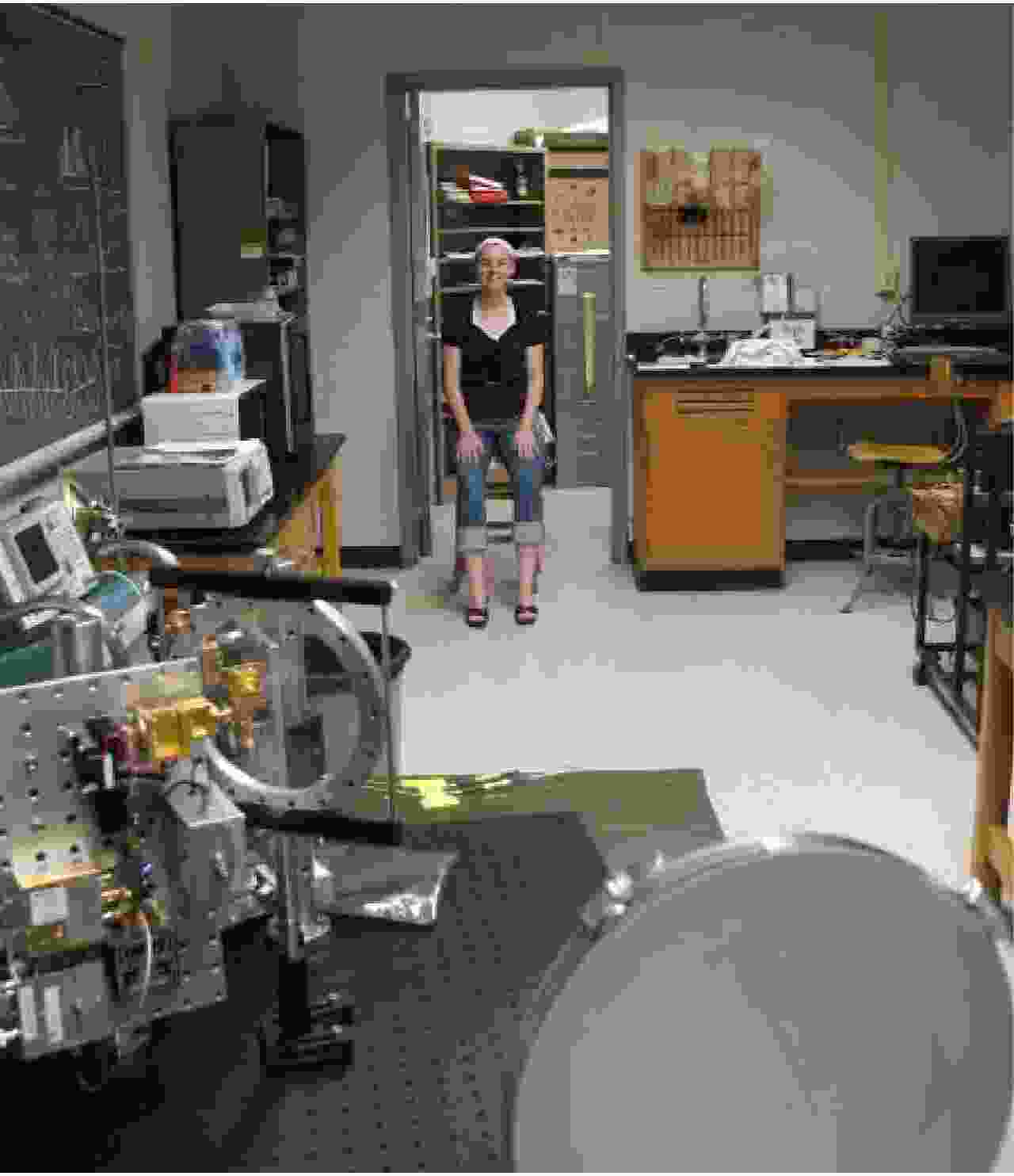
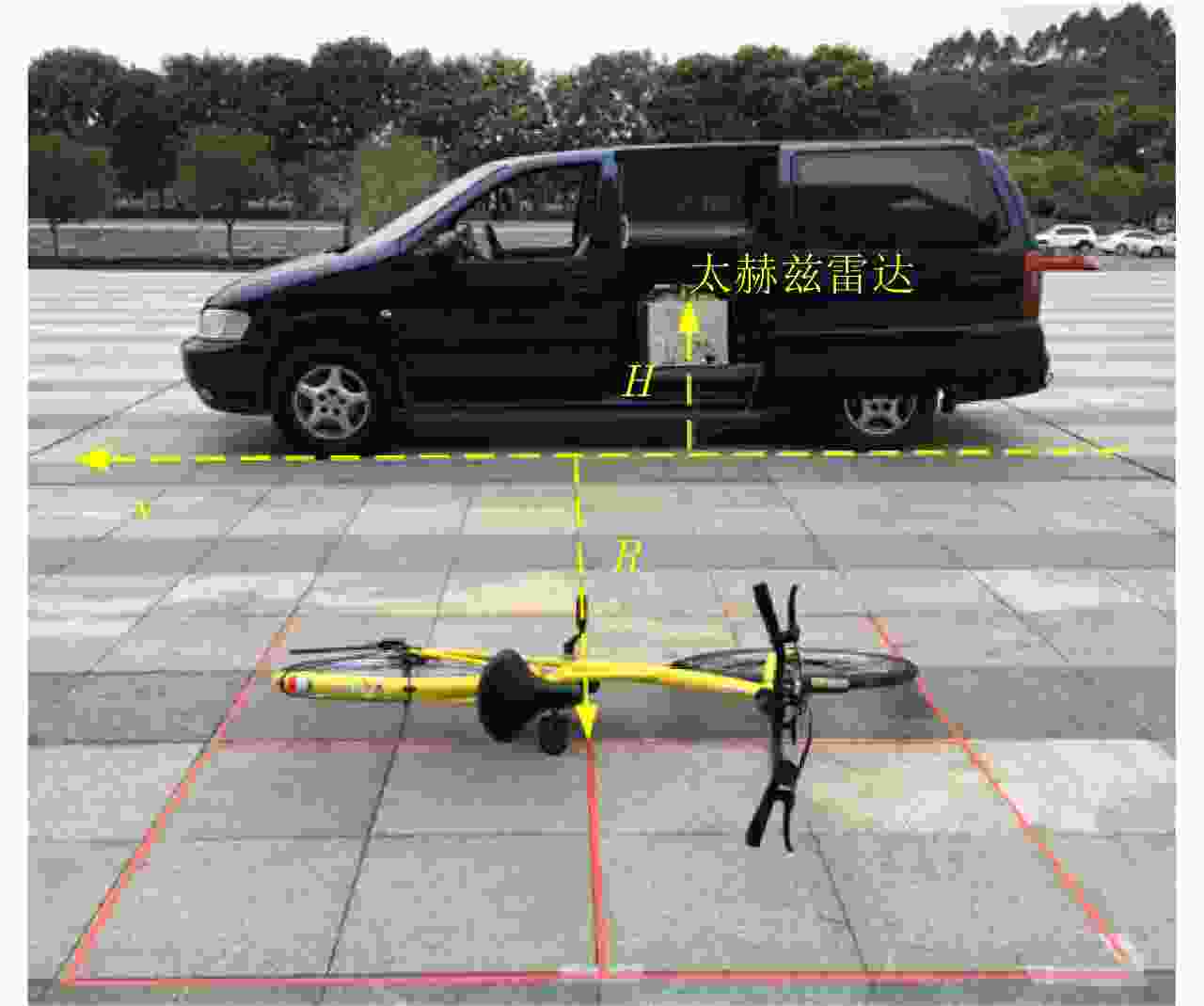
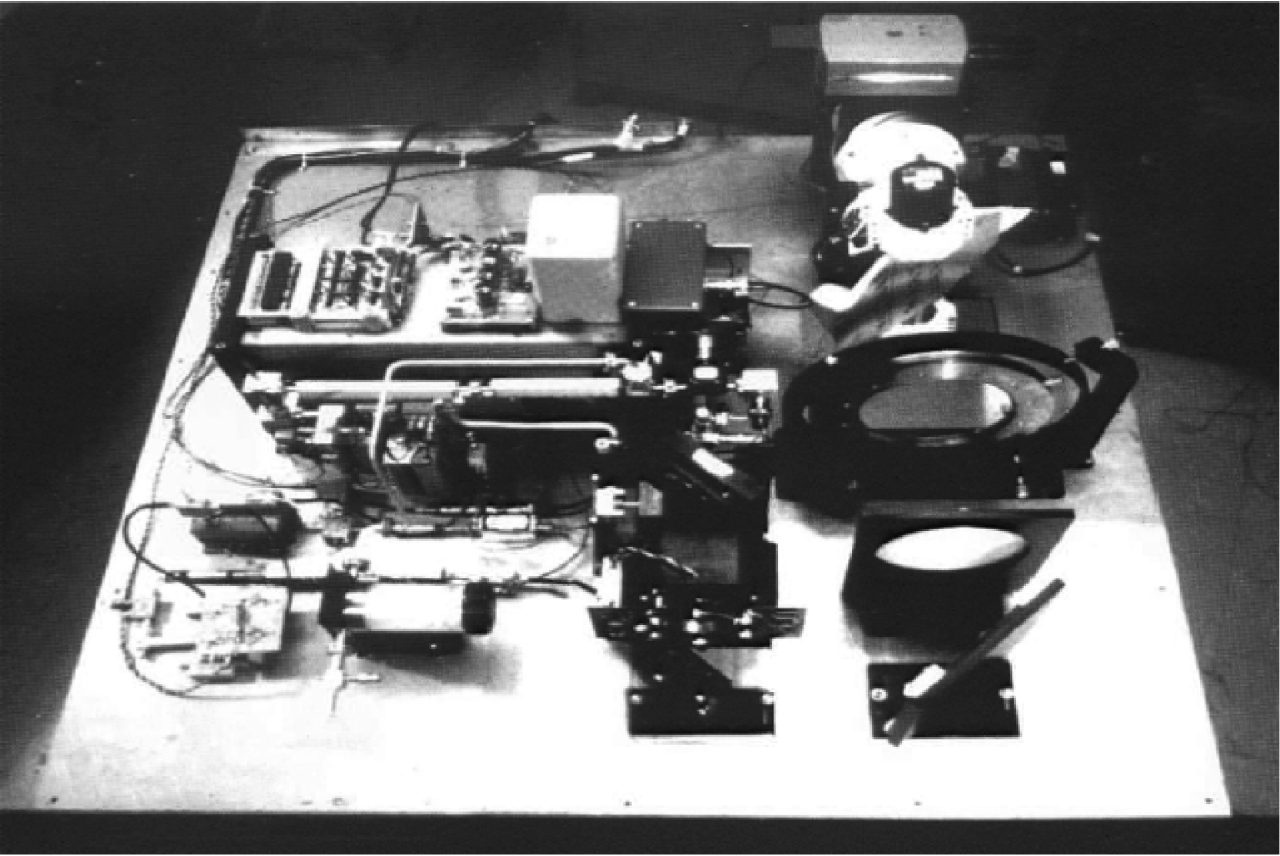
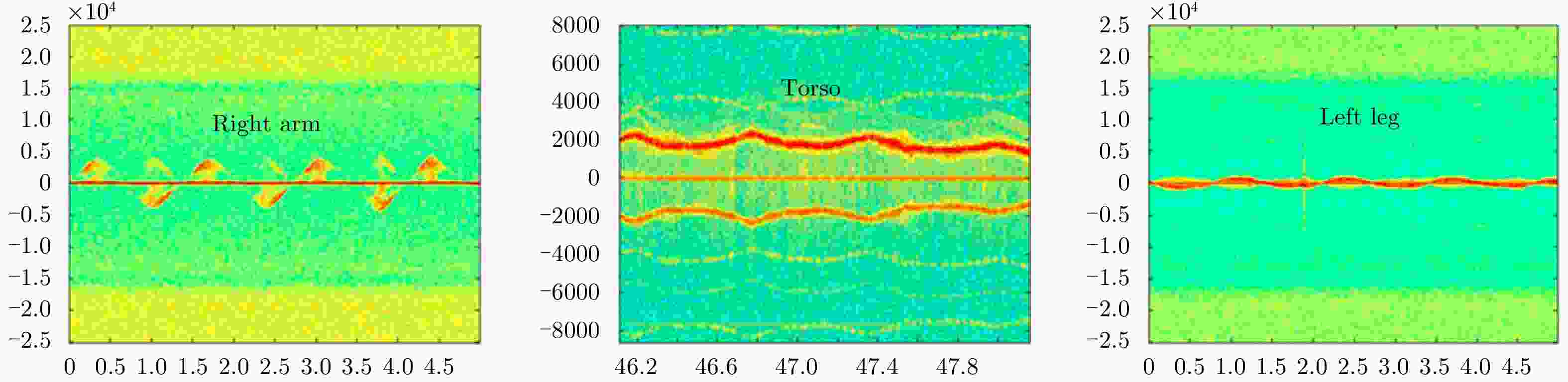
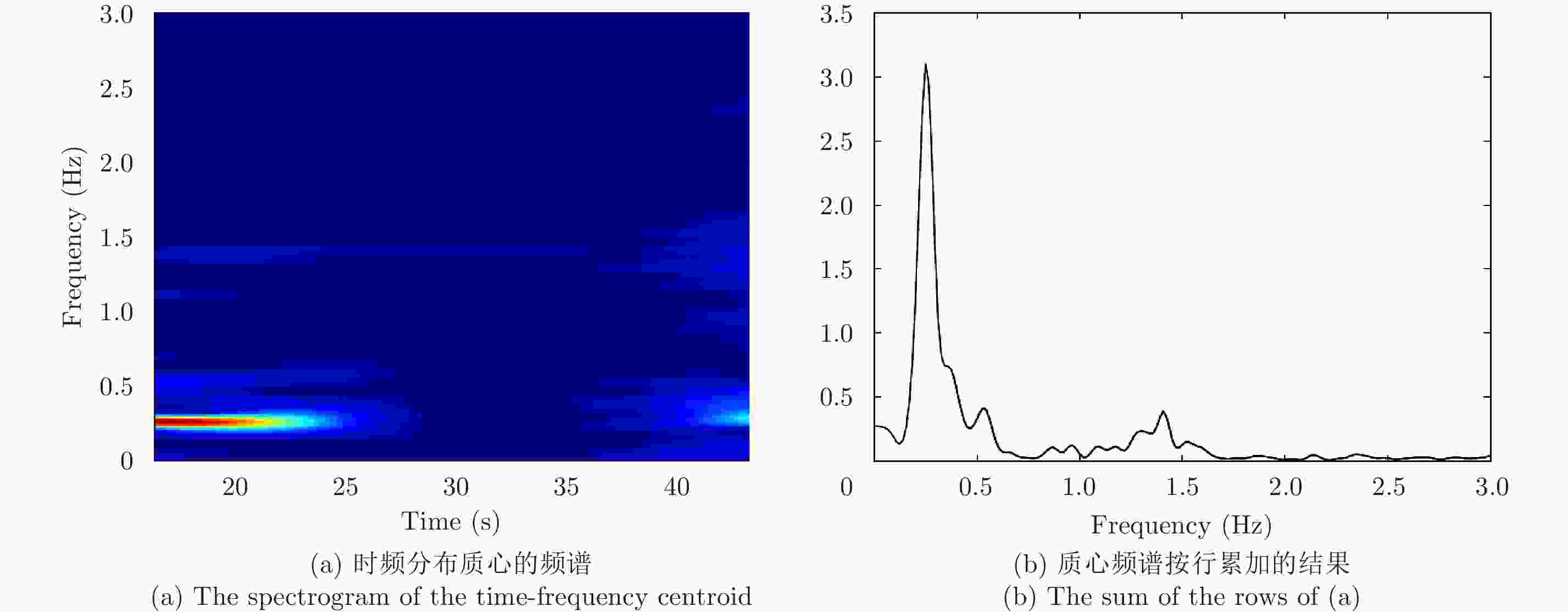
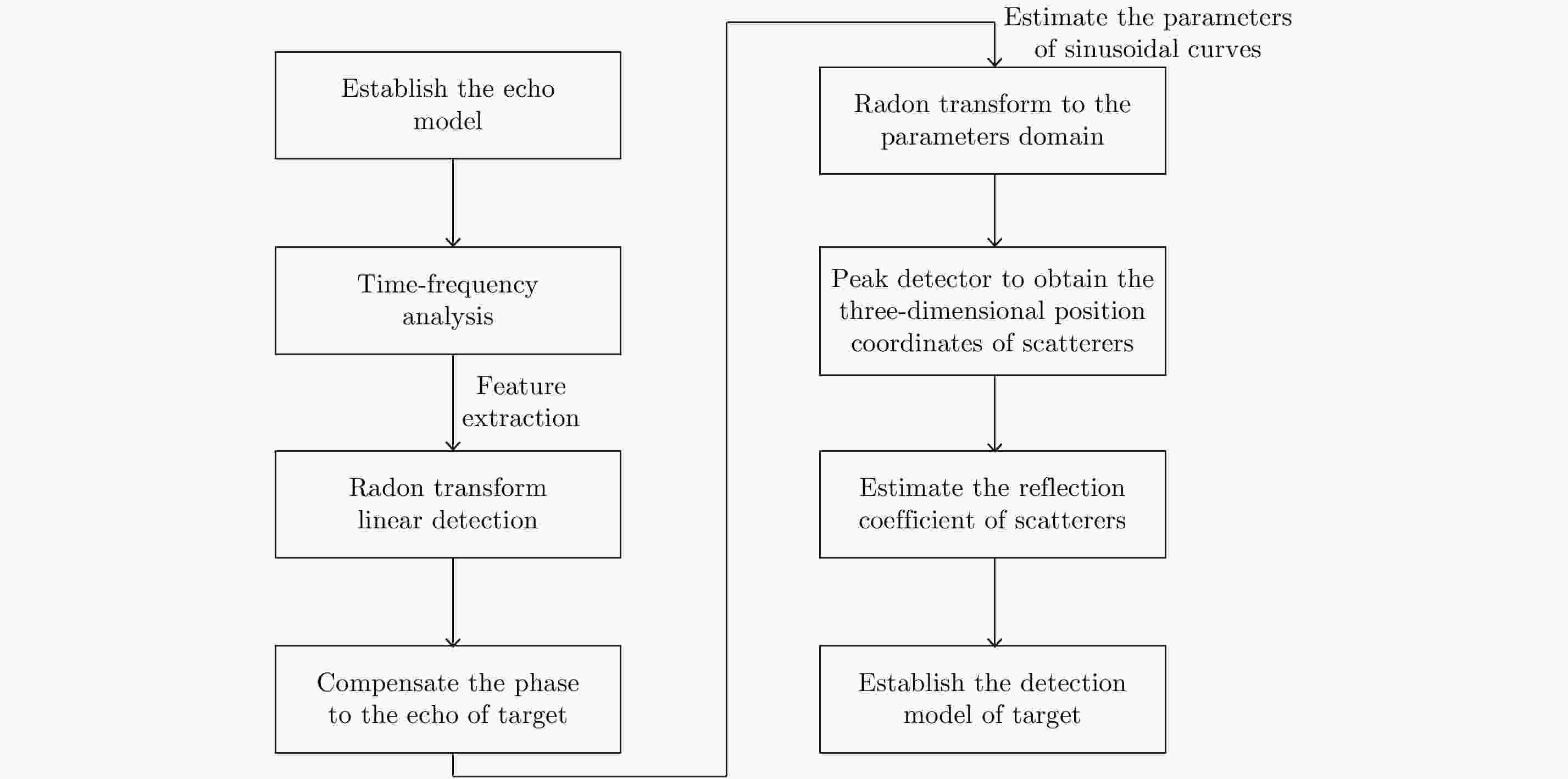
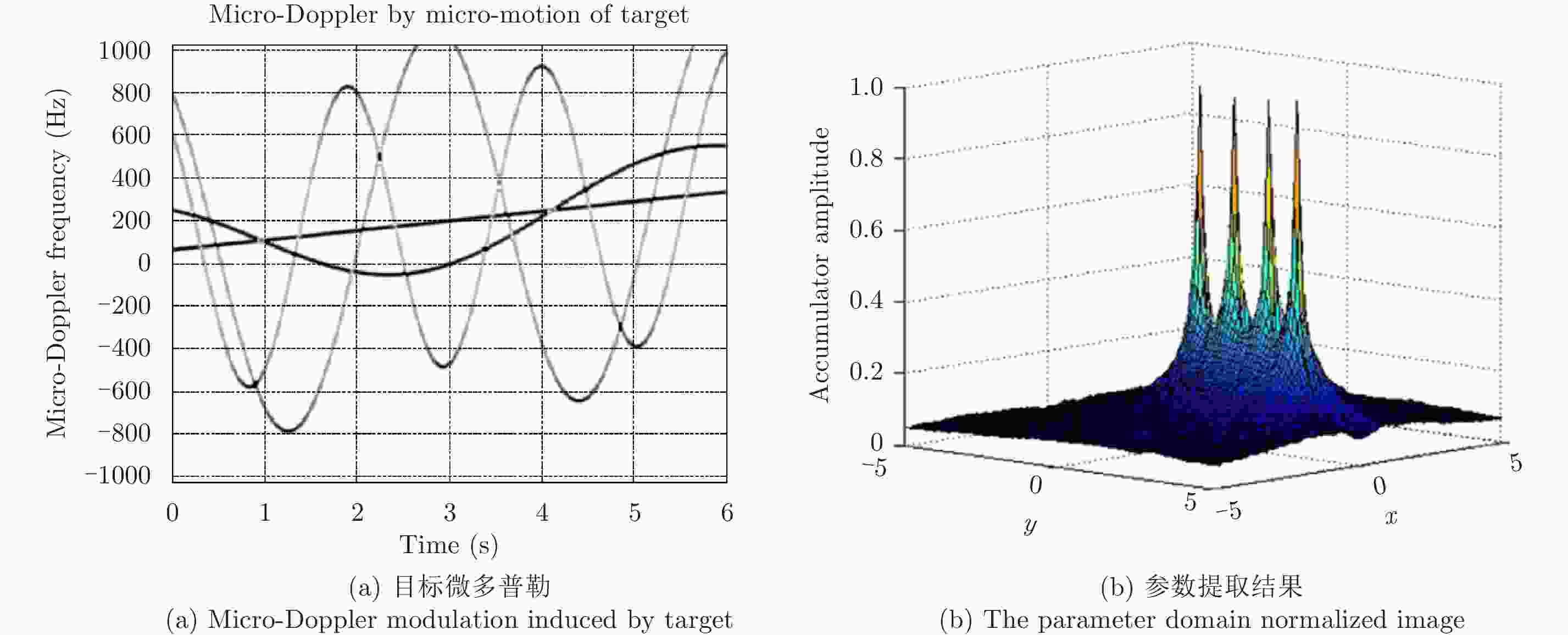
Advancements in Research on Micro-motion Feature Extraction in the Terahertz Region
-
摘要: 微动特征是目标探测与识别的重要辅助特征。随着近年来太赫兹研究的兴起,太赫兹雷达目标微动特征提取正在逐渐凸显出其特殊优势。本文首先对近年来国内外太赫兹频段雷达目标微动特征提取方面的研究进行整理总结,从太赫兹频段微动特性分析、微动特征提取和微动目标成像等几个方面进行了深入的介绍和分析。然后针对太赫兹频段的优势和特殊性,介绍了本单位在太赫兹微动目标特性分析、特征提取和高分辨高帧频成像方面的工作。最后对太赫兹雷达目标微动特征提取的发展趋势进行了展望,并分析了本领域值得进一步深入研究的技术方向和有待解决的技术难题。Abstract: With years of development and accumulation, a considerable amount of research has focused on micro-motion, an important auxiliary feature in radar target detection and recognition. With the recent rise of terahertz, micro-motion feature extraction in the terahertz region has increasingly highlighted its advantages. Herein, we systematically surveyed the recent research on terahertz radar micro-motion feature extraction and discussed micro-motion feature analysis, micro-motion feature extraction, and micro-motion target imaging. And then we emphatically introduced the work of our research team, including the theoretical and experimental research on micro-motion feature analysis, micro-motion feature extraction and high-resolution/high-frame micro-motion target imaging. Furthermore, we analyzed the growing trend of micro-motion feature extraction in the terahertz region, and pointed out the new technology directions worth to be studied further and the technical challenges to be solved.
-
Key words:
- Terahertz radar /
- Micro-motion /
- Micro-Doppler /
- Feature extraction /
- Parameter estimation
-
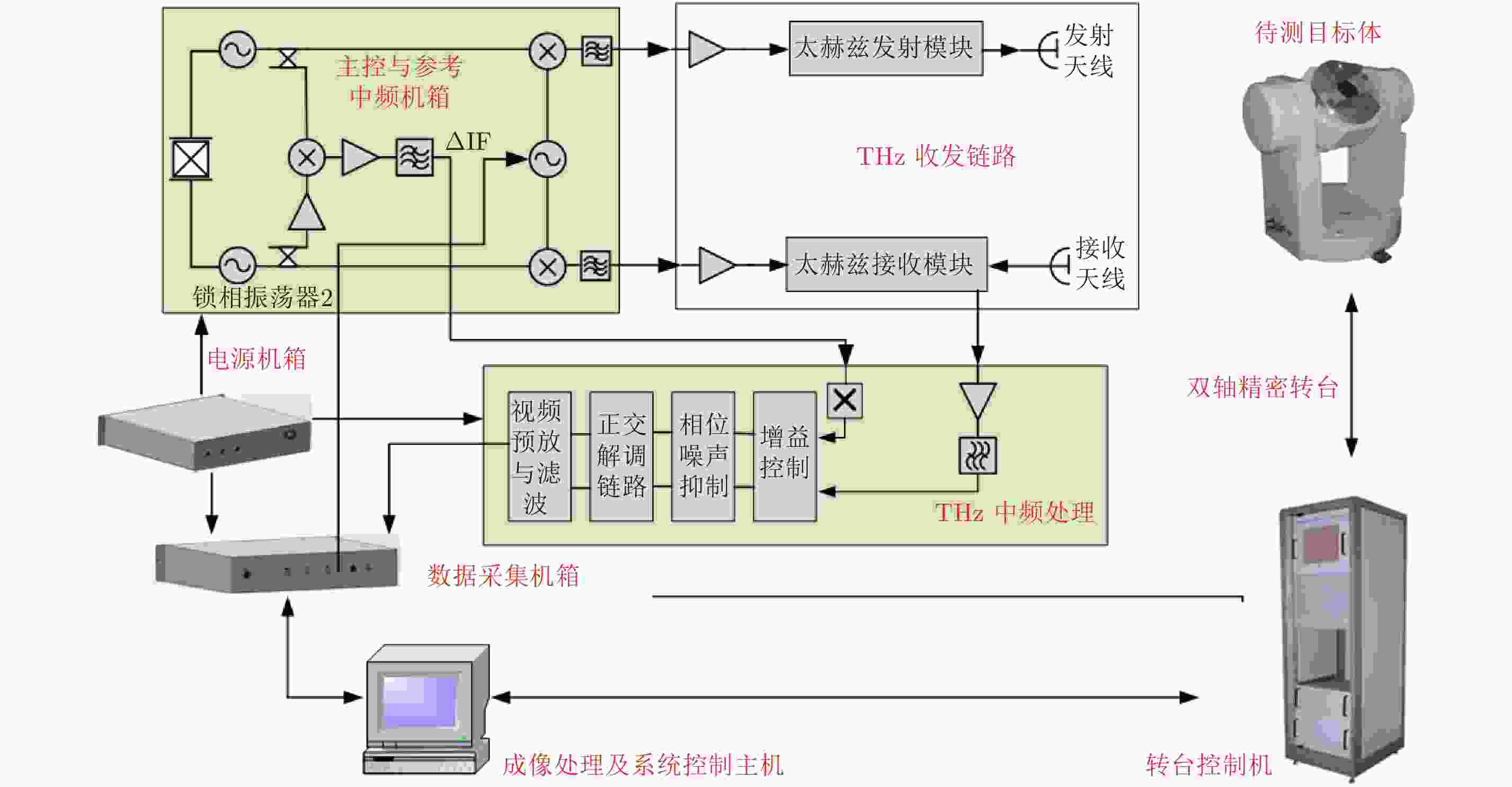
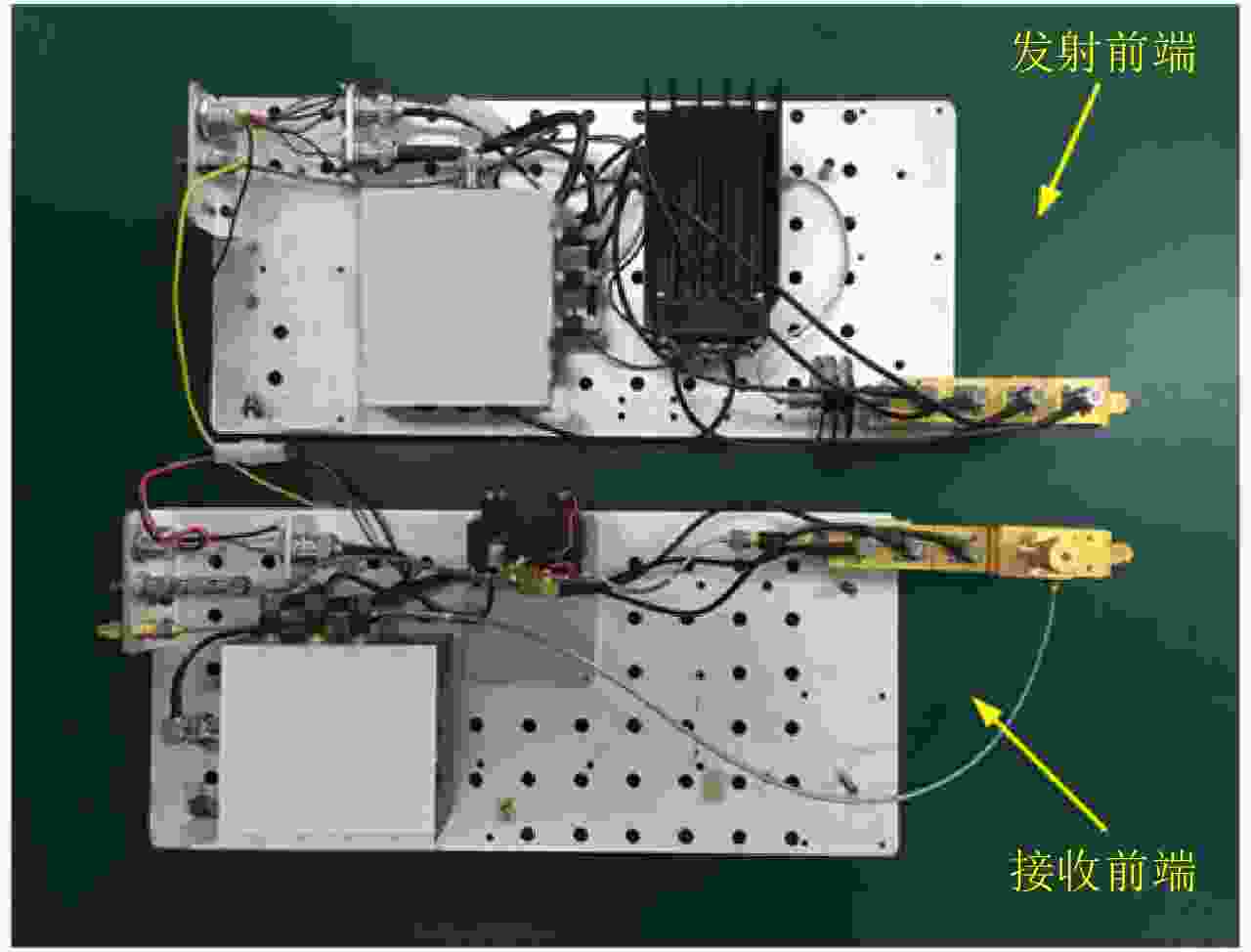
表 1 结构复用太赫兹雷达系统主要参数
Table 1. The main parameters of the 440 GHz terahertz radar system with reusable structure
工作频率(GHz) 中心频率(GHz) 带宽(GHz) 发射功率(mW) 倍频次数 工作温度(°) 存储温度(°) 217~227 222 10.0 10.0 Typ 16 +20~+40 0~+70 325.5~340.5 333 15.0 1.0 Typ 24 434~454 444 20.0 5.0 Typ 32 651~681 (设计) 666 30.0 — 48 1312~1352 (设计) 1332 40.0 — 96 -
[1] Federici J F, Schulkin B, Huang F, et al. THz imaging and sensing for security applications—explosives, weapons and drugs[J]. Semiconductor Science Technology, 2005, 20(7): S266–S280. DOI: 10.1088/0268-1242/20/7/018 [2] Redo-Sanchez A and Zhang X C. Terahertz science and technology trends[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2008, 14(2): 260–269. DOI: 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.913959 [3] Van Exter M and Grischkowsky D R. Characterization of an optoelectronic terahertz beam system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1990, 38(11): 1684–1691. DOI: 10.1109/22.60016 [4] 杨光鲲, 袁斌, 谢东彦, 等. 太赫兹技术在军事领域的应用[J]. 激光与红外, 2011, 41(4): 376–380. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.04.003Yang Guang-kun, Yuan Bin, Xie Dong-yan, et al. Analysis on the use of THz technology in the military application[J]. Laser&Infrared, 2011, 41(4): 376–380. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.04.003 [5] 王忆锋, 毛京湘. 太赫兹技术的发展现状及应用前景分析[J]. 光电技术应用, 2008, 23(1): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2008.01.001Wang Yi-feng and Mao Jing-xiang. Analysis on development status of terahertz technology and application prospect[J]. Electro-optic Technology Application, 2008, 23(1): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1255.2008.01.001 [6] Caris M, Stanko S, Palm S, et al.. 300 GHz radar for high resolution SAR and ISAR applications[C]. Proceedings of the 16th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, 2015: 577–580. [7] Wang R J, Deng B, Qin Y L, et al. Bistatic terahertz radar azimuth-elevation imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(6): 702–713. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2014.2348413 [8] Liang M Y, Zhang C L, Zhao R, et al. Experimental 0.22 THz stepped frequency radar system for ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Infrared,Millimeter,and Terahertz Waves, 2014, 35(9): 780–789. DOI: 10.1007/s10762-014-0079-7 [9] Zhang B, Pi Y M, and Li J. Terahertz imaging radar with inverse aperture synthesis techniques: System structure, signal processing, and experiment results[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(1): 290–299. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2342495 [10] Sun Z Y, Li C, Gu S M, et al. Fast three-dimensional image reconstruction of targets under the illumination of terahertz Gaussian beams with enhanced phase-shift migration to improve computation efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(4): 479–490. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2014.2326004 [11] 刘玮, 李超, 张群英, 等. 一种用于人体安检的三维稀疏太赫兹快速成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 271–277. DOI: 10.12000/JR15116Liu Wei, Li Chao, Zhang Qun-ying, et al. Fast three-dimensional sparse holography imaging algorithm for personal security verification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 271–277. DOI: 10.12000/JR15116 [12] Gu S M, Li C, Gao X, et al. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of targets under the illumination of terahertz Gaussian beam—theory and experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4): 2241–2249. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2209892 [13] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Llombart N, et al. THz imaging radar for standoff personnel screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 169–182. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2159556 [14] Llombart N, Cooper K B, Dengler R J, et al. Time-delay multiplexing of two beams in a terahertz imaging radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(7): 1999–2007. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2050106 [15] Chen V C, Li F Y, Ho S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. [16] 庄钊文, 刘永祥, 黎湘. 目标微动特性研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(3): 520–525. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.028Zhuang Zhao-wen, Liu Yong-xiang, and Li Xiang. The achievements of target characteristic with micro-motion[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(3): 520–525. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.028 [17] Chen V C. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler with time-frequency transform[C]. Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Pocono Manor, PA, 2000: 463–466. [18] Chen V C. Detection and analysis of human motion by radar[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008: 1–4. [19] Chen V C. Joint time-frequency analysis for radar signal and imaging[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, 2008: 5166–5169. [20] Chen V C. Spatial and temporal independent component analysis of micro-Doppler features[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, 2005: 348–353. [21] Chen V C. Doppler signatures of radar backscattering from objects with micro-motions[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 291–300. DOI: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070137 [22] Chen V C, Li F, Ho S S, et al. Analysis of micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar,Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(4): 271–276. DOI: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030743 [23] Chen V C, Lipps R, and Bottoms M. Advanced synthetic aperture radar imaging and feature analysis[C]. Proceedings of International Radar Conference, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2003: 22–29. [24] Chen V C. Micro-Doppler effect of micromotion dynamics: A review[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 5102, Independent Component Analyses, Wavelets, and Neural Networks, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2003, 5102: 240–249. [25] 罗迎, 张群, 王国正, 等. 基于复图像OMP分解的宽带雷达微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(4): 361–369. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20065Luo Ying, Zhang Qun, Wang Guo-zheng, et al. Micro-motion signature extraction method for wideband radar based on complex image OMP decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 361–369. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20065 [26] Mcmillan R W, Trussell C W, Bohlander R A, et al. An experimental 225 GHz pulsed coherent radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1991, 39(3): 555–562. DOI: 10.1109/22.75300 [27] Petkie D T, Benton C, and Bryan E. Millimeter-wave radar for vital signs sensing[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7308, Radar Sensor Technology XIII, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2009, 7308: 73080A. [28] Petkie D T, Bryan E, Benton C, et al.. Remote respiration and heart rate monitoring with millimeter-wave/terahertz radars[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7117, Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology, Cardiff, Wales, United Kingdom, 2008, 7117: 71170I. [29] Petkie D T, Bryan E, Benton C, et al.. Millimeter-wave radar systems for biometric applications[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7485, Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology II, Berlin, Germany, 2009, 7485: 748502. [30] Moulton M C, Bischoff M L, Benton C, et al.. Micro-doppler radar signatures of human activity[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7837, Millimetre Wave and Terahertz Sensors and Technology III, Toulouse, France, 2010, 7837: 78370L. [31] Massar M L. Time-frequency analysis of terahertz radar signals for rapid heart and breath rate detection[D]. [Master dissertation], Air Force Institute of Technology, 2008. [32] Li J and Pi Y M. Target detection for terahertz radar networks based on micro-Doppler signatures[J]. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 2015, 17(2): 115–121. DOI: 10.1504/IJSNET.2015.067861 [33] 李晋, 皮亦鸣, 杨晓波. 基于微动特征提取的太赫兹雷达目标检测算法研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2010, 24(9): 803–807. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1187.2010.00803Li Jin, Pi Yi-ming, and Yang Xiao-bo. Research on terahertz radar target detection algorithm based on the extraction of micro motion feature[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2010, 24(9): 803–807. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1187.2010.00803 [34] Li J, Pi Y M, and Yang X B. Micro-Doppler signature feature analysis in terahertz band[J]. Journal of Infrared,Millimeter,and Terahertz Waves, 2010, 31(3): 319–328. [35] Xu Z W, Tu J, Li J, et al. Research on micro-feature extraction algorithm of target based on terahertz radar[J].EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2013, 2013(1): 77. DOI: 10.1186/1687-1499-2013-77 [36] 李晋, 皮亦鸣, 杨晓波. 太赫兹频段目标微多普勒信号特征分析[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2009, 23(10): 25–30Li Jin, Pi Yi-ming, and Yang Xiao-bo. Analysis of micro-Doppler effect in terahertz band[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2009, 23(10): 25–30 [37] 刘通, 徐政五, 吴元杰, 等. 太赫兹频段下基于EMD的人体生命特征检测[J]. 信号处理, 2013, 29(12): 1650–1659Liu Tong, Xu Zheng-wu, Wu Yuan-jie, et al. Human life feature detection based on EMD method in THz band[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 29(12): 1650–1659 [38] Xu Z W and Liu T. Vital sign sensing method based on EMD in terahertz band[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2014, 2014(1): 75. DOI: 10.1186/1687-6180-2014-75 [39] 徐政五. 基于太赫兹雷达的人体心跳和微动特征检测方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.Xu Z W. The human heartbeat and micro-feature detection based on Thz radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015. [40] Huang Z W, He Z H, Sun Z Y, et al.. Ananlysis and compensation of vibration error of high frequency synthetic aperture radar[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, 2016: 1138–1141. [41] Wang Y, Wang Z F, Zhao B, et al. Enhancement of azimuth focus performance in high-resolution SAR imaging based on the compensation for sensors platform vibration[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(16): 6333–6345. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2584622 [42] Barber B C. Some effects of target vibration on SAR images[C]. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2011: 1–4. [43] Wang Y, Wang Z F, Zhao B, et al. Compensation for high-frequency vibration of platform in SAR imaging based on adaptive chirplet decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 792–795. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2544945 [44] Zhang Y, Sun J P, Lei P, et al. High-frequency vibration compensation of helicopter-borne THz-SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(3): 1460–1466. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140615 [45] Chen H Y, Jiang W D, Liu Y X, et al. Nonuniform stretch processing for the range profile of a target with micro-motion[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2006, 16(11): 1205–1213. DOI: 10.1080/10020070612330131 [46] 陈行勇, 黎湘, 姜斌. 基于微多普勒特征的空中目标识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2006, 28(10): 30–33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2006.10.009Chen Hang-yong, Li Xiang, and Jiang Bin. Identification of air-target based on its micro-Doppler feature[J]. Modern Radar, 2006, 28(10): 30–33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2006.10.009 [47] 陈行勇, 黎湘, 郭桂蓉, 等. 基于旋翼微动雷达特征的空中目标识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2006, 28(3): 372–375. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2006.03.014Chen Hang-yong, Li Xiang, Guo Gui-rong, et al. Identification of airtarget based on the micromotion radar signatures of blades[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2006, 28(3): 372–375. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2006.03.014 [48] 陈行勇, 刘永祥, 姜卫东, 等. 雷达目标微动分辨[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2007, 29(3): 361–364. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2007.03.008Chen Hang-yong, Liu Yong-xiang, Jiang Wei-dong, et al. Micro-motion resolution of radar targets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2007, 29(3): 361–364. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2007.03.008 [49] 陈行勇, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. 雷达目标微多普勒特征提取[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(2): 222–226. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.02.015Chen Hang-yong, Liu Yong-xiang, Li Xiang, et al. Extraction of micro-Doppler signatures for radar target[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 23(2): 222–226. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.02.015 [50] 陈行勇, 王祎, 肖昌达, 等. 微摆动雷达目标微多普勒分析[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2010, 33(1): 76–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2010.01.019Chen Hang-yong, Wang Wei, Xiao Chang-da, et al. Micro-Doppler analysis of radar targets with micro-swing[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2010, 33(1): 76–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9167.2010.01.019 [51] 陈行勇, 刘永祥, 姜卫东, 等. 微动目标多普勒谱分析和参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2008, 24(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.01.001Chen Hang-yong, Liu Yong-xiang, Jiang Wei-dong, et al. Analysis of Doppler spectrum and parameters estimation for target with micro-motion[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 24(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.01.001 [52] 陈行勇, 刘永祥, 黎湘, 等. 微多普勒分析和参数估计[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2006, 25(5): 360–363. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.05.010Chen Hang-yong, Liu Yongxiang, Li Xiang, et al. Analysis of micro-Doppler and parameters estimation[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2006, 25(5): 360–363. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9014.2006.05.010 [53] 陈行勇, 姜卫东, 刘永祥, 等. 相位匹配处理微动目标ISAR成像[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(3): 435–440. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.010Chen Hang-yong, Jiang Wei-dong, Liu Yong-xaing, et al. Phase matching processing for ISAR imaging of target with micro-motion[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(3): 435–440. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.010 [54] 陈行勇, 刘永祥, 姜卫东, 等. 微动目标合成距离像数学分析[J]. 电子学报, 2007, 35(3): 585–589. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.042Chen Hang-yong, Liu Yong-xiang, Jiang Wei-dong, et al. Mathematics of synthesizing range profile of target with micro-motion[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(3): 585–589. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.042 [55] 张翼, 朱玉鹏, 黎湘. 基于微多普勒特征的目标微动参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022Zhang Yi, Zhu Yu-peng, and Li Xiang. Micro-motion parameter estimation of ballistic missile target based on micro-Doppler feature[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(7): 1120–1124. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.07.022 [56] 张翼, 朱玉鹏, 程永强, 等. 基于微多普勒特征的人体目标雷达回波信号分析[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(10): 1616–1623. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.10.023Zhang Yi, Zhu Yu-peng, Cheng Yong-qiang, et al. Human target radar echo signal analysis based on micro-Doppler characteristic[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(10): 1616–1623. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.10.023 [57] 张翼, 程永强, 朱玉鹏, 等. 人体目标雷达回波建模[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2011, 23(3): 438–445. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.03.018Zhang Yi, Cheng Yong-qiang, Zhu Yu-peng, et al. Human target radar echo modeling[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2011, 23(3): 438–445. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.03.018 [58] 张翼, 邱兆坤, 朱玉鹏, 等. 基于微多普勒特征的人体步态参数估计[J]. 信号处理, 2010, 26(6): 917–922. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.06.021Zhang Yi, Qiu Zhao-kun, Zhu Yu-peng, et al. Human gait parameter estimation based on micro-Doppler feature[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 26(6): 917–922. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.06.021 [59] 张翼, 朱玉鹏, 刘峥, 等. 基于微多普勒特征的人体上肢运动参数估计[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2009, 29(3): 20–25, 38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7202.2009.03.006Zhang Yi, Zhu Yu-peng, Liu Zheng, et al. Parameter estimation of human upper limbs motion based on micro-Doppler features[J]. Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement, 2009, 29(3): 20–25, 38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7202.2009.03.006 [60] 李康乐, 姜卫东, 黎湘. 弹道目标微动特征分析与提取方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(1): 115–118Li Kang-le, Jiang Wei-dong, and Li Xiang. Micro-motion feature analysis and extraction methods for ballistic targets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(1): 115–118 [61] 李康乐, 刘永祥, 姜卫东, 等. 基于逆Radon变换的微动目标重构研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2010, 8(1): 74–79, 86. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2010.01.015Li Kang-le, Liu Yong-xiang, Jiang Wei-dong, et al. Reconstruction of target with micro-motions based on inverse Radon transform[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2010, 8(1): 74–79, 86. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2010.01.015 [62] 霍凯, 李康乐, 姜卫东, 等. 基于循环平稳特征的正弦调制相位信号参数估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(2): 355–359. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00072Huo Kai, Li Kang-le, Jiang Wei-dong, et al. Parameters estimation of signals with sinusoid modulated phase based on cyclostationary character[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2010, 32(2): 355–359. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00072 [63] 彭勃. 正弦调频傅里叶变换方法及雷达目标微动特性反演技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2014.Peng B. Sinusoidal frequency modulation fourier transform and research on micro-doppler signature retrieval for radar targets[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University and Defense Technology, 2014. [64] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Chattopadhyay G, et al. A high-resolution imaging radar at 580 GHz[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2008, 18(1): 64–66. DOI: 10.1109/LMWC.2007.912049 [65] Trischman J A, Bennett J R, Melendez K A, et al.. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging at 580 GHz[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter and Terahertz Waves, Pasadena, CA, 2016: 1–2. [66] Essen H, Wahlen A, Sommer R, et al.. Development of a 220-GHz experimental radar[C]. Proceedings of 2008 German Microwave Conference, Germany, 2011: 1–4. [67] Liu B C, Wang T, and Bao Z. Doppler ambiguity resolving in compressed azimuth time and range frequency domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(11): 3444–3458. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2001236 [68] Yang Q, Deng B, Wang H Q, et al. A Doppler aliasing free micro-motion parameter estimation method in the terahertz band[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2017, 2017(1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s13638-017-0845-z [69] Yang Q, Deng B, Wang H Q, et al.. Doppler aliasing free micro-motion parameter estimation algorithm based on the spliced time-frequency image and inverse radon transform[C]. Proceedings of International Conference on Information and Communications Technologies, Nanjing, China, 2014: 1–6. [70] Jagannathan A, Gatesman A J, Horgan T, et al.. Effect of periodic roughness and surface defects on the terahertz scattering behavior of cylindrical objects[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7671, Terahertz Physics, Devices, and Systems IV: Advanced Applications in Industry and Defense, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2010, 7671: 76710E. [71] Jagannathan A, Gatesman A J, and Giles R H. Characterization of roughness parameters of metallic surfaces using terahertz reflection spectra[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(13): 1927–1929. DOI: 10.1364/OL.34.001927 [72] Digiovanni D A, Gatesman A J, Giles R H, et al.. Backscattering of ground terrain and building materials at submillimeter-wave and terahertz frequencies[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 8715, Passive and Active Millimeter-Wave Imaging XVI, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, 2013, 8715: 871507. [73] Digiovanni D A, Gatesman A J, Goyette T M, et al.. Surface and volumetric backscattering between 100 GHz and 1.6 THz[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 9078, Passive and Active Millimeter-Wave Imaging XVII, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, 2014: 90780A. [74] Yang Q, Qin Y, Deng B, et al.. Research on terahertz scattering characteristics of the precession cone[C]. 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Mechanical Automation, Wuhan, 2016. [75] Yang Q, Qin Y L, Deng B, et al. Micro-doppler ambiguity resolution for wideband terahertz radar using intra-pulse interference[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(5): 993. DOI: 10.3390/s17050993 [76] Yang Q, Deng B, Zhang Y, et al. Parameter estimation and imaging of rough surface rotating targets in the terahertz band[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2017, 11(4): 045001. [77] Yang Q, Deng B, Qin Y, et al.. Analysis of the high frequency vibration on radar imaging in the terahertz band[C]. 2nd International Conference on Computer Science and Mechanical Automation, Wuhan, 2016. [78] Yang Q, Qin Y L, Zhang K, et al. Experimental research on vehicle-borne SAR imaging with THz radar[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2017, 59(8): 2048–2052. DOI: 10.1002/mop.v59.8 [79] Yang Q, Deng B, Wang H Q, et al. Experimental research on imaging of precession targets with THz radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(25): 2059–2061. DOI: 10.1049/el.2016.3494 [80] Yang Q, Deng B, Wang H Q, et al.. Research on imaging of precession targets based on range-instantaneous Doppler in the terahertz band[C]. Proceedings of 2017 International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition, London, 2017: 14–15. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: