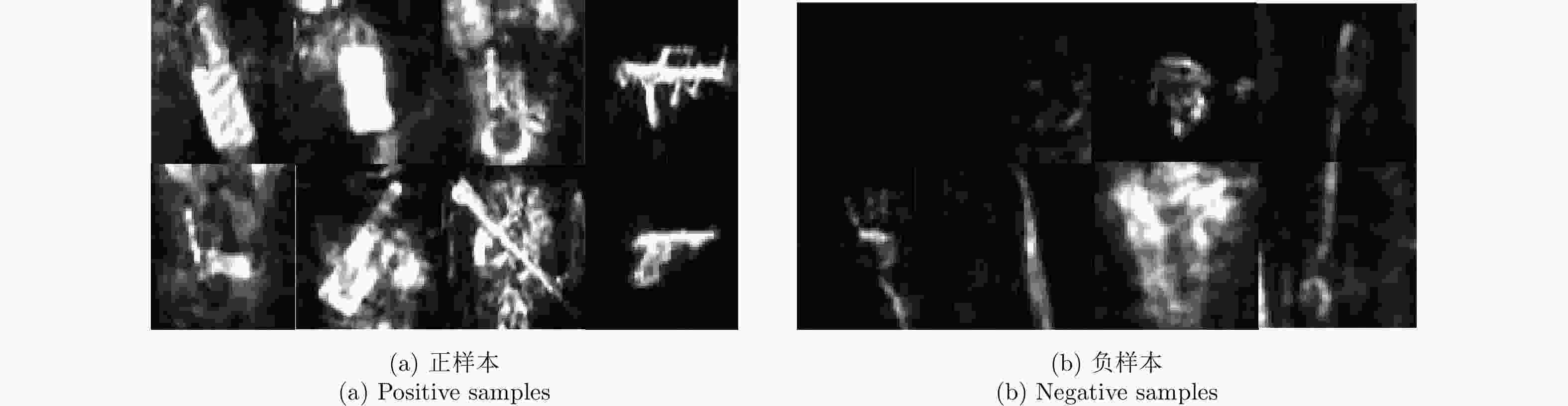
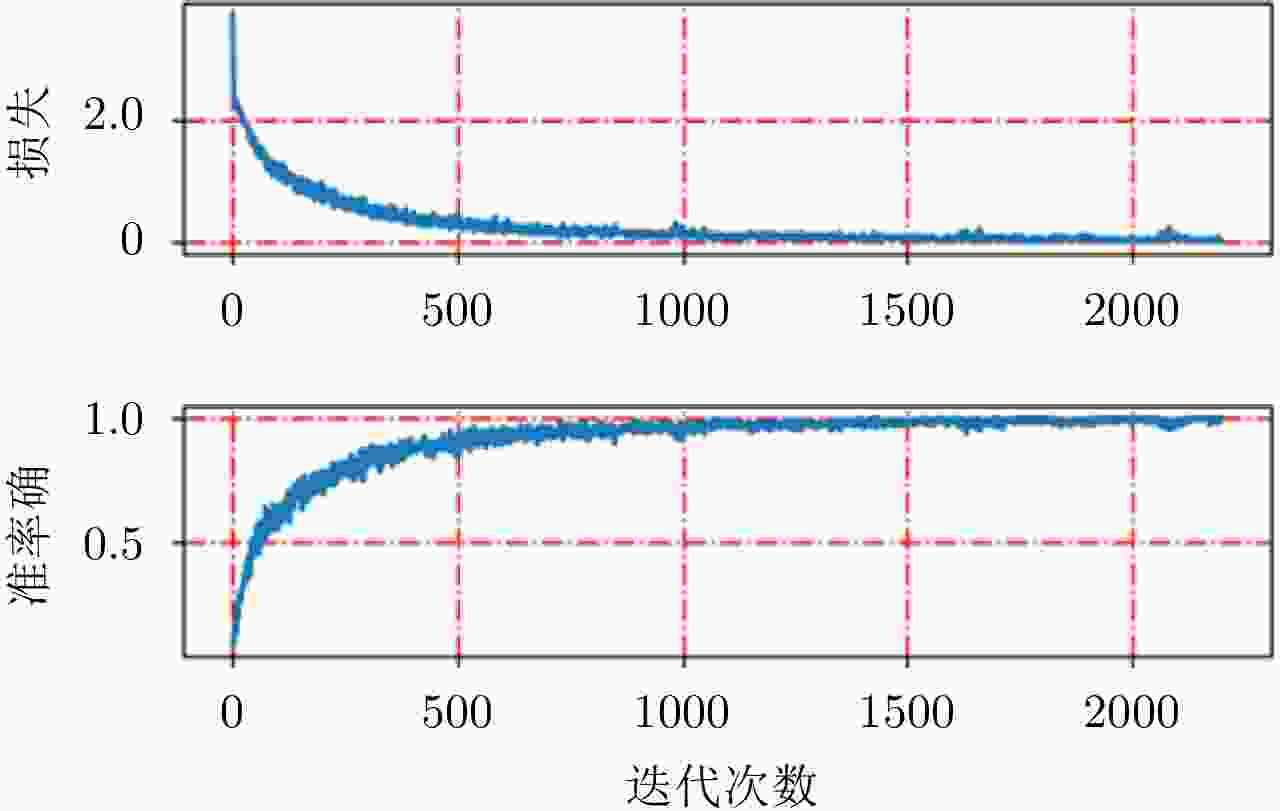
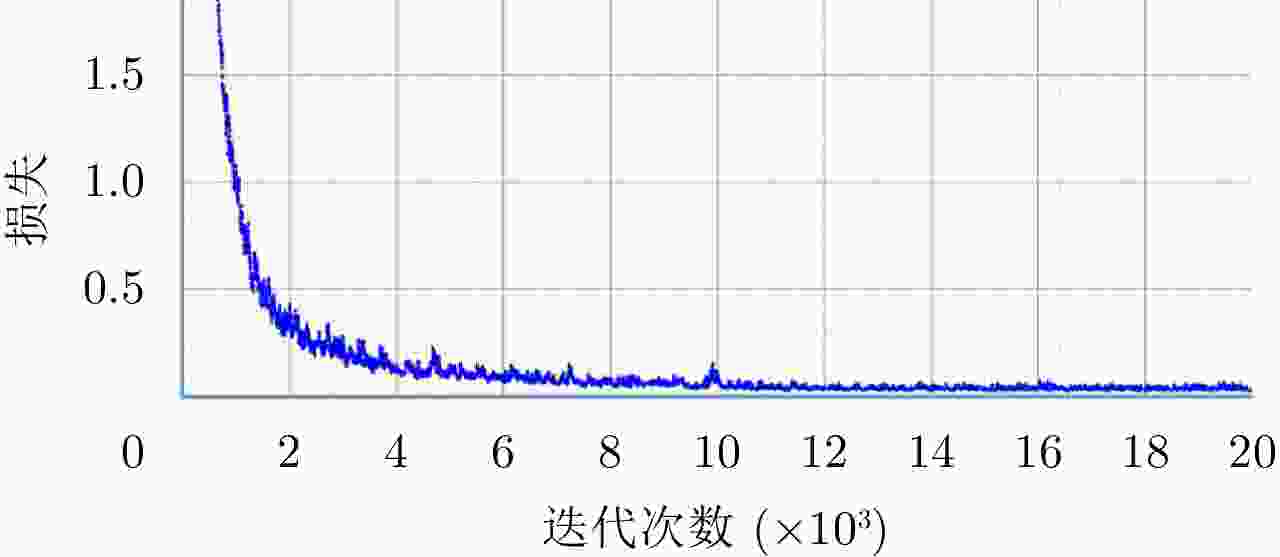
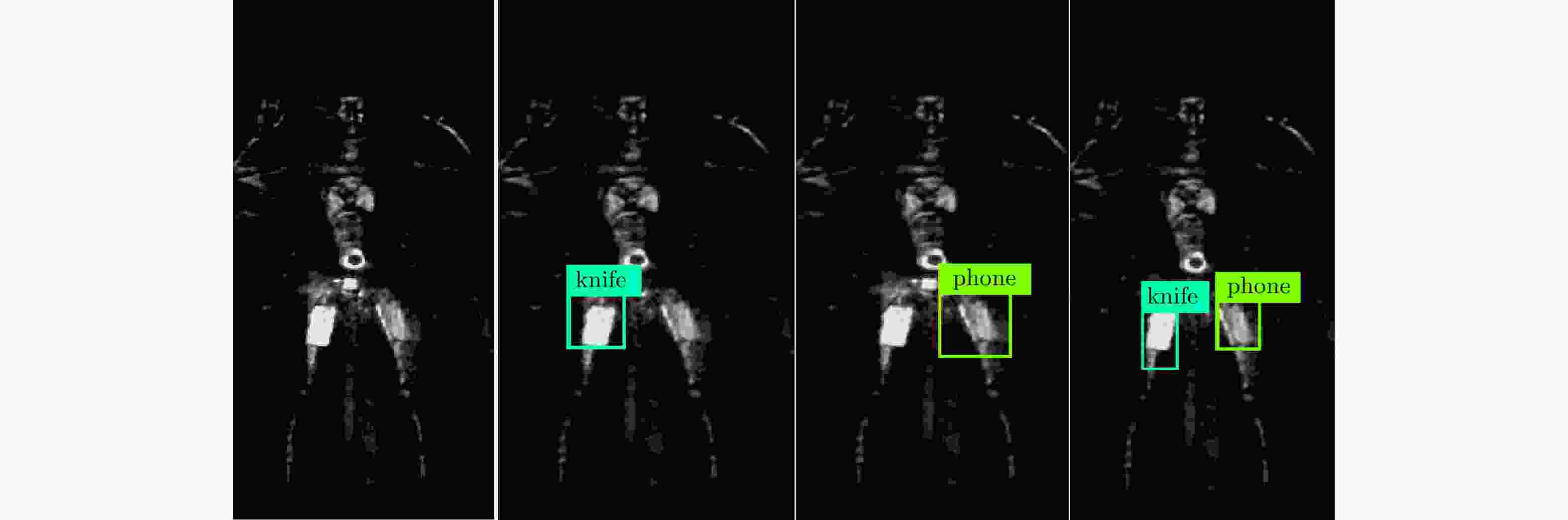
-
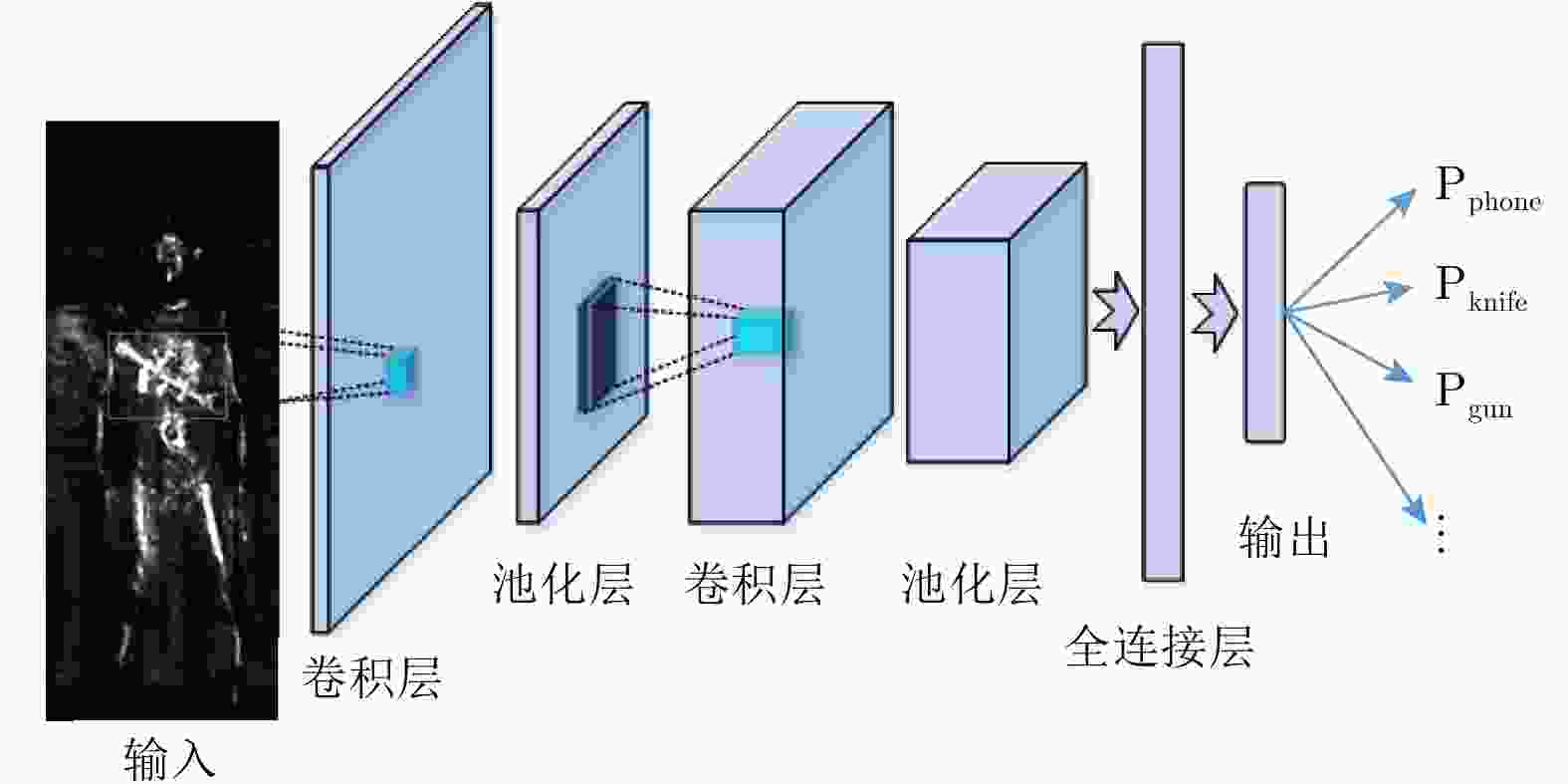
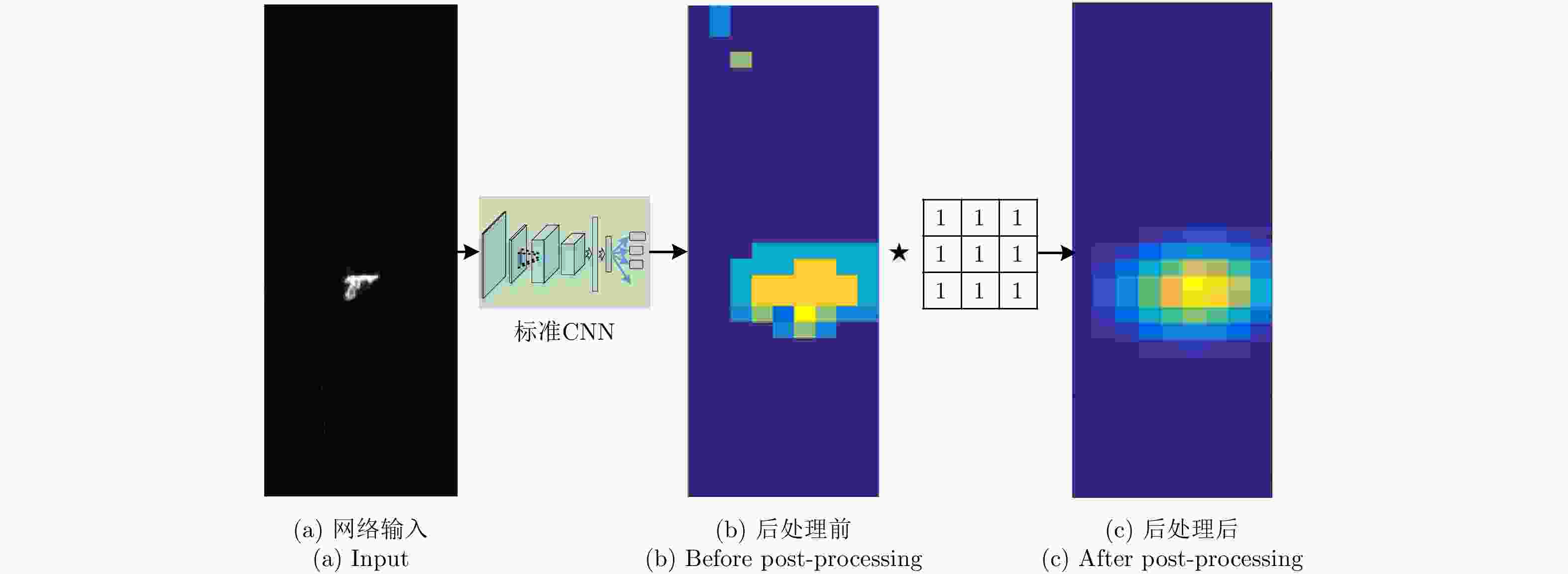
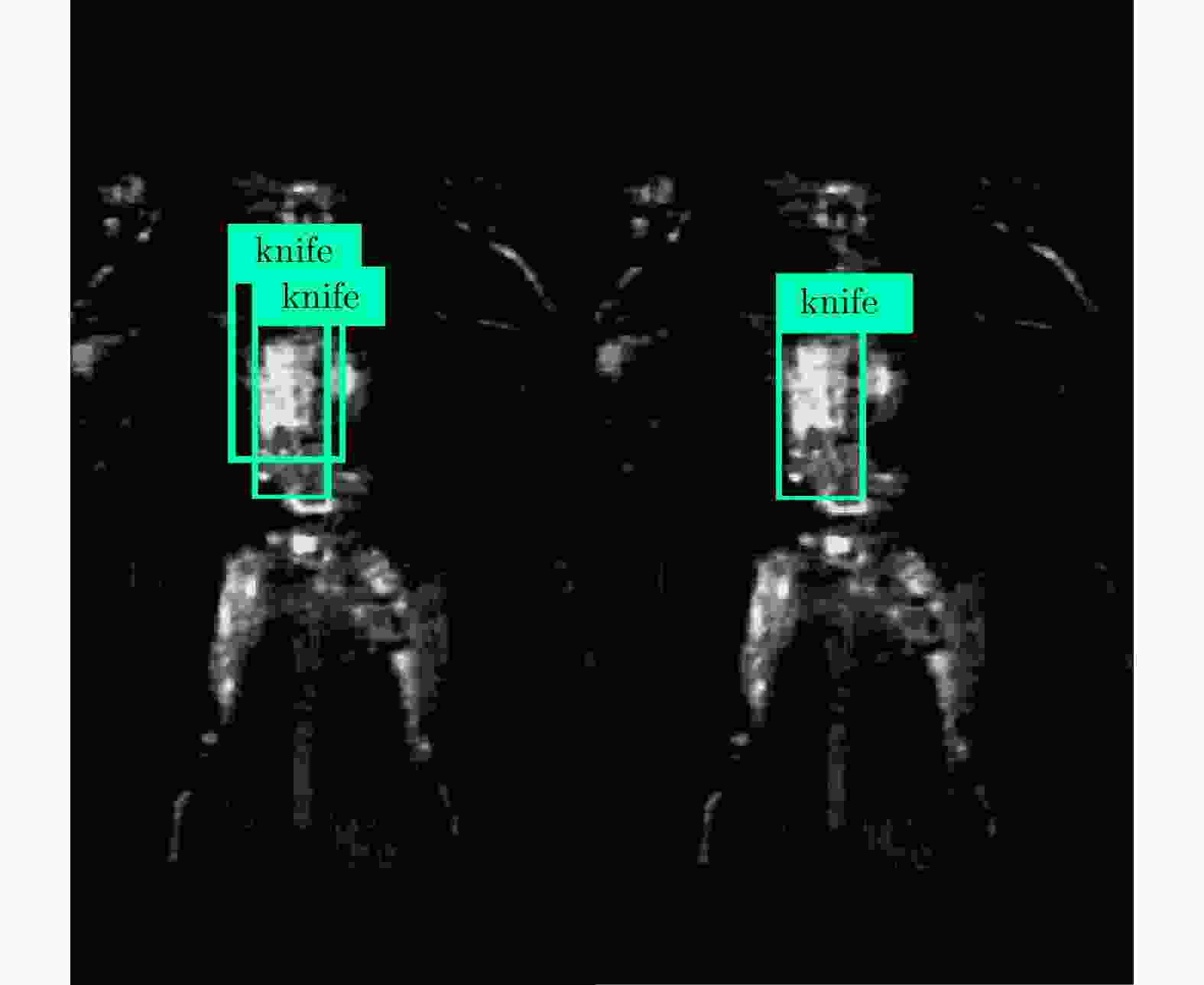
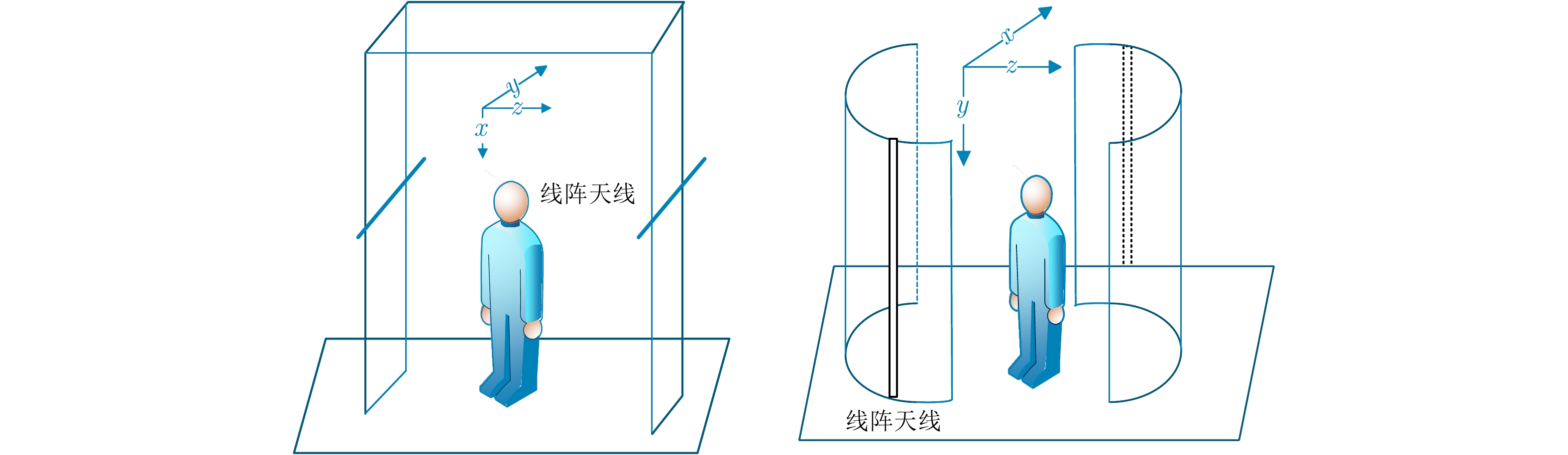
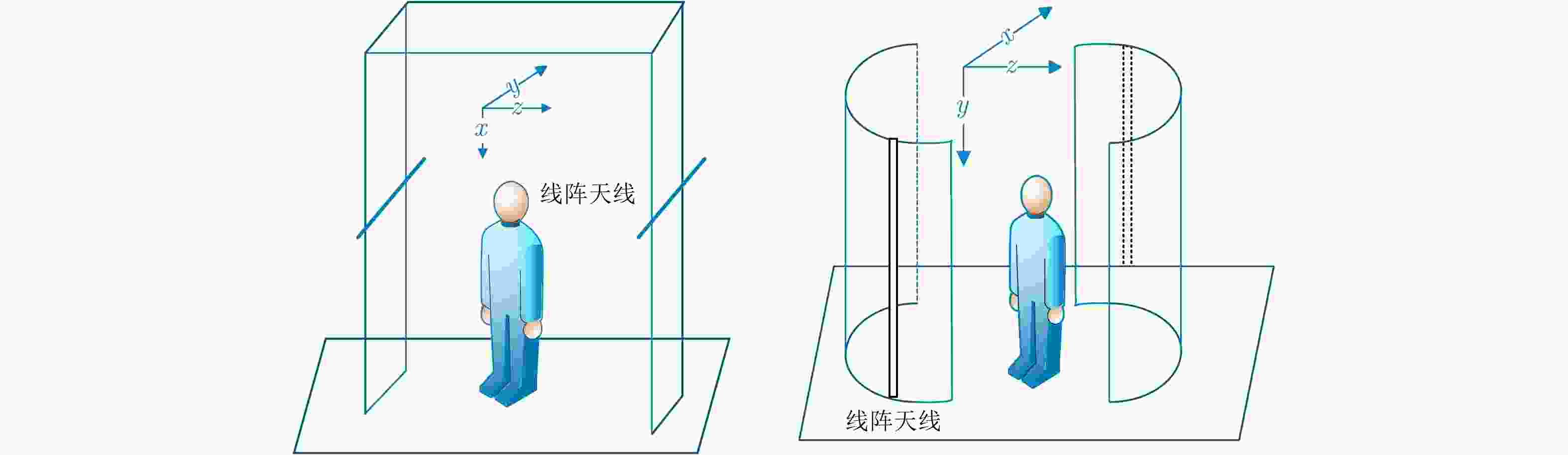
摘要: 主动式毫米波阵列3维成像系统是人体安检成像系统的研究热点,该文对主动式毫米波阵列3维系统工作模式、信号模型和成像算法进行了介绍,并将深度学习中的卷积神经网络(CNN)热图检测方法和边框回归检测技术应用于人体安检成像异物检测。研究表明,基于热图的检测方法和基于YOLO的检测方法均可实现异物检测。基于热图的检测方法网络结构简单、易训练,但由于需要遍历整幅待检测图像,运算时间长,且生成的检测框尺寸固定,无法适应异物尺寸变化。基于YOLO的检测算法网络结构复杂、训练耗时长,但该方法在检测速度与检测框精度上优势明显,更利于机场安检等对实时性要求较高的检测应用。Abstract: Active mm-wave linear-array 3D imaging system has become one of the active research areas in the field of imaging for human security. In this paper, the operating mode, signal model, and imaging algorithm are introduced. Deep learning algorithms, including the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with heat map and You Only Look Once (YOLO) network, were used for the object detection of human security image. The results show that the method based on heat map and YOLO can both detect foreign objects. We find that the CNN with heat map has a simple network construction and can be easily trained, but the detection process needs to traverse the whole image, which is relatively time-consuming, and the size of the detection region cannot adapt to the objects. On the contrary, though with a relatively complex construction, YOLO network has advantages in terms of detection efficiency and accuracy. Furthermore, the size of the detection region can adapt to the objects, which is more suitable for the human security imaging application.
-
表 1 YOLO网络检测结果(%)
Table 1. The YOLO network detection results (%)
类名 平均精确率(AP) gun 95.43 phone 89.86 knife 90.88 mAP 92.06 -
[1] CURRIE N C, DEMMA F J, FERRIS D D JR, et al. ARPA/NIJ/Rome laboratory concealed weapon detection program: An overview[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 2755, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition V, Orlando, USA, 1996: 492–502. [2] FARHAT N H and GUARD W R. Millimeter wave holographic imaging of concealed weapons[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1971, 59(9): 1383–1384. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1971.8441 [3] GONZALEZ-VALDES B, ALLAN G, RODRIGUEZ-VAQUEIRO Y, et al. Sparse array optimization using simulated annealing and compressed sensing for near-field millimeter wave imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(4): 1716–1722. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2290801 [4] 成彬彬, 李慧萍, 安健飞, 等. 太赫兹成像技术在站开式安检中的应用[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2015, 13(6): 843–848. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201506.0843CHENG Binbin, LI Huiping, AN Jianfei, et al. Application of terahertz imaging in standoff security inspection[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2015, 13(6): 843–848. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201506.0843 [5] 温鑫, 黄培康, 年丰, 等. 主动式毫米波近距离圆柱扫描三维成像系统[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(6): 1044–1049. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.06.05WEN Xin, HUANG Peikang, NIAN Feng, et al. Active millimeter-wave near-field cylindrical scanning three-dimensional imaging system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(6): 1044–1049. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.06.05 [6] APPLEBY R and WALLACE H B. Standoff detection of weapons and contraband in the 100 GHz to 1 THz region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(11): 2944–2956. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.908543 [7] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. [8] AHONEN T, HADID A, and PIETIKAINEN M. Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(12): 2037–2041. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.244 [9] VIOLA P and JONES M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features[C]. Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, USA, 2001: I-511–I-518. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2001.990517. [10] Kelly E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745 [11] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [12] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [13] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. [14] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91–99. [15] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [16] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [17] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [18] GOMEZ-MAQUEDA I, ALMOROX-GONZALEZ P, CALLEJERO-ANDRES C, et al. A millimeter-wave imager using an illuminating source[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2013, 14(4): 132–138. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2013.2248652 [19] 师君. 双基地SAR与线阵SAR原理及成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2009.SHI Jun. Research on principles and imaging techniques of bistatic SAR & LASAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2009. [20] ROTHE R, GUILLAUMIN M, and VAN GOOL L. Non-maximum suppression for object detection by passing messages between windows[C]. Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 2014: 290–306. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: