Robust Classification of PolSAR Images Based on Pinball loss Support Vector Machine
-
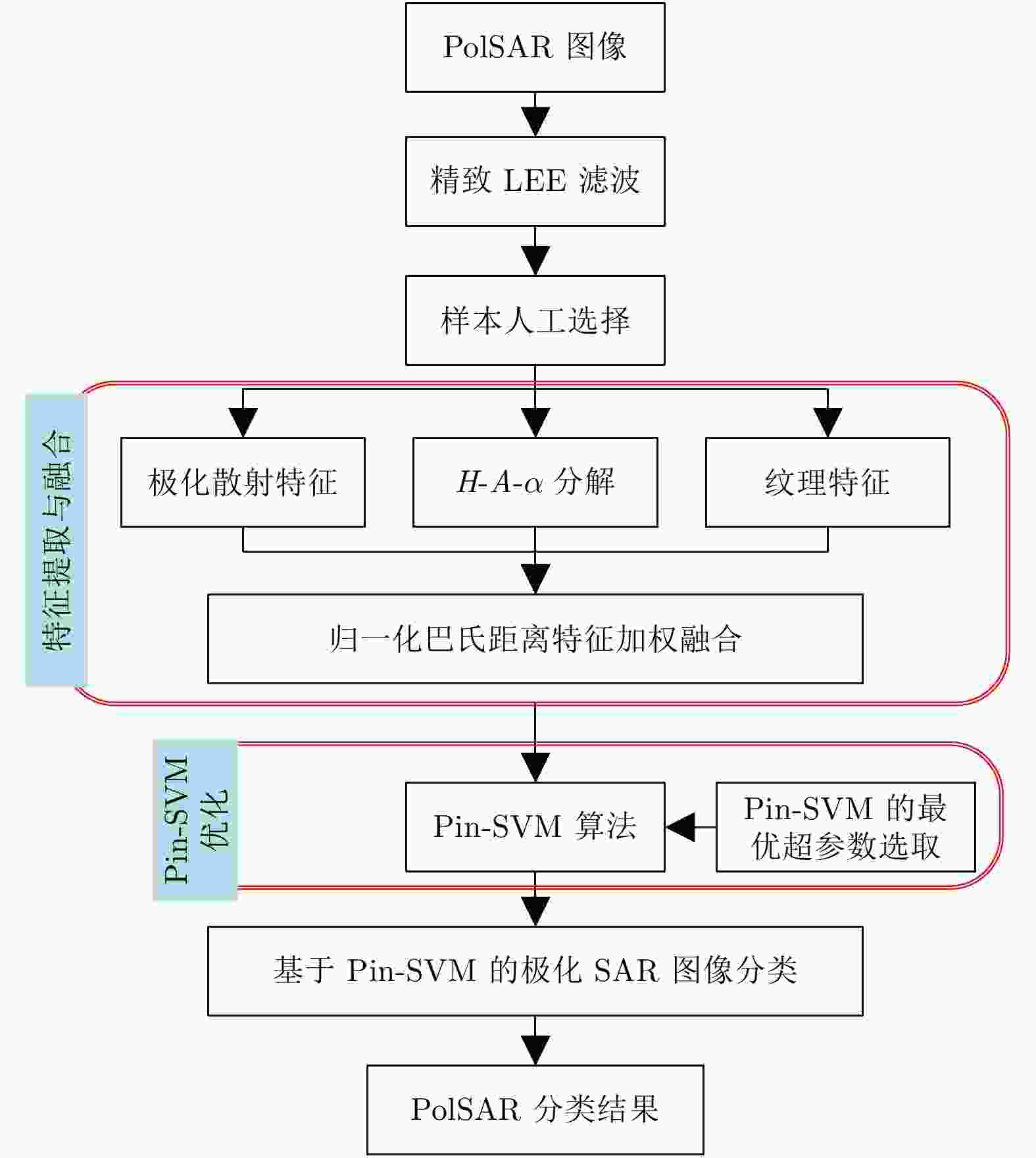
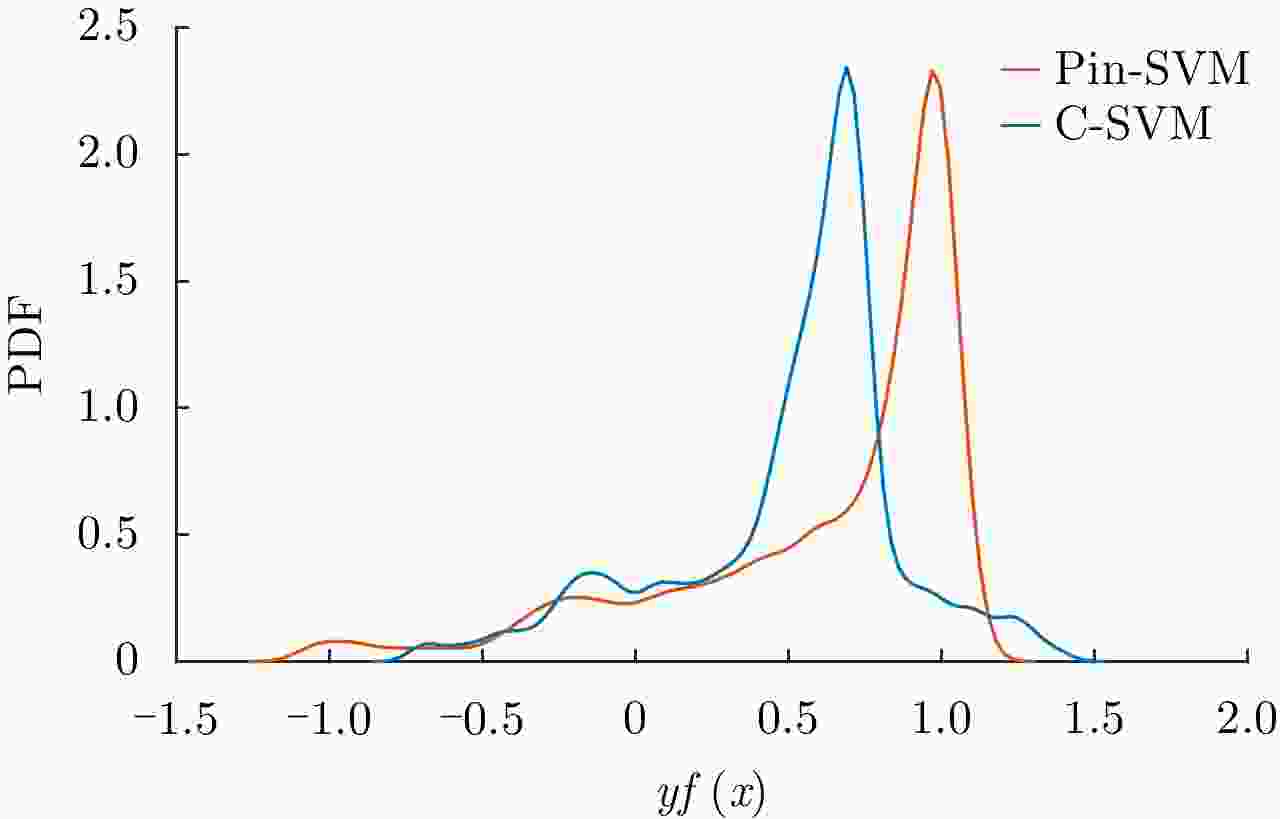
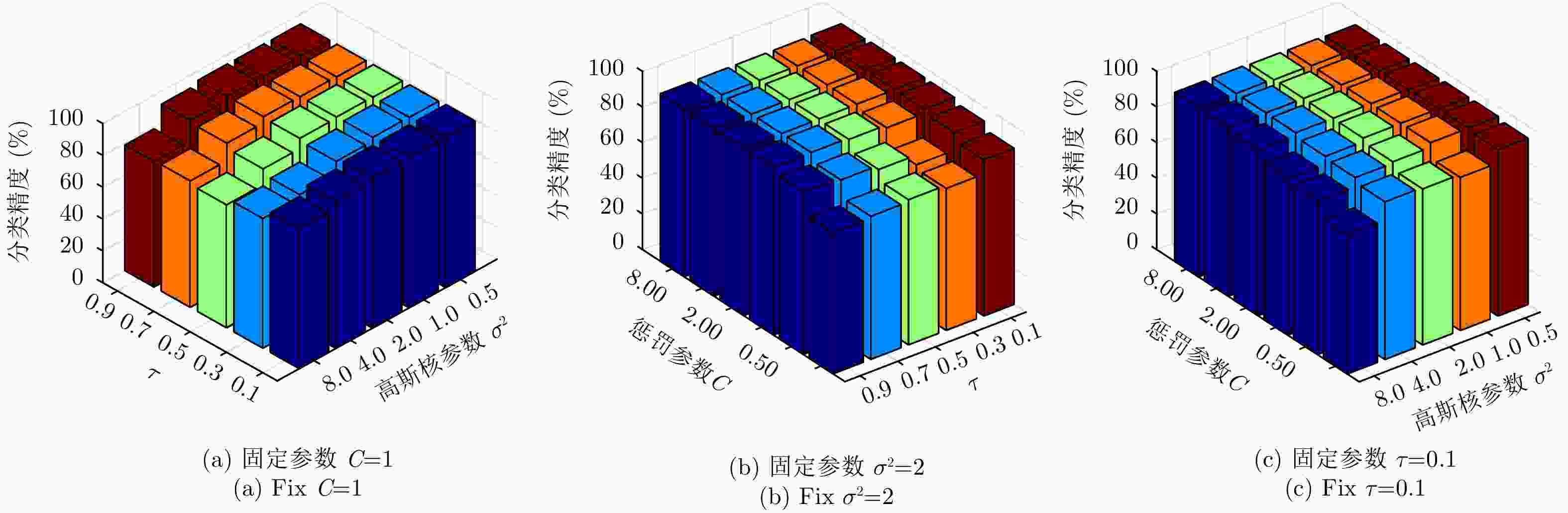
摘要: 考虑到极化合成孔径雷达(PolSAR)图像标注信息量低以及相干斑噪声难以消除的问题,该文从鲁棒统计学习的角度提出了一种基于Pin-SVM的极化SAR图像鲁棒分类方法,根据极化SAR图像的散射特性和地物的纹理特性,通过求解两类样本之间的最大分位数距离来确定分类超平面,在无需迭代的前提下得到更加鲁棒的分类结果。相比传统的基于最大间隔的极化SAR图像分类算法,该文所提算法一方面在对极化SAR图像提取到的特征中包含的噪声具有更好的鲁棒性,另一方面对于训练样本的抽样范围不敏感,即重采样具有更好的鲁棒性。利用EMISAR的Foulum地区极化SAR数据进行了算法验证,多种情况的对比实验的结果验证了该算法的有效性。Abstract: Given the problems that the amount of supervised information in the Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) image is low and the speckle noise is difficult to eliminate, in this study, a robust classification algorithm for PolSAR image based on Pinball loss Support Vector Machine (Pin-SVM) is proposed from the perspective of robust statistical learning. On the basis of the scattering characteristics of PolSAR images and the texture characteristics of surface features, the proposed algorithm determines the optimal decision hyperplane by solving the maximum quantile distance between the samples of two classes, which can provide more robust results without iteration. Compared with the traditional PolSAR image classification algorithms that solve the maximum margin, on one hand, the proposed algorithm is robust to the noise contained in the features extracted from PolSAR images. On the other hand, the proposed algorithm is insensitive to the sampling range of training samples, which means that it has better robustness to resampling. The experimental results of EMISAR-Foulum PolSAR data prove the validity of the proposed algorithm through comparative tests in a variety of situations.
-
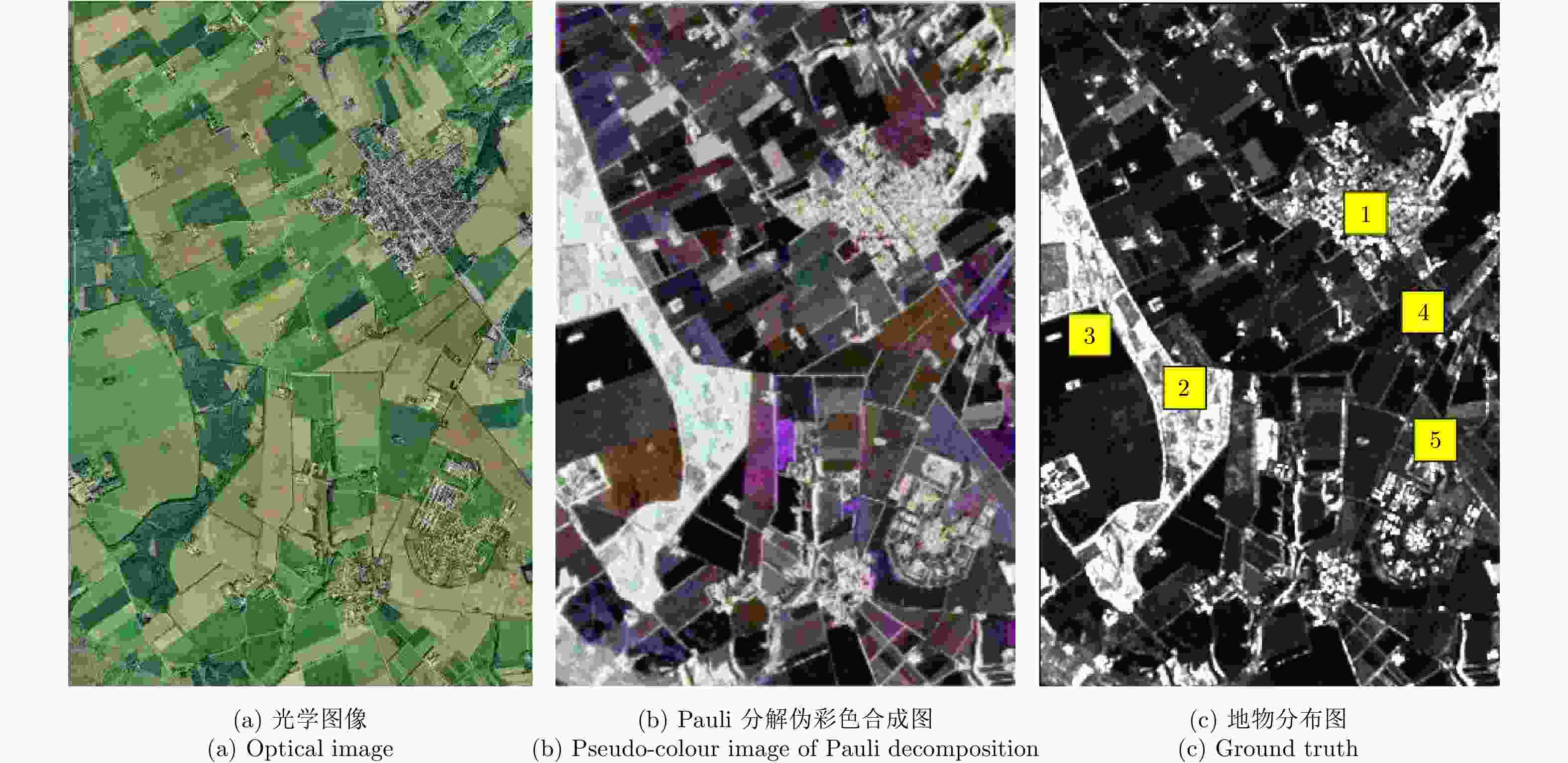
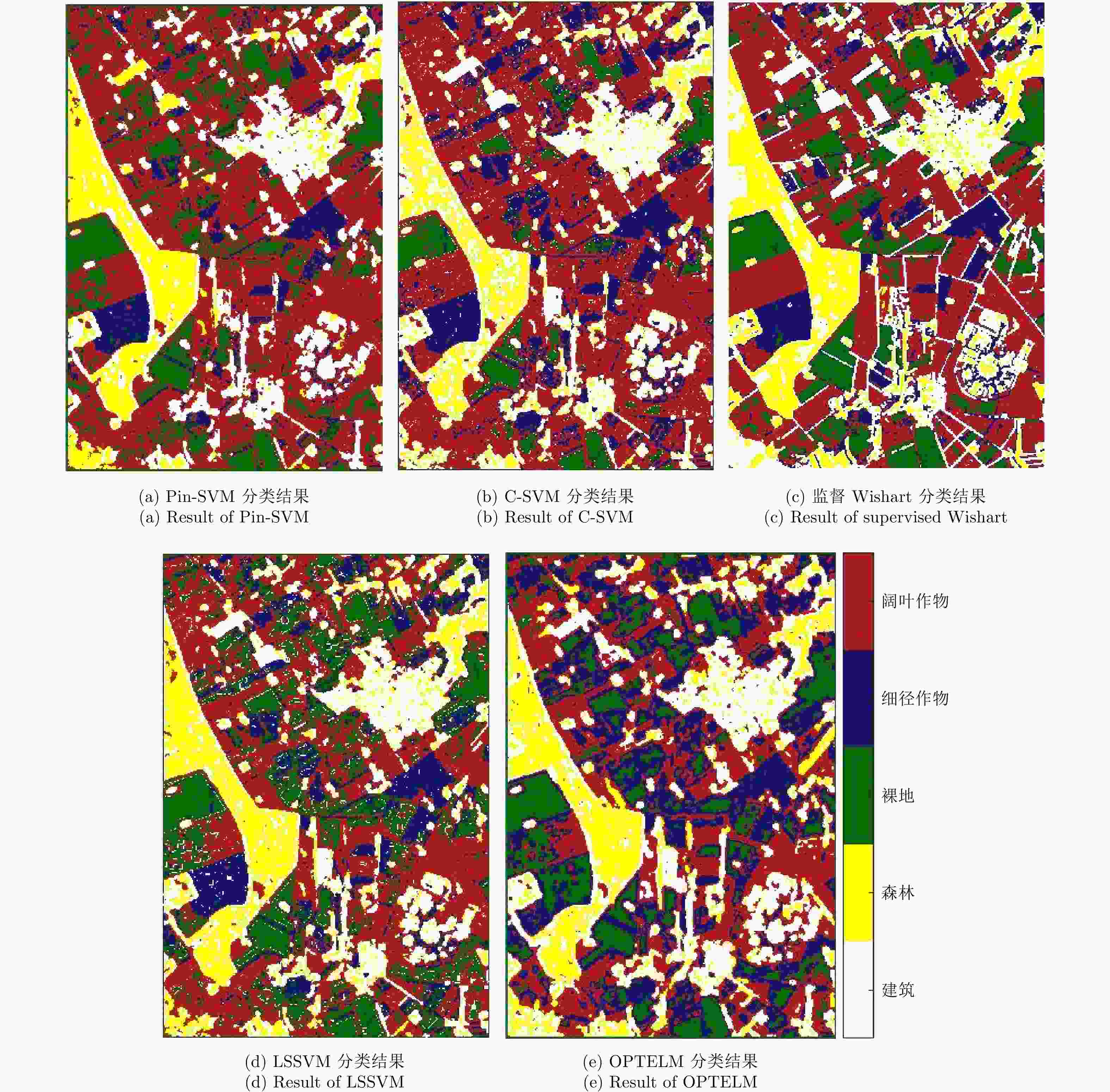
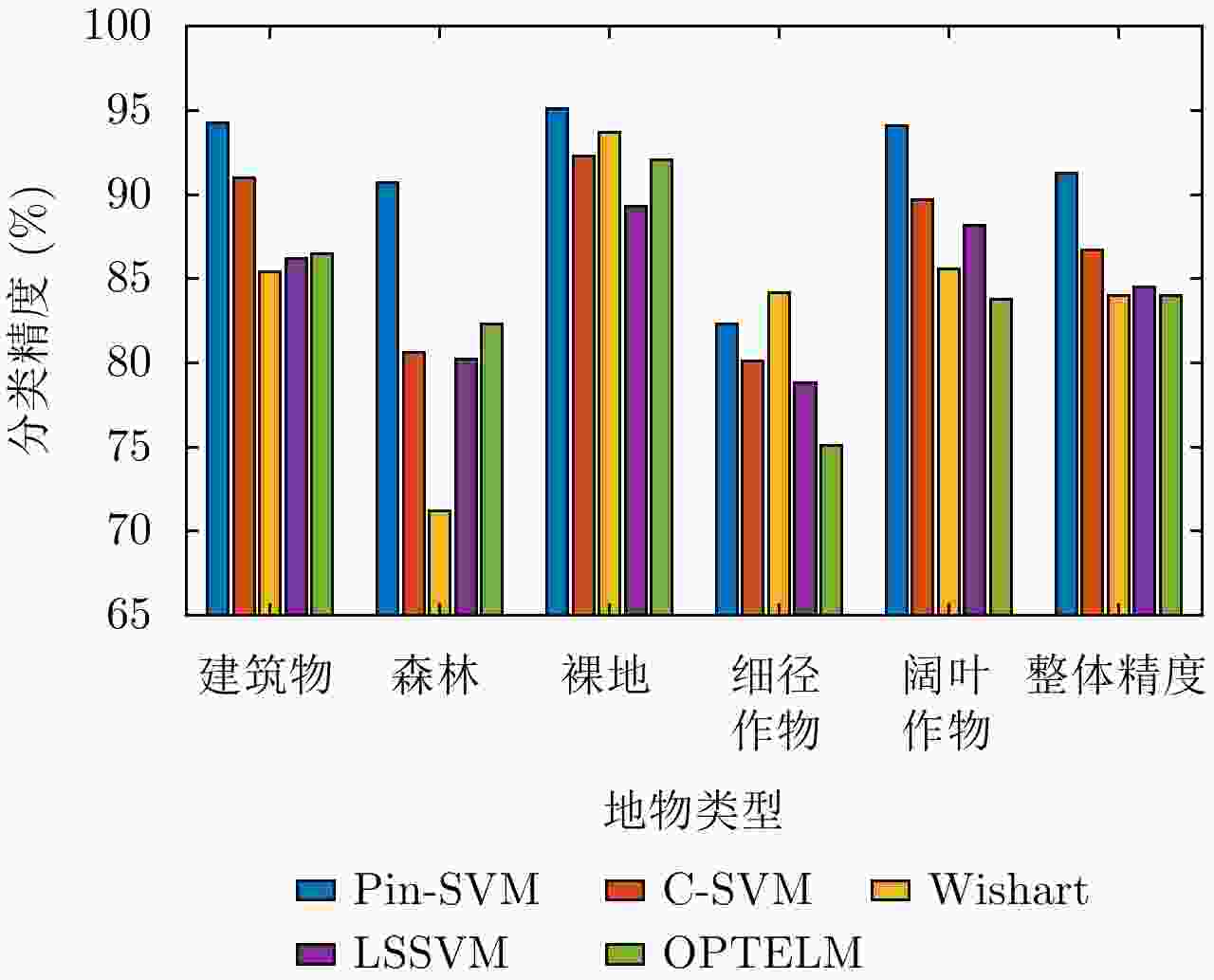
表 1 不同分类器对测试样本的分类精度(%)
Table 1. Classification accuracy comparison of different classifiers
分类器 地物类型 整体精度 建筑物 森林 裸地 细径作物 阔叶作物 Pin-SVM 94.3 90.7 95.1 82.3 94.1 91.3 C-SVM 91.0 80.6 92.3 80.1 89.7 86.7 Wishart 85.4 71.2 93.7 84.2 85.6 84.0 LSSVM 86.2 80.2 89.3 78.8 88.2 84.5 OPTELM 86.5 82.3 92.1 75.1 83.8 84.0 表 2 重采样实验结果
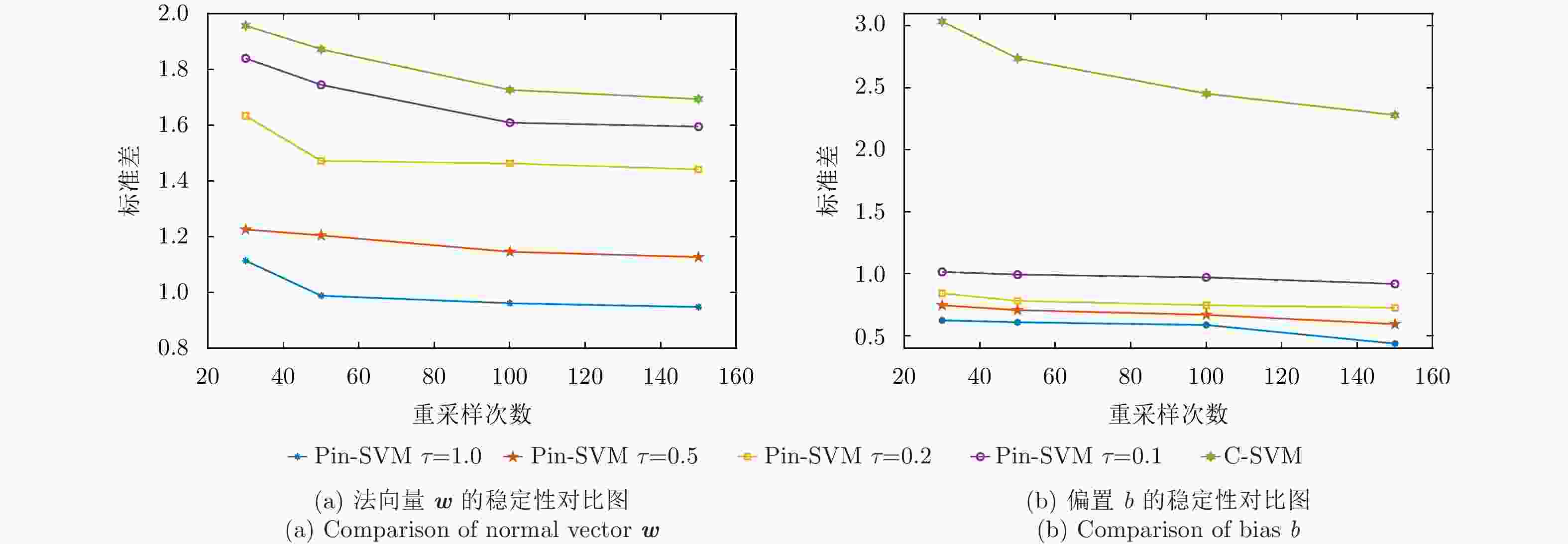
Table 2. Experimental results of the resampling
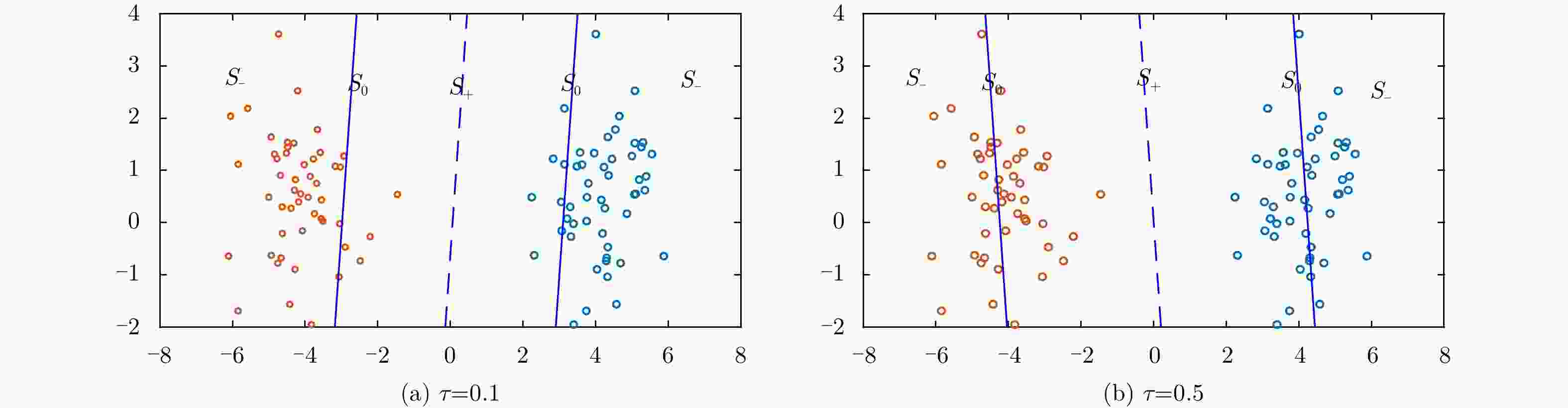
分类器 重采样 30次 50次 100次 150次 Pin-SVM w $8.96 \pm 1.11$ $8.69 \pm 0.99$ $8.57 \pm 0.96$ $8.63 \pm 0.95$ $\tau {\rm{ = }}1.0$ b $ - 5.91 \pm 0.62$ $ - 5.95 \pm 0.61$ $ - 5.93 \pm 0.59$ $ - 5.93 \pm 0.44$ Pin-SVM w $9.43 \pm 1.23$ $9.54 \pm 1.20$ $9.42 \pm 1.15$ $9.68 \pm 1.13$ $\tau {\rm{ = 0}}{\rm{.5}}$ b $ - 6.93 \pm 0.75$ $ - 7.02 \pm 0.71$ $ - 6.91 \pm 0.67$ $ - 6.85 \pm 0.59$ Pin-SVM w $11.43 \pm 1.63$ $11.22 \pm 1.47$ $11.09 \pm 1.46$ $11.31 \pm 1.44$ $\tau {\rm{ = 0}}{\rm{.2}}$ b $ - 8.53 \pm 0.84$ $ - 8.53 \pm 0.78$ $ - 8.41 \pm 0.75$ $ - 8.39 \pm 0.73$ Pin-SVM w $12.30 \pm 1.84$ $12.12 \pm 1.74$ $12.23 \pm 1.61$ $12.09 \pm 1.59$ $\tau {\rm{ = 0}}{\rm{.1}}$ b $ - 9.57 \pm 1.02$ $ - 9.88 \pm 0.99$ $ - 9.50 \pm 0.97$ $ - 9.62 \pm 0.92$ C-SVM w $13.29 \pm 1.96$ $12.98 \pm 1.87$ $13.42 \pm 1.73$ $13.12 \pm 1.69$ b $ - 16.15 \pm 3.04$ $ - 15.81 \pm 2.74$ $ - 15.92 \pm 2.45$ $ - 15.48 \pm 2.28$ -
[1] CHEN Qiang, KUANG Gangyao, LI J, et al. Unsupervised land cover/land use classification using PolSAR imagery based on scattering similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(3): 1817–1825. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2012.2205389 [2] LI Wenmei, CHEN Erxue, LI Zengyuan, et al. Forest aboveground biomass estimation using polarization coherence tomography and PolSAR segmentation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(2): 530–550. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.999383 [3] FOUCHER S, LANDRY T, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, et al. An evaluation of PolSAR speckle filters on compact-pol images[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 5089–5092. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352466. [4] LIU Xunan and CHENG Bo. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering for high-resolution SAR images using RADARSAT-2 POLSAR SLC data[C]. Proceedings of 2012 International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing, Xiamen, China, 2012: 329–334. doi: 10.1109/CVRS.2012.6421284. [5] 滑文强, 王爽, 侯彪. 基于半监督学习的SVM-Wishart极化SAR图像分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138HUA Wenqiang, WANG Shuang, and HOU Biao. Semi-supervised learning for classification of polarimetric SAR images based on SVM-Wishart[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138 [6] ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Unsupervised classification of polsar imagery based on consensus similarity network fusion[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 3266–3269. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8127694. [7] BI Haixia, SUN Jian, and XU Zongben. Unsupervised PolSAR image classification using discriminative clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3531–3544. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2675906 [8] FERRO-FAMIL L, POTTIER E, and LEE J S. Unsupervised classification of multifrequency and fully polarimetric SAR images based on the H/A/Alpha-Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(11): 2332–2342. doi: 10.1109/36.964969 [9] SHANG Fang and HIROSE A. Use of Poincare sphere parameters for fast supervised PolSAR land classification[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 3175–3178. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2013.6723501. [10] DABBOOR M and SHOKR M. A new likelihood ratio for supervised classification of fully polarimetric SAR data: An application for sea ice type mapping[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 84: 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.06.010 [11] ZHANG Lamei, SUN Liangjie, ZOU Bin, et al. Fully polarimetric SAR image classification via sparse representation and polarimetric features[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 3923–3932. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2359459 [12] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [13] VAPNIK V N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory[M]. New York, US: Springer-Verlag, 2000: 267–290. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-3264-1. [14] MAGHSOUDI Y, COLLINS M J, and LECKIE D G. Radarsat-2 polarimetric SAR data for boreal forest classification using SVM and a wrapper feature selector[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(3): 1531–1538. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2259219 [15] CHEN Wenshuai, HAI Dong, GOU Shuiping, et al. Classification of PolSAR images based on SVM with Self-Paced learning optimization[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 4491–4494. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8517452. [16] SUYKENS J A K and VANDEWALLE J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers[J]. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9(3): 293–300. doi: 10.1023/a:1018628609742 [17] WANG Yidan, YANG Liming, and YUAN Chao. A robust outlier control framework for classification designed with family of homotopy loss function[J]. Neural Networks, 2019, 112: 41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.01.013 [18] BO Liefeng, WANG Ling, and JIAO Licheng. Recursive finite newton algorithm for support vector regression in the primal[J]. Neural Computation, 2007, 19(4): 1082–1096. doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.19.4.1082 [19] WU Yichao and LIU Yufeng. Robust truncated hinge loss support vector machines[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2007, 102(479): 974–983. doi: 10.1198/016214507000000617 [20] LIU Dalian, SHI Yong, and TIAN Yingjie. Ramp loss nonparallel support vector machine for pattern classification[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2015, 85: 224–233. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2015.05.008 [21] HUANG Xiaolin, SHI Lei, and SUYKENS J A K. Support vector machine classifier with pinball loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(5): 984–997. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2013.178 [22] BO Liefeng, WANG Ling, and JIAO Licheng. Feature scaling for kernel fisher discriminant analysis using leave-one-out cross validation[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(4): 961–978. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.4.961 [23] SCHOLKOPF B, MIKA S, BURGES C J C, et al. Input space versus feature space in kernel-based methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1999, 10(5): 1000–1017. doi: 10.1109/72.788641 [24] ZHANG Lamei, ZOU Bin, CAI Hongjun, et al. Multiple-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 603–607. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2008.2000795 [25] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [26] HARALICK R M, SHANMUGAM K, and DINSTEIN I. Textural features for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(6): 610–621. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314 [27] DEKKER R J. Texture analysis of urban areas in ERS SAR imagery for map updating[C]. Proceedings of IEEE/ISPRS Joint Workshop on Remote Sensing and Data Fusion over Urban Areas, Rome, Italy, 2001: 226–230. doi: 10.1109/DFUA.2001.985885. [28] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, and DE GRANDI G. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and its implication for classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2363–2373. doi: 10.1109/36.789635 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: