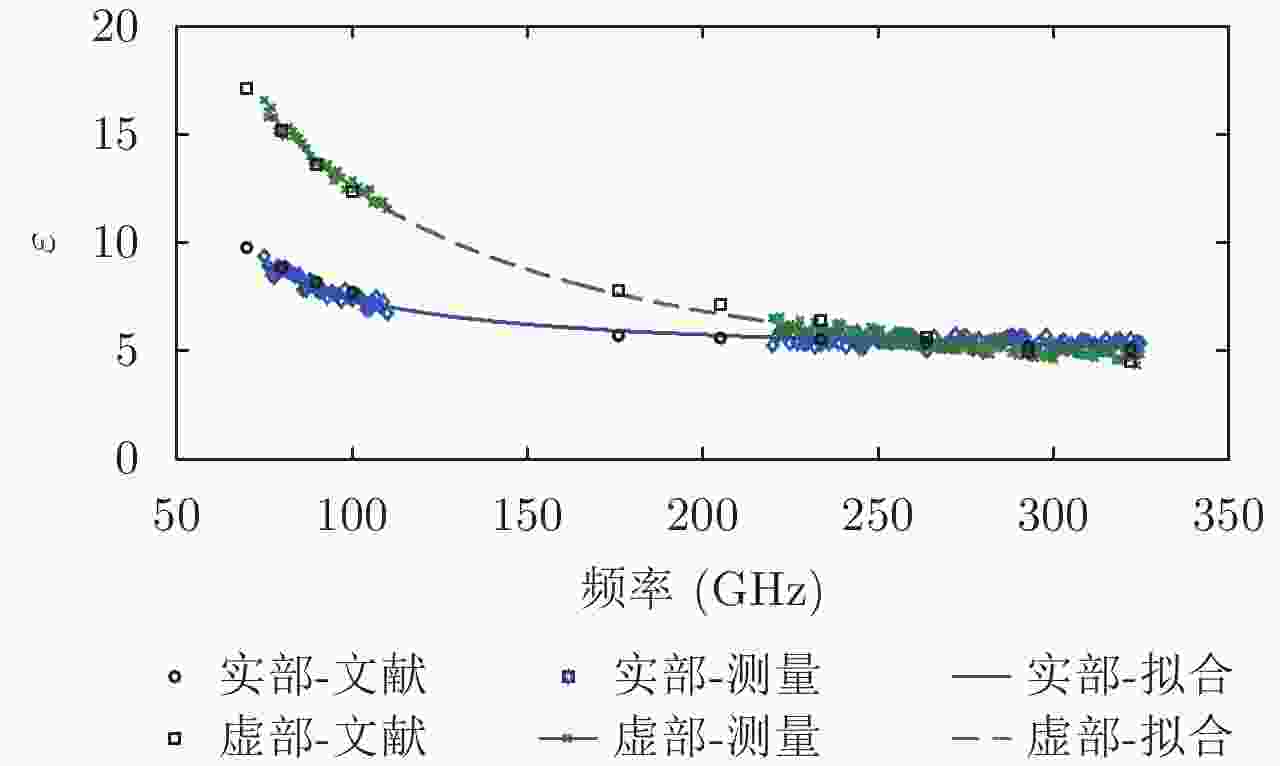
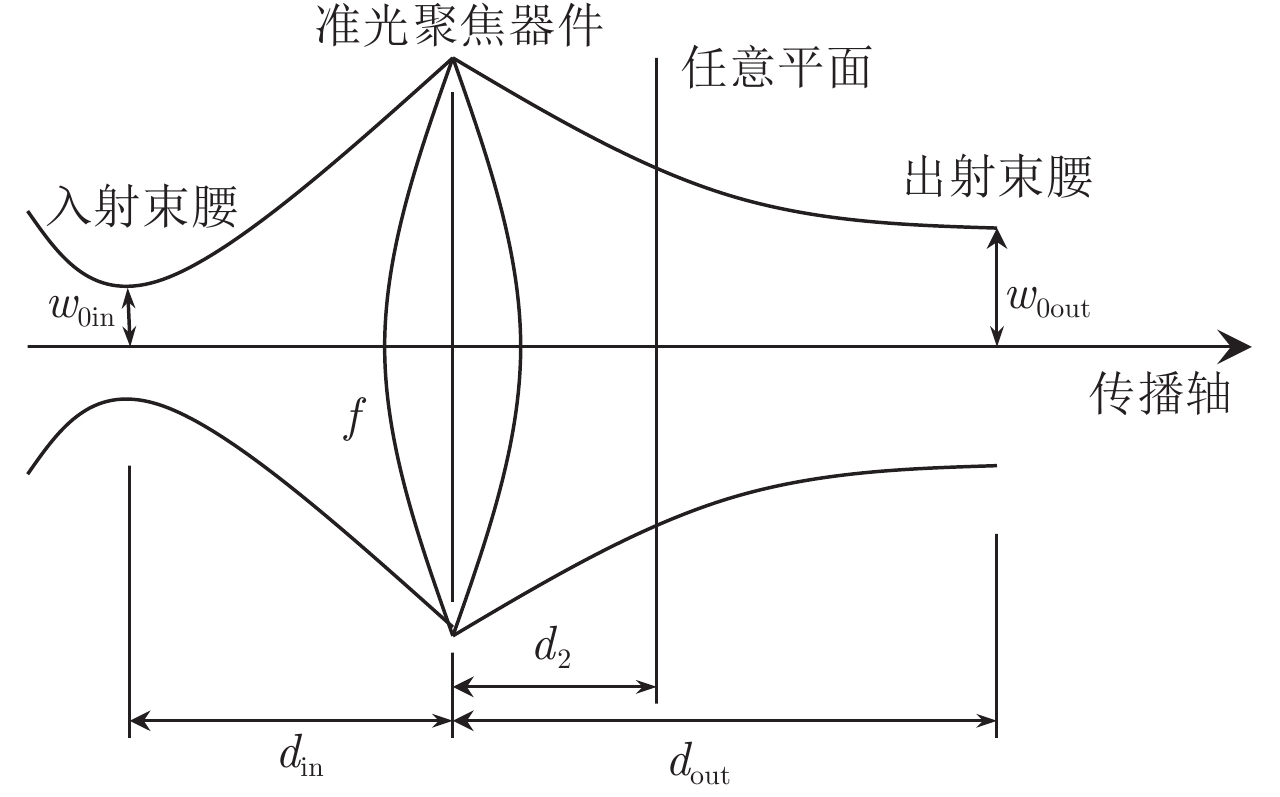
| [1] |
刘小明. 介电常数及其测量技术[M]. 北京: 北京邮电大学出版社, 2015: 1–16.Liu Xiao-ming. Dielectric and Measurement Techniques[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2015: 1–16.
|
| [2] |
Janssen M A, Paganelli F, Lorenz R D, et al. Dielectric properties of titan’s surface using the Cassini RADAR radiometer[J]. Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, 2006, 38(9): 586.
|
| [3] |
Zhang L B, Zhou P H, Zhang H B, et al. A broadband radar absorber based on perforated magnetic polymer composites embedded with FSS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2014, 50(5): 4004305. DOI: 10.1109/TMAG.2013.2293129
|
| [4] |
陈权, 曾江源, 李震, 等. 遥感监测介电常数与土壤含水率关系模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(12): 171–175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.12.028Chen Quan, Zeng Jiang-yuan, Li Zhen, et al. Relationship model of soil moisture and dielectric constant monitored with remote sensing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(12): 171–175. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.12.028
|
| [5] |
连懿, 陈圣波, 孟治国, 等. 基于嫦娥二号卫星微波辐射计亮温数据反演月壤介电常数[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(11): 1644–1650. DOI: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.158Lian Yi, Chen Shengbo, Meng Zhiguo, et al. Dielectric constant of Lunar soil derived from Chang’E-2 passive microwave radiometer measurements[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2014, 39(11): 1644–1650. DOI: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.158
|
| [6] |
杨洋, 景磊. 金属介电常数对雷达目标散射截面的影响[J]. 激光与红外, 2013, 43(2): 155–158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2013.02.008Yang Yang and Jing Lei. Impact of the metal permittivity on radar target scattering cross section[J]. Laser&Infrared, 2013, 43(2): 155–158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2013.02.008
|
| [7] |
潘顺康, 吕善伟, 王伟, 等. 介质参数对吸收体电磁散射影响[J]. 桂林电子科技大学学报, 2007, 27(3): 171–174. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-808X.2007.03.001Pan Shun-kang, Lv Shan-wei, Wang Wei, et al. Effects of dielectric parameters on electromagnetic scattering of absorber[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Electronic Technology, 2007, 27(3): 171–174. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-808X.2007.03.001
|
| [8] |
ASTM. ASTM D150–2011 Standard test methods for AC loss characteristics and permittivity (dielectric constant) of solid electrical insulation[S]. ASTM, 2011.
|
| [9] |
Baker-Jarvis J, Vanzura E J, and Kissick W A. Improved technique for determining complex permittivity with the transmission/reflection method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1990, 38(8): 1096–1103. DOI: 10.1109/22.57336
|
| [10] |
Stuchly M A, Athey T W, Samaras G M, et al. Measurement of radio frequency permittivity of biological tissues with an open-ended coaxial line: Part II—Experimental results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1982, 30(1): 87–92. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.1982.1131022
|
| [11] |
Komiyama B, Kiyokawa M, and Matsui T. Open resonator for precision dielectric measurements in the 100 GHz band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1991, 39(10): 1792–1796. DOI: 10.1109/22.88556
|
| [12] |
Siegel P H. Terahertz technology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(3): 910–928. DOI: 10.1109/22.989974
|
| [13] |
魏明贵, 梁达川, 谷建强, 等. 太赫兹时域雷达成像研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 222–229. DOI: 10.12000/JR14125Wei Ming-gui, Liang Da-chuan, Gu Jian-qiang, et al. Terahertz radar imaging based on time-domain spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 222–229. DOI: 10.12000/JR14125
|
| [14] |
俞俊生, 陈晓东. 毫米波与亚毫米波准光技术[M]. 北京: 北京邮电大学出版社, 2010: 1–10.Yu Jun-sheng and Chen Xiao-dong. Millimeter Wave and Sub-millimeter Wave Quasi-optical Technologies[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2010: 1–10.
|
| [15] |
Liu X M, Chen H J, Yang B, et al. Dielectric property measurement of gold nanoparticle dispersions in the millimeter wave range[J]. Journal of Infrared,Millimeter,and Terahertz Waves, 2013, 34(2): 140–151. DOI: 10.1007/s10762-013-9957-7
|
| [16] |
Goldsmith P F. Quasioptical Systems: Gaussian Beam Quasioptical Propogation and Applications[M]. New York: IEEE Press, 1998: 1–50.
|
| [17] |
Soares P A G, Pinho P, and Wuensche C A. High performance corrugated horn antennas for CosmoGal satellite[J]. Procedia Technology, 2014, 17: 667–673. DOI: 10.1016/j.protcy.2014.10.198
|
| [18] |
Olver A D, Clarricoats P J B, Kishk A A, et al.. Microwave Horns and Feeds[M]. New York: IEEE Press, 1994: 229–315.
|
| [19] |
Ade P A, Wylde R J, and Zhang J. Ultra-Gaussian Horns for ClOVER—A B-Mode CMB experiment[C]. Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Charlottesville, USA, 2009: 128–137.
|
| [20] |
Granet C and James G L. Design of corrugated horns: A primer[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2005, 47(2): 76–84. DOI: 10.1109/MAP.2005.1487785
|
| [21] |
Yang B, Wylde R J, Martin D H, et al. Determination of the gyrotropic characteristics of hexaferrite ceramics from 75 to 600 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(12): 3587–3597. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2086290
|
| [22] |
Gagnon N, Shaker J, Roy L, et al. Low-cost free-space measurement of dielectric constant at Ka band[J]. IEE Proceedings-Microwaves,Antennas and Propagation, 2004, 151(3): 271–276. DOI: 10.1049/ip-map:20040264
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
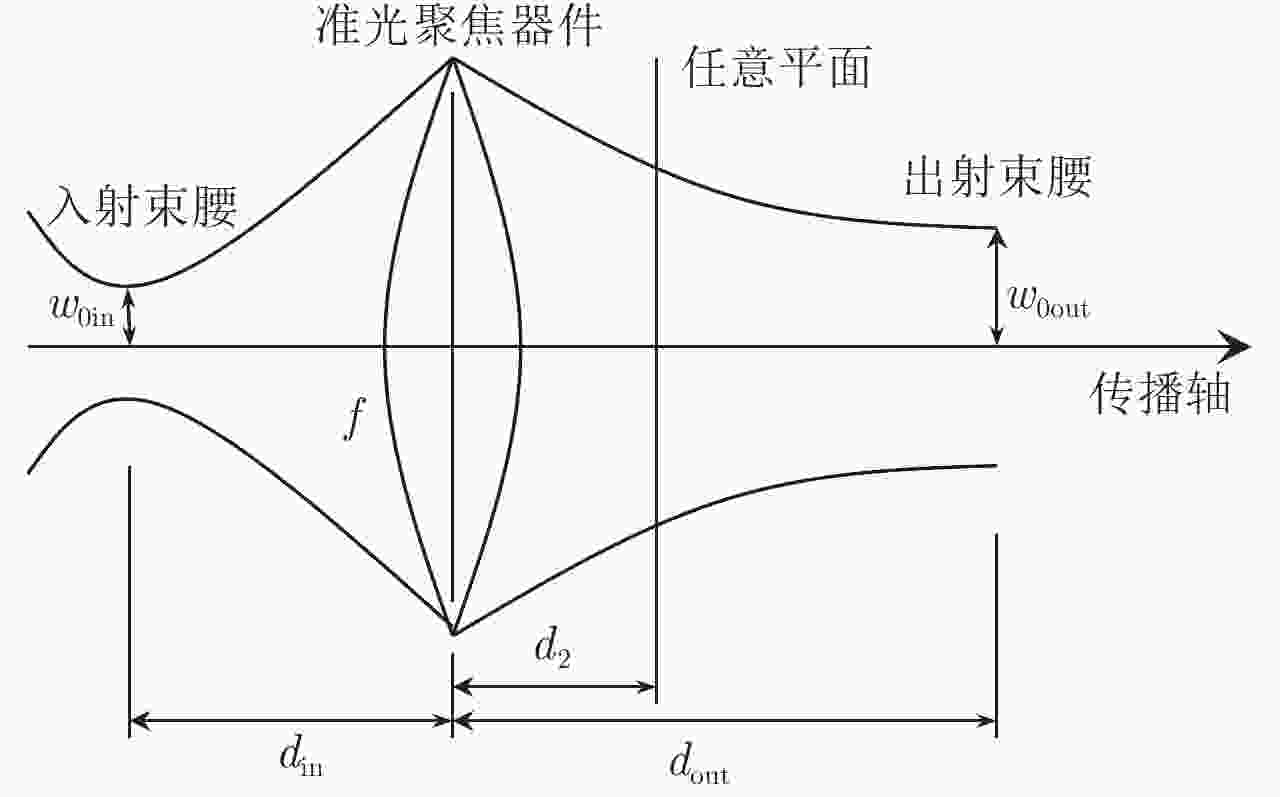
 下载:
下载: