-
摘要:
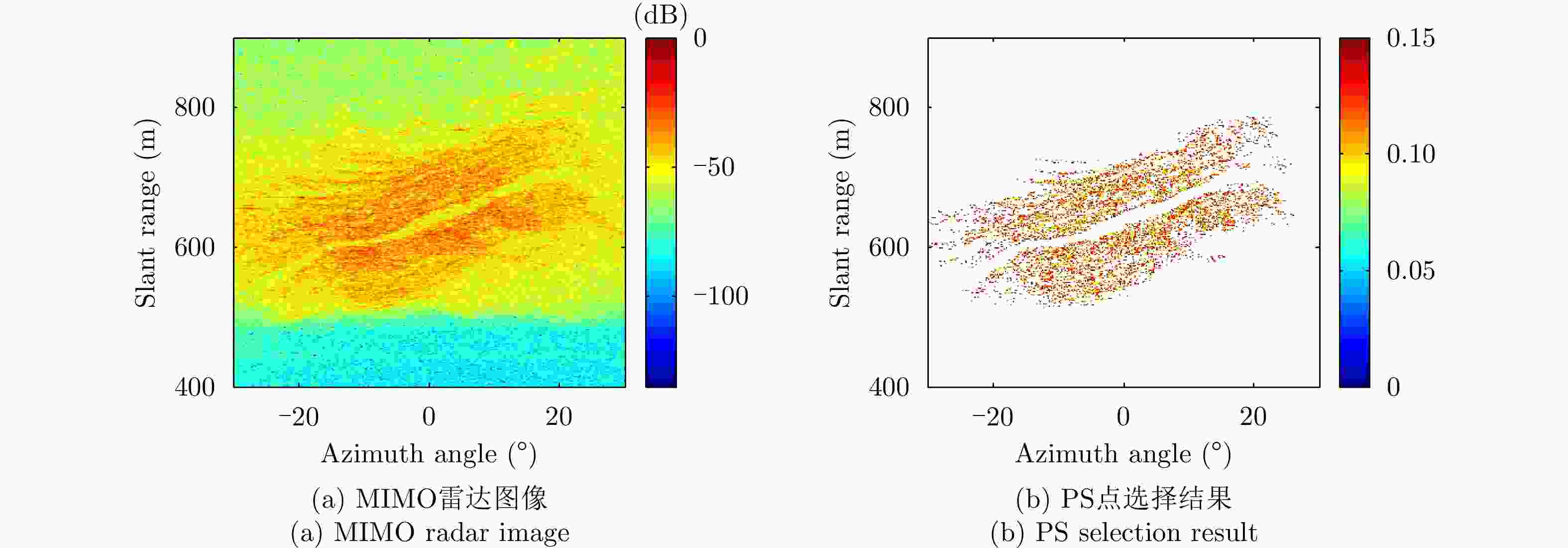
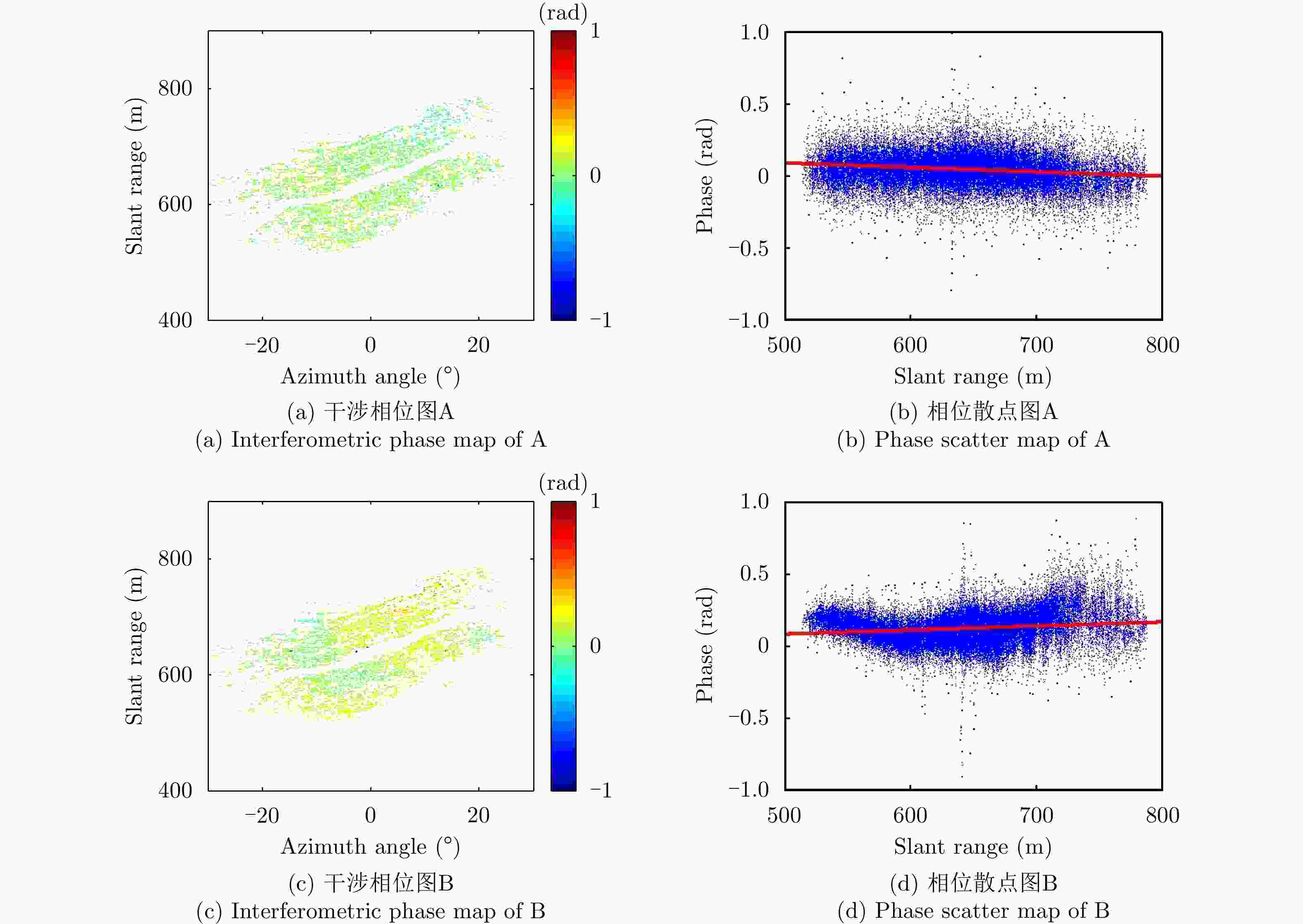
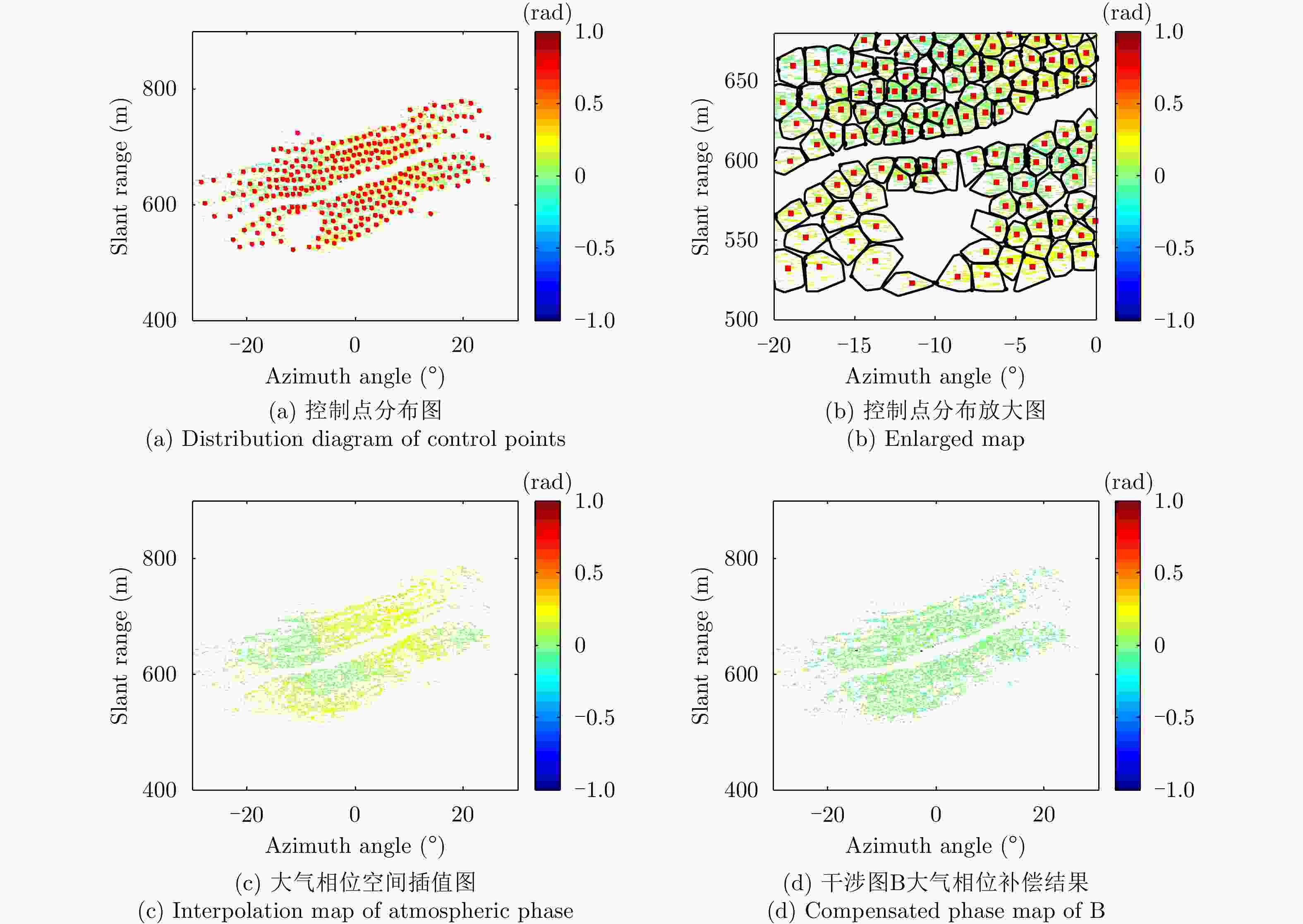
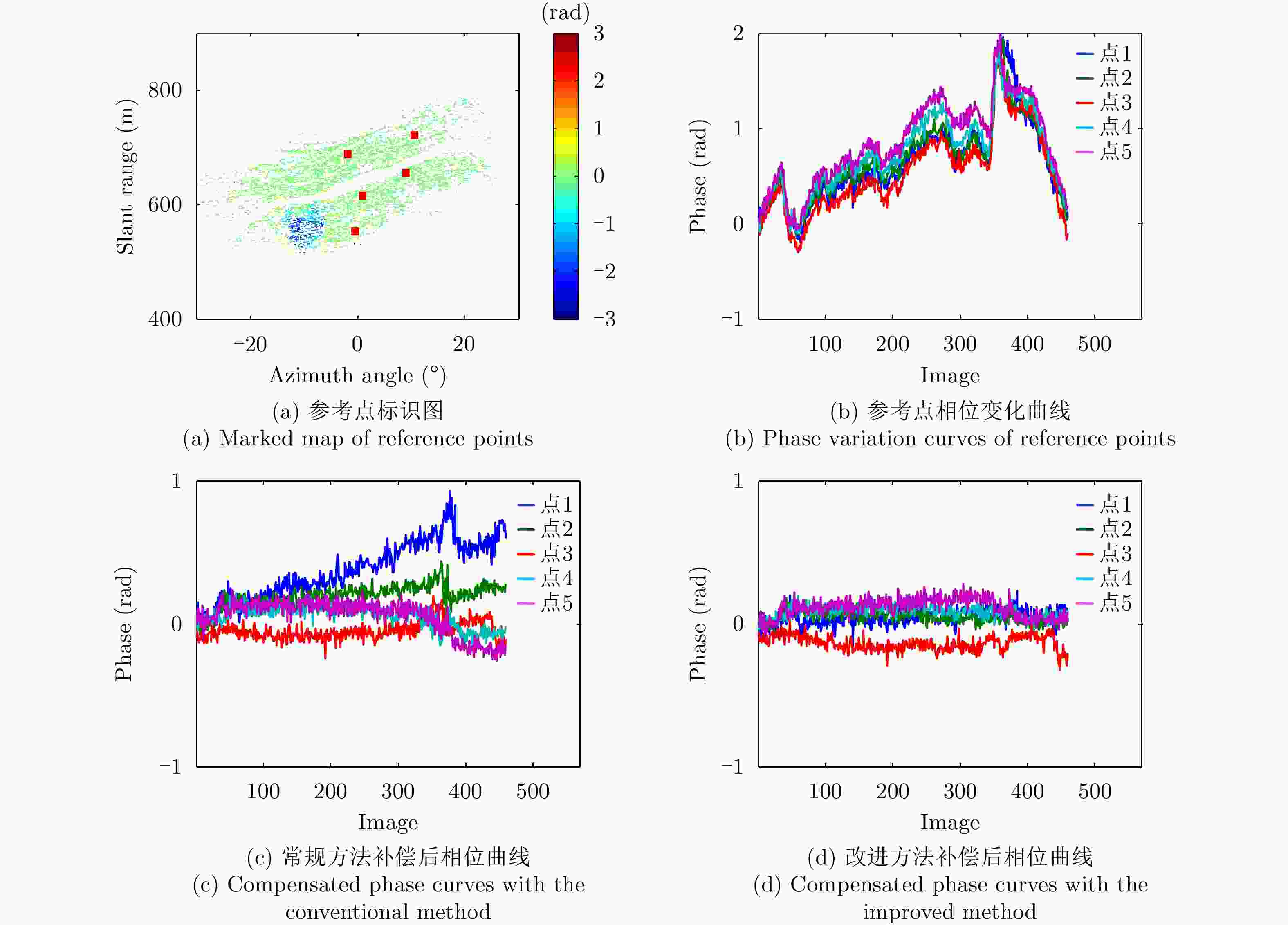
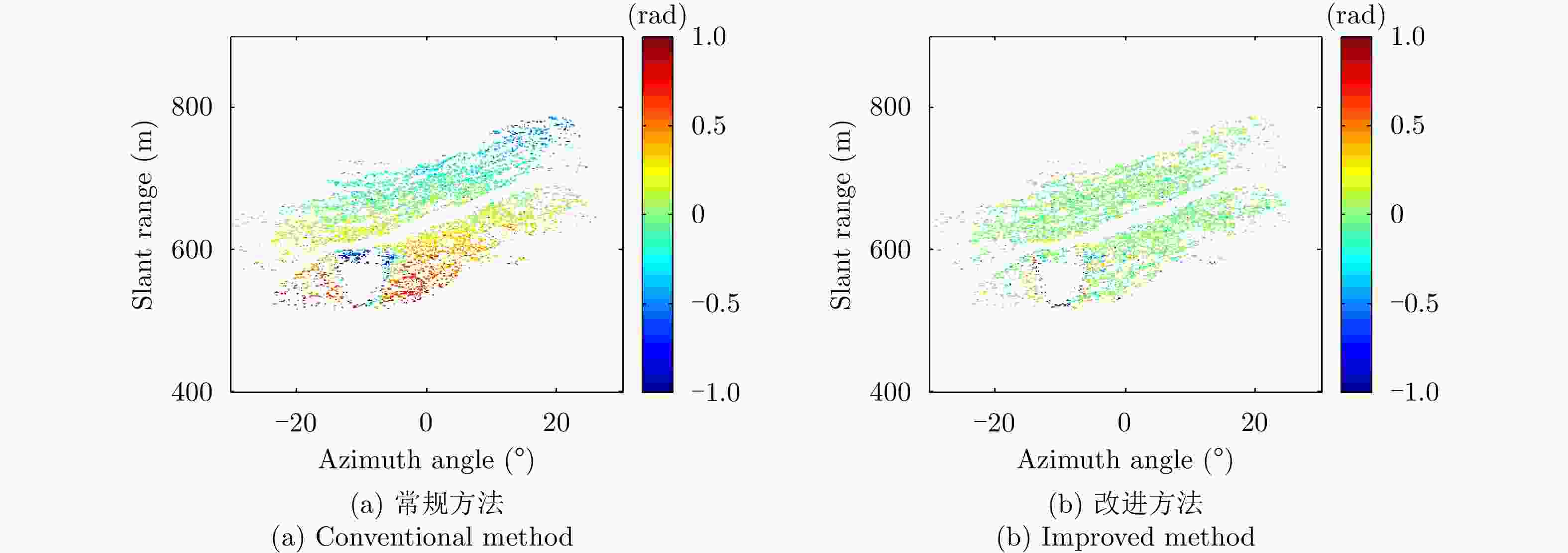
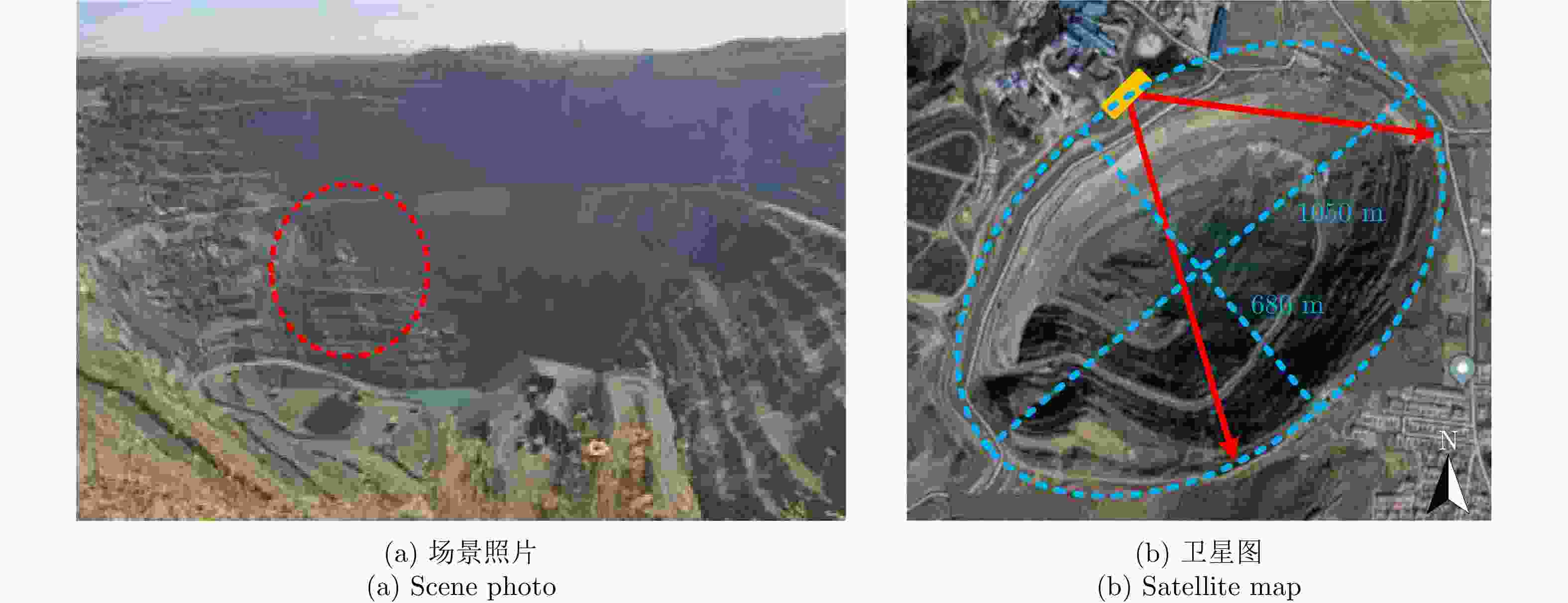
采用基于永久散射体(PS)技术的大气相位(AP)补偿方法对地基干涉合成孔径雷达(GB-InSAR) 干涉相位图进行分析时,部分图像的干涉相位随距离呈现出复杂的非线性,导致无法建立合理的多参数模型来模拟大气相位,常规的补偿方法不再适用。该文提出一种改进的GB-InSAR图像非线性大气相位补偿方法,首先采用常规方法对干涉相位图进行大气相位补偿,并根据PS点的补偿后相位序列的标准差,进行稳定PS点的选择,然后对稳定PS点进行子区域划分,通过反距离加权插值估计出所有PS点的大气相位,从而实现大气相位的有效补偿。采用该文所提方法,对460幅雷达图像进行了处理,相比于常规方法,可以有效地补偿干涉相位图中的非线性大气相位分量。基于若干高稳定参考点的对比结果表明,该方法减小了最大约1 rad的相位测量误差。
-
关键词:
- 地基干涉合成孔径雷达 /
- 大气相位补偿 /
- 非线性变化 /
- 稳定永久散射体 /
- 反距离加权插值
Abstract:When the Permanent Scatterer (PS) technique is utilized to compensate the Atmospheric Phase (AP) for Ground-Based Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (GB-InSAR) images, a proper parametric model should be built to describe the AP. However, for some interferograms, the AP may nonlinearly vary with the PS range, and this cannot be effectively compensated via the conventional method. This paper proposes an improved method to compensate the nonlinear AP. Here, the conventional method is first used to compensate all the phase interferograms. By calculating the standard deviation of the phase sequence of every PS and setting a proper threshold, a large number of stable PSs are selected. Then these stable PSs are divided into a certain number of sub-regions, and some control points are determined. With the inverse distance weighting interpolation, the APs of all the PSs are estimated and compensated. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, 460 radar images are processed, and the results are made compared with those of the conventional method. The nonlinear AP could be better compensated with the proposed method to avoid misunderstanding of the motional area. Several reference PSs are selected to make quantitative comparisons, and measurement error up to 1 rad could be reduced.
-
[1] 刘斌, 葛大庆, 李曼, 等. 地基合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术及其应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2017, 29(1): 1–6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.01LIU Bin, GE Daqing, LI Man, et al. Ground-based interferometric synthetic aperture radar and its applications[J]. Remote Sensing for Land &Resources, 2017, 29(1): 1–6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.01 [2] 曾涛, 邓云开, 胡程, 等. 地基差分干涉雷达发展现状及应用实例[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 154–170. doi: 10.12000/JR18115ZENG Tao, DENG Yunkai, HU Cheng, et al. Development state and application examples of ground-based differential interferometric radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 154–170. doi: 10.12000/JR18115 [3] 董杰, 董妍. 基于气象数据的地基雷达大气扰动校正方法研究[J]. 测绘工程, 2014, 23(10): 72–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2014.10.017DONG Jie and DONG Yan. Atmospheric artifact compensation for deformation monitoring with ground-based radar[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2014, 23(10): 72–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2014.10.017 [4] IANNINI L and GUARNIERI A M. Atmospheric phase screen in ground-based radar: Statistics and compensation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 537–541. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.1590876 [5] 黄长军, 夏红梅, 周吕. 基于GCP方法的地基InSAR大气扰动误差改正分析[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2018, 41(10): 8–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2018.10.003HUANG Changjun, XIA Hongmei, and ZHOU Lyu. Atmospheric disturbance error correction in GB-InSAR based on ground control point[J]. Geomatics &Spatial Information Technology, 2018, 41(10): 8–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2018.10.003 [6] 徐亚明, 周校, 王鹏, 等. GB-SAR构建永久散射体网改正气象扰动方法[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2016, 41(8): 1007–1012, 1020. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140507XU Yaming, ZHOU Xiao, WANG Peng, et al. A method of constructing permanent scatterers network to correct the meteorological disturbance by GB-SAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(8): 1007–1012, 1020. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140507 [7] NOFERINI L, PIERACCINI M, MECATTI D, et al. Permanent scatterers analysis for atmospheric correction in ground-based SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(7): 1459–1471. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2005.848707 [8] IGLESIAS R, FABREGAS X, AGUASCA A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen compensation in ground-based SAR with a multiple-regression model over mountainous regions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2436–2449. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.1590876 [9] HU Cheng, DENG Yunkai, TIAN Weiming, et al. A PS processing framework for long-term and real-time GB-SAR monitoring[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(16): 6298–6314. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1590876 [10] 张祥, 陆必应, 宋千. 地基SAR差分干涉测量大气扰动误差校正[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2011, 9(6): 502–506, 512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.06.004ZHANG Xiang, LU Biying, and SONG Qian. Atmospheric disturbance correction in ground-based SAR differential interferometry[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2011, 9(6): 502–506, 512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2011.06.004 [11] HU Cheng, ZHU Mao, ZENG Tao, et al. High-precision deformation monitoring algorithm for GBSAR system: Rail determination phase error compensation[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 59(8): 082307. doi: 10.1007/s11432-015-5446-z [12] 张建萍, 刘希玉. 基于聚类分析的K-means算法研究及应用[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2007, 24(5): 166–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2007.05.051ZHNAG Jianping and LIU Xiyu. Application in cluster′s analysis is analyzed in children development period[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2007, 24(5): 166–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2007.05.051 [13] 朱吉祥, 张礼中, 周小元, 等. 反距离加权法在区域滑坡危险性评价中的应用[J]. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(3): 136–140. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2012.03.009ZHU Jixiang, ZHANG Lizhong, ZHOU Xiaoyuan, et al. Application of inverse distance weighted method to regional landslide hazards assessment[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(3): 136–140. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2012.03.009 [14] 刘作利, 刘景玉, 申修强, 等. 唐山马兰庄铁矿露天开采边坡变形监测的GB-InSAR技术[J]. 现代矿业, 2018(4): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2018.04.047LIU Zuoli, LIU Jingyu, SHEN Xiuqiang, et al. Deformation monitoring of the open-pit slope of Malanshan iron mine in Tangshan city based on GB-InSAR[J]. Modern Mining, 2018(4): 165–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2018.04.047 [15] TIAN Weiming, ZHAO Zheng, HU Cheng, et al. GB-InSAR-based DEM generation method and precision analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 997. doi: 10.3390/rs11090997 [16] HU Cheng, WANG Jingyang, TIAN Weiming, et al. Design and imaging of ground-based multiple-input multiple-output synthetic aperture radar (MIMO SAR) with non-collinear arrays[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 598. doi: 10.3390/s17030598 -



 作者中心
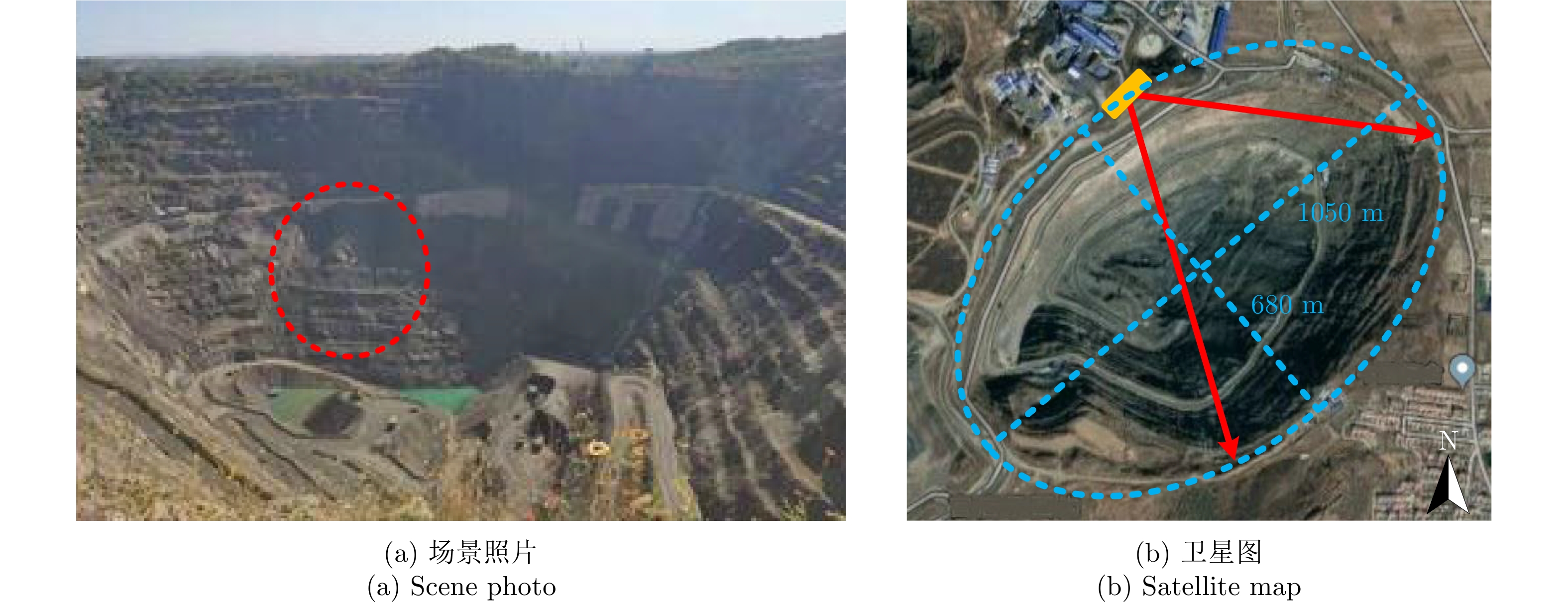
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: