A Weak Target Detection Method in Sea Clutter Based on Joint Space-time-frequency Decomposition
-
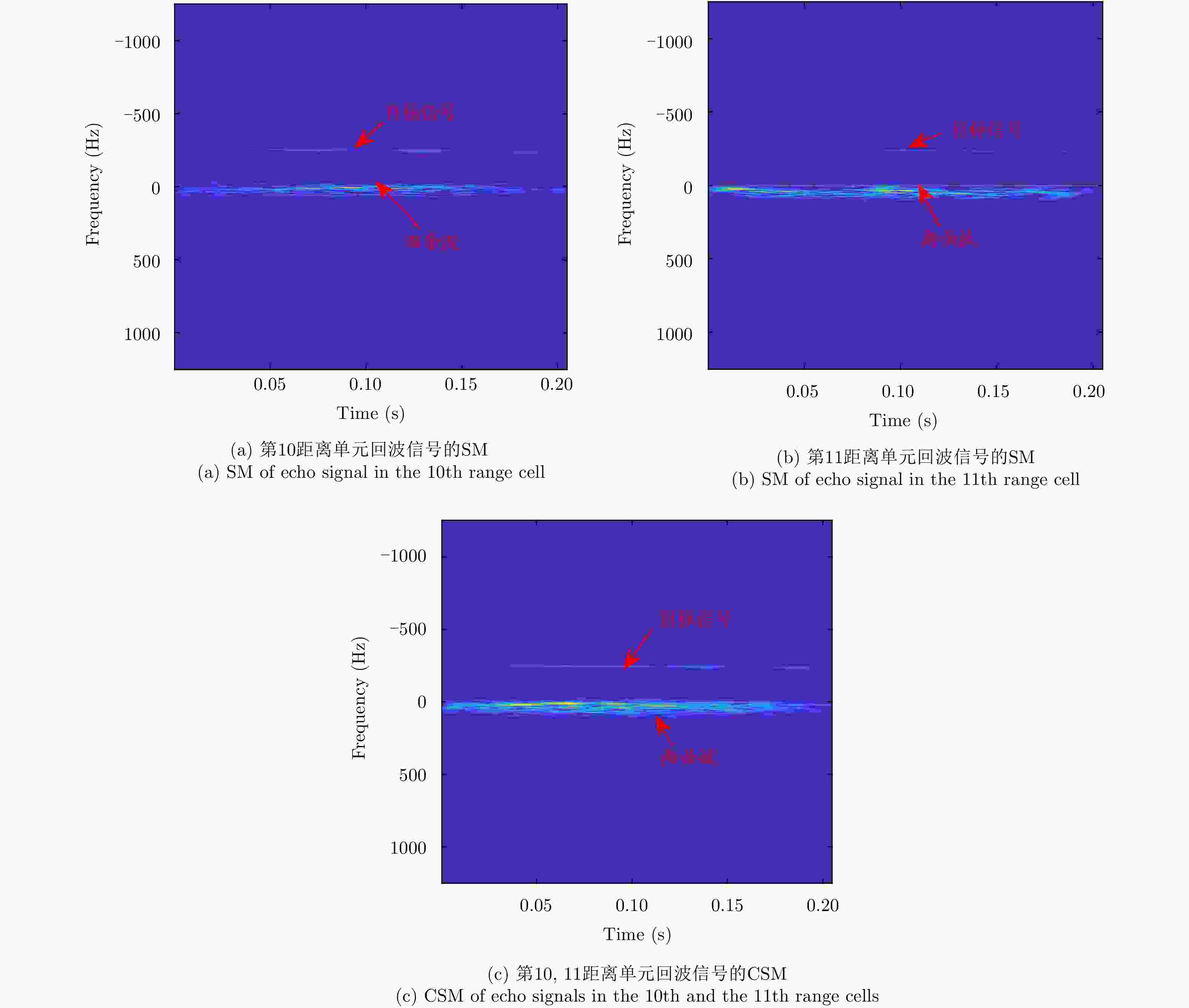
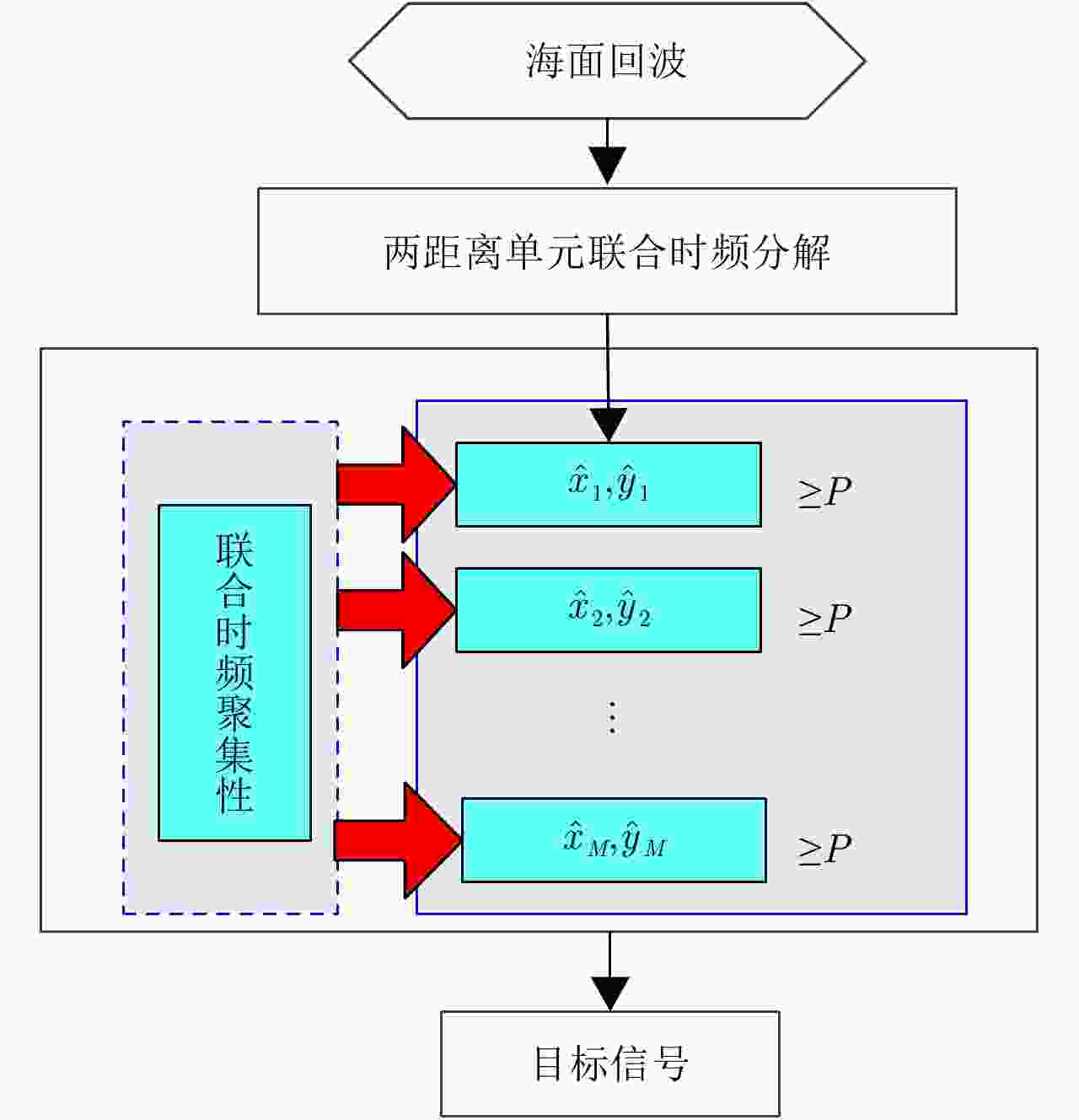
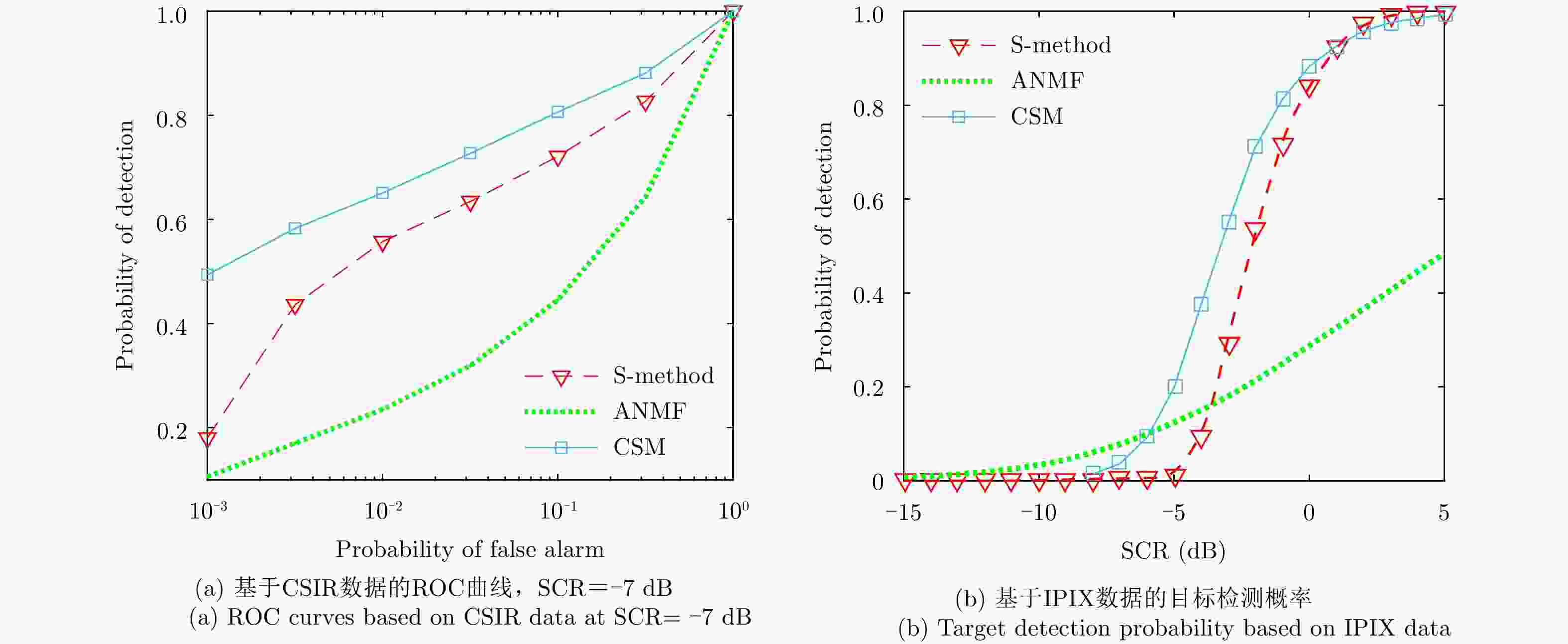
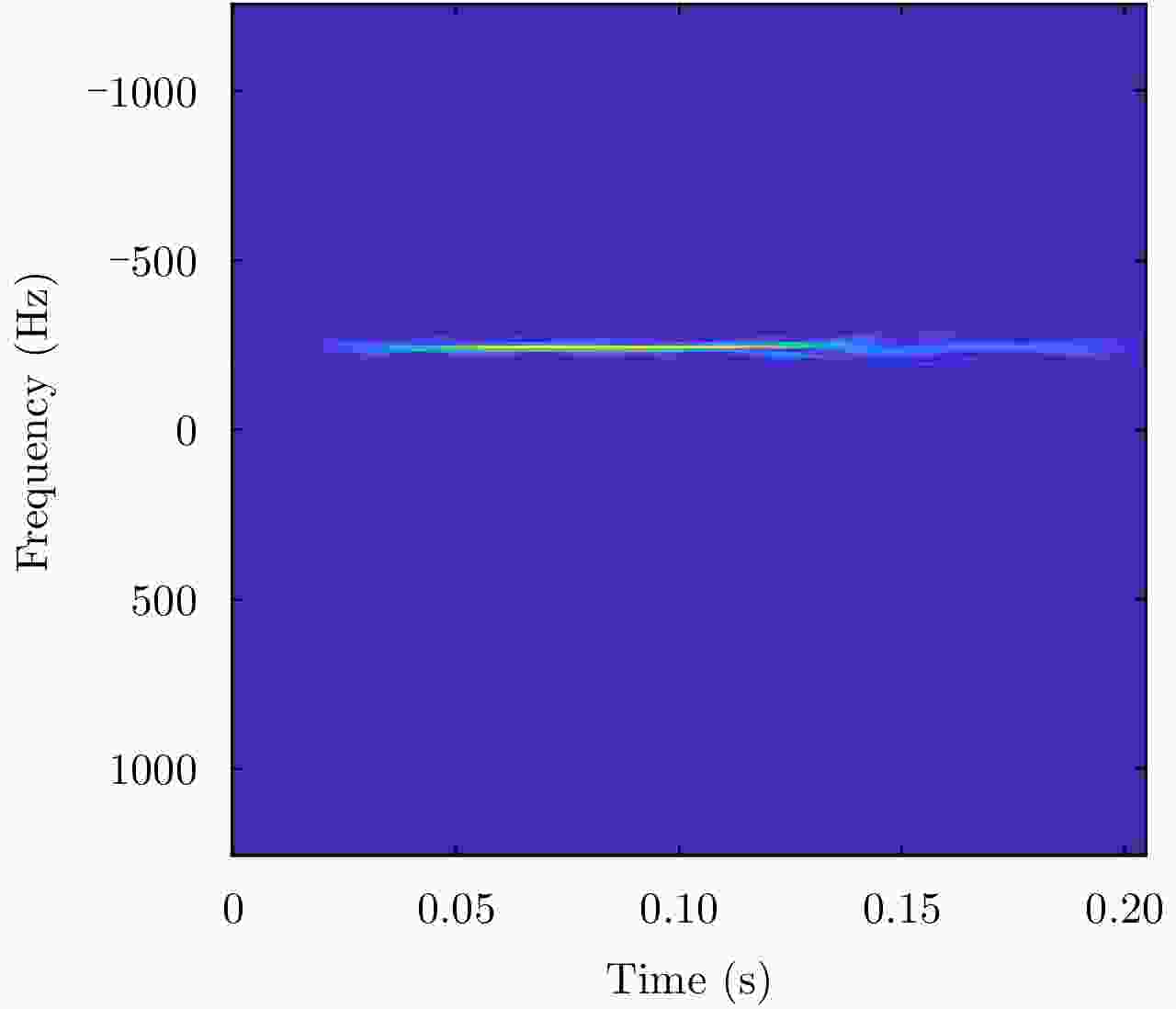
摘要: 海面目标不仅影响其位置处波浪运动,还会影响其周围的水域,其雷达回波信号分布于多个相邻的距离单元,所以目标回波信号表现出明显的空域相关性。该文根据海面目标信号的空间相关性提出了一种基于空域联合时频分解的海面微弱目标检测方法。该文提出的一种两信号互S-方法将相邻两个距离单元的回波信号变换到时频域,再利用互维格纳-威尔逆变换实现两距离单元信号的联合时频分解,最后根据分解分量的联合时频聚集性实现目标检测。实测X波段雷达海面回波的处理结果表明该文方法能够较精确地从海面回波中检测出微弱目标,并且能够显示目标的瞬时运动特性。Abstract: The target on the sea destroys the movement of the sea and affects an area around the target. Therefore, radar echoes from a target on the sea can be found in several successive range cells. Analysis of the echoes shows that the echoes of the target have a long range correlation in space. In this paper, we propose a target detection method by using the joint space-time-frequency decomposition, according to the diffidence between the target echoes and the sea clutter. Therein, the cross S-Method is proposed, which can be considered as the summation of the cross Wigner-Ville representations of the signal components and the sea clutter components, respectively. By using the inverse transform of the cross Wigner-Ville representation, we decompose the echoes from successive range cells. Then a signature, revealing the cross time-frequency concentration, is used to find the signal component in the decomposed signal components. The proposed method is evaluated by the X-band sea echoes with a simulated target or a real target. Results demonstrate that the proposed method not only detects the weak target in high accuracy, but also provides its instantaneous state.
-
Key words:
- Time-frequency distribution /
- S-Method /
- Signal decomposition /
- Sea clutter /
- Target detection
-
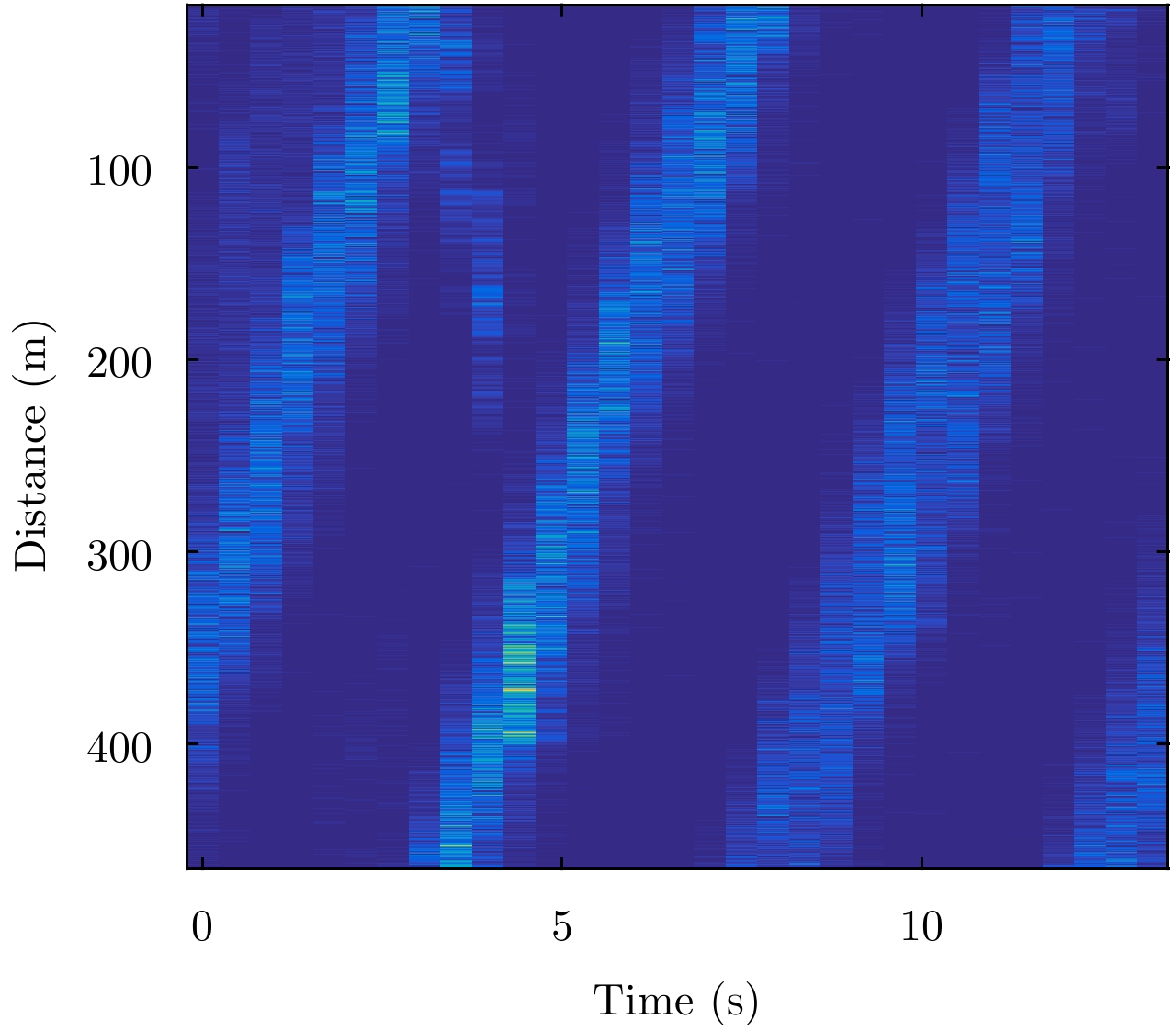
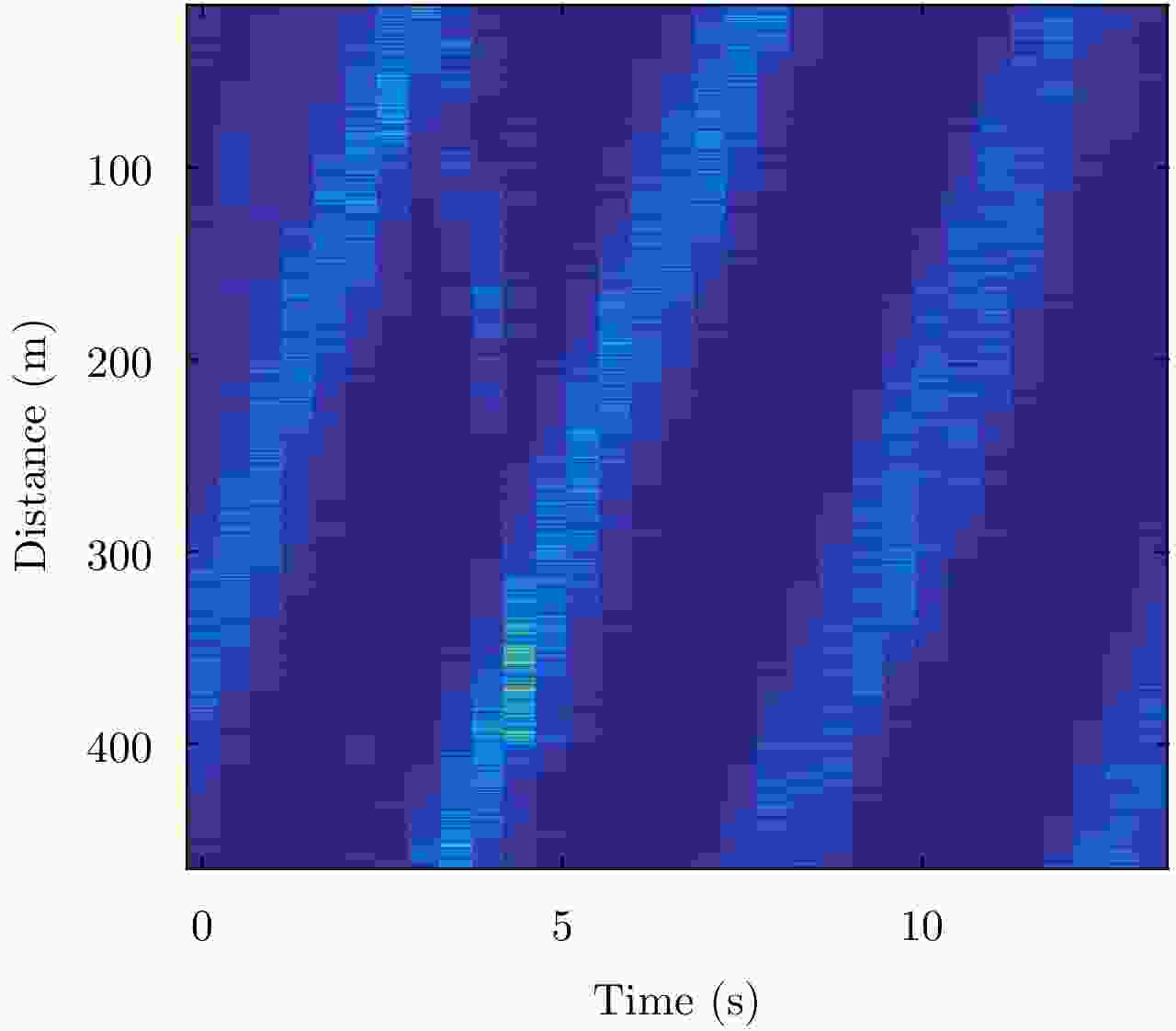
表 1 实测海面回波的参数
Table 1. Parameters of measured sea surface echo
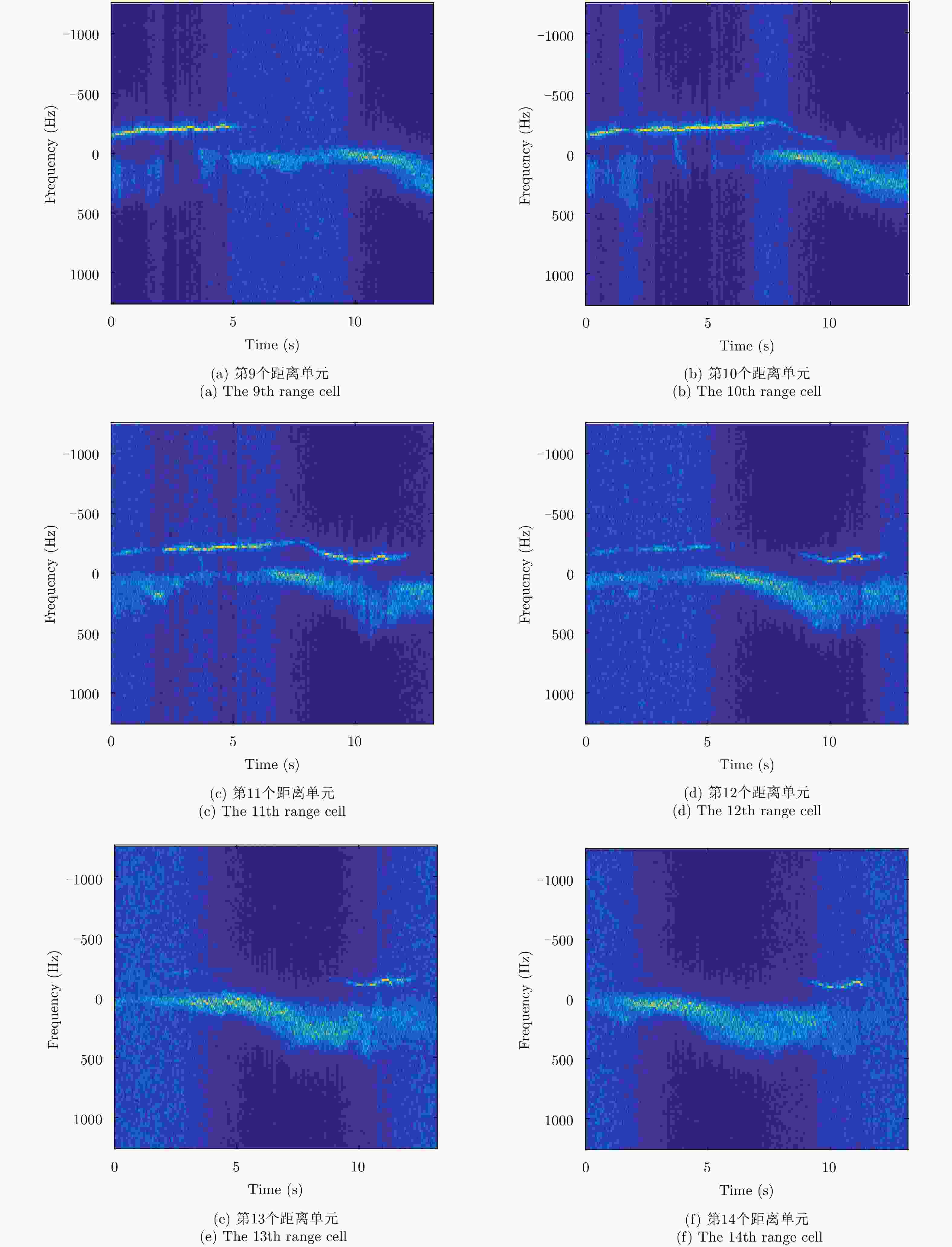
参数 值 雷达波段 X 雷达工作带宽(MHz) 10 采样距离(m) 3000.3~3465.3 距离单元数目 31 每个距离单元的采样点 33001 有目标的距离单元 11 受目标影响的距离单元 9~14 距离分辨率 15 m, 15 m采样 雷达高度(m) 56 脉冲重复频率PRF(Hz) 2500 方位角(°N) 165.22 俯仰角(°) 1.187 风向(°N) 191.26 风速(m/s) 9 波浪方向(°N) 160 主要波浪高度(m) 2.88 -
[1] VALENZUELA G R. Theories for the interaction of electromagnetic and oceanic waves—a review[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1978, 13(1/4): 61–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00913863 [2] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友. 微多普勒理论在海面目标检测中的应用及展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, and HE You. Applications and prospect of micro-motion theory in the detection of sea surface target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102 [3] 左磊, 李明, 张晓伟, 等. 基于改进Hough变换的海面微弱目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 923–928. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00373ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaowei, et al. Small-target detection in sea clutter based on improved Hough transform[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 923–928. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00373 [4] 陈小龙, 刘宁波, 宋杰, 等. 海杂波FRFT域分形特征判别及动目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Ningbo, SONG Jie, et al. Fractal feature discriminant of sea clutter in FRFT domain and moving target detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486 [5] 武鹏, 王俊, 王文光. 基于极化特征分解的海上小目标检测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(4): 816–822. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00678WU Peng, WANG Jun, and WANG Wenguang. Small target detection in sea clutter based on polarization characteristics decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 816–822. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00678 [6] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077 [7] 陈建军, 黄孟俊, 邱伟, 等. 海杂波下的双门限恒虚警目标检测新方法[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(9): 2135–2141.CHEN Jianjun, HUANG Mengjun, QIU Wei, et al. A novel method for CFAR detector with Bi-thresholds in sea clutter[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(9): 2135–2141. [8] ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaowei, et al. An efficient method for detecting slow-moving weak targets in sea clutter based on time-frequency iteration decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3659–3672. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2224665 [9] PANAGOPOULOS S and SORAGHAN J J. Small-target detection in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(7): 1355–1361. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.827259 [10] THAYAPARAN T and KENNEDY S. Detection of a manoeuvring air target in sea-clutter using joint time-frequency analysis techniques[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2004, 151(1): 19–30. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20040158 [11] YASOTHARAN A and THAYAPARAN T. Time-frequency method for detecting an accelerating target in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(4): 1289–1310. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.314573 [12] 关键, 张建. 基于固有模态能量熵的微弱目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(10): 2494–2499. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00147GUAN Jian and ZHANG Jian. Weak target detection based on intrinsic mode energy entropy[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(10): 2494–2499. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00147 [13] ZHANG Y, QIAN S, and THAYAPARAN T. Detection of a manoeuvring air target in strong sea clutter via joint time-frequency representation[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 216–222. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070047 [14] STANKOVIĆ L, THAYAPARAN T, and DAKOVIC M. Signal decomposition by using the S-method with application to the analysis of HF radar signals in sea-clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4332–4342. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.880248 [15] ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaomei, et al. CFAR detection of range-spread targets based on the time-frequency decomposition feature of two adjacent returned signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(24): 6307–6319. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2282274 [16] 时艳玲, 林毓峰, 梁丹丹. 非平稳海杂波背景下子带分段ANMF检测器[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(4): 782–789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.11SHI Yanling, LIN Yufeng, and LIANG Dandan. Subband segmented ANMF detector in non-stationary sea clutter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 782–789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.11 [17] BAKKER R and CURRIE B. The IPIX radar database. Cognitive systems Laboratory-McMaster University[EB/OL]. http://soma.mcmaster.ca//ipix.php, 2015. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: