Classification of Drones Based on Micro-Doppler Radar Signatures Using Dual Radar Sensors
-
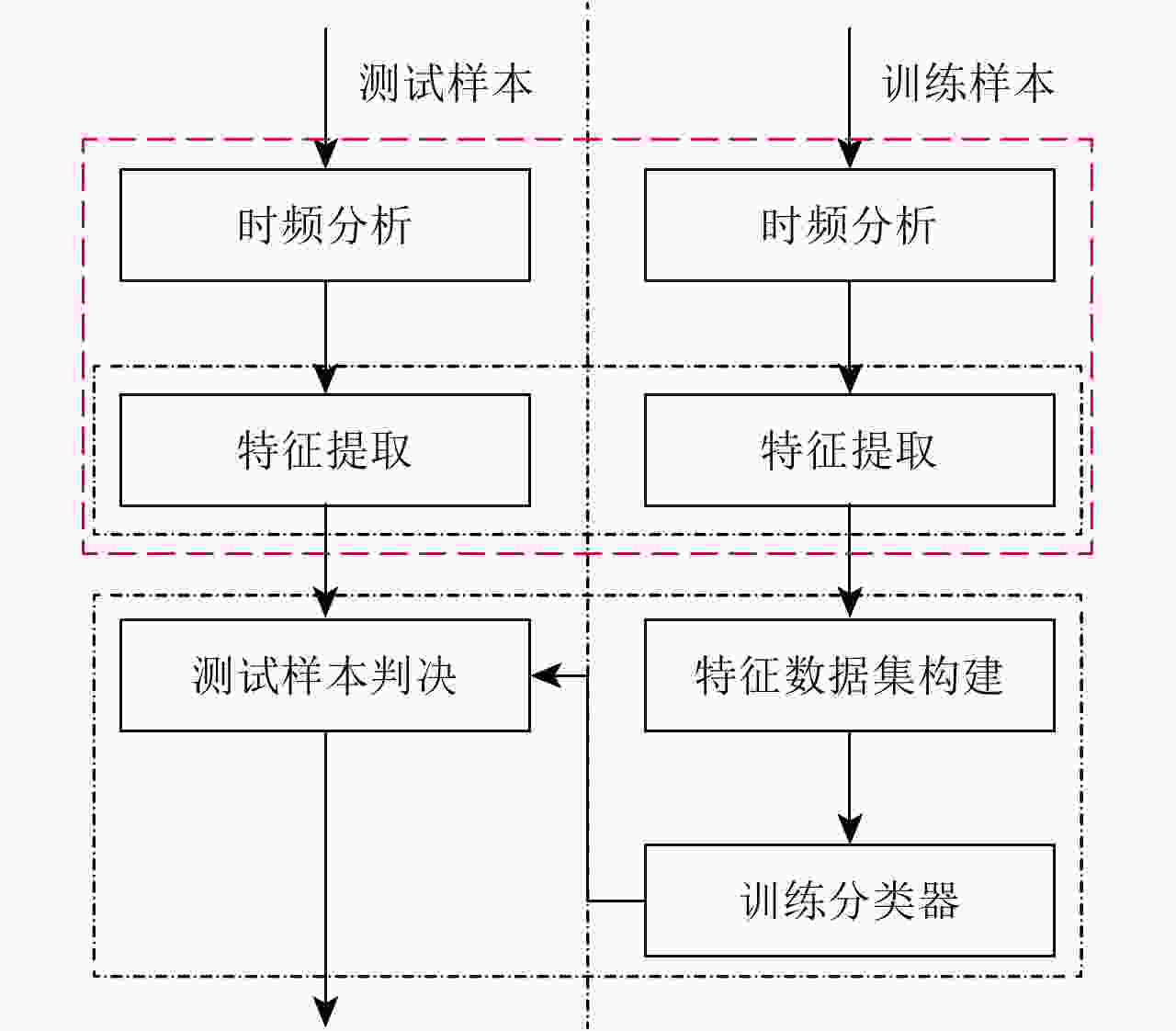
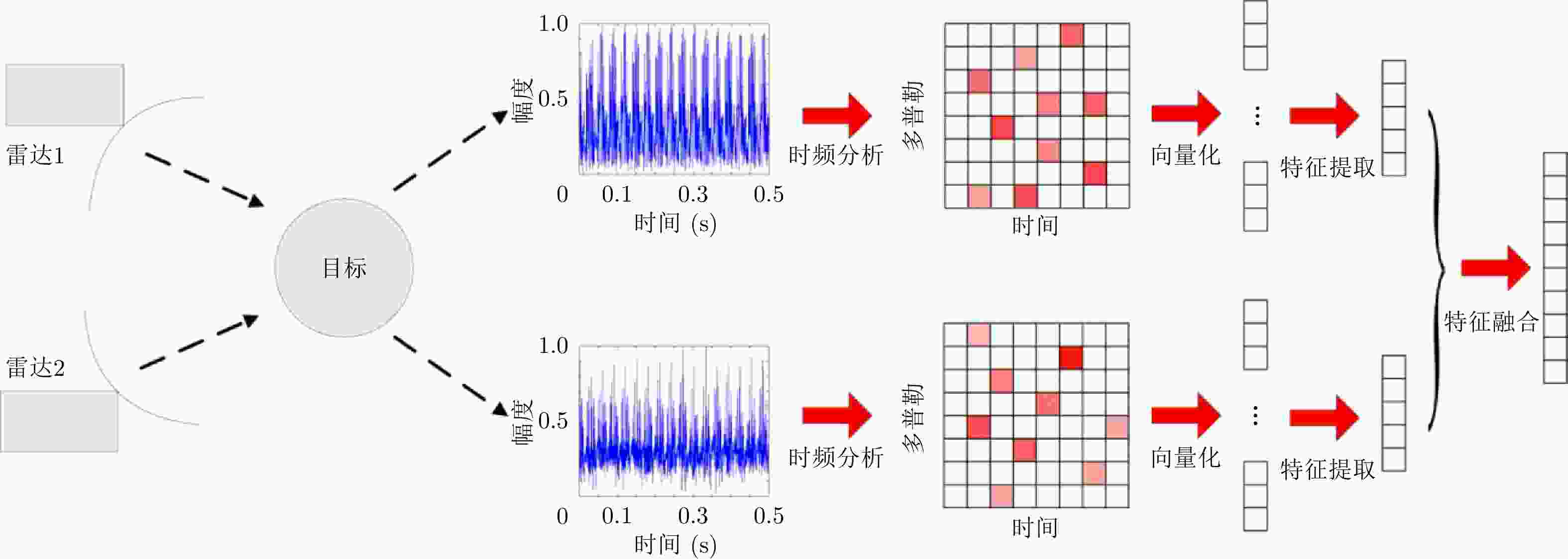
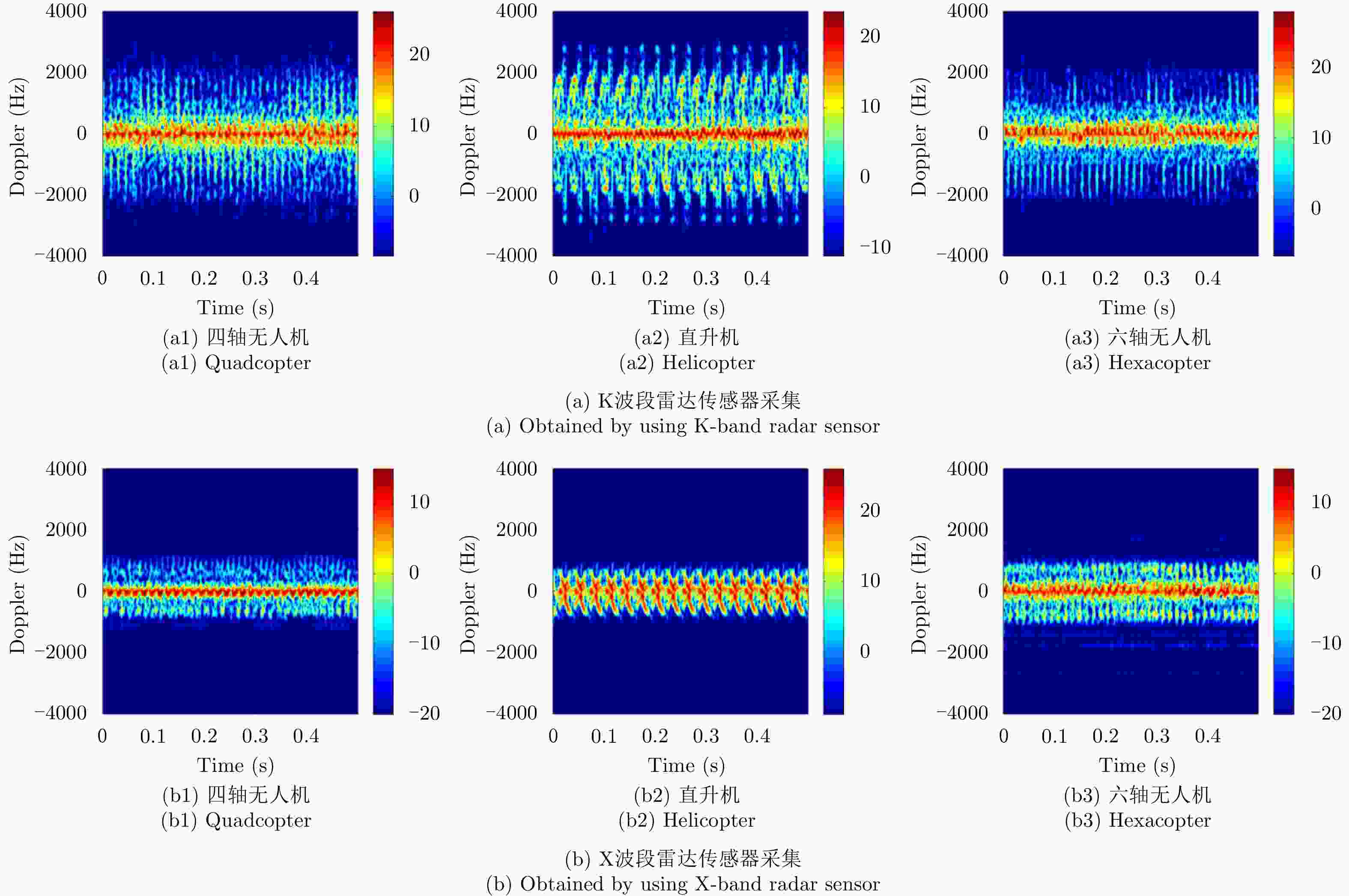
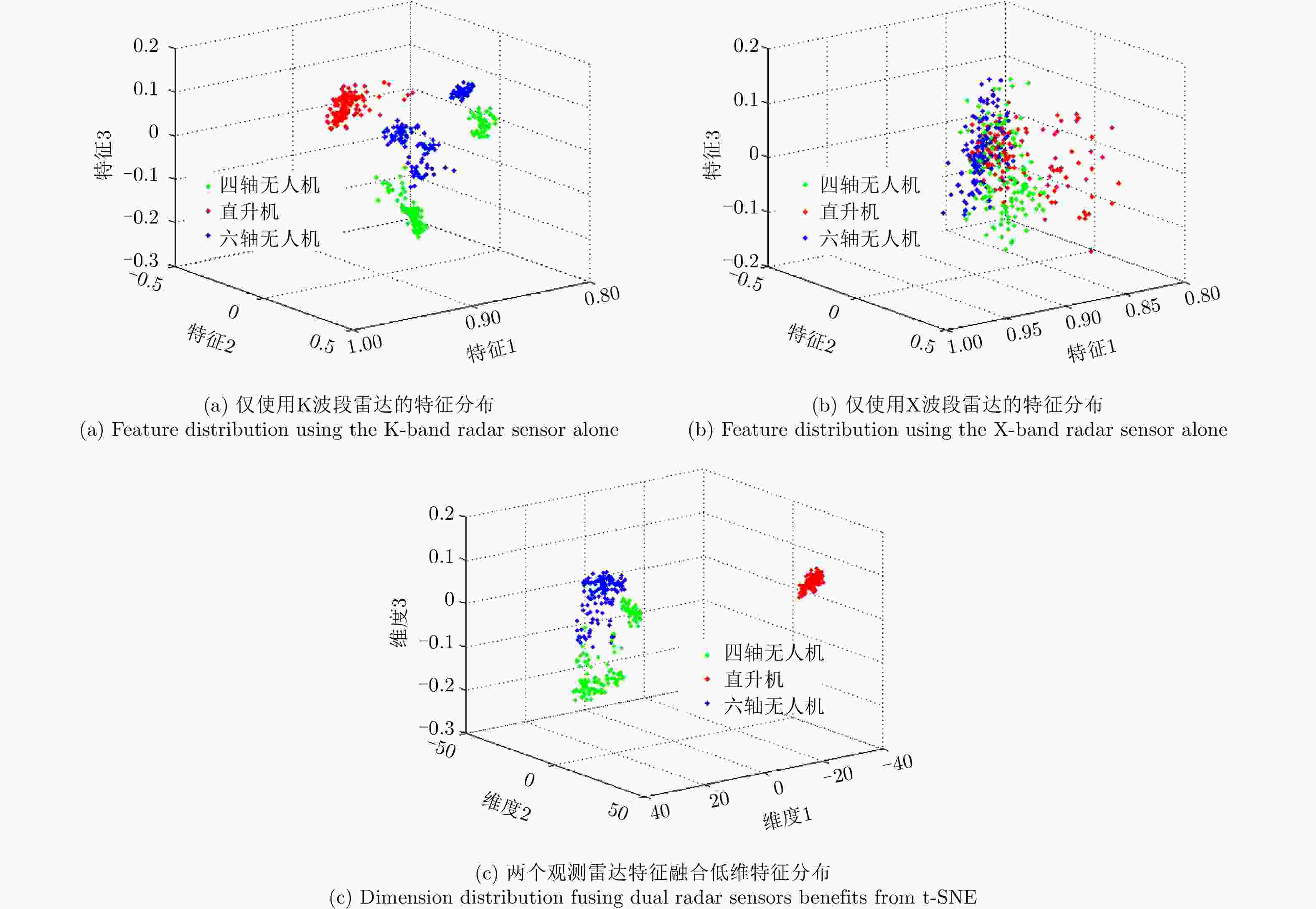
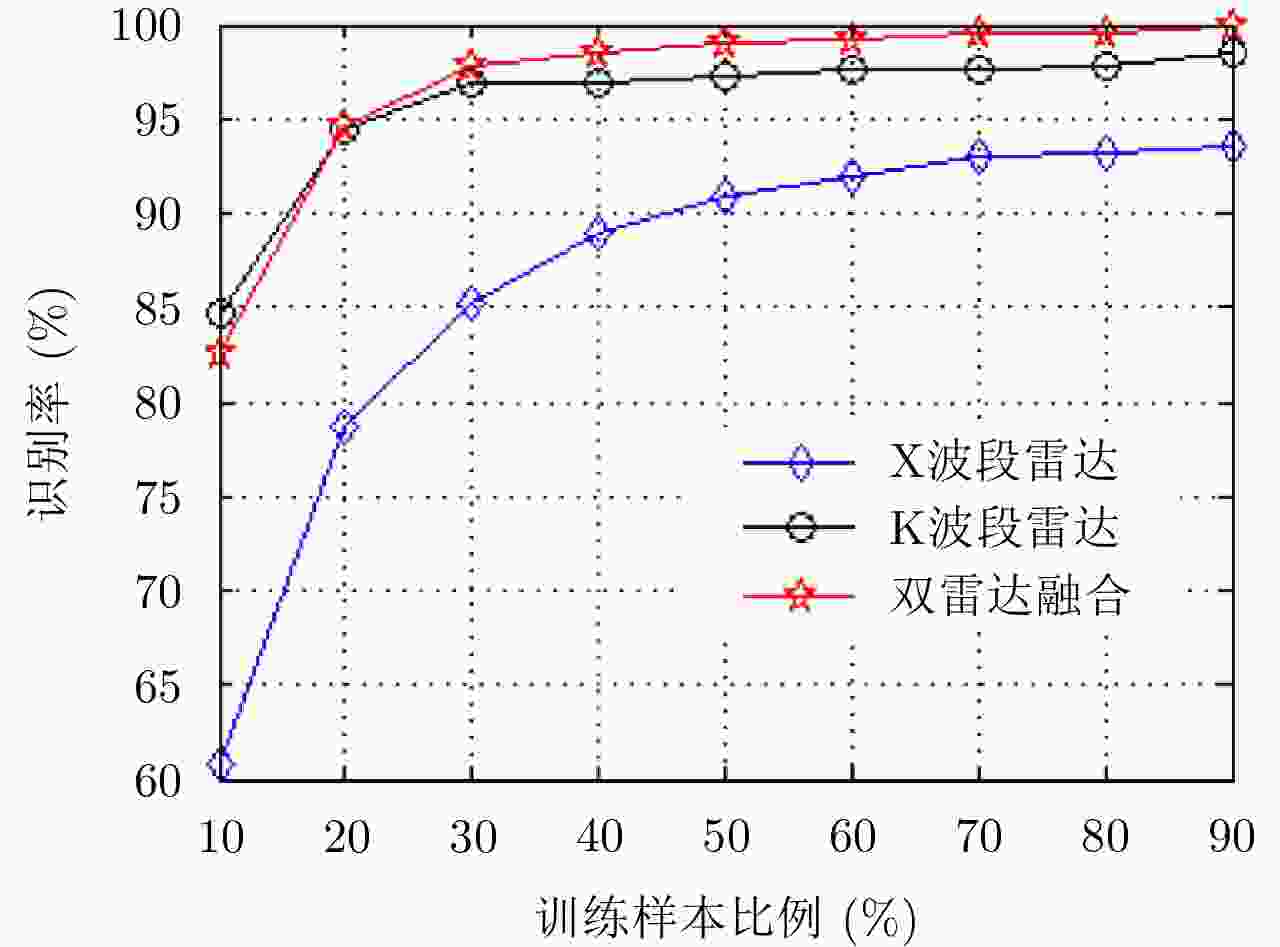
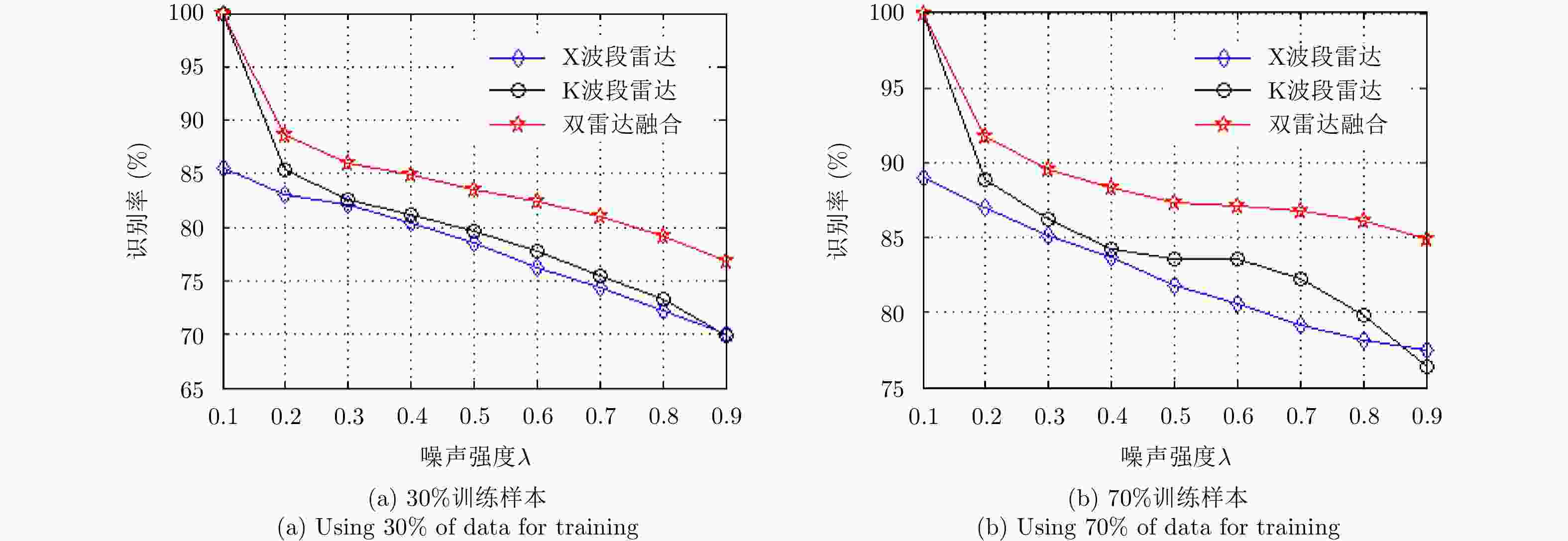
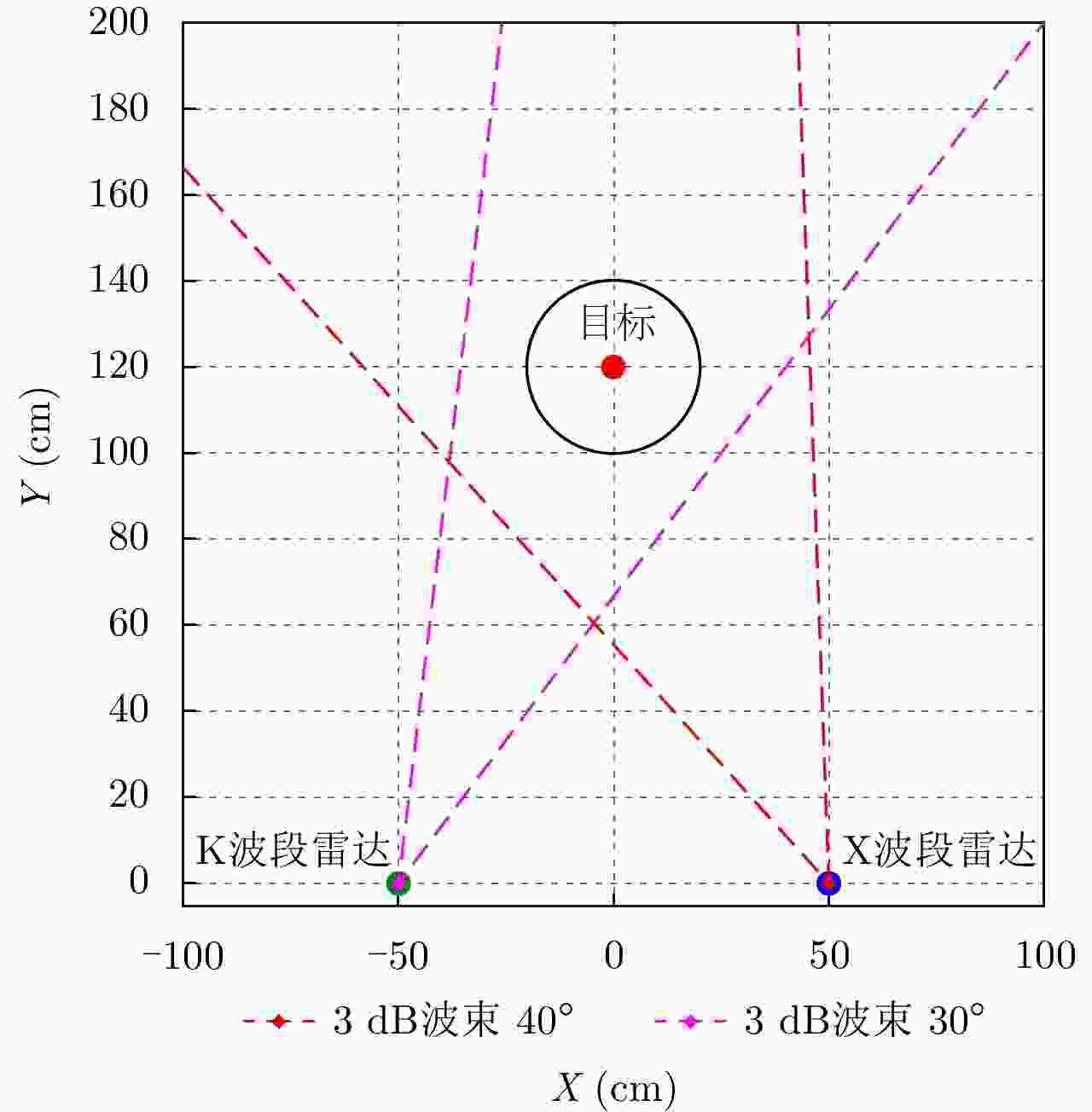
摘要: 无人机的日益流行在带来便利的同时也造成了潜在的威胁,对无人机进行分类识别具有重要意义。雷达微多普勒信号能够区分不同类型的无人机。为了提高基于微多普勒的无人机分类的鲁棒性,该文提出了一种多角度雷达观测微动特征融合的无人机识别方法。首先利用多部雷达同时从不同角度观测目标;然后对采集的雷达数据分别进行短时傅里叶变换(Short-Time Fourier Transform, STFT),得到时频谱图;接着利用主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis, PCA)从时频谱图中提取特征,将两个不同角度雷达传感器得到的特征融合在一起;最后利用支持向量机(Support Vector Machine, SVM)进行训练与分类识别。基于实际雷达数据的实验结果表明:两个雷达传感器观测融合得到的分类精度优于单个雷达传感器的分类精度,最终识别准确率较仅利用X波段雷达传感器方法提升了5%以上。Abstract: Classification of drones is important due to their increasing popularity and potential threats. The micro-Doppler signatures that depend on the rotation of rotor blades facilitate the classification of drones. To enhance the robustness of micro-Doppler based classification of drones, dual radar sensing classification scheme is proposed in this paper. First, time-frequency spectrograms are obtained by performing a short-time Fourier transform on the radar data collected by two radar sensors that have similar angular diversity. Then, principal components analysis is utilized to extract the features from the time-frequency spectrograms and the features obtained by the two radar sensors are fused together. Finally, the classification results are obtained by using the support vector machine. The experimental results show that the classification accuracy obtained by the fusion of dual radar sensors is 5% higher than that obtained by only using a single radar sensor.
-
Key words:
- Micro-Doppler /
- Drones /
- Target classification /
- Multi-angle and multi-band observation
-
表 1 仅利用K波段雷达传感器识别混合矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix using only the K-band radar sensor
目标类型 分类结果 四翼机 直升机 六翼机 四翼机 97.74% 0.00% 4.54% 直升机 0.00% 100% 2.67% 六翼机 2.26% 0.00% 92.79% 表 2 仅利用X波段雷达传感器识别混合矩阵
Table 2. Confusion matrix using only the X-band radar sensor
目标类型 分类结果 四翼机 直升机 六翼机 四翼机 90.01% 10.36% 22.38% 直升机 0.36% 88.26% 0.08% 六翼机 9.63% 1.38% 77.54% 表 3 融合双观测角度的雷达传感器识别混合矩阵
Table 3. Confusion matrix fusing dual-angle radar sensors
目标类型 分类结果 四翼机 直升机 六翼机 四翼机 98.88% 0.00% 3.42% 直升机 0.00% 99.69% 1.98% 六翼机 1.12% 0.31% 94.60% -
[1] De Wit J J M, Harmanny R I A, and Prémel-Cabic G. Micro-Doppler analysis of small UAVs[C]. Proceedings of the 9th European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012: 210–213. [2] De Wit J J M, Harmanny R I A, and Molchanov P. Radar micro-Doppler feature extraction using the Singular Value Decomposition[C]. Proceedings of 2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, France, 2014: 1–6. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.7060268. [3] 夏铭禹, 赵凯, 倪威. 要地防控反无人机系统及其关键技术[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2018, 40(2): 53–60, 71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.02.010Xia Ming-yu, Zhao Kai, and Ni Wei. Anti-UAV system and key technology for key point defense[J]. Command Control&Simulation, 2018, 40(2): 53–60, 71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2018.02.010 [4] Mohajerin N, Histon J, Dizaji R, et al.. Feature extraction and radar track classification for detecting UAVs in civillian airspace[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 674–679. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2014.6875676. [5] Ritchie M, Fioranelli F, Griffiths H, et al.. Micro-drone RCS analysis[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015: 452–456. DOI: 10.1109/RadarConf.2015.7411926. [6] Schroder A, Renker M, Aulenbacher U, et al.. Numerical and experimental radar cross section analysis of the quadrocopter DJI phantom 2[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015: 463–468. DOI: 10.1109/RadarConf.2015.7411928. [7] 白杨, 吴洋, 殷红成, 等. 无人机极化散射特性室内测量研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 647–657. DOI: 10.12000/JR16032Bai Yang, Wu Yang, Yin Hong-cheng, et al. Indoor measurement research on polarimetric scattering characteristics of UAV[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 647–657. DOI: 10.12000/JR16032 [8] Torvik B, Olsen K E, and Griffiths H. Classification of birds and UAVs based on radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(9): 1305–1309. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2582538 [9] Chen V C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2011: 35–60. [10] Kim Y and Ling H. Human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures using a support vector machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1328–1337. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2012849 [11] Fioranelli F, Ritchie M, and Griffiths H. Classification of unarmed/armed personnel using the NetRAD multistatic radar for micro-Doppler and singular value decomposition features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1933–1937. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2439393 [12] Kim Y and Toomajian B. Hand gesture recognition using micro-Doppler signatures with convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 7125–7130. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2617282 [13] Li G, Zhang R, Ritchie M, et al. Sparsity-driven micro-Doppler feature extraction for dynamic hand gesture recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(2): 655–665. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2761229 [14] Stove A G and Sykes S R. A Doppler-based target classifier using linear discriminants and principal components[C]. Proceedings of 2003 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2003: 107–125. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2003.1278734. [15] 熊丁丁, 崔国龙, 孔令讲, 等. 基于互相关熵的非高斯背景下微动参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 300–308. DOI: 10.12000/JR17007Xiong Dingding, Cui Guolong, Kong Lingjiang, et al. Micro-motion parameter estimation in non-Gaussian noise via mutual correntropy[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 300–308. DOI: 10.12000/JR17007 [16] 王宝帅. 基于微多普勒效应的空中飞机目标分类研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015: 4–22.Wang Bao-shuai. Study on classification of airplane targets based on micro-Doppler effect[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2015: 4–22. [17] Molchanov P, Egiazarian K, Astola J, et al. . Classification of small UAVs and birds by micro-Doppler signatures[C]. Proceedings of 2013 European Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2013: 172–175. [18] Kim B K, Kang H S, and Park S O. Drone classification using convolutional neural networks with merged Doppler images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 38–42. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2624820 [19] Ren J F and Jiang X D. Regularized 2-D complex-log spectral analysis and subspace reliability analysis of micro-Doppler signature for UAV detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 69: 225–237. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.04.024 [20] Ritchie M, Fioranelli F, Borrion H, et al. Multistatic micro-Doppler radar feature extraction for classification of unloaded/loaded micro-drones[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(1): 116–124. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0063 [21] Zhang R, Li G, Clemente C, et al. Multi-aspect micro-Doppler signatures for attitude-independent L/N quotient estimation and its application to helicopter classification[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(4): 701–708. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0271 [22] Van Der Maaten L and Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(11): 2579–2605. [23] Vapnik V N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1995: 112–150. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: