Sparse Imaging of Building Layouts in Ultra-wideband Radar
-
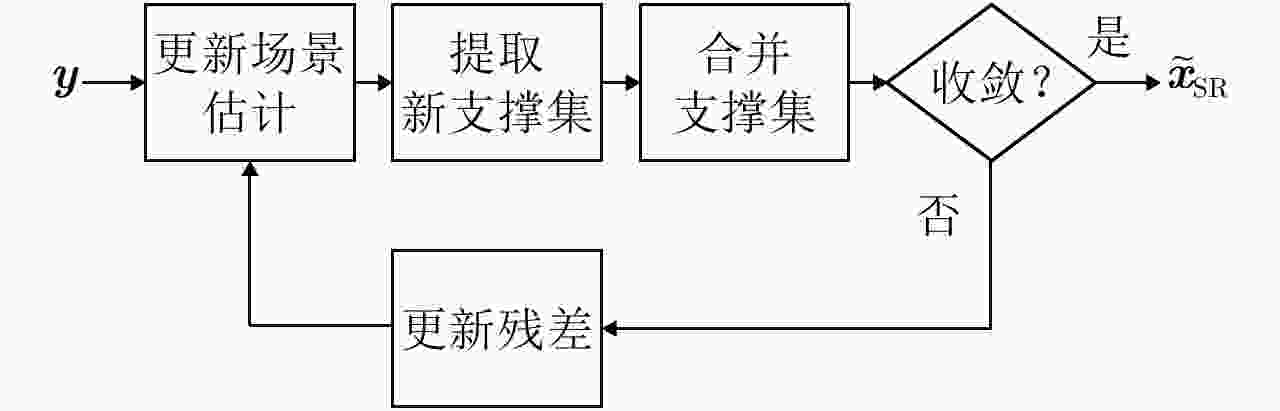
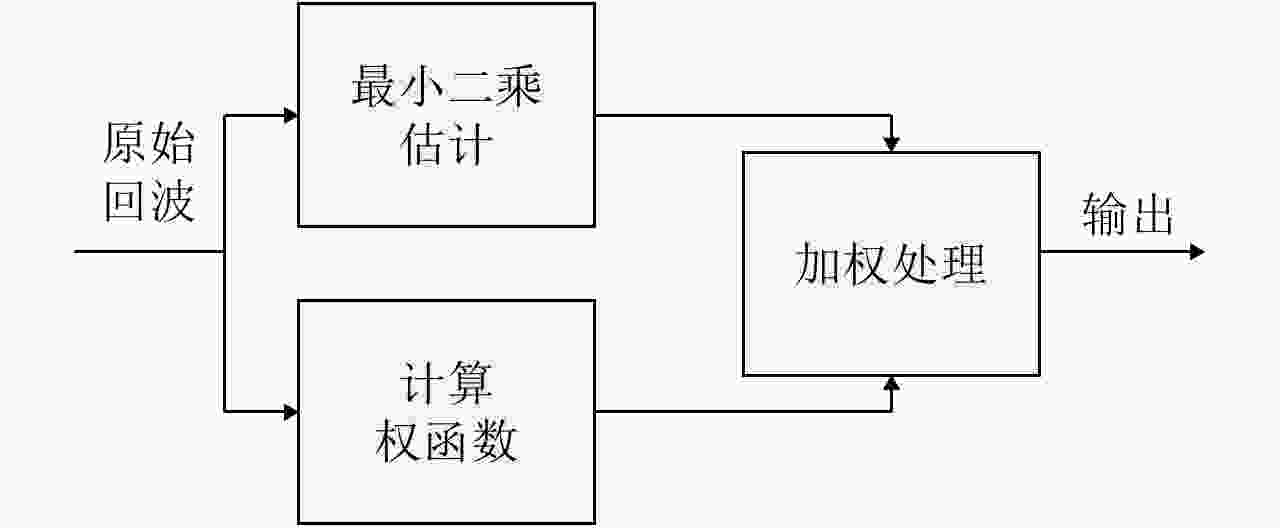
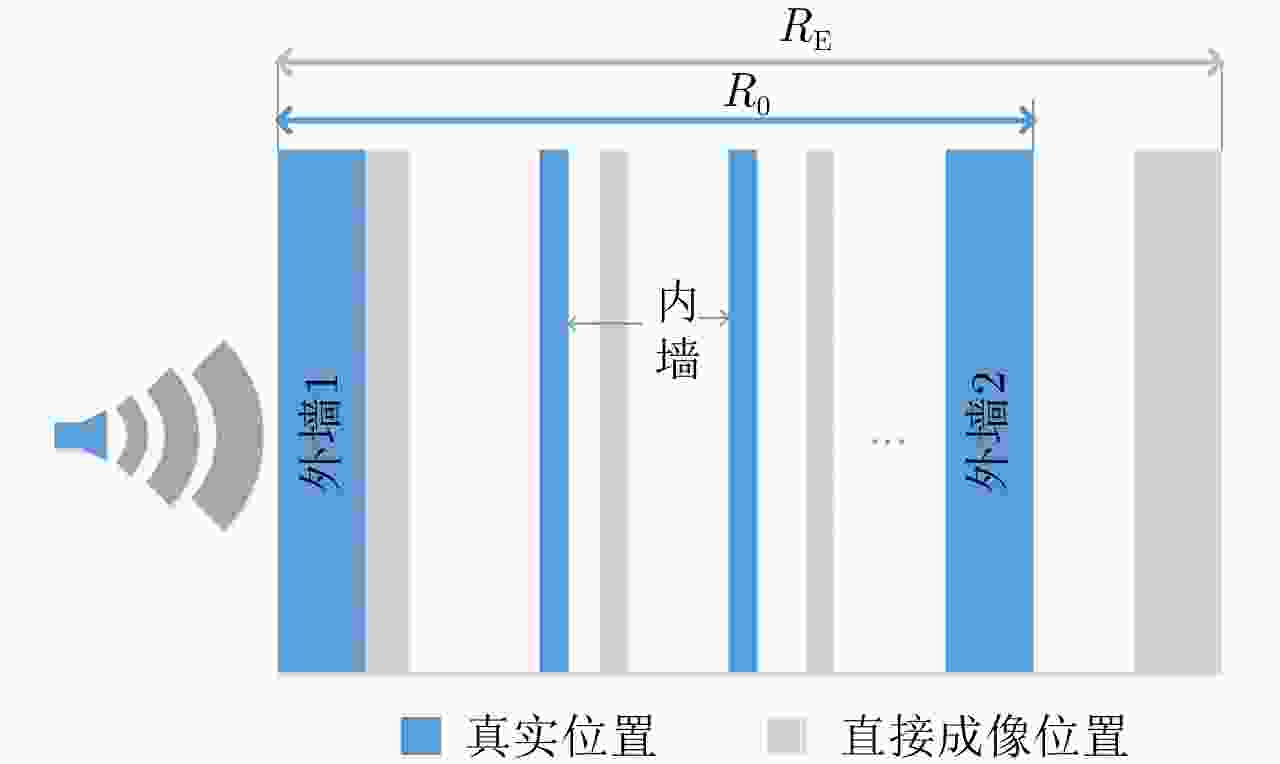
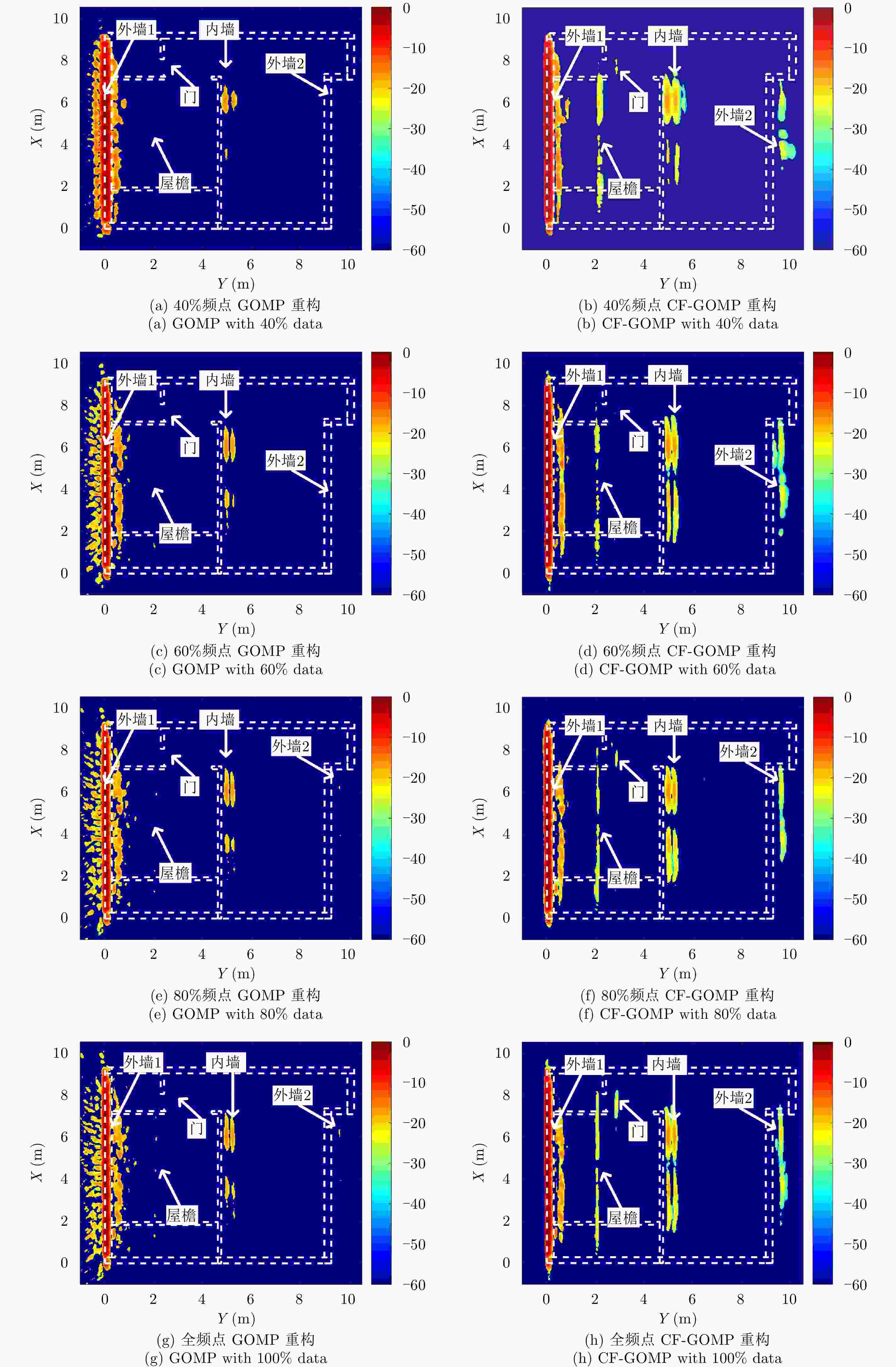
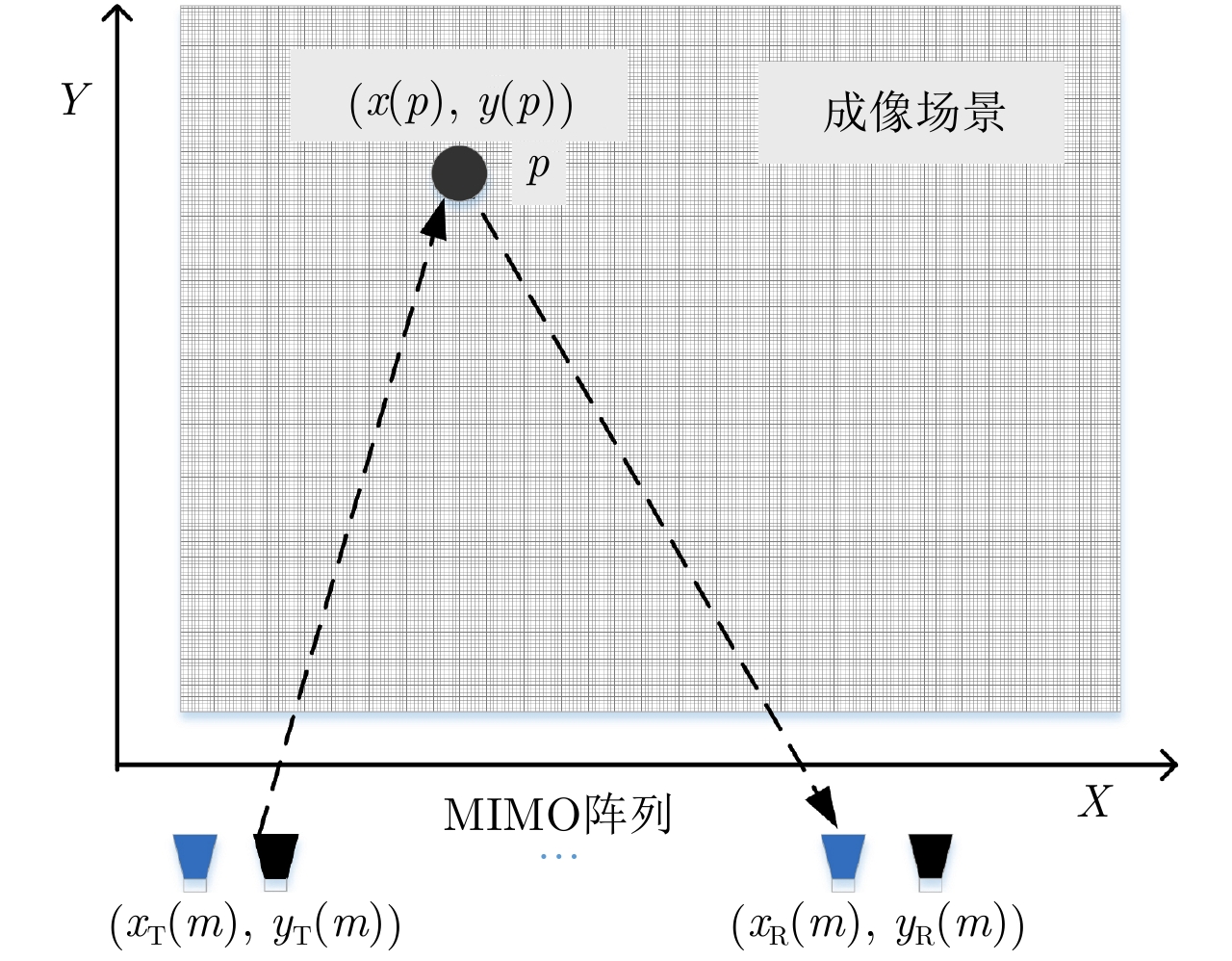
摘要: 超宽带雷达具备穿透墙体获得建筑物内部结构布局的能力,为建筑物内人员探测定位提供更丰富的信息。传统成像常存在较为严重的旁瓣,而且墙后目标成像位置也会受墙体影响而产生偏移。为提高成像质量,稀疏重构技术被引入穿墙成像领域,但传统方法对弱散射目标的重构概率较低。该文提出结合相干因子(Coherence Factor, CF)加权的稀疏重构方法,在稀疏重构提取支撑集的过程中,利用CF增强成像的结果来提高支撑集原子的正确性,降低稀疏重构过程中强散射目标旁瓣的影响,最终提高场景中弱散射目标的重构概率。同时建立了多层墙体位置校正模型,将场景校正放到稀疏重构之后进行,从而以较低的计算复杂度降低墙体定位误差。实测数据处理结果表明,相比于传统的稀疏成像方法,相同的数抽取比例下,该文提出的方法能够有效提高场景中弱散射目标重构概率,并将建筑物内部墙体定位误差降低至10 cm以内。Abstract: Ultra-WideBand (UWB) radar can reconstruct the layout of a building, providing rich information for detecting and locating humans in buildings. Traditional imaging methods suffer from serious sidelobes and location displacement of behind-the-wall target because of the influence of walls. Sparse recovery is introduced into the field of through-the-wall imaging to improve the imaging quality. However, the reconstruction probability of weak scattering targets is low in traditional methods. In this study, the combination of sparse recovery method and Coherence Factor (CF) weighting is proposed to improve the reconstruction probability of weak scattering targets inside a room. The quasi-establishment of the support set can be improved during sparse imaging by reducing the effect of the sidelobes of strong scattering targets with CF, ultimately enhancing the robustness of the sparse imaging of the building layout. A location correction model for multiple walls after sparse imaging is established, based on which the locating error of walls can be reduced with a low amount of calculation. The results of the measured data reveal that compared with the traditional generalized orthogonal matching pursuit method, the proposed methods can improve the reconstruction probability of weak scattering targets and reduce the locating error of the inner layouts of buildings to less than 10 cm.
-
Key words:
- Ultra-WideBand (UWB) radar /
- Through-the-wall imaging /
- Sparse recovery /
- Building layout
-
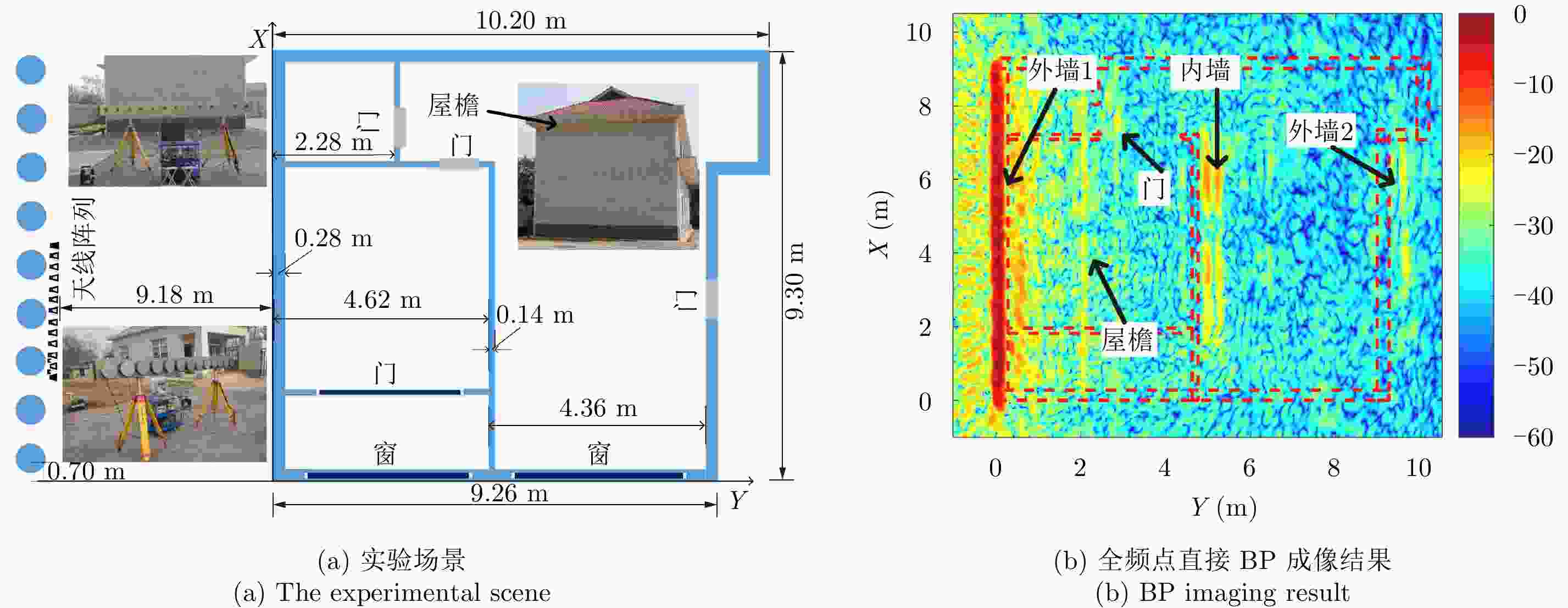
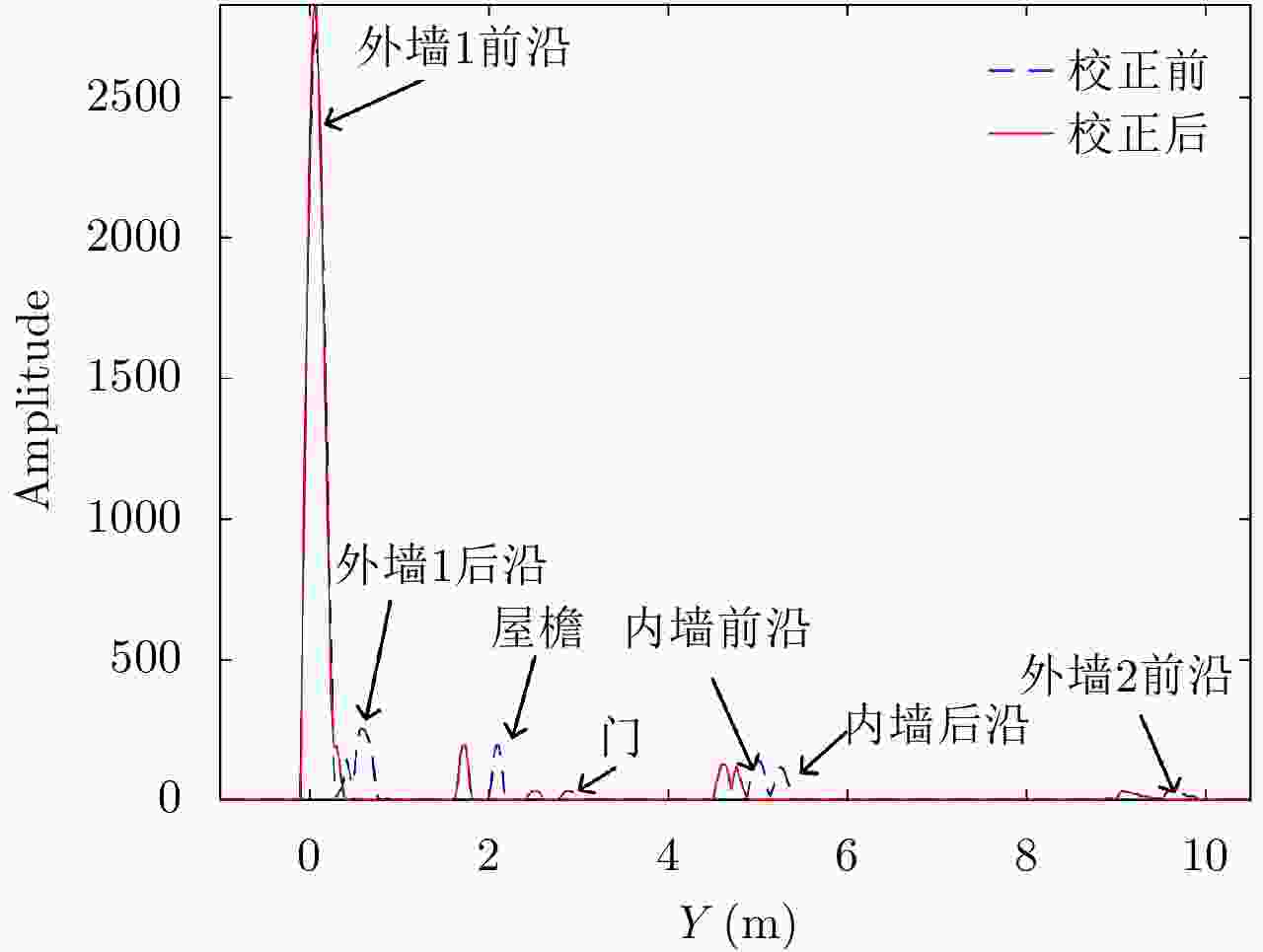
表 1 各墙体校正前后y方向位置对比
Table 1. The position contrast on y axis before and after correction of each wall
结构名称 校正前位置(m) 真实位置(m) 校正后位置(m) 校正前误差(m) 校正后误差(m) 外墙1后沿 0.614 0.280 0.297 0.334 0.017 内墙前沿 5.024 4.620 4.591 0.404 –0.029 内墙后沿 5.254 4.760 4.793 0.494 0.033 外墙2前沿 9.491 8.980 9.059 0.511 0.079 -
[1] Amin M. Compressive Sensing for Urban Radar[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2015: 49–86. [2] Chen B, Jin T, Lu B Y, et al. Building interior layout reconstruction from through-the-wall radar image using MST-based method[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2014, 2014: 31. DOI: 10.1186/1687-6180-2014-31 [3] 胡俊. 远距离超宽带穿墙雷达人体目标成像关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2014: 33–57.Hu Jun. Study of human target imaging with long-range ultra-wideband through-wall imaging radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014: 33–57. [4] Anwar N S N and Abdullah M Z. Sidelobe suppression featuring the phase coherence factor in 3-D through-the-wall radar imaging[J]. Radioengineering, 2016, 25(4): 730–740. DOI: 10.13164/re.2016.0730 [5] Burkholder R J and Browne K E. Coherence factor enhancement of through-wall radar images[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2010, 9: 842–845. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2010.2069078 [6] 吴一戎, 洪文, 张冰尘, 等. 稀疏微波成像研究进展(科普类)[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(4): 383–395. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14105Wu Yi-Rong, Hong Wen, Zhang Bing-chen, et al. Current developments of sparse microwave imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(4): 383–395. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14105 [7] 刘记红, 徐少坤, 高勋章, 等. 压缩感知雷达成像技术综述[J]. 信号处理, 2011, 27(2): 251–260. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.02.016Liu Ji-hong, Xu Shao-kun, Gao Xun-zhang, et al. A review of radar imaging technique based on compressed sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 27(2): 251–260. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2011.02.016 [8] 李少东, 杨军, 陈文峰, 等. 基于压缩感知理论的雷达成像技术与应用研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 495–508. DOI: 10.1109/JEIT150874Li Shao-dong, Yang Jun, Chen Wen-feng, et al. Overview of radar imaging technique and application based on compressive sensing theory[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 495–508. DOI: 10.1109/JEIT150874 [9] 顾福飞, 池龙, 张群, 等. 基于压缩感知的稀疏阵列MIMO雷达成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(10): 2452–2457. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00287Gu Fu-fei, Chi Long, Zhang Qun, et al. An imaging method for MIMO radar with sparse array based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2011, 33(10): 2452–2457. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00287 [10] Carmi A Y, Mihaylova L S, and Godsill S J. Compressed Sensing & Sparse Filtering[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 396–461. [11] Eldar Y C and Kutyniok G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 348–393. [12] 孙洪, 张智林, 余磊. 从稀疏到结构化稀疏: 贝叶斯方法[J]. 信号处理, 2012, 28(6): 759–773. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.06.001Sun Hong, Zhang Zhi-lin, and Yu Lei. From sparsity to structured sparsity: Bayesian perspective[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 28(6): 759–773. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2012.06.001 [13] Wang J, Kwon S, and Shim B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(12): 6202–6216. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2218810 [14] 杨俊刚. 利用稀疏信息的正则化雷达成像理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2013: 19–30.Yang Jun-gang. Research on sparsity-driven regularization radar imaging theory and method[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2013: 19–30. [15] 孙鑫. 超宽带穿墙雷达成像方法与技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015: 37–68.Sun Xin. Research on method and technique of ultra-wideband through-the-wall radar imaging[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015: 37–68. [16] Song Y P, Jin T, Lu B Y, et al. An extended virtual aperture imaging model for through-the-wall sensing and its environmental parameters estimation[J]. Radioengineering, 2014, 23(3): 842–851. [17] Jin T, Chen B, and Zhou Z M. Image-domain estimation of wall parameters for autofocusing of through-the-wall SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(3): 1836–1843. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2206395 [18] 刘记红, 黎湘, 徐少坤, 等. 基于改进正交匹配追踪算法的压缩感知雷达成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(6): 1344–1350. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01097Liu Ji-hong, Li Xiang, Xu Shao-kun, et al. Compressed sensing radar imaging methods based on modified orthogonal matching pursuit algorithms[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(6): 1344–1350. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.01097 [19] Fang J, Xu Z B, Zhang B C, et al. Fast compressed sensing SAR imaging based on approximated observation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(1): 352–363. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2263309 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: