Terrain Classification of Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Based on Deep Learning and Conditional Random Field Model
-
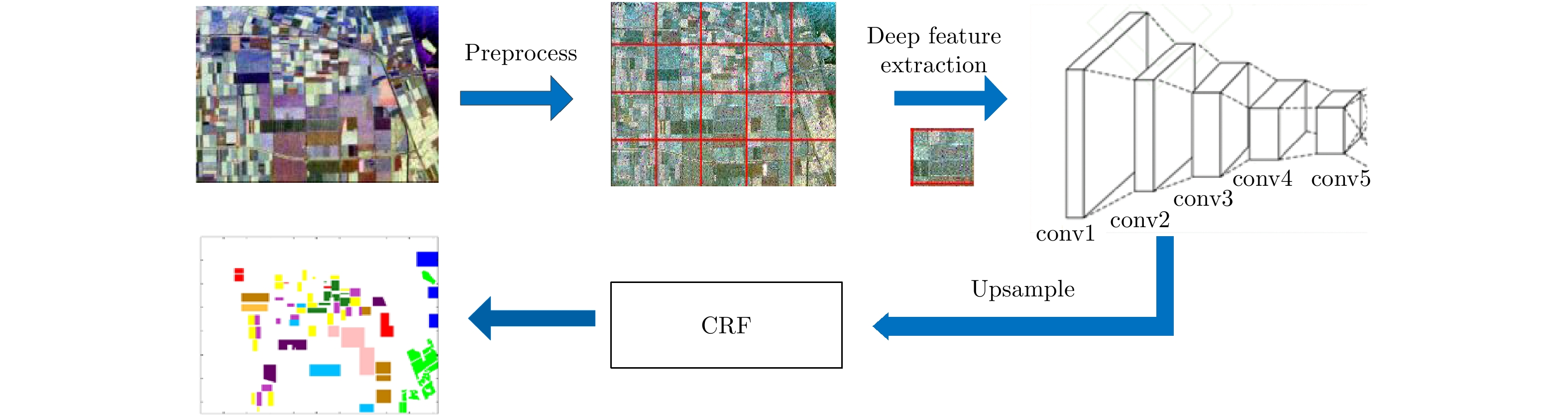
摘要: 近年来,极化合成孔径雷达(PolSAR)图像地物分类得到了深入研究。传统的PolSAR图像地物分类方法采用的特征往往需要针对具体问题进行设计,特征表征性不强。因此,该文提出一种基于卷积神经网络(CNN)和条件随机场(CRF)模型的PolSAR图像地物分类方法。利用预训练好的实现图像分类任务的卷积神经网络模型(VGG-Net-16)提取表征能力更强的图像特征,再通过CRF模型对多特征及上下文信息的有效利用来实现图像的地物分类。实验结果表明,与3种利用传统经典特征的方法相比,该方法能够提取更有效的特征,取得了更高的总体分类精度和Kappa系数。Abstract: In recent years, Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) image classification has been investigated extensively. The traditional PolSAR image terrain classification methods result in a weak feature representation. To overcome this limitation, this study aims to propose a terrain classification method based on deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Conditional Random Field (CRF). The pre-trained VGG-Net-16 model was used to extract more powerful image features, and then the terrain from the images was classified through the efficient use of multiple features and context information by conditional random fields. The experimental results show that the proposed method can extract more features effectively in comparison with the three methods using traditional classical features and it can also achieve a higher overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient.
-
表 1 传统方法中用到的特征
Table 1. The features used in the traditional methods
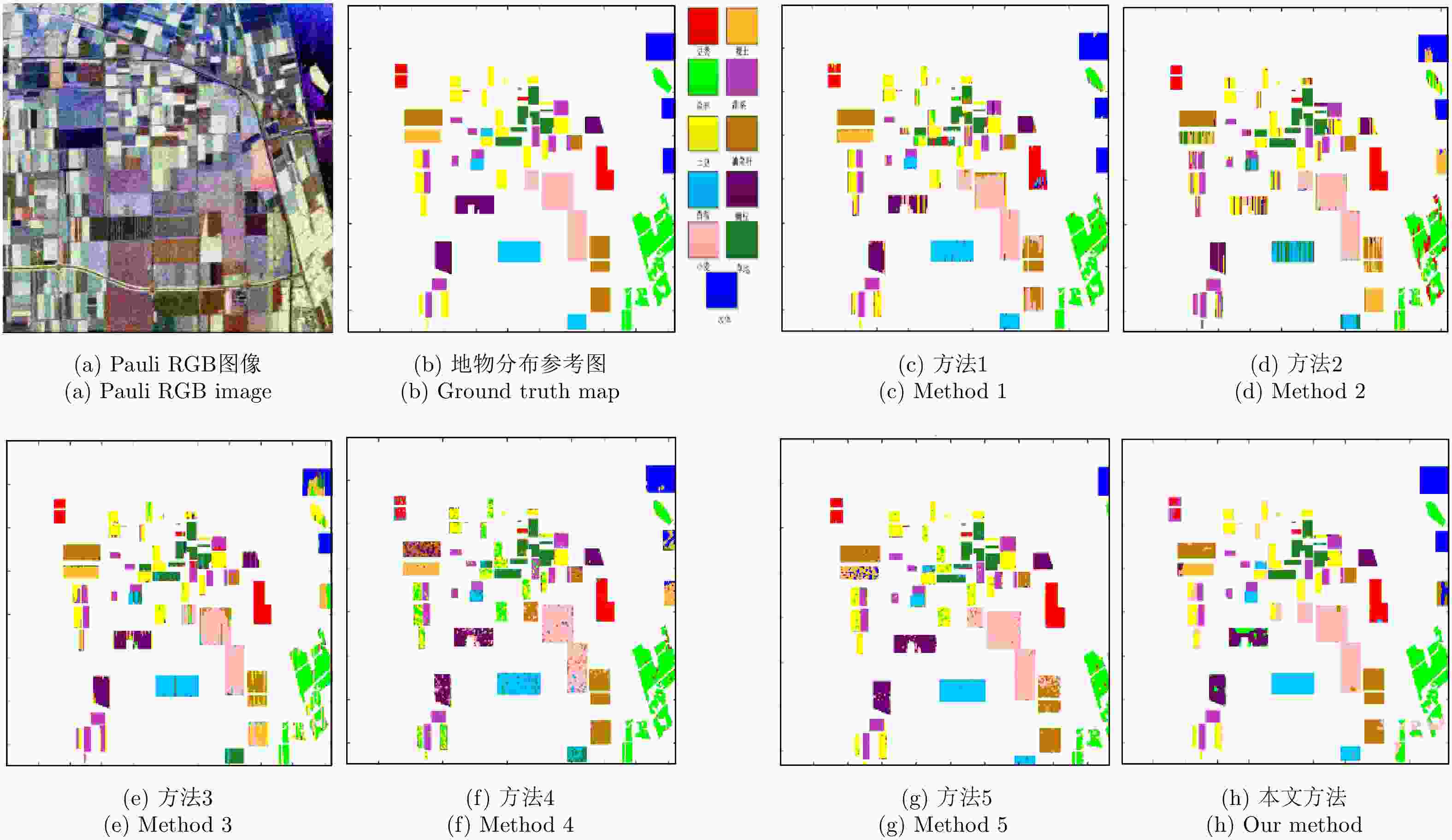
Cloude分解 Freeman分解 协方差矩阵对角线 $H,\alpha ,A,{\lambda _{1}},{\lambda _{{2}}},{\lambda _{{3}}}$ Ps, Pd, Pv C11, C22, C33 表 2 Flevoland数据分类精度
Table 2. The classification accuracy of Flevoland data
类别 方法1 方法2 方法3 方法4 方法5 本文方法 豆类 0.971 0.833 0.967 0.863 0.920 0.808 森林 0.759 0.940 0.733 0.943 0.945 0.868 土豆 0.680 0.840 0.821 0.578 0.872 0.808 苜蓿 0.609 0.892 0.719 0.781 0.932 0.990 小麦 0.934 0.881 0.864 0.792 0.936 0.981 裸地 0.514 0.871 0.903 0.980 0.998 0.899 甜菜 0.913 0.903 0.895 0.905 0.897 0.978 油菜籽 0.572 0.782 0.627 0.758 0.934 0.964 豌豆 0.589 0.821 0.820 0.801 0.901 0.854 草地 0.962 0.774 0.838 0.912 0.802 0.968 水体 0.701 0.970 0.526 0.703 0.988 0.888 总精度 0.751 0.870 0.778 0.797 0.933 0.905 Kappa系数 0.720 0.854 0.752 0.774 0.911 0.890 训练(s) 798 771 877 1211 7066 1052 测试(s) 2.9 2.7 3.0 4.1 8.4 3.8 表 3 Oberpfaffenhofen数据分类精度
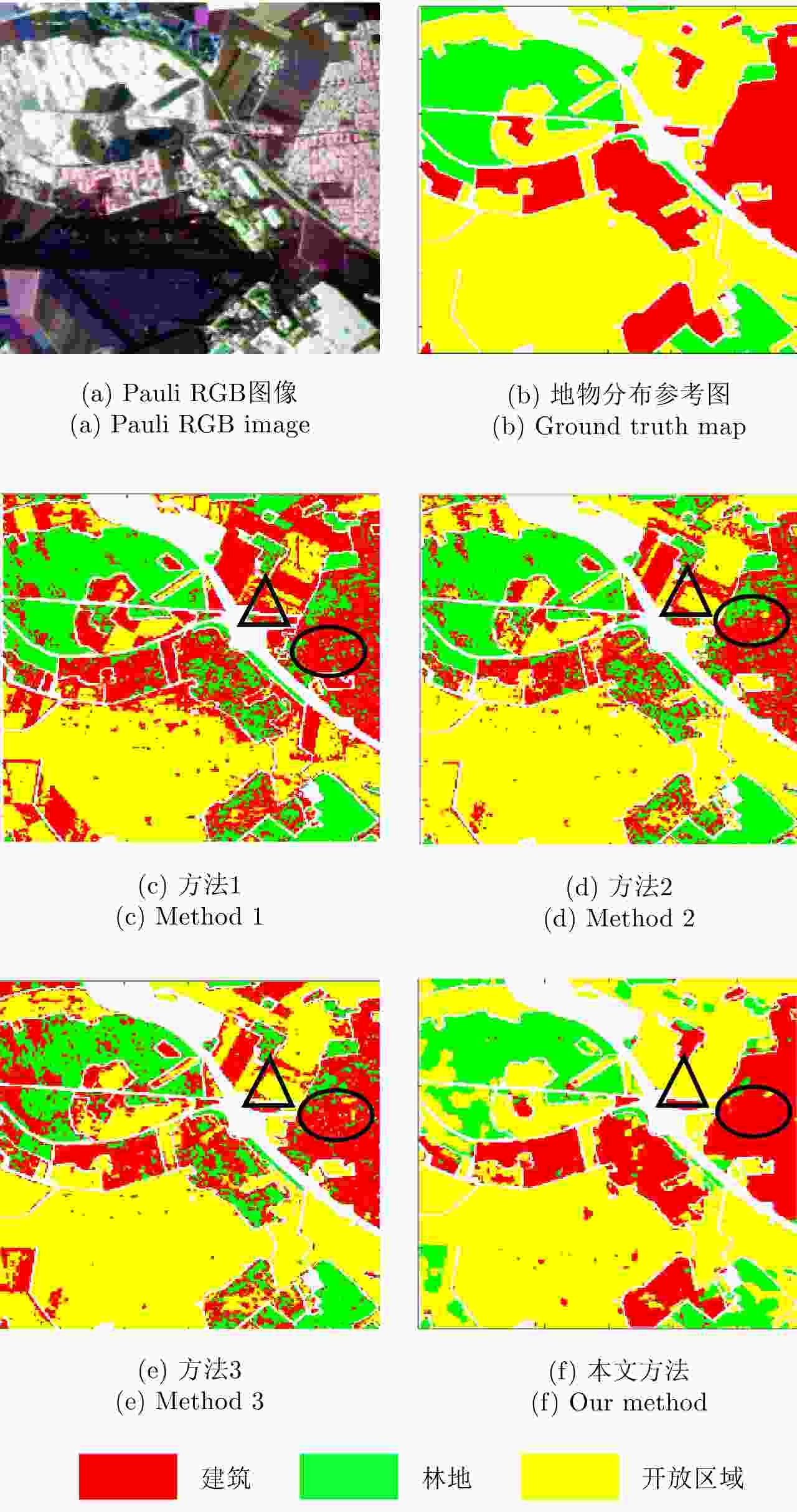
Table 3. The classification accuracy of Oberpfaffenhofen data
类别 方法1 方法2 方法3 本文方法 建筑区域 0.696 0.645 0.712 0.903 林地 0.895 0.896 0.700 0.777 开放区域 0.622 0.843 0.874 0.947 总精度 0.691 0.804 0.800 0.903 Kappa系数 0.529 0.680 0.668 0.834 -
[1] NOVAK L M and BURL M C. Optimal speckle reduction in polarimetric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1990, 26(2): 293–305. doi: 10.1109/7.53442 [2] RANSON K J, SUN G, WEISHAMPEL J F, et al. An evaluation of AIRSAR and SIR-C/XSAR images for northern forest ecological studies in Maine, USA[C]. Proceedings of 1995 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’95. Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Firenze, Italy, 1995: 994–996. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1995.521118. [3] YANG W, ZHANG X, CHEN L J, et al. Semantic segmentation of polarimetric SAR imagery using conditional random fields[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2010: 1593–1596. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2010.5652378. [4] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [5] ZHAO L W, ZHOU X G, JIANG Y M, et al. Iterative classification of polarimetric SAR image based on the freeman decomposition and scattering entropy[C]. Proceedings of the 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Huangshan, China, 2007: 473–476. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2007.4418653. [6] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, and KWOK R. Classification of multi-look polarimetric SAR imagery based on complex wishart distribution[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1994, 15(11): 2299–2311. doi: 10.1080/01431169408954244 [7] BEAULIEU J M and TOUZI R. Segmentation of textured polarimetric SAR scenes by likelihood approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(10): 2063–2072. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2004.835302 [8] WU Y H, JI K F, YU W X, et al. Region-based classification of polarimetric SAR images using wishart MRF[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 668–672. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2002263 [9] 周晓光, 匡纲要, 万建伟. 极化SAR图像分类综述[J]. 信号处理, 2008, 24(5): 806–812. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.05.023ZHOU Xiao-guang, KUANG Gang-yao, and WAN Jian-wei. A review of polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 24(5): 806–812. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.05.023 [10] 胡涛, 李卫华, 秦先祥, 等. 基于深度CRF模型的图像语义分割方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 19(5): 52–57.HU Tao, LI Wei-hua, QIN Xian-xiang, et al. An image semantic segmentation based on deep CRF model[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition) , 2018, 19(5): 52–57. [11] XIE W, JIAO L C, HOU B, et al. POLSAR image classification via wishart-AE model or wishart-CAE model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3604–3615. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2698076 [12] ZHAO Z Q, JIAO L C, ZHAO J Q, et al. Discriminant deep belief network for high-resolution SAR image classification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 686–701. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.028 [13] GAO F, HUANG T, WANG J, et al. Dual-branch deep convolution neural network for polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(5): 447. doi: 10.3390/app7050447 [14] ZHOU Y, WANG H P, XU F, et al. Polarimetric SAR image classification using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1935–1939. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2618840 [15] ZHANG Z M, WANG H P, XU F, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 [16] WANG L, XU X, DONG H, et al. Multi-pixel simultaneous classification of PolSAR image using convolutional neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 769. doi: 10.3390/s18030769 [17] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. doi: 10.1145/3065386. [18] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al.. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. [19] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014. [20] RAZAVIAN A S, AZIZPOUR H, SULLIVAN J, et al. CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014: 512–519. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2014.131. [21] MIKA S, SCHÖLKOPF B, SMOLA A, et al.. Kernel PCA and de-noising in feature spaces[C]. Proceedings of 1998 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems II, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999: 536–542. [22] LAFFERTY J D, MCCALLUM A, and PEREIRA F C N. Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Machine Learning, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001: 282–289. [23] LI S Z. Markov Random Field Modeling in Computer Vision[M]. New York: Springer, 1995. [24] PLATT J C. Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines and comparisons to regularized likelihood methods[C]. Proceedings of the Advances in large Margin Classifiers, Cambrige, MA, USA, 1999: 61–74. [25] DOMKE J. Learning graphical model parameters with approximate marginal inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(10): 2454–2467. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.31 [26] VEDALDI A and LENC K. MatConvNet: Convolutional neural networks for MATLAB[C]. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 689–692. doi: 10.1145/2733373.2807412. [27] 韩萍, 韩宾宾. 基于典型散射差异指数的PolSAR图像Lee滤波[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(2): 287–294.HAN Ping and HAN Bin-bin. Lee filter of PolSAR image based on typical scattering difference index[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 287–294. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: