Radar Echo Scattering Modeling and Image Simulations of Full-scale Convex Rough Targets at Terahertz Frequencies
-
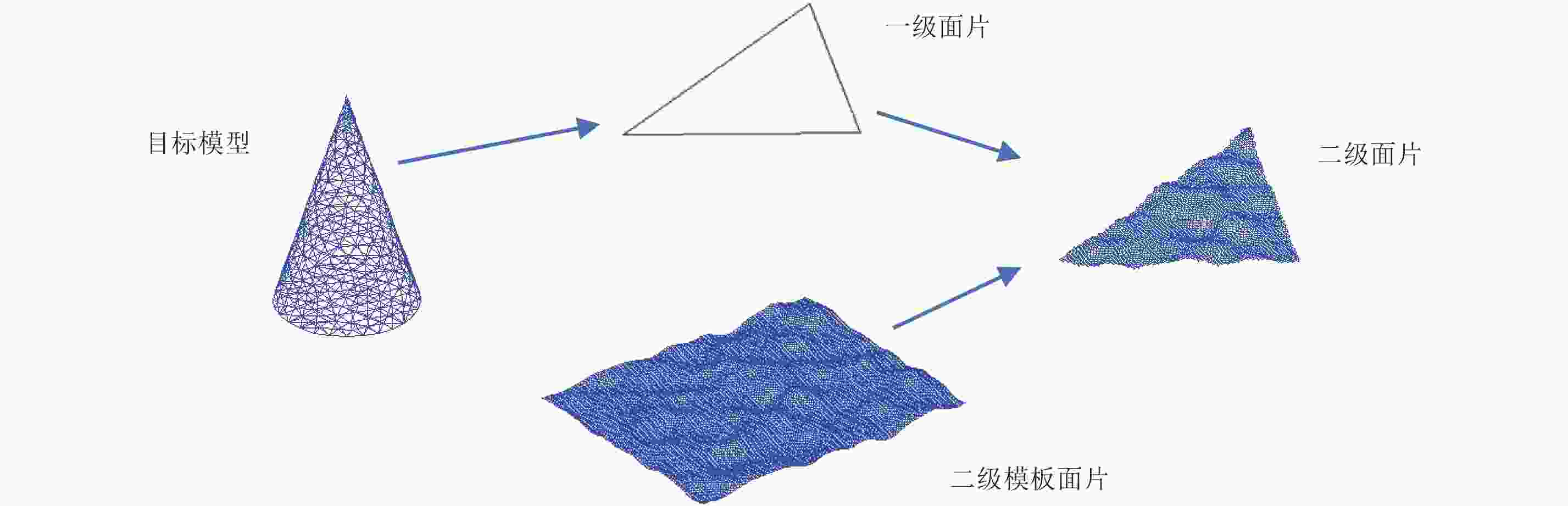
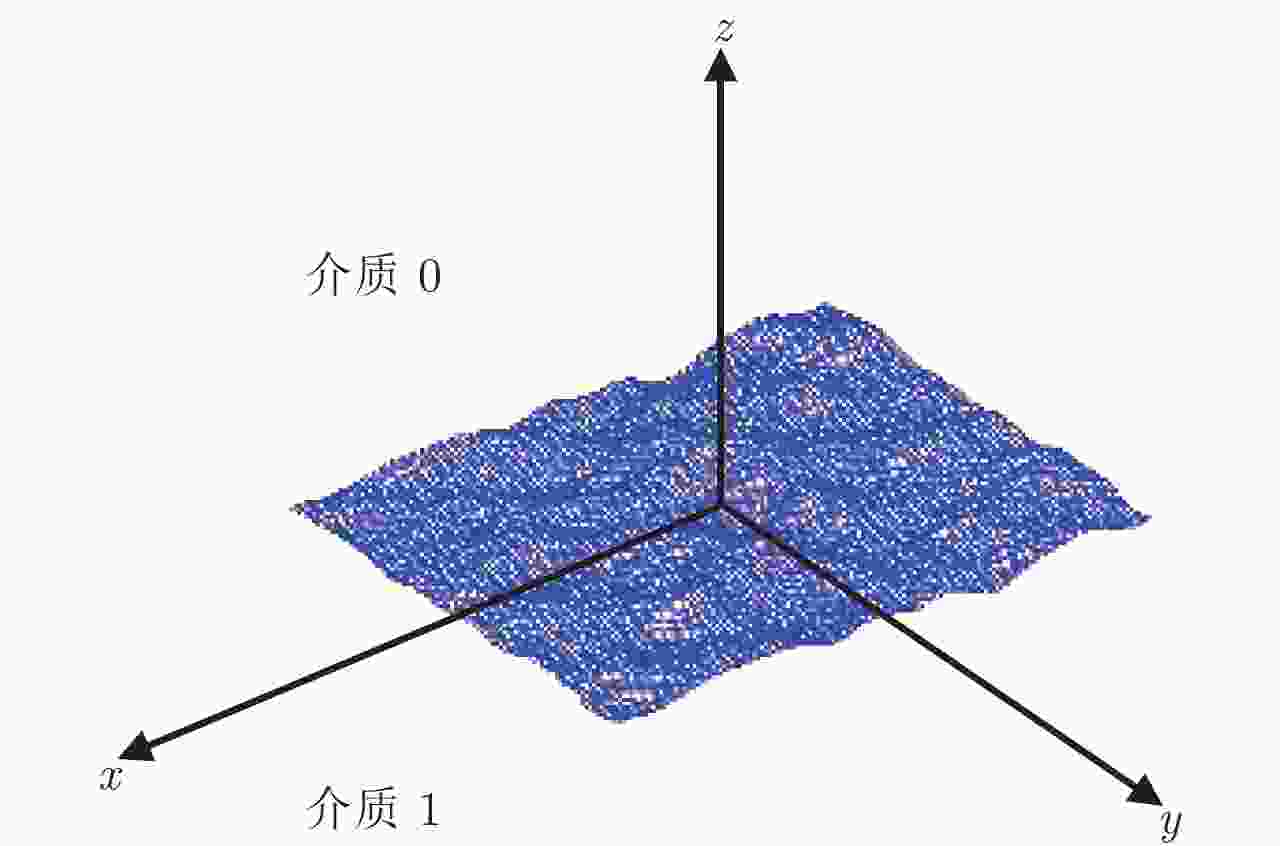
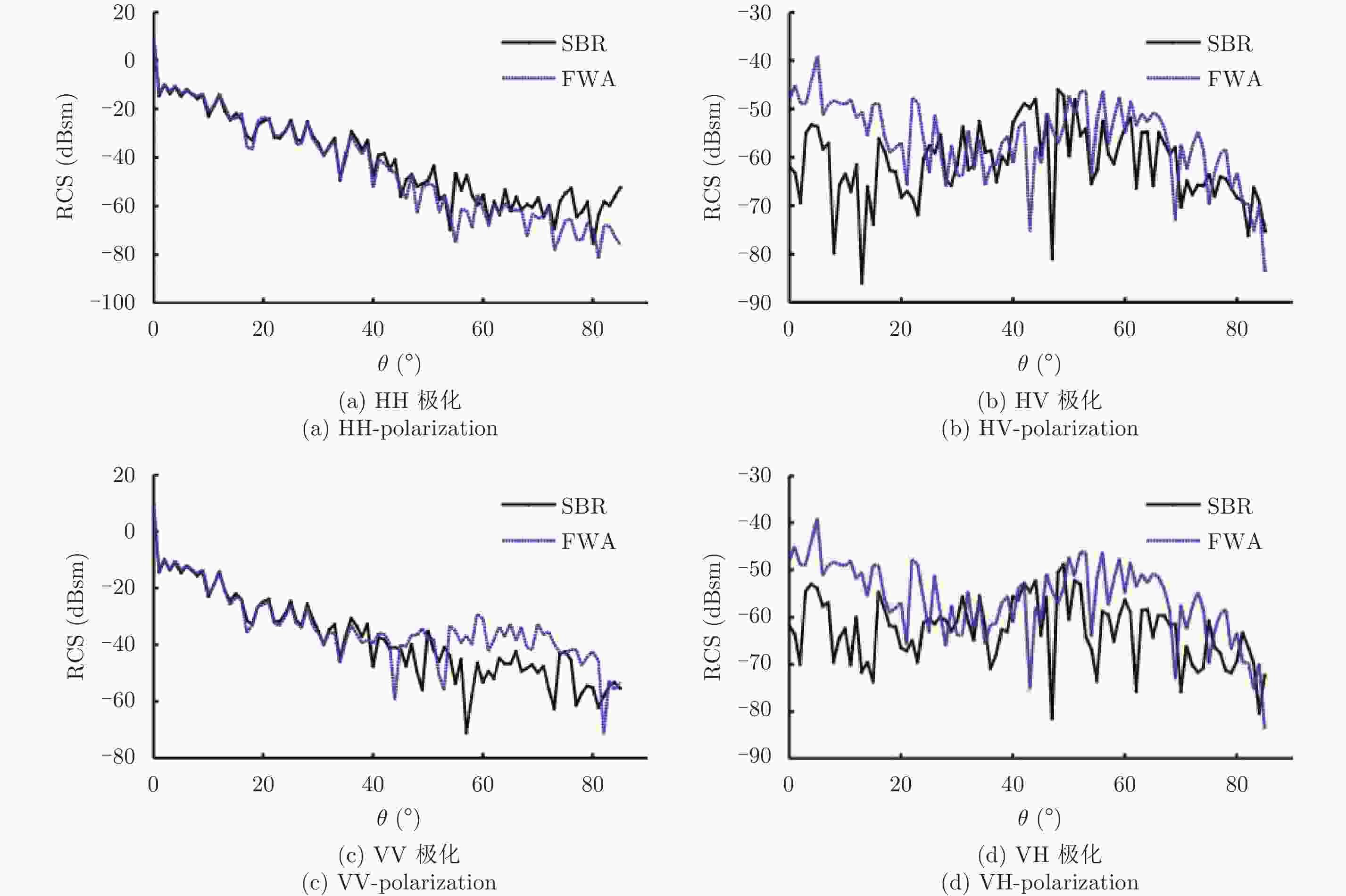
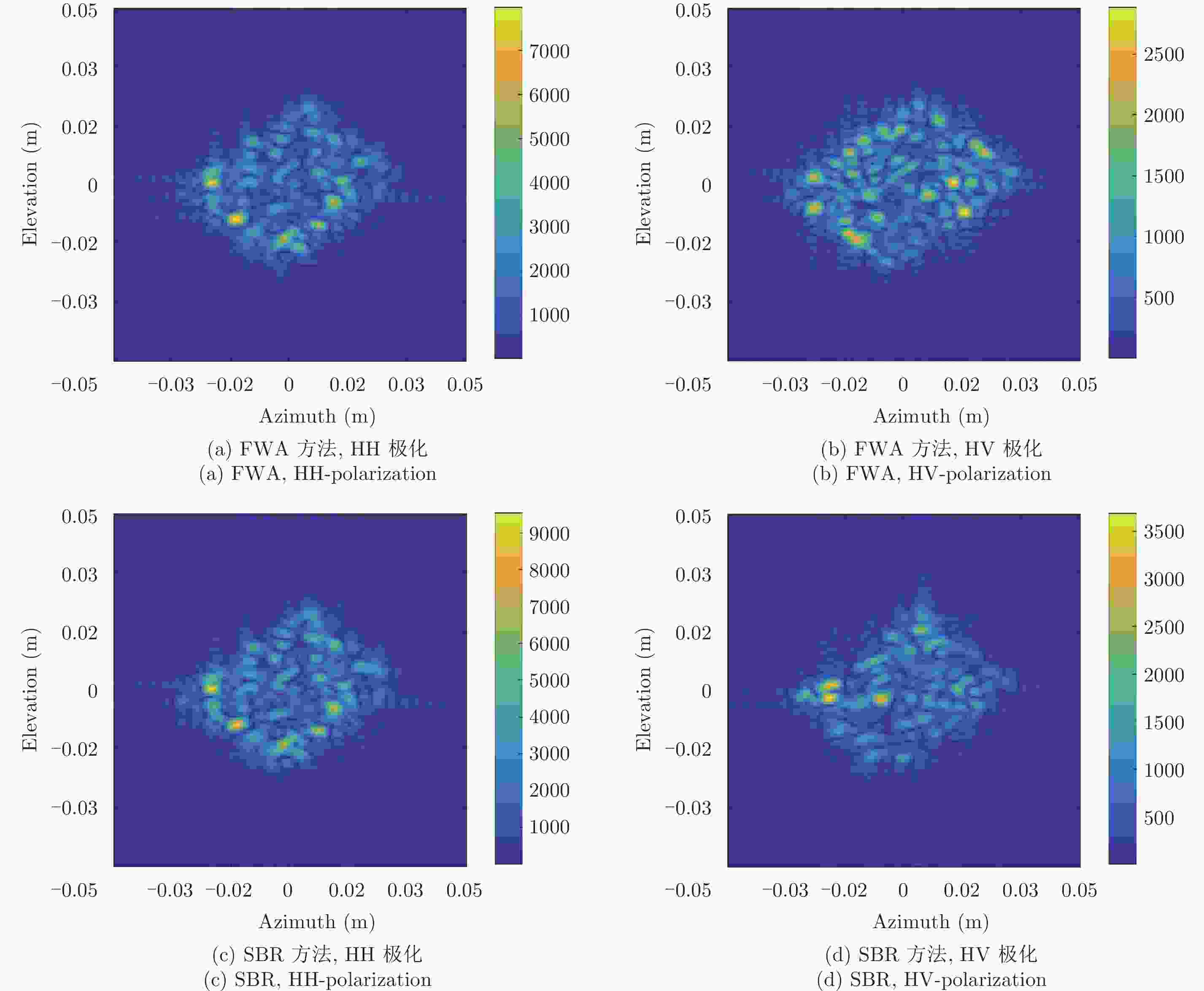
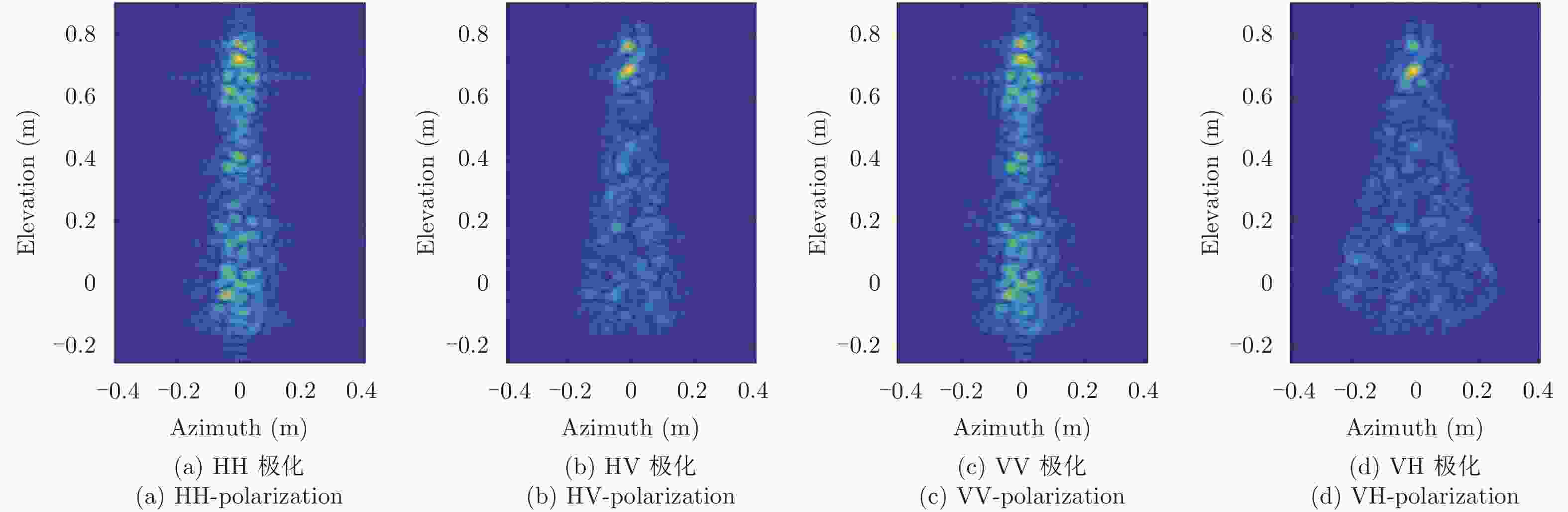
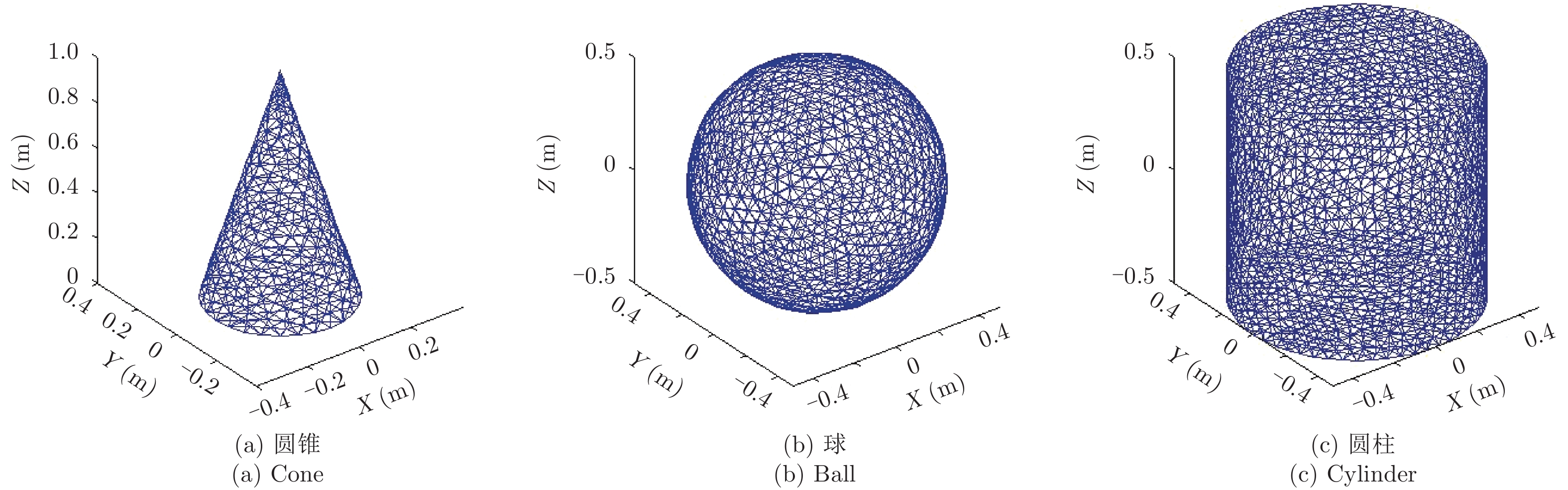
摘要: 回波仿真是研究雷达成像体制、算法及后续应用的前提条件,目标散射建模又是回波仿真的重要一环。在THz频段,目标常常具有超电大尺寸,这使得利用经典电磁计算方法面临现实困难。而波长的减小使得目标表面粗糙起伏成为不能忽略的因素,这使得传统基于点散射模型的回波生成手段难以适用。如何对目标进行THz散射建模及高效的雷达回波生成成为亟待解决的问题。该文提出了基于面片分级的半确定性建模方法,采用粗糙面全波法计算面片的散射场,再将各面片散射场转换至目标坐标系并相干叠加得到带有相位信息的雷达回波。利用小尺寸粗糙模型,通过与高频数值方法进行对比,验证了该文方法的有效性,并给出了全尺寸锥体的成像结果。初步解决了THz频段全尺寸凸体粗糙目标散射建模及回波生成问题,为后续成像体制和算法研发打下了基础。Abstract: Echo simulation is a precondition for developing radar imaging systems, algorithms, and subsequent applications. Electromagnetic scattering modeling of the target is key to echo simulation. At terahertz (THz) frequencies, targets are usually of ultra-large electrical size that makes applying classical electromagnetic calculation methods unpractical. In contrast, the short wavelength makes the surface roughness of targets a factor that cannot be ignored, and this makes the traditional echo simulation methods based on point scattering hypothesis in applicable. Modeling the scattering characteristics of targets and efficiently generating its radar echoes in THz bands has become a problem that must be solved. In this paper, a hierarchical semi-deterministic modeling method is proposed. A full-wave algorithm of rough surfaces is used to calculate the scattered field of facets. Then, the scattered fields of all facets are transformed into the target coordinate system and coherently summed. Finally, the radar echo containing phase information can be obtained. Using small-scale rough models, our method is compared with the standard high-frequency numerical method, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method. Imaging results of a full-scale cone-shape target is presented, and the scattering model and echo generation problem of the full-scale convex targets with rough surfaces in THz bands are preliminary solved; this lays the foundation for future research on imaging regimes and algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Terahertz waves /
- Echo simulation /
- Rough surface /
- Electric-Large
-
表 1 小尺寸粗糙矩形板回波生成及成像仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of echo generation and image simulation for the rough rectangular plate
参数 数值 方位向转角(°) 10 方位向采样间隔(°) 0.25 俯仰向转角(°) 10 俯仰向采样间隔(°) 0.25 中心方位角(°) 45 方位向分辨率(cm) 0.29 方位向不混叠距离(cm) 11.5 俯仰向分辨率(cm) 0.29 俯仰向不混叠距离(cm) 11.5 中心俯仰角(°) 45 表 2 小尺寸粗糙矩形板回波生成资源消耗
Table 2. Memory costs and time needs of echo simulation for the rough plate
计算方法 计算内存消耗(MB) 计算耗时(s) CST软件 156 ≈58900 本文方法 143 489 表 3 全尺寸锥体回波生成及成像仿真参数
Table 3. Parameters of echo generation and image simulation for the full-scale cone
参数 数值 方位向转角(°) 1 方位向采样间隔(°) 0.04 俯仰向转角(°) 1 俯仰向采样间隔(°) 0.025 中心方位角(°) 45 方位向分辨率(cm) 2.86 方位向不混叠距离(cm) 0.72 俯仰向分辨率(cm) 2.86 俯仰向不混叠距离(cm) 1.15 中心俯仰角(°) 55 表 4 全尺寸锥体回波生成资源消耗
Table 4. Memory costs and time needs of echo simulation for the full-scale cone
计算方法 计算内存消耗(MB) 计算耗时(s) CST软件 — — 本文方法 2969 ≈317000 -
[1] Rahman A and Rahman A K. Effective testing for wafer reject minimization by terahertz analysis and sub-surface imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 25th Annual SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference, Saratoga Springs, NY, USA, 2014: 151–155. [2] Llombart N and Blazquez B. Refocusing a THz imaging radar: Implementation and measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(3): 1529–1534. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2296320 [3] Siegel P H. Terahertz technology in biology and medicine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2004, 52(10): 2438–2447. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.835916 [4] Appleby R and Wallace H B. Standoff detection of weapons and contraband in the 100 GHz to 1 THz region[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(11): 2944–2956. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2007.908543 [5] Dengler R J, Maiwald F, and Siegel P H. A compact 600 GHz electronically tunable vector measurement system for submillimeter wave imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006: 1923–1926. [6] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Llombart N, et al. Penetrating 3-D imaging at 4- and 25-m range using a submillimeter-wave radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(12): 2771–2778. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.2007081 [7] Cooper K B, Dengler R J, Llombart N, et al. THz imaging radar for standoff personnel screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(1): 169–182. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2159556 [8] Blazquez B, Cooper K B, and Llombart N. Time-delay multiplexing with linear arrays of THz radar transceivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2014, 4(2): 232–239. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2013.2296146 [9] Essen H, Biegel G, Sommer R, et al.. High resolution tower-turntable ISAR with the millimetre wave radar cobra (35/94/220 GHz)[C]. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4. [10] Am Weg C, Von Spiegel W, Henneberger R, et al. Fast active THz cameras with ranging capabilities[J]. Journal of Infrared,Millimeter,and Terahertz Waves, 2009, 30(12): 1281–1296. [11] Gu S M, Li C, Gao X, et al. Terahertz aperture synthesized imaging with fan-beam scanning for personnel screening[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(12): 3877–3885. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2221738 [12] 张彪, 皮亦鸣, 李晋. 采用格林函数分解的太赫兹逆合成孔径雷达近场成像算法[J]. 信号处理, 2014, 30(9): 993–999. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2014.09.001Zhang Biao, Pi Yi-ming, and Li Jin. Terahertz inverse synthetic aperture radar near-field imaging algorithm using Green’s function decomposition[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2014, 30(9): 993–999. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2014.09.001 [13] Gao J K, Qin Y L, Deng B, et al. Terahertz wide-angle imaging and analysis on plane-wave criteria based on inverse synthetic aperture techniques[J]. Journal of Infrared,Millimeter,and Terahertz Waves, 2016, 37(4): 373–393. DOI: 10.1007/s10762-016-0249-x [14] Cheng B B, Jiang G, Wang C, et al. Real-Time imaging with a 140 GHz inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2013, 3(5): 594–605. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2013.2268317 [15] 崔振茂, 高敬坤, 陆彬, 等. 340 GHz稀疏MIMO阵列实时3-D成像系统[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2017, 36(1): 102–106. DOI: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2017.01.018Cui Zhen-mao, Gao Jing-kun, Lu Bin, et al. Real time 3D imaging system based on sparse MIMO array at 340 GHz[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2017, 36(1): 102–106. DOI: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2017.01.018 [16] Gao J K, Cui Z M, Cheng B B, et al. Fast three-dimensional image reconstruction of a standoff screening system in the terahertz regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2018, 8(1): 38–51. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2017.2764383 [17] Jagannathan A, Gatesman A J, Horgan T, et al.. Effect of periodic roughness and surface defects on the terahertz scattering behavior of cylindrical objects[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE Volume 7671, Terahertz Physics, Devices, and Systems IV: Advanced Applications in Industry and Defense, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2010, 7671: 76710E. [18] 王瑞君, 邓彬, 王宏强, 等. 不同表面结构特征圆柱导体的太赫兹散射特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2013, 25(6): 1549–1554. DOI: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1549Wang Rui-jun, Deng Bin, Wang Hong-qiang, et al. Scattering characteristics for cylindrical conductor woth different surface micro-structure in terahertz regime[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2013, 25(6): 1549–1554. DOI: 10.3788/HPLPB20132506.1549 [19] 高敬坤, 王瑞君, 邓彬, 等. THz频段粗糙导体圆锥的极化成像特性[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2015, 13(3): 401–408. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201503.0401Gao Jing-kun, Wang Rui-jun, Deng Bin, et al. Characteristics of polarized imaging of a conducting cone with surface roughness at terahertz frequencies[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2015, 13(3): 401–408. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201503.0401 [20] 杨啸宇, 高敬坤, 邓彬, 等. 太赫兹雷达细微结构成像仿真与特性分析[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2017, 15(2): 165–171. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201702.0165Yang Xiao-yu, Gao Jing-kun, Deng Bin, et al. Radar imaging simulation and characteristics analysis of the fine structure at terahertz frequencies[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2017, 15(2): 165–171. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201702.0165 [21] 杨洋, 姚建铨, 张镜水, 等. 粗糙铜表面对低频太赫兹波的散射实验[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2013, 32(1): 36–39, 79. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00036Yang Yang, Yao Jian-quan, Zhang Jing-shui, et al. Terahertz scattering on rough copper surface[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2013, 32(1): 36–39, 79. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00036 [22] 杨洋, 刘兵, 张镜水, 等. 粗糙金属表面的高频太赫兹散射特性[J]. 激光与红外, 2014, 44(8): 922–926. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2014.08.020Yang Yang, Liu Bing, Zhang Jing-shui, et al. Influence of rough metal surface on the scattering properties of terahertz frequency[J]. Laser&Infrared, 2014, 44(8): 922–926. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2014.08.020 [23] 杨洋. 太赫兹波在粗糙金属球体目标上的散射特性[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2014, 12(6): 783–787. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201406.0783Yang Yang. Scattering characteristics of THz wave on rough metal sphere target[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2014, 12(6): 783–787. DOI: 10.11805/TKYDA201406.0783 [24] 杨洋, 姚建铨, 唐世星, 等. 粗糙表面对雷达目标散射截面的影响[J]. 激光与红外, 2011, 41(7): 800–803. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.07.019Yang Yang, Yao Jian-quan, Tang Shi-xing, et al. Influence of the rough surface on radar target scattering cross section[J]. Laser&Infrared, 2011, 41(7): 800–803. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2011.07.019 [25] Jansen C, Priebe S, Moller C, et al. Diffuse scattering from rough surfaces in THz communication channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Terahertz Science and Technology, 2011, 1(2): 462–472. DOI: 10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2153610 [26] Zhuo L, Tie J C, Xing J Z, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristics of PEC targets in the terahertz regime[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2009, 51(1): 39–50. DOI: 10.1109/MAP.2009.4939018 [27] 江月松, 张志国, 华厚强. 基于快速物理光学法的太赫兹目标RCS计算[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(12): 1211001Jiang Yue-song, Zhang Zhi-guo, and Hua Hou-qiang. RCS simulation of targets in THz band based on fast physical optics algorithm[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2014, 34(12): 1211001 [28] 程志华, 谢拥军, 樊君. 复杂目标的太赫兹波近场RCS快速计算[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(8): 1999–2004. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01473Cheng Zhi-hua, Xie Yong-jun, and Fan Jun. Fast computation of near field RCS of complex objects in terahertz band[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(8): 1999–2004. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01473 [29] 华厚强, 江月松, 苏林, 等. 自由空间复杂导体目标的太赫兹RCS高频分析方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(3): 687–693. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.03.004Hua Hou-qiang, Jiang Yue-song, Su Lin, et al. High-frequency analysis on THz RCS of complex conductive targets in free space[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(3): 687–693. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.03.004 [30] 江月松, 聂梦瑶, 张崇辉, 等. 粗糙表面涂覆目标的太赫兹波散射特性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(2): 024101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.64.024101Jiang Yue-song, Nie Meng-yao, Zhang Chong-hui, et al. Terahertz scattering property for the coated object of rough surface[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(2): 024101. DOI: 10.7498/aps.64.024101 [31] 李昌泽, 童创明, 王童, 等. 非均匀不稳定表面粗糙目标的太赫兹波段散射特性分析[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2016, 35(2): 234–242. DOI: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.02.020Li Chang-ze, Tong Chuang-ming, Wang Tong, et al. Analysis of terahertz wave scattering characteristics of non-uniform unstable roughness surface target[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2016, 35(2): 234–242. DOI: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2016.02.020 [32] 郭立新, 王蕊, 吴振森. 随机粗糙面散射的基本理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.Guo Li-xin , Wang Rui, and Wu Zhen-sen. Basic Theory and Method of Random Rough Surface Scattering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [33] Tsang L and Kong J A. Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves, Advanced Topics[M]. New York: Wiley, 2004. [34] Bahar E. Scattering cross sections for composite random surfaces: Full wave analysis[J]. Radio Science, 1981, 16(6): 1327–1335. DOI: 10.1029/RS016i006p01327 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: