Antenna Phase Center Calibration for Array InSAR System Based on Orthogonal Subspace
-
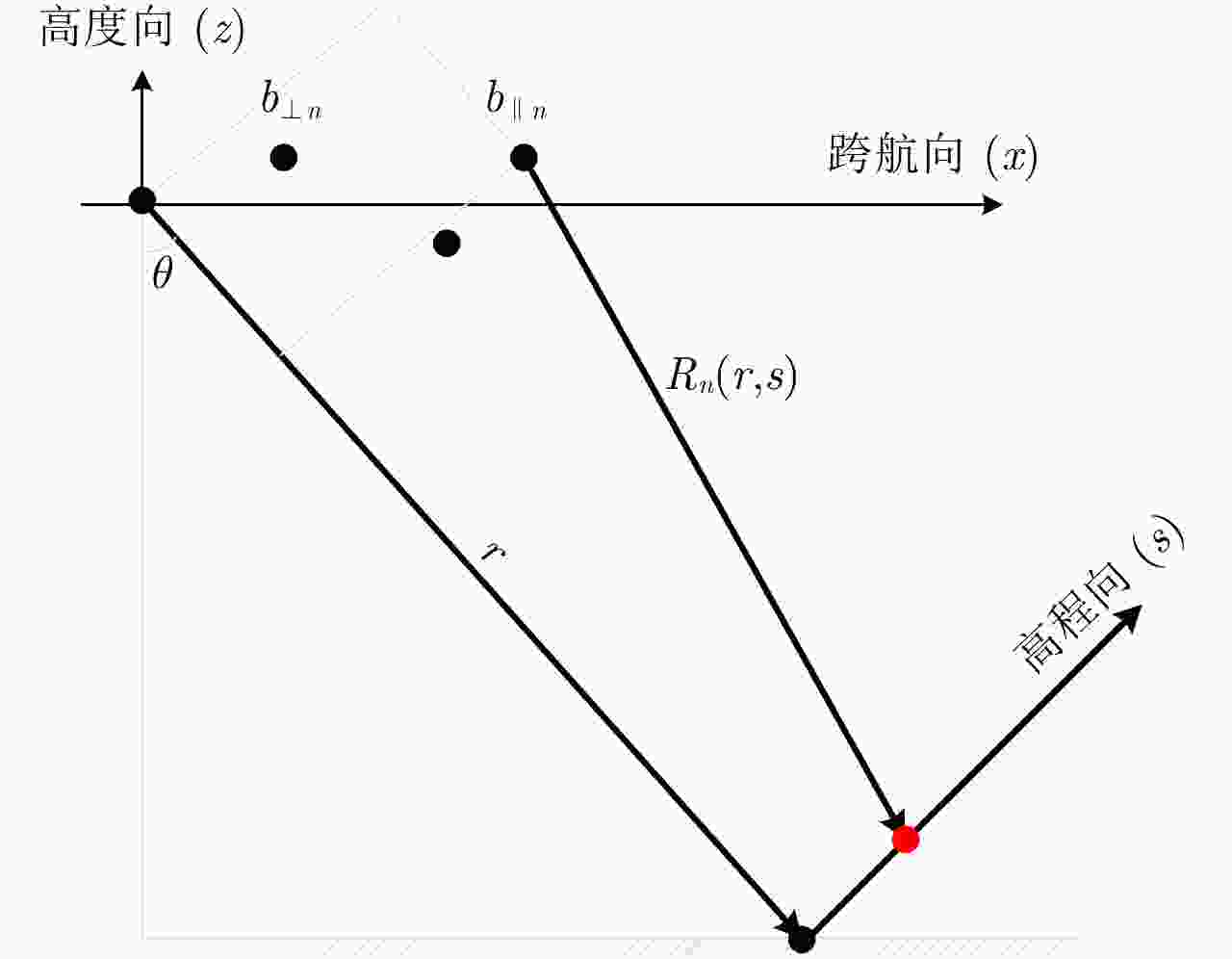
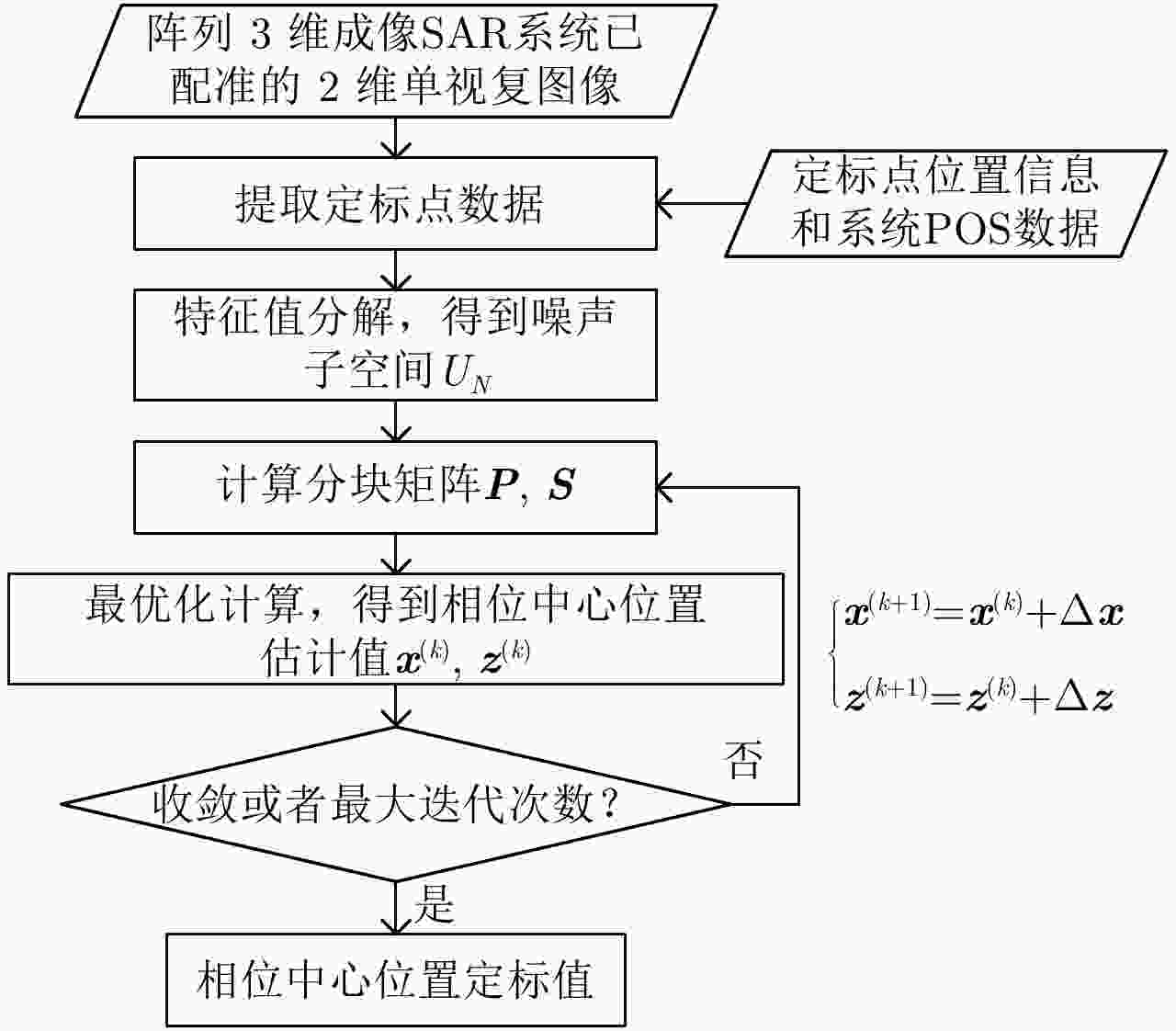
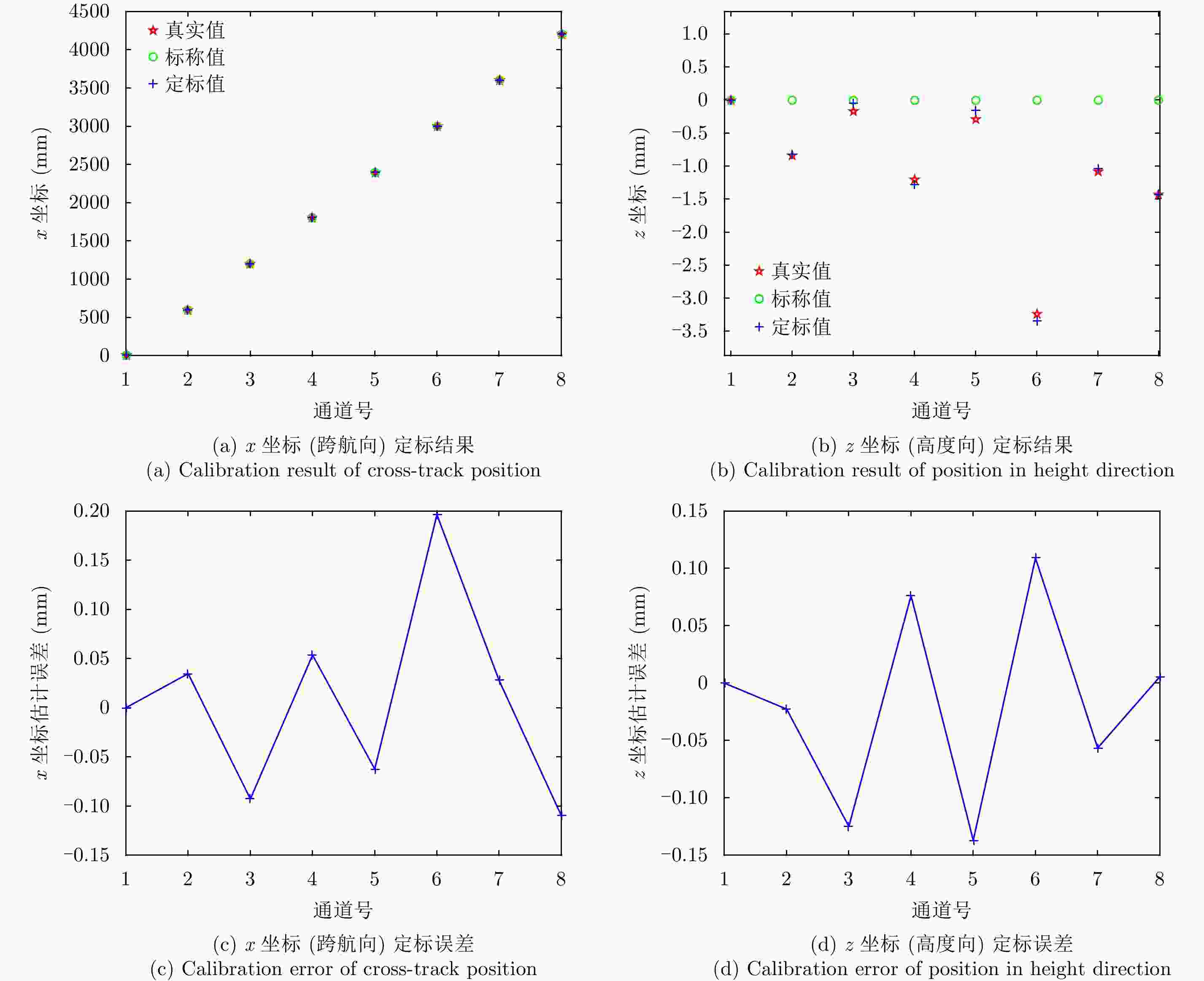
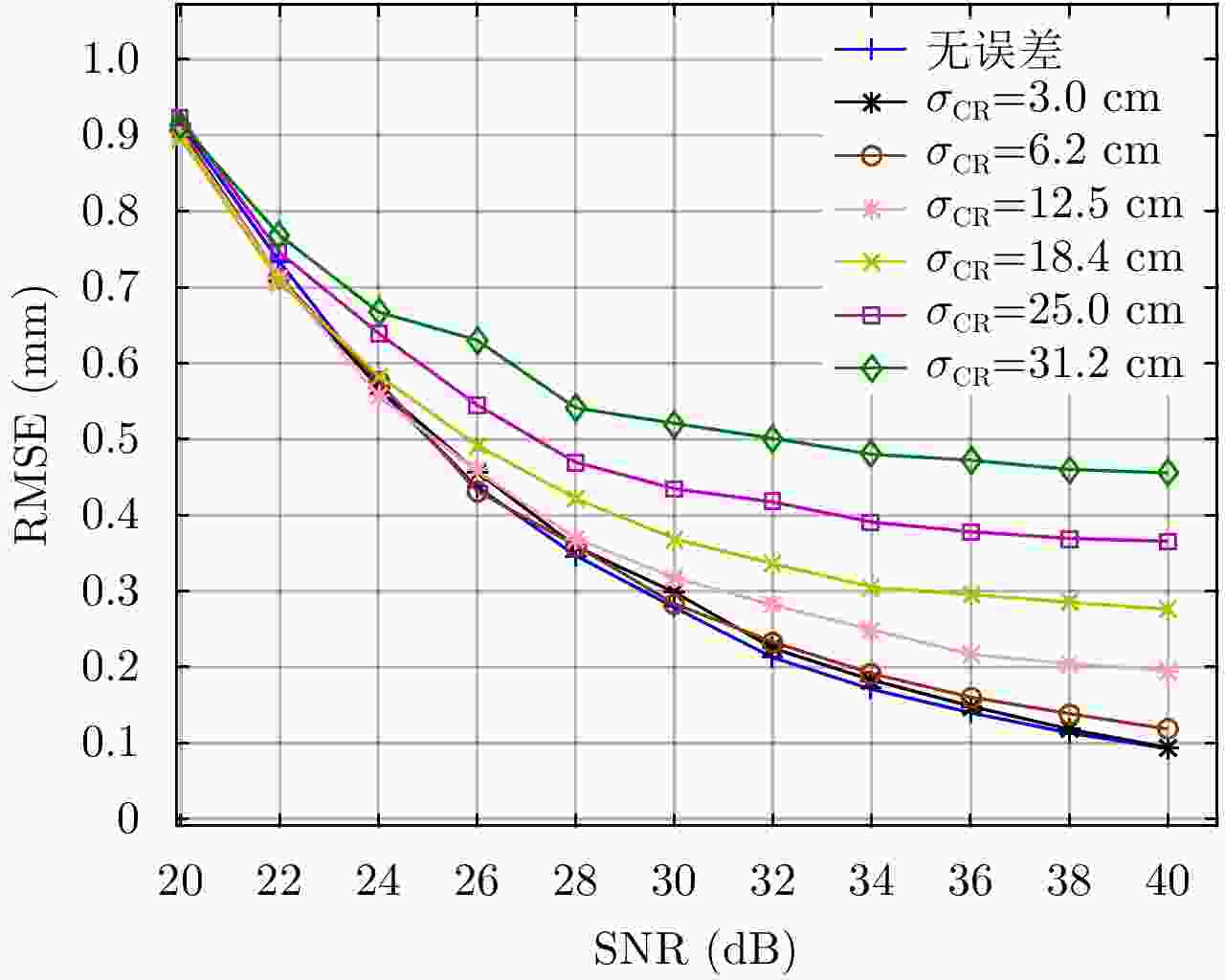
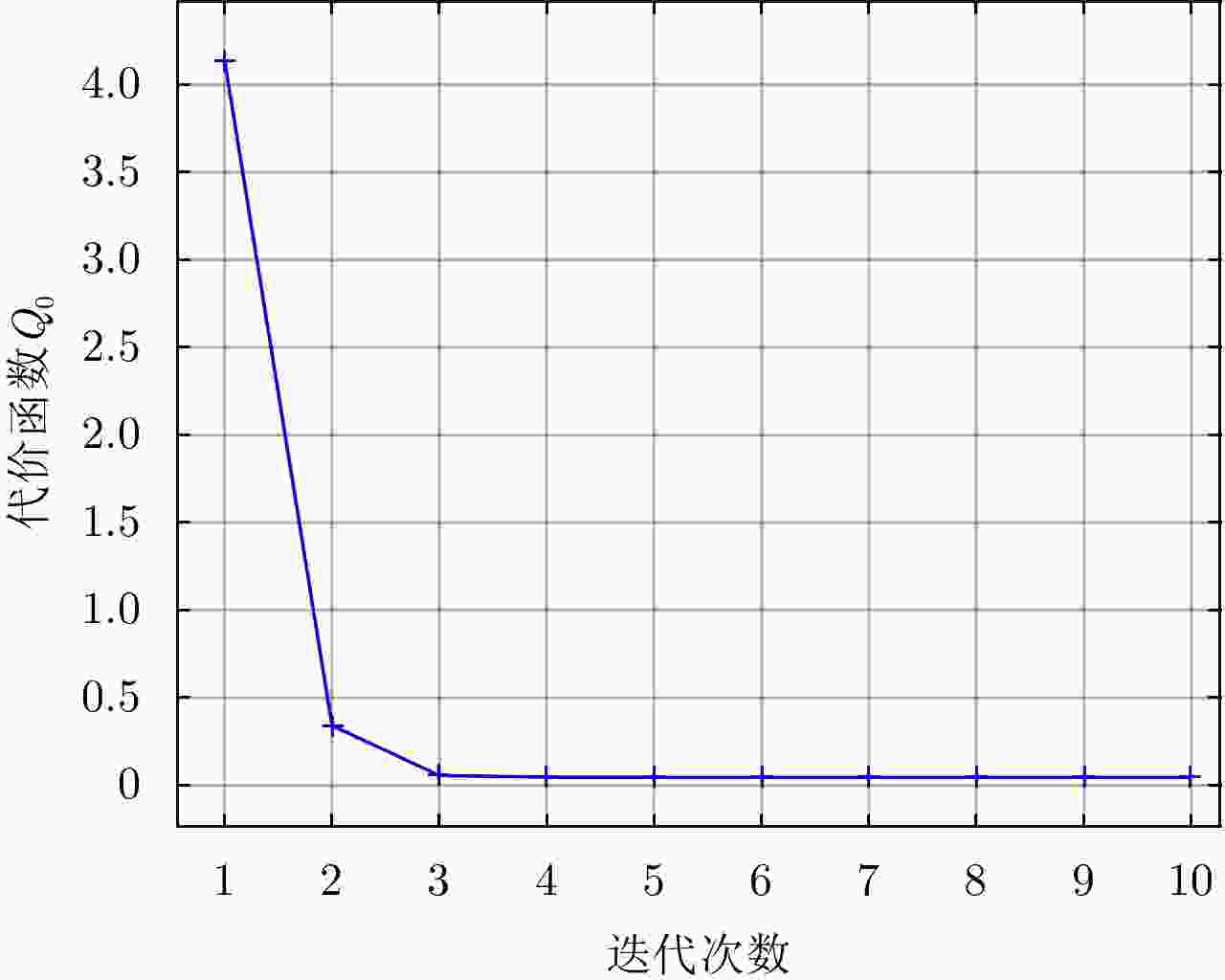
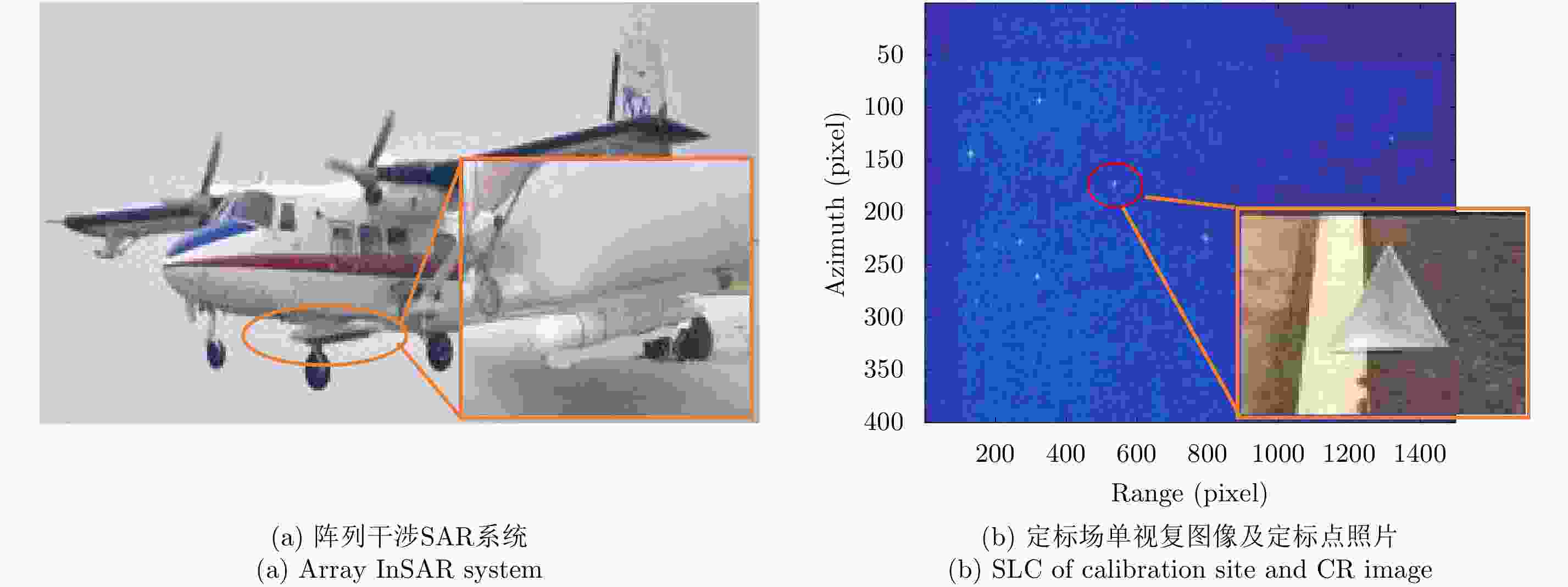
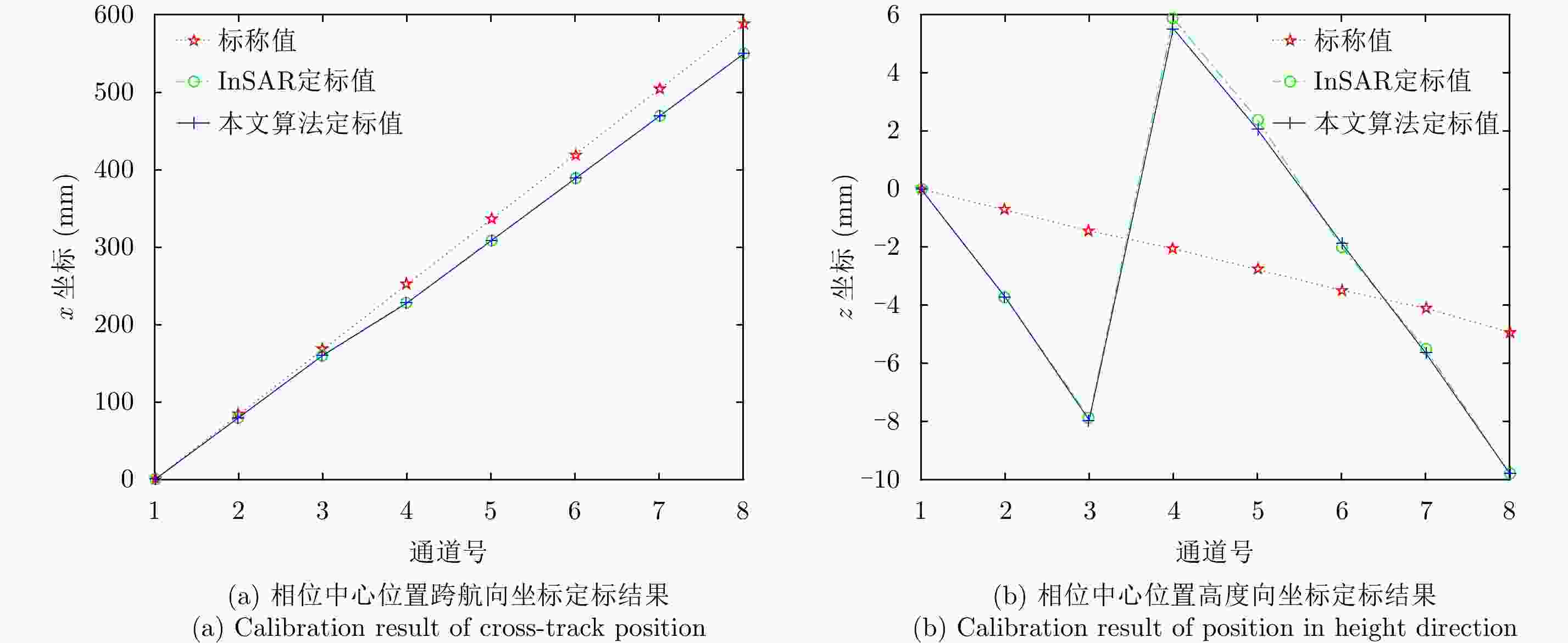
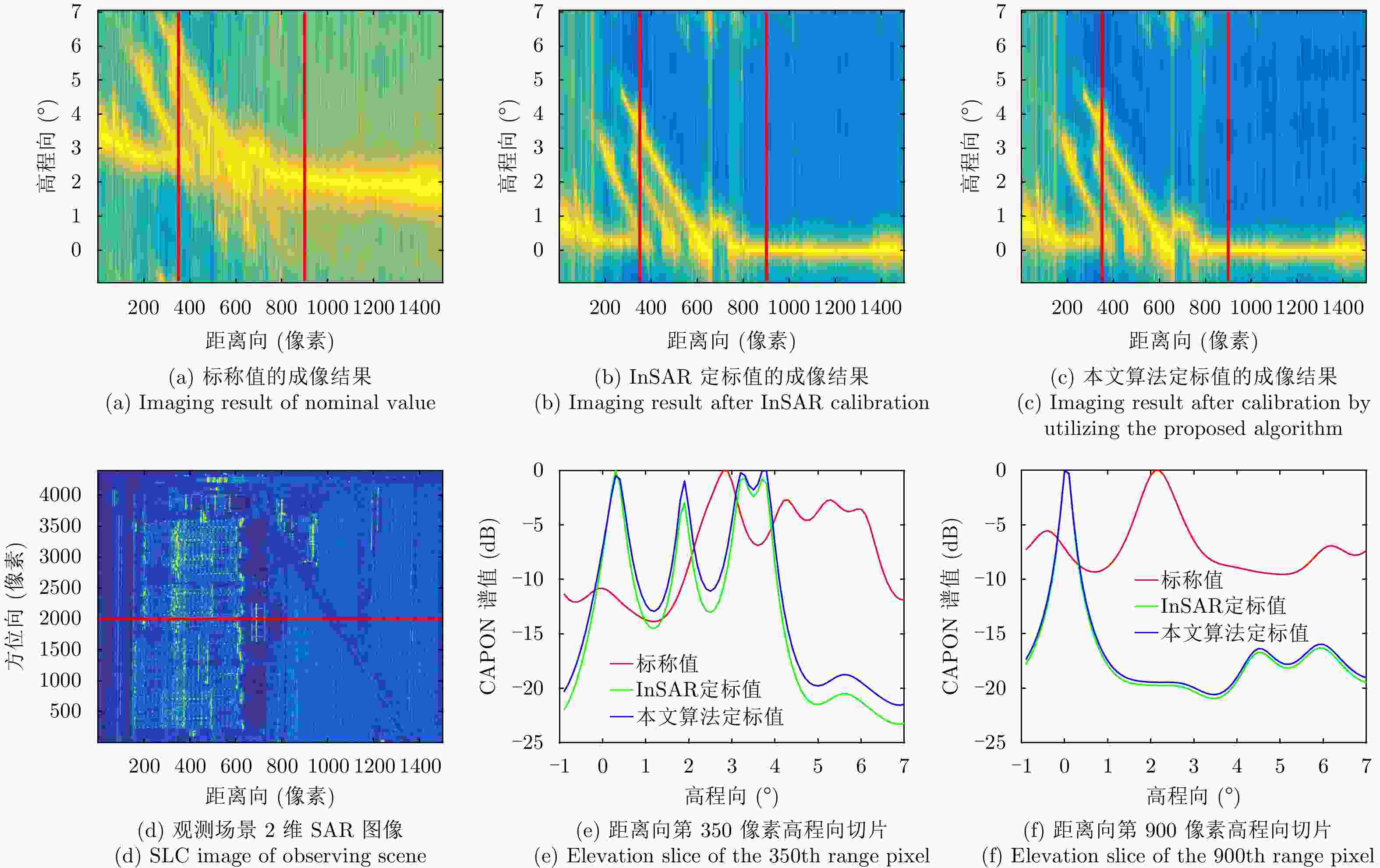
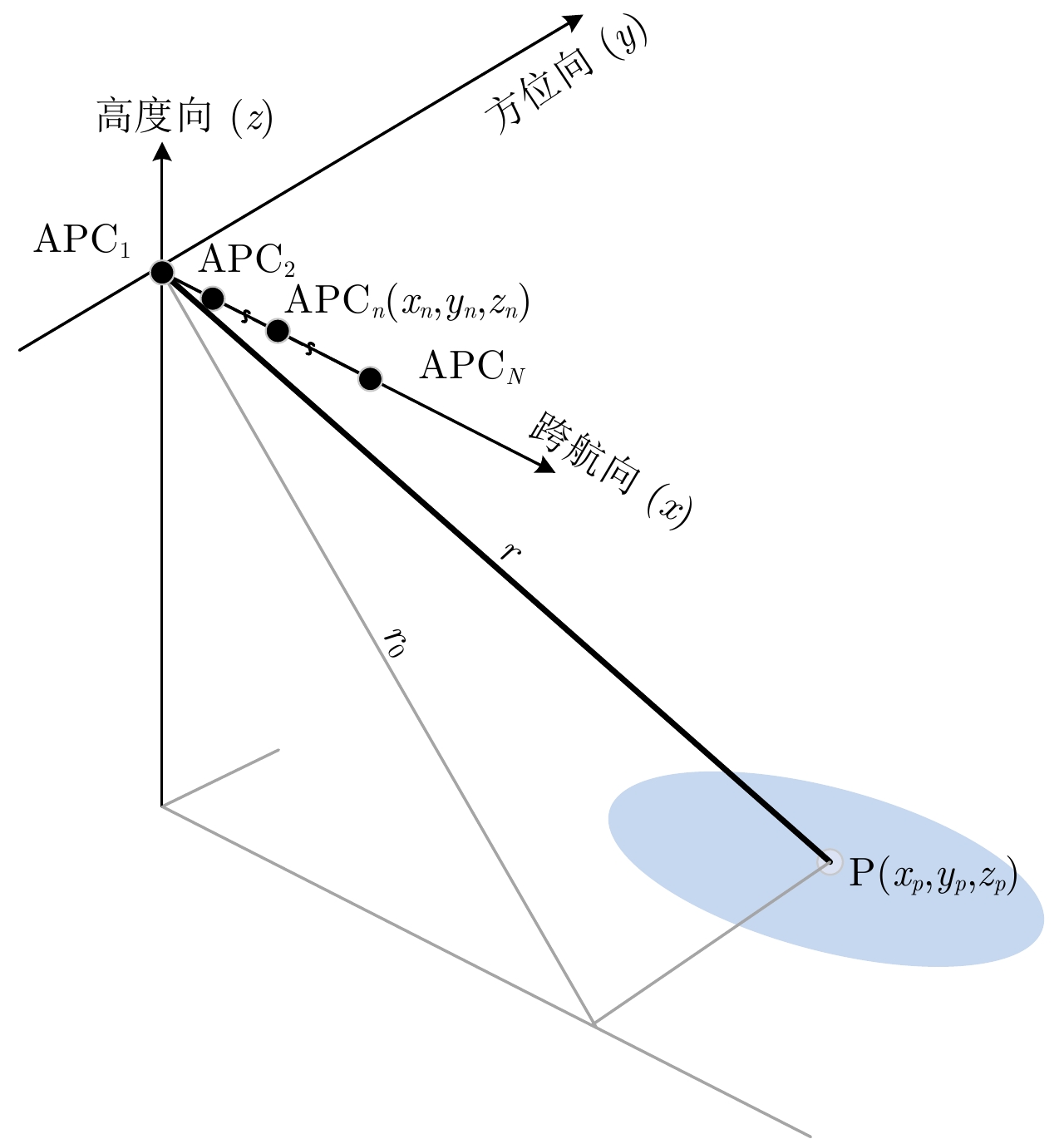
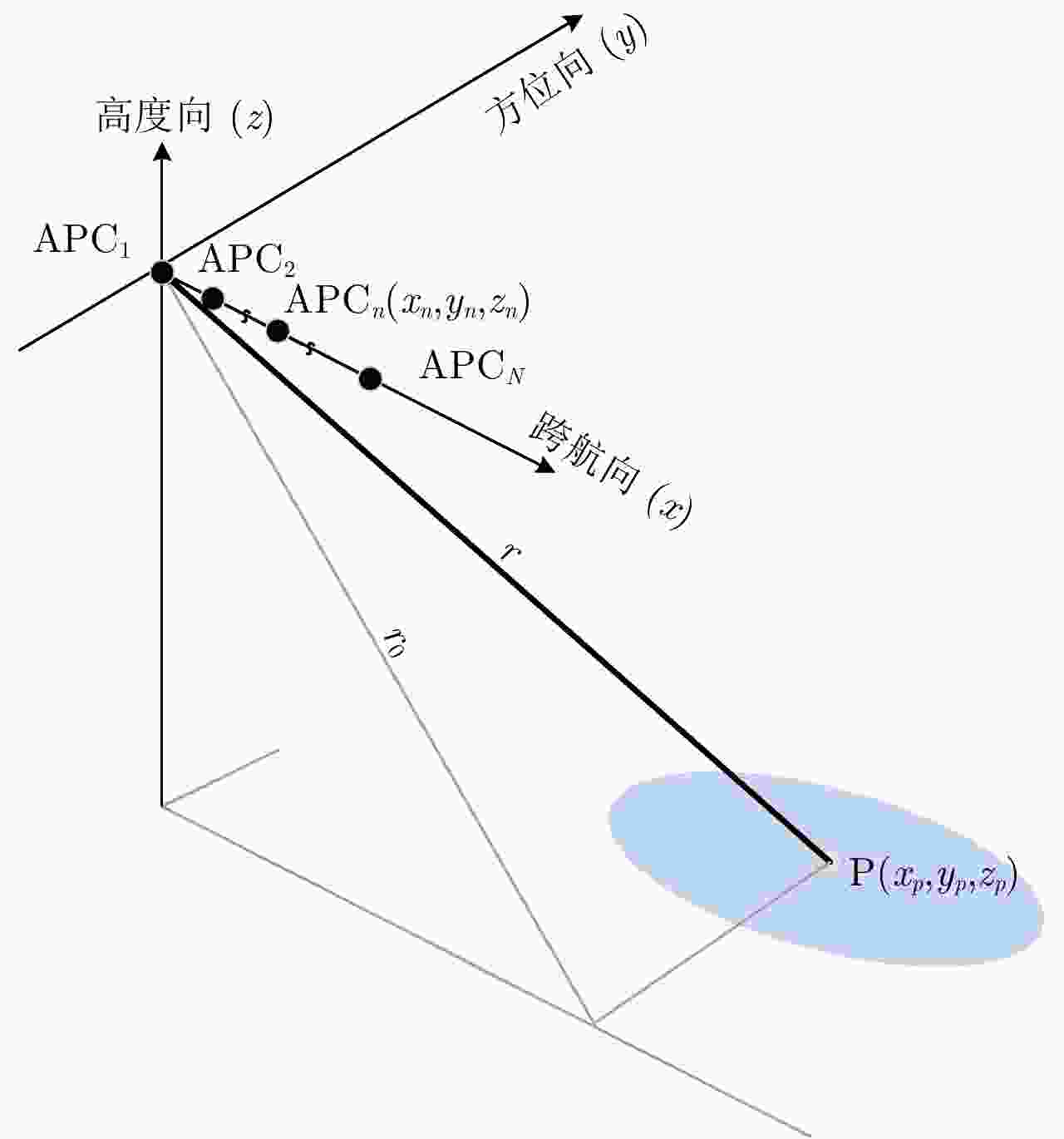
摘要: 阵列干涉合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)系统采用距离脉冲压缩、方位合成孔径和高度实孔径的方式,能够获得观测场景的3维SAR图像。在实际系统中多个通道的天线相位中心位置信息通常难以精确获得,如果不进行定标而直接进行成像处理将会造成高度维成像质量降低。针对天线相位中心位置定标问题,该文分析了天线相位中心位置误差对高度维成像造成的影响,提出了一种基于子空间正交原理的相位中心位置定标方法。该方法利用2维SAR单视复图像中的定标点数据,通过特征值分解得到噪声子空间,利用子空间正交原理同时求解多个通道对应的天线相位中心位置。针对阵列干涉SAR系统应用,该文给出了相位中心位置定标处理流程,最后通过仿真和实际数据处理验证了定标方法的有效性。Abstract: The array InSAR system obtains a three-dimensional image of an observed scene using a combination of pulse compression and synthetic and real aperture techniques. However, Antenna Phase Center (APC) errors can occur within a practical array InSAR system, which thus degrades the imaging quality in a height direction. The aim of this paper is to improve calibration problems occurring with APC errors. The effect of APC errors is analyzed, and a calibration method based on the orthogonal subspace principle is proposed that utilizes SAR Single Look Complex (SLC) to obtain the noise subspace through eigenvalue decomposition. The subspace orthogonal principle is then used to solve the APC positions of multiple channels simultaneously. In addition, a calibration scheme for the APC position is presented for application with an array InSAR system. The effectiveness of the proposed calibration method is verified using simulations and experimental results.
-
表 1 仿真实验中的系统参数
Table 1. System parameters of simulation data
参数名称 参数取值 工作频率 15 GHz (Ku-Band) 基线长度 4.2 m 带宽 500 MHz PRF 2000 Hz 飞行相对高度 1000 m 飞行速度 60 m/s 方位向波束宽度 2° 距离向波束宽度 30°~60° 信噪比 30 dB -
[1] 张红, 江凯, 王超, 等. SAR层析技术的研究与应用[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2010, 25(2): 282–287Zhang Hong, Jiang Kai, Wang Chao, et al. The current status of SAR tomography[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2010, 25(2): 282–287 [2] Zhang F B, Liang X D, Wu Y R, et al. 3D surface reconstruction of layover areas in continuous terrain for multi-baseline SAR interferometry using a curve model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(8): 2093–2112. DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1030042 [3] 张福博, 梁兴东, 吴一戎. 一种基于地形驻点分割的多通道SAR三维重建方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(10): 2287–2293. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150244Zhang Fu-bo, Liang Xing-dong, and Wu Yi-rong. 3-D reconstruction for multi-channel SAR interferometry using terrain stagnation point based division[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2015, 37(10): 2287–2293. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150244 [4] Zhu X X and Bamler R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 [5] Schmitt M, Shahzad M, and Zhu X X. Reconstruction of individual trees from multi-aspect TomoSAR data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 165: 175–185. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.05.012 [6] Tebaldini S and Ferro-Famil L. High resolution three-dimensional imaging of a snowpack from ground-based SAR data acquired at X and Ku band[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2015: 77–80. [7] Reigber A and Moreira A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. DOI: 10.1109/36.868873 [8] 丁振宇, 谭维贤, 王彦平, 等. 基于波数域子孔径的机载三维SAR偏航角运动误差补偿[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(4): 467–473. DOI: 10.12000/JR15016Ding Zhen-yu, Tan Wei-xian, Wang Yan-ping, et al. Yaw angle error compensation for airborne 3-D SAR based on wavenumber-domain subblock[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(4): 467–473. DOI: 10.12000/JR15016 [9] Tebaldini S and Guarnieri A M. On the role of phase stability in SAR multibaseline applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2953–2966. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2043738 [10] 朱海洋, 洪峻, 明峰. 相位中心偏差对机载阵列天线下视3D-SAR成像影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 910–916. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00776Zhu Hai-yang, Hong Jun, and Ming Feng. Analysis of impact of phase center variations in linear array antena downward-looking 3D-SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 910–916. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00776 [11] 朱海洋. 阵列下视3D-SAR相位中心定标方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2012.Zhu Hai-yang. Study on phase center calibration methods of linear array downward-looking 3D-SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Chinese Acedamy of Science, 2012. [12] 韩阔业. 基于稀疏线阵的机载合成孔径雷达成像模型、方法与实验研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015.Han Kuo-ye. Study on model, algorithm and experiment for airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging based on sparse linear array antennas[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [13] Pardini M, Papathanassiou K, Bianco V, et al.. Phase calibration of multibaseline SAR data based on a minimum entropy criterion[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 5198–5201. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352438. [14] Tebaldini S, Rocca F, d’Alessandro M M, et al. Phase calibration of airborne tomographic SAR data via phase center double localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1775–1792. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2488358 [15] Fornaro G, Lombardini F, and Serafino F. Three-dimensional multipass SAR focusing: Experiments with long-term spaceborne data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 702–714. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843567 [16] Urasawa F, Yamada H, Yamaguchi Y, et al.. Fundamental study on multi-baseline SAR tomography by Pi-SAR-L2[C]. Proceedings of the URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, Seoul, South Korea, 2016: 514–515. DOI: 10.1109/URSIAP-RASC.2016.7601342. [17] 柳祥乐. 多基线层析成像合成孔径雷达研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2007.Liu Xiang-le. Study on multibaseline tomography synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007. [18] 赵逸超, 朱宇涛, 粟毅, 等. 用于线阵三维SAR成像的二维快速ESPRIT算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 591–599. DOI: 10.12000/JR15065Zhao Yi-chao, Zhu Yu-tao, Su Yi, et al. Two-dimensional fast ESPRIT algorithm for linear array SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 591–599. DOI: 10.12000/JR15065 [19] Zhu X X and Bamler R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 [20] Schmitt M and Stilla U. Compressive sensing based layover separation in airborne single-pass multi-baseline InSAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 313–317. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2204230 [21] 李杭, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 基于高斯混合聚类的阵列干涉SAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020Li Hang, Liang Xing-dong, Zhang Fu-bo, et al. 3D imaging for array InSAR based on Gaussian mixture model clustering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020 [22] Stoica P and Nehorai A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer-Rao bound[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(5): 720–741. DOI: 10.1109/29.17564 [23] 张福博. 阵列干涉SAR三维重建信号处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015.Zhang Fu-bo. Research on signal processing of 3-D reconstruction in linear array Synthetic Aperture Radar interferometry[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Acedamy of Science, 2015. [24] Freeman A. SAR calibration: An overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(6): 1107–1121. DOI: 10.1109/36.193786 [25] 焦培南, 张忠治. 雷达环境与电波传播特性[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007.Jiao Pei-nan and Zhang Zhong-zhi. Radio Environment and Radio Wave Propagation Characteristics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: