POA Correction Method Using High-resolution Full-polarization SAR Image
-
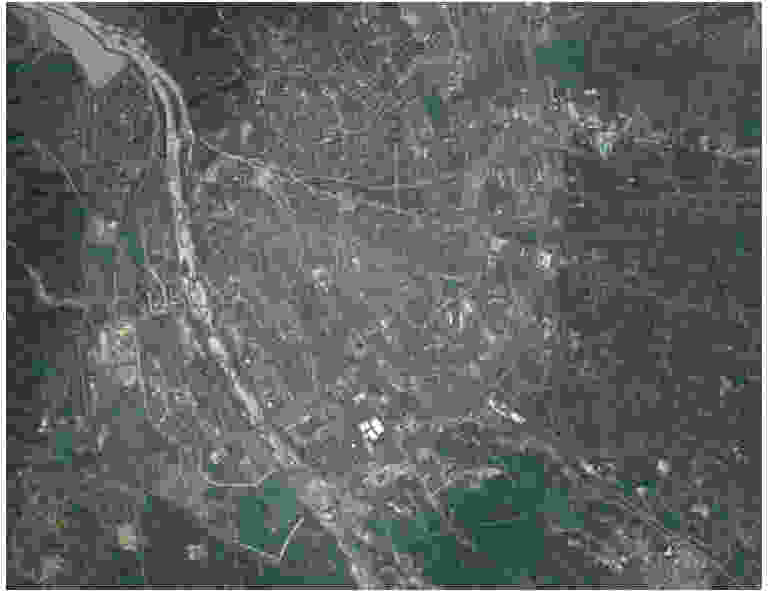
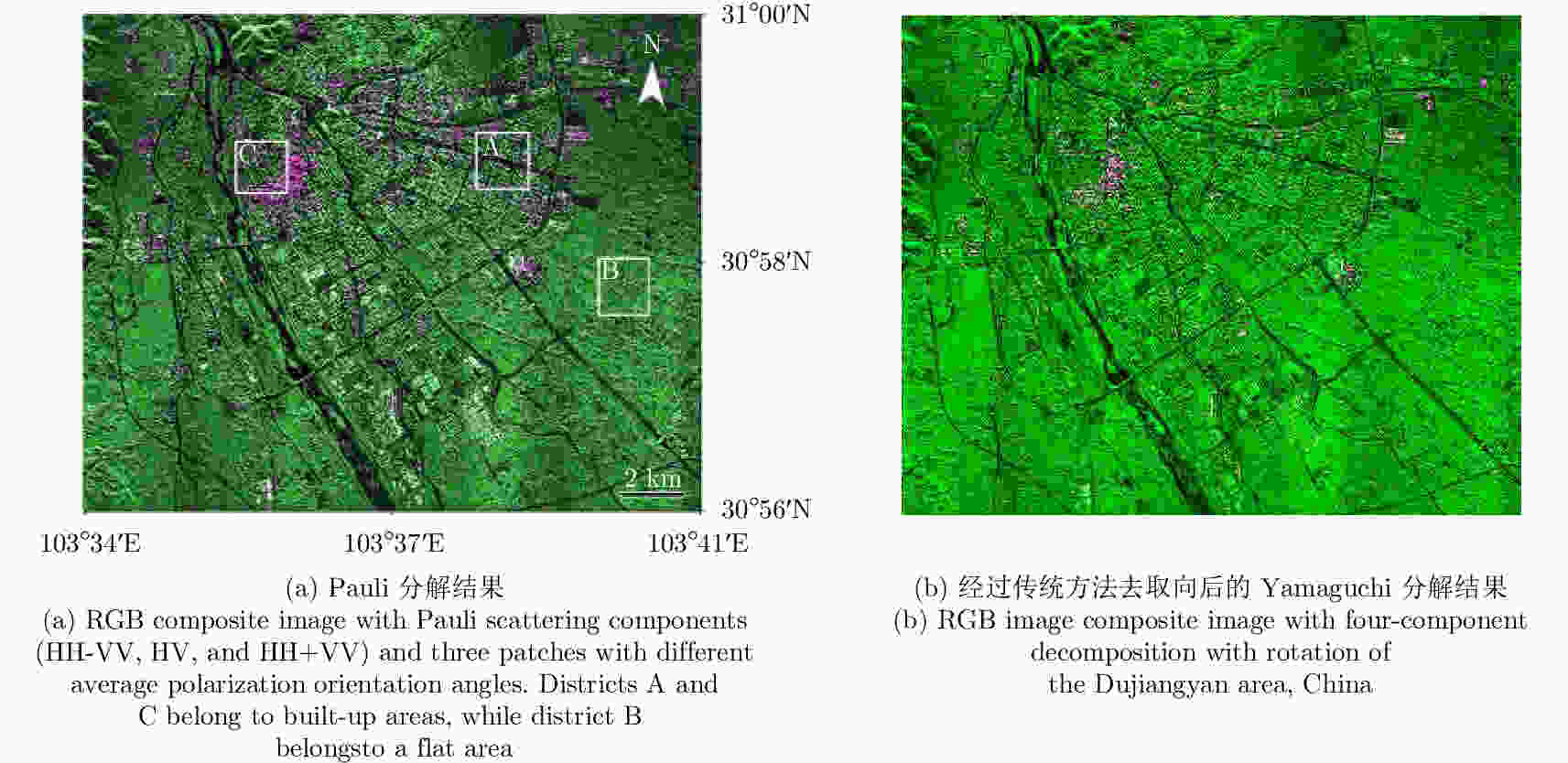
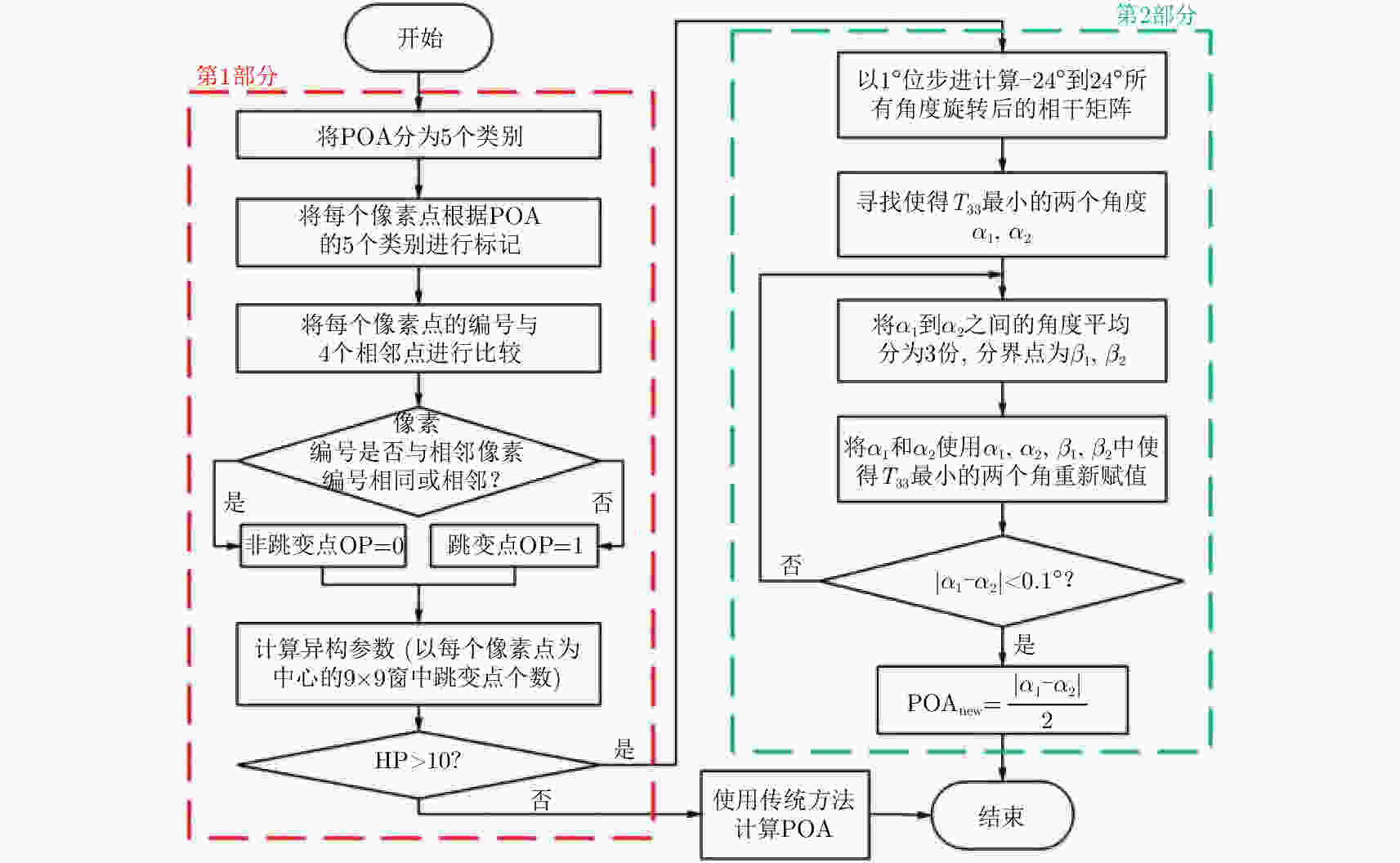
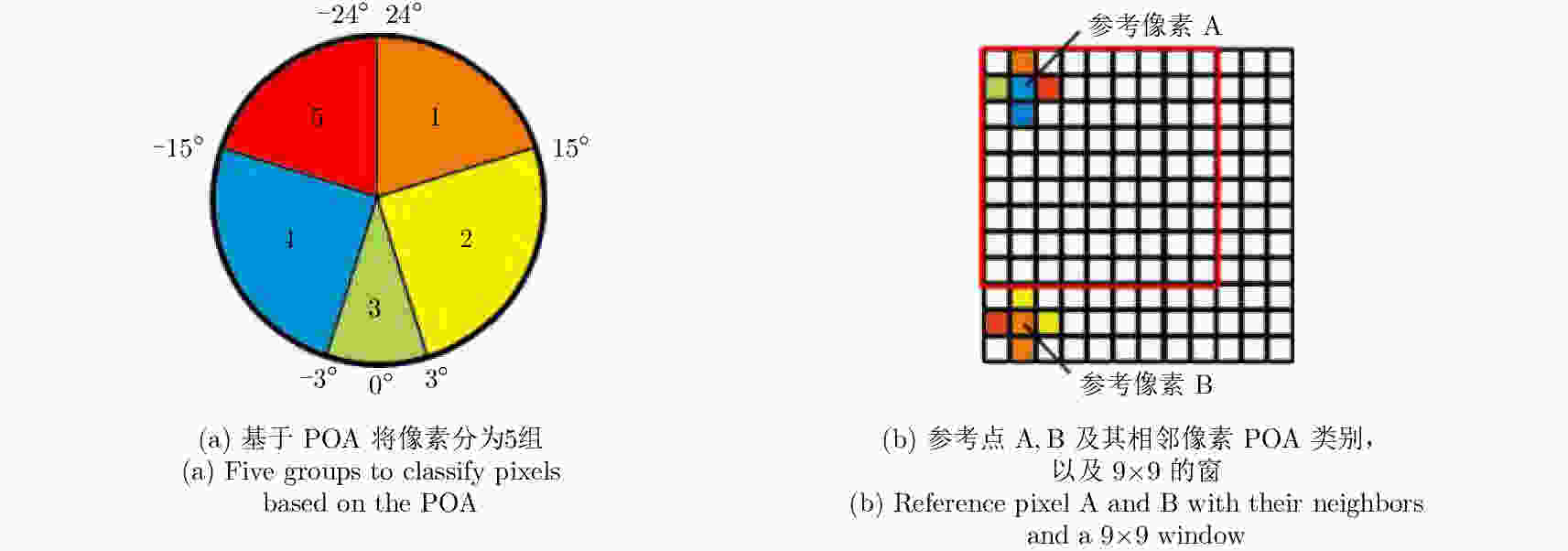
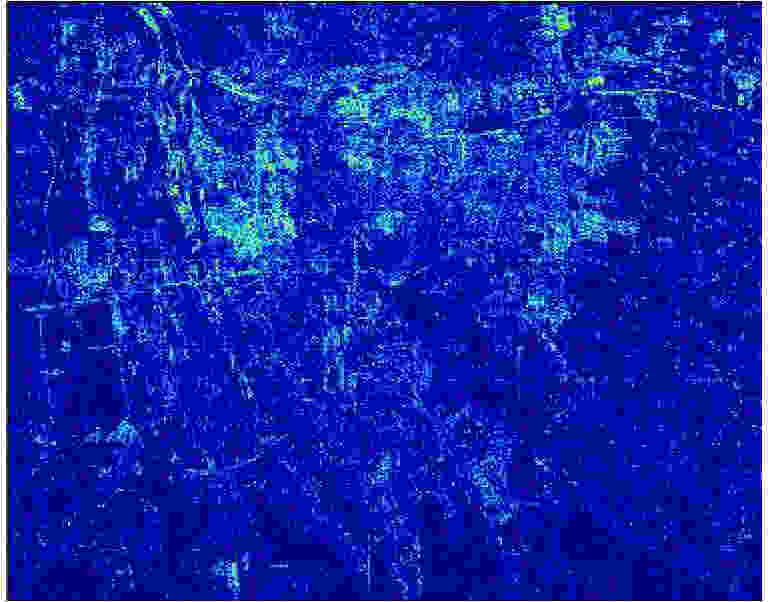
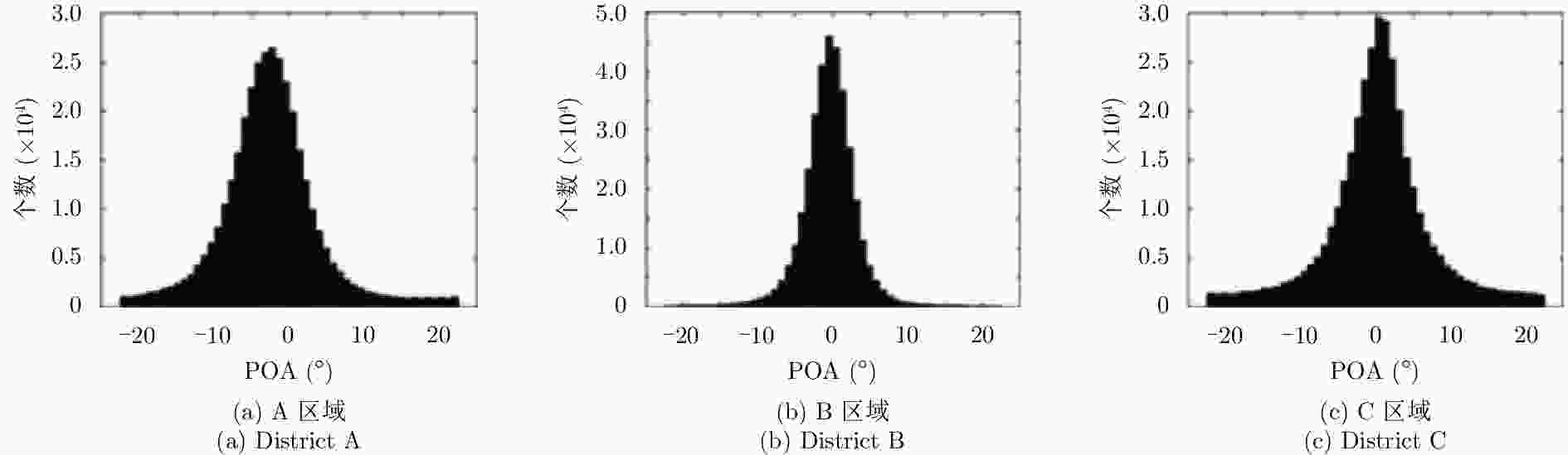
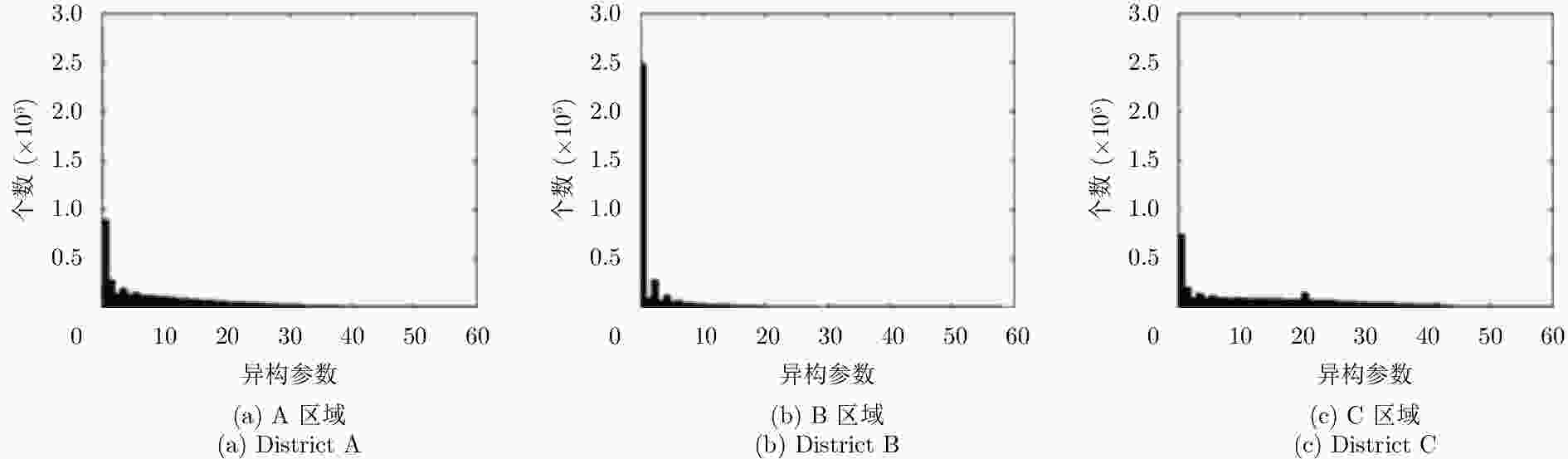
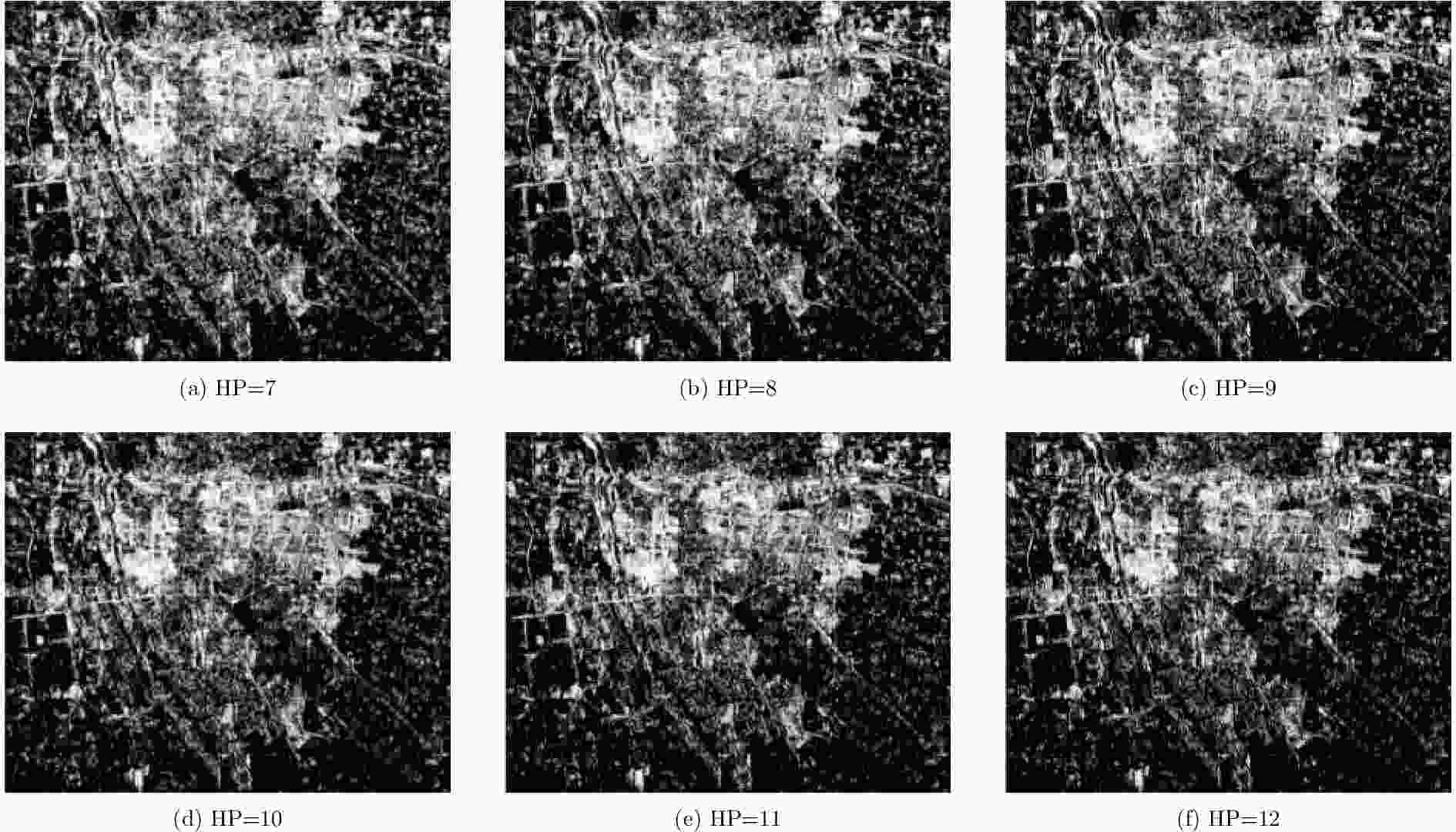
摘要: 城市地区极化分解对于监测城市扩张速度并研究其对生态环境的影响非常重要。全极化合成孔径雷达(PolSAR)允许我们使用极化目标分解方法来检测地物散射机制,是一种对城区变化进行监测的手段。然而,目标的极化方向角(POA)会影响极化分解结果,导致体散射过估等问题,使得极化分解结果不能正确地体现目标的散射机理。传统的去取向方法只对主导极化方向角较小的地区起到去取向的作用,对取向角较大区域没有明显的效果。该文针对以上问题提出了一种基于高分辨率城市区域图像的POA校正方法。首先,高分辨率图像中城市建筑区域的POA会因为地物变化出现跳变的现象,可以利用POA的随机性对城市地区的范围进行估计。其次,使用线性逼近方法来获取城区中使交叉极化项最小的POA。利用该文提出的POA校正算法,可以使取向角导致的误分解问题得到缓解,提高分解结果的准确度。该算法使用2009年于四川都江堰地区获取的机载X波段全极化数据进行验证,得到了明显的改进结果,城市区域的体散射分量得到了显著的提升。Abstract: Polarimetric decomposition in urban areas is important for monitoring the speed of city expansion and studying its ecological environmental influence. Using fully Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) is a method for consistent observation of large-range urban changes. In the last two decades, most research on decomposition methods have stated that Polarization Orientation Angle (POA) would affect the results of decomposition by overestimating the volume scattering contribution of urban areas. The available deorientation methods cannot rotate built-up areas with large POAs. This paper proposes an algorithm for decomposition of high-resolution urban area images based on a POA correction method. First, for high-resolution images of built-up areas, the POA changes radically pixel by pixel. An approximate assessment of urban areas can be accomplished using POA randomness. Then, to search for the true POA of large dominant POA areas (most built-up regions), the linear approximation method is used to locate POAs that can minimize cross-polarized terms. Thereby, the inaccurate decomposition that occurs by the deviation of POA can be fixed, and the accuracy of results improves. The fully PolSAR data of the Dujiangyan area in Sichuan Province, China are used to confirm the algorithm’s effectiveness. The data are acquired by an X-band airborne SAR sensor designed by the Institute of Electronics, China Academy of Sciences (IECAS).
-
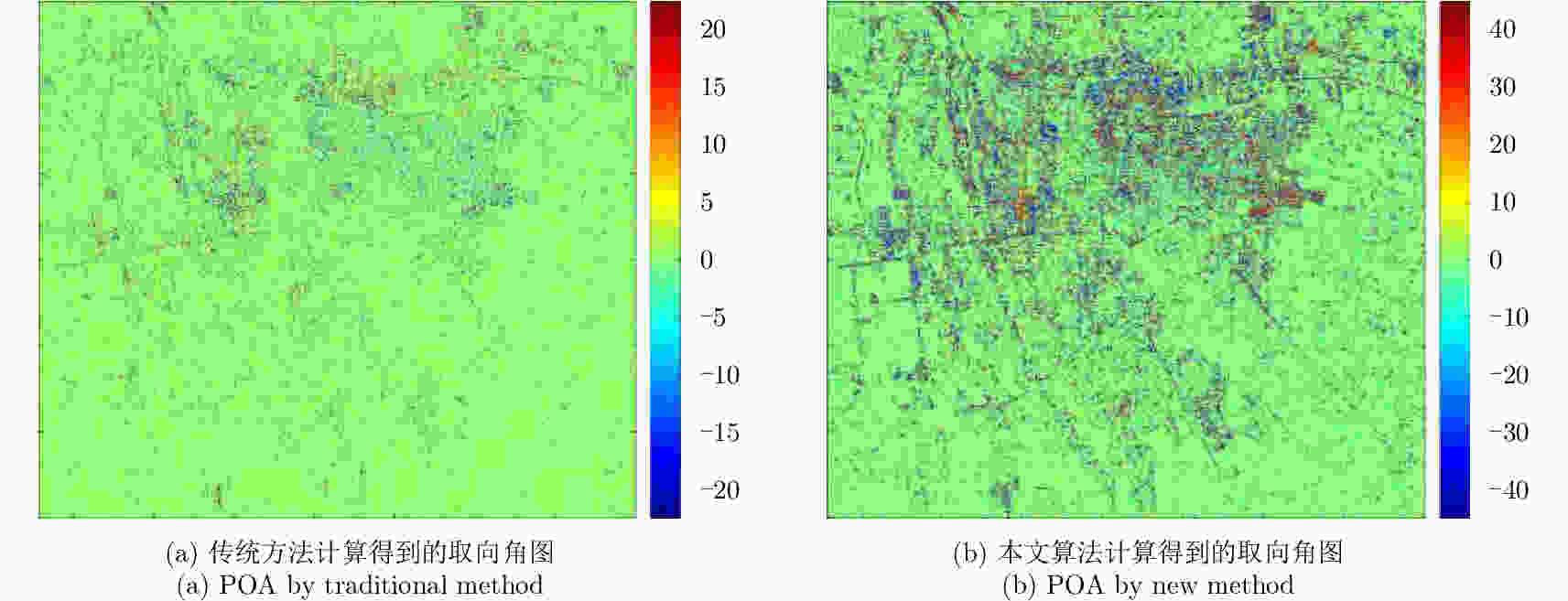
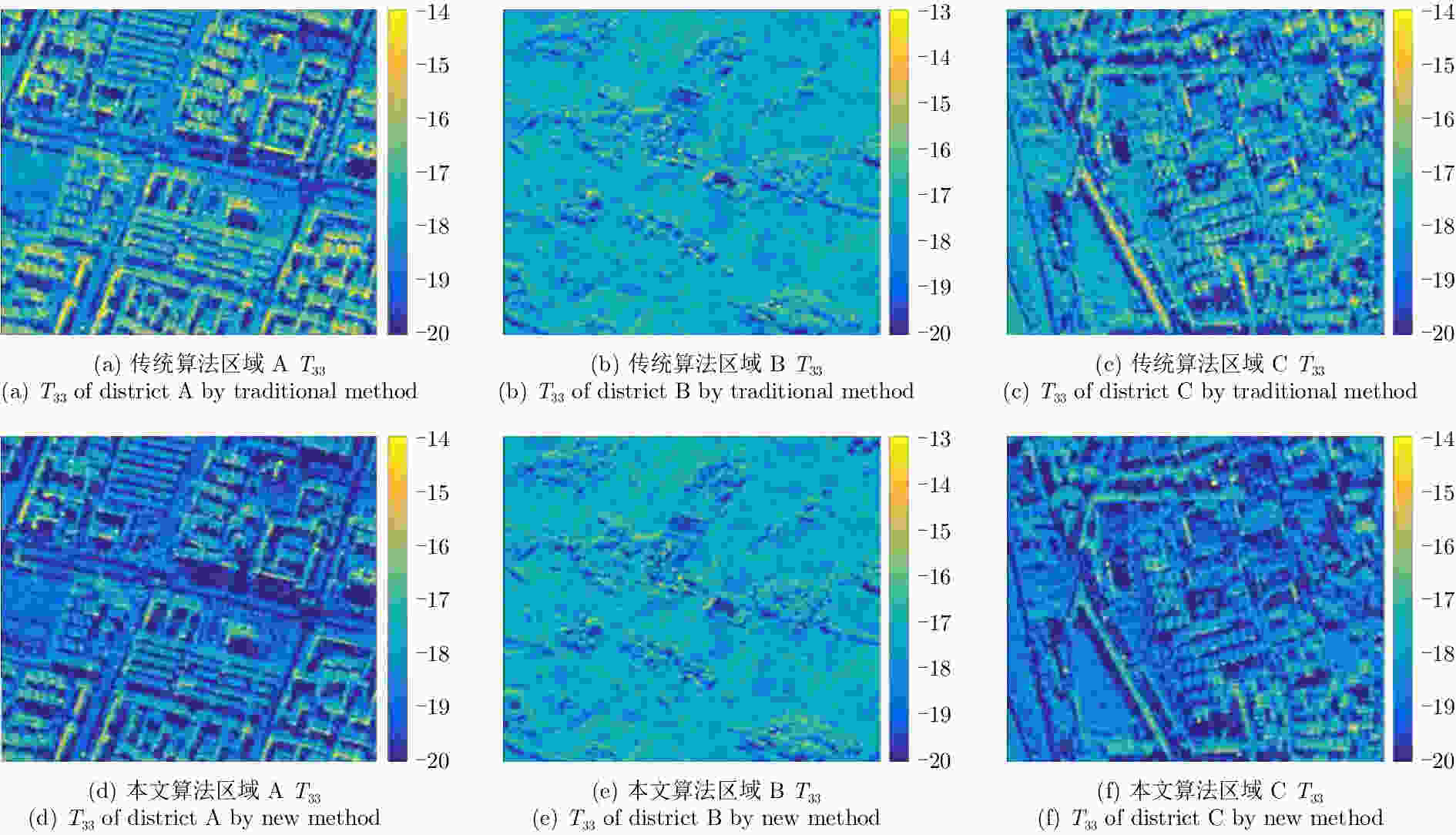
表 1 A, B, C区域中交叉极化T33项平均值
Table 1. Average T33 of districts A, B and C after rotation using POAs calculated by the traditional method and the new method
区域 传统方法T33平均值 本文方法T33平均值 A 4.6321e–08 1.5611e–08 B 3.5252e–08 3.5252e–08 C 2.9456e–08 1.3435e–08 表 2 A, B, C区域中各散射分量占总功率的百分比
Table 2. Percentage of scattering powers with traditional method and the new method
区域 算法 Ps Pv Pd A 传统算法 1.04 84.83 2.69 本文算法 20.29 62.84 2.84 B 传统算法 0.74 90.35 2.79 本文算法 14.72 72.61 10.16 C 传统算法 29.34 23.60 43.85 本文算法 18.35 20.73 56.06 -
[1] 赵春雷, 王亚梁, 阳云龙, 等. 雷达极化信息获取及极化信号处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR16092Zhao Chun-lei, Wang Ya-liang, Yang Yun-long, et al. Review of radar polarization information acquisition and polarimetric signal processing techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. DOI: 10.12000/JR16092 [2] Cloude S R and Pottier E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. DOI: 10.1109/36.485127 [3] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. DOI: 10.12000/JR16039Wang Xue-song. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. DOI: 10.12000/JR16039 [4] 王超, 张红, 陈曦, 等. 全极化合成孔径雷达图像处理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008Wang Chao, Zhang Hong, Chen Xi, et al.. Full Polarimetric SAR Image Processing[M]. Beijing: Beijing Science Press, 2008 [5] Krogager E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. DOI: 10.1049/el:19900979 [6] Van Zyl J J. Unsupervised classification of scattering behavior using radar polarimetry data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1989, 27(1): 36–45. DOI: 10.1109/36.20273 [7] Cloude S R. Target decomposition theorems in radar scattering[J]. Electronics Letters, 1985, 21(1): 22–24. DOI: 10.1049/el:19850018 [8] Pottier E. Unsupervised classification scheme and topography derivation of POLSAR data based on the H/A/α polarimetric decomposition theorem[C]. Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Radar Polarimetry, Nantes, France, 1998: 535–548 [9] 陈思伟, 李永祯, 王雪松, 等. 极化SAR目标散射旋转域解译理论与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. DOI: 10.12000/JR17033Chen Si-wei, Li Yong-zhen, Wang Xue-song, et al. Polarimetric SAR target scattering interpretation in rotation domain: Theory and application[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. DOI: 10.12000/JR17033 [10] Xu F and Jin Y Q. Deorientation theory of polarimetric scattering targets and application to terrain surface classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(10): 2351–2364. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.855064 [11] Yamaguchi Y, Sato A, Boerner W M, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with rotation of coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2251–2258. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2099124 [12] Lee J S, Schuler D L, and Ainsworth T L. Polarimetric SAR data compensation for terrain azimuth slope variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2153–2163. DOI: 10.1109/36.868874 [13] Lee J S, Schuler D L, Ainsworth T L, et al. On the estimation of radar polarization orientation shifts induced by terrain slopes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(1): 30–41. DOI: 10.1109/36.981347 [14] Kimura H. Radar polarization orientation shifts in Built-Up areas[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(2): 217–221. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915737 [15] Chen S W, Wang X S, Xiao S P, et al. General polarimetric model-based decomposition for coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1843–1855. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2255615 [16] Chen S W, Ohki M, Shimada M, et al. Deorientation effect investigation for model-based decomposition over oriented Built-Up areas[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 273–277. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2203577 [17] Chen S W, Li Y Z, Wang X S, et al. Modeling and interpretation of scattering mechanisms in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar: Advances and perspectives[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 79–89. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312099 [18] Chen S W and Sato M. Tsunami damage investigation of built-up areas using multitemporal spaceborne full polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4): 1985–1997. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2210050 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: