Research on Co-channel Interference Suppression Method for Passive Radar Based on the Jiont Processing of Primary and Reference Channels
-
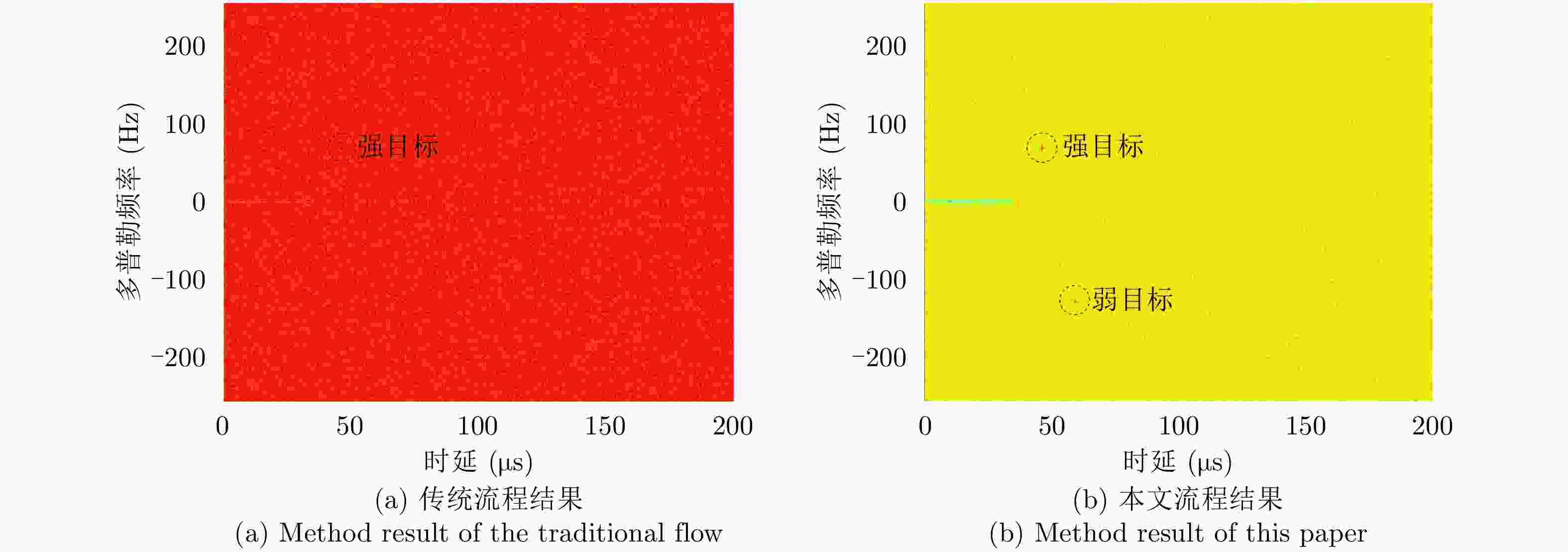
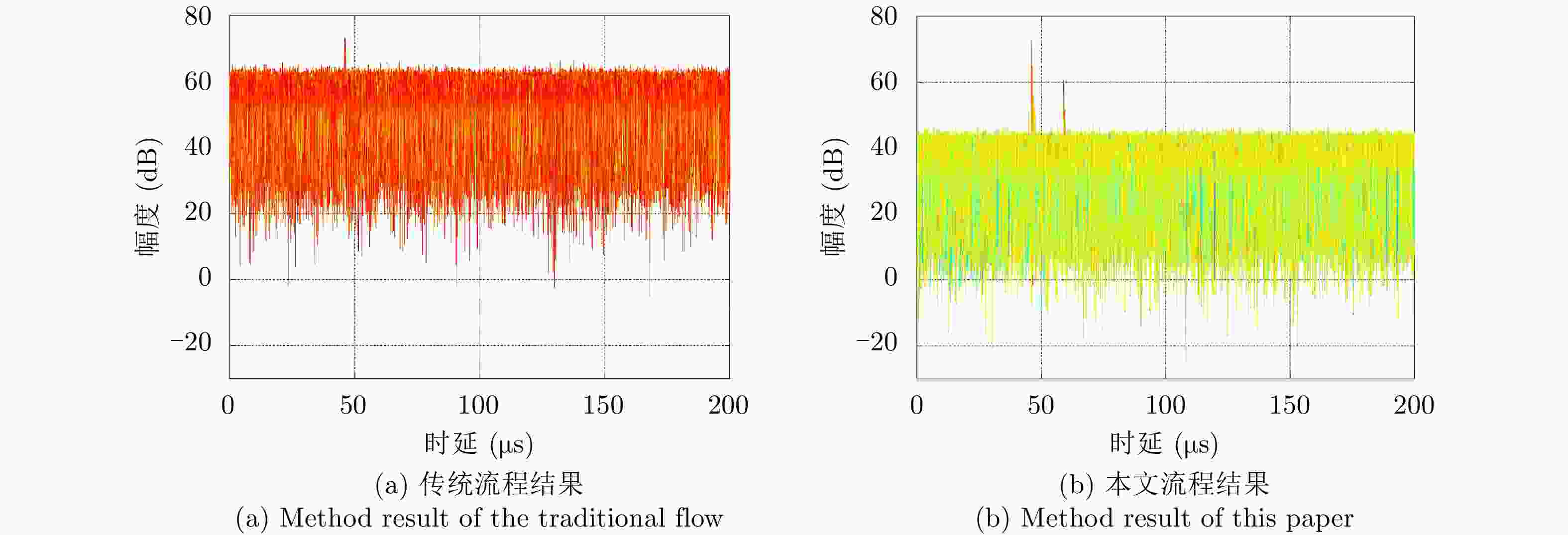
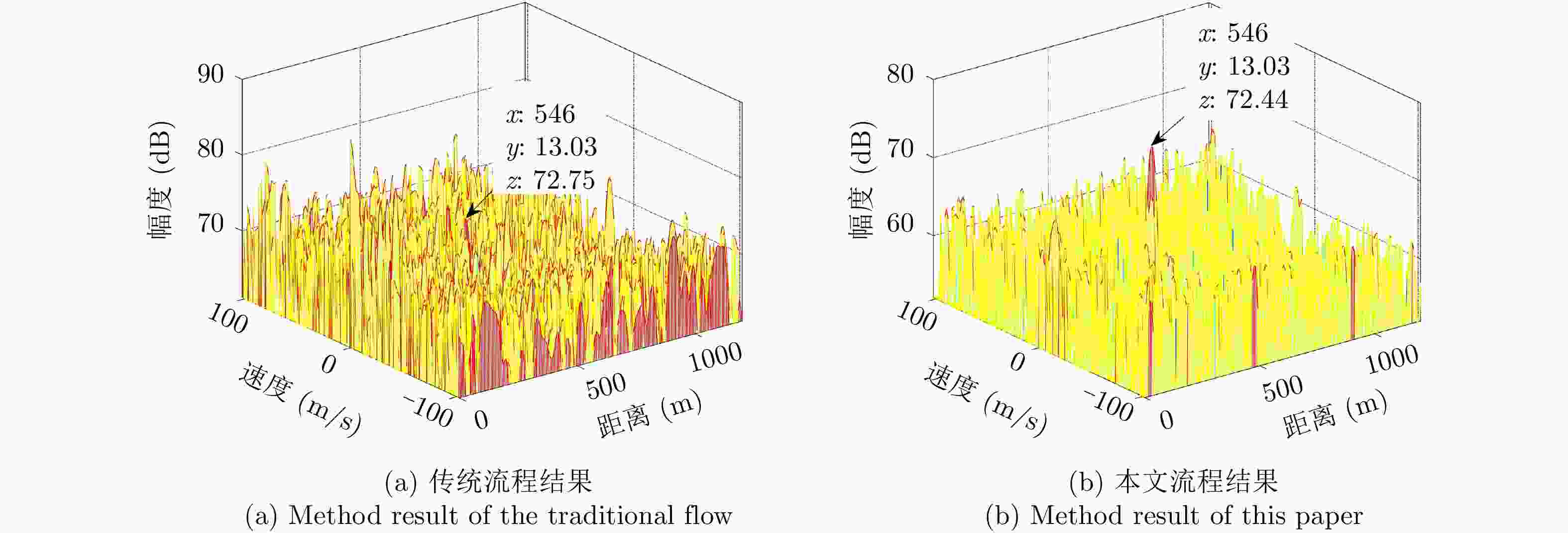
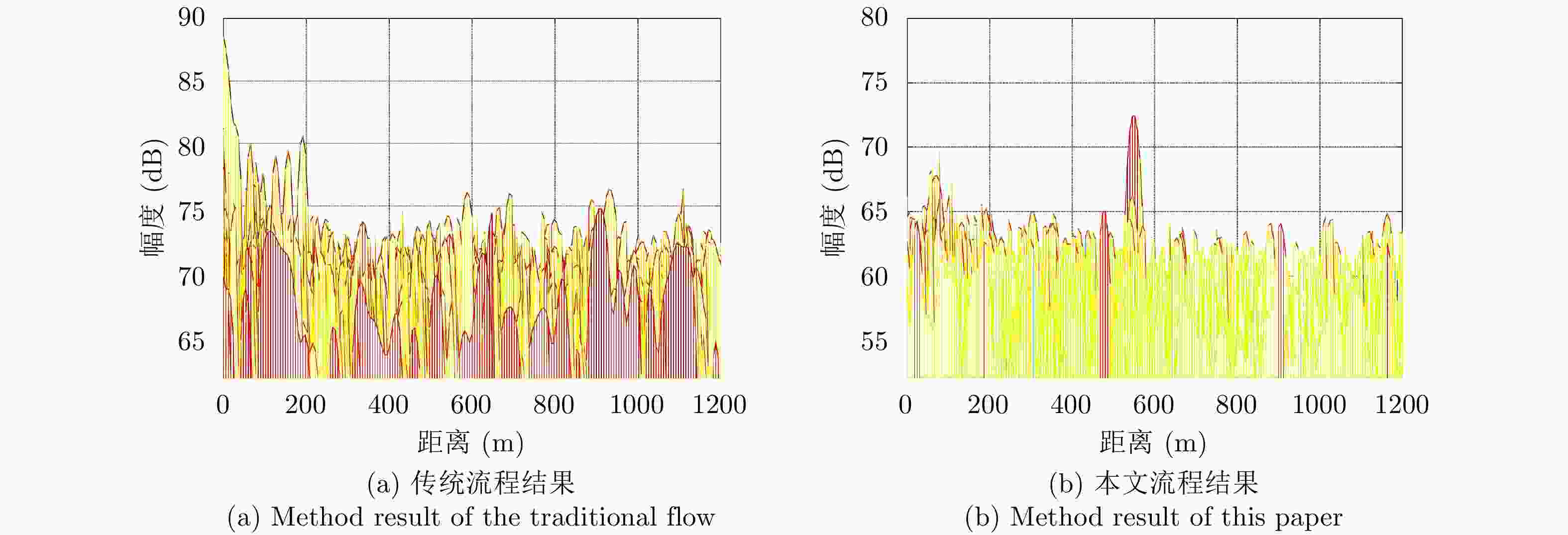
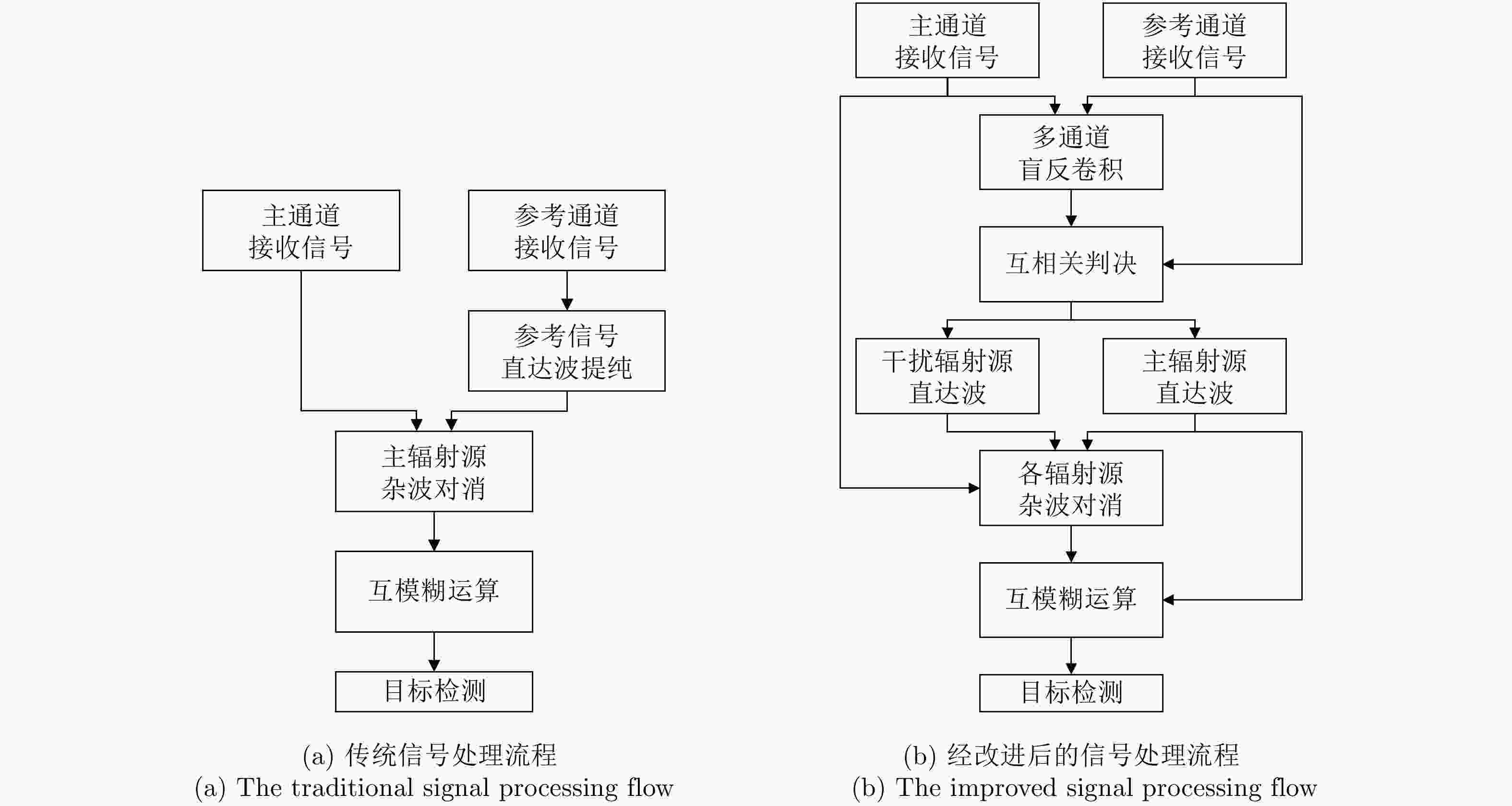
摘要: 基于民用通信信号的无源雷达由于其辐射源分布密集,主通道与参考通道容易同时受同频辐射源干扰,严重影响检测效果。针对上述问题,该文提出了一种加入同频干扰抑制的信号处理流程。改进流程首先对所有通道接收信号联合处理,使用多通道盲反卷积算法估计各个辐射源直达波,再利用各通道主辐射源信号能量占比差异识别主辐射源直达波作为参考信号,然后对主通道中各辐射源杂波信号进行对消,最后用主辐射源直达波与对消剩余信号进行互模糊运算,完成目标检测。改进流程可以在不改变现有系统硬件条件的情况下有效抑制同频干扰,提升对消比,降低互模糊函数底噪,减少漏警。仿真分析与实测数据验证说明了该方法的正确性和有效性。Abstract: The illuminators of passive radar based civil communication signals are densely distributed. As a result, the co-channel illuminator always interferes with the primary and reference channels, resulting in poor detection performance. To solve the aforementioned problem, an improved signal processing flow with co-channel interference suppression is proposed in this paper. First, signals from all channels were processed jointly. The direct-path wave of each illuminator was estimated using the multi-channel blind deconvolution algorithm. Then, the direct-path wave of the primary illuminator was identified as the reference signal by applying the difference in the proportion of the primary illuminator signal energy among channels. Then, the clutter of each illuminator in the primary channel was suppressed by utilizing each of the above estimated signals. Finally, the residual signal, after cancellation, was used to compute the cross-ambiguity functions with the identified direct-path wave of the primary illuminator for target detection. The improved flow can promote the cancellation ratio and reduce the bottom noise of the cross-ambiguity function and missed alarm. Co-channel interference can be effectively suppressed using the improved processing flow without changing the radar system’s hardware. The validity of the proposed method were confirmed by the results of the simulation and experiment.
-
表 1 多通道盲反卷积算法步骤
Table 1. Algorithm procedure of multi-channel blind deconvolution
参数:${\text{κ}},{\rm{batchsize}},L,\alpha ,\beta ,b,h,r$
输入:${\text{x}}\left( n \right)$
初始化:${{\text{W}}_{\rm{0}}} = {\text{I}},{{\text{W}}_k} = {\text{0}}\left( {k = 1,2, ·\!·\!· ,L - 1} \right),{\text{y}}\left( n \right) = {\text{x}}\left( n \right),{{\text{υ}}_k} = {\text{0}}$
循环:
(1) 随机选取${{\text{q}}_1},{{\text{q}}_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{{\text{q}}_{{\rm{batchsize}}}} \in {\text{κ}} $;
(2) 对每个${{\text{h}}_i} \in \left\{ {{{\text{q}}_1},{{\text{q}}_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{{\text{q}}_{{\rm{batchsize}}}}} \right\}$,估计${\text{K}}_{{{\text{y}}^{\left( {{{\text{h}}_i}} \right)}}}^{\left( { - {{\text{h}}_i}} \right)}\left( n \right)$;
(3) 对$k = 0{\rm{ ,1,}} ·\!·\!· {\rm{,}}L - 1$,更新${{\text{υ}}_k}$,${{\text{W}}_k}$:
${{\text{υ}}_k} \leftarrow \beta {{\text{υ}}_k} + \left( {1 - \beta } \right){\rm{E}}\left\{ {\left[ {\sum\nolimits_{{{\text{h}}_i} \in \left\{ {{{\text{q}}_1},{{\text{q}}_2}, ··· ,{{\text{q}}_{{\rm{batchsize}}}}} \right\}} {{\text{K}}_{{{\text{y}}^{\left( {{{\text{h}}_i}} \right)}}}^{\left( { - {{\text{h}}_i}} \right)}\left( n \right) + 2\left( {{\text{y}}\left( n \right) - {\text{x}}\left( n \right)} \right) + {\text{Φ}}\left( n \right)} } \right]{\text{x}}{{\left( {n - k} \right)}^{\rm{T}}}} \right\}$
${{\text{W}}_k} \leftarrow {{\text{W}}_k} - \alpha {{\text{υ}}_k}$;
(4) 更新${\text{y}}\left( n \right)$:${\text{y}}\left( n \right) \leftarrow \sum\limits_{k = {\rm{0}}}^{L - 1} {{{\text{W}}_k}{\text{x}}\left( {n - k} \right)} $;
(5) 判断:收敛或达到最大迭代次数后结束循环。表 2 主通道1接收信号成分
Table 2. Signal component of primary channel 1
信号源 信号成分 参数 直达波 多径1 多径2 多径3 强目标1 弱目标2 主辐射源 时延(μs) 0.1 0.3 1.6 2.1 46.1 59.1 幅度(dB) –0.41 –19.53 –28.29 –35.09 –33.15 –43.10 干扰辐射源1 时延(μs) 0 0.7 1.2 2.4 19.9 幅度(dB) –3.10 –19.27 –20.57 –29.79 –33.98 干扰辐射源2 时延(μs) 0 0.5 1.7 2.6 幅度(dB) –2.55 –18.63 –21.75 –33.31 表 3 主通道2接收信号成分
Table 3. Signal component of primary channel 2
信号源 信号成分 参数 直达波 多径1 多径2 多径3 强目标1 弱目标2 主辐射源 时延(μs) 0.1 0.8 1.6 2.2 46.1 59.1 幅度(dB) –0.16 –20.17 –28.62 –32.52 –30.74 –40.56 干扰辐射源1 时延(μs) 0 0.3 1.5 2.4 幅度(dB) –3.28 –19.99 –23.13 –36.34 干扰辐射源2 时延(μs) 0 0.5 1.8 2.3 幅度(dB) –2.56 –19.58 –25.93 –30.22 表 4 参考通道接收信号成分
Table 4. Signal component of reference channel
信号源 信号成分 参数 直达波 多径1 多径2 多径3 主辐射源 时延(μs) 0 1.1 1.7 2.9 幅度(dB) 0 –22.05 –28.64 –34.42 干扰辐射源1 时延(μs) 0.2 0.7 1.3 2.8 幅度(dB) –10.17 –22.82 –23.99 –33.00 干扰辐射源2 时延(μs) 0.1 0.5 1.5 2.3 幅度(dB) –9.37 –24.40 –26.03 –35.21 -
[1] HOWLAND P. Editorial: Passive radar systems[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(3): 105–106. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20059064 [2] KRYSIK P, SAMCZYNSKI P, MALANOWSKI M, et al. Detection of fast maneuvering air targets using GSM based passive radar[C]. The 2012 13th International Radar Symposium, Warsaw, Poland, 2012: 69–72. doi: 10.1109/IRS.2012.6233291. [3] WANG Haitao, WANG Jun, and LI Hongwei. Target detection using CDMA based passive bistatic radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 23(6): 858–865. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2012.00105 [4] 王本静, 易建新, 万显荣, 等. LTE外辐射源雷达帧间模糊带分析与抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 514–522. doi: 10.12000/JR18025WANG Benjing, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Inter-frame ambiguity analysis and suppression of LTE signal for passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 514–522. doi: 10.12000/JR18025 [5] 万显荣. 基于低频段数字广播电视信号的外辐射源雷达发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027WAN Xianrong. An overview on development of passive radar based on the low frequency band digital broadcasting and TV signals[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 109–123. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20027 [6] 饶云华, 明燕珍, 林静, 等. WiFi外辐射源雷达参考信号重构及其对探测性能影响研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 284–292. doi: 10.12000/JR15108RAO Yunhua, MING Yanzhen, LIN Jing, et al. Reference signal reconstruction and its impact on detection performance of WiFi-based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 284–292. doi: 10.12000/JR15108 [7] OCHIAI H. High-order moments and gaussianity of single-carrier and OFDM signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2015, 63(12): 4964–4976. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2485991 [8] WU Qiang, TESTA M, and LARKIN R. On design of linear RF power amplifier for CDMA signals[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, 1998, 8(4): 283–292. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-047X(199807)8:4<283::AID-MMCE2>3.0.CO;2-H [9] 赵永科, 吕晓德. 一种联合优化的无源雷达实时目标检测算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 666–674. doi: 10.12000/JR14005ZHAO Yongke and LÜ Xiaode. A joint-optimized real-time target detection algorithm for passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 666–674. doi: 10.12000/JR14005 [10] FU Yan, WAN Xianrong, ZHANG Xun, et al. Parallel processing algorithm for multipath clutter cancellation in passive radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 121–129. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0106 [11] YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, LI Deshi, et al. Robust clutter rejection in passive radar via generalized subband cancellation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1931–1946. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805228 [12] LU Min, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Co-channel interference in DTMB-based passive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018: 1. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2882959 [13] LI Jichuan, ZHAO Yaodong, ZHAO Yongke, et al. Direct path wave purification for passive radar with normalized least mean square algorithm[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing, Kunming, China, 2013: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/icspcc.2013.6663987. [14] BERTHILLOT C, SANTORI A, RABASTE O, et al. BEM reference signal estimation for an airborne passive radar antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2833–2845. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2716458 [15] BOURNAKA G, BARUZZI A, HECKENBACH J, et al. Experimental validation of beamforming techniques for localization of moving target in passive radar[C]. The 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1710–1713. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7131274. [16] WANG Feng, WEI Shuang, and JIANG Defu. Co-frequency interference suppression for aerostat passive bistatic radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2018, 27(3): 658–666. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.08.017 [17] KOHNO K, KAWAMOTO M, and INOUYE Y. A matrix pseudoinversion lemma and its application to block-based adaptive blind deconvolution for MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2010, 57(7): 1449–1462. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2010.2050222 [18] HAYKIN S S. Adaptive Filter Theory[M]. India: Pearson Education India, 2005: 1–15. [19] COMON P. Independent component analysis, a new concept?[J]. Signal Processing, 1994, 36(3): 287–314. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(94)90029-9 [20] MATSUOKA K, OHBA Y, TOYOTA Y, et al. Blind separation for convolutive mixture of many voices[C]. The International Workshop on Acoustic Echo and Noise Control, Kyoto, Japan, 2003: 279–282. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: