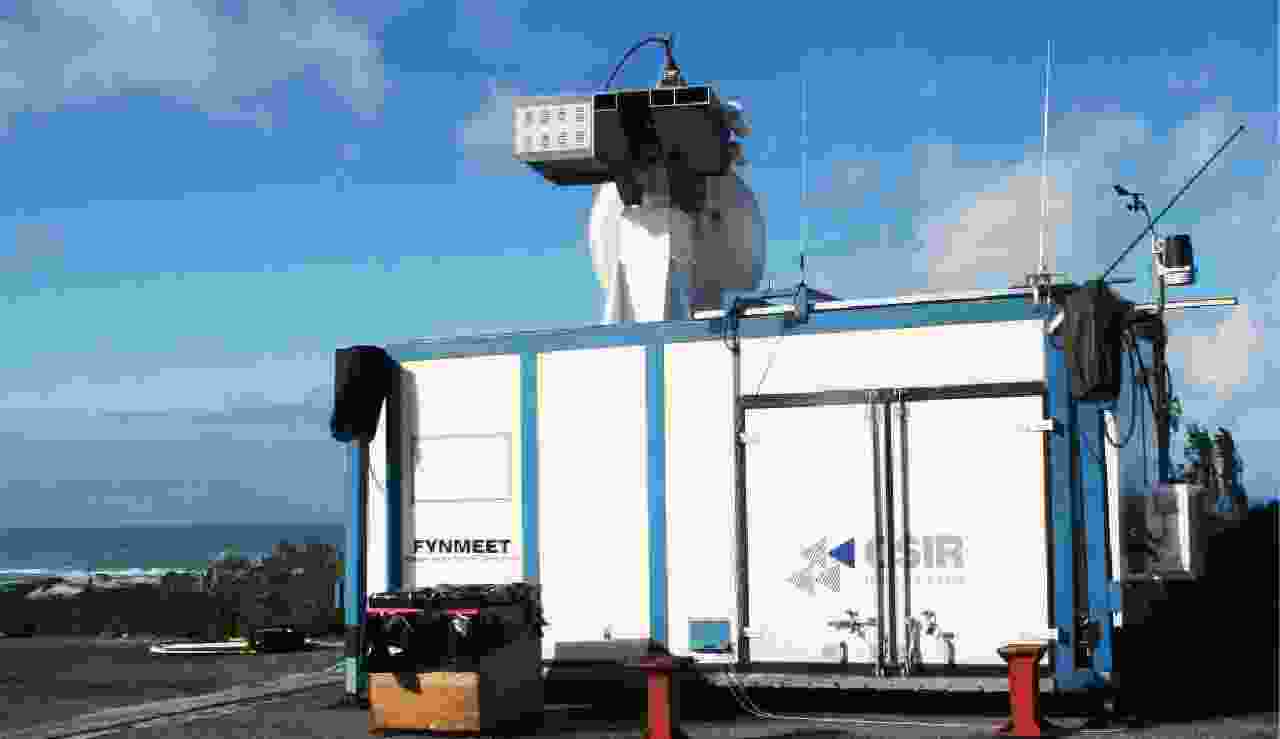
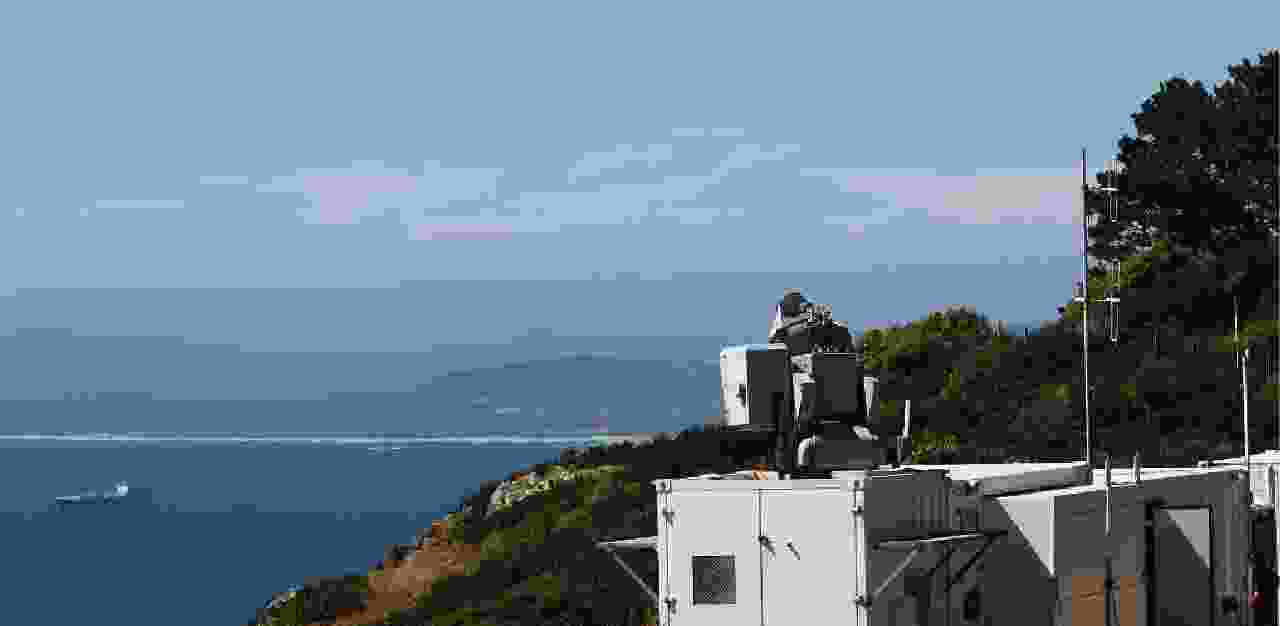
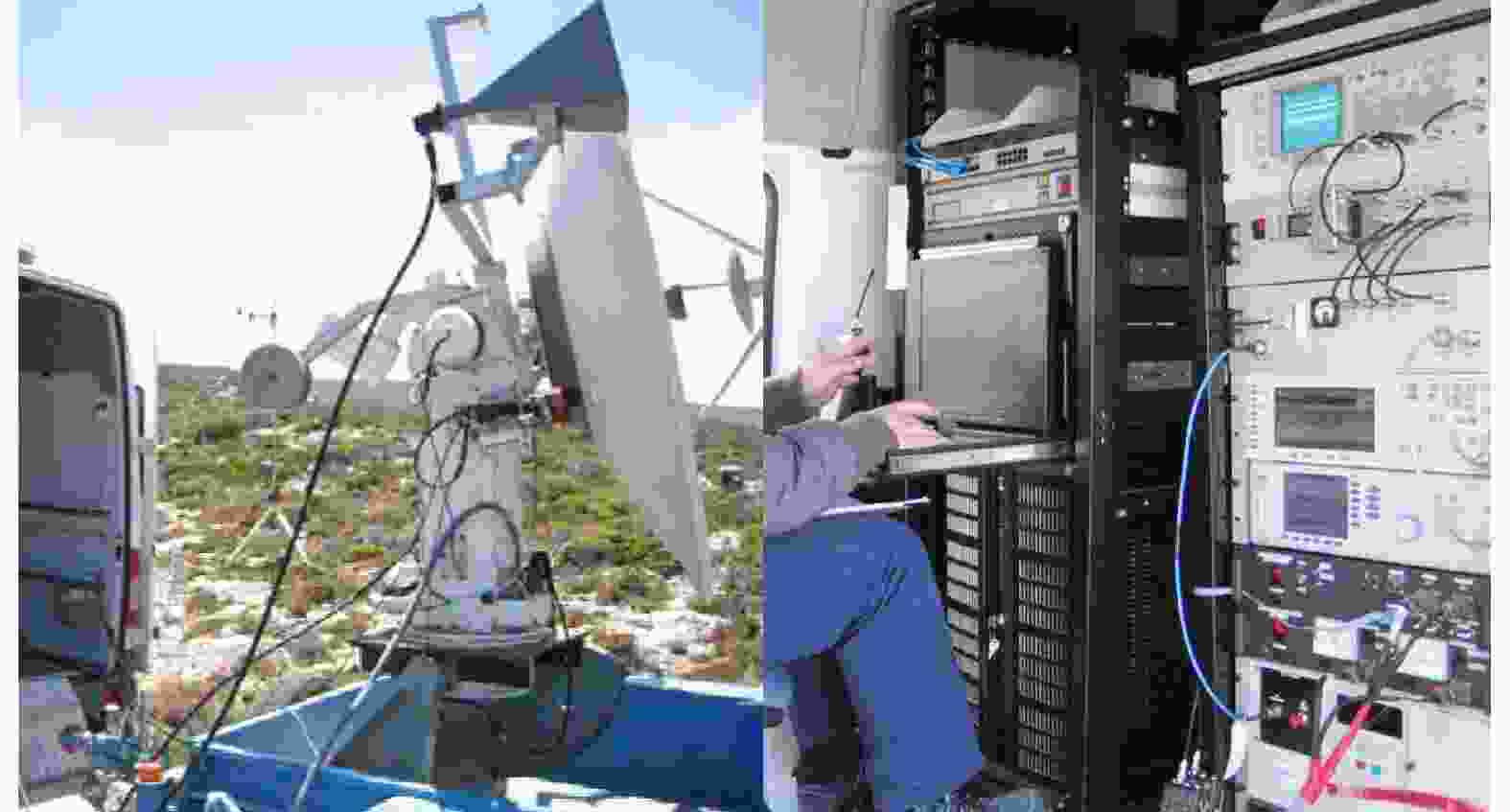
-
摘要: 在复杂海洋环境条件下,海上目标探测性能受海杂波的影响很大。海杂波影响因素众多,机理复杂,特征描述和抑制难度大,需要开展长期、系统、持续、深入研究。开展海杂波测量试验并获取不同参数影响下的测量数据,是有效支撑该研究的重要前提。该文重点围绕海杂波测量试验情况,从岸基试验和机载试验两个方面,对加拿大、南非、澳大利亚、美国、西班牙、德国等国家开展的典型外场试验进行了归类梳理和总结,回顾了美国和日本开展的造浪池海杂波测量试验,并简要介绍了国内开展的海杂波测量试验和烟台的海上目标探测试验中心建设情况。最后,对后续试验仍需重点关注的方向做了展望,包括系统性、持续性的海杂波测量试验仍需进一步开展,任务背景牵引的海杂波测量试验及数据分析仍需强化,面向智能雷达应用的海杂波和目标回波数据集亟需构建。Abstract: In complex marine environments, sea clutter greatly affects the detection performance of maritime targets. Because the influencing factors of sea clutter are numerous and the mechanism is complex, there are great difficulties in feature description and sea clutter suppression, and it is necessary to carry out long-term, systematic, continuous, and in-depth research. Carrying out sea clutter measurement experiments and obtaining measurement data under the influence of different parameters is an important prerequisite for supporting this research. This paper mainly focuses on the sea clutter measurements that have been carried out. First, typical experiments in various countries such as Canada, South Africa, Australia, the United States, Spain, and Germany are categorized and summarized from the aspects of shore-based experiment and airborne experiment. Then, sea clutter measurement experiments with wave tank conducted by the United States and Japan are reviewed, and domestic sea clutter measurement experiments as well as the construction of the maritime target detection experimental center in Yantai are briefly introduced. Finally, the future research directions that should be emphasized are projected: more systematic and continuous sea clutter measurement experiments need to be conducted; experiment and data analysis under explicit task background need to be strengthened; and sea clutter and target datasets that meet the requirement of intelligent radar applications need to be urgently constructed.
-
Key words:
- Sea clutter /
- Target detection /
- Measurement experiments /
- Property description /
- Radar
-
表 1 IPIX雷达参数
Table 1. IPIX radar parameters
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 9.39 波束宽度(°) 0.9 峰值功率(kW) 8 距离分辨率(m) 30 脉宽(μs) 0.2 距离采样间隔(m) 15 重频(PRF) (kHz) 1 中频频率(MHz) 150 天线增益(dB) 45.7 量化位数 8位 表 2 Fynmeet雷达系统性能参数
Table 2. Fynmeet system and performance specifications
分机 参数 参数值 发射机 频率范围(GHz) 6.5~17.5 峰值功率(kW) 2 PRF范围(kHz) 0~30 波形 固定频、步进频、捷变频等 天线 类型 双偏置反射器 增益(dB) ≥ 30 波束宽度(°) ≤ 2 旁瓣(dB) ≤ –25 接收机 动态范围(dB) 60/120 采集范围(km) 0.2~15 距离门 1~96个,15 m/45 m分辨率 采样类型 I/Q中频采样 镜像干扰抑制(dBc) ≤ –41 表 3 地理位置和环境参数汇总
Table 3. Summary of geometry and environment conditions
参数 不同架设位置的参数值 OTB 信号山 雷达高度(m) 67 294 与海岸线距离(km) 1.2 1.25 方位角范围 90°N~225°N 240°N~20°N 擦地角(°) 0.3~3 0.3~10 最大观测距离(km) 15 60 平均风速(m/s) 0~10.3 0~20.58 最大风速(m/s) 20.58 30.87 主导风向 180°N~270°N 130°N~140°N, 320°N~330°N 有效波高(m) 1~3.8 1~6 最大波高(m) 7.31 11.26 涌浪方向 135°N~180°N 230°N~270°N 表 4 S波段雷达主要性能参数
Table 4. Specifications of the S-band radar system
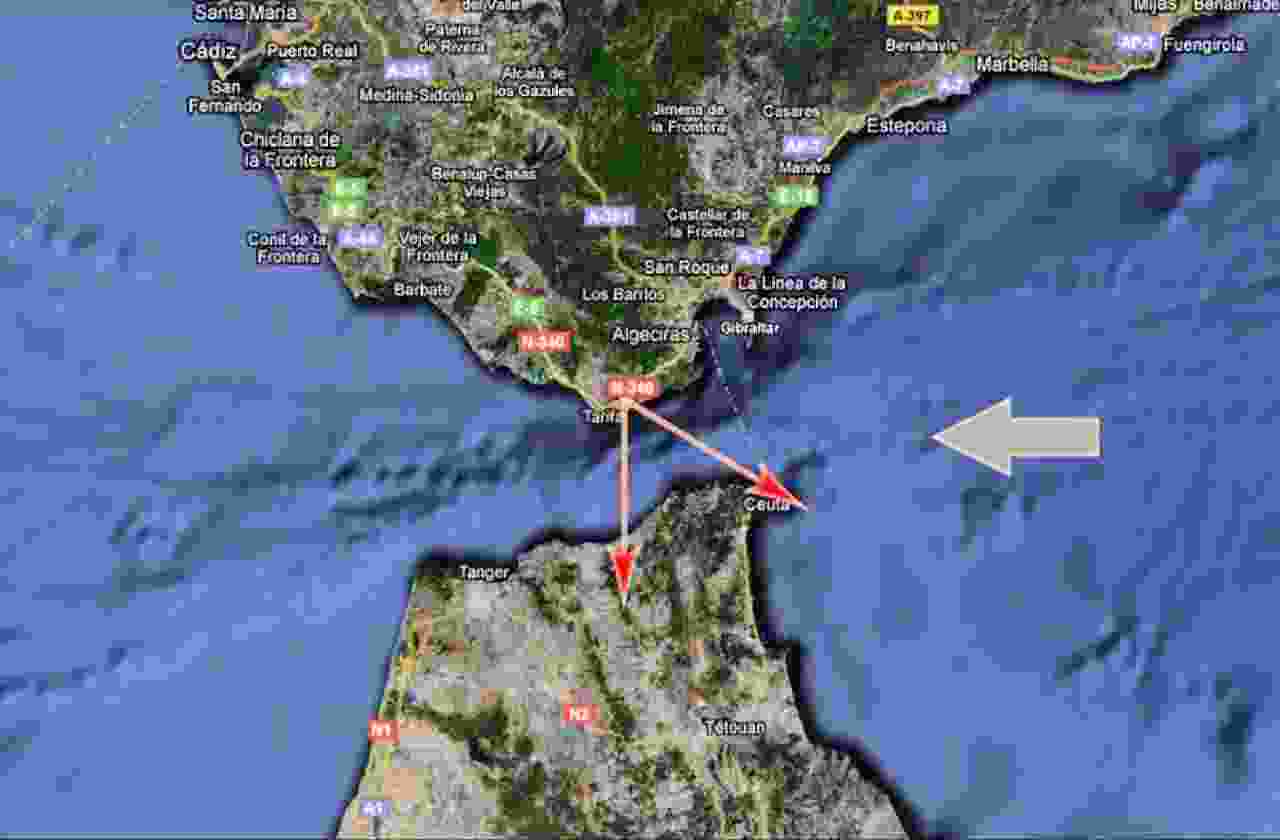
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 3.2~3.3 瞬时发射带宽(MHz) 50 瞬时接收带宽(MHz) 10 接收机通道数 4路,实际使用3路 存储深度 支持至少连续300 s连续采样 输出功率(kW) 1 占空比(%) 6.5 中频频率(MHz) 125 量化位数 14位 极化方式 HH, VV 表 5 XPAR和发射机的主要性能参数
Table 5. Specifications of the XPAR and transmitter
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 1.3 发射机波束宽度(°) 120 发射机峰值功率(W) 500 发射机带宽(MHz) 5 发射天线增益(dBi) 12 脉宽(μs) 20 PRF (kHz) 5 通道间方位间隔 0.5倍波长 通道波束宽度(°) 120 阵列波束宽度(波束形成后)(°) 6.3 接收天线增益(dBi) 12 中频频率(MHz) 175 量化位数 14位 极化方式 VV 表 6 记录的气象和波浪参数
Table 6. Recorded weather and wave parameters
参数 参数值 kix022数据 kix040数据 平均风向(°) 340 230 与阵列法线夹角(°) 162 52 平均波浪方向(°) 231 222 平均风速(m/s) 4.5 4.7 阵风风速(m/s) 7.2 25 温度(°C) 15.0 15.2 有效波高(m) 2.4 2.8 最大波高(m) 3.4 6.6 表 7 X波段雷达参数
Table 7. X-band radar parameters
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 9.5~10.0 峰值功率(kW) 500 脉宽(ns) 2.5(脉压后) 距离分辨率(m) 0.3 PRF (kHz) 2 信号处理 I/Q通道同步解调,8位量化,
500 MHz采样率采集波门宽度 156 m,包含512个距离单元 采集模式 聚束模式 波束宽度(°) 2.4(水平)/4(俯仰) 极化方式 HH或VV 表 8 LFMCW雷达参数和试验参数
Table 8. LFMCW radar and experimental parameters
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 28~30 极化 HH 带宽(GHz) 2 (最大值) PRF (kHz) 3 (最大值) 波束宽度(°) 3 距离分辨率(m) 0.08, 0.16和0.8 波门中心与雷达的距离(m) 1080, 1755 波门宽度(m) 108 擦地角(°) 2.52~2.79, 1.58~1.68 方位角(°) 138, 180 平均风向(°) 270 海况 3~4级(由风速等级推断) 表 9 NetRAD系统参数
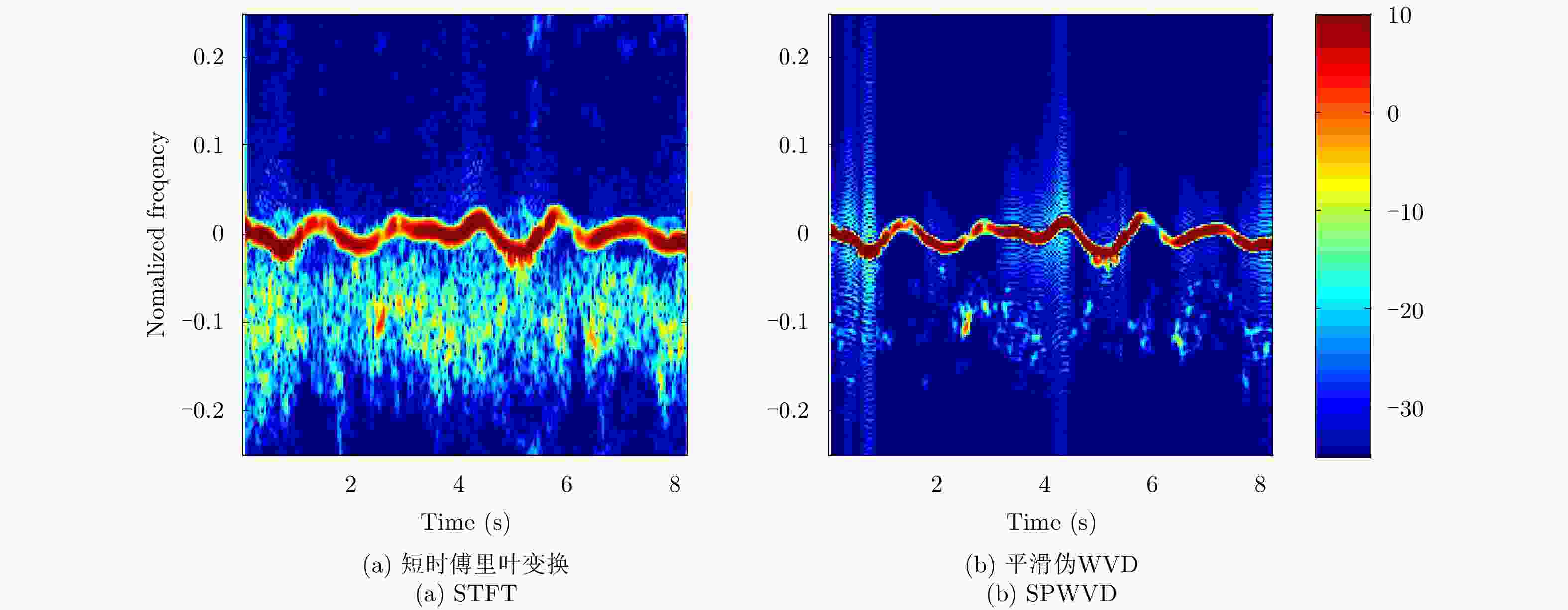
Table 9. NetRAD system parameters
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 2.45 带宽(MHz) 45 峰值功率(dBm) 57.7 单基地距离分辨率(m) 4.9 PRF (kHz) 1 脉宽(μs) 0.4~20 极化 HH, VV 波束宽度(°) 11.3 (俯仰)/8.9 (水平) 天线增益(dBi) 23.8 表 10 RSTER系统参数
Table 10. RSTER system parameters
参数 参数值 工作频率(MHz) 400~500 带宽(MHz) 0.2 天线增益(dBi) 29 峰值功率(kW) 100 平均功率(kW) 6 PRF (kHz) 0.25~1.5 波束宽度(°) 9 (水平)/6 (俯仰) 表 11 MCARM计划的雷达参数
Table 11. Radar parameters of the MCARM program
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 1.25 峰值功率(kW) 20 波形 LFM信号或加窗的射频信号 脉冲压缩比 63 PRF (kHz) 单基地:0.5, 2, 7
双基地:0.313, 23距离分辨率(m) 120 发射天线波束宽度(°) 7.5 天线单元数 16列8行,共128个单元 接收机通道数 24路 接收机带宽(MHz) 0.8 表 12 LSCL试验的主要参数
Table 12. Main parameters of the LSCL experiment
参数 参数值 波段 X波段 脉宽(ns) 32 采样率(MHz) 70 PRF 大多数为1250 Hz 波束内的脉冲数 最多21个 CNR 约30%高于10 dB 风向 逆风、侧风和顺风 擦地角 平均为1.56° 数据总时长(h) 约5.6 风速等级 3个架次分布为3级、6级和4级 表 13 雷达系统参数和海洋环境参数
Table 13. Radar system and environmental parameters
类别 参数 参数值 雷达系统 工作频率(GHz) 9.375 峰值功率(kW) 8 最大占空比(%) 2 距离分辨率(m) 1.5 PRF (Hz) 500 带宽(MHz) 96 波束宽度(°) 3.8 (水平)/8 (俯仰) 海洋环境 海况 2~3级 有效波高(m) 3~4 波长(m) 15 波周期(s) 10~12 涌浪方向 西北方向 风向 从西北到东南 风速(m/s) 5.14~6.17 表 14 典型试验参数
Table 14. Typical experimental parameters
参数 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 10.1 LFM带宽(MHz) 200 极化 HH, VV, HV, VH 脉宽(μs) 20 距离分辨率(m) 0.5 距离向采样点数 1024个 方位角(°) 0~360 PRF (Hz) 540 方位向3 dB波束宽度 2.4° 飞行高度(km) 1.353 平台速度(km/h) 约291 表 15 两型机载雷达系统试验参数
Table 15. Experimental parameters of two airborne radar systems
参数类型 XWEAR雷达系统 PAMIR雷达系统 工作频率(GHz) 9.75 9.45 峰值功率(kW) 50 1.28 极化 HH VV 距离分辨率(m) 最高为0.3,试验时小于1 最高为0.1,试验时7.5 试验时工作模式 聚束模式 扫描MTI条带模式 PRF (kHz) 1 3 试验地点 Halifax东海岸(44°30$ '$N, 63°25$ '$W) 德国Helgoland和Wilhelmshaven之间的北海 载机飞行高度(km) 1.828, 3.932, 7.01 2.5 飞行速度(m/s) 100 100 擦地角(°) 7, 15, 28 20 波高范围(m) 1.97~2.21 (有效波高) 0.9~1.5 (涌浪高度) 表 16 造浪池试验雷达系统主要参数
Table 16. Main radar system parameters of wave tank experiment
参数 FMCW雷达 MIDAS雷达 IIS雷达 雷达体制 调频连续波 脉冲多普勒 连续波散射计 工作频率(GHz) 4~8 (典型值为6) 3.15, 9.75, 15.75, 34.75, 94 3.2, 5.4, 9.6 带宽 125 MHz~4 MHz (典型值为4 MHz) 500 MHz – 波束宽度(°) 3 5 13.7/16.6 天线类型 抛物面天线 喇叭天线(3.15 GHz时为抛物面天线) 喇叭天线 极化方式 双极化(HH, VV) 双极化(HH, VV) 单极化(HH或VV) PRF (kHz) 1 2 1 擦地角(°) 6 3~24 30~75 表 17 C波段雷达主要试验参数
Table 17. Main parameters of the C-band radar experiment
参类 参数值 工作频率(GHz) 5.5 PRF(kHz) 1 脉宽 1 μs,压缩比3 波束宽度 锥形波束,2.2° 天线转速 90°/s 极化 HH 采集数据空间范围 方位角范围:50°;距离范围:7 km 信号处理 500 MHz采样率,I/Q同步采集 海况 3~4级(根据Beaufort风速等级推断) -
[1] WARD K, TOUGH R, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed., London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013. [2] WARD K D and WATTS S. Use of sea clutter models in radar design and development[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 146–157. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0132 [3] SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed., New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., 2008. [4] 何友, 黄勇, 关键, 等. 海杂波中的雷达目标检测技术综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2014.12.001HE You, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. An overview on radar target detection in sea clutter[J]. Modern Radar, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2014.12.001 [5] 丁昊. 雷达海杂波特性与目标检测方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 海军航空工程学院, 2016.DING Hao. Research on radar sea clutter property and target detection algorithms[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2016. [6] 丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069DING Hao, DONG Yunlong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069 [7] DROSOPOULOS A. Description of the OHGR database[R]. Technical Note 94–14, 1994. [8] DE WIND H J, CILLIERS J C, and HERSELMAN P L. DataWare: Sea clutter and small boat radar reflectivity databases[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(2): 145–148. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2009.935415 [9] ANTIPOV I. Analysis of sea clutter data[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-0647, 1998. [10] DONG Yunhan and MERRETT D. Statistical measures of S-band sea clutter and targets[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-2221, 2008. [11] DONG Yunhan and MERRETT D. Analysis of L-band multi-channel sea clutter[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-2455, 2010. [12] POSNER F L. Spiky sea clutter at high range resolutions and very low grazing angles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(1): 58–73. doi: 10.1109/7.993229 [13] CARRETERO-MOYA J, GISMERO-MENOYO J, BLANCO-DEL-CAMPO Á, et al. Statistical analysis of a high-resolution sea-clutter database[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2024–2037. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2033193 [14] SIEGEL A, OCHADLICK A, DAVIS JR J, et al. Spatial and temporal correlation of LOGAN-1 high-resolution radar sea clutter data[C]. Proceedings of 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1994: 818–821. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1994.399273. [15] RINO C L, ECKERT E, SIEGEL A, et al. X-band low-grazing-angle ocean backscatter obtained during LOGAN 1993[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1997, 22(1): 18–26. doi: 10.1109/48.557536 [16] HAIR T, LEE T, and BAKER C J. Statistical properties of multifrequency high-range-resolution sea reflections[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1991, 138(2): 75–79. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0012 [17] ISHII S, SAYAMA S, and MIZUTANI K. Effect of changes in sea-surface state on statistical characteristics of sea clutter with X-band radar[J]. Wireless Engineering and Technology, 2011, 2(3): 5829. doi: 10.4236/wet.2011.23025 [18] FABBRO V, BIEGEL G, FÖRSTER J, et al. Measurements of sea clutter at low grazing angle in Mediterranean coastal environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6379–6389. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2727057 [19] AL-ASHWAL W A, BAKER C J, BALLERI A, et al. Statistical analysis of simultaneous monostatic and bistatic sea clutter at low grazing angles[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(10): 621–622. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.0557 [20] AL-ASHWAL W A, WOODBRIDGE K, and GRIFFITHS H D. Analysis of bistatic sea clutter-Part I: Average reflectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1283–1292. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120426 [21] AL-ASHWAL W A, WOODBRIDGE K, and GRIFFITHS H D. Analysis of bistatic sea clutter-Part II: Amplitude statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1293–1303. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120434 [22] RITCHIE M, STOVE A, WOODBRIDGE K, et al. NetRAD: Monostatic and bistatic sea clutter texture and Doppler spectra characterization at S-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5533–5543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2567598 [23] FIORANELLI F, RITCHIE M, GRIFFITHS H, et al. Analysis of polarimetric bistatic sea clutter using the NetRAD radar system[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(8): 1356–1366. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0416 [24] GRECO M, STINCO P, GINI F, et al. Impact of sea clutter nonstationarity on disturbance covariance matrix estimation and CFAR detector performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1502–1513. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545205 [25] HERSELMAN P L, BAKER C J, and DE WIND H J. An analysis of X-band calibrated sea clutter and small boat reflectivity at medium-to-low grazing angles[J]. International Journal of Navigation and Observation, 2008, 2008: 347518. doi: 10.1155/2008/347518 [26] HERSELMAN P L and BAKER C J. Analysis of calibrated sea clutter and boat reflectivity data at C- and X-band in South African coastal waters[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Edinburgh, UK, 2007. doi: 10.1049/cp:20070616. [27] 陈帅. 海杂波背景下的过采样MTD方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.CHEN Shuai. Oversampling MTD method in sea clutter background[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2014. [28] 陈小龙, 关键, 于晓涵, 等. 基于短时稀疏时频分布的雷达目标微动特征提取及检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, YU Xiaohan, et al. Radar micro-Doppler signature extraction and detection via short-time sparse time-frequency distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040 [29] DALEY J C, RANSONE J T, BURKETT J A, et al. Sea-clutter measurements on four frequencies[R]. Report No. 6806, 1968. [30] TITI G W and MARSHALL D F. The ARPA/navy mountaintop program: Adaptive signal processing for airborne early warning radar[C]. Proceedings of 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1996: 1165–1168. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1996.543572. [31] LITTLE M O and BERRY W P. Real-time multichannel airborne radar measurements[C]. Proceedings of 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, NY, USA, 1997: 138–142. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1997.588238. [32] HIMED B and SOUMEKH M. Synthetic aperture radar-moving target indicator processing of multi-channel airborne radar measurement data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(6): 532–543. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20050128 [33] STEHWIEN W. Sea clutter measurements using an airborne X-band radar[C]. Proceedings of OCEANS’93, Victoria, BC, Canada, 1993, 1: 125–130. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS.1993.326036. [34] STEHWIEN W. Statistics and correlation properties of high resolution X-band sea clutter[C]. Proceedings of 1994 IEEE National Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1994: 46–51. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1994.328096. [35] ANTIPOV I. Statistical analysis of northern Australian coastline sea clutter data[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-1236, 2001. [36] CRISP D J, STACY N J S, and GOH A S. Ingara medium-high incidence angle polarimetric sea clutter measurements and analysis[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-1818, 2006. [37] MCDONALD M, CERUTTI-MAORI D, and DAMINI A. Characterisation and cancellation of medium grazing angle sea clutter[C]. The 7th European Radar Conference, Paris, France, 2010: 172–175. [38] DAMINI A, MCDONALD M, and HASLAM G E. X-band wideband experimental airborne radar for SAR, GMTI and maritime surveillance[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(4): 305. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030654 [39] BRENNER A R and ENDER J H G. Demonstration of advanced reconnaissance techniques with the airborne SAR/GMTI sensor PAMIR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 152–162. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20050044 [40] MCDONALD M K and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Coherent radar processing in sea clutter environments, part 1: Modelling and partially adaptive STAP performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1797–1817. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140897 [41] MCDONALD M K and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Coherent radar processing in sea clutter environments, Part 2: Adaptive normalised matched filter versus adaptive matched filter performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1818–1833. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140898 [42] WATTS S, ROSENBERG L, BOCQUET S, et al. Doppler spectra of medium grazing angle sea clutter; Part 1: Characterisation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(1): 24–31. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0148 [43] WATTS S, ROSENBERG L, BOCQUET S, et al. Doppler spectra of medium grazing angle sea clutter; Part 2: Model assessment and simulation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(1): 32–42. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0149 [44] ROSENBERG L. Characterization of high grazing angle X-band sea-clutter Doppler spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(1): 406–417. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120809 [45] DONG Yunhan. High grazing angle and high resolution sea clutter: Correlation and polarization analyses[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-1972, 2007. [46] WEINBERG G V. An investigation of the Pareto distribution as a model for high grazing angle clutter[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-2525, 2011. [47] ROSENBERG L. Sea-spike detection in high grazing angle X-band sea-clutter[R]. Technical Report DSTO-TR-2820, 2013. [48] LAMONT-SMITH T, WASEDA T, and RHEEM C K. Measurements of the Doppler spectra of breaking waves[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2007, 1(2): 149–157. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060109 [49] LAMONT-SMITH T. An empirical model of EM scattering from steepening wave profiles derived from numerical computations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(6): 1447–1454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.811551 [50] LAMONT-SMITH T. Investigation of the variability of Doppler spectra with radar frequency and grazing angle[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2004, 151(5): 291–298. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20040859 [51] LAMONT-SMITH T. Azimuth dependence of Doppler spectra of sea clutter at low grazing angle[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2008, 2(2): 97–103. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20070099 [52] LAMONT-SMITH T, MITOMI M, KAWAMURA T, et al. Electromagnetic scattering from wind blown waves and ripples modulated by longer waves under laboratory conditions[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 265–279. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0072 [53] LEE P H Y, BARTER J D, LAKE B M, et al. Lineshape analysis of breaking-wave Doppler spectra[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1998, 145(2): 135–139. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19981822 [54] 赵海云, 张瑞永, 武楠, 等. 基于实测数据的海杂波特性分析[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2009, 7(3): 214–218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.03.011ZHAO Haiyun, ZHANG Ruiyong, WU Nan, et al. Analysis of sea clutter characteristics based on measured data[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2009, 7(3): 214–218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.03.011 [55] 刘志高, 徐向东, 刘斌. 某低空警戒雷达海杂波数据的统计特性分析[J]. 空军雷达学院学报, 2004, 18(4): 1–3, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8691.2004.04.001LIU Zhigao, XU Xiangdong, and LIU Bin. Statistical analysis of sea clutter feature data from a low-altitude surveillance radar[J]. Journal of Air Force Radar Academy, 2004, 18(4): 1–3, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8691.2004.04.001 [56] 张忠, 袁业术, 孟宪德. 舰载超视距雷达背景杂波统计特性分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2002, 24(9): 19–22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2002.09.007ZHANG Zhong, YUAN Yeshu, and MENG Xiande. Background clutters statistical characteristics in shipborne radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2002, 24(9): 19–22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2002.09.007 [57] 周超, 刘泉华. Ku波段实验雷达海杂波实测数据分析[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(12): 1573–1578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.12.005ZHOU Chao and LIU Quanhua. Analysis of field sea clutter data of Ku band[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(12): 1573–1578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.12.005 [58] 杨俊岭, 李大治, 万建伟, 等. 海杂波尖峰特性研究及仿真分析[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2007, 19(8): 1836–1840. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.08.046YANG Junling, LI Dazhi, WAN Jianwei, et al. Sea spike characteristics studies and simulation analyses[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2007, 19(8): 1836–1840. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2007.08.046 [59] XU Shuwen, SHUI Penglang, and YAN Xueying. Non-coherent detection of radar target in heavy-tailed sea clutter using bi-window non-linear shrinkage map[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2016, 10(9): 1031–1039. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2015.0564 [60] 康士峰, 葛德彪, 罗贤云, 等. 多波段多极化海杂波特性的实验研究[J]. 微波学报, 2000, 16(5): 463–468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2000.z1.003KANG Shifeng, GE Debiao, LUO Xianyun, et al. Experimental study on multi-band and multi-polarization characteristics of sea clutter[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2000, 16(5): 463–468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6122.2000.z1.003 [61] 张金鹏, 张玉石, 李清亮, 等. 基于不同散射机制特征的海杂波时变多普勒谱模型[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(3): 034101. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20171612ZHANG Jinpeng, ZHANG Yushi, LI Qingliang, et al. A time-varying Doppler spectrum model of radar sea clutter based on different scattering mechanisms[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(3): 034101. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20171612 [62] 夏晓云, 黎鑫, 张玉石, 等. 基于相位的岸基雷达地海杂波分割方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(3): 552–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.10XIA Xiaoyun, LI Xin, ZHANG Yushi, et al. Sea-land clutter segmentation method of shore-based radar based on phase information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 552–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.10 [63] 许心瑜, 张玉石, 黎鑫, 等. UHF波段海杂波时间相关性的海浪状态影响分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(6): 1203–1207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.03XU Xinyu, ZHANG Yushi, LI Xin, et al. Influence of sea condition on the temporal correlation properties of UHF band sea clutter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(6): 1203–1207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.03 [64] 张玉石, 许心瑜, 吴振森, 等. L波段小擦地角海杂波幅度均值与风速关系建模[J]. 电波科学学报, 2015, 30(2): 289–294. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014042001ZHANG Yushi, XU Xinyu, WU Zhensen, et al. Modeling windspeed behavior of L-band sea clutter average reflectivity at low grazing angles[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2015, 30(2): 289–294. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2014042001 [65] 张玉石, 尹雅磊, 许心瑜, 等. 海杂波测量定标的姿态修正数据处理方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(3): 607–612. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140659ZHANG Yushi, YIN Yalei, XU Xinyu, et al. Data processing method of posture correction for calibration of sea clutter measurement[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(3): 607–612. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140659 [66] 许心瑜, 张玉石, 黎鑫, 等. L波段小擦地角海杂波KK分布建模[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(7): 1304–1308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.07.13XU Xinyu, ZHANG Yushi, LI Xin, et al. KK distribution modeling with L band low grazing sea clutter[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(7): 1304–1308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.07.13 [67] 张玉石, 许心瑜, 尹雅磊, 等. L波段小擦地角海杂波幅度统计特性研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(5): 1044–1048. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01139ZHANG Yushi, XU Xinyu, YIN Yalei, et al. Research on amplitude statistics of L-band low grazing angle sea clutter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(5): 1044–1048. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01139 [68] DING Hao, GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, et al. New spatial correlation models for sea clutter[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1833–1837. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2430371 [69] DING Hao, GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, et al. Modeling of heavy tailed sea clutter based on the generalized central limit theory[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(11): 1591–1595. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2596322 [70] GUAN J, LIU N B, HUANG Y, et al. Fractal characteristic in frequency domain for target detection within sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 293–306. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0250 [71] GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, HUANG Yong, et al. Fractal Poisson model for target detection within spiky sea clutter[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 411–415. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2203578 [72] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HE You, et al. Detection of low observable moving target in sea clutter via fractal characteristics in fractional Fourier transform domain[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2013, 7(6): 635–651. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0116 [73] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, BAO Zhonghua, et al. Detection and extraction of target with micromotion in spiky sea clutter via short-time fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1002–1018. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2246574 [74] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, Liu Ningbo, et al. Maneuvering target detection via Radon-fractional Fourier transform-based long-time coherent integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(4): 939–953. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2297682 [75] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function-based detection and estimation method for marine target with micromotion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2225–2240. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2358456 [76] CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Yong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Radon-fractional ambiguity function-based detection method of low-observable maneuvering target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 815–833. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130791 [77] 黄勇, 陈小龙, 关键. 实测海尖峰特性分析及抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(3): 334–342. doi: 10.12000/JR14108HUANG Yong, CHEN Xiaolong, and GUAN Jian. Property analysis and suppression method of real measured sea spikes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(3): 334–342. doi: 10.12000/JR14108 [78] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077 [79] 丁昊, 薛永华, 黄勇, 等. 均匀和部分均匀杂波中子空间目标的斜对称自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(4): 418–430. doi: 10.12000/JR14133DING Hao, XUE Yonghua, HUANG Yong, et al. Persymmetric adaptive detectors of subspace signals in homogeneous and partially homogeneous clutter[J]. Journal Radars, 2015, 4(4): 418–430. doi: 10.12000/JR14133 [80] 丁昊, 王国庆, 刘宁波, 等. 逆Gamma纹理背景下两类子空间目标的自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088DING Hao, WANG Guoqing, LIU Ningbo, et al. Adaptive detectors for two types of subspace targets in an inverse Gamma textured background[J]. Journal Radars, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
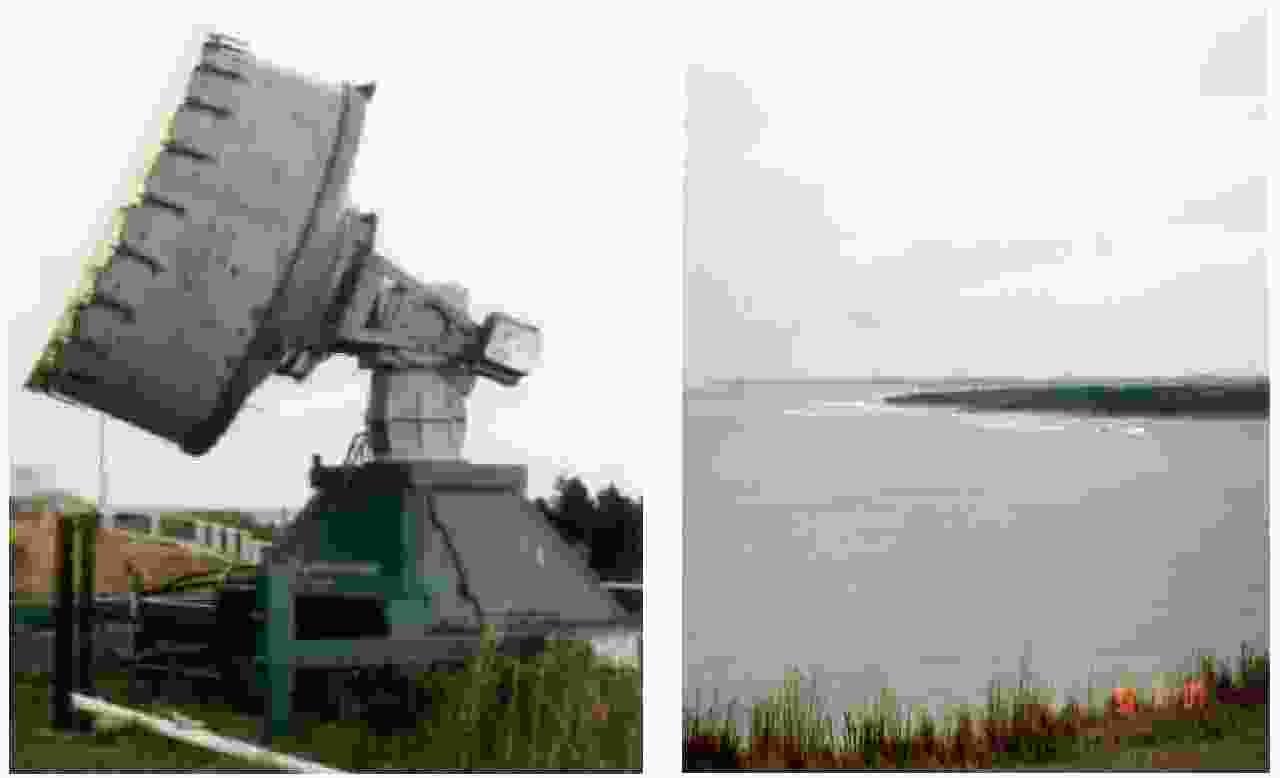

 下载:
下载: