-
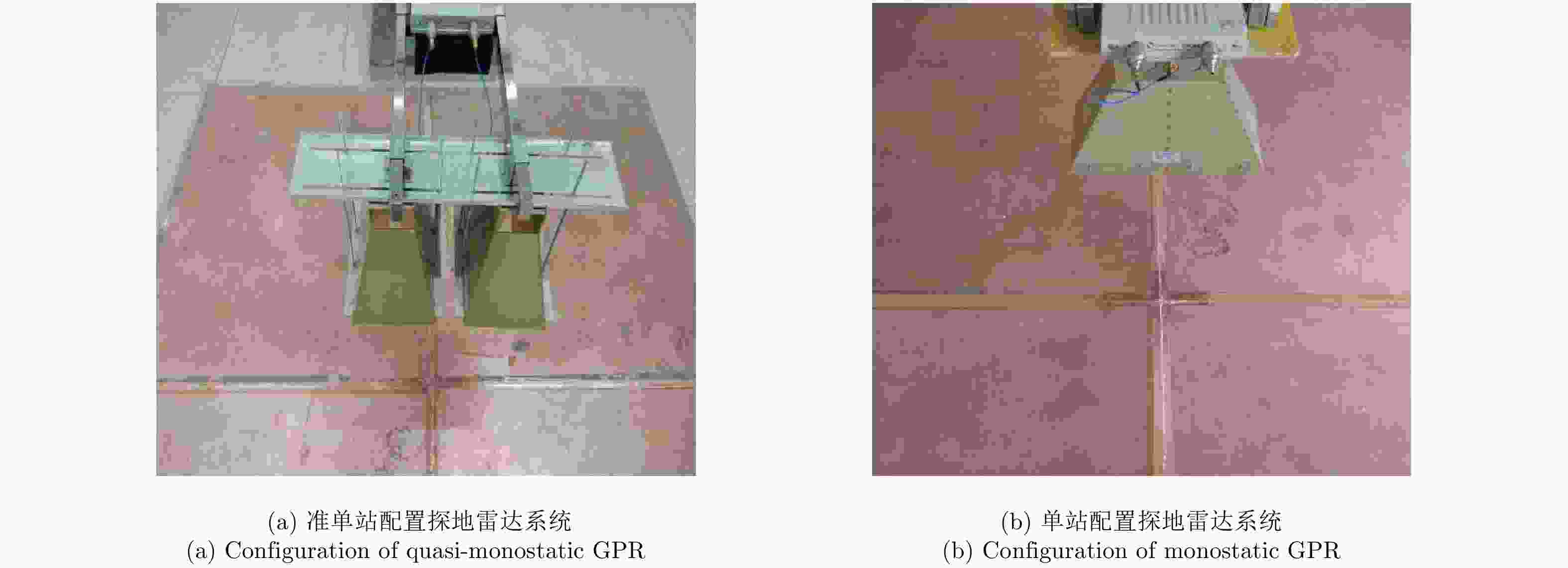
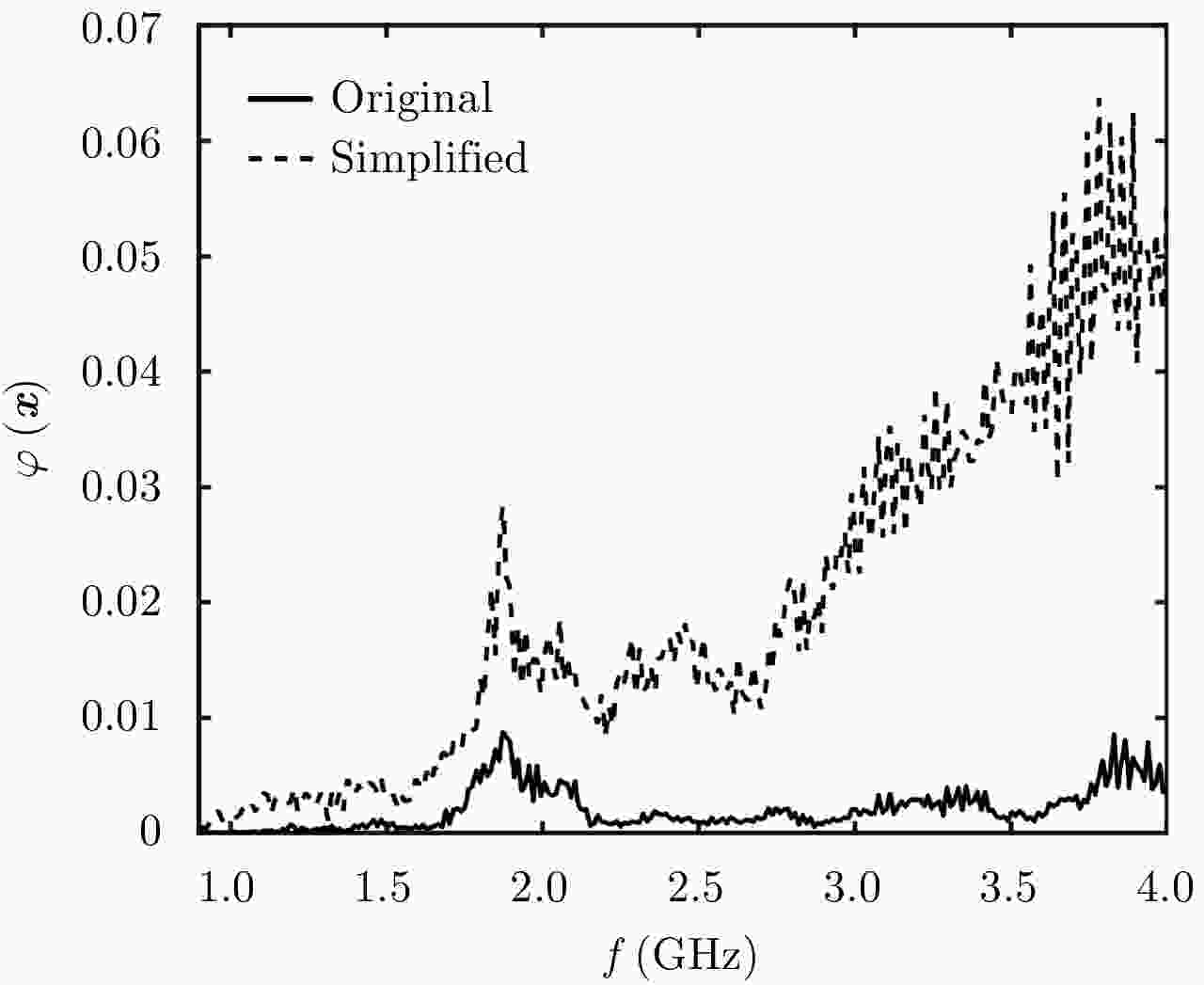
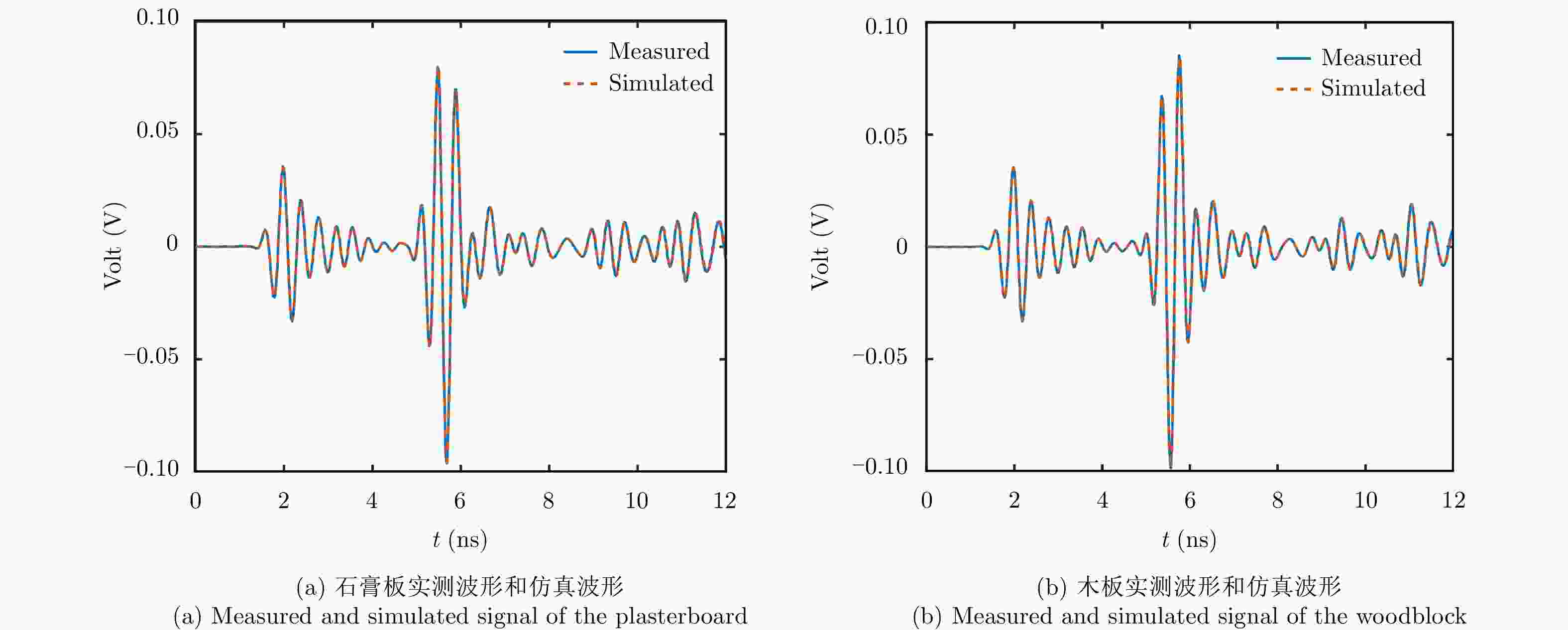
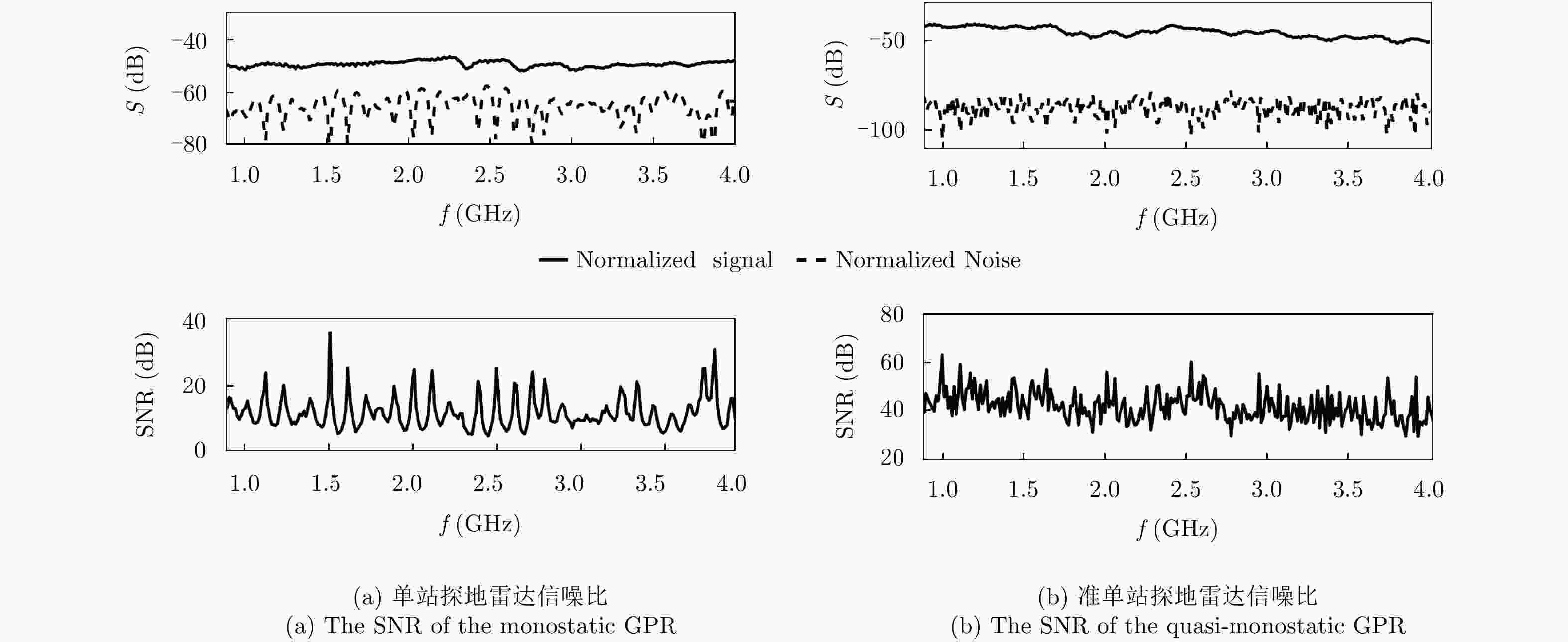
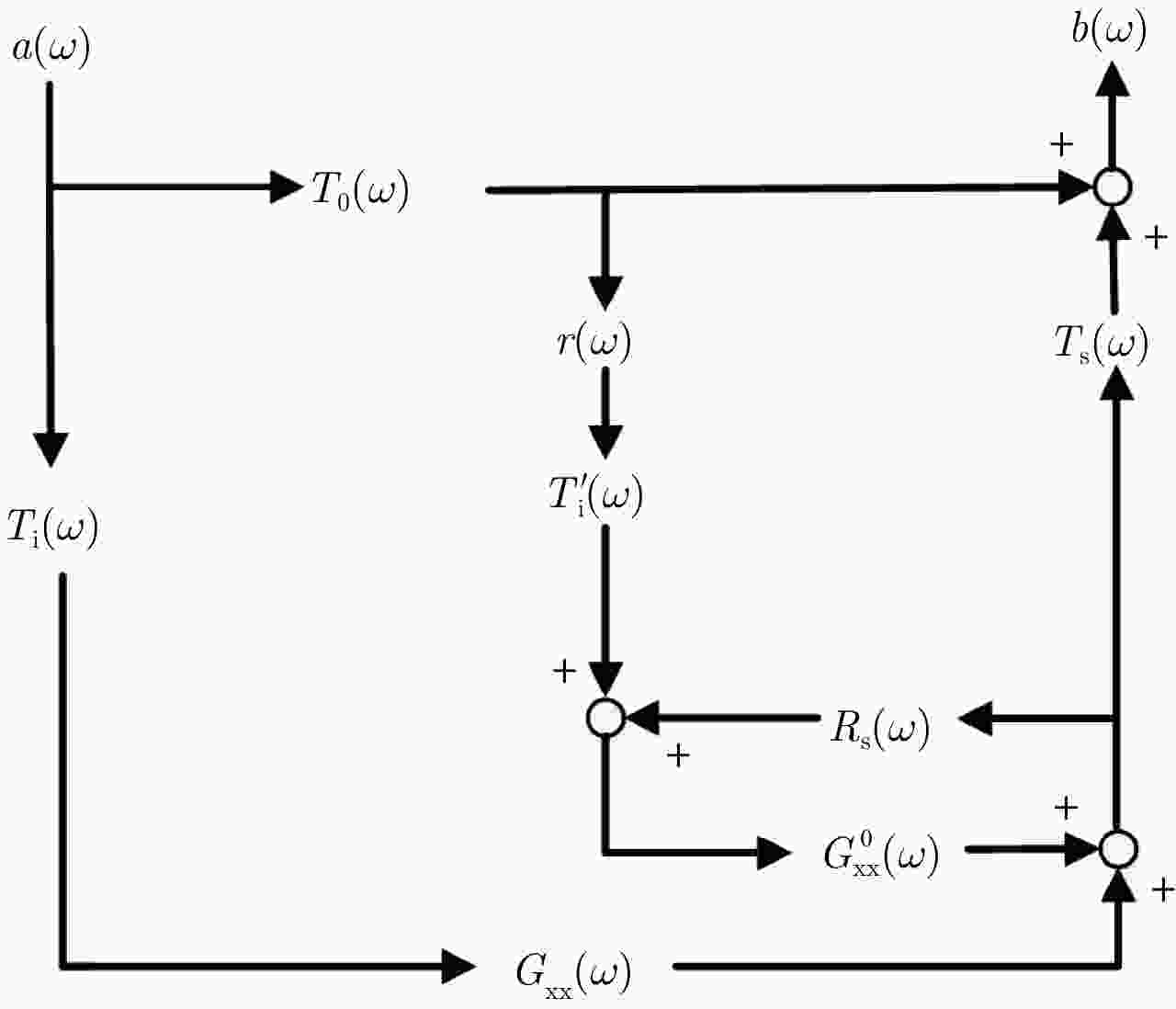
摘要: 探地雷达是一种被广泛使用的无损检测技术。利用探地雷达对分层媒质进行全波反演时,构建精确的探地雷达正演模型具有十分重要的意义。该文提出一种可用于准单站配置的步进频探地雷达的建模方法。在该模型中,探地雷达系统及其与分层媒质间的相互作用被表示成线性方程,天线对雷达信号的影响被表示为只与频率有关的传输函数。为验证模型准确性,该文在实验室条件下搭建了准单站配置的步进频探地雷达系统,并对已知厚度的石膏板和木板的雷达测量信号进行全波反演。反演结果表明:石膏板和木板的厚度估计误差均不超过0.3 mm,验证了所提出的正演模型具有高准确度。利用石膏板和木板搭建分层模型,该文进一步比较了准单站配置和单站配置步进频探地雷达系统对介电常数差异较小的分层媒质的反演性能。实验结果表明:准单站配置探地雷达能获得更精确的反演参数。通过对分界面反射信号的信噪比估计可知,准单站配置比单站配置探地雷达系统能获得高出约10 dB的信噪比,因此具有更好的反演性能。Abstract: Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a widely used non-destructive testing tool. Constructing an appropriate forward model is crucial for GPR to perform a full-waveform inversion of layered media. In this paper, a forward model for the quasi-monostatic Stepped-Frequency GPR (SFGPR) is proposed. In the model, the GPR and its interaction with the layered medium are represented as a linear equation in which the effects of the antennas are represented by a set of frequency-dependent transfer functions. To verify the accuracy of the proposed model, the authors constructed a quasi-monostatic SFGPR in a laboratory condition and performed a full-waveform inversion of the measurement signals of plasterboard and woodblock with known thickness. In the inversion results, the thickness estimation errors of the plasterboard and woodblock are not more than 0.3 mm, indicating that the proposed forward model has a very high accuracy. The inversion performances of the quasi-monostatic and monostatic SFGPR are further compared for the layered medium constructed with plasterboard and woodblock, which has a small permittivity difference. The results show that the quasi-monostatic SFGPR can obtain more accurate inversion parameters. By estimating the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of the reflected signal from the interface, it is found that the SNR obtained by the quasi-monostatic configuration is 10 dB higher than that of the monostatic; therefore, the quasi-monostatic GPR has the better inversion performance.
-
表 1 准单站探地雷达石膏板反演结果
Table 1. Inversion results of the plasterboard with the quasi-monostatic GPR
高度(mm) 反演相对介电常数 反演厚度(mm) 厚度估计误差(mm) 534.3 2.32 28.7 0.3 522.5 2.33 28.3 0.1 515.3 2.32 28.6 0.2 表 2 准单站探地雷达木板反演结果
Table 2. Inversion results of the woodblock with quasi-monostatic GPR
高度(mm) 反演相对介电常数 反演厚度(mm) 厚度估计误差(mm) 531.5 2.72 19.2 0.2 523.2 2.73 18.8 0.2 512.4 2.74 18.7 0.3 表 3 简化模型对石膏板的反演结果
Table 3. Inversion results of the plasterboard with simplified model
高度(mm) 反演相对介电常数 反演厚度(mm) 厚度估计误差(mm) 533.8 2.43 28.0 0.4 522.0 2.45 27.6 0.8 514.7 2.44 27.9 0.5 表 4 准单站配置雷达3层结构反演结果
Table 4. Inversion results of the three-layer structure with quasi-monostatic GPR
天线高度
(mm)反演石膏板
介电常数石膏板反演厚度
(mm)石膏板厚度误差
(mm)反演木板
介电常数木板反演厚度
(mm)木板厚度误差
(mm)532.2 2.34 28.1 0.3 2.71 19.5 0.5 524.2 2.32 28.8 0.4 2.72 19.4 0.4 510.3 2.31 28.9 0.5 2.75 18.5 0.5 表 5 单站配置雷达3层结构反演结果
Table 5. Inversion results of the three-layer structure with monostatic GPR
天线高度
(mm)反演石膏板
介电常数石膏板反演厚度
(mm)石膏板厚度误差
(mm)反演木板
介电常数木板反演厚度
(mm)木板厚度误差
(mm)535.3 2.31 27.8 0.6 2.63 20.1 1.1 525.2 2.30 28.9 0.5 2.78 18.1 0.9 513.3 2.33 27.7 0.7 2.65 19.8 0.8 -
[1] 刘澜波, 钱荣毅. 探地雷达: 浅表地球物理科学技术中的重要工具[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8): 2606–2617. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150802LIU Lan-bo and QIAN Rong-yi. Ground penetrating radar: A critical tool in near-surface geophysics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8): 2606–2617. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150802 [2] ZHANG J W, YE S B, YI L, et al. A Hybrid method applied to improve the efficiency of full-waveform inversion for pavement characterization[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 2916. doi: 10.3390/s18092916 [3] KLĘSK P, KAPRUZIAK M, and OLECH B. Statistical moments calculated via integral images in application to landmine detection from Ground Penetrating Radar 3D scans[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2018, 21(3): 671–684. doi: 10.1007/s10044-016-0592-5 [4] DEIANA R, LEUCCI G, and MARTORANA R. New perspectives on geophysics for archaeology: A special issue[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2018, 39(6): 1035–1038. doi: 10.1007/s10712-018-9500-4 [5] LAHOUAR S and AL-QADI I L. Automatic detection of multiple pavement layers from GPR data[J]. NDT & E International, 2008, 41(2): 69–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ndteint.2007.09.001 [6] LAMBOT S, SLOB E C, VAN DEN BOSCH I, et al. Modeling of ground-penetrating radar for accurate characterization of subsurface electric properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2555–2568. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834800 [7] WARREN C and GIANNOPOULOS A. Creating finite-difference time-domain models of commercial ground-penetrating radar antennas using Taguchi’s optimization method[J]. Geophysics, 2011, 76(2): G37–G47. doi: 10.1190/1.3548506 [8] HYUN S Y, KIM S Y, and KIM Y S. An equivalent feed model for the FDTD analysis of antennas driven through a ground plane by coaxial lines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 57(1): 161–167. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.2009650 [9] VENKATARAYALU N V, GAN Y B, LEE R, et al. Application of hybrid FETD-FDTD method in the modeling and analysis of antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(9): 3068–3072. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.928809 [10] ALKHALIFEH K, HISLOP G, OZDEMIR N A, et al. Efficient MoM simulation of 3-D antennas in the vicinity of the ground[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(12): 5335–5344. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2618482 [11] GENTILI G G and SPAGNOLINI U. Electromagnetic inversion in monostatic ground penetrating radar: TEM horn calibration and application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(4): 1936–1946. doi: 10.1109/36.851775 [12] LAMBOT S, SLOB E, and VEREECKEN H. Fast evaluation of zero-offset green’s function for layered media with application to ground-penetrating radar[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(21): L21405. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031459 [13] The data sheet of the portable VNA[OL]. http://www.c-oppermountaintech.com/products/12/S5048/. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: