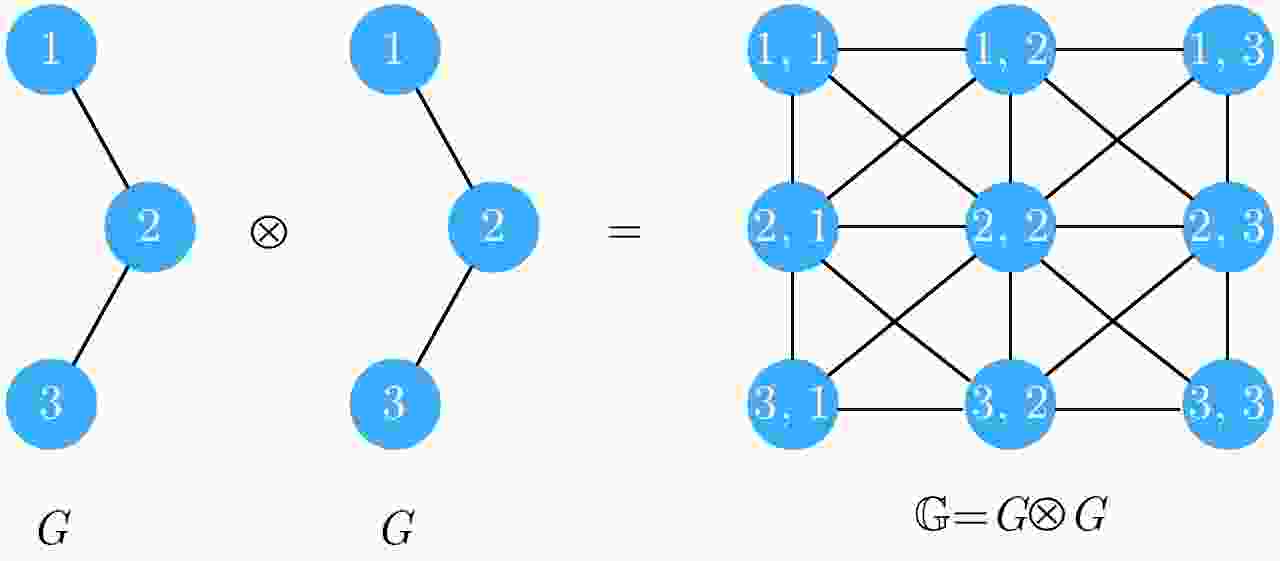
An Unsupervised PolSAR Image Classification Algorithm Based on Tensor Product Graph Diffusion
-
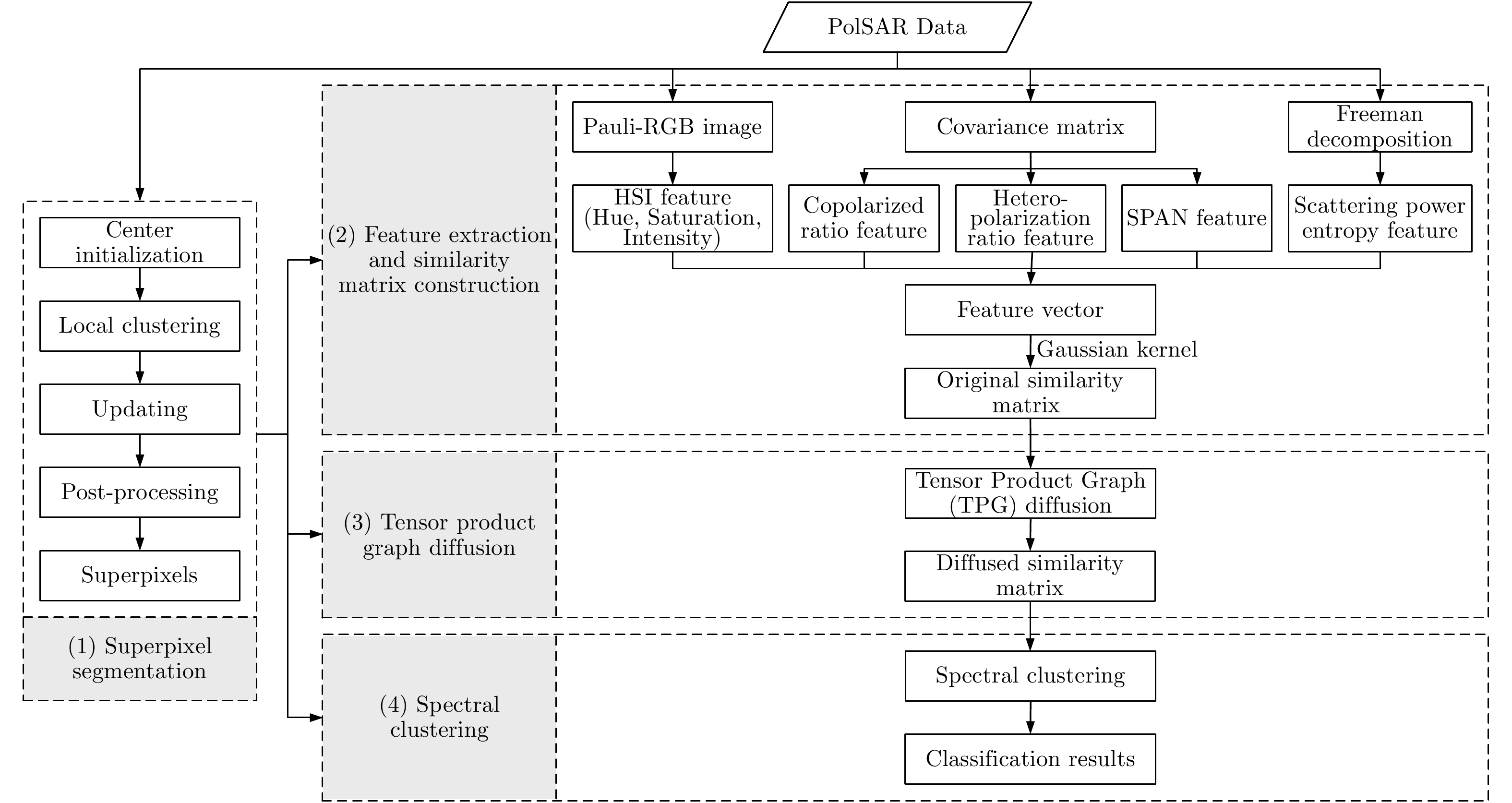
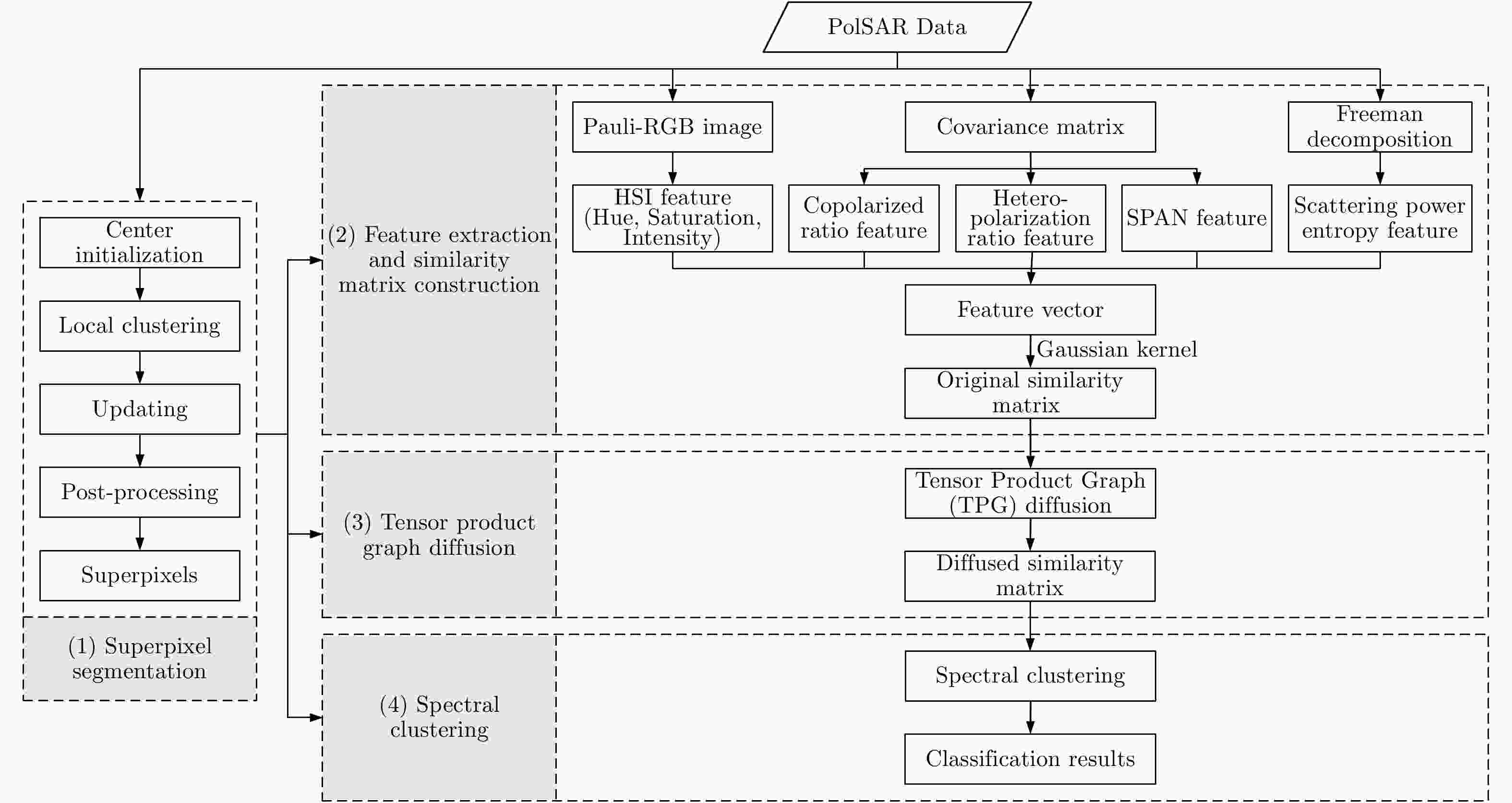
摘要: 针对相似度表达的困难性以及极化SAR图像中固有的相干斑噪声问题,该文提出了一种基于张量积(TPG)扩散的非监督极化SAR图像地物分类算法。张量积扩散一般用于光学图像的分割或检索,目前研究表明,其已可用于极化SAR(PolSAR)图像地物分类。基于张量积扩散可以稳健地度量数据点之间的测地线距离,因此能够更好地挖掘数据点之间内在的相似度信息。首先,将极化SAR图像进行分割,生成许多超像素;其次,基于超像素提取7种特征并生成一个特征向量,进而利用高斯核构建相似度矩阵;再次,基于已构建的相似度矩阵,利用张量积扩散沿着数据点的内在流形结构进行相似度的传播,实现全局的相似性度量,从而获得一个具有更强判别能力的相似度矩阵;最后,基于此相似度矩阵进行谱聚类以得到地物分类结果。该文在仿真和实测极化SAR图像上均进行了大量实验,并与4种经典算法进行对比,结果表明该方法可以有效地结合空间邻域相似度信息并取得更高的分类精度。Abstract: To overcome the difficulty of similarity expression and the effects of speckle noise in unsupervised classification of Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) images, a novel unsupervised PolSAR image terrain classification algorithm based on Tensor Product Graph (TPG) diffusion has been developed herein. Generally, TPG diffusion is usually utilized for optical image segmentation or image retrieval. In the present study, it can be used for PolSAR image terrain classification. TPG diffusion can robustly estimate geodesic distances ; therefore, it can be used for mining the intrinsic affinity between data points. First, the PolSAR image is over-segmented into many superpixels. Second, seven features are extracted based on the segmented superpixels to form a feature vector and construct a similarity matrix by using the Gaussian kernel. Third, TPG diffusion is performed on this similarity matrix to obtain another similarity matrix with stronger discriminability by propagating affinity information along the mainfold structure of data to achieve the global affinity measure. Finally, spectral clustering based on the diffused similarity matrix is adopted to perform terrain classification. Extensive experiments conducted on both simulated and real-world PolSAR images demonstrate that our approach can effectively combine neighborhood information and achieve higher classification accuracy, compared to four other competitive state-of-the-art methods.
-
Key words:
- PolSAR image /
- Unsupervised classification /
- Tensor Product Graph (TPG) /
- Diffusion /
- Superpixel /
- Spectral clustering
-
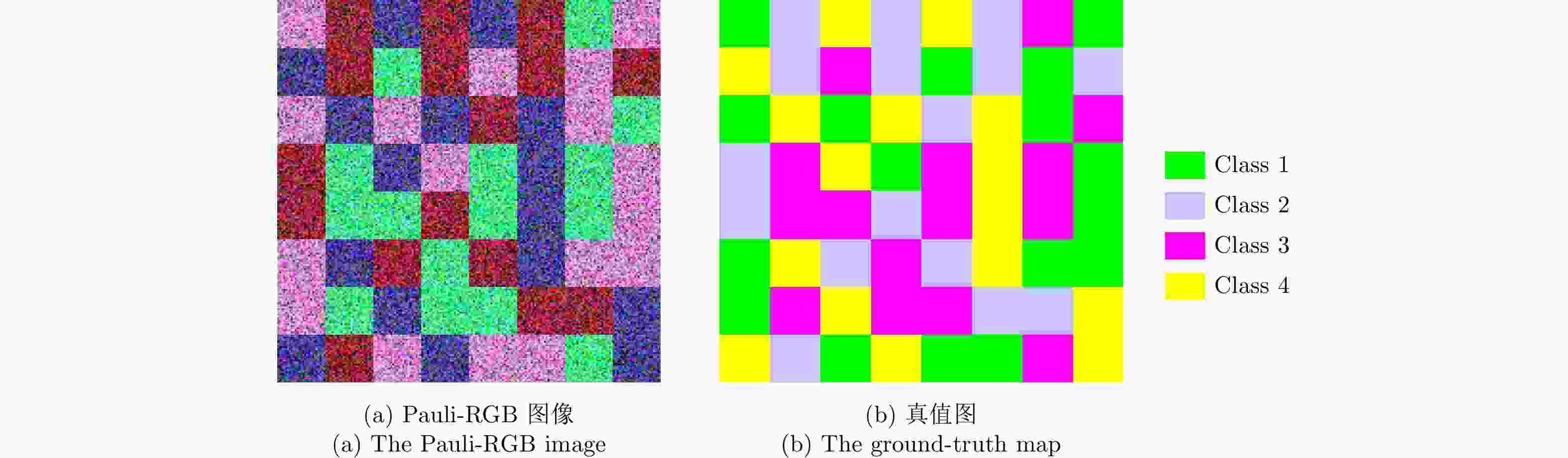
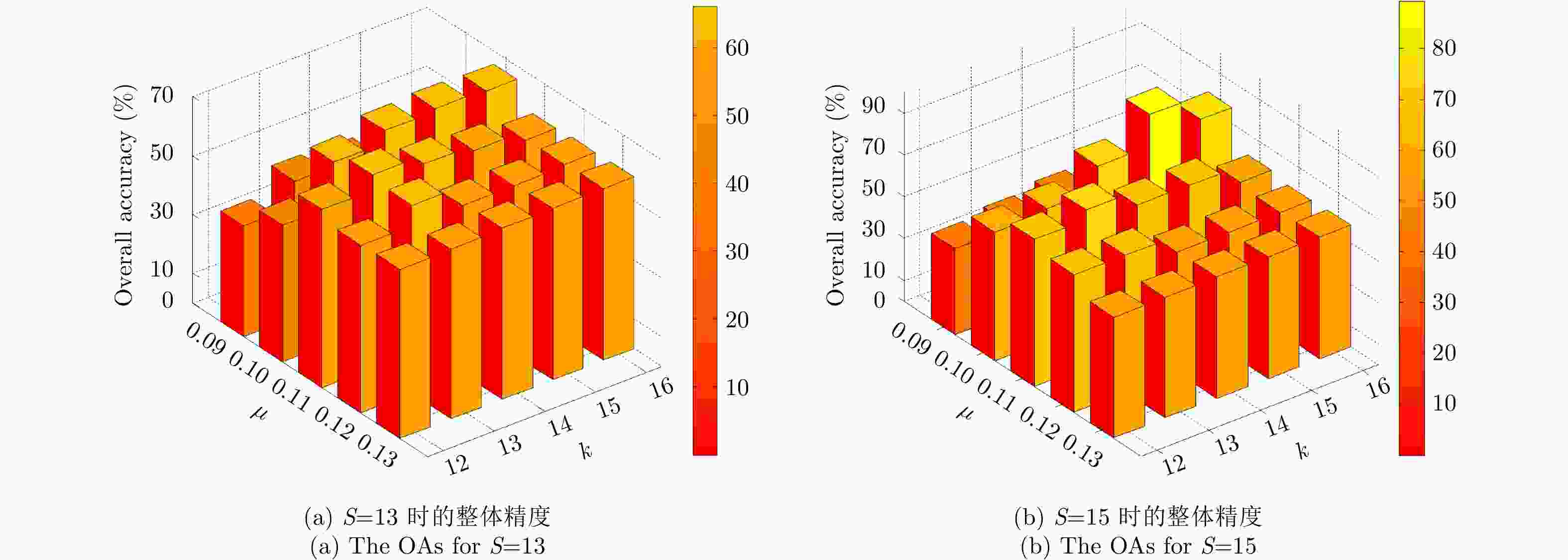
表 1 OM方法基于仿真数据的5种评价度量结果
Table 1. The five evaluation criteria of the OM method for the simulated PolSAR image
类别 类别1 类别2 类别3 类别4 UA 类别1 7822 26 19 2758 0.7362 类别2 3 9751 9 237 0.9751 类别3 12 47 9228 88 0.9843 类别4 14 96 11 9879 0.9879 PA 0.9963 0.9830 0.9958 0.7622 OA: 91.70%, K: 0.8894 表 2 PM方法基于仿真数据的5种评价度量结果
Table 2. The five evaluation criteria of the PM method for the simulated PolSAR image
类别 类别1 类别2 类别3 类别4 UA 类别1 10308 26 19 272 0.9701 类别2 3 9751 9 237 0.9751 类别3 16 47 9228 84 0.9843 类别4 15 96 11 9878 0.9878 PA 0.9967 0.9830 0.9958 0.9434 OA: 97.91%, K: 0.9722 表 3 两种算法基于实测极化SAR图像的整体精度和Kappa系数
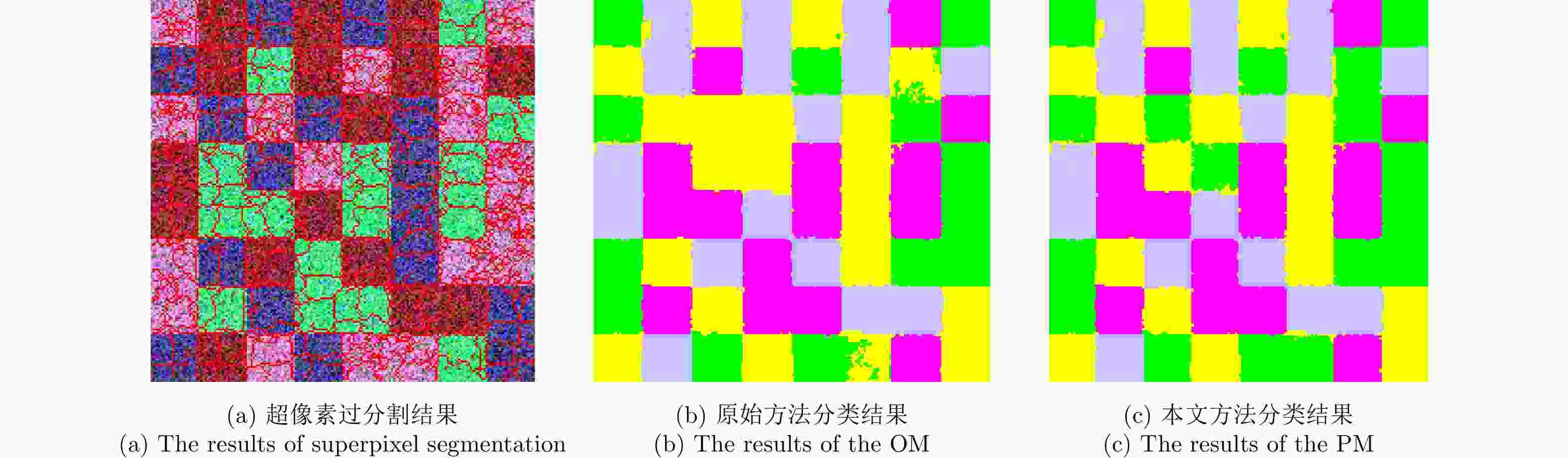
Table 3. The OAs and Ks of two methods for the real-world PolSAR image
算法 精度 K OA (%) OM算法 0.6193 78.51 PM算法 0.8097 89.36 表 4 5种算法基于仿真极化SAR图像的3种评价度量结果
Table 4. The three evaluation criteria of five methods for the simulated PolSAR image
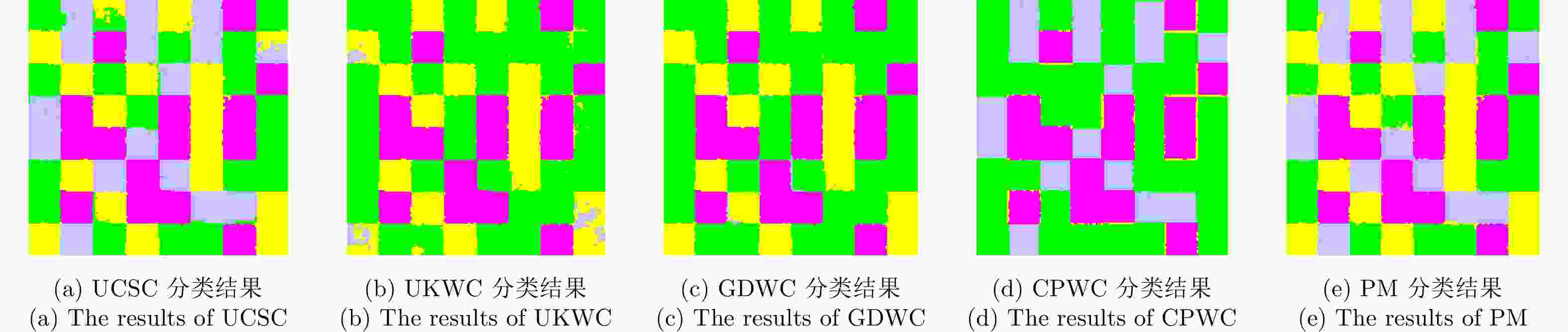
算法 精度 类别1 类别2 类别3 类别4 K OA (%) UCSC 0.9400 0.9857 0.9919 0.9504 0.9541 96.56 UKWC 0.5012 0.0000 0.9919 0.9459 0.6194 71.62 GDWC 0.5071 0.2242 0.9958 0.9808 0.6470 73.68 CPWC 0.5007 1.0000 0.9312 0.1633 0.6118 71.05 PM 0.9967 0.9830 0.9958 0.9434 0.9722 97.91 表 5 5种算法基于实测极化SAR图像的3种评价度量结果
Table 5. The three evaluation criteria of five methods for the real-world PolSAR image
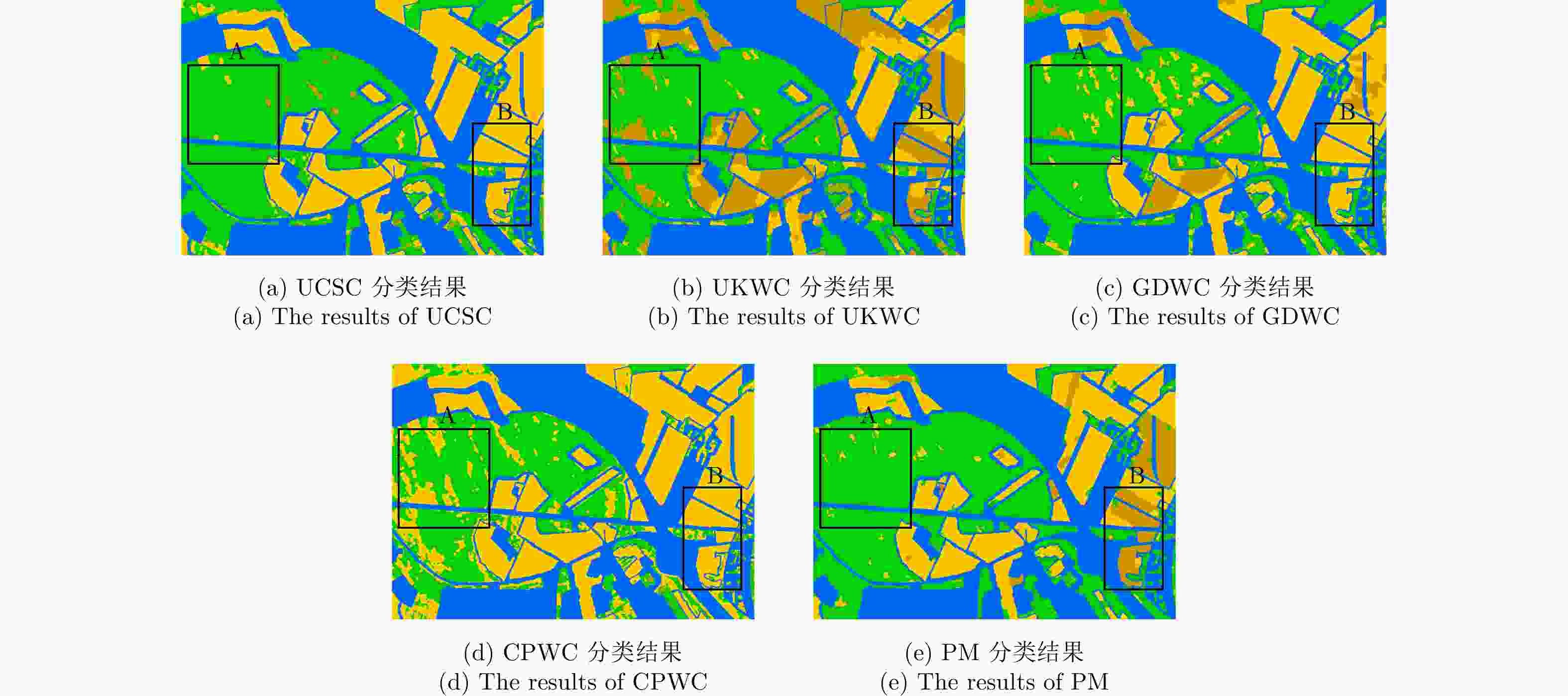
算法 精度 林地 开放区1 开放区2 K OA (%) UCSC 0.9638 0.5477 0.0004 0.5940 77.09 UKWC 0.9657 0.8154 0.5011 0.6666 79.81 GDWC 0.9514 0.6030 0.7830 0.6645 80.74 CPWC 0.9984 0.4307 0.0014 0.4407 65.73 PM 0.9707 0.7461 0.9226 0.8097 89.36 -
[1] SHI Lei, ZHANG Lefei, ZHAO Lingli, et al. Adaptive Laplacian Eigenmap-based dimension reduction for ocean target discrimination[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(7): 902–906. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2553046 [2] 杨文, 钟能, 严天恒, 等. 基于黎曼流形的极化SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 433–441. doi: 10.12000/JR17031YANG Wen, ZHONG Neng, YAN Tianheng, et al. Classification of polarimetric SAR images based on the Riemannian manifold[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 433–441. doi: 10.12000/JR17031 [3] LIU Wensong, YANG Jie, LI Pingxiang, et al. A novel object-based supervised classification method with active learning and random forest for PolSAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1092. doi: 10.3390/rs10071092 [4] SHI Lei, ZHANG Lefei, ZHAO Lingli, et al. The potential of linear discriminative Laplacian Eigenmaps dimensionality reduction in polarimetric SAR classification for agricultural areas[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 86: 124–135. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.09.013 [5] WANG Shuang, LIU Kun, PEI Jingjing, et al. Unsupervised classification of fully polarimetric SAR images based on scattering power entropy and copolarized ratio[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 622–626. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2216249 [6] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, POTTIER E, et al. Unsupervised terrain classification preserving polarimetric scattering characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(4): 722–731. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.819883 [7] RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of polsar data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 [8] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, AINSWORTH T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621 [9] 钟能, 杨文, 杨祥立, 等. 基于混合Wishart模型的极化SAR图像非监督分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133ZHONG Neng, YANG Wen, YANG Xiangli, et al. Unsupervised classification for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on Wishart mixture models[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133 [10] WU Yonghui, JI Kefeng, YU Wenxian, et al. Region-based classification of polarimetric SAR images using Wishart MRF[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 668–672. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2002263 [11] VON LUXBURG U. A tutorial on spectral clustering[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2007, 17(4): 395–416. doi: 10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z [12] YANG Yifang, WANG Yuping, XUE Xingsi, et al. A novel spectral clustering method with superpixels for image segmentation[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(1): 161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.10.053 [13] HU Jingliang, WANG Yuanyuan, GHAMISI P, et al. Evaluation of polsar similarity measures with spectral clustering[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 3254–3257. [14] LI Yonggang, ZHANG Shichao, CHENG Debo, et al. Spectral clustering based on hypergraph and self-re-presentation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(16): 17559–17576. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-4131-6 [15] YANG Xingwei, PRASAD L, and JAN LATECKI L. Affinity learning with diffusion on tensor product graph[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 28–38. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.60 [16] ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, LUO Tiancheng, et al. A fast superpixel segmentation algorithm for PolSAR images based on edge refinement and revised Wishart distance[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1687. doi: 10.3390/s16101687 [17] CAO Fang, HONG Wen, WU Yirong, et al. An unsupervised segmentation with an adaptive number of clusters using the SPAN/H/α/A space and the complex Wishart clustering for fully polarimetric SAR data analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3454–3467. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907601 [18] ZHOU Xiaofeng, WANG Shuang, HUA Wenqiang, et al. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data based on a novel polarization feature[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 4594–4599. [19] 张月, 邹焕新, 邵宁远, 等. 基于相似度网络融合的极化SAR图像地物分类[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 295–302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.09ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Terrain classification of polarimetric SAR images based on consensus similarity network fusion[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 295–302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.09 [20] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 [21] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 [22] YANG Xingwei, SZYLD D B, and JAN LATECKI L. Diffusion on a tensor product graph for semi-supervised learning and interactive image segmentation[J]. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 2011, 169: 147–172. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385981-5.00004-5 [23] VAN LOAN C F. The ubiquitous Kronecker product[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2000, 123(1/2): 85–100. [24] QIN Xianxiang, ZOU Huanxin, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Simulation of spatially correlated PolSAR images using inverse transform method[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2015, 9(1): 095082. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.9.095082 [25] HOU Biao, WU Qian, WEN Zaidao, et al. Robust semisupervised classification for PolSAR image with noisy labels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6440–6455. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2728186 [26] SONG Wanying, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Unsupervised PolSAR image classification and segmentation using Dirichlet process mixture model and Markov random fields with similarity measure[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3556–3568. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2684301 [27] VASILE G, TROUVÉ E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: