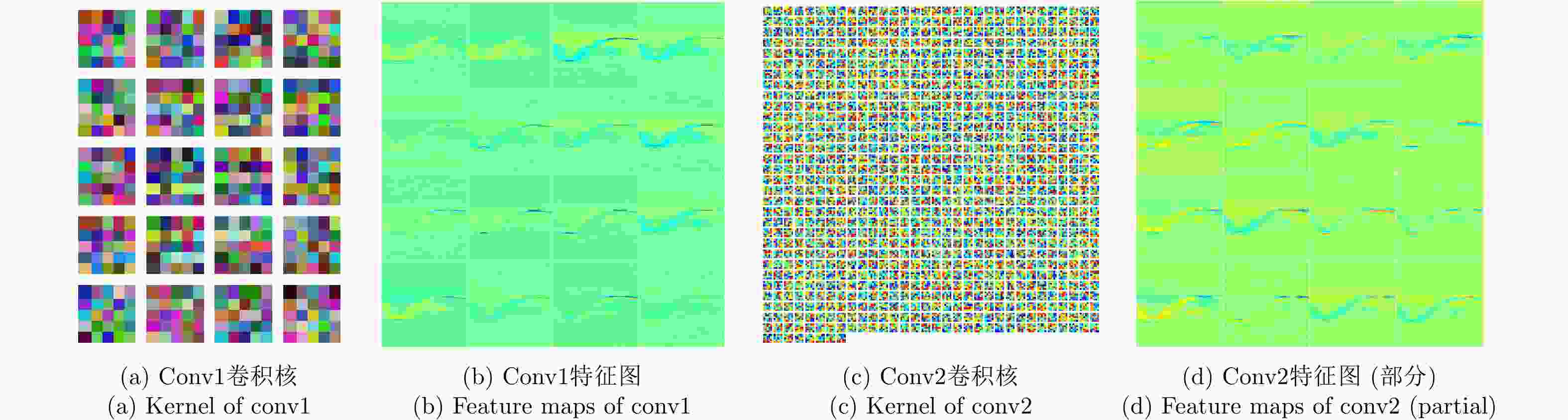
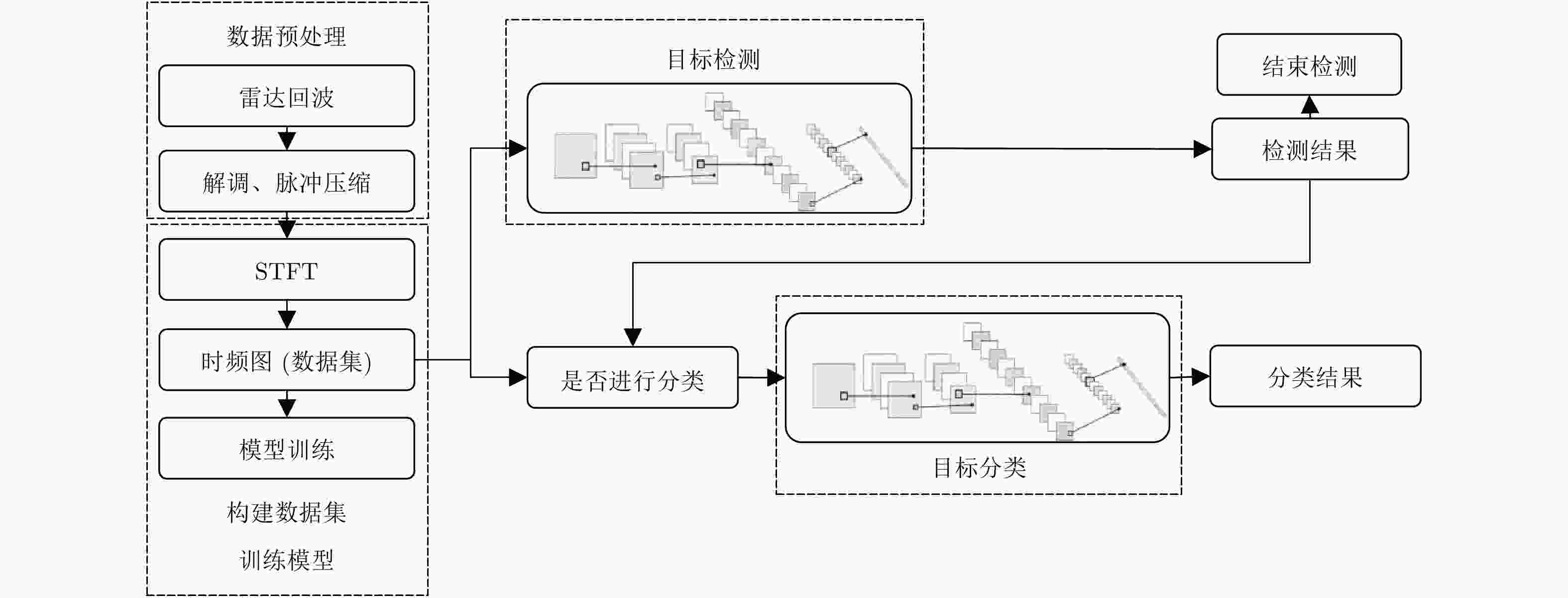
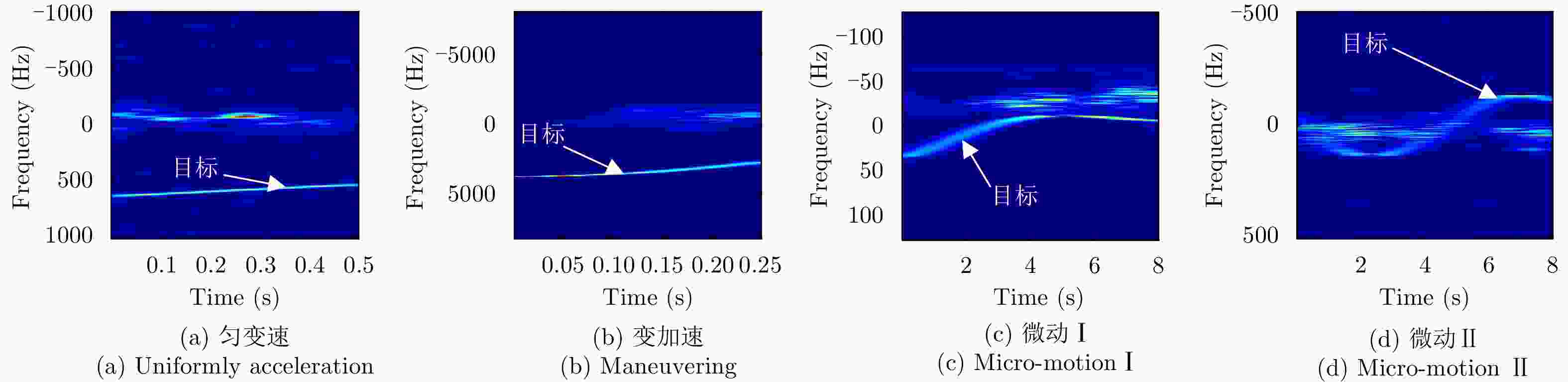
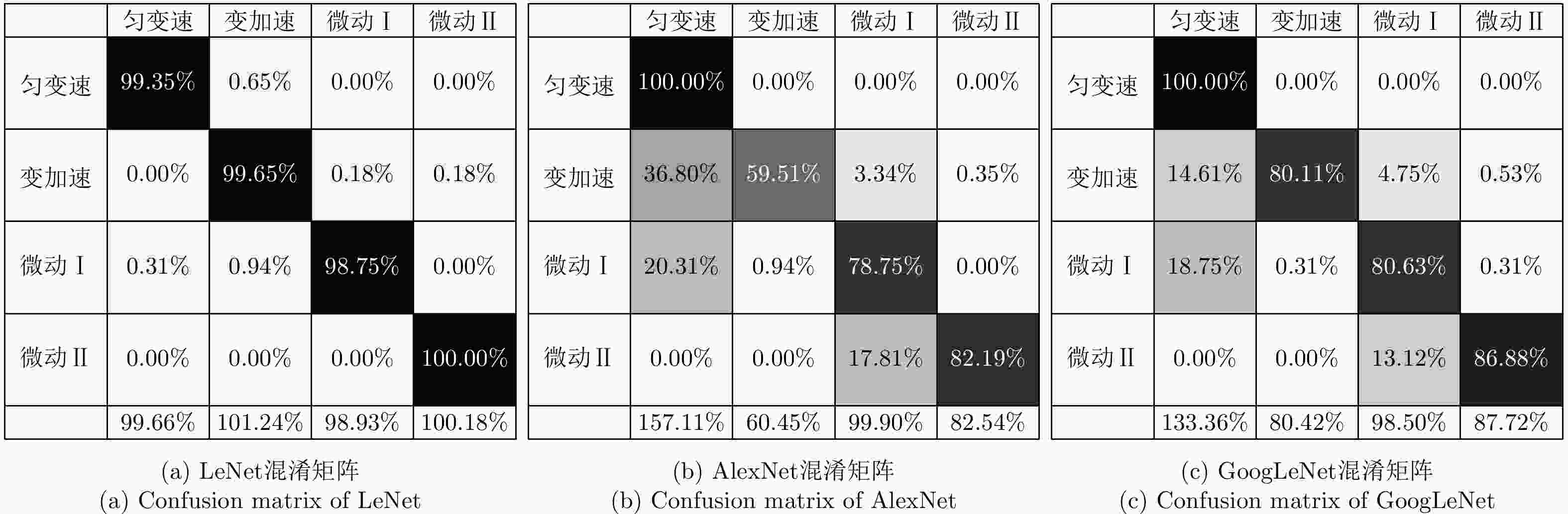
Detection and Classification of Maritime Target with Micro-motion Based on CNNs
-
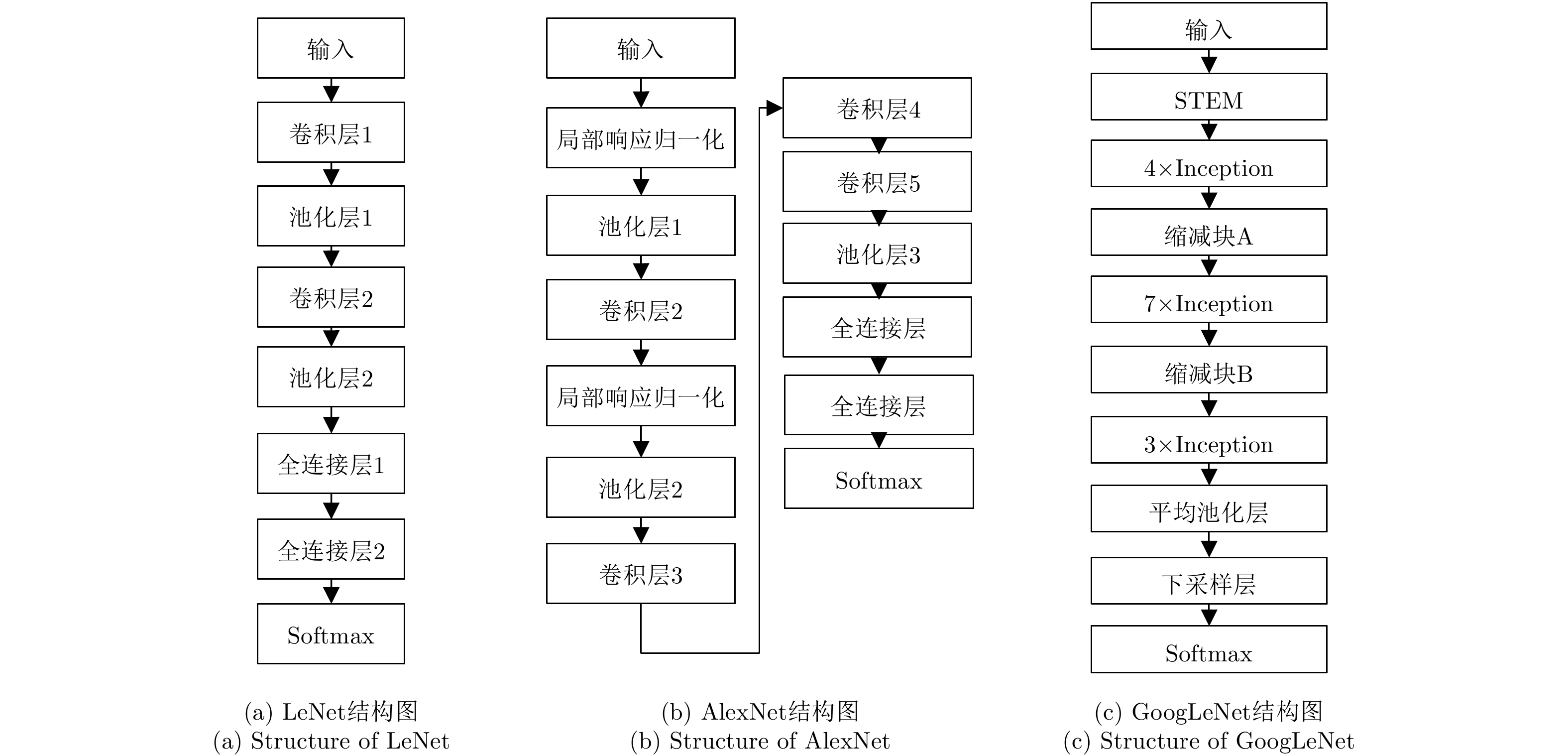
摘要: 该文利用深度学习的高维特征泛化学习能力,将卷积神经网络(CNN)用于海上目标微多普勒的检测和分类。首先,在海面微动目标模型的基础上,在实测海杂波背景中分别构建4种类型微动信号的2维时频图,并作为训练和测试数据集;然后,分别采用LeNet, AlexNet和GoogLeNet 3种CNN模型进行二元检测和多种微动类型分类,并进行比较,研究信杂比对检测和分类性能的影响。最后,与传统的支持向量机方法进行比较,结果表明,所提方法能够智能学习微动特征,具有更好的检测和分类性能,可为杂波背景下的雷达动目标检测和识别提供新的技术途径。Abstract: In this paper, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are used to detect and classify micro-Doppler effects of maritime targets by using generalized learning ability for high-dimensional features. Based on the micro-motion model of maritime targets, two-dimensional time-frequency maps of four types of micro-motion signals are constructed in the measured sea clutter background. These maps were used as training and test datasets. Furthermore, three types of CNN models, i.e., LeNet, AlexNet, and GoogleNet, are used in binary detection and multiple micro-motion classifications. The effects of signal-to-noise ratio on detection and classification performance are also studied. Compared with the traditional support vector machine method, the proposed method can learn the micro-motion features intelligently, and has performed better in detection and classification. Thus, this study can provide a new technical approach for radar target detection and recognition under a cluttered background.
-
表 1 微动参数设置
Table 1. Configuration of micro-motion parameters
运动类型 初速度
(m/s)加速度
(m/s2)急动度
(m/s3)采样点数 运动类型 角速度 微动周期(s) 采样点数 匀加速 [5, 15] [–16, 16] – 211 Hz, 0.50 s 微动Ⅰ [16] $\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{x{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.34, 0.42] rad/s
$\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{y{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.15, 0.17] rad/s
$\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{z{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.07, 0.09] rad/s${T_x}$=26.4
${T_y}$=11.2
${T_z}$=33.028 Hz, 8 s 非匀变速 [50, 300] [–160, 160] [–160, 160] 214 Hz, 0.25 s 微动Ⅱ [16] $\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{x{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.61, 0.65] rad/s
$\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{y{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.95, 1.07] rad/s
$\left| {{{\bar \omega }_{z{\rm m}}}} \right|$=[0.52, 0.56] rad/s${T_x}$=12.2
${T_y}$=6.7
${T_z}$=14.2210 Hz, 8 s 表 2 CNN模型训练时长
Table 2. Training time of CNN models
模型 目标检测模型 目标分类模型 LeNet AlexNet GoogLeNet LeNet AlexNet GoogLeNet 训练用时(min) 68.00 37.52 175.00 27.92 38.40 54.43 表 3 不同模型目标检测结果
Table 3. Results of target detection of different models
模型 LeNet AlexNet GoogLeNet 虚警概率 1.24% 0.04% 0.24% 检测概率 92.28% 84.44% 90.94% 仿真时间(min) 41.92 57.15 43.77 表 4 基于CNN和SVM的海面目标检测与分类结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of maritime targets detection and classification results based on CNN and SVM
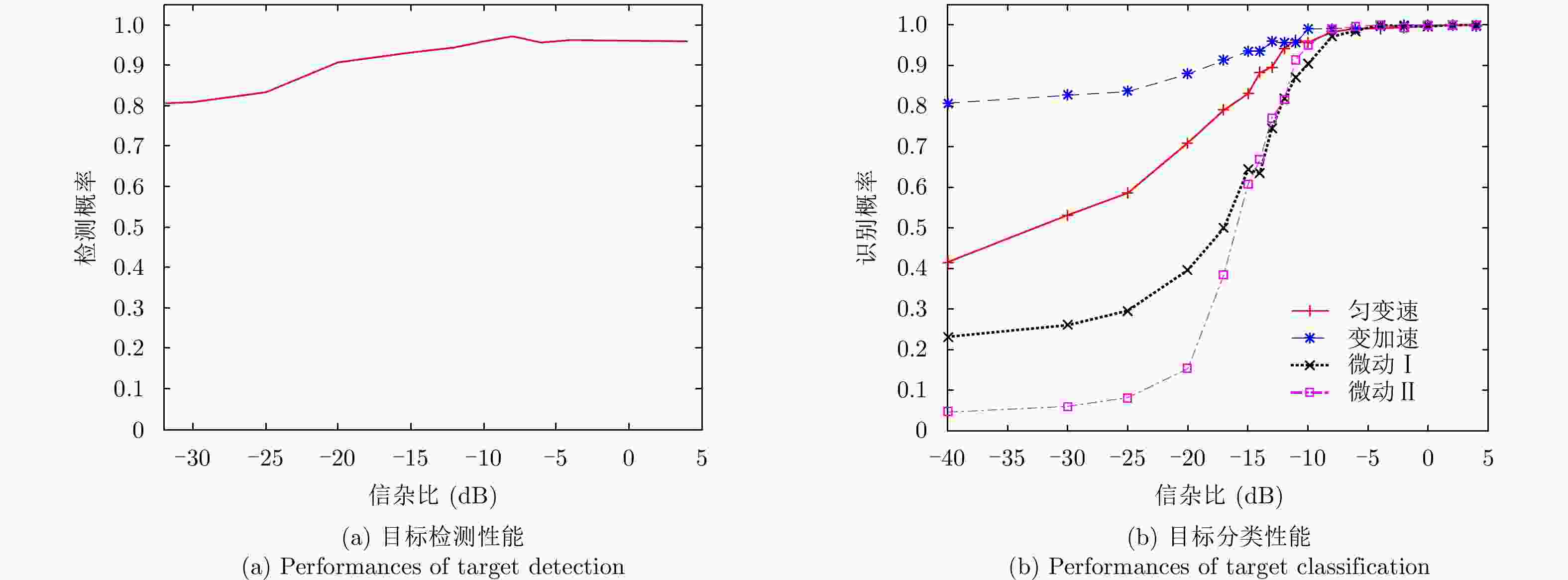
分类方法 虚警概率 检测概率(%) 识别概率(SCR=–4 dB)(%) SCR=4 dB SCR=–4 dB SCR=–12 dB SCR=–20 dB 匀变速 变加速 微动Ⅰ 微动Ⅱ CNN 0.0290 95.80 96.30 94.11 90.62 100.00 100.00 99.65 100.00 SVM 0.2207 80.52 79.90 77.81 77.31 84.30 84.46 73.56 94.25 -
[1] Darzikolaei M A, Ebrahimzade A, and Gholami E. Classification of radar clutters with artificial neural network[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation, Tehran, Iran, 2015: 577–581. [2] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友. 微多普勒理论在海面目标检测中的应用及展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102Chen Xiao-long, Guan Jian, and He You. Applications and prospect of micro-motion theory in the detection of sea surface target[J].Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102 [3] 罗迎, 张群, 王国正, 等. 基于复图像OMP分解的宽带雷达微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 361–369. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20065Luo Ying, Zhang Qun, Wang Guo-zheng, et al. Micro-motion signature extraction method for wideband radar based on complex image OMP decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 361–369. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20065 [4] Chen X L, Guan J, Bao Z H, et al. Detection and extraction of target with micromotion in spiky sea clutter via short-time fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1002–1018. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2246574 [5] Chen X L, Guan J, Li X Y, et al. Effective coherent integration method for marine target with micromotion via phase differentiation and radon-Lv’s distribution[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1284–1295. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0100 [6] Wagner S A. SAR ATR by a combination of convolutional neural network and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(6): 2861–2872. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2016.160061 [7] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. DOI: 10.12000/JR16037Tian Zhuang-zhuang, Zhan Rong-hui, Hu Jie-min, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. DOI: 10.12000/JR16037 [8] Kim Y and Toomajian B. Hand gesture recognition using micro-Doppler signatures with convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 7125–7130. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2617282 [9] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. DOI: 10.12000/JR18040Wang Jun, Zheng Tong, Lei Peng, et al. Survey of study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. DOI: 10.12000/JR18040 [10] 徐彬, 陈渤, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于注意循环神经网络模型的雷达高分辨率距离像目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 2988–2995. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161034Xu Bin, Chen Bo, Liu Hong-wei, et al. Attention-based recurrent neural network model for radar high-resolution range profile target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 2988–2995. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161034 [11] 王星, 周一鹏, 周冬青, 等. 基于深度置信网络和双谱对角切片的低截获概率雷达信号识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2972–2976. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160031Wang Xing, Zhou Yi-peng, Zhou Dong-qing, et al. Research on low probability of intercept radar signal recognition using deep belief network and bispectra diagonal slice[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2972–2976. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160031 [12] 徐真, 王宇, 李宁, 等. 一种基于CNN的SAR图像变化检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. DOI: 10.12000/JR17075Xu Zhen, Wang Robert, Li Ning, et al. A novel approach to change detection in SAR images with CNN classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. DOI: 10.12000/JR17075 [13] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. DOI: 10.12000/JR16130Xu Feng, Wang Hai-peng, and Jin Ya-qiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. DOI: 10.12000/JR16130 [14] 陈小龙, 董云龙, 李秀友, 等. 海面刚体目标微动特征建模及特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR15079Chen Xiao-long, Dong Yun-long, Li Xiu-you, et al. Modeling of micromotion and analysis of properties of rigid marine targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR15079 [15] Prusa J D and Khoshgoftaar T M. Improving deep neural network design with new text data representations[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2017, 4: 7. DOI: 10.1186/s40537-017-0065-8 [16] 高建军. 多径和海杂波干扰下的舰船ISAR成像及横向定标[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2010.Gao Jian-jun. ISAR ship imaging and cross-range scaling with multipath and sea clutter interference[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: