Optimization Method and Analysis of Data Acquisition Strategy Based on Interference SAR with GNSS Transmitters
-
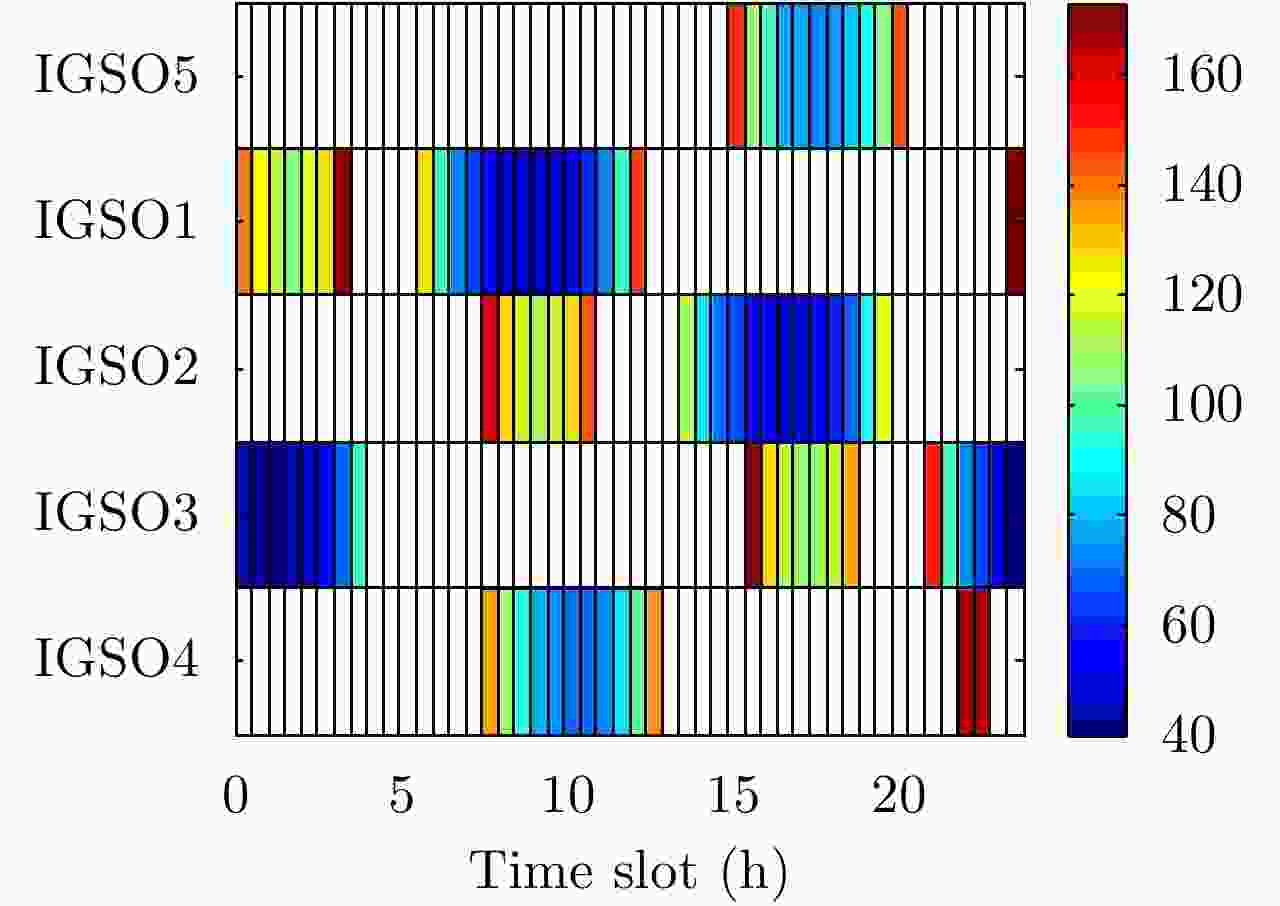
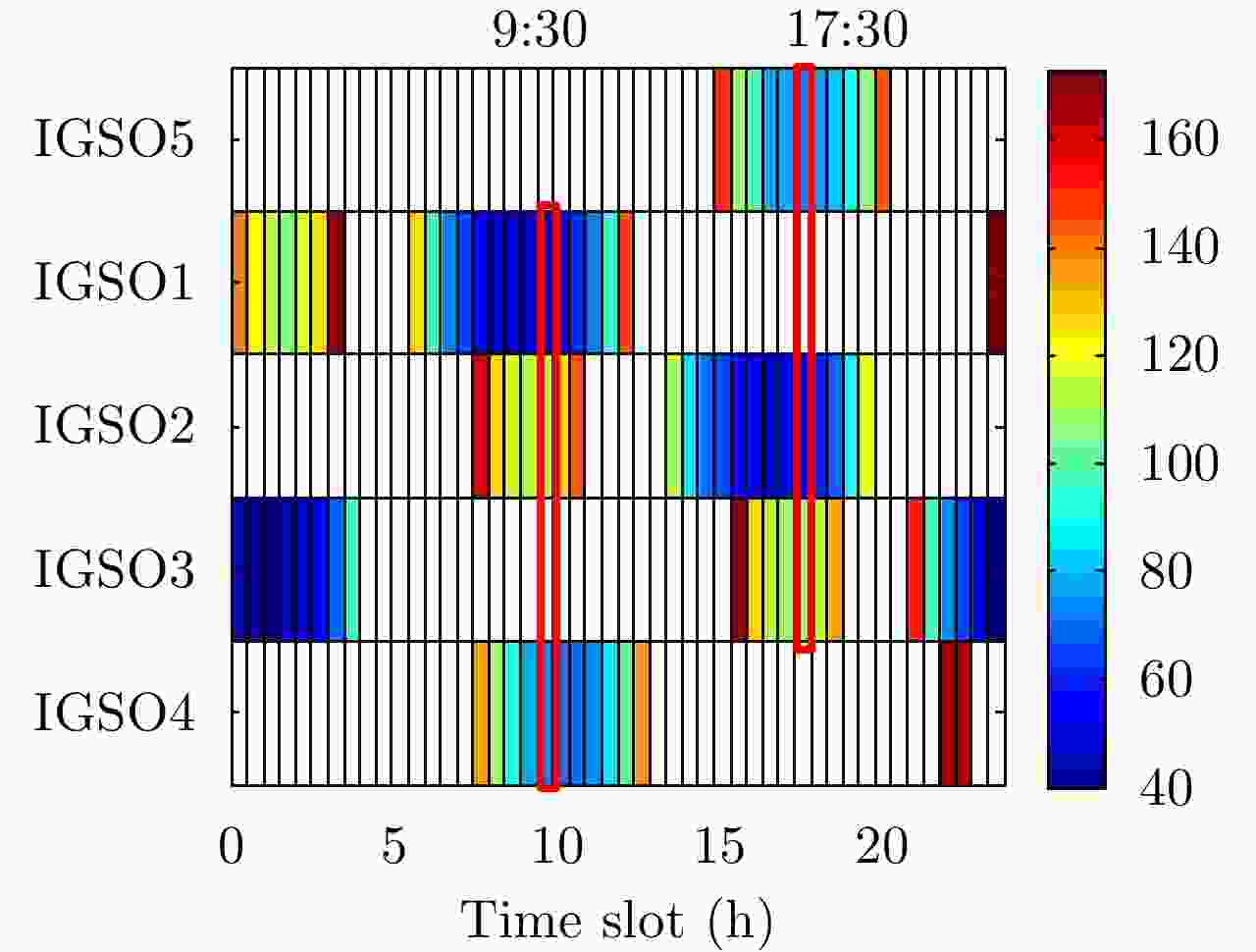
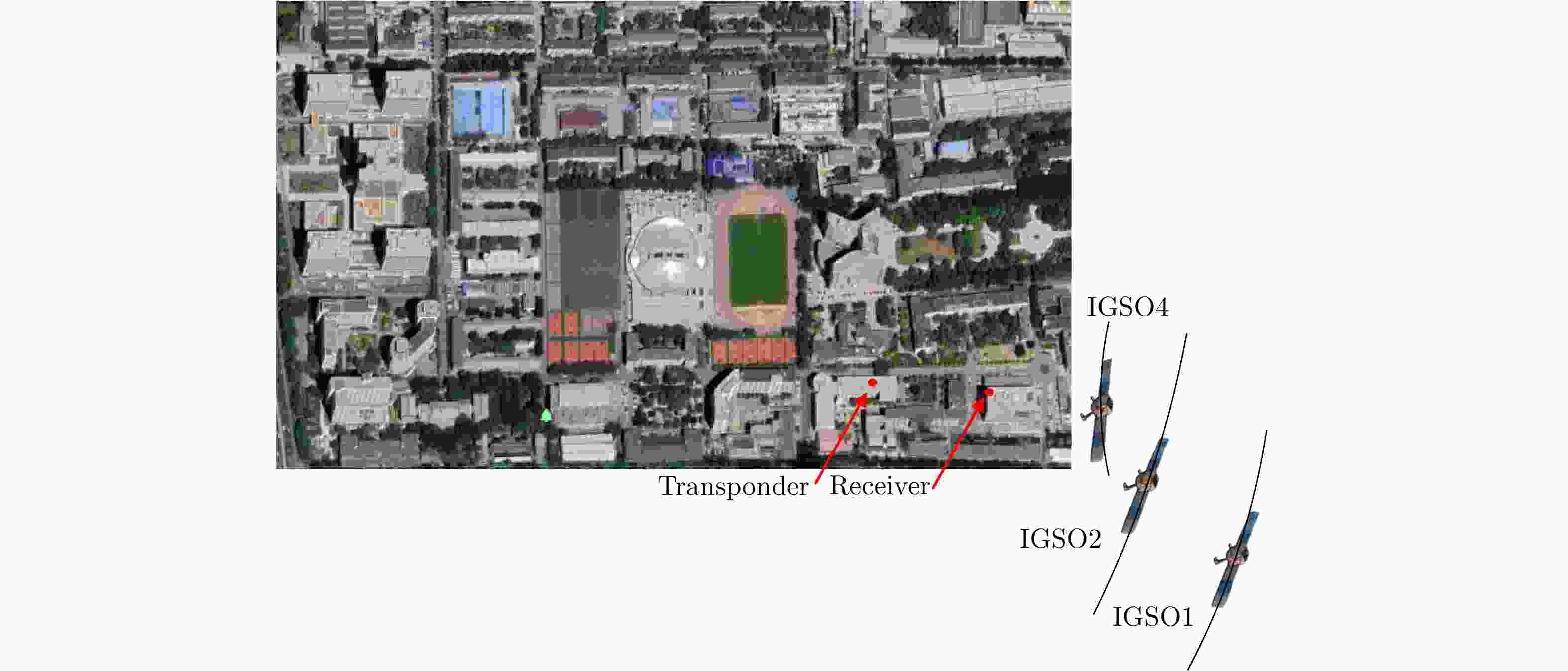
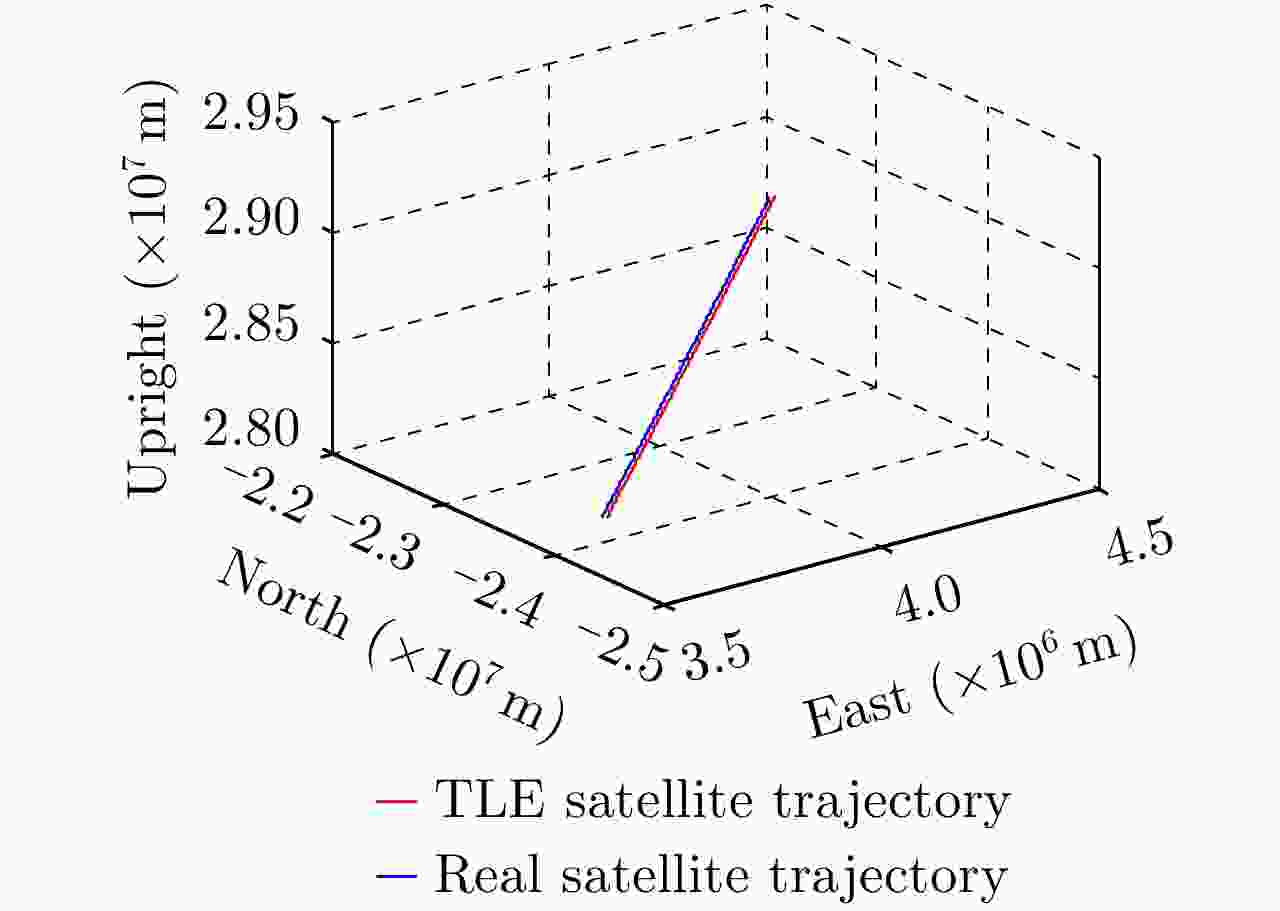
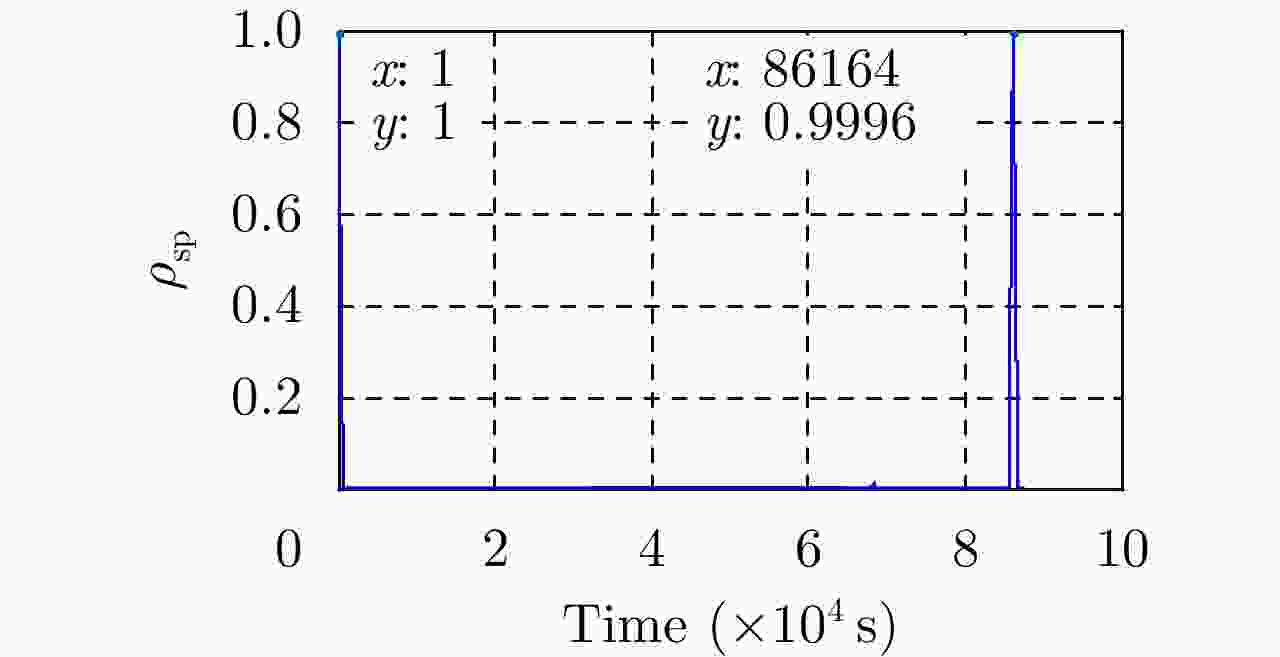
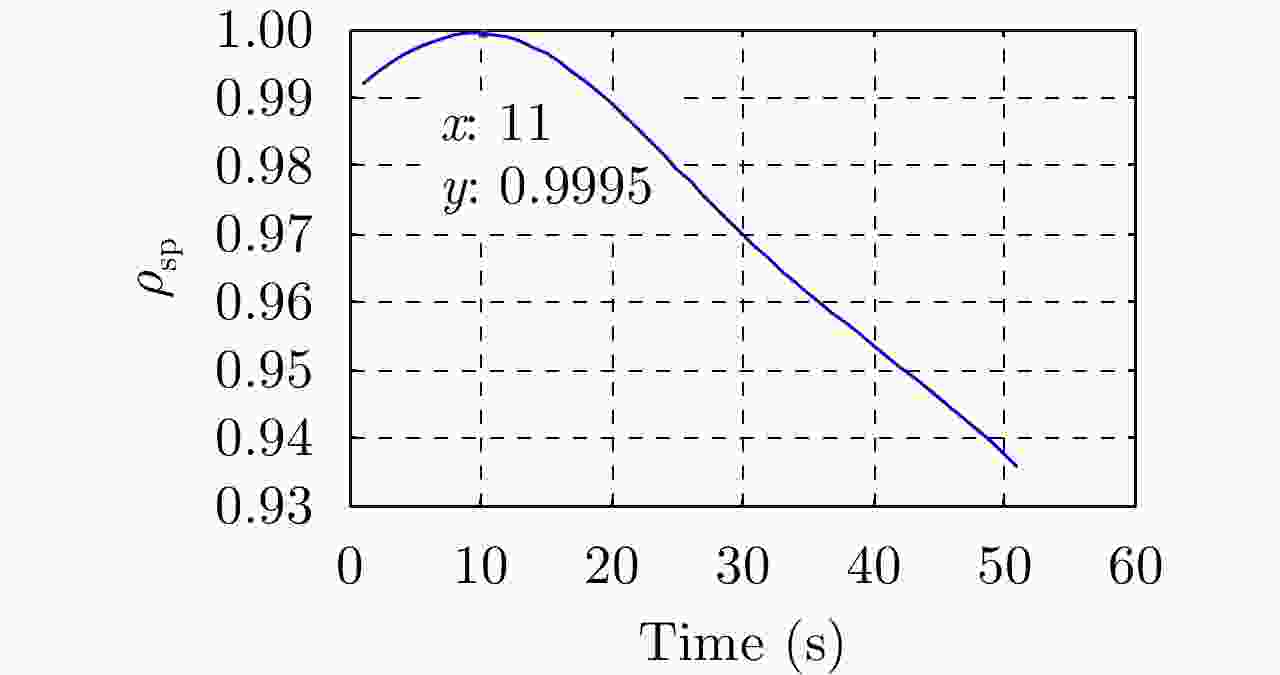
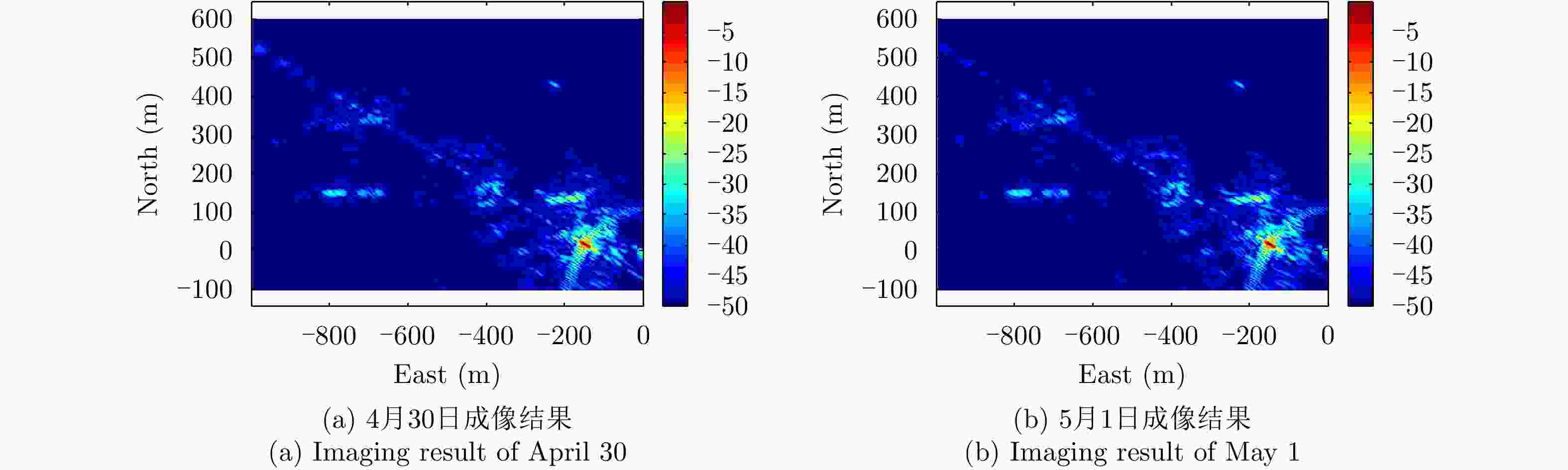
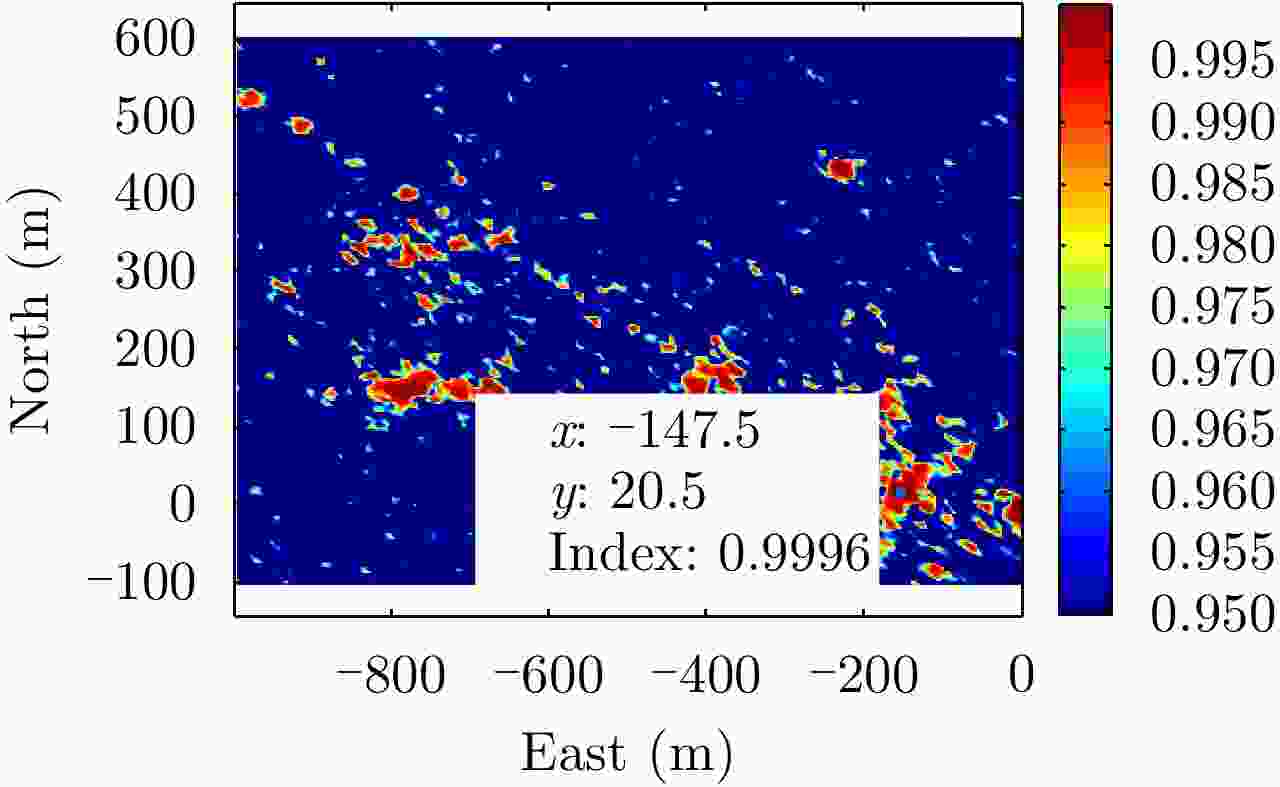
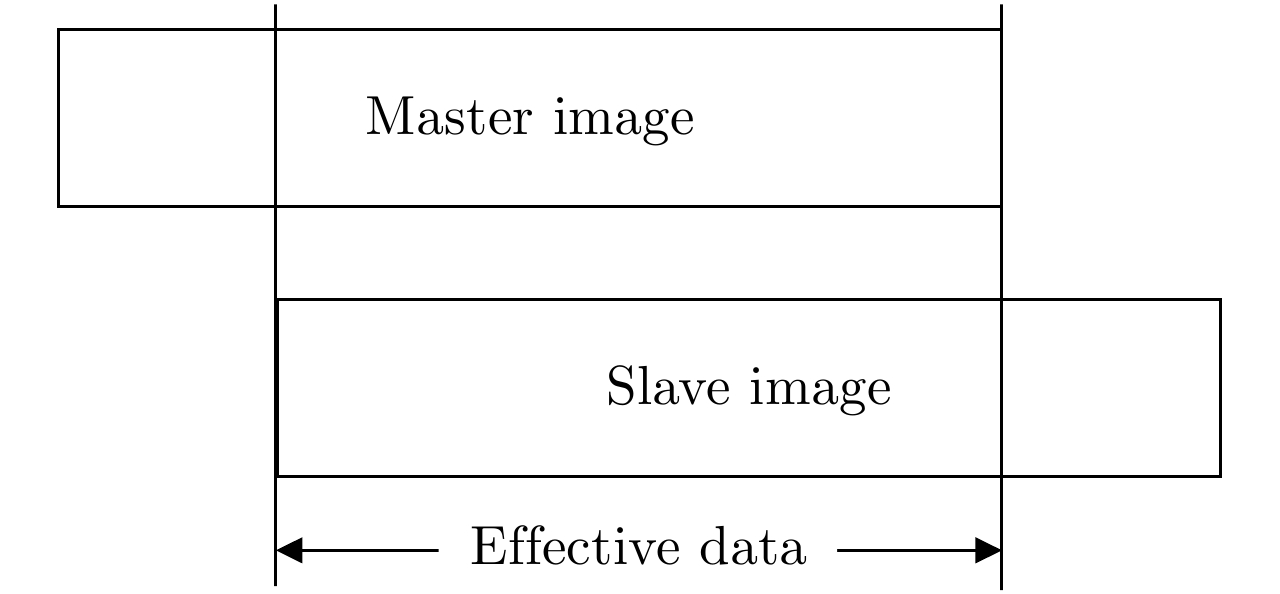
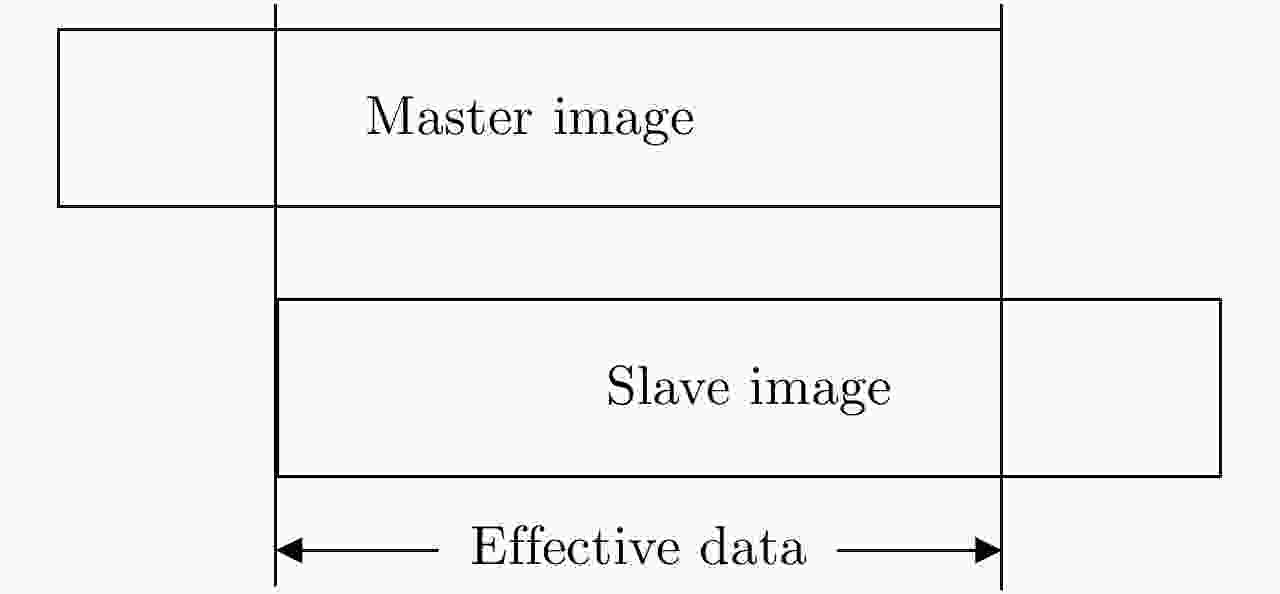
摘要: 基于导航卫星的干涉SAR(GNSS-InSAR)使用在轨导航卫星作为照射源,近地面部署接收机,利用导航卫星的星座特性以及重轨特性,可实现区域性的连续观测。对于场景1维/3维形变反演而言,需要连续时间的数据采集,由于导航卫星并非严格意义上的重轨,且重轨时间具有不确定性,原始数据冗余度高,数据对齐时截取量大,数据有效性低。该文针对GNSS-InSAR场景数据采集时间精确性问题,提出了一种重轨数据采集优化模型,该方法通过实际轨迹与TLE预测轨迹相结合的方式,通过空间相干系数的滑窗轨迹对齐,以获取相邻天导航卫星重轨时间间隔,实现精确的GNSS-InSAR数据采集,在降低原始数据冗余度下,保证数据的有效合成孔径时间。实测数据表明所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Interference Synthetic Aperture Radar based on the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS-InSAR) uses in-orbit navigation satellites as transmitters of opportunity and receivers are deployed near the ground. Continuous regional observation can be achieved by the constellation and repeat-pass characteristics of the navigation satellites. Continuous-time data collection is required for 1D/3D deformation retrieval of the scene, just like city, bridge, and slope. Since the navigation satellites are not strictly repeat pass and time of repeat pass is uncertain, the original data redundancy is high and interception amount is large when data are aligned, reducing the effect of data. This study focuses on the time accuracy of data acquisition in deformation retrieval of GNSS-InSAR and proposes a repeat-pass data acquisition optimization model, which combines the actual trajectory with the STK, two-line element set prediction trajectory, and sliding window trajectory of the spatial coherence coefficient. Data are aligned to determine the time interval of the adjacent navigation satellites, enabling accurate GNSS-InSAR data acquisition and ensuring effective data accumulation time under reduced original data redundancy. The measured data show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 数据采集试验仿真参数
Table 1. Data acquisition test simulation parameters
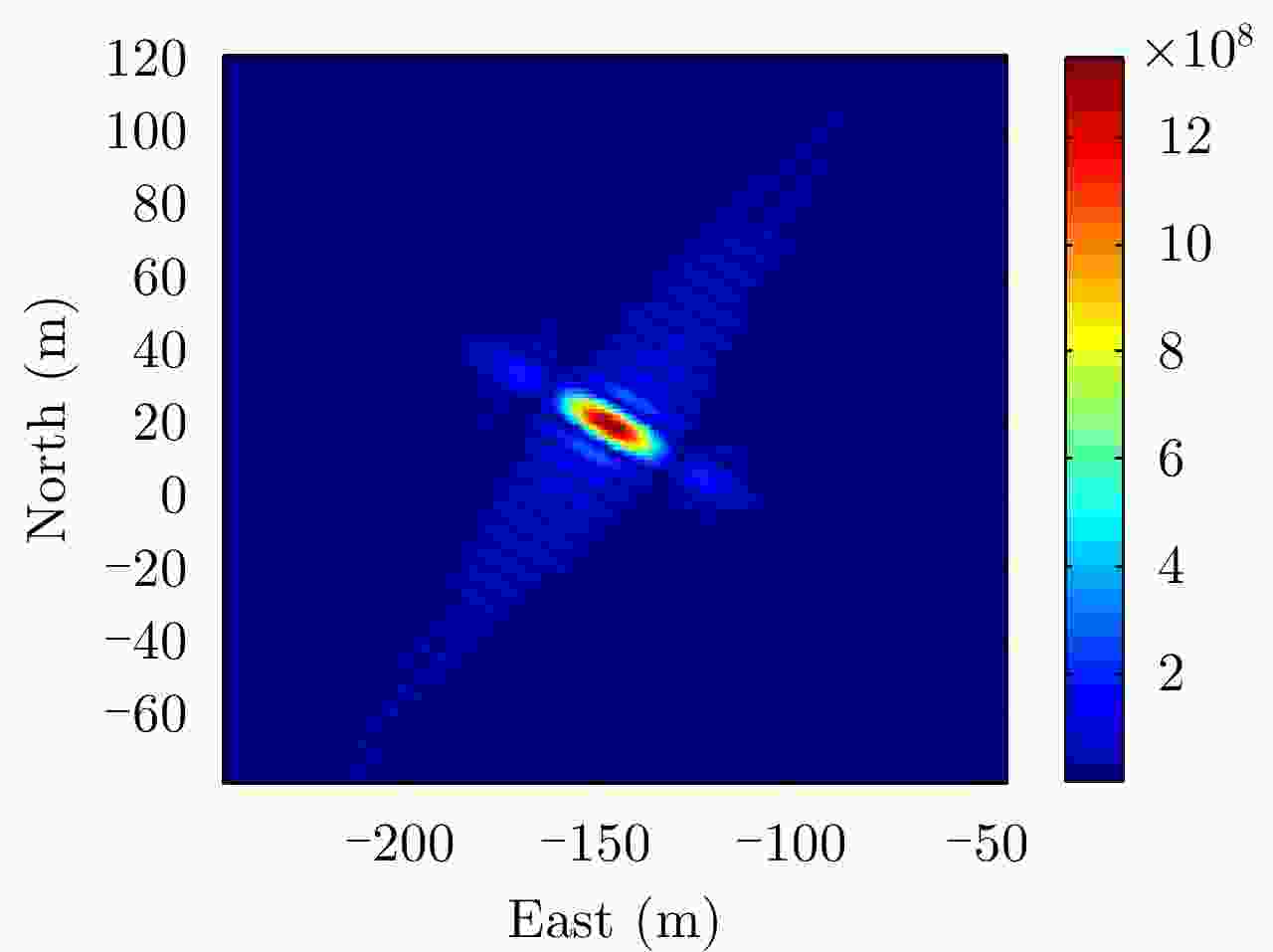
参数 值 照射源 北斗 IGSO1~5 PRF 1000 Hz 带宽 10.23 MHz 合成孔径时间 600 s TLE文件更新日期 2019年4月29日 预定数据采集日期 2019年4月30日 -
[1] CHERNIAKOV M. Space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar—prospective and problems[C]. Proceedings of RADAR 2002, Edinburgh, UK, 2002. [2] ANTONIOU M and CHERNIAKOV M. Experimental demonstration of passive GNSS-based SAR imaging modes[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013. [3] ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. A novel subsidence monitoring technique based on space-surface bistatic differential interferometry using GNSS as transmitters[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–16. [4] ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. Bistatic SAR imaging processing and experiment results using BeiDou-2/Compass-2 as illuminator of opportunity and a fixed receiver[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, Singapore, 2015. [5] FAN Xuezhen, LIU Feifeng, ZHANG Tian, et al. Passive SAR with GNSS transmitters: Latest results and research progress[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017. [6] ANTONIOU M, CHERNIAKOV M, and MA Hui. Space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar with navigation satellite transmissions: A review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–20. [7] LIU Feifeng, ANTONIOU M, ZENG Zhangfan, et al. Point spread function analysis for BSAR with GNSS transmitters and long dwell times: Theory and experimental confirmation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 781–785. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2223655 [8] MA Hui, ANTONIOU M, and CHERNIAKOV M. Passive GNSS-based SAR resolution improvement using joint Galileo E5 signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1640–1644. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2417594 [9] ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. Space-surface bistatic SAR image enhancement based on repeat-pass coherent fusion with Beidou-2/Compass-2 as illuminators[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614337 [10] ANTONIOU M, LIU F, ZENG Z, et al. Coherent change detection using GNSS-based passive SAR: First experimental results[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012. [11] TZAGKAS D, ANTONIOU M, and CHERNIAKOV M. Coherent change detection experiments with GNSS-based passive SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2016 European Radar Conference, London, UK, 2016. [12] LIU Feifeng, FAN Xuezhen, ZHANG Tian, et al. GNSS-based SAR interferometry for 3-D deformation retrieval: Algorithms and feasibility study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5736–5748. [13] DONG Xichao, HU Cheng, TIAN Weiming, et al. Feasibility study of inclined geosynchronous SAR focusing using Beidou IGSO signals[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(12): 129302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-5524-x [14] LIU Feifeng, FAN Xuezhen, ZHANG Lingzhi, et al. GNSS-based SAR for urban area imaging: Topology optimization and experimental confirmation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(12): 4668–4682. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1569790 [15] ZHANG Qilei, ANTONIOU M, CHANG Wenge, et al. Spatial decorrelation in GNSS-based SAR coherent change detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 219–228. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2321145 [16] ZEBKER H A and VILLASENOR J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(5): 950–959. doi: 10.1109/36.175330 [17] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [18] ZENG Tao, CHERNIAKOV M, and LONG Teng. Generalized approach to resolution analysis in BSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(2): 461–474. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1468741 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: