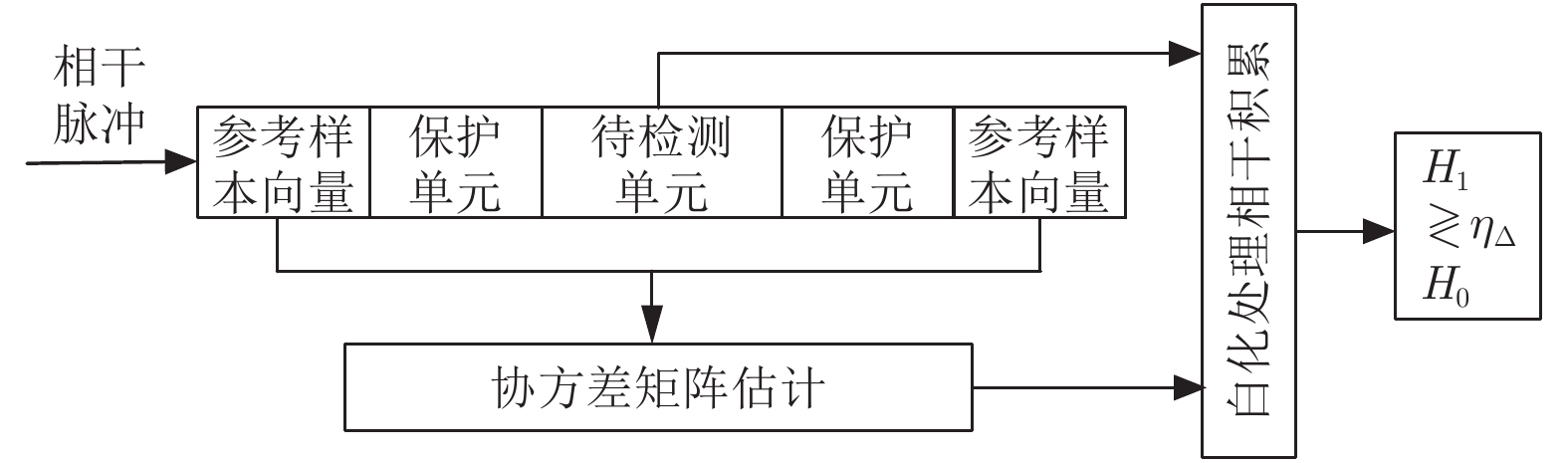
-
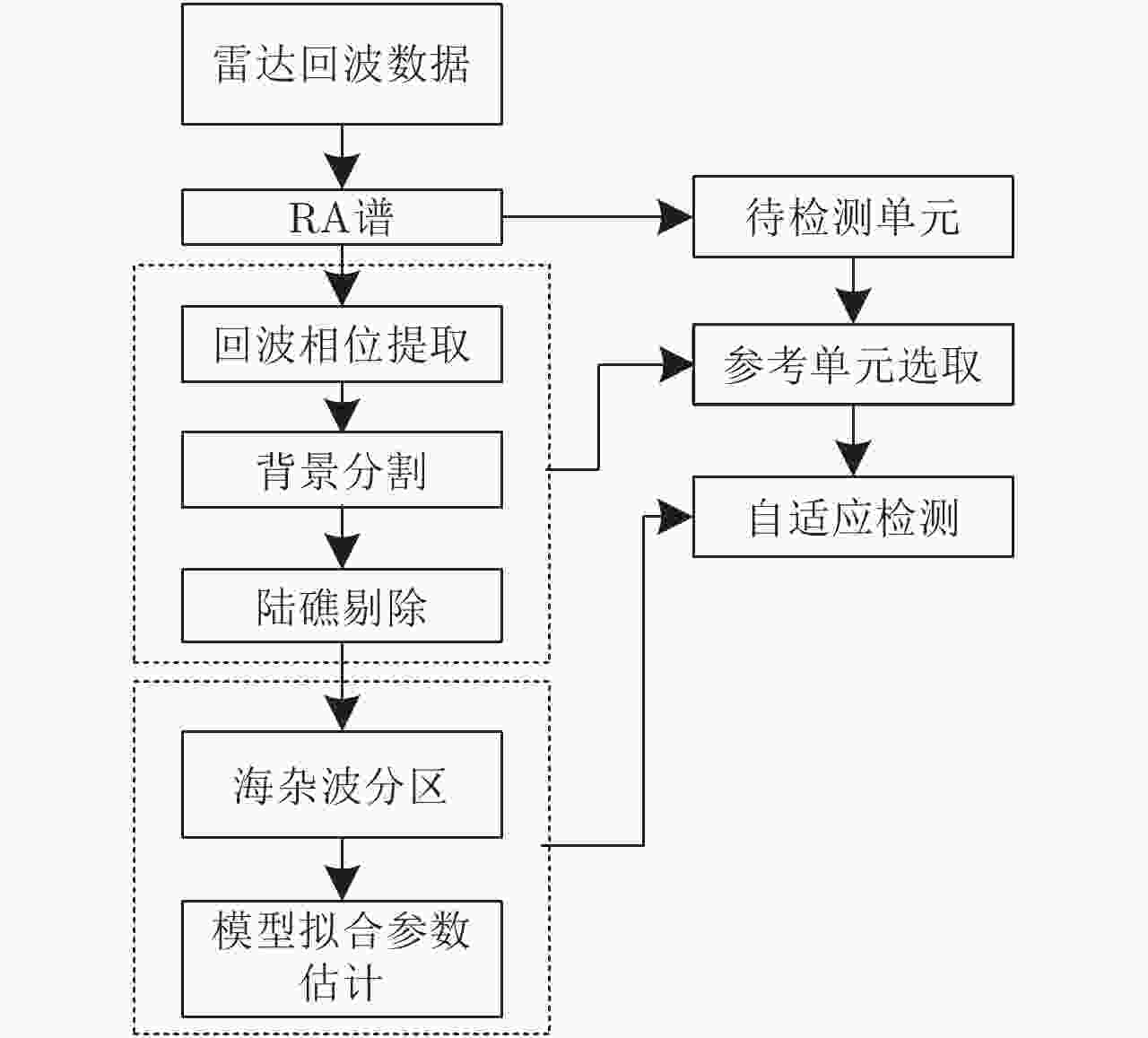
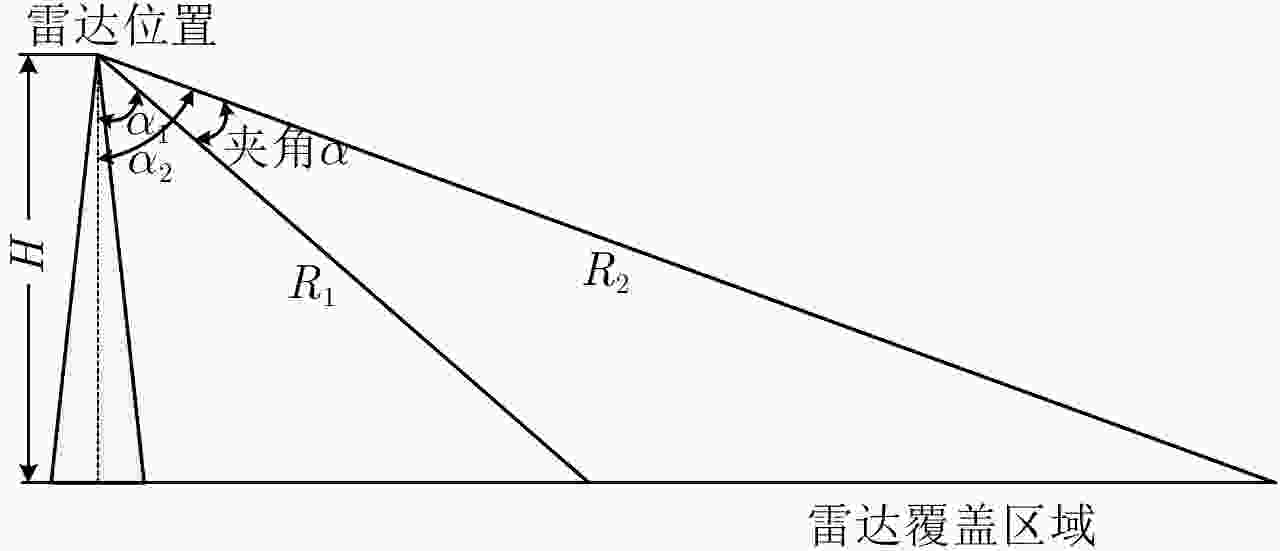
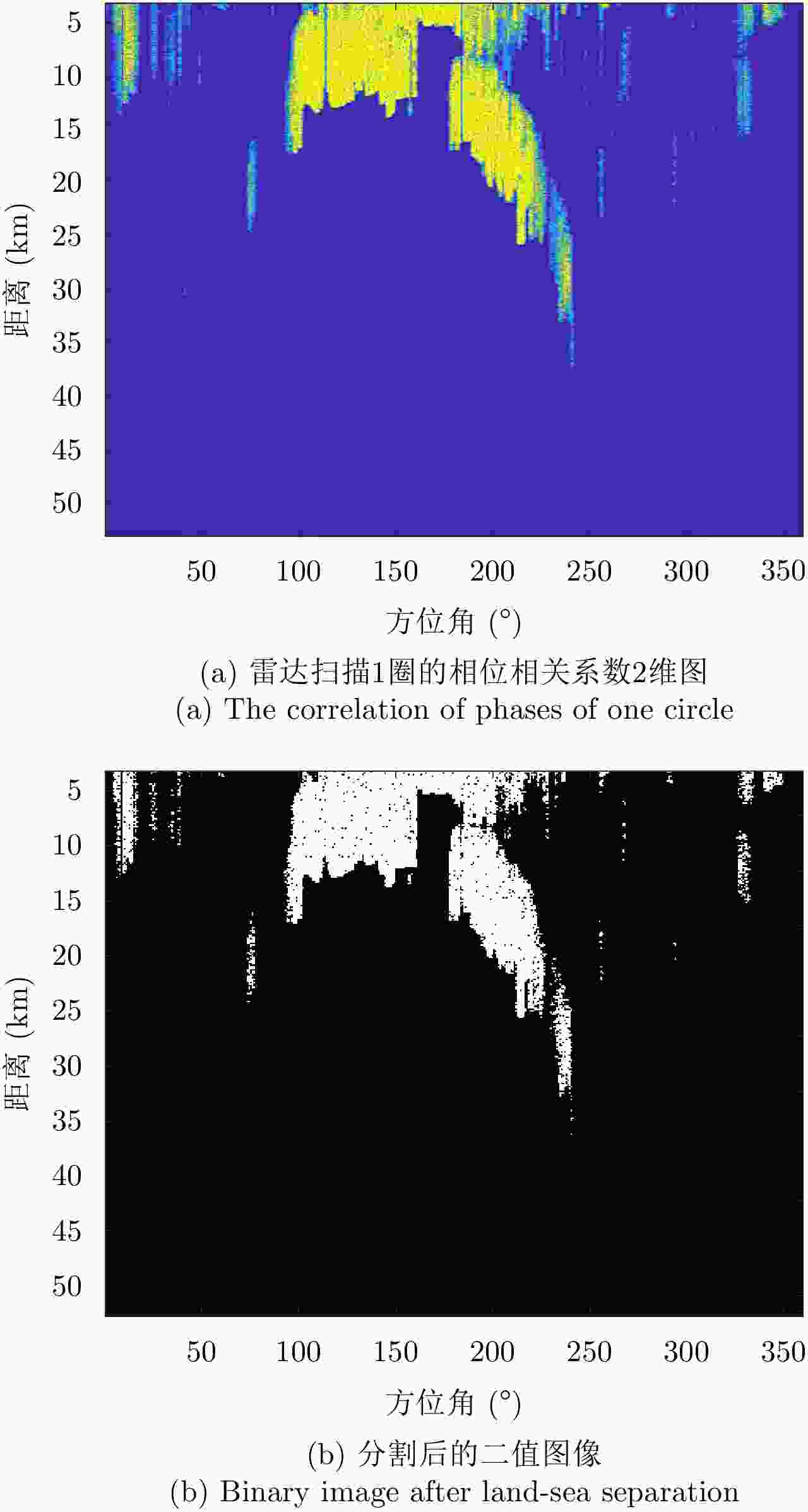
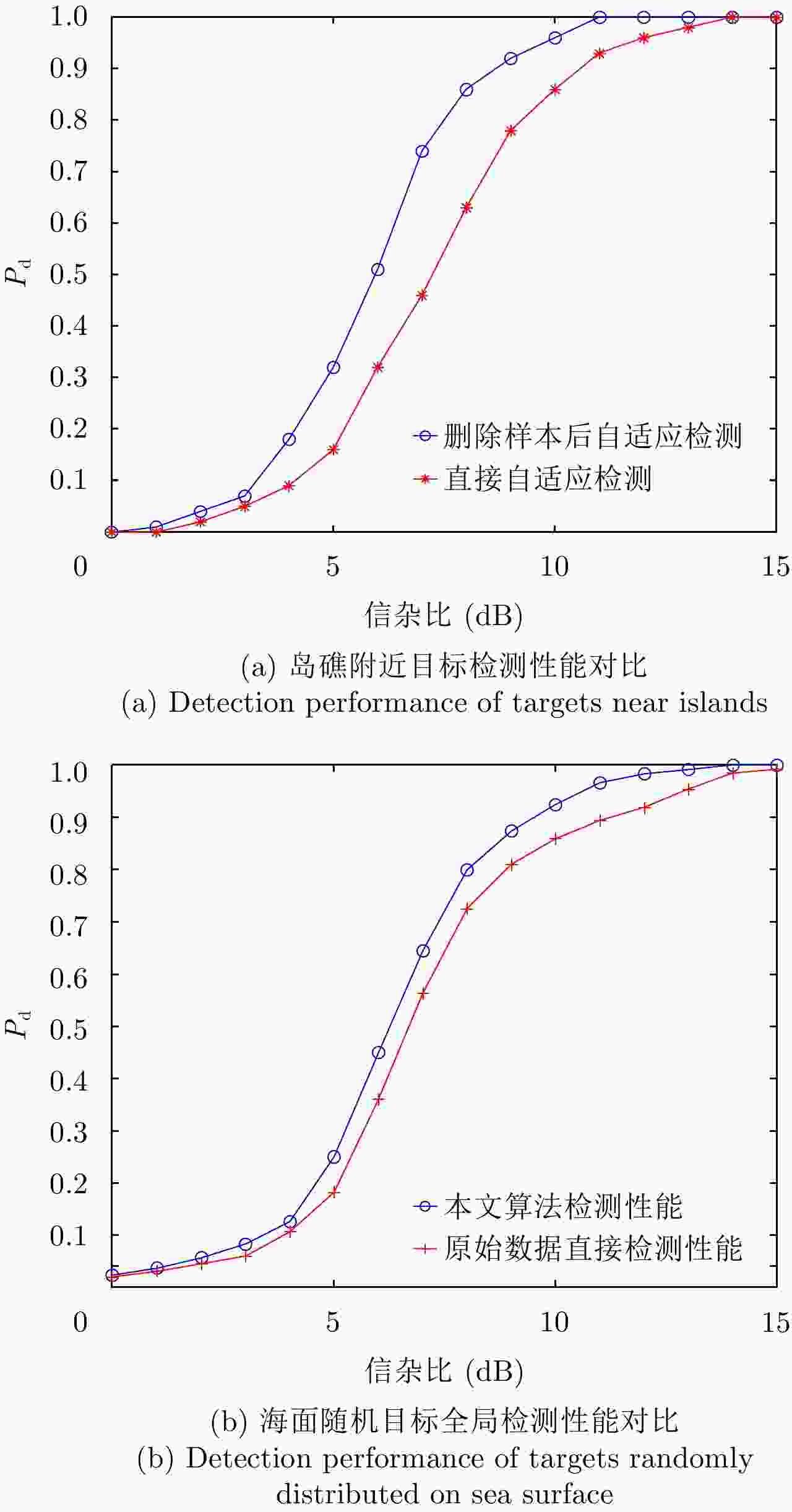
摘要: 自适应检测技术可有效提升岸对海警戒雷达海面目标探测性能,但海岛和陆地会导致成片或离散强杂波点,污染协方差矩阵估计的样本,海杂波的复杂性使得整片海杂波难以采用单一模型描述。为解决海面目标自适应检测时面临的非均匀样本参与协方差矩阵估计时杂波抑制性能严重下降问题和海杂波建模准确性不高的问题,该文提出一种面向海面目标检测的陆海分离和海面分区算法。首先,根据陆地回波序列的相位之间具有强相关性,而海洋回波序列为随机值这一特性,区分陆地杂波和海杂波;然后,根据擦地角对海杂波分区,拟合出每个分区的最优分布后选择合适的检测器进行自适应检测;最后,基于某S波段雷达实测数据验证该算法,检测结果与性能分析表明该算法相对传统算法可有效提高海面目标的检测率。Abstract: Adaptive detection can effectively improve the detection performance of marine surveillance radars; however, the islands or lands introduce discrete or flaky strong clutter, which may result in wrong covariance matrix estimation. Meanwhile, the complexity of the sea clutter complicates the use of a single model to describe the whole sea clutter. To solve the problem of serious degradation of clutter suppression performance when non-uniform samples participate in covariance matrix estimation and inaccuracy of sea clutter modeling, a land-sea separation and sea surface zoning algorithms are proposed for sea surface target detection. First, the land clutter and sea clutter are distinguished according to the characteristics that the phases of land echo sequences are strongly correlated while the phases of ocean echo sequences are random. Second, the sea surface is zoned according to the rubbing angle; further, the optimal distribution suited for each sea clutter zone is fitted and the appropriate adaptive detection method is selected according to the clutter distribution. Finally, the proposed algorithm is validated based on the measured data of an S-band radar. The results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the detection performance of sea surface targets compared with the traditional detection algorithm.
-
Key words:
- Marine Surveillance radar /
- Land-sea separation /
- Sea surface zoning /
- Adaptive detection
-
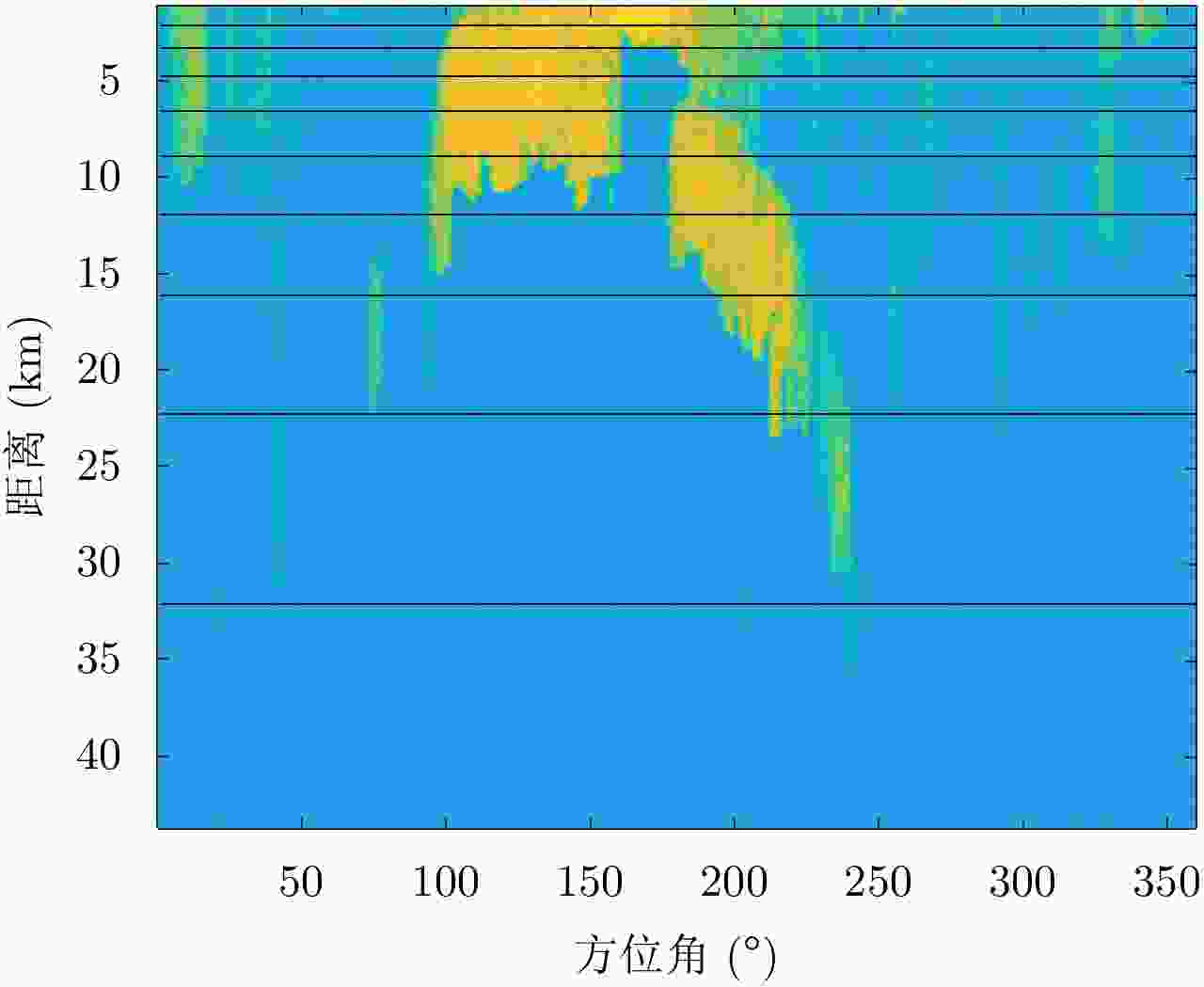
表 1 分块后拟合结果
Table 1. Fitting result of uniformly partitioned data
所假设的分布 Rayleigh Lognormal Weibull K 拟合后服从分布的分块数 3 1 6 10 表 2 杂波分区后的拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting results of partitioned data according to the rubbing angle
分块 最优分布 分块 最优分布 1 Weibull 2 K分布 3 Weibull 4 Weibull 5 Weibull 6 Weibull 7 Weibull 8 K分布 9 K分布 10 K分布 -
[1] 何友, 黄勇, 关键, 等. 海杂波中的雷达目标检测技术综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2014.12.001HE You, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. An overview on radar target detection in sea clutter[J]. Modern Radar, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2014.12.001 [2] 刘思彤, 程红, 孙文邦, 等. 面向海上目标的海陆分离方法研究[J]. 电子设计工程, 2014, 22(15): 96–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2014.15.031LIU Sitong, CHENG Hong, SUN Wenbang, et al. Studies of sea-land segment methods oriented to targets on the sea[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2014, 22(15): 96–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2014.15.031 [3] KALKAN K, BAYRAM B, MAKTAV D, et al. Comparison of support vector machine and object based classification methods for coastline detection[J]. International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, XL-7/W2: 125–172. [4] NIEDERMEIER A, ROMANEESSEN E, and LEHNER S. Detection of coastlines in SAR images using wavelet methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2270–2281. doi: 10.1109/36.868884 [5] LIU Chun, YANG Jian, YIN Junjun, et al. Coastline detection in SAR images using a hierarchical level set segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(11): 4908–4920. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2613279 [6] LEE J S, JURKEVICH L, DEWAELE P, et al. Speckle filtering of synthetic aperture radar images: A review[J]. Remote Sensing Reviews, 1994, 8(4): 313–340. doi: 10.1080/02757259409532206 [7] BO G, DELLEPIANE S, DE LAURENTIIS R. Semiautomatic coastline detection in remotely sensed images[C]. Proceedings of IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, USA, 2000. [8] 赵巨波, 符燕, 耿文东. 海杂波统计特性分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2005, 27(11): 4–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2005.11.002ZHAO Jubo, FU Yan, and GENG Wendong. Analysis of sea clutter statistical characteristics[J]. Modern Radar, 2005, 27(11): 4–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2005.11.002 [9] 丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069DING Hao, DONG Yunlong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069 [10] KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745 [11] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446 [12] CONTE E, LOPS M, and RICCI G. Asymptotically optimum radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(2): 617–625. doi: 10.1109/7.381910 [13] CONTE E, LOPS M, and RICCI G. Adaptive detection schemes in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(4): 1058–1069. doi: 10.1109/7.722671 [14] CONTE E, DE MAIO A, and RICCI G. Covariance matrix estimation for adaptive CFAR detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(2): 415–426. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1008976 [15] OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
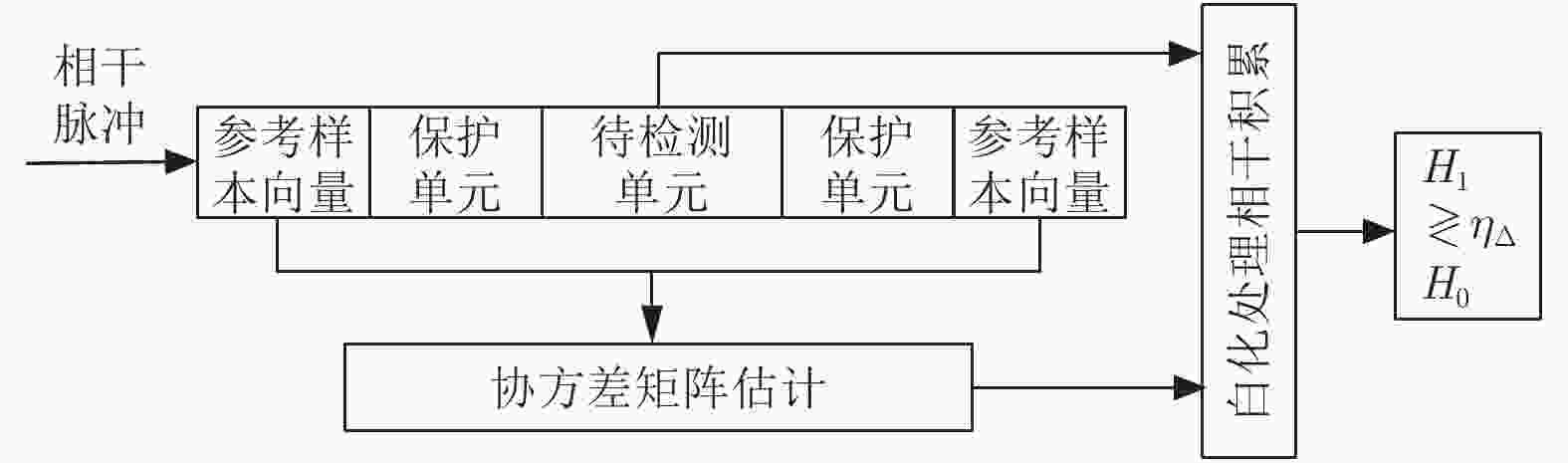
 下载:
下载: