Channel Phase Mismatch Calibration for Multichannel in Azimuth SAR Imaging Aided by Digital Elevation Model
-
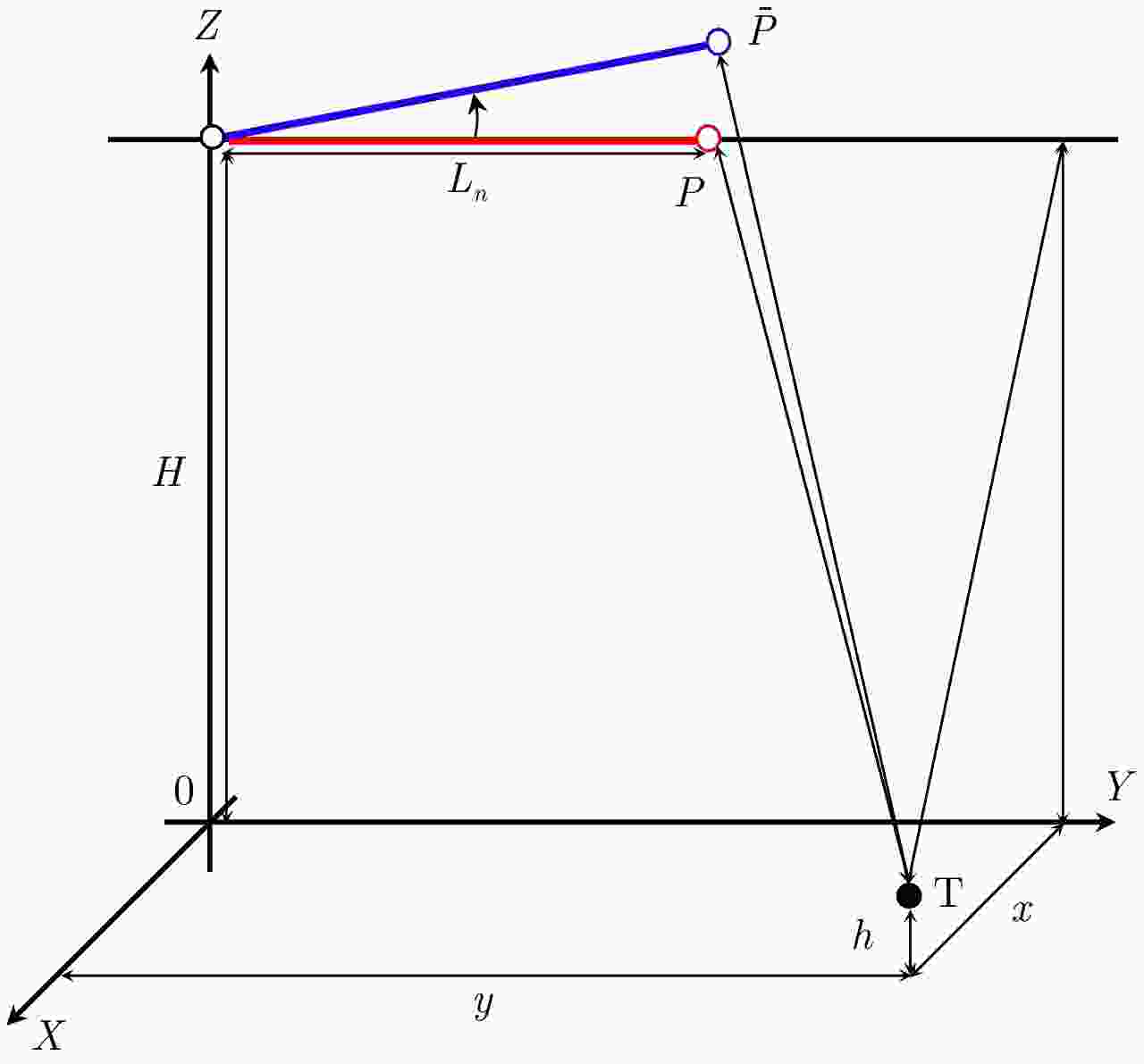
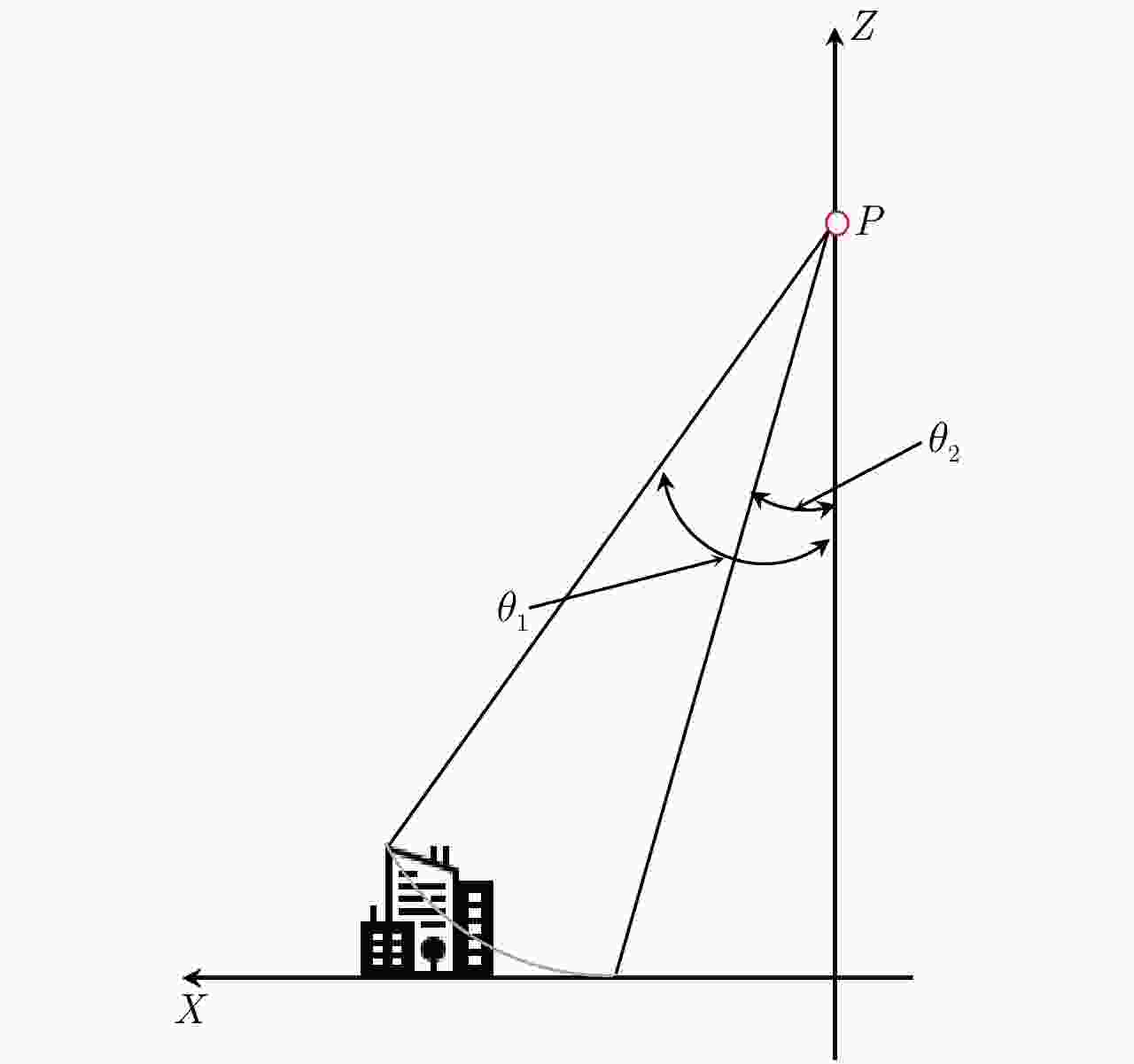
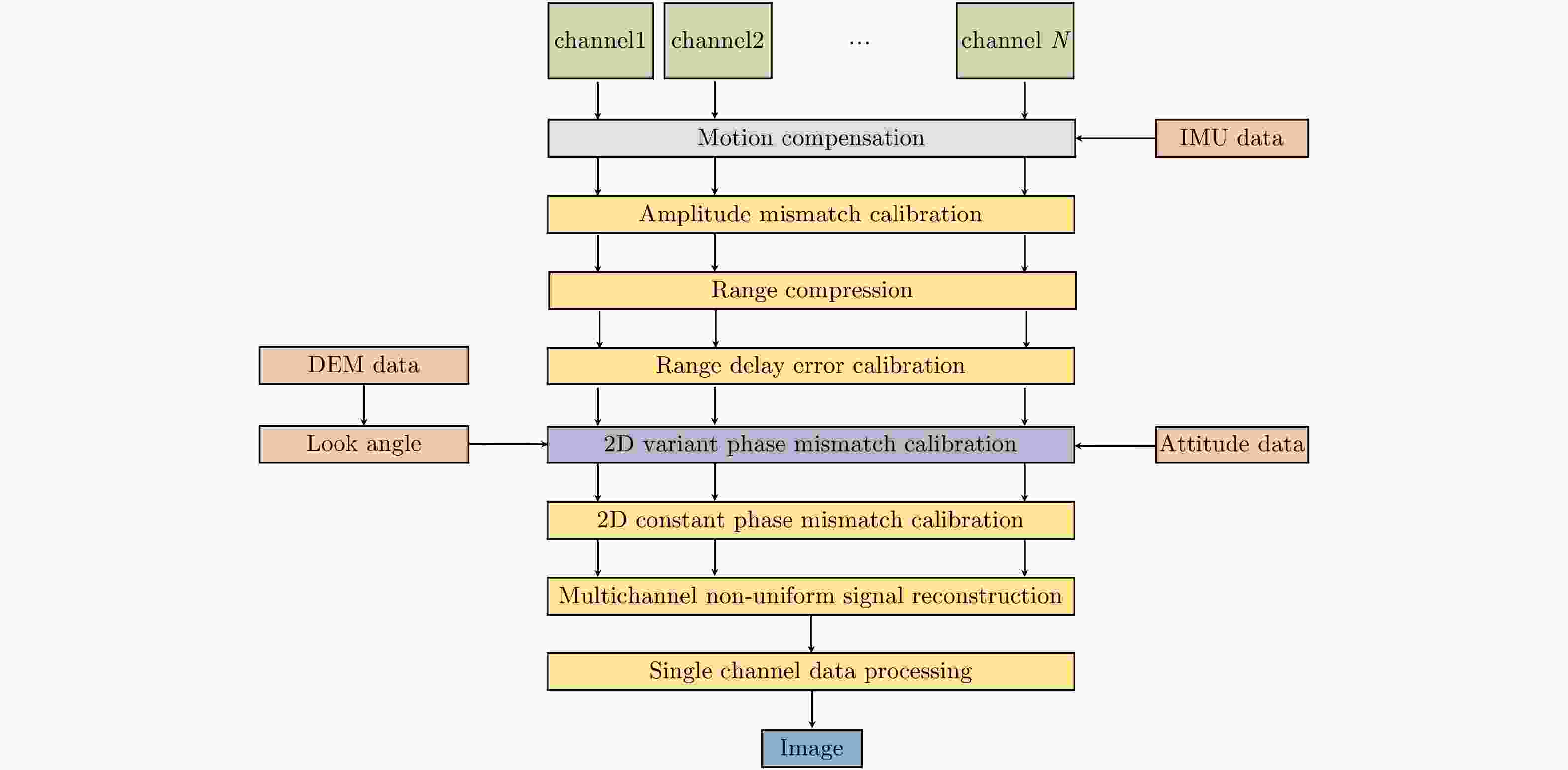
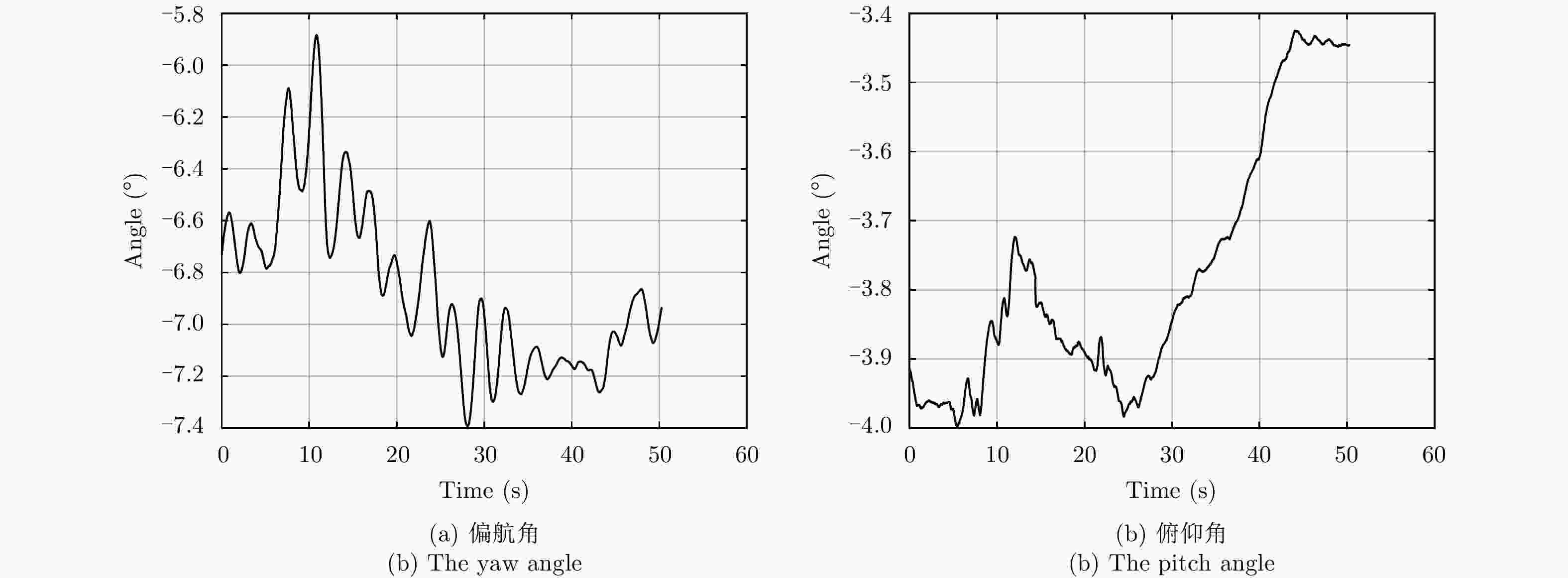
摘要: 在方位多通道合成孔径雷达(SAR)系统中,进行非均匀采样重建之前,由于通道特性不一致导致的幅度相位差异必须进行校正,以避免图像中出现“鬼影”虚假目标,影响图像判读。方位多通道SAR工作过程中,平台偏航和俯仰导致的通道相位失配具有方位时变和距离空变特点。目前基于平台姿态信息的通道相位失配校正方法均未考虑地形高程起伏带来的影响。该文提出一种新的方位多通道SAR相位失配校正方法,基于辅助数字高程模型(DEM)信息和平台姿态信息,获得更加精确的场景下视角,在地形起伏较大的场景显著提高了通道间相位失配估计精度。针对提出的算法,开展仿真实验,针对虚假目标抑制效果开展定量评估。同时选取场景高程起伏较大场景开展了机载飞行试验数据处理,并对实验结果进行分析,验证算法的有效性。Abstract: In multichannel Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data processing, the phase and amplitude characteristics of all channels should be well calibrated before multichannel data reconstruction; otherwise, the imaging result will be degraded and suffer from ghost targets. The yaw and pitch of the SAR platform, which change in azimuth and range, respectively, will cause phase mismatch among different channels. The currently developed attitude-aided phase mismatch calibration method does not consider the topographic relief. On the basis of the external Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and attitude information, a new phase mismatch calibration method is proposed in this study. The proposed method performs better than other methods in mountainous areas. A simulation experiment and the corresponding quantitative assessment are conducted. Then, the newly proposed method is applied to airborne multichannel SAR experimental data for further verification.
-
表 1 仿真机载实验参数
Table 1. System parameters of the simulated airborne experiment
系统参数 数值 通道数目 4 飞行高度(m) 3000 平台速度(m/s) 120 载频(GHz) 5.4 发射信号带宽(MHz) 210 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 150 多普勒带宽(Hz) 384 表 2 仿真实验定量评估结果(dB)
Table 2. Quantitative assessment result of the simulation (dB)
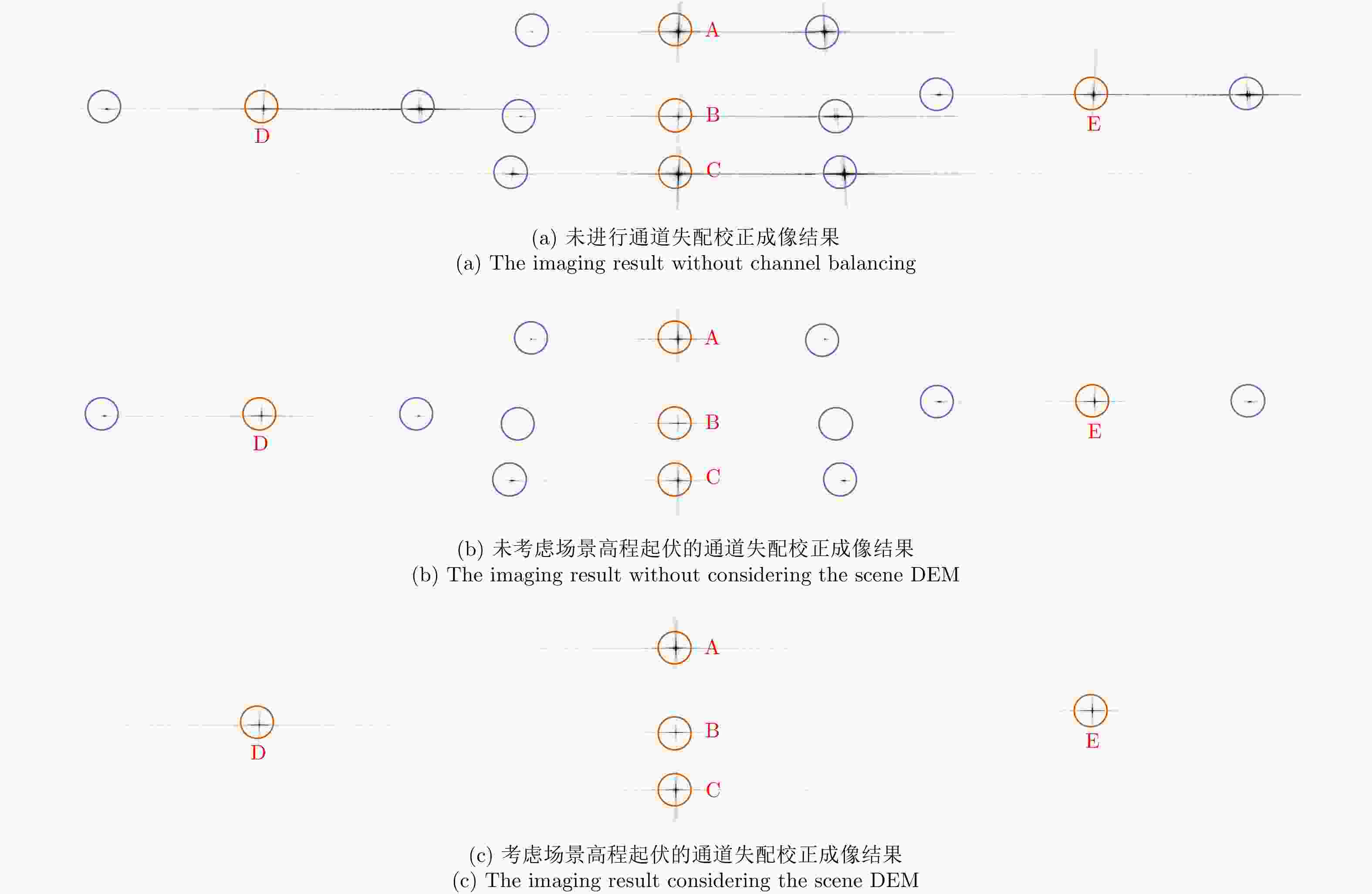
目标 未校正 未考虑高程起伏 考虑高程起伏 A –5 –34 –53 B –7 –50 –50 C –5 –28 –53 D –6 –37 –51 E –5 –27 –52 表 3 C波段方位向4通道机载SAR实验参数
Table 3. Experimental parameters of the C-band azimuth four channel airborne SAR system
系统参数 数值 通道数目 4 平台高度(m) 3000 平台速度(m/s) 129.64 载频(GHz) 5.4 发射信号带宽(MHz) 210 方位向天线尺寸(m) 0.624 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 137.19 -
[1] GEBERT N, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. High resolution wide swath SAR imaging with digital beam-forming-performance analysis, optimization, system design[C]. Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Dresden, Germany, 2006: 341–344. [2] ZHANG Lei, XING Mengdao, QIU Chengwei, et al. Adaptive two-step calibration for high resolution and wide-swath SAR imaging[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(4): 548–559. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2008.0158 [3] SUN Jili, YU Weidong, and DENG Yunkai. The SAR payload design and performance for the GF-3 mission[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10): E2419. doi: 10.3390/s17102419 [4] KIM J H, YOUNIS M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. First spaceborne demonstration of digital beamforming for azimuth ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 579–590. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201947 [5] WILLIAMS D, LEDANTEC P, CHABOT M, et al. RADARSAT-2 image quality and calibration update[C]. Proceedings of 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014: 1–4. [6] SHIMADA M. ALOS-2 Science program[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 2400–2403. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2013.6723303. [7] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 260–264. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.832700 [8] ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Multichannel HRWS SAR imaging based on range-variant channel calibration and multi-Doppler-direction restriction ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4306–4327. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281329 [9] LI Jianbing, LI Xiaoping, LIN Mingfu, et al. Maximum-likelihood-based Doppler centroid estimation algorithm for MC-HRWS SAR system[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(22): 1630–1631. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.2723 [10] GUO Xiaojiang, GAO Yesheng, WANG Kaizhi, et al. Improved channel error calibration algorithm for azimuth multichannel SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(7): 1022–1026. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2561961 [11] FENG Jin, GAO Canguan, ZHANG Yi, et al. Phase mismatch calibration of the multichannel SAR based on azimuth cross correlation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 903–907. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2227107 [12] 刘艳阳, 李真芳, 杨桃丽, 等. 一种单星方位多通道高分辨率宽测绘带SAR系统通道相位偏差时域估计新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(12): 2913–2919. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00562LIU Yanyang, LI Zhenfang, YANG Taoli, et al. A novel channel phase bias estimation method for spaceborne along-track multi-channel HRWS SAR in time-domain[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(12): 2913–2919. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00562 [13] 张磊, 全英汇, 邢孟道, 等. 一种子空间投影的高分辨宽测绘带SAR成像通道均衡方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(1): 1–6. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01821ZHANG Lei, QUAN Yinghui, XING Mengdao, et al. An SSP based channel calibration for high-resolution and wide-swath SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(1): 1–6. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01821 [14] LIU Yanyang, LI Zhenfang, WANG Zhibin, et al. On the baseband Doppler centroid estimation for multichannel HRWS SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2050–2054. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2318511 [15] ZINK M, BACHMANN M, BRAUTIGAM B, et al. TanDEM-X: The new global DEM takes shape[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2014, 2(2): 8–23. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2014.2318895 [16] 范怀涛, 张志敏, 李宁. 基于特征分解的方位向多通道SAR相位失配校正方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 346–354. doi: 10.12000/JR17012FAN Huaitao, ZHANG Zhimin, and LI Ning. Channel phase mismatch calibration for multichannel in azimuth SAR imaging based on Eigen-structure method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 346–354. doi: 10.12000/JR17012 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: