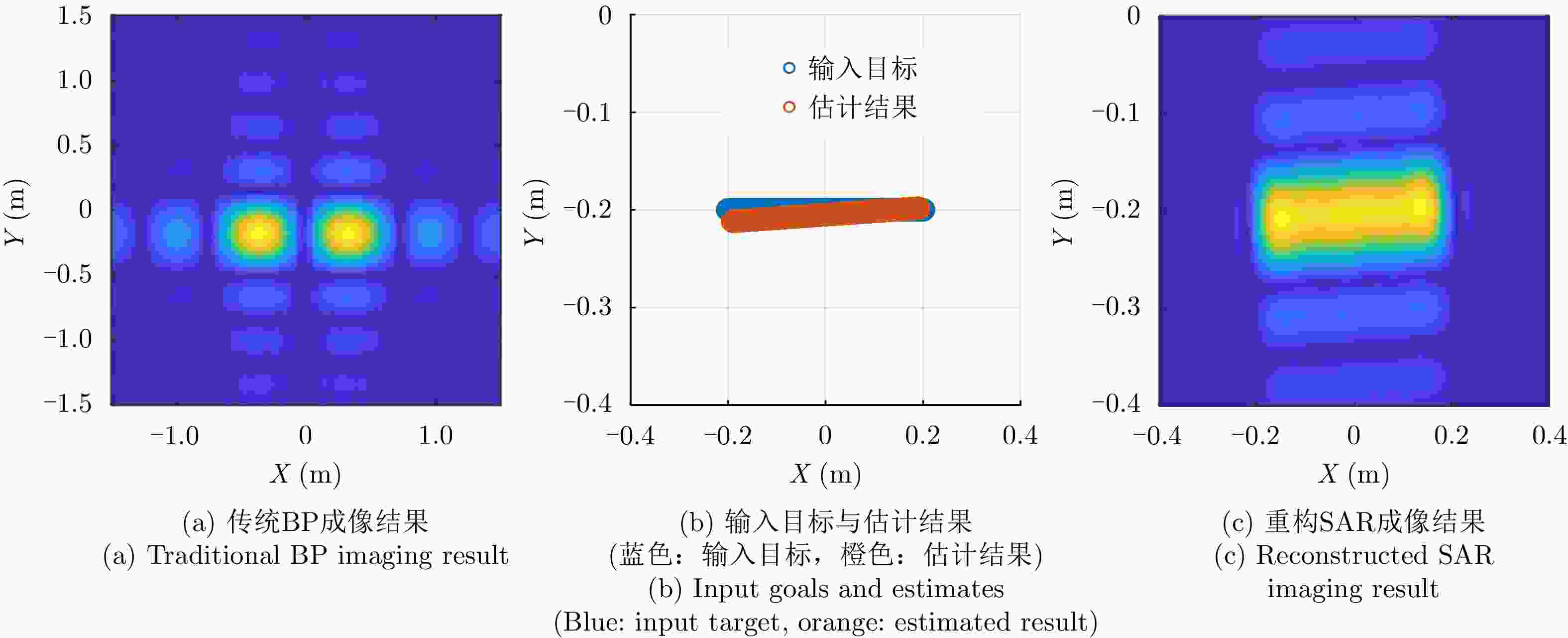
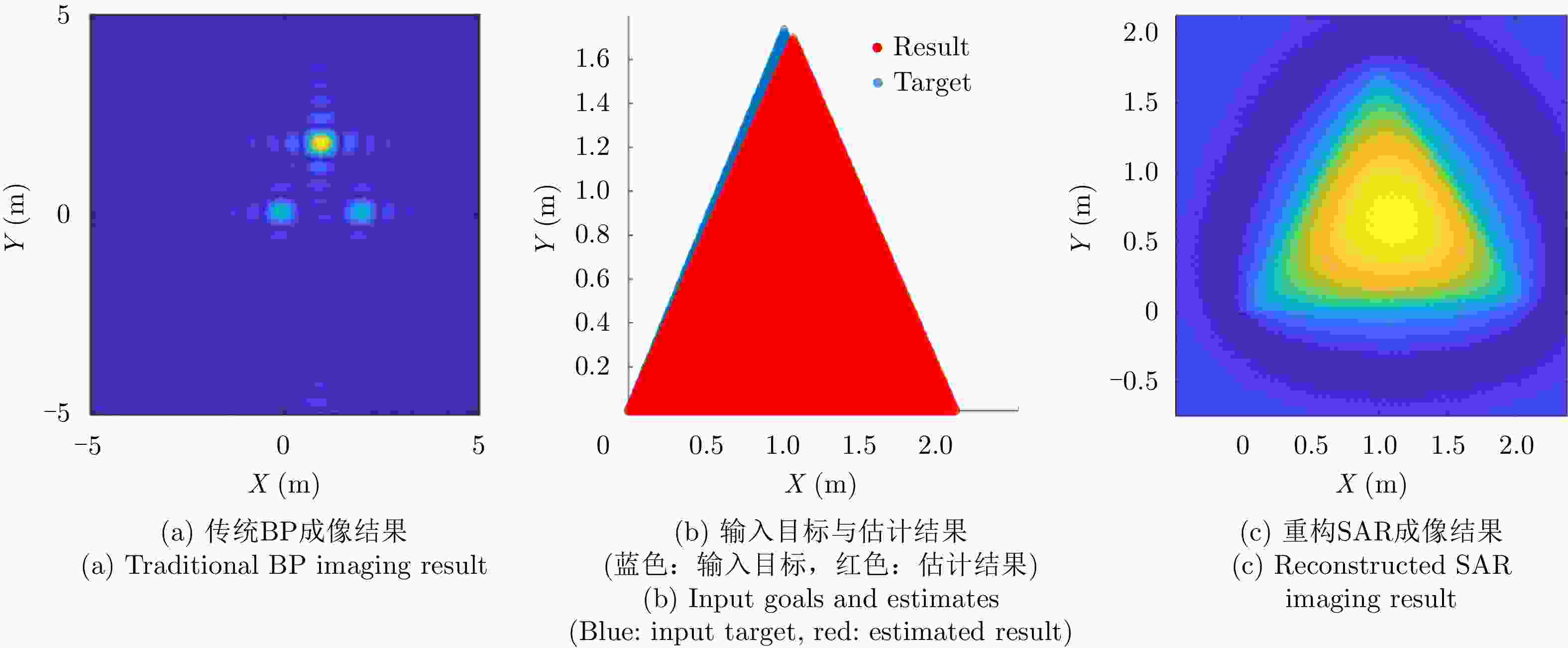
-
摘要: 在复杂场景(特别是城区场景)合成孔径雷达(SAR)遥感成像中,存在大量线、面目标,如城区中的道路和建筑物边缘等目标,这些线面目标微波散射信号方向性强。传统SAR从单一视角获取场景的散射信息,且传统成像算法均基于点目标模型,使得传统SAR图像中线面目标主要特征表现为一系列的强散射点,而非线散射特征和面散射特征,最终造成SAR图像中目标不连续,SAR图像解译困难。因此,该文通过建立典型线段、三角面元目标的参数化回波模型,对线面目标SAR成像机理进行了深入细致的研究;并基于提出的参数化模型对线面目标进行参数化成像,即首先基于贝叶斯理论和所提的参数化模型对典型的线面目标进行分类判决,随后采用再成像的方式获得有效表征线、面目标散射特征的SAR图像,为线、面目标SAR图像解译提供有效支撑。最后,数值仿真实验成功验证了所提算法的有效性和正确性。Abstract: In the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) remote sensing imagery of complicated scenes (especially urban scenes), there are a large number of lines and surfaces, such as roads in urban areas and the surfaces of buildings. These microwave-signal-scattering features have strong directivity. Traditional SAR acquires the scattering information of a scene from a single observation, and traditional imaging algorithms are based on the point target model, which makes the main features of the lines and surfaces in traditional SAR images appear as a series of strong scattering points rather than line-scattering and surface-scattering features. This outcome ultimately causes the target to be discontinuous in the SAR image, thus making the SAR image difficult to interpret. Therefore, in this study, we conducted an in-depth and meticulous investigation of the SAR imaging mechanism for lines and surfaces by establishing a parametric echo model of typical lines and triangular surfaces. Based on the proposed parametric model, we performed parametric imaging of these lines and surfaces. Based on our results, we propose a parametric imaging method, in which the typical lines and surfaces are classified and determined based on Bayesian theory and the proposed parametric model. Then, an SAR image can be obtained that effectively characterizes the scattering features of the line and surface targets by visual imaging, which effectively facilitates SAR image interpretation. The results of our numerical simulation experiments verify the validity of the proposed method.
-
表 1 雷达部分参数
Table 1. Some radar parameters
雷达参数 数值 波长 0.05 m 带宽 300 MHz 距离向频点数 60 方位角 0.075 rad 方位向脉冲数 360 表 2 目标参数分布
Table 2. Target parameter distribution
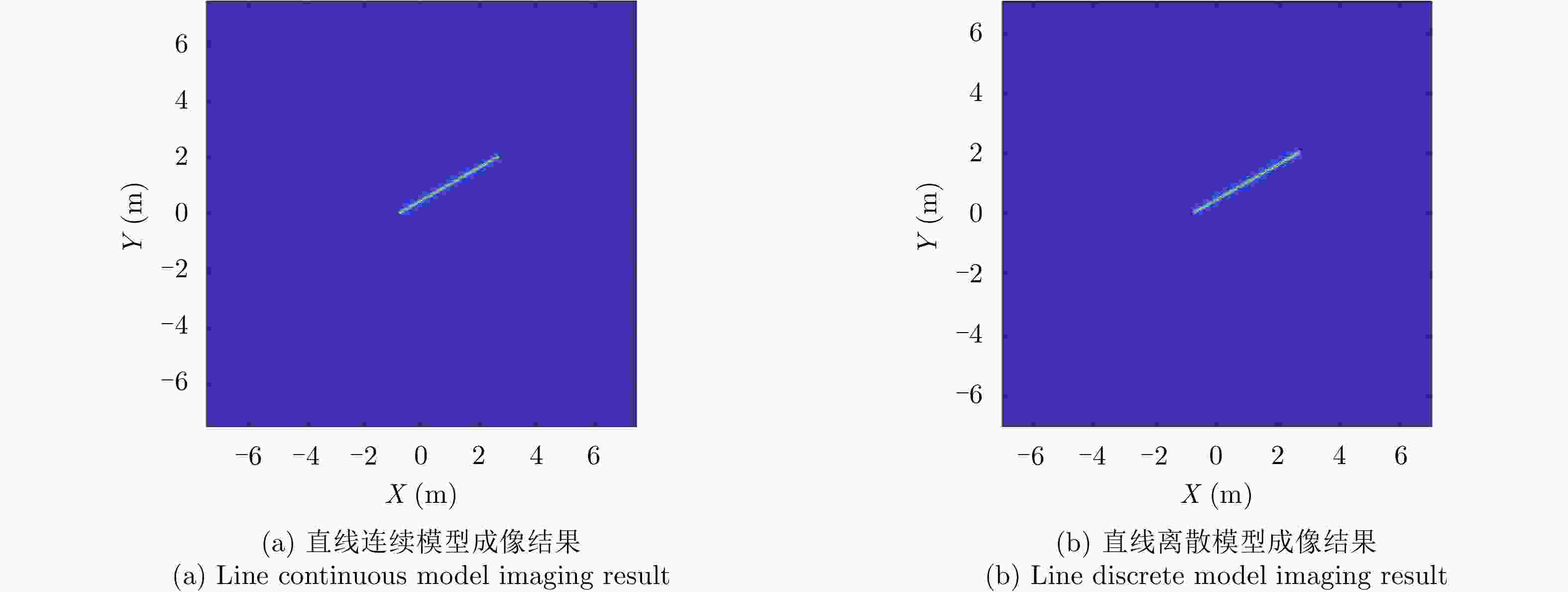
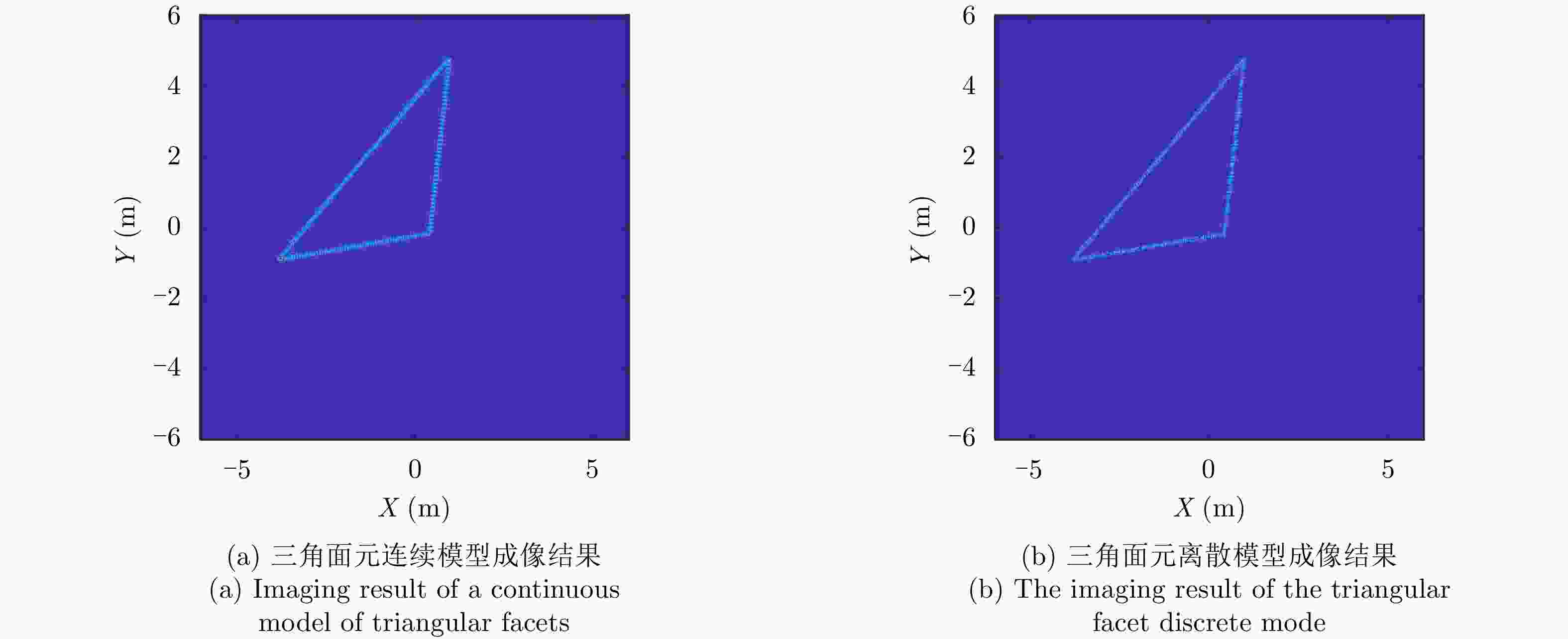
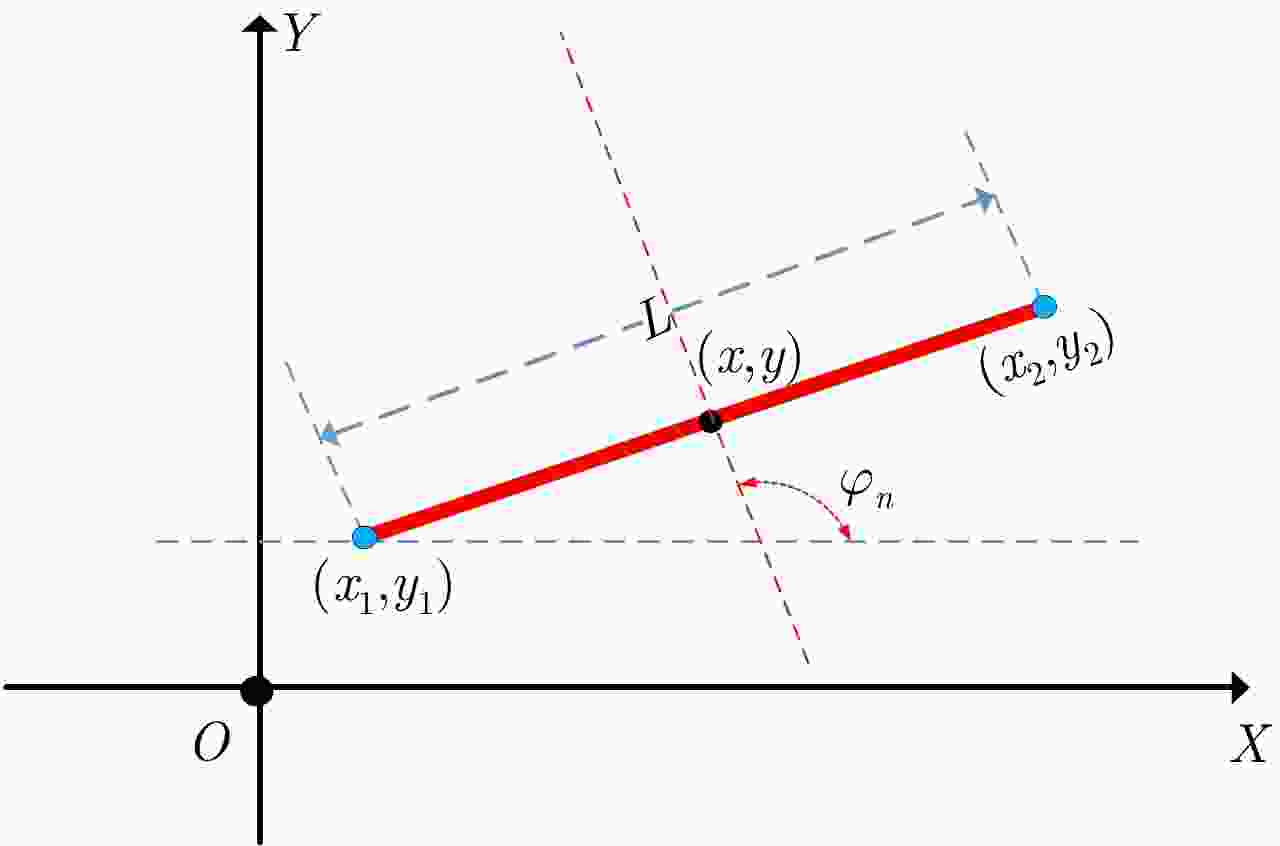
目标类型 参数 参数分布 线段 长度L 截断高斯分布$L \in \left[ {0.5,8} \right]$, $\mu = 6,\varSigma = 1$ 法线角度${\varphi _n}$ $\left[ {0,2{\rm{\pi }}} \right]$均匀分布 折线 边长${L_1}$, ${L_2}$ 截断高斯分布$L \in \left[ {0.1,3} \right]$, $\mu = 2,\varSigma = 0.5$ 倾斜角度${\phi _l}$ $\left[ {0,2{\rm{\pi }}} \right]$均匀分布 三角形,三角面元 边长${L_1},{L_2},{L_3}$ 截断高斯分布$L \in \left[ {0.1,3} \right]$, $\mu = 2,\varSigma = 0.5$ 倾斜角度${\phi _t}$ $\left[ {0,2{\rm{\pi }}} \right]$均匀分布 表 3 基于贝叶斯理论的模型判决分类统计结果
Table 3. Statistical results of model decision classification based on Bayesian theory
输入目标(数量) 直线 折线 三角形 三角面元 直线(N=100) 87% 12% 1% 折线(N=100) 28% 64% 1% 7% 三角形(N=200) 7% 66.5% 26.5% 0 三角面(N=100) 0 0 0 100% 表 4 直线段重构SAR参数
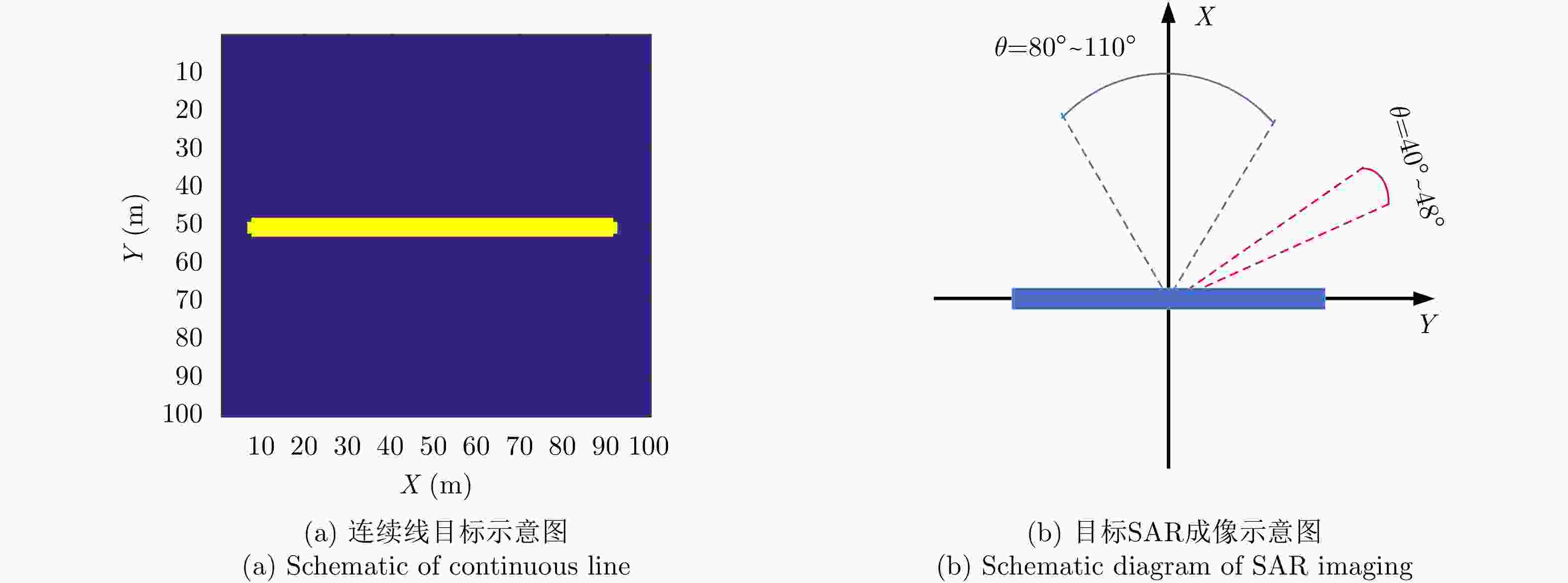
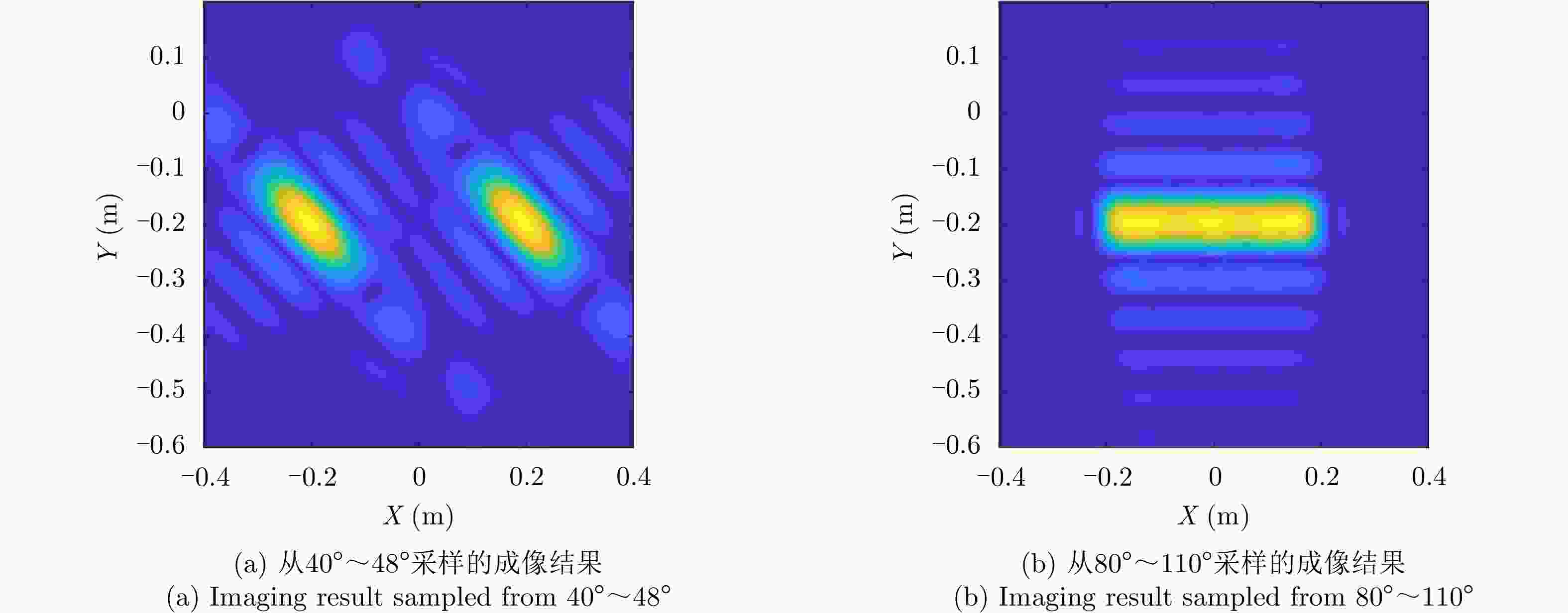
Table 4. Line: SAR parameters for reconstruction
雷达参数 具体数值 观测角度$\tilde \theta $ 80:0.01:110 重构带宽 3 GHz 表 5 三角面元:重构SAR参数
Table 5. Triangular surface: SAR parameters for reconstruction
雷达参数 具体数值 观测角度$\tilde \theta $ 0.1:0.1:360 频率$\tilde f$ 25 MHz:20 MHz:6.125 GHz -
[1] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. New York, USA: Wiley, 1991. [2] ZENG Tao, LIU Luosi, and DING Zegang. Improved stepped-frequency SAR imaging algorithm with the range spectral-length extension strategy[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(5): 1483–1494. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2196681 [3] DING Zegang, LIU Luosi, ZENG Tao, et al. Improved motion compensation approach for squint airborne SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4378–4387. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2265327 [4] ZENG Tao, LI Yinghe, DING Zegang, et al. Subaperture approach based on azimuth-dependent range cell migration correction and azimuth focusing parameter equalization for maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6718–6734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2447393 [5] XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Imaging simulation of polarimetric SAR for a comprehensive terrain scene using the mapping and projection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(11): 3219–3234. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.879544 [6] GORHAM L A and MOORE L J. SAR image formation toolbox for MATLAB[C]. The SPIE 7699, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII. Orlando, USA, 2010. [7] CUMMING I G and WONG F H C. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 3. [8] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 [9] FARRELL T J, PATTERSON M S, and WILSON B. A diffusion theory model of spatially resolved, steady‐state diffuse reflectance for the noninvasive determination of tissue optical properties in vivo[J]. Medical Physics, 1992, 19(4): 879–888. doi: 10.1118/1.596777 [10] MILLER E K and LAGER D L. Inversion of one-dimensional scattering data using Prony’s method[J]. Radio Science, 1982, 17(1): 211–217. doi: 10.1029/RS017i001p00211 [11] POTTER L C, CHIANG D M, CARRIERE R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641 [12] GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750 [13] SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley, 1999. [14] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 [15] Wei Y, Chen X, Fan Y, et al. Analysis and identification of continuous line target in SAR echo based on sidelobe features[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 5979–5981. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0327 [16] BISHOP C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2006, 161–171. [17] 张连文, 郭海鹏. 贝叶斯网引论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006, 172–180.ZHANG Lianwen and GUO Haipeng. Introduction to Bayesian Networks[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006, 172–180. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: