Track-Before-Detect Algorithm Based on Improved Auxiliary Particle PHD Filter under Clutter Background
-
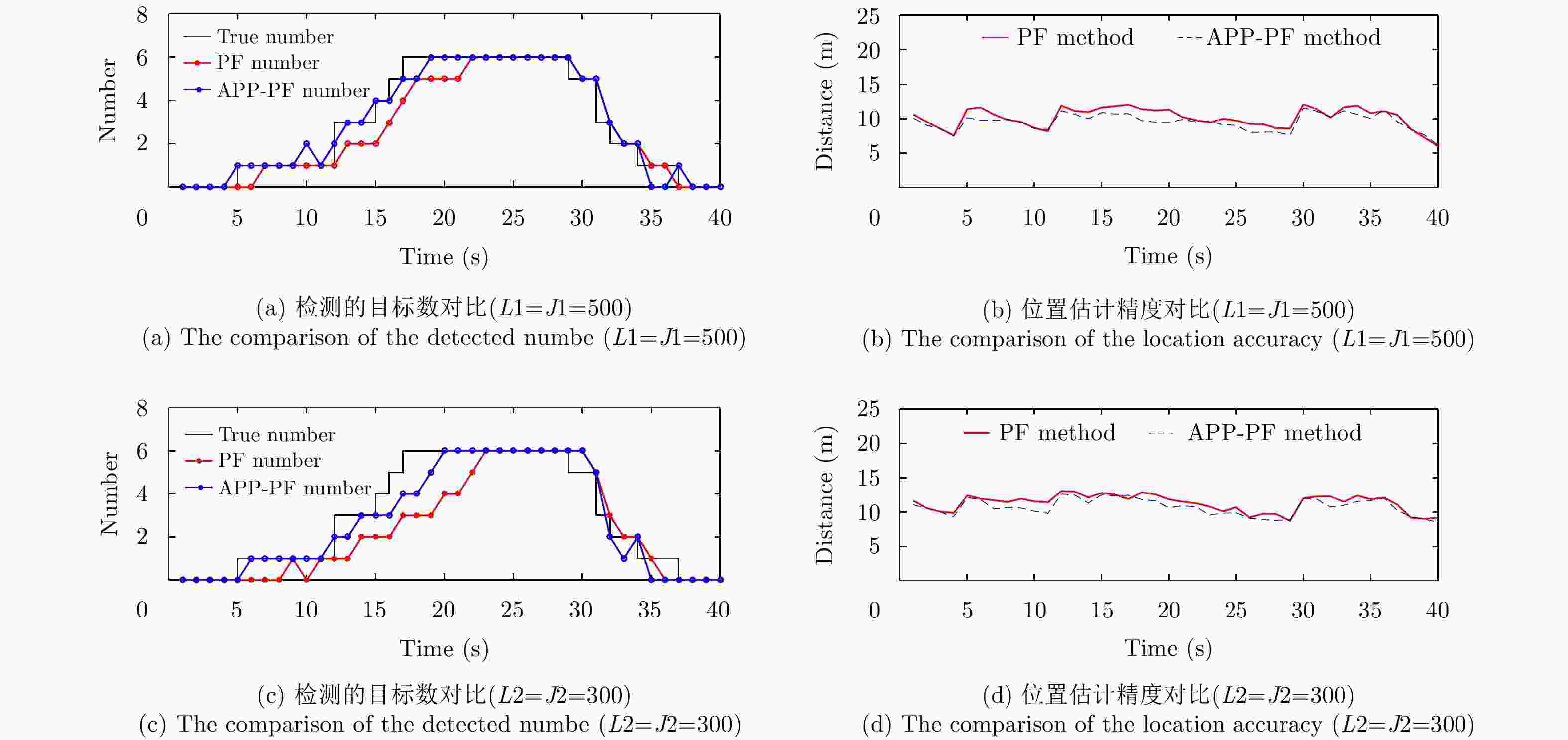
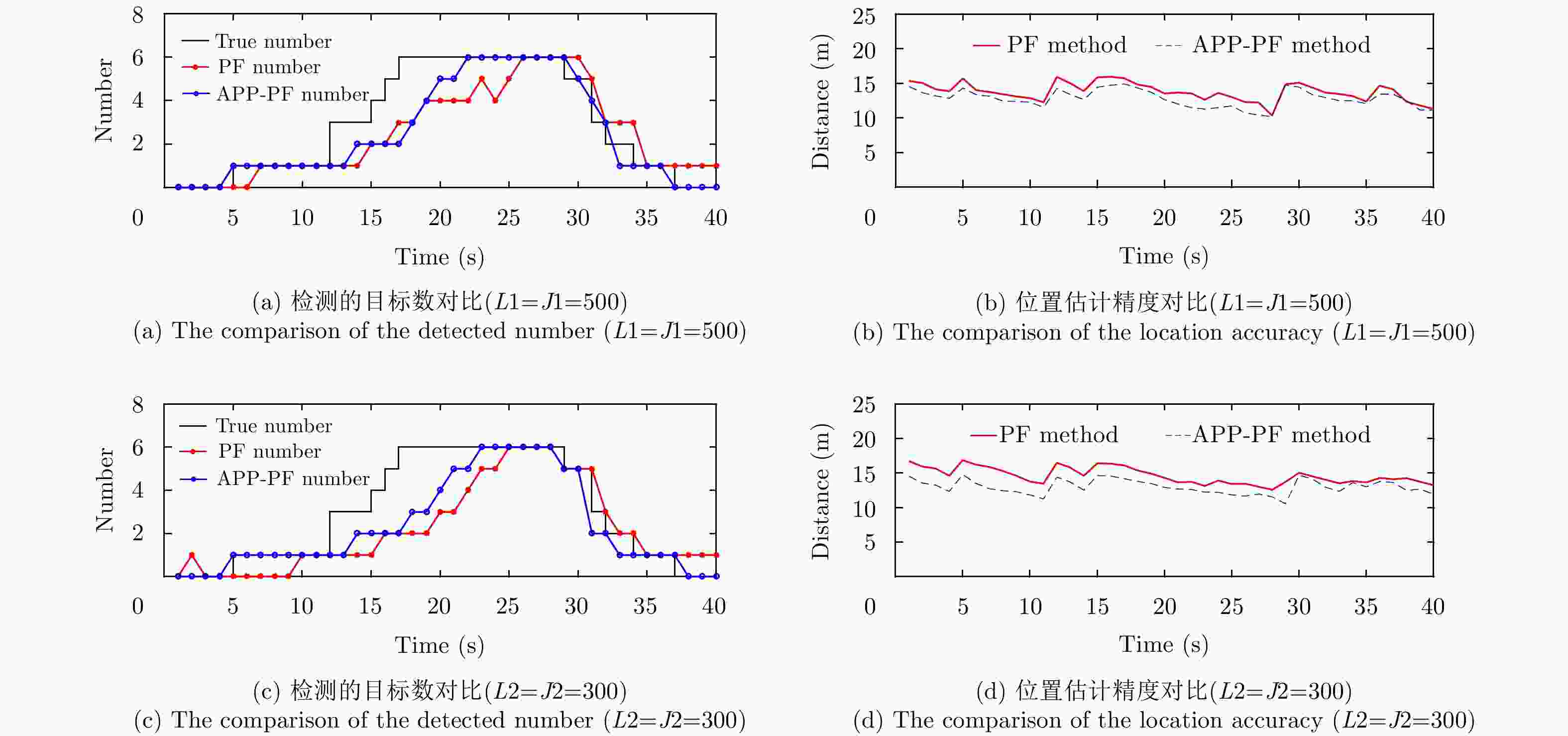
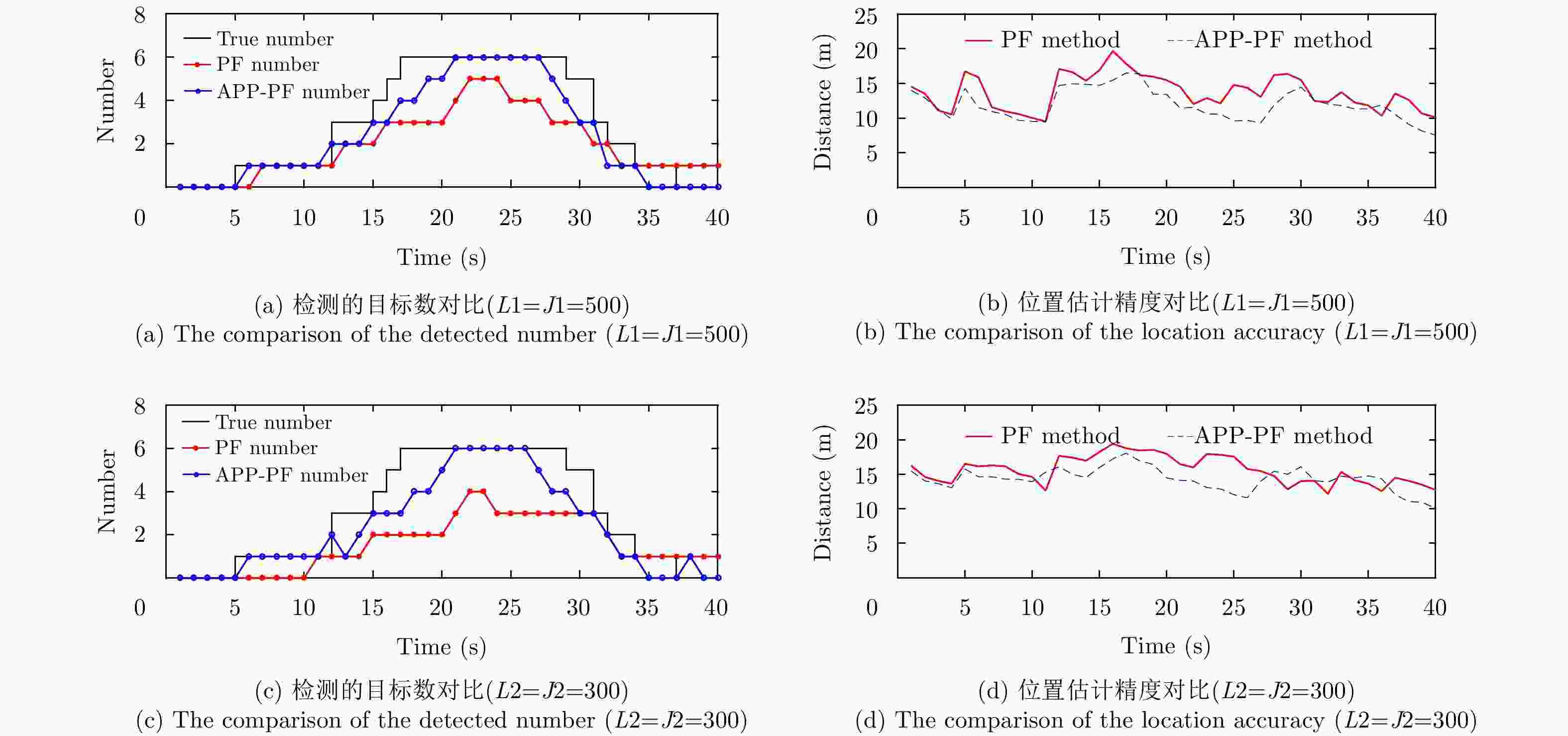
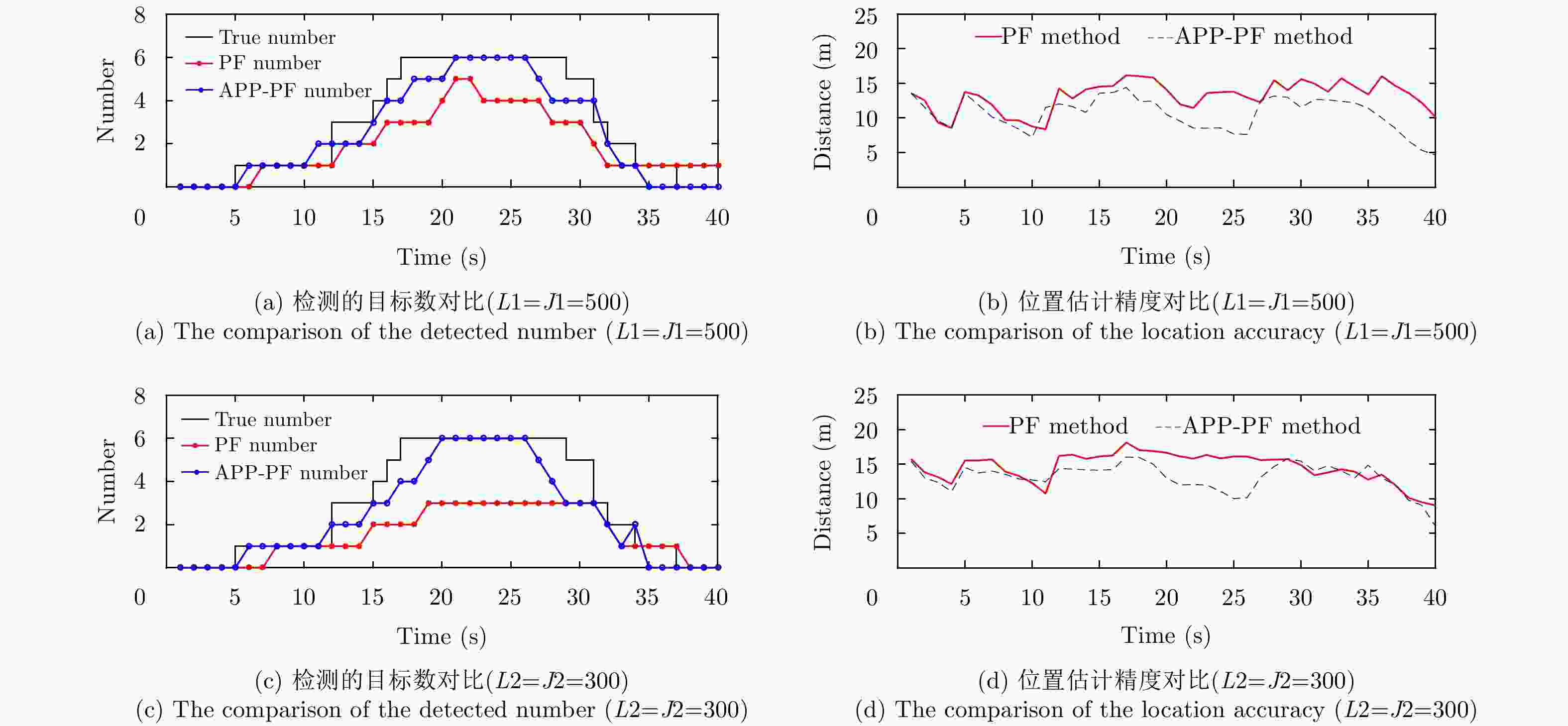
摘要: 在杂波背景条件下,现有的基于概率假设密度(PHD)滤波的粒子滤波检测前跟踪(TBD)算法,存在对密集多目标数目估计不准,使用粒子数目较多会造成维数灾难的问题。因此,该文引入两层粒子的概念,将基于平行分割(PP)理论的辅助粒子滤波(APF)应用于基于概率假设密度的检测前跟踪 (PHD-TBD)算法中,提出基于概率假设密度滤波的平行分割辅助粒子滤波检测前跟踪(APP-PF-PHD-TBD)算法以提高目标数目及状态估计精度。仿真实验证明,相对于现有基于PHD的粒子滤波检测前跟踪算法,该算法在目标数目和状态估计精度上具有显著的性能优势,在密集目标场景下,优势尤为突出。最后,利用导航雷达实测所得海杂波背景数据证明,该算法在应用中性能更加优异。Abstract: Under the clutter background condition, the existing particle filter pre-detection tracking algorithm based on Probability Hypothesis Density (PHD) filtering is not accurate enough to estimate the number of targets in dense multi-objectives. In this study, the concept of two-layer particle is introduced. The Auxiliary Particle Filter (APF) based on Parallel Partition (PP) theory is applied to PHD-TBD. The Auxiliary Parallel Partition Particle Filter (which is based on APF and PP) Track-Before-Detect based on the Probability Hypothesis Density filter (APP-PF-PHD-TBD) algorithm is proposed to improve the target number and state estimation accuracy. The simulation results show that, compared with the existing PHD-filtering-based particle filter track-before-detect algorithm, the proposed algorithm has significant performance advantages in target number and state estimation accuracy. These advantages are particularly obvious in dense target scenarios. Finally, the sea clutter background data obtained using the navigation radar prove that the proposed algorithm outperforms the existing PHD-filtering-based particle filter track-before-detect algorithm in application.
-
表 1 实验1中目标运动状态
Table 1. The state of the targets in Exp.1
目标 初始状态[m, m/s, m, m/s, rad/s, —] 出现帧 消失帧 1 [50, 20, 750, 0, 0, I] 5 36 2 [1250, 45, 1500, 25, 0, I] 12 28 3 [50, 75, 400, –40, 0, I] 12 30 4 [50, 60, 1900, –0.5, 0, I] 15 31 5 [50, 100, 1250, 0, 0, I] 16 33 6 [500, 90, 1000, 0.2, 0, I] 17 30 表 2 实验2中目标运动状态
Table 2. The state of the targets in Exp.2
目标 初始状态[m, m/s, m, m/s, rad/s, —] 出现帧 消失帧 1 [50, 55, 750, 0, ${\text{π}}$/720, I] 5 36 2 [150, –75, 1250, –80, –${\text{π}}$/270, I] 12 28 3 [1600, –75, 400, 25, –${\text{π}}$/180, I] 12 30 4 [150, 0, 1000, –60, 0, I] 15 31 5 [500, 50, 1250, –50, ${\text{π}}$/360, I] 16 33 6 [500, –0.6, 600, 50, ${\text{π}}$/180, I] 17 30 表 3 实验3中目标运动状态
Table 3. The state of the targets in Exp.3
目标 初始状态[m, m/s, m, m/s, —] 出现帧 消失帧 1 [2500, 8, 1050, 8, I] 5 36 2 [4000, –7, 4000, –7, I] 12 30 3 [2500, –5, 2250, –5, I] 16 33 4 [1200, 10, 2000, 10, I] 12 28 表 4 实验1算法蒙特卡洛实验平均运行时间(s)
Table 4. The mean running time of per Monte Carlo experiment in Exp. 1 (s)
算法 单个目标粒子数 9 dB 8 dB 6 dB PF-PHD-TBD 500 14.7771 18.4788 16.1523 300 17.9281 16.9987 19.4703 APP-PF-PHD-TBD 500 29.5866 29.9445 27.9817 300 26.7950 21.5654 22.0255 表 5 实验2算法蒙特卡洛实验平均运行时间(s)
Table 5. The mean running time of per Monte Carlo experiment in Exp. 2 (s)
算法 单个目标粒子数 9 dB 8 dB 6 dB PF-PHD-TBD 500 11.5948 12.0970 9.1321 300 9.5399 7.6792 8.4194 APP-PF-PHD-TBD 500 31.5074 32.7218 28.6130 300 30.5533 29.8249 26.3135 表 6 实验3算法蒙特卡洛实验平均运行时间(s)
Table 6. The mean running time of per Monte Carlo experiment in Exp. 3 (s)
算法 运行时间 PF-PHD-TBD 25.3594 APP-PF-PHD-TBD 40.1553 -
[1] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002CHEN Xiao-long, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002 [2] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友, 等. 高分辨稀疏表示及其在雷达动目标检测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. doi: 10.12000/JR16110CHEN Xiao-long, GUAN Jian, HE You, et al. High-resolution sparse representation and its applications in radar moving target detection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. doi: 10.12000/JR16110 [3] ZWAGA J H, DRIESSEN H, and MEIJER W D. Track-before-detect for surveillance radar: A recursive filter-based approach[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 4728, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2002, Orlando, USA, 2002: 103–115. DOI: 10.1117/12.478496. [4] 杨亚波, 夏永红, 匡华星, 等. 雷达微弱目标检测前跟踪技术研究综述[J]. 雷达与对抗, 2015, 35(2): 22–28.YANG Ya-bo, XIA Yong-hong, KUANG Hua-xing, et al. An overview on track-before-detect technique for radar weak targets[J]. Radar &ECM, 2015, 35(2): 22–28. [5] 战立晓, 汤子跃, 朱振波. 雷达微弱目标检测前跟踪算法综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2013, 35(4): 45–52, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2013.04.010ZHAN Li-xiao, TANG Zi-yue, and ZHU Zhen-bo. An overview on track-before-detect algorithms for radar weak targets[J]. Modern Radar, 2013, 35(4): 45–52, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2013.04.010 [6] BOERS Y and DRIESSEN J N. Multitarget particle filter track before detect application[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2004, 151(6): 351–357. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20040841 [7] 吴孙勇, 薛秋条, 朱圣棋, 等. 杂波环境下基于粒子滤波的微弱扩展目标检测前跟踪算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 252–258. doi: 10.12000/JR16128WU Sun-yong, XUE Qiu-tiao, ZHU Sheng-qi, et al. Track-before-detect algorithm for weak extended target based on particle filter under clutter environment[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 252–258. doi: 10.12000/JR16128 [8] 李洋漾, 李雯, 易伟, 等. 基于DP-TBD的分布式异步迭代滤波融合算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 254–262. doi: 10.12000/JR17057LI Yang-yang, LI Wen, YI Wei, et al. A distributed asynchronous recursive filtering fusion algorithm via DP-TBD[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 254–262. doi: 10.12000/JR17057 [9] MAHLER R P S M. Multitarget bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119 [10] VO B N and MA W K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881190 [11] VO B N and MA W K. A closed-form solution for the probability hypothesis density filter[C]. Proceedings of the 2005 7th International Conference on Information Fusion, Philadelphia, USA, 2005: 856–863. DOI: 10.1109/ICIF.2005.1591948. [12] 吴伟, 尹成友. 一种用于多目标跟踪的增强型SMC-PHD滤波算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 406–413. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20094WU Wei and YIN Cheng-you. An improved SMC-PHD filter for multiple targets tracking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 406–413. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20094 [13] PUNITHAKUMAR K, KIRUBARAJAN T, and SINHA A. A sequential monte carlo probability hypothesis density algorithm for multitarget track-before-detect[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 5913, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2005, San Diego, USA, 2005: 1–8. DOI: 10.1117/12.618438. [14] Vo B N, Vo B T, Pham N T, et al. Reply to " Comments on ‘Joint detection and estimation of multiple objects from image observations’”[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(3): 1540–1541. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2173686 [15] 占荣辉, 刘盛启, 欧建平, 等. 基于序贯蒙特卡罗概率假设密度滤波的多目标检测前跟踪改进算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(11): 2593–2599. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.02029ZHAN Rong-hui, LIU Sheng-qi, OU Jian-ping, et al. Improved multitarget track before detect algorithm using the sequential Monte Carlo probability hypothesis density filter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(11): 2593–2599. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.02029 [16] DAUM FRED and HUANG J. Curse of dimensionality and particle filters[C]. Proceedings of 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2003: 1979–1993. DOI: 10.1109/AERO.2003.1235126. [17] 林再平, 周一宇, 安玮. 改进的概率假设密度滤波多目标检测前跟踪算法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2012, 31(5): 475–480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2012.00475LIN Zai-ping, ZHOU Yi-yu, and AN WEI. Improved multitarget track-before-detect using probability hypothesis density filter[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2012, 31(5): 475–480. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2012.00475 [18] DENG X, PI Y, MORELANDE M, et al. Track-before-detect procedures for low pulse repetition frequency surveillance radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2011, 5(1): 65–73. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0245 [19] 童慧思, 张颢, 孟华平, 等. PHD滤波器在多目标检测前跟踪中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(9): 2046–2051.TONG Hui-si, ZHANG Hao, MENG Hua-ping, et al. Probability hypothesis density filter multitarget track-before-detect application[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(9): 2046–2051. [20] Geelen B D B. Accurate solution for the modified bessel function of the first kind[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 1995, 23(2): 105–109. doi: 10.1016/0965-9978(95)00069-9 [21] YI W, MORELANDE M R, KONG L J, et al. A computationally efficient particle filter for multitarget tracking using an independence approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(4): 843–856. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2229999 [22] KREUCHER C, KASTELLA K, and HERO III A O. Multitarget tracking using the joint multitarget probability density[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(4): 1396–1414. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1561892 [23] GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, GRAJAL J, and MORELANDE M R. Two-layer particle filter for multiple target detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(3): 1569–1588. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6558005 [24] ÚBEDA-MEDINA, GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, and GRAJAL J. Adaptive auxiliary particle filter for track-before-detect with multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(5): 2317–2330. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2691958 [25] PITT M K and SHEPHARD N. Filtering via simulation: Auxiliary particle filters[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1999, 94(446): 590–599. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1999.10474153 [26] GARCÍA FERNÁNDEZ Á F. Detection and tracking of multiple targets using wireless sensor networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, 2011: 61–78. [27] SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2008.920469 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: