Array-interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Point Cloud Filtering Based on Spatial Clustering Seed Growth Algorithm
-
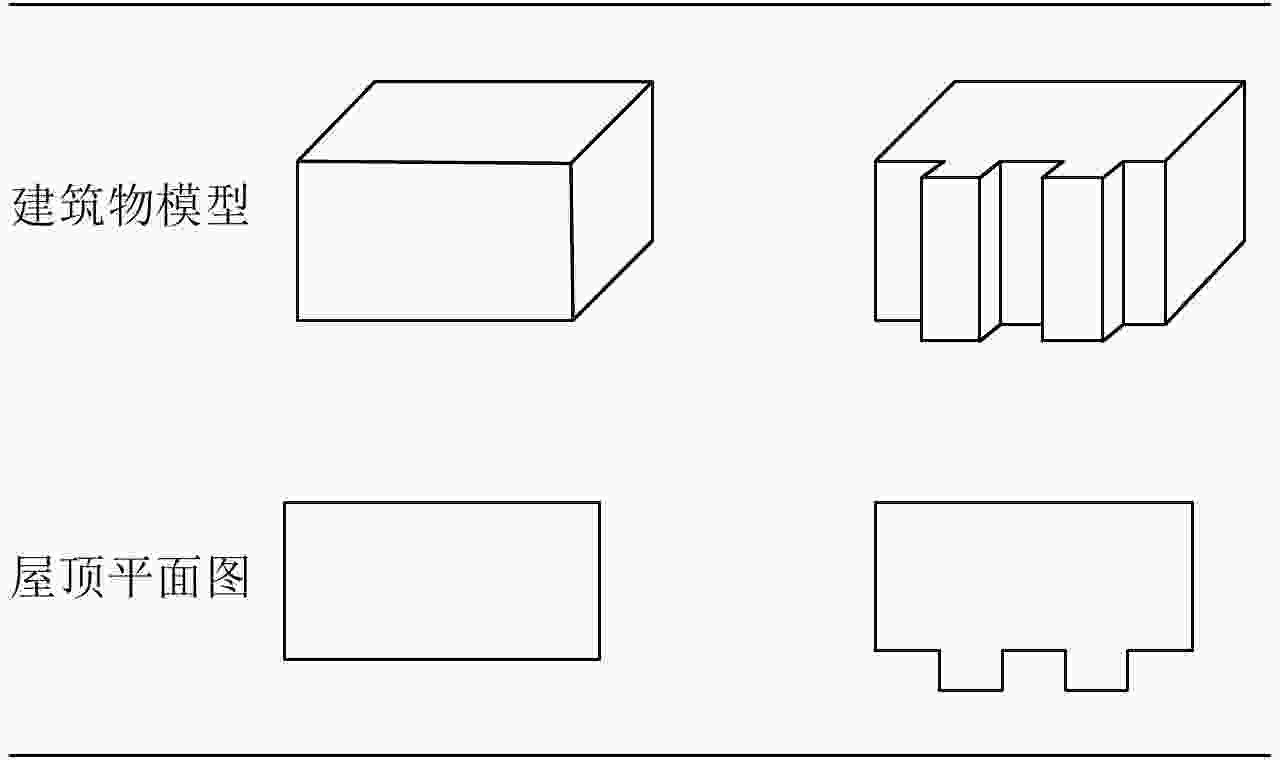
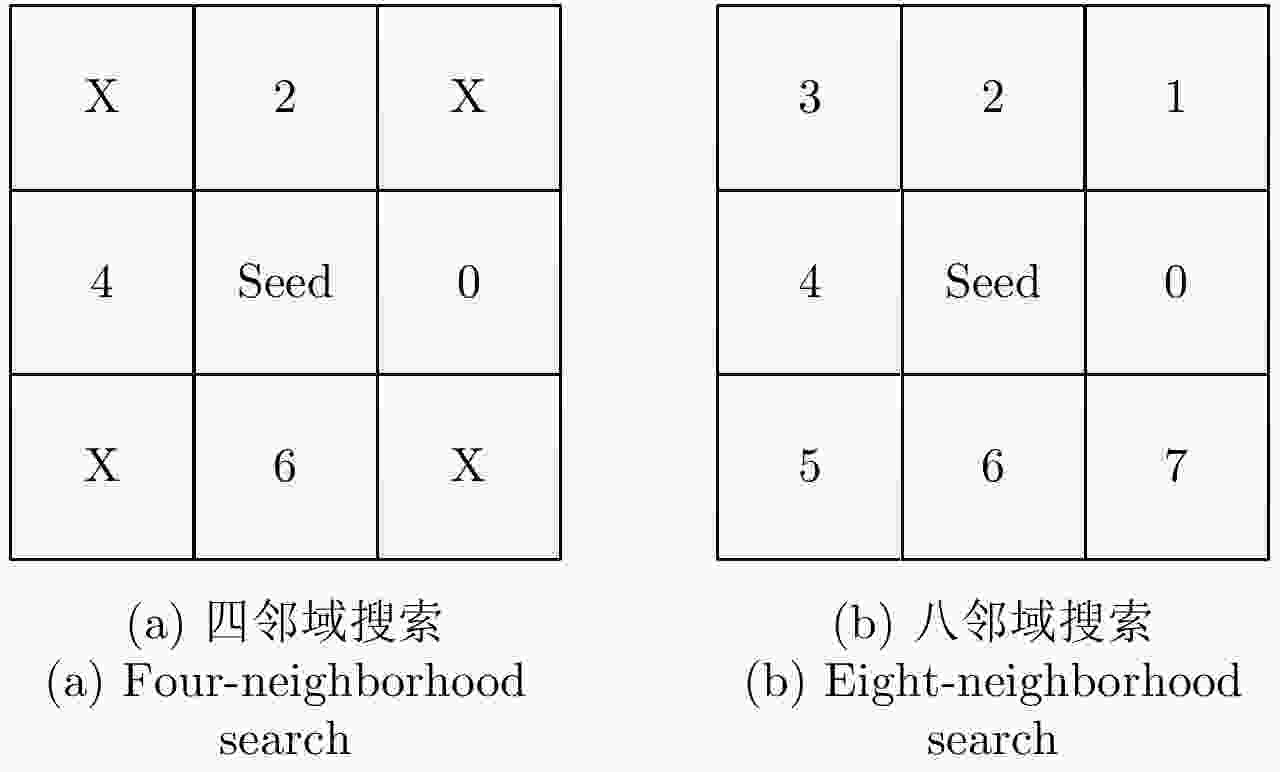
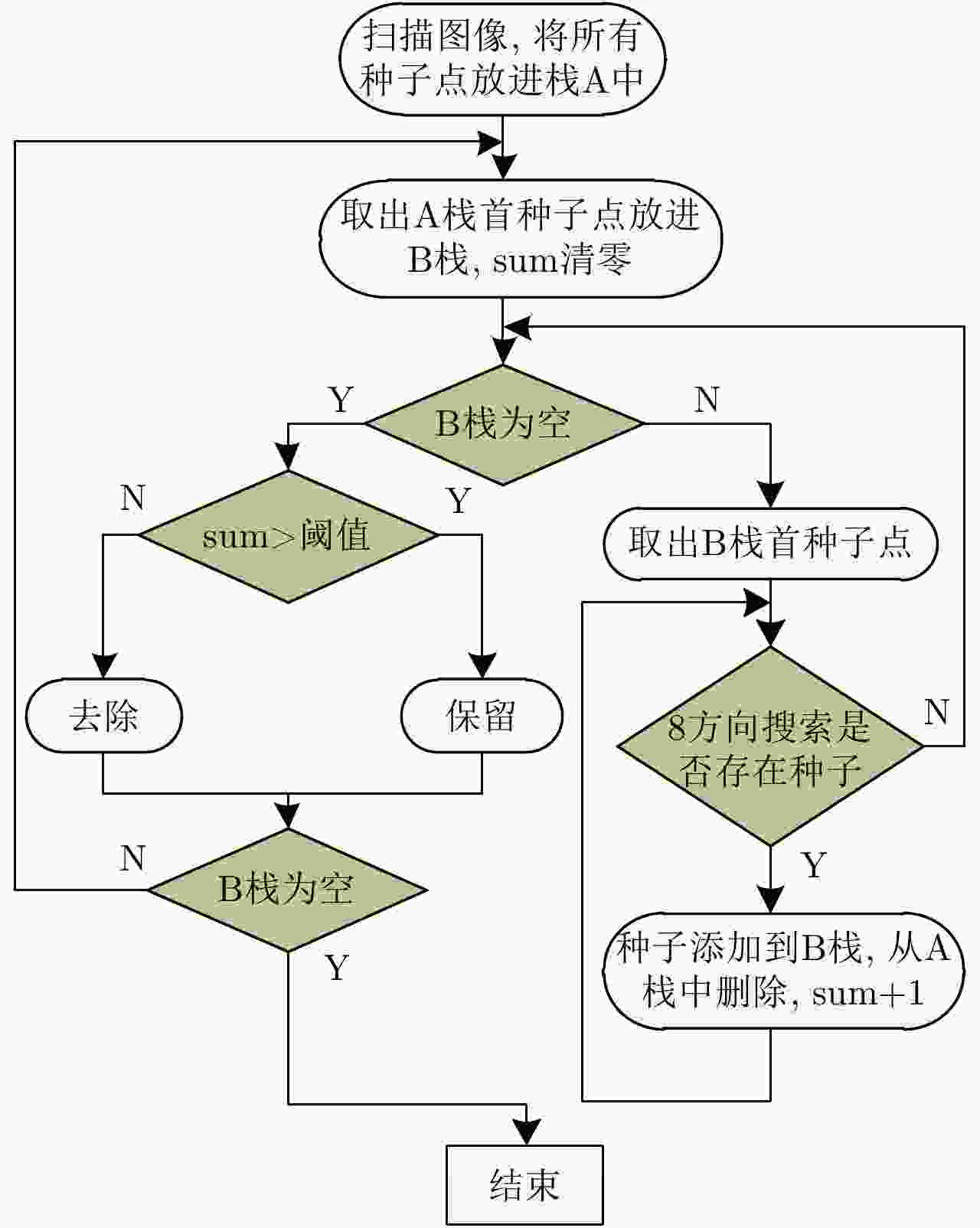
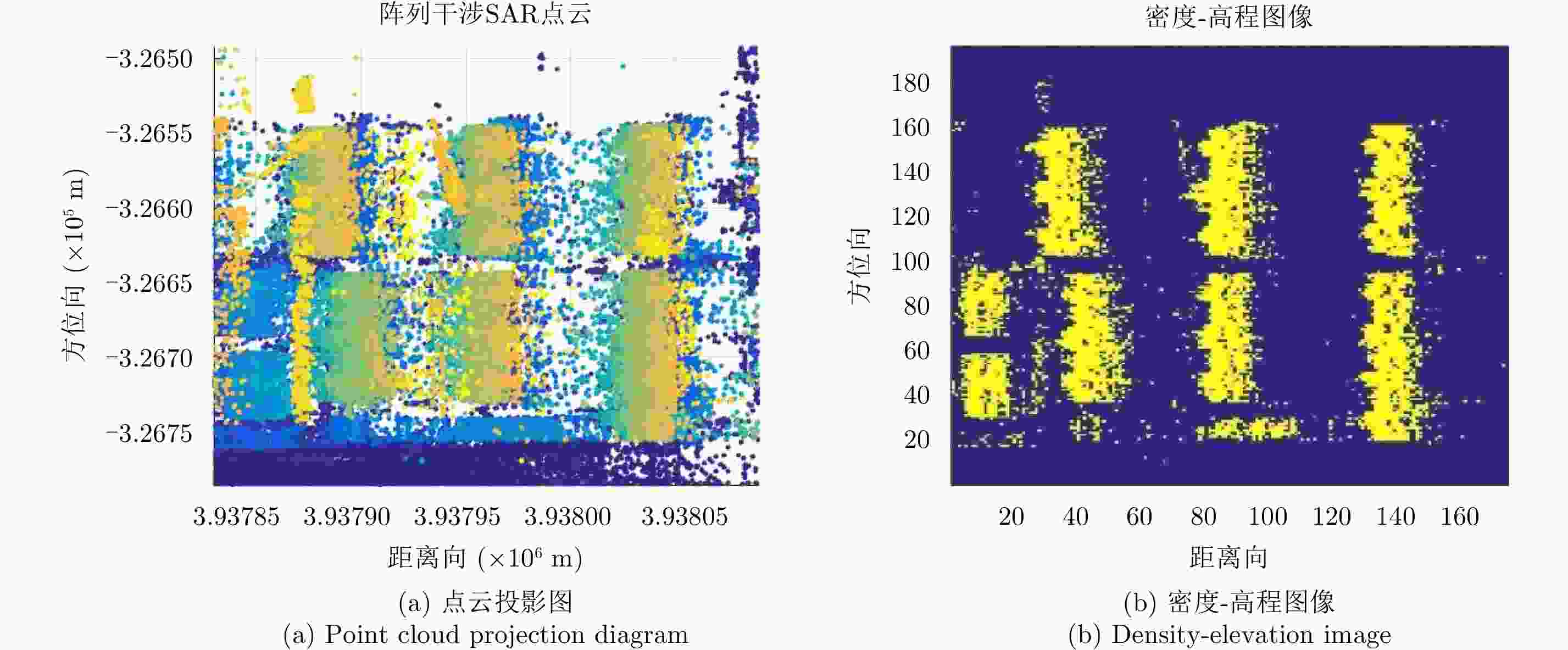
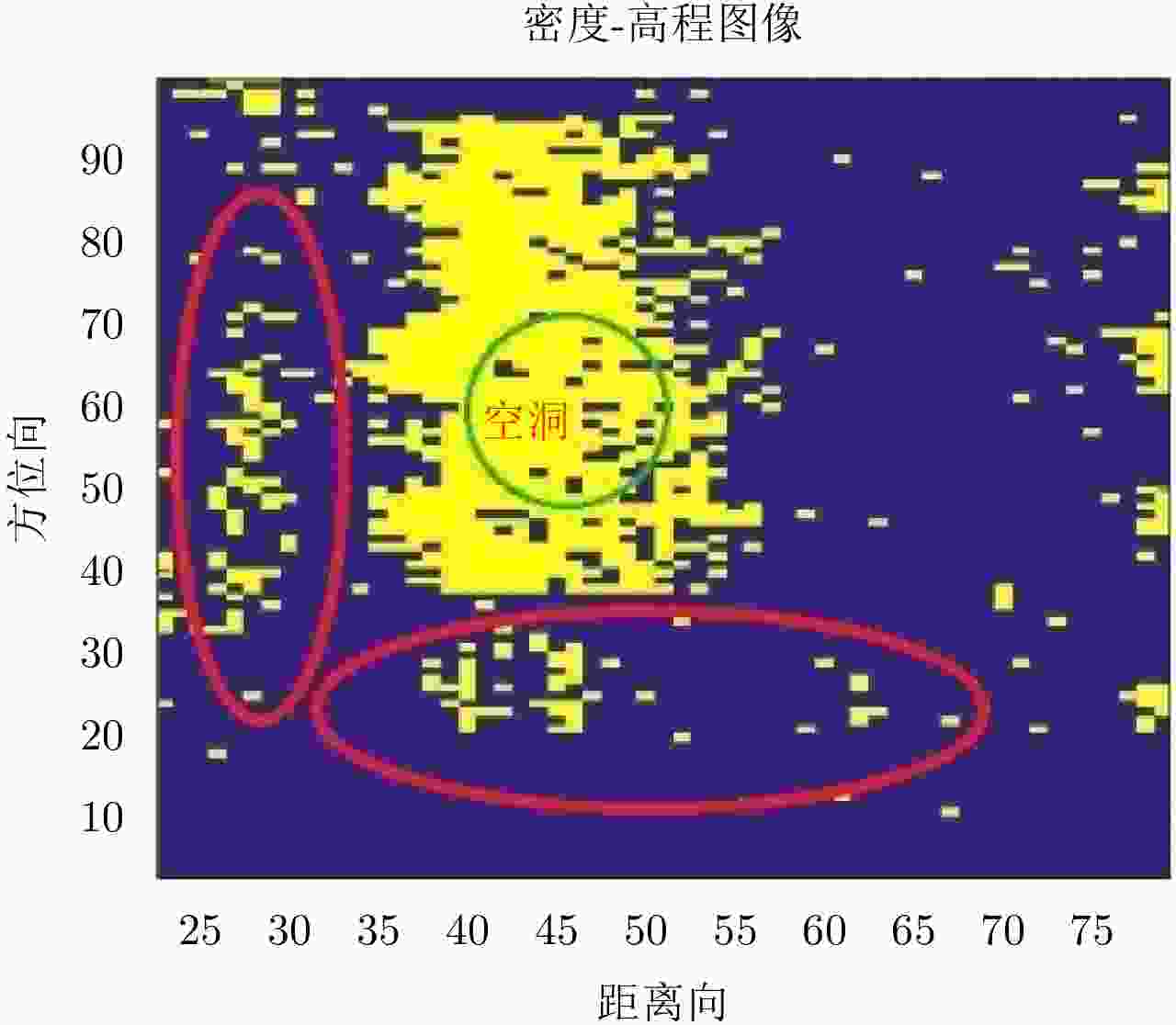
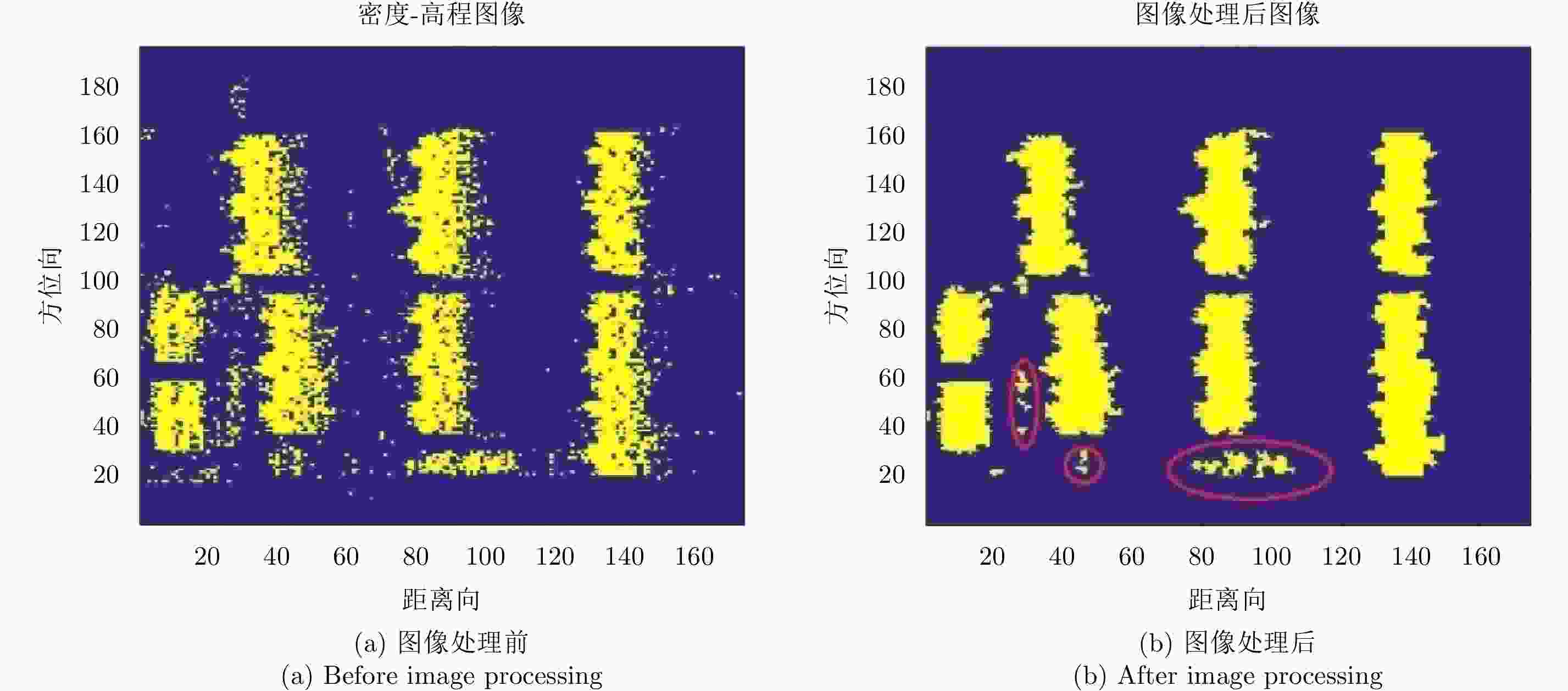
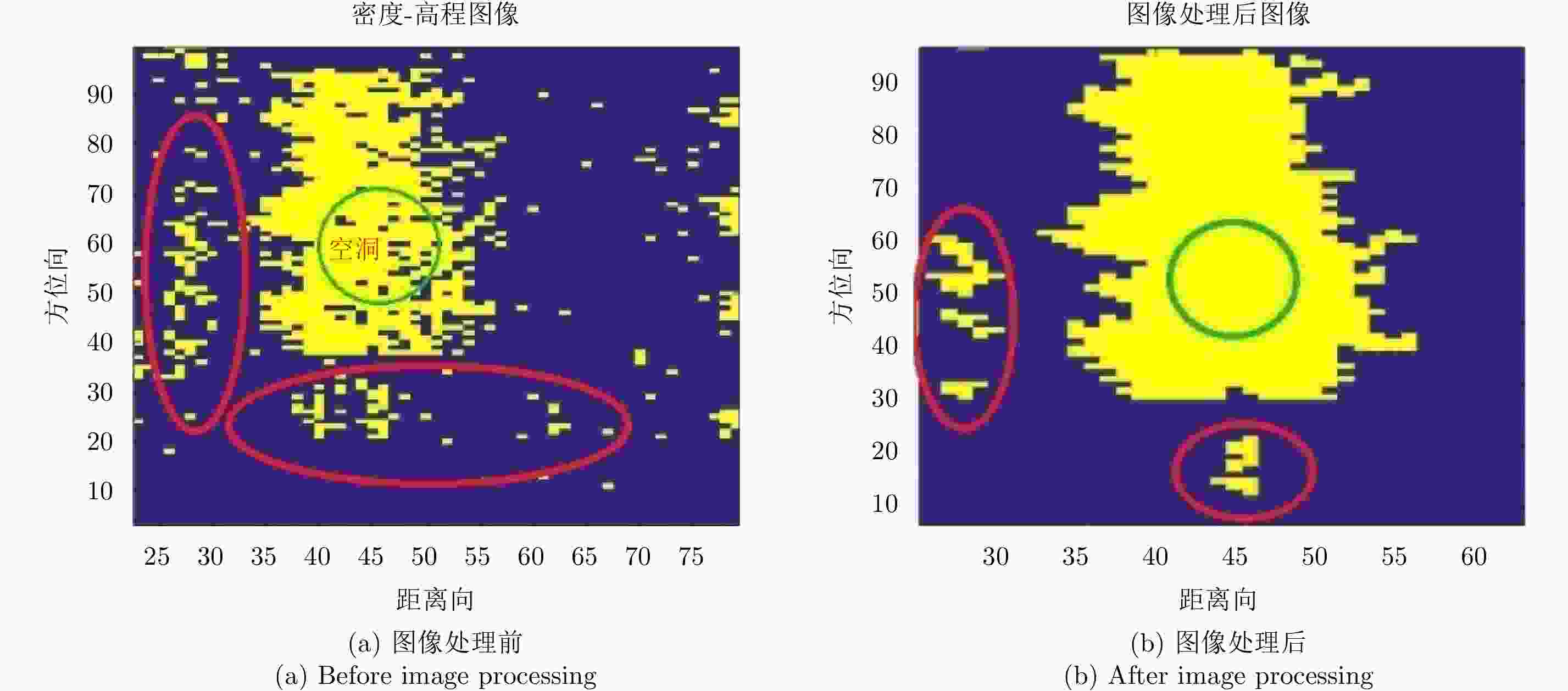
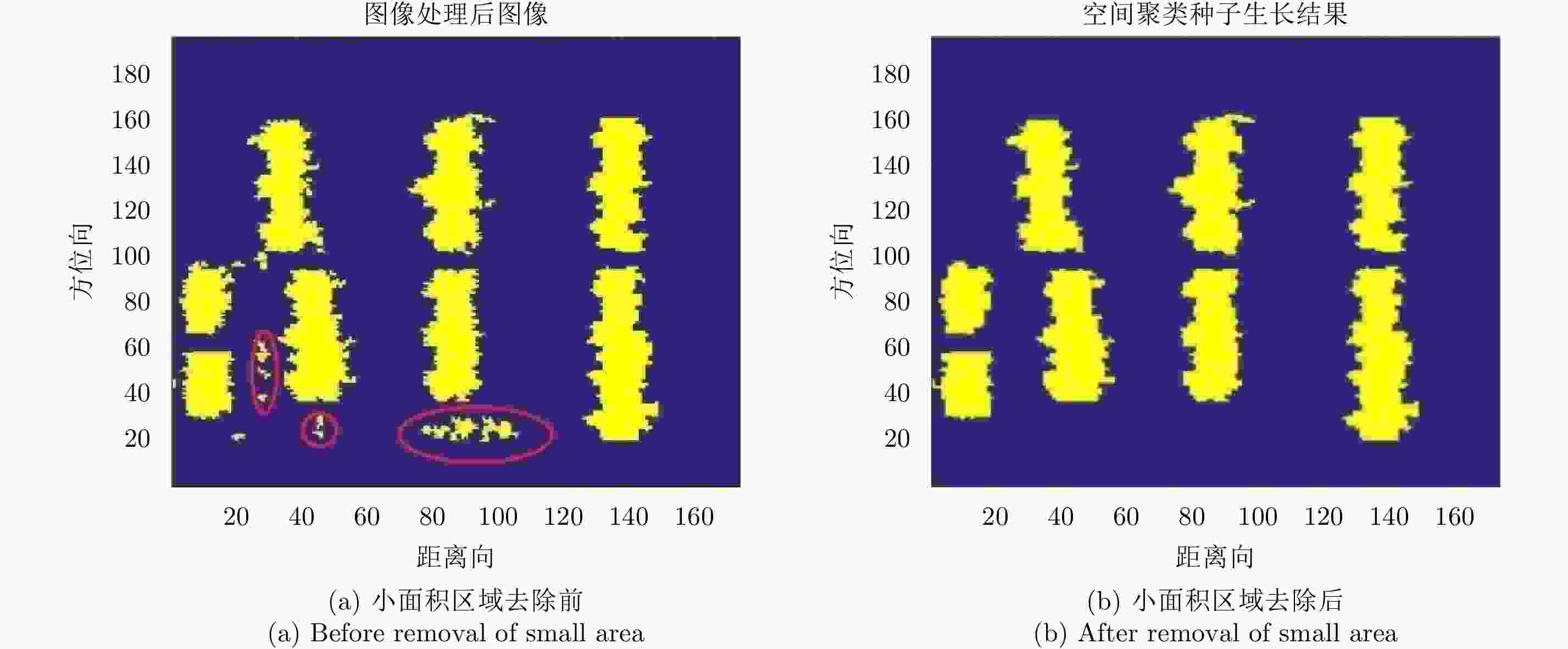
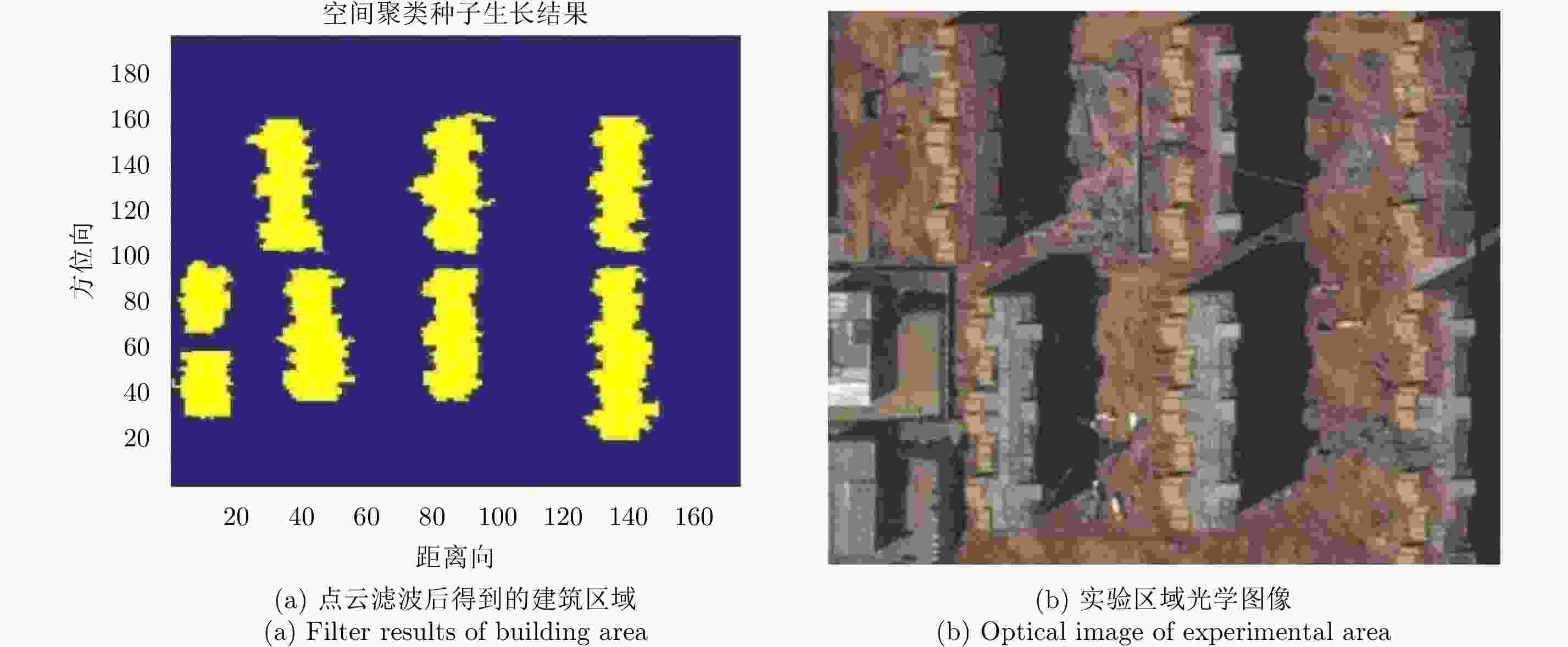
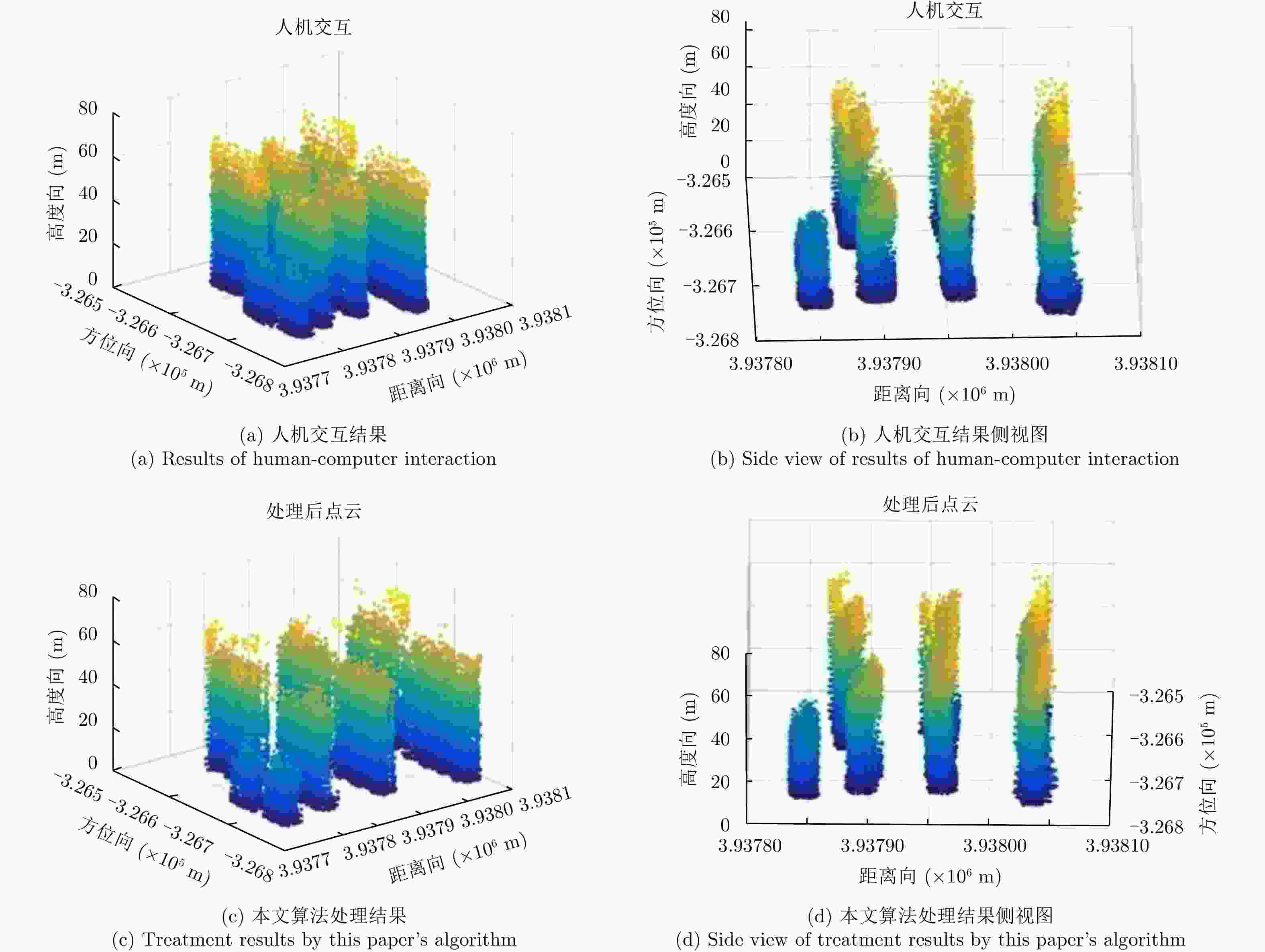
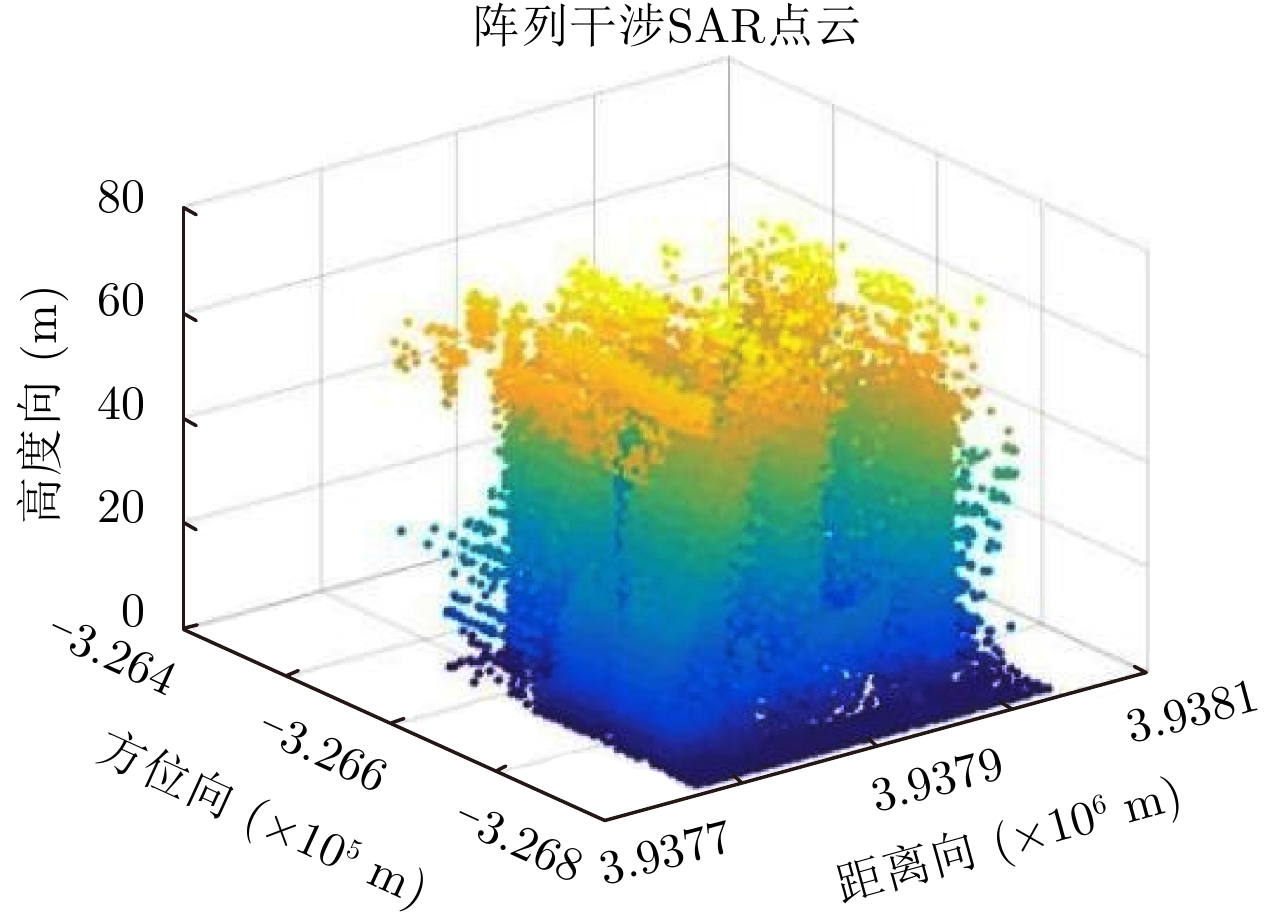
摘要: 阵列干涉合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)通过在交轨向布置多个天线,结合方位向的合成孔径和斜距向的大带宽信号,具备了3维分辨能力,且多个阵元保证了其在高程向的空间采样,能够解决干涉SAR(Interferometric SAR, InSAR)测绘中的叠掩问题,实现观测场景的3维成像。但是获得场景区域的3维点云分布中存在较多杂点,高程向误差较大,所以传统的激光雷达(Light Detection And Ranging, LiDAR)点云滤波方法不适用于阵列干涉SAR点云的滤波处理。针对该问题,该文提出基于空间聚类种子生长算法的阵列干涉SAR点云滤波算法,应用密度和高程双重阈值生成密度-高程图像,通过图像处理手段去除小型杂点,利用空间聚类种子生长算法将植被等从点云数据中去除,完成点云滤波处理。利用国内首次机载阵列干涉SAR实验数据,通过与传统LiDAR滤波方法进行比较,验证了该文算法的有效性,为后续建筑物提取和精细化处理提供保障。Abstract: By arranging multiple antennas in the intersection direction and combining the synthetic aperture of azimuth direction and large bandwidth signal with oblique distance, array-interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) can generate a three-dimensional resolution and ensure the elevation spacial sampling due to its multiple array element, which could avoid the layover problem in surveying and mapping in the Interference SAR (InSAR) and realize the three-dimensional imaging of the observation scene. However, considering the existence of too much noise in the three-dimensional point cloud distribution in the scene area and the large elevation error, the traditional Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) point cloud filtering method is not suitable for the filtering processing of the array-interferometric SAR point cloud. In order to solve this problem, an array-interferometric SAR point cloud filtering algorithm based on spatial clustering seed growth algorithm is proposed, in which the density-elevation image is generated by the double threshold of density and elevation, the small clutter is removed by image processing, and the vegetation is removed from the point cloud data by using the spatial clustering seed growth algorithm, thus the point cloud filtering process is completed. Using the first airborne array-interferometric SAR experimental data, the validity of the proposed algorithm is verified compared to the traditional LiDAR filtering method, which provides the guarantee for the subsequent building extraction and meticulous treatment.
-
表 1 滤波算法质量评价表
Table 1. Filter algorithm quality evaluation table
滤波算法 After filtering Tp Fp FN Completeness (100%) Correctness (100%) Quality (100%) 本文算法 64858 63753 1105 2381 96.40 98.30 94.81 形态学滤波 81443 64032 17441 2102 96.82 78.62 76.64 坡度滤波 84039 64395 19944 1739 97.37 76.63 75.07 -
[1] Cumming I G and Wong F H著. 洪文, 胡东辉, 译. 合成孔径雷达成像-算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007: 3–5.Cumming I G and Wong F H. Hong Wen and Hu Dong-hui, Trans. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007: 3–5. [2] Dorninger P and Pfeifer N. A comprehensive automated 3D approach for building extraction, reconstruction, and regularization from airborne laser scanning point clouds[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(11): 7323–7343. DOI: 10.3390/s8117323 [3] Filin S. Surface clustering from airborne laser scanning data[J]. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2002, 32(3A): 119–124. [4] Elaksher A F and Bethel J S. Reconstructing 3D buildings from Lidar data[C]. Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission III Symposium on Photogrammetric Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 2002: 1–6. [5] Forlani G, Nardinocchi C, Scaioni M, et al. Complete classification of raw LIDAR data and 3D reconstruction of buildings[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2006, 8(4): 357–374. DOI: 10.1007/s10044-005-0018-2 [6] Zhu X X and Shahzad M. Facade reconstruction using Multiview Spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3541–3552. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2273619 [7] Shahzad M and Zhu X X. Reconstructing 2-D/3-D building shapes from spaceborne Tomographic Synthetic Aperture Radar data[C]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume XL-3, 2014, ISPRS Technical Commission III Symposium, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014. [8] Shahzad M and Zhu X X. Automatic detection and reconstruction of 2-D/3-D building shapes from Spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1292–1310. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2477429 [9] Sithole G and Vosselman G. Experimental comparison of filter algorithms for bare-earth extraction from airborne laser scanning point clouds[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2004, 59(1/2): 85–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2004.05.004 [10] Vosselman G. Slope based filtering of laser altimetry data[J]. International Archives of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2000, 33(B3/2): 935–942. [11] 黄先锋, 李卉, 王潇, 等. 机载LiDAR数据滤波方法评述[J]. 测绘学报, 2009, 38(5): 466–469Huang Xian-feng, Li Hui, Wang Xiao, et al. Filter algorithms of airborne LiDAR data: Review and prospects[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2009, 38(5): 466–469 [12] Zhu X X and Bamler R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [13] Lombardini F. Differential tomography: A new framework for SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(1): 37–44. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.838371 [14] Shahzad M and Zhu X X. Robust reconstruction of building facades for large areas using spaceborne TomoSAR point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(2): 752–769. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2327391 [15] 栾晓岩. 一种TIN生成算法及其三维显示[J]. 海洋测绘, 2004, 24(5): 39–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2004.05.012Luan Xiao-yan. The method of building TIN and its three-dimensional display[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2004, 24(5): 39–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2004.05.012 [16] 李杭, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 基于高斯混合聚类的阵列干涉SAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020Li Hang, Liang Xing-dong, Zhang Fu-bo, et al. 3D imaging for array InSAR based on Gaussian mixture model clustering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. DOI: 10.12000/JR17020 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: