-
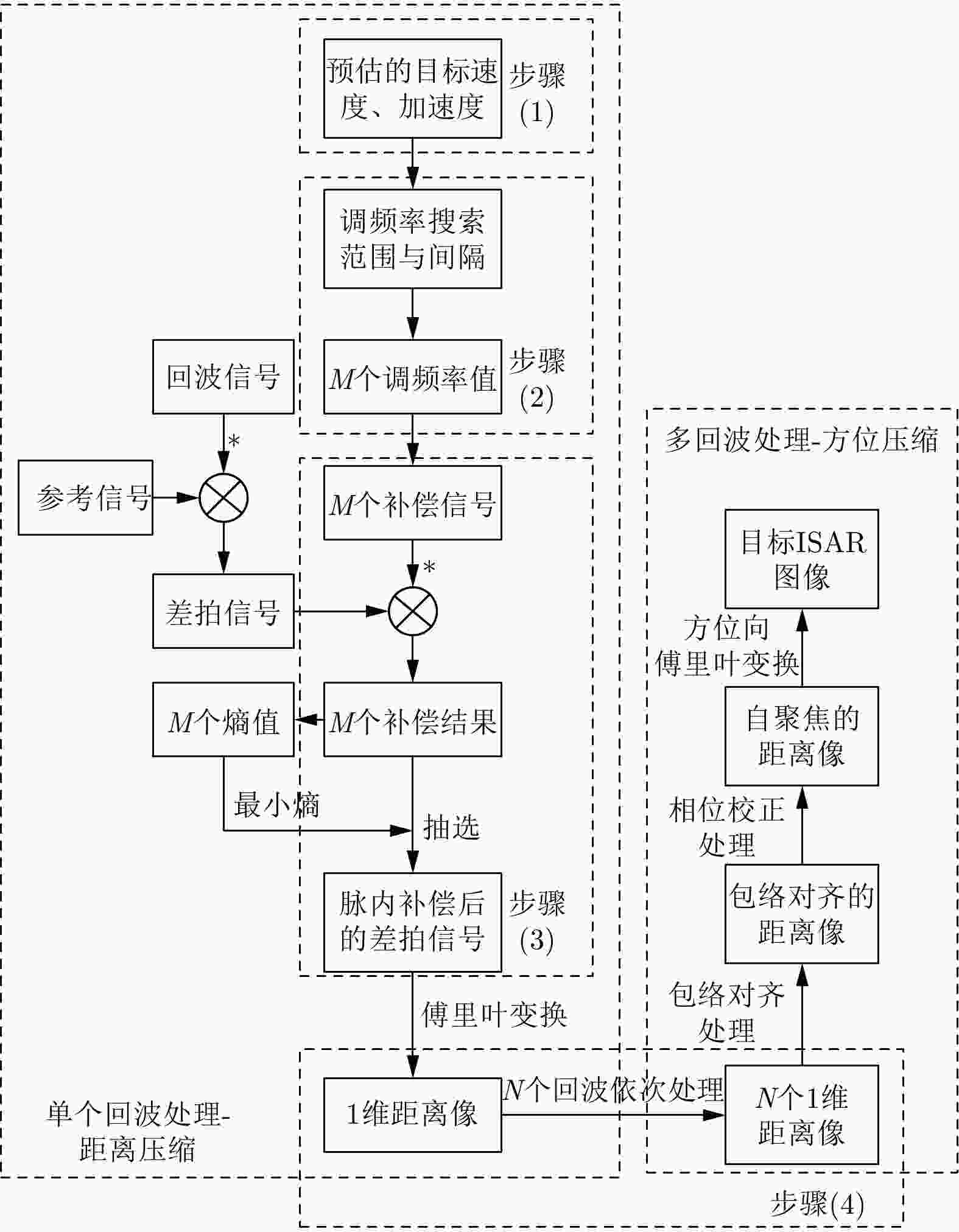
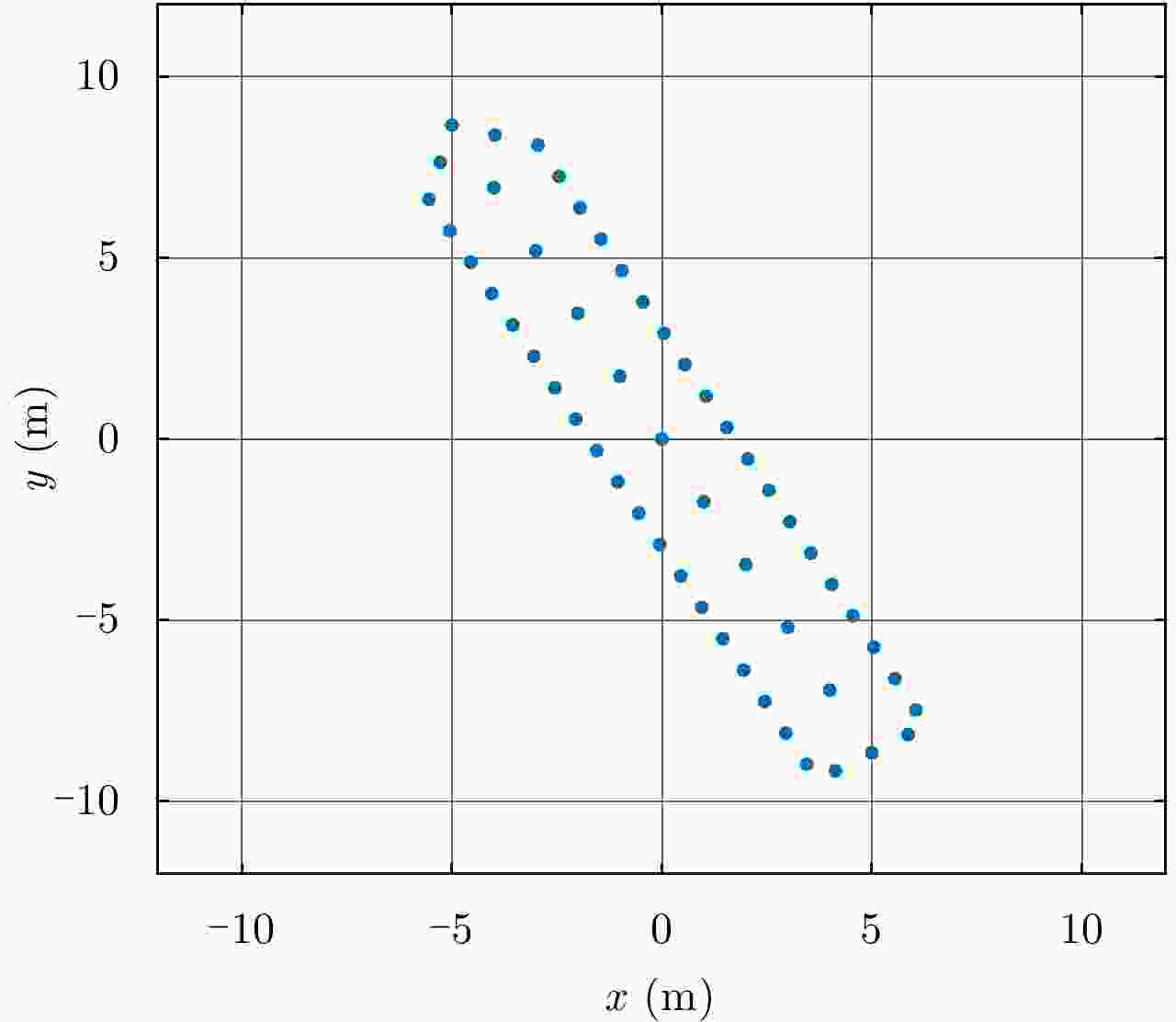
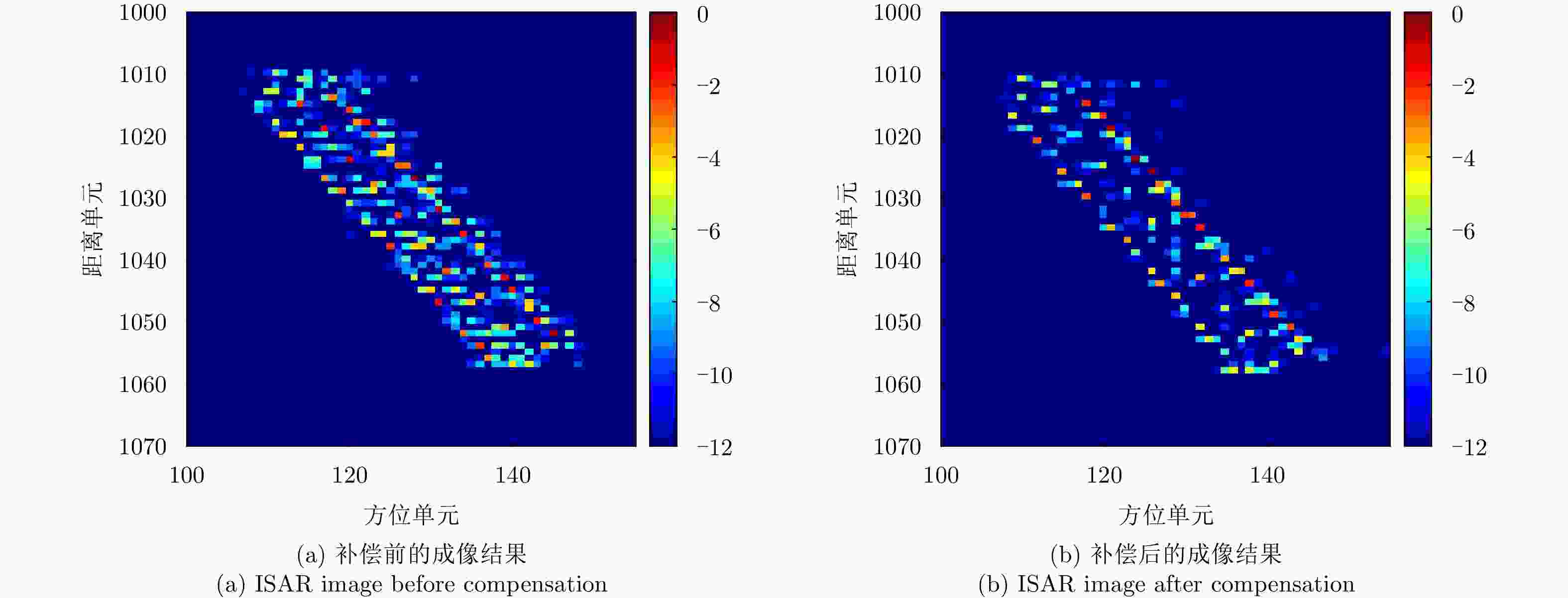
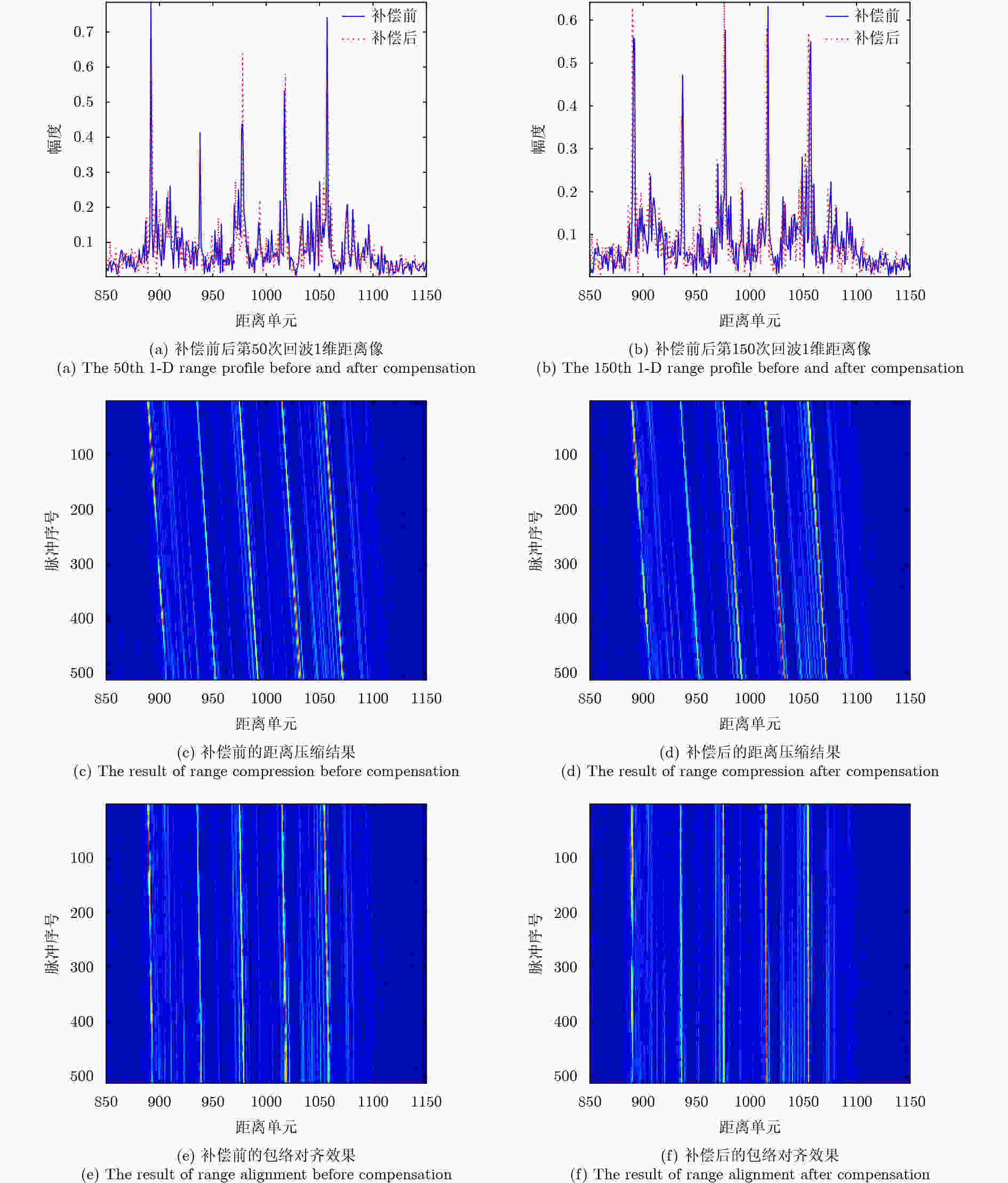
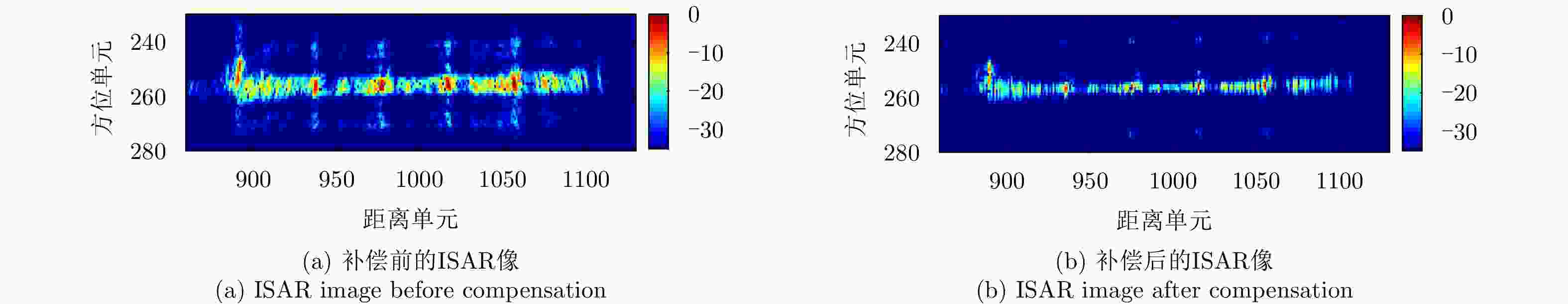
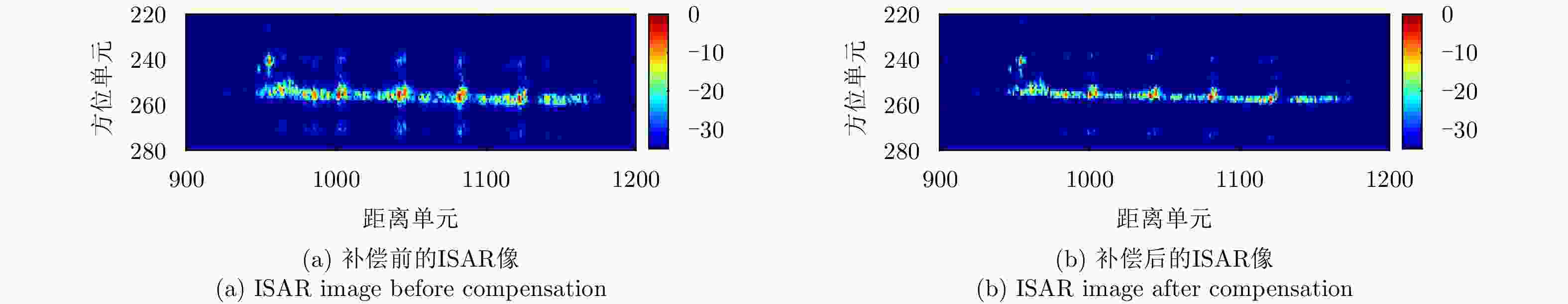
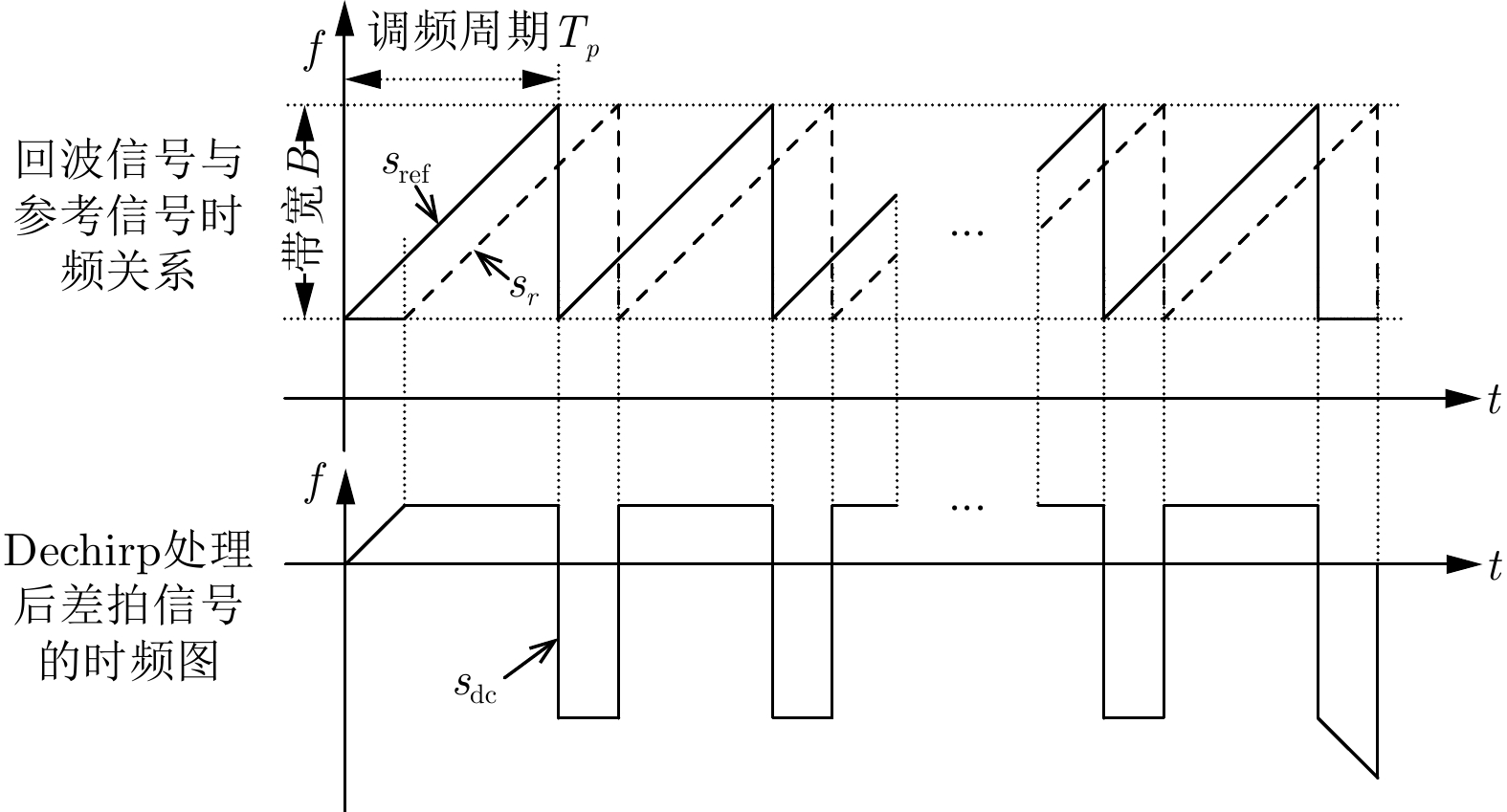
摘要: 调频连续波逆合成孔径雷达(FMCW-ISAR)具有造价低、功耗低和重量轻的优点,因此被广泛用于对各类目标成像。FMCW信号可以看作是占空比为1的脉冲信号,其脉冲宽度相对较长,在此期间内目标的运动常常不可忽略。此时,利用传统的“走-停”模式和距离-多普勒(R-D)算法得到的ISAR像将出现距离-方位2维的模糊,导致图像分辨率下降。该文针对FMCW-ISAR对舰船目标实测数据成像时出现的模糊现象进行了研究,首先建立目标的运动模型,并分析目标在调频周期内的运动分量对距离压缩结果和最终成像结果的影响,最后提出相应的脉内补偿方法以改善图像分辨率。对比补偿前后对仿真模型与实测数据的成像结果,该文所提出的脉内补偿方法能够有效抑制1维距离像的展宽,提高FMCW-ISAR的成像质量。
-
关键词:
- 调频连续波逆合成孔径雷达 /
- 舰船目标成像 /
- “走-停”模式 /
- 脉内补偿
Abstract: Given its advantages of low cost, low weight, and low power consumption, Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave-Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (FMCW-ISAR) has been widely used for imaging many kinds of targets. Since the FMCW signal can be regarded as a pulse signal whose duty ratio is one and pulse duration is relatively long, the motion of targets usually cannot be neglected. In this circumstance, the stop-go assumption is not valid, so ISAR images obtained using the traditional Range-Doppler (R-D) procedure exhibit two-dimensional blurring, which results in decreased resolution. In this paper, we investigate the blur problems of FMCW-ISAR in imaging ship targets, and construct a target motion model. Then, we analyze the influence of the in-pulse motion component in range profiles and final images. We propose a corresponding in-pulse compensation method to improve the resolution of ISAR images. A comparison with the imaging results of real measured echo data verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method in diminishing the 1-D-profile broadening and improving image quality. -
表 1 仿真雷达参数
Table 1. Parameters of radar in simulation
参数 数值 载频 X波段 调频周期(ms) 2 带宽(MHz) 400 积累时长(s) 2.56 目标速度(m/s) 50 目标加速度(m/s2) 10 -
[1] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 19–27.CHEN Xiao-long, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. [2] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.BAO Zhen, XING Meng-dao, and WANG Tong. Technology of Radar Imaging[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005. [3] CHEN Z P, ZHANG W C, and LING Q Q. A novel phase compensation method for ISAR imaging in wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 23–29. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13023 [4] 李宁, 汪玲, 张弓. 多基ISAR舰船侧视及俯视高分辨率成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 163–170. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20021LI Ning, WANG Ling, and ZHANG Gong. High-resolution side-view and top-view imaging method of ship targets using multistatic ISAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 163–170. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20021 [5] ZHANG X K, REN J W, SHAO Z L, et al. Vehicles detection experiments with Ka-band FMCW ISAR[C]. Proceedings of 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Singapore, 2017: 291–294. [6] 杨琪, 邓彬, 蒋彦雯, 等. 基于调频连续波的太赫兹频段转台成像方法研究[J]. 空间电子技术, 2013(4): 25–28, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.04.007YANG Qi, DENG Bin, JIANG Yan-wen, et al. Study of terahertz rotating platform imaging algorithm based on FMCW[J]. Space Electronic Technology, 2013(4): 25–28, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7135.2013.04.007 [7] SU F L, SU Y, and GAO J J. Range Doppler imaging for LFMCW ISAR based on azimuth interpolation[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 11th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2012: 2048–2052. [8] SU F L, YANG H X, and GAO J J. Imaging for inverse synthetic aperture radar with linear frequency modulation continuous wave signal[C]. Proceedings of the 2012 5th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Chongqing, China, 2012: 1817–1821. [9] CHANG W, LI Z H, JIN K, et al. Long-distance imaging with frequency modulation continuous wave and inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(6): 653–659. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0326 [10] CHANG W, LI Z, JIN K, et al. Imaging of space targets in FMCW-ISAR[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–4. DOI: 10.1049/CP.2013.0214. [11] 朱小鹏, 张群, 罗迎, 等. 基于调频连续波的双基逆合成孔径雷达研究[J]. 电波科学学报, 2011, 26(4): 771–776.ZHU Xiao-peng, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. ISAR imaging analysis of bi-static FMCW radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2011, 26(4): 771–776. [12] 常雯, 李增辉, 杨健. 基于迭代Radon-Wigner变换的FMCW-ISAR目标速度估计及速度补偿[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 54(4): 464–468.CHANG Wen, LI Zeng-hui, and YANG Jian. Velocity estimation and compensation in FMCW-ISAR based on the iterative Radon-Wigner transform[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology) , 2014, 54(4): 464–468. [13] GIUSTI and MARTORELLA M. Range Doppler and image autofocusing for FMCW inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2807–2823. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034666 [14] 张昆帆, 马德宝, 王丰, 等. 一种新的一维距离像补偿方法[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2011, 12(4): 452–457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2011.04.015ZHANG Kun-fan, MA De-bao, WANG Feng, et al. New method of compensation for profile[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2011, 12(4): 452–457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0673.2011.04.015 [15] 刘磊. 逆合成孔径雷达二维及三维成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.LIU Lei. Study of two-dimensional and three-dimensional inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging methods[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2016. [16] 唐鹏飞, 林钱强, 袁斌, 等. 基于积分二次相位函数和分数阶Fourier变换的多分量LFM信号参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2012, 28(7): 926–931. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.07.003TANG Peng-fei, LIN Qian-qiang, YUAN Bin, et al. Parameter estimation of multi-component LFM signals using integrated quadratic phase function and fractional Fourier transform[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 28(7): 926–931. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.07.003 [17] 涂志宇. 高速运动目标逆合成孔径雷达运动补偿研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京理工大学, 2004.TU Zhi-yu. Research on motion compensation of inverse synthetic aperture radar for high-speed-moving targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2004. [18] 刘永坦. 雷达成像技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 1999: 187–194.LIU Yong-tan. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1999: 187–194. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: