Research Progresses in Radar Feature Extraction, Imaging, and Recognition of Target with Micro-motions
-
摘要: 微动目标的雷达特征提取、成像与识别技术是雷达目标精确识别领域极具发展潜力的研究方向之一。该文首先简要阐述了微动的相关概念,然后综述了近年来微动目标回波建模、微动特征提取、微动目标成像以及基于微动特征的雷达目标分类与识别等方面的研究现状,并介绍了几种典型前沿应用,最后对微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别的研究发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: The technique of radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions has become one of the most potential research directions in the field of radar target accurate recognition. In this paper, the concept of micro-motion is first introduced briefly. Subsequently, the achievements of echo modeling, feature extraction, imaging, and identification of micro-motion targets are summarized. Several typical frontier applications are then introduced. Finally, the future development trends of the research are discussed.
-
Key words:
- Micro-motion /
- Micro-Doppler /
- Feature extraction /
- Radar imaging /
- Target recognition
-
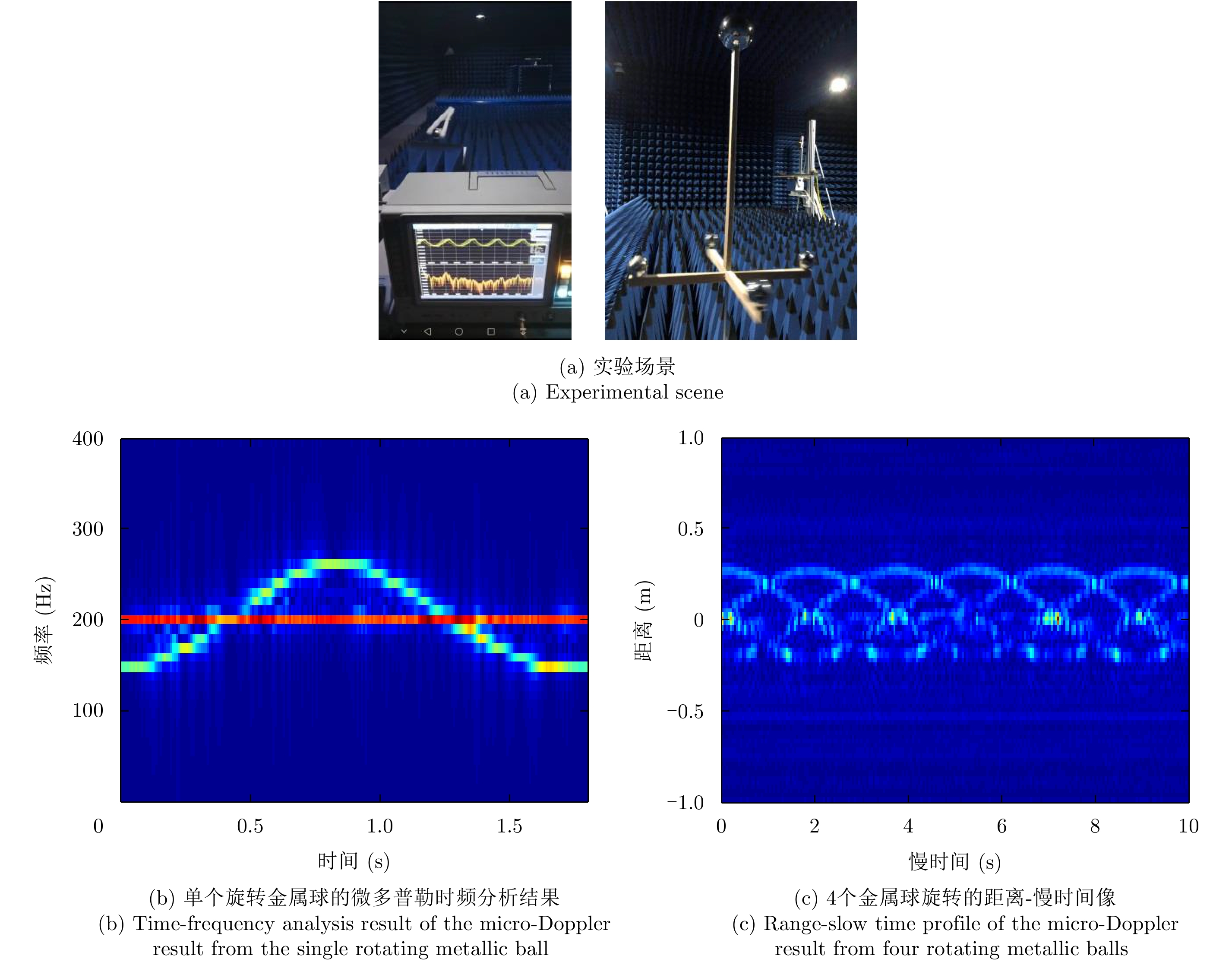
表 1 分布式MIMO雷达系统(2个发射阵元和4个接收阵元)每对收发阵元获得的有3个旋转散射点目标的微动特征
Table 1. Micro-motion feature of a rotating target with three scatterers received by transceivers in a distributed MIMO radar system (2 transmitters and 4 receivers)
T R 1 2 3 4 1 



2 



-
[1] 张群, 罗迎. 雷达目标微多普勒效应[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 1–17.Zhang Qun and Luo Ying. Micro-Doppler Effect of Radar Targets[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 1–17. [2] Zhang Q, Luo Y, and Chen Y A. Micro-Doppler Characteristics of Radar Targets[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 1–11. [3] Chen V C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar[M]. Boston, London: Artech House, 2011: 35–78. [4] Thayaparan T, Stanković L, and Djurović I. Micro-Doppler-based target detection and feature extraction in indoor and outdoor environments[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2008, 345(6): 700–722. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2008.01.003 [5] Chen V C, Li F, Ho S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. [6] Liu L H, McLernon D, Ghogho M, et al. Ballistic missile detection via micro-Doppler frequency estimation from radar return[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2012, 22(1): 87–95. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsp.2011.10.009 [7] Chen V C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 291–300. DOI: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070137 [8] 马梁, 刘进, 王涛, 等. 旋转对称目标滑动型散射中心的微Doppler特性[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2011, 41(5): 605–616.Ma Liang, Liu Jin, Wang Tao, et al.. Micro-Doppler characteristics of sliding-type scattering center on rotationally symmetric target[J]. SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences, 2011, 54(9): 1957–1967. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-011-4254-3. [9] 陈小龙, 董云龙, 李秀友, 等. 海面刚体目标微动特征建模及特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR15079Chen Xiao-long, Dong Yun-long, Li Xiu-you, et al. Modeling of micromotion and analysis of properties of rigid marine targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR15079 [10] 黄健, 李欣, 黄晓涛, 等. 基于微多普勒特征的坦克目标参数估计与身份识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(5): 1050–1055. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00669Huang Jian, Li Xin, Huang Xiao-tao, et al. Micro-Doppler features based parameter estimation and identification of tank[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2010, 32(5): 1050–1055. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00669 [11] 张翼, 程永强, 朱玉鹏, 等. 人体目标雷达回波建模[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2011, 23(3): 438–445. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.03.018Zhang Yi, Cheng Yong-qiang, Zhu Yu-peng, et al. Human target radar echo modeling[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2011, 23(3): 438–445. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.03.018 [12] Chen V C. Detection and analysis of human motion by radar[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–4. [13] Ghaleb A, Vignaud L, and Nicolas J M. Micro-Doppler analysis of wheels and pedestrians in ISAR imaging[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 301–311. DOI: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070113 [14] Zhang Q, Zeng Y S, He Y Q, et al.. Avian detection and identification with high-resolution radar[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–6. [15] Zhu F, Luo Y, Zhang Q, et al. ISAR imaging for avian species identification with frequency-stepped chirp signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(1): 151–155. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2028902 [16] Bai X R, Zhou F, and Bao Z. High-resolution 3-D imaging of group rotating targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1066–1077. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2013.110750 [17] Liu Y X, Chen H Y, Li X, et al.. Radar micro-motion target resolution[C]. Proceedings of 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006: 1411–1414. [18] Zhao M M, Zhang Q, Luo Y, et al. Micromotion feature extraction and distinguishing of space group targets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(2): 174–178. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2633426 [19] Fioranelli F, Ritchie M, and Griffiths H. Multistatic human micro-Doppler classification of armed/unarmed personnel[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(7): 857–865. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0360 [20] 罗迎, 张群, 朱仁飞, 等. 多载频MIMO雷达中目标旋转部件三维微动特征提取方法[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(9): 1975–1981Luo Ying, Zhang Qun, Zhu Ren-fei, et al. Three-dimensional micro-motion feature extraction of target with rotating parts in multi-carrier MIMO radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(9): 1975–1981 [21] Luo Y, Zhang Q, Qiu C W, et al. Three-dimensional micromotion signature extraction of rotating targets in OFDM-LFM MIMO radar[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 140: 733–759. DOI: 10.2528/PIER13042202 [22] Luo Y, Zhang Q, Yuan N, et al. Three-dimensional precession feature extraction of space targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1313–1329. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.110545 [23] Zhang Q, Yeo T S, Tan H S, et al. Imaging of a moving target with rotating parts based on the Hough transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 291–299. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907105 [24] Xing M, Wu R, and Bao Z. High resolution ISAR imaging of high speed moving targets[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2005, 152(2): 58–67. DOI: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045084 [25] Bai X R, Zhou F, Xing M D, et al. High resolution ISAR imaging of targets with rotating parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System, 2011, 47(4): 2530–2543. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034649 [26] Peng B, Wei X Z, Deng B, et al. A Sinusoidal frequency modulation Fourier transform for radar-based vehicle vibration estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2014, 63(9): 2188–2199. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2014.2308031 [27] He Q F, Zhang Q, Luo Y, et al. Sinusoidal frequency modulation Fourier-Bessel series for multicomponent SFM signal estimation and separation[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2017: 5852171. [28] Suresh P, Thayaparan T, Obulesu T, et al. Extracting micro-Doppler radar signatures from rotating targets using Fourier-Bessel transform and time-frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3204–3210. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2271706 [29] Suresh P, Thayaparan T, and Venkataramaniah K. Fourier-Bessel transform and time-frequency-based approach for detecting manoeuvring air target in sea-clutter[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(5): 481–491. [30] 冯德军, 陈志杰, 王雪松, 等. 基于一维距离像的导弹目标运动特征提取方法[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2005, 27(6): 43–47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.06.010Feng De-jun, Chen Zhi-jie, Wang Xue-song, et al. A method for extracting moving feature of ballistic missile targets from high resolution range profiles[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2005, 27(6): 43–47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.06.010 [31] 马梁, 王涛, 冯德军, 等. 旋转目标距离像长度特性及微运动特征提取[J]. 电子学报, 2008, 36(12): 2273–2279. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.12.001Ma Liang, Wang Tao, Feng De-jun, et al. The characteristic of range profile and micro-motion feature extraction for rotary target[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(12): 2273–2279. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.12.001 [32] 雷腾, 刘进忙, 余付平, 等. 基于时间-距离像的弹道目标进动特征提取新方法[J]. 信号处理, 2012, 28(1): 73–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.01.011Lei Teng, Liu Jin-mang, Yu Fu-ping, et al. A new procession signature extraction method of ballistic target based on range-profile[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 28(1): 73–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.01.011 [33] 毕莉, 赵锋, 高勋章, 等. 基于一维像序列的进动目标尺寸估计研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(8): 1825–1830. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00835Bi Li, Zhao Feng, Gao Xun-zhang, et al. Study on precessional target’s dimension estimation based on HRRPs[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2010, 32(8): 1825–1830. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00835 [34] Rihaczek A W and Hershkowitz S J. Theory and Practice of Radar Target Identification[M]. Boston, London: Artech House, 2000. [35] Ai X F, Zou X H, Li Y Z, et al. Bistatic scattering centres of cone-shaped targets and target length estimation[J]. SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences, 2012, 55(12): 2888–2898. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-012-4749-6 [36] 艾小锋, 邹小海, 李浩智, 等. T/R-R双基地雷达进动目标参数估计与ISAR成像[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(6): 1148–1153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.06.013Ai Xiao-feng, Zou Xiao-hai, Li Hao-zhi, et al. Parameter estimation and ISAR imaging of precession targets using T/R-R bistatic radars[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(6): 1148–1153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.06.013 [37] 金光虎, 高勋章, 黎湘, 等. 基于ISAR像序列的弹道目标进动特征提取[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(6): 1233–1238Jin Guang-hu, Gao Xun-zhang, Li Xiang, et al. Precession feature extraction of ballistic targets based on dynamic ISAR image sequence[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(6): 1233–1238 [38] 陈蓉, 冯存前, 贺思三, 等. 采用ISAR像估计弹道目标微动特征的方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(7): 1500–1505. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.07.11Chen Rong, Feng Cun-qian, He Si-san, et al. Micro-motion features estimation method using ISAR images for ballistic targets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(7): 1500–1505. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.07.11 [39] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [40] 李康乐. 雷达目标微动特征提取与估计技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2010.Li Kang-le. Research on feature extraction and parameters estimation for radar targets with micro-motions[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2010. [41] Whitelonis N and Ling H. Radar signature analysis using a joint time-frequency distribution based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(2): 755–763. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2291893 [42] Deprem Z and Çetín A. Cross-term-free time-frequency distribution reconstruction via lifted projections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1): 479–491. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140080 [43] Liu H C, Jiu B, Liu H W, et al. A novel ISAR imaging algorithm for micromotion targets based on multiple sparse bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1772–1776. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2308536 [44] Luo Y, Zhang Q, Qiu C W, et al. Micro-Doppler feature extraction for wideband imaging radar based on complex image orthogonal matching pursuit decomposition[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2013, 7(8): 914–924. [45] 张栋, 冯存前, 贺思三, 等. 组网雷达弹道目标三维进动特征提取[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 42(2): 146–151. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2015.02.024Zhang Dong, Feng Cun-qian, He Si-san, et al. Extraction of three-dimensional precession features of ballistic targets in netted radar[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2015, 42(2): 146–151. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2015.02.024 [46] 赵双, 鲁卫红, 冯存前, 等. 基于窄带雷达网的弹道目标三维进动特征提取[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 98–105. DOI: 10.12000/JR15129Zhao Shuang, Lu Wei-hong, Feng Cun-qian, et al. Three-dimensional precession feature extraction of ballistic targets based on narrowband radar network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 98–105. DOI: 10.12000/JR15129 [47] Hu J, Zhang Q, Luo Y, et al. Three-dimensional interferometric imaging and precession feature extraction of space targets in wideband radar[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 016029. [48] 黎湘, 高勋章, 刘永祥. 复杂运动目标ISAR成像技术进展与展望[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2014, 29(4): 508–515. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.004Li Xiang, Gao Xun-zhang, and Liu Yong-xiang. Research advances in ISAR imagery of complex motion target[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2014, 29(4): 508–515. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2014.04.004 [49] Sato T. Shape estimation of space debris using single-range Doppler interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(2): 1000–1005. DOI: 10.1109/36.752218 [50] Wang Q, Xing M D, Lu G Y, et al. Single range matching filtering for space debris radar imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(4): 576–580. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.903059 [51] 张磊, 李亚超, 刘燕, 等. 基于时频特性的窄带高速自旋目标运动估计及成像算法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2010, 40(6): 863–875.Zhang Lei, Li Ya-chao, Liu Yan, et al.. Time-frequency characteristics based motion estimation and imaging for high speed spinning targets via narrowband waveforms[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Information Sciences, 2010, 53(8): 1628–1640. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-010-4027-4. [52] Ding X F, Fan M M, Wei X Z, et al. Narrowband imaging method for spatial precession cone-shaped targets[J]. SCIENCE CHINA Technological Sciences, 2010, 53(4): 942–949. DOI: 10.1007/s11431-010-0112-6 [53] 丁小峰, 姚辉伟, 范梅梅, 等. 基于层析投影算法的空间旋转目标窄带雷达成像[J]. 信号处理, 2010, 26(5): 648–653. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.05.002Ding Xiao-feng, Yao Hui-wei, Fan Mei-mei, et al. Narrowband imaging for spatial rotating targets based on tomography algorithm[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 26(5): 648–653. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.05.002 [54] 雷腾, 刘进忙, 李松, 等. 基于MP稀疏分解的弹道中段目标微动ISAR成像新方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2011, 33(12): 2649–2654. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.15Lei Teng, Liu Jin-mang, Li Song, et al. A novel ISAR imaging method of ballistic midcourse targets based on MP sparse decomposition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(12): 2649–2654. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.12.15 [55] Zou F, Fu Y W, and Jiang W D. Micro-motion effect in inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of ballistic mid-course targets[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(6): 1548–1577. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-012-1175-2 [56] Kang W W, Zhang Y H, and Dong X. Micro-Doppler effect removal for ISAR imaging based on bivariate variational mode decomposition[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 74–81. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0104 [57] Yuan B, Chen Z P, and Xu S Y. Micro-Doppler analysis and separation based on complex local mean decomposition for aircraft with fast-rotating parts in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1285–1298. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2249588 [58] Stanković L, Orović I, Stanković S, et al. Compressive sensing based separation of nonstationary and stationary signals overlapping in time-frequency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(18): 4562–4572. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2271752 [59] Wang Q, Xing M D, Lu G Y, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional radar imaging for rapidly spinning targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 22–30. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909086 [60] Xing M D, Wang Q, Wang G Y, et al. A matched-filter-bank-based 3-D imaging algorithm for rapidly spinning targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2106–2113. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010499 [61] Zhang L, Xing M D, Qiu C W, et al. Two-dimensional spectrum matched filter banks for high-speed spinning-target three-dimensional ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 368–372. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2013487 [62] Bai X R, Xing M D, Zhou F, et al. High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of spinning space debris[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 2352–2362. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010854 [63] Bai X R and Bao Z. Imaging of rotation-symmetric space targets based on electromagnetic modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 1680–1689. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120772 [64] Bai X R and Bao Z. High-resolution 3D imaging of precession cone-shaped targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(8): 4209–4219. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2329004 [65] Bai X R, Zhou F, and Bao Z. High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of space targets in micromotion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3428–3440. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2431119 [66] Ai X F, Huang Y, Zhao F, et al. Imaging of spinning targets via narrow-band T/R-R bistatic radars[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 362–366. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2205893 [67] 梁必帅, 张群, 娄昊, 等. 基于微动特征关联的空间非对称自旋目标雷达三维成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(6): 1381–1388. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01147Liang Bi-shuai, Zhang Qun, Lou Hao, et al. A method of three-dimensional imaging based on micro-motion feature association for spatial asymmetrical spinning targets[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(6): 1381–1388. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01147 [68] 梁必帅, 张群, 娄昊, 等. 基于微动特征关联的空间自旋目标宽带雷达三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(9): 2133–2140. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01537Liang Bi-shuai, Zhang Qun, Lou Hao, et al. Three-dimensional broadband radar imaging of space spinning targets based on micro-motion parameter correlation[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(9): 2133–2140. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01537 [69] Sun Y X, Luo Y, Zhang Q, et al. Time-varying three-dimensional interferometric imaging for space rotating targets with stepped-frequency chirp signal[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(9): 1397–1405. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0009 [70] Gschwendtner A B and Keicher W E. Development of coherent laser radar at Lincoln Laboratory[J]. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 2000, 12(2): 383–396. [71] Lei J J and Lu C. Target classification based on micro-Doppler signatures[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2005: 179–183. [72] Nanzer J A and Rogers R L. Bayesian classification of humans and vehicles using micro-Doppler signals from a Scanning-beam radar[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2009, 19(5): 338–340. DOI: 10.1109/LMWC.2009.2017620 [73] Lin Y and Le Kernec J. Performance analysis of classification algorithms for activity recognition using micro-Doppler feature[C]. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Hong Kong, China, 2017: 480–483. [74] Smith G E, Woodbridge K, and Baker C J. Template based micro-Doppler signature classification[C]. 2006 European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 2006: 158–161. [75] 李开明, 张群, 罗迎, 等. 地面车辆目标识别研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2014, 42(3): 538–546. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.03.018Li Kai-ming, Zhang Qun, Luo Ying, et al. Review of ground vehicles recognition[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(3): 538–546. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.03.018 [76] 王晓丹, 王积勤. 雷达目标识别技术综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2003, 25(5): 22–26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2003.05.007Wang Xiao-dan and Wang Ji-qin. A survey of radar target recognition technique[J]. Modern Radar, 2003, 25(5): 22–26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2003.05.007 [77] Van Eeden W D, De Villiers J P, Berndt R J, et al. Micro-Doppler radar classification of humans and animals in an operational environment[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 102: 1–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.02.019 [78] Bilik I and Khomchuk P. Minimum divergence approaches for robust classification of ground moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(1): 581–603. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6129657 [79] Graley J, Murray T S, Mendat D R, et al.. Action recognition using micro-Doppler signatures and a recurrent neural network[C]. Proceedings of the 51st Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Baltimore, MD, USA, 2017: 1–5. [80] Lan J H, Zhang Z H, and Xiong S. Acoustic detection for vehicle targets and recognition by data fusion[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Ottawa, Canada, 2005: 551–553. [81] Yang L, Li G, Ritchie M, et al.. Gait classification based on micro-Doppler features[C]. Proceedings of 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–4. [82] Zabalza J, Clemente C, Di Caterina G, et al. Robust PCA micro-Doppler classification using SVM on embedded systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 2304–2310. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130082 [83] Vishwakarma S and Ram S S. Dictionary learning for classification of indoor micro-Doppler signatures across multiple carriers[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 2017: 0992–0997. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944348. [84] 方菲菲, 余稳. 基于PCA-LDA-SVM的多普勒雷达车型识别算法[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2012, 27(1): 111–116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.01.019Fang Fei-fei and Yu Wen. Vehicle recognition algorithm with doppler radar based on PCA-LDA-SVM[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition&Processing, 2012, 27(1): 111–116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2012.01.019 [85] Javier R J and Kim Y. Application of linear predictive coding for human activity classification based on micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1831–1834. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2311819 [86] Smith G E, Woodbridge K, and Baker C J. Radar micro-Doppler signature classification using dynamic time warping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1078–1096. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545175 [87] 冯存前, 李靖卿, 贺思三, 等. 组网雷达中弹道目标微动特征提取与识别综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 609–620. DOI: 10.12000/JR15084Feng Cun-qian, Li Jing-qing, He Si-san, et al. Micro-Doppler feature extraction and recognition based on netted radar for ballistic targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 609–620. DOI: 10.12000/JR15084 [88] Chen X L, Guan J, Li X Y, et al. Effective coherent integration method for marine target with micromotion via phase differentiation and radon-Lv’s distribution[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1284–1295. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0100 [89] Chen X L, Guan J, Bao Z H, et al. Detection and extraction of target with micromotion in spiky sea clutter via short-time fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1002–1018. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2246574 [90] 孙挺, 程旭. 一种基于全极化回波的微多普勒增强算法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(9): 2071–2076. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.003Sun Ting and Cheng Xu. A novel method of micro-Doppler signature enhancement based on full polarization echoes[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(9): 2071–2076. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2017.09.003 [91] Damarla T, Bradley M, Mehmood A, et al. Classification of animals and people ultrasonic signatures[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(5): 1464–1472. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2012.2236550 [92] Shi X R, Zhou F, Liu L, et al. Textural feature extraction based on time-frequency spectrograms of humans and vehicles[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1251–1259. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0432 [93] Amin M G, Ahmad F, Zhang Y D, et al. Human gait recognition with cane assistive device using quadratic time-frequency distributions[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1224–1230. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0119 [94] Saho K, Fujimoto M, Masugi M, et al. Gait classification of young adults, elderly non-fallers, and elderly fallers using micro-Doppler radar signals: Simulation study[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(8): 2320–2321. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2678484 [95] Mikhelson I V, Bakhtiari S, Elmer II T W, et al. Remote sensing of heart rate and patterns of respiration on a stationary subject using 94-GHz millimeter-wave interferometry[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(6): 1671–1677. DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2111371 [96] Xu Z W, Wu Y J, and Lu X Q. Time-frequency analysis of terahertz radar signal for vital signs sensing based on radar sensor[J]. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 2013, 13(4): 241–253. DOI: 10.1504/IJSNET.2013.055587 [97] Chen V C. Radar micro-Doppler signatures-principle and applications[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2012, 10(3): 231–240. [98] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. DOI: 10.12000/JR16039Wang Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. DOI: 10.12000/JR16039 [99] Petkie D T, Bryan E, Benton C, et al.. Remote respiration and heart rate monitoring with millimeter-wave/terahertz radars[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7117, Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology, Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom, 2008, 7117: 71170I. DOI: 10.1117/12.800356. [100] 杨琪, 邓彬, 王宏强, 等. 太赫兹雷达目标微动特征提取研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(1): 22–45. DOI: 10.12000/JR17087Yang Qi, Deng Bin, Wang Hongqiang, et al. Advancements in research on micro-motion feature extraction in the terahertz region[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(1): 22–45. DOI: 10.12000/JR17087 [101] Mehmood A, Sabatier J M, Bradley M, et al. Extraction of the velocity of walking human’s body segments using ultrasonic Doppler[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 128(5): EL316. DOI: 10.1121/1.3501115 [102] Lecun Y, Bengio Y, and Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. DOI: 10.1038/nature14539 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: