A Novel Terahertz Frequency Scanning Antenna Based on Slotted Waveguide Arrays
-
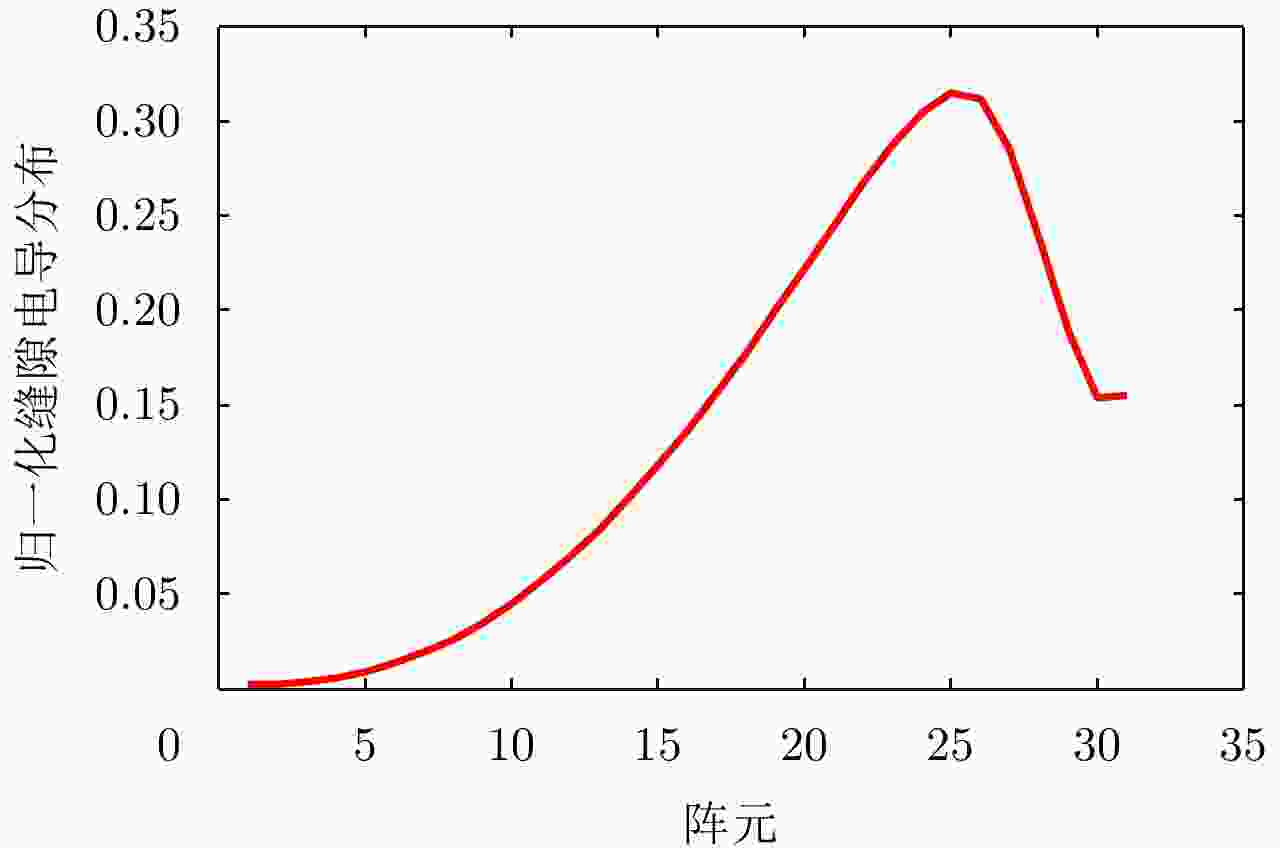
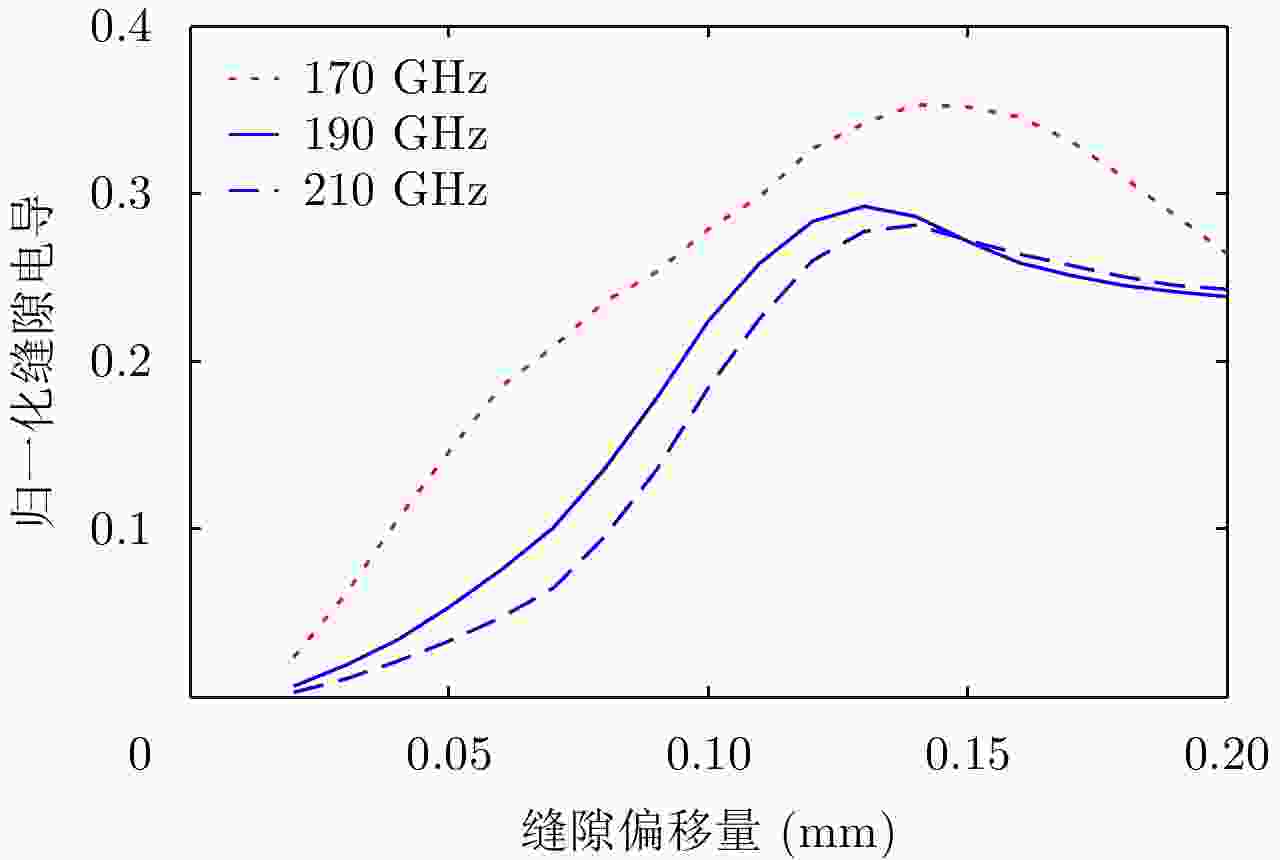
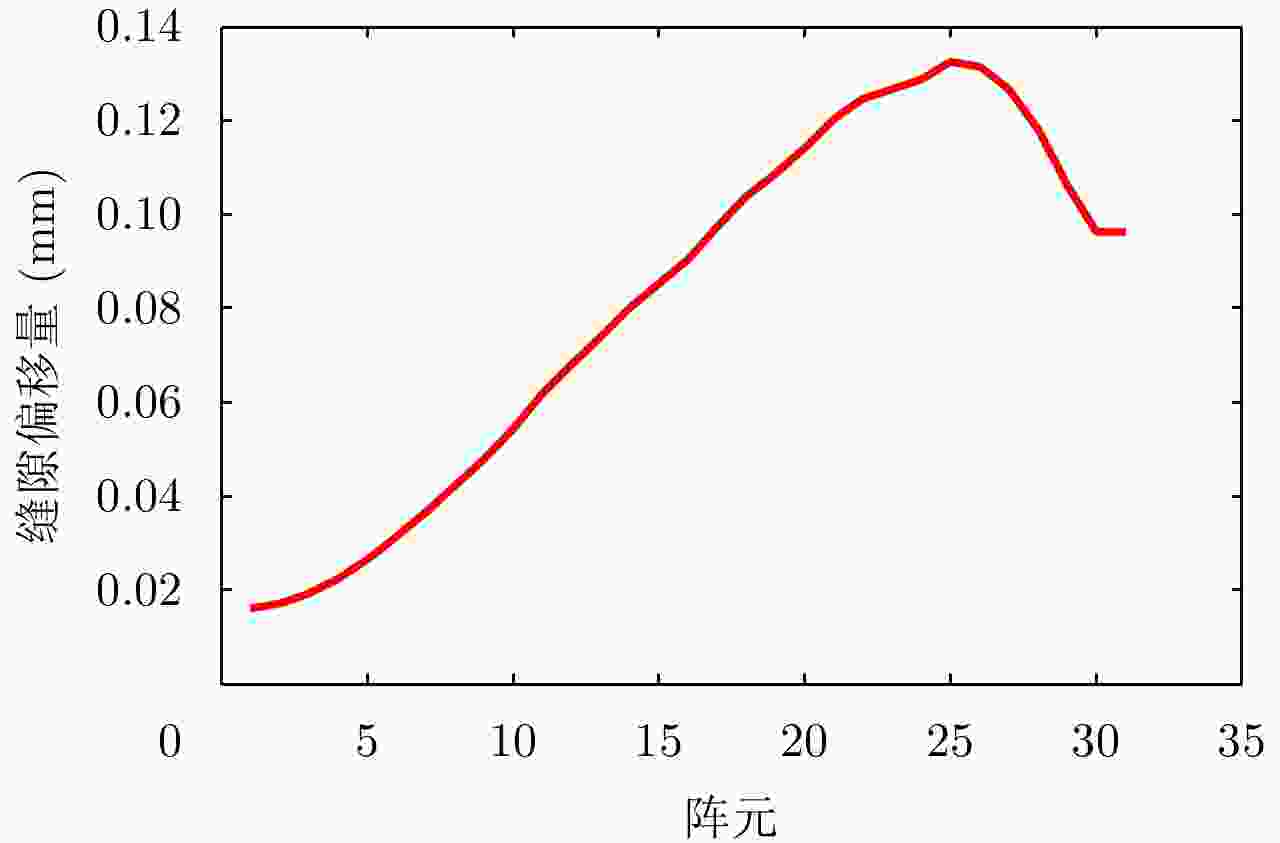
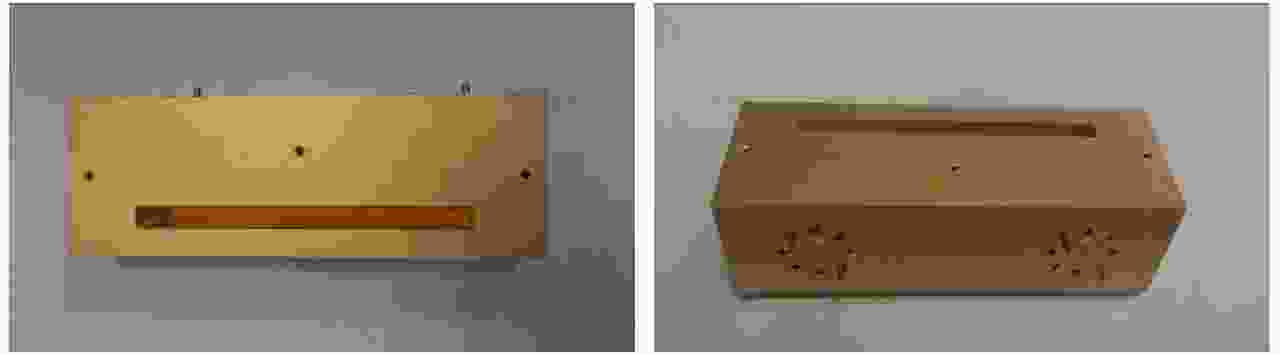
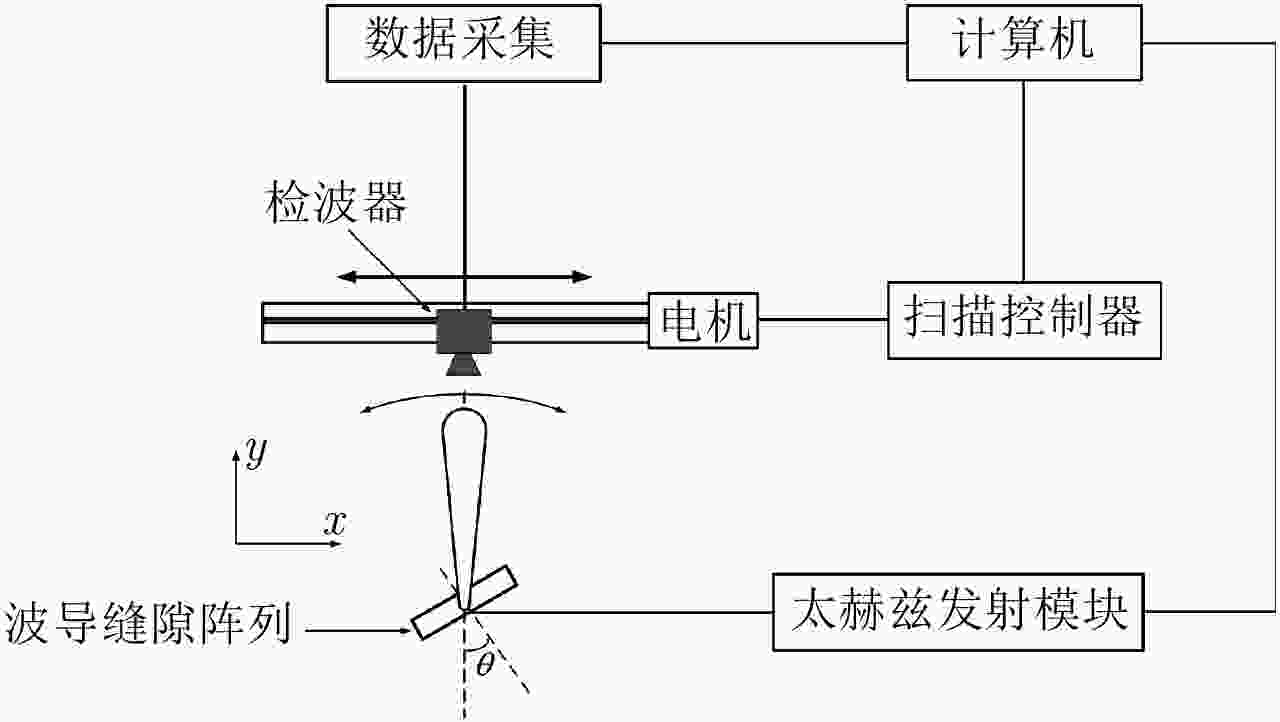
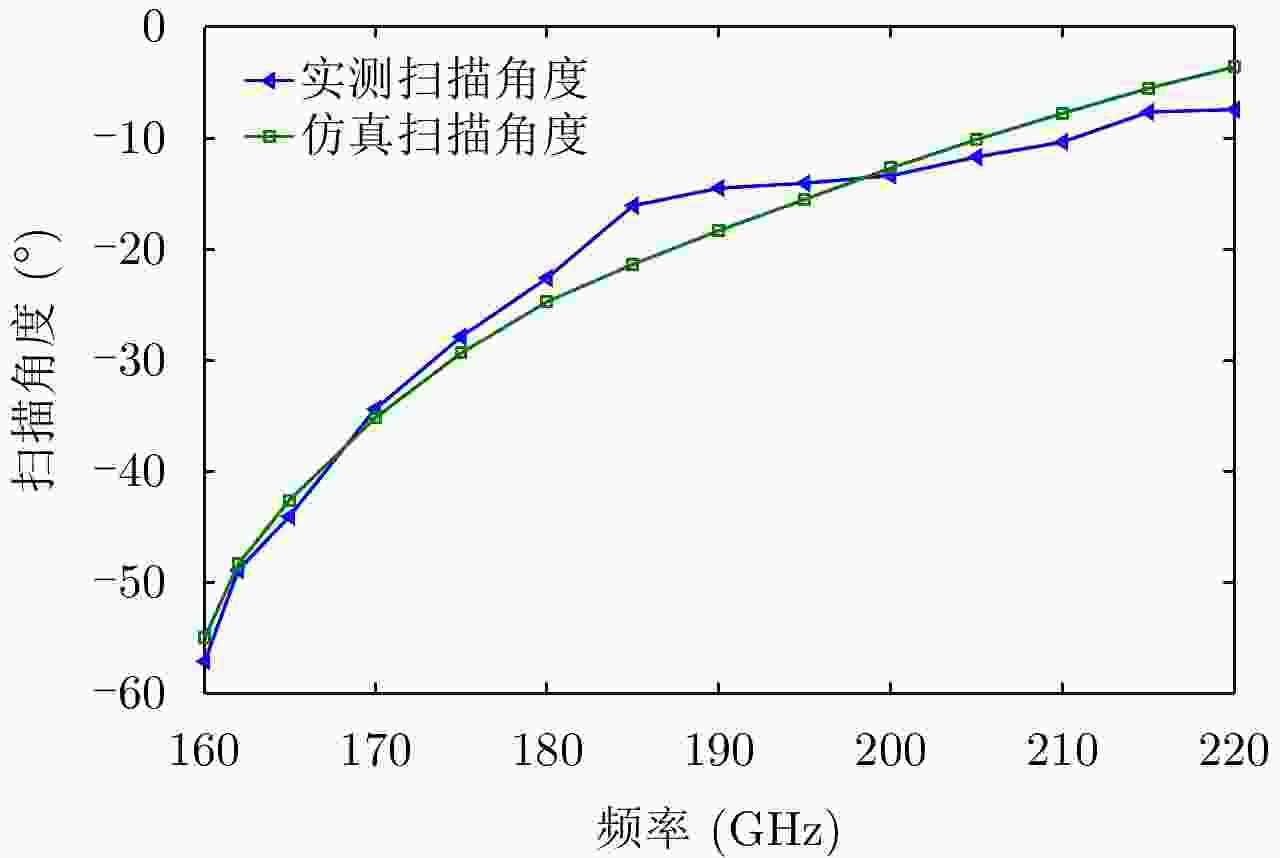
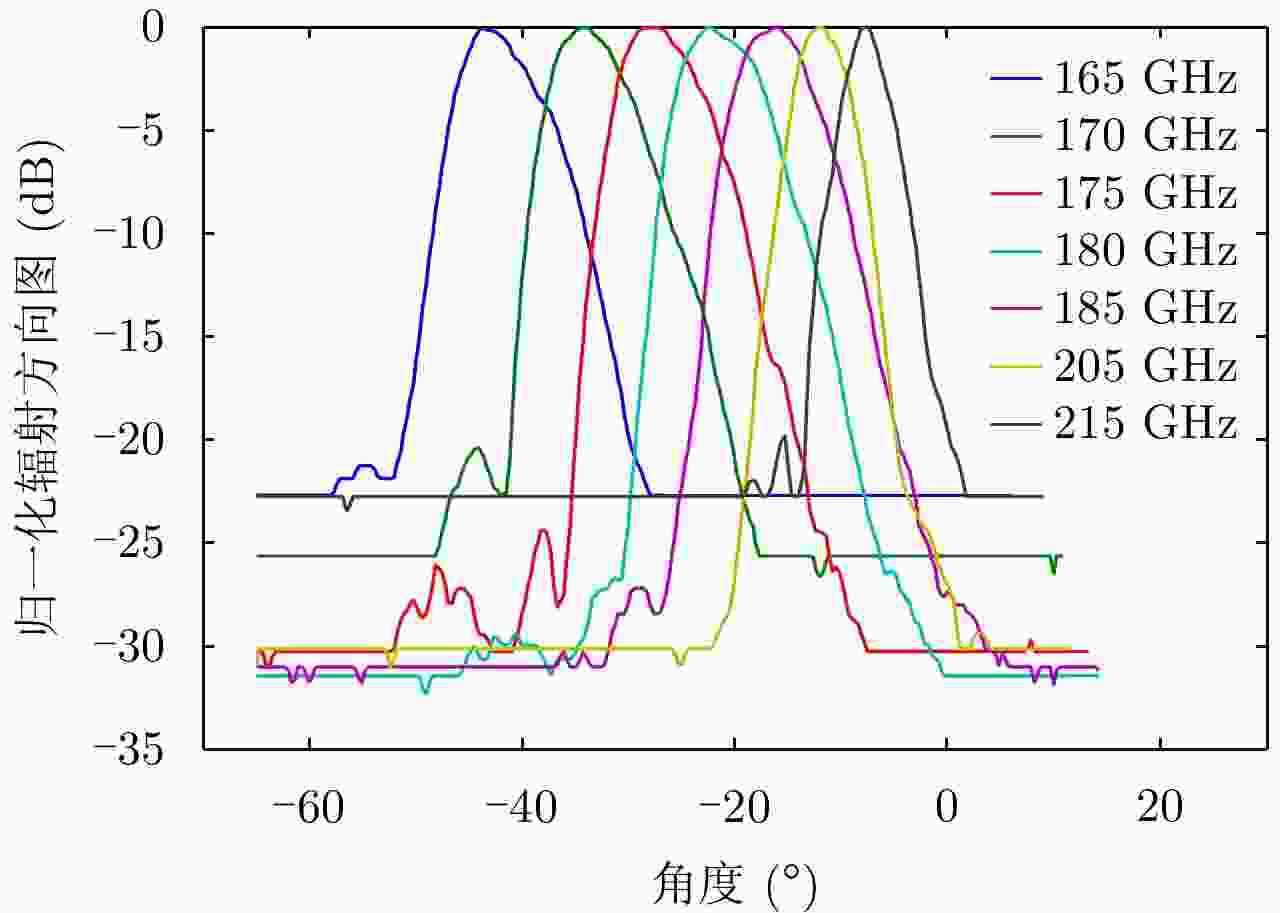
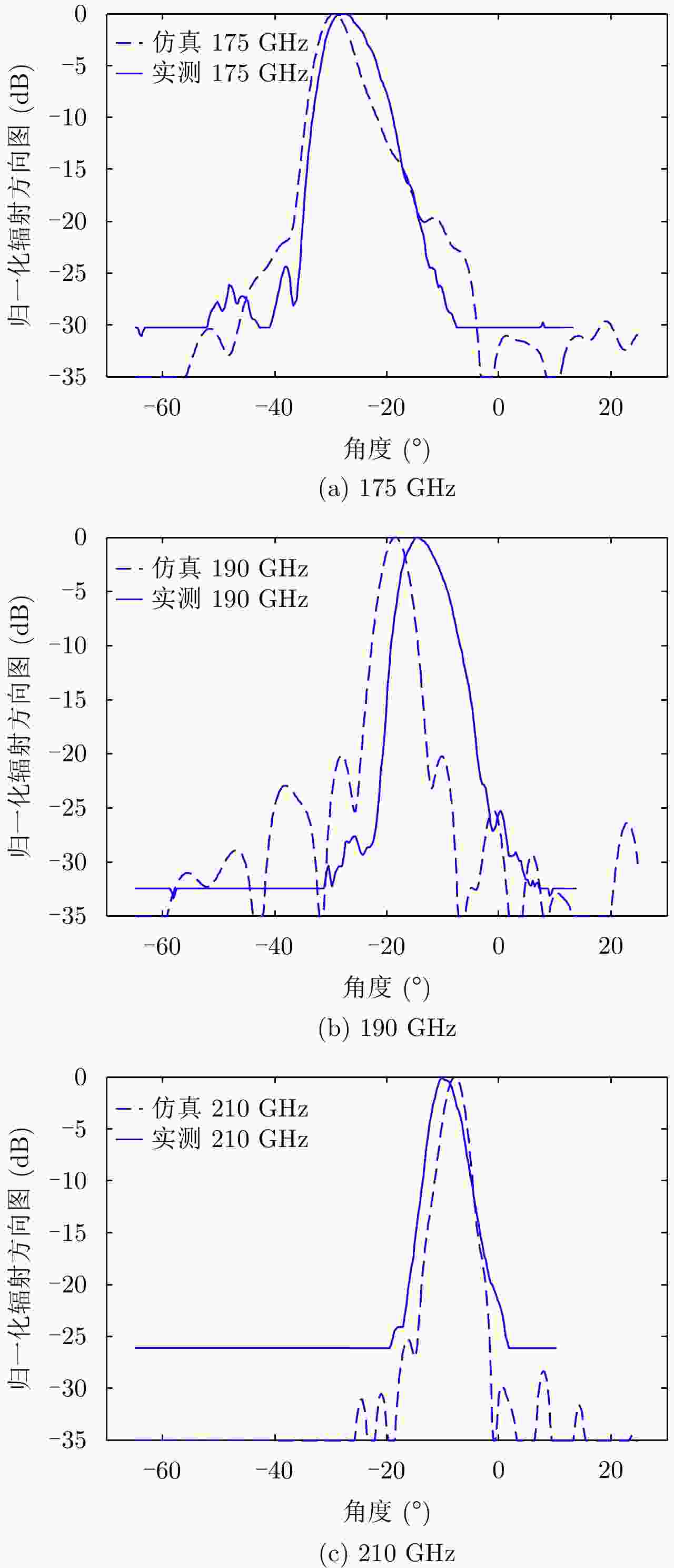
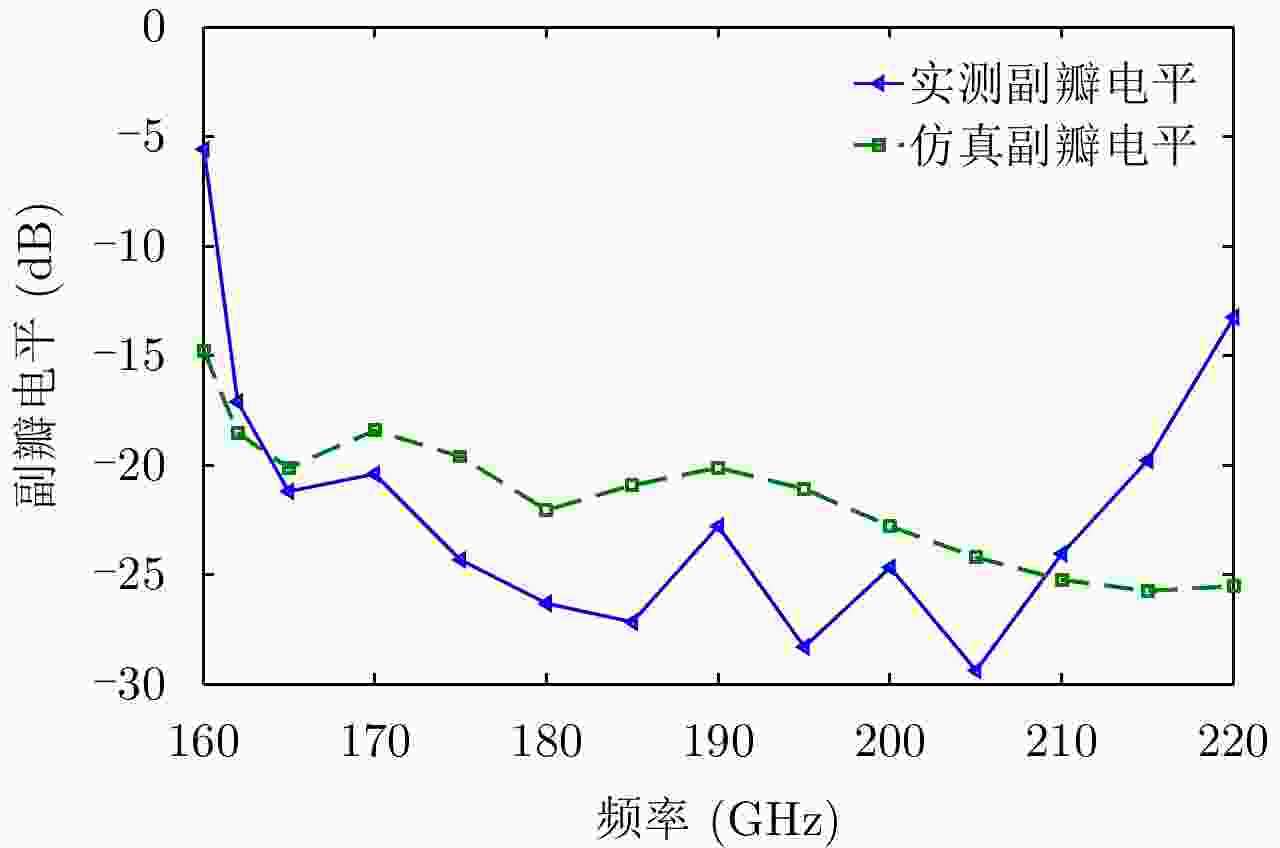
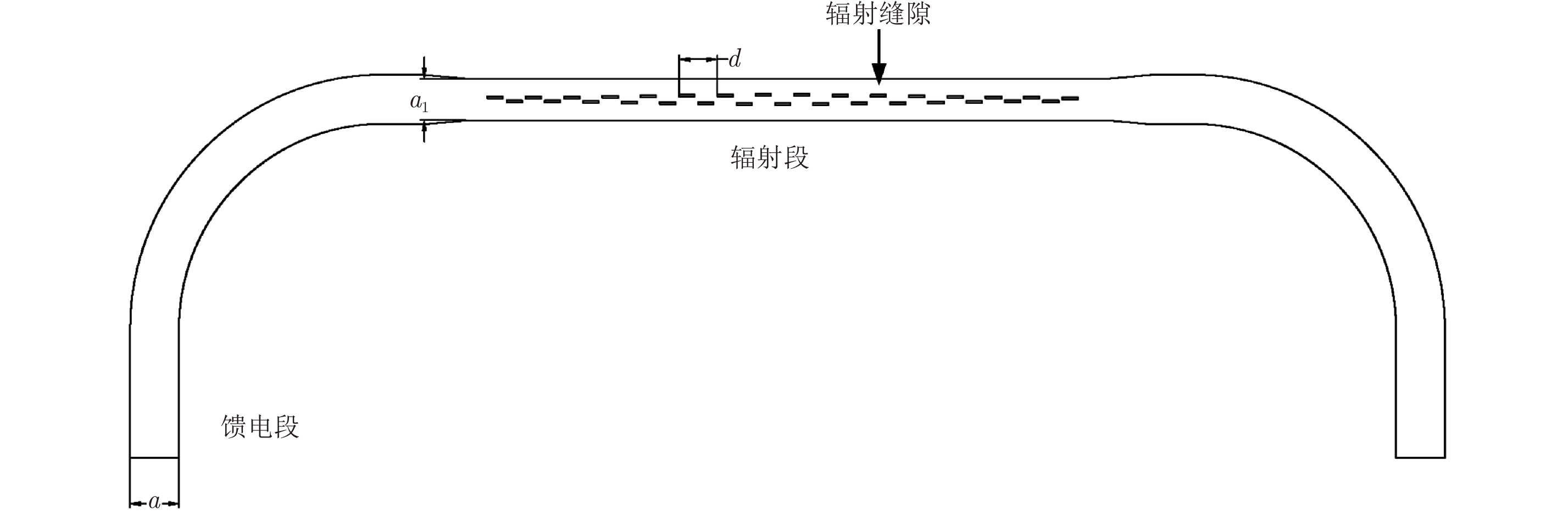
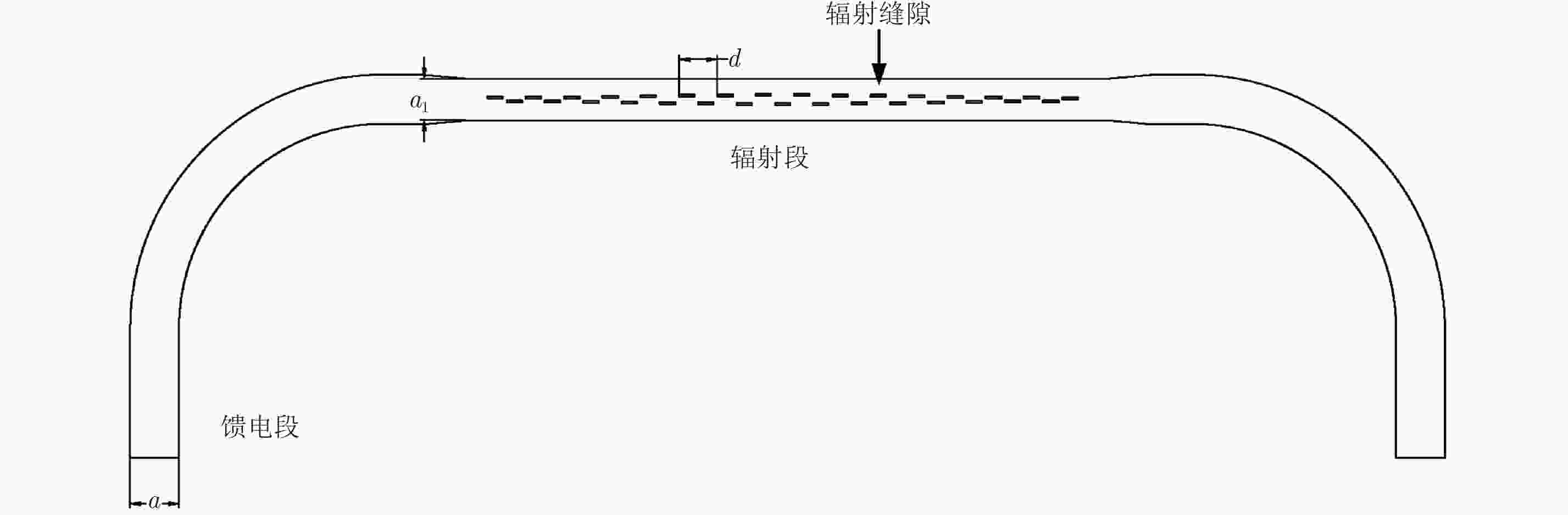
摘要: 为缩短太赫兹系统成像时间,该文提出将频率扫描天线应用于太赫兹成像系统中,并设计了一种基于波导缝隙阵列的太赫兹频率扫描天线。该文采用泰勒综合法降低副瓣电平,通过软件仿真结合功率传输法设计最优的缝隙分布。太赫兹波导缝隙阵列天线具有加工简单、成本低的优势,通过太赫兹准光测试系统对天线性能进行测试,实测天线扫描角度可达40°,增益约为15 dB,副瓣电平抑制优于–20 dB。测试结果表明太赫兹波导缝隙天线具有扫描角度大和副瓣低的优良特性,在太赫兹成像和目标探测等领域有巨大的应用价值。Abstract: This research proposes a novel terahertz frequency scanning antenna based on slotted waveguide arrays, and the antenna consisted of 31 elements in a linear array. Usually, the mechanical steering scheme is employed to realize two-dimensional terahertz imaging for most of the systems that inherently have a low frame rate limitation. As an attractive scheme to obtain high frame rate, electrical beam steering by frequency scanning antennas is the preferable approach. Previous scanning waveguide arrays operating on terahertz band cannot suppress sidelobe levels effectively. Thus, to fulfill the requirement of high radiation efficiency, low waveguide loss, and low sidelobe levels, arranging the slots to conform to Taylor distribution was considered. The distributions effectively become frequency-dependent for the beam-steering concept. Compared with the uniform slot distribution, a Taylor distribution ensures broadband radiation patterns with low sidelobe levels. Furthermore, the offset of the slots has been optimized through a power transmission method in combination with full wave simulation. The frequency-controlled beam steering concept and the sidelobe suppression effect were verified by the quasi-optical measurements in the 0.2 THz band. The fabricated slot-array antenna has large angle scanning ability and a low sidelobe property. In addition, the measured scanning range is larger than 50° with a moderate gain of 15 dB over the frequency band 165~215 GHz. The sidelobe levels are remarkably inhibited over 20 dB normalized to the mainlobe level, and the measured radiation patterns and sidelobe suppression effects agree well with HFSS full-wave simulation. The proposed beam-steering antenna has potential applications for THz imaging with a high frame rate.
-
表 1 太赫兹频率扫描天线性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of the Terahertz frequency scanning antennas
-
[1] Appleby R and Bruce Wallace H. Standoff detection of weapons and contraband in the 100 GHz to 1 THz region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(11): 2944–2956. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2007.908543 [2] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Llombart N, et al. THz imaging radar for standoff personnel screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 169–182. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2159556 [3] Shah U, Decrossas E, Jung-Kubiak C, et al. Submillimeter-wave 3.3-bit RF MEMS phase shifter integrated in micromachined waveguide[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2016, 6(5): 706–715. [4] Johnson R C. Antenna Engineering Handbook[M]. 3rd Ed., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993: 19–26. [5] Li S C, Li C, Zhang Xi J, et al. Achievement of beam steering in terahertz band based on frequency-scanning grating-reflector antenna[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(3): 136–138. DOI: 10.1049/el.2013.3708 [6] Li S C, Li C, Zhang Xi J, et al. A planar binary structure for realizing frequency controlled beam-steering at 0.2-Terahertz band[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 13: 1007–1010. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2326794 [7] Basu A and Itoh T. Dielectric waveguide-based leaky-wave antenna at 212 GHz[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1998, 46(11): 1665–1673. DOI: 10.1109/8.736619 [8] Zandieh A, Abdellatif A S, Taeb A, et al. Low-cost and high-efficiency antenna for millimeter-wave frequency-scanning applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2013, 12: 116–119. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2013.2243572 [9] Dong Y D and Itoh T. Composite right/left-handed substrate integrated waveguide and half mode substrate integrated waveguide leaky-wave structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2011, 59(3): 767–775. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2103025 [10] Xu J F, Hong W, Tang H J, et al. Half-mode substrate integrated waveguide leaky-wave antenna for millimeter wave applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2008, 7: 85–88. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2008.919353 [11] Patrovsky A and Wu K. Substrate integrated image guide (SIIG)—A planar dielectric waveguide technology for millimeter-wave application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2006, 54(6): 2872–2879. [12] Mondal P and Wu K. A leaky-wave antenna in substrate integrated non-radiative dielectric (SINRD) waveguide with controllable scanning rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(4): 2294–2297. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2231914 [13] Alvarez Y, Camblor R, Garcia C, et al. Submillimeter-wave frequency scanning system for imaging applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(11): 5689–5696. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2275747 [14] Camblor R, Ver Hoeye S, Fernández M, et al. Full 2-D submillimeter-wave frequency scanning array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(9): 4486–4494. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2722538 [15] 赵一, 曹祥玉, 张迪, 等. 一种兼有高增益和宽带低散射特征的波导缝隙天线设计[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(3): 034101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.63.034101Zhao Yi, Cao Xiang-Yu, Zhang Di, et al. Design of high-gain broadband low-RCS waveguide slot antenna[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(3): 034101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.63.034101 [16] 刘涛, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 基于超材料的吸波体设计及其波导缝隙天线应[J]. 物理学报, 2012, 61(18): 184101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.61.184101Liu Tao, Cao Xiang-Yu, Gao Jun, et al. Design of metamaterial absorber and its applications for waveguide slot antenna[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(18): 184101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.61.184101 [17] 李文强, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 基于超材料吸波体的低雷达散射截面波导缝隙阵列天线[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(9): 094102. DOI: 10.7498/aps.64.094102Li Wen-Qiang, Cao Xiang-Yu, Gao Jun, et al. Low-RCS waveguide slot array antenna based on a metamaterial absorber[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(9): 094102. DOI: 10.7498/aps.64.094102 [18] Rengarajan S R, Zawadzki M S, and Hodges R E. Waveguide-slot array antenna designs for low-average-sidelobe specifications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2010, 52(6): 89–98. DOI: 10.1109/MAP.2010.5723227 [19] Cullens E D, Ranzani L, Vanhille K J, et al. Micro-fabricated 130–180 GHz frequency scanning waveguide arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(8): 3647–3654. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2201089 [20] Ranzani L, Kuester D, Vanhille K J, et al. G-Band micro-fabricated frequency-steered arrays with 2°/GHz beam steering[J].IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(5): 566–573. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2013.2271381 [21] Melezhik P N, Razskazovskiy V B, Reznichenko N G, et al.. High-efficiency millimeter wave coherent radar for airport surface movement monitoring and control[C]. Proceedings of the 8th European Radar Conference, Manchester, UK, 2011: 361–364. [22] Pollard B D and Sadowy G. Next generation millimeter-wave radar forsafe planetary landing[C]. The 2005 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2005: 1213–1219. [23] Martin C A, Clark S E, Lovberg J A, et al.. Real-time wide-field-of-view passive millimeter-wave imaging[C]. Proceedings of SPIE Infrared and Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Systems: Design, Analysis, Modeling, and Testing, Orlando, FL, 2002: 341–349. [24] Yang S T and Ling H. Application of a microstrip leaky wave antenna for range-azimuth tracking of humans[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1384–1388. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2243401 [25] Geibig T, Shoykhetbrod A, Hommes A, et al.. Compact 3D imaging radar based on FMCW driven frequency-scanning antennas[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016: 1–5. [26] Hosseininejad S E and Komjani N. Optimum design of traveling-wave SIW slot array antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(4): 1971–1975. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2233704 [27] Robinson J and Rahmat-Samii Y. Particle swarm optimization in electromagnetics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2004, 52(2): 397–407. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2004.823969 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: