Millimeter-wave Human Security Imaging Based on Frequency-domain Sparsity and Rapid Imaging Sparse Array Architecture
-
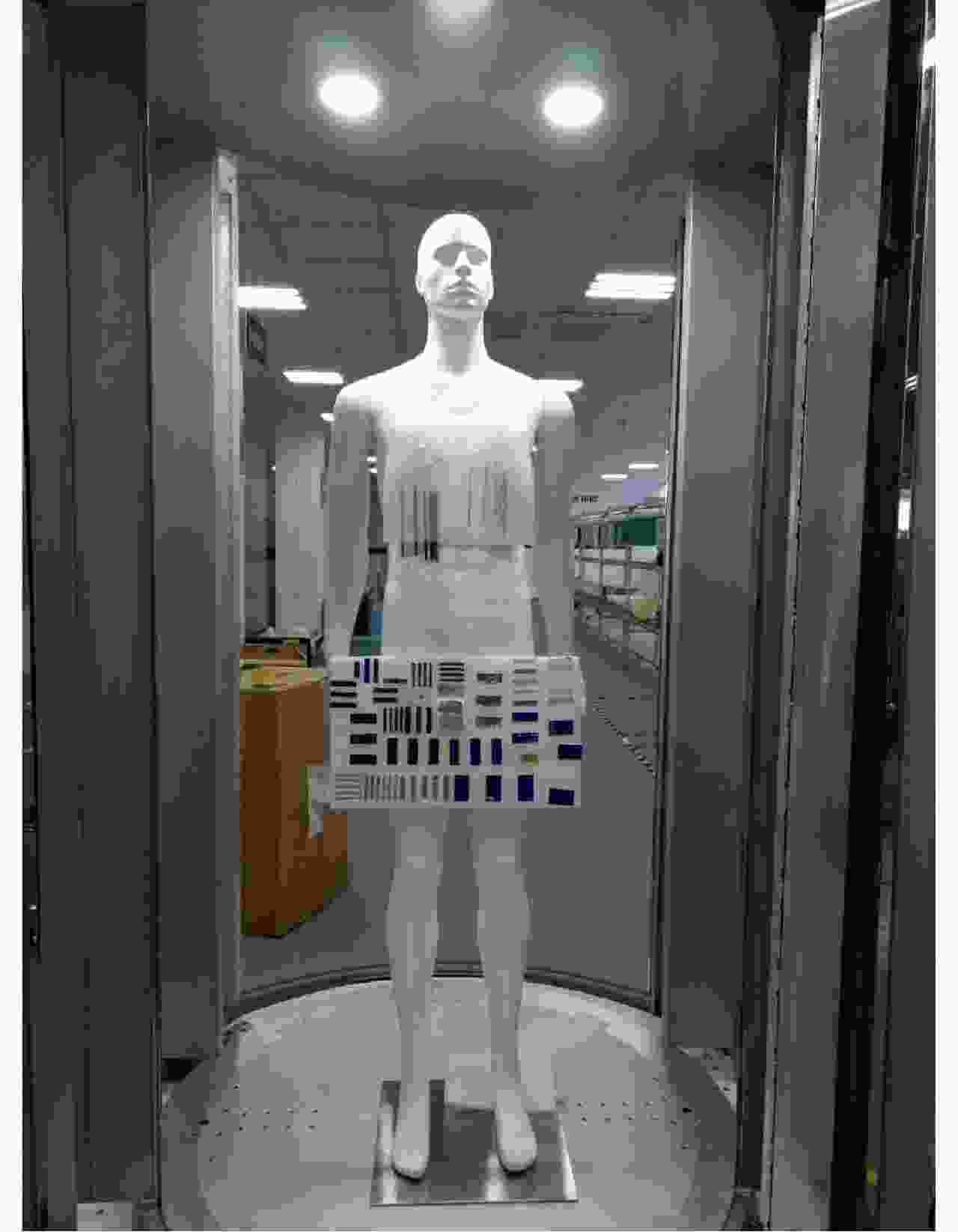
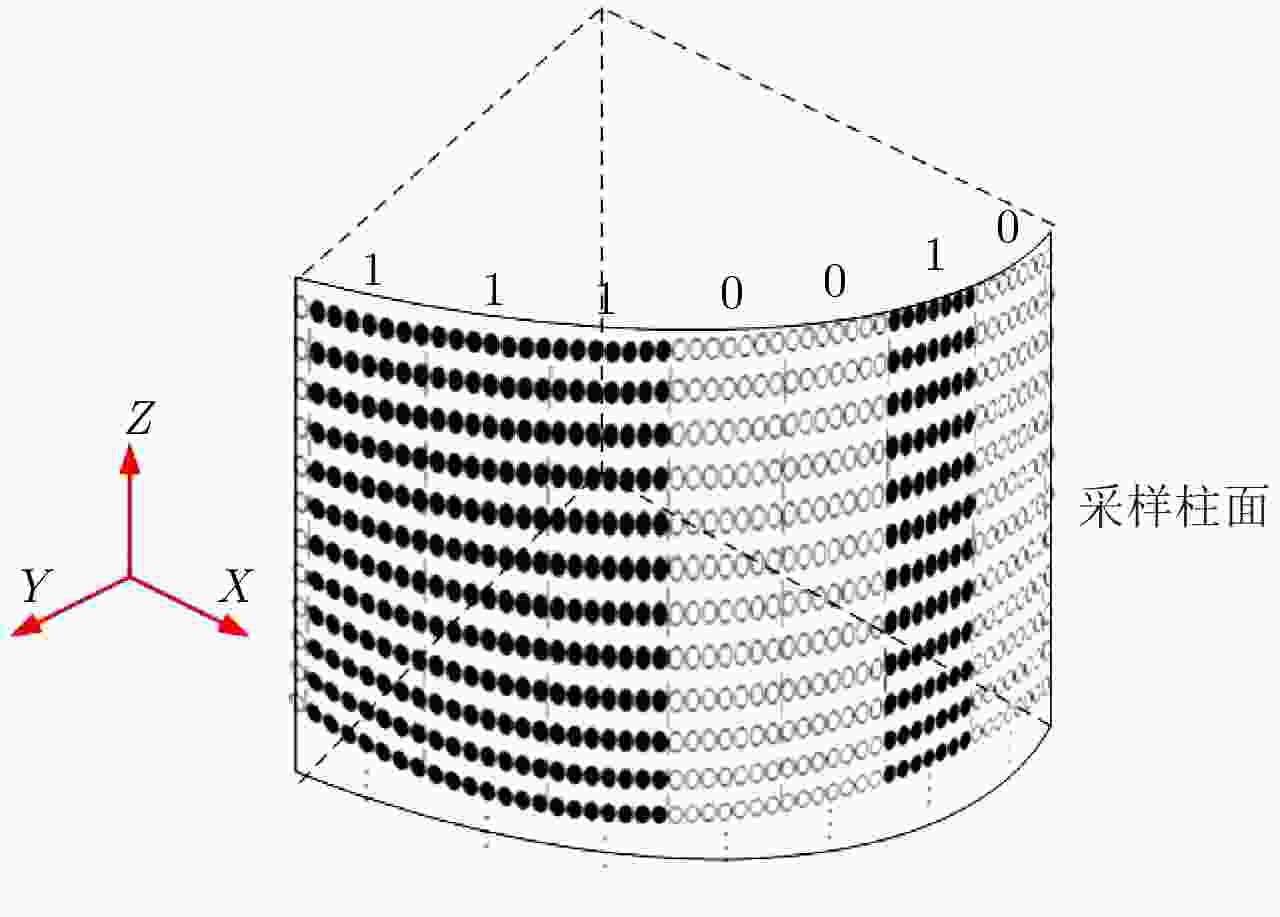
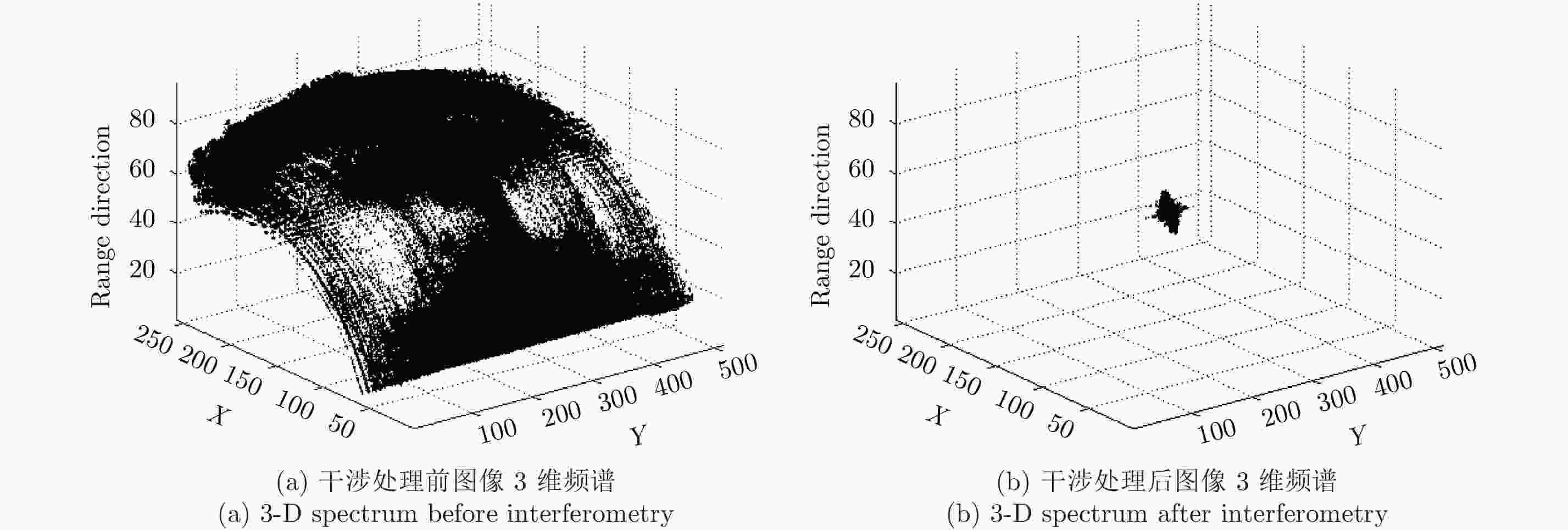
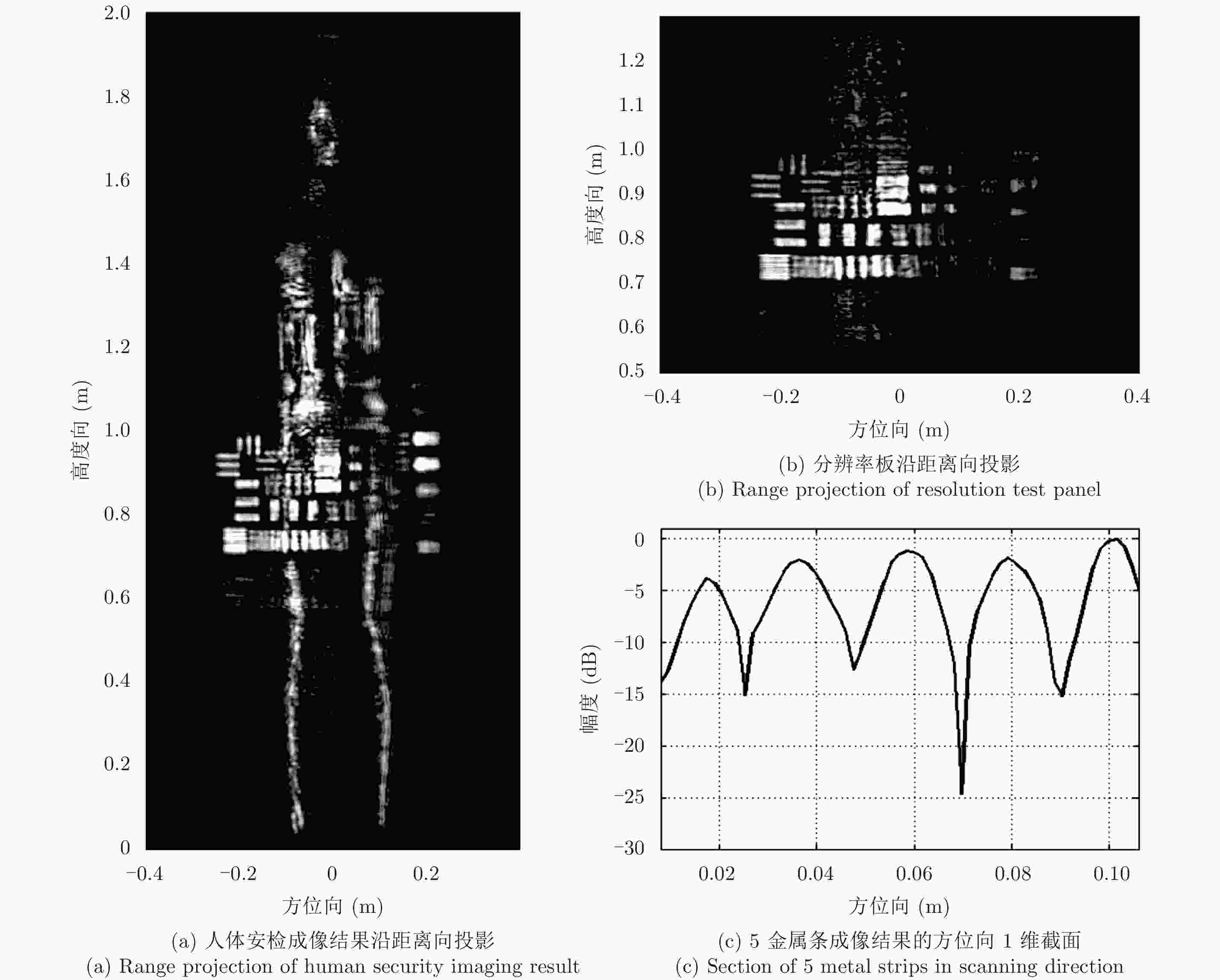
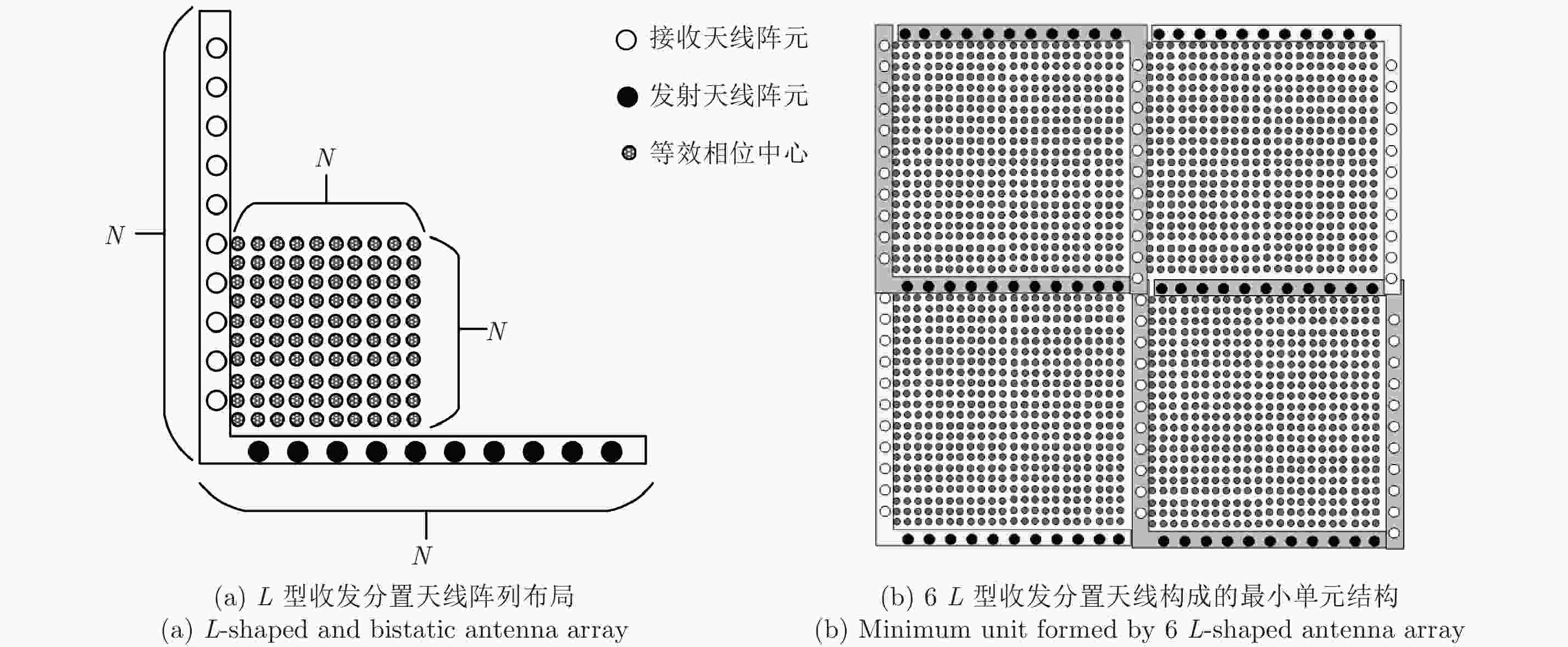
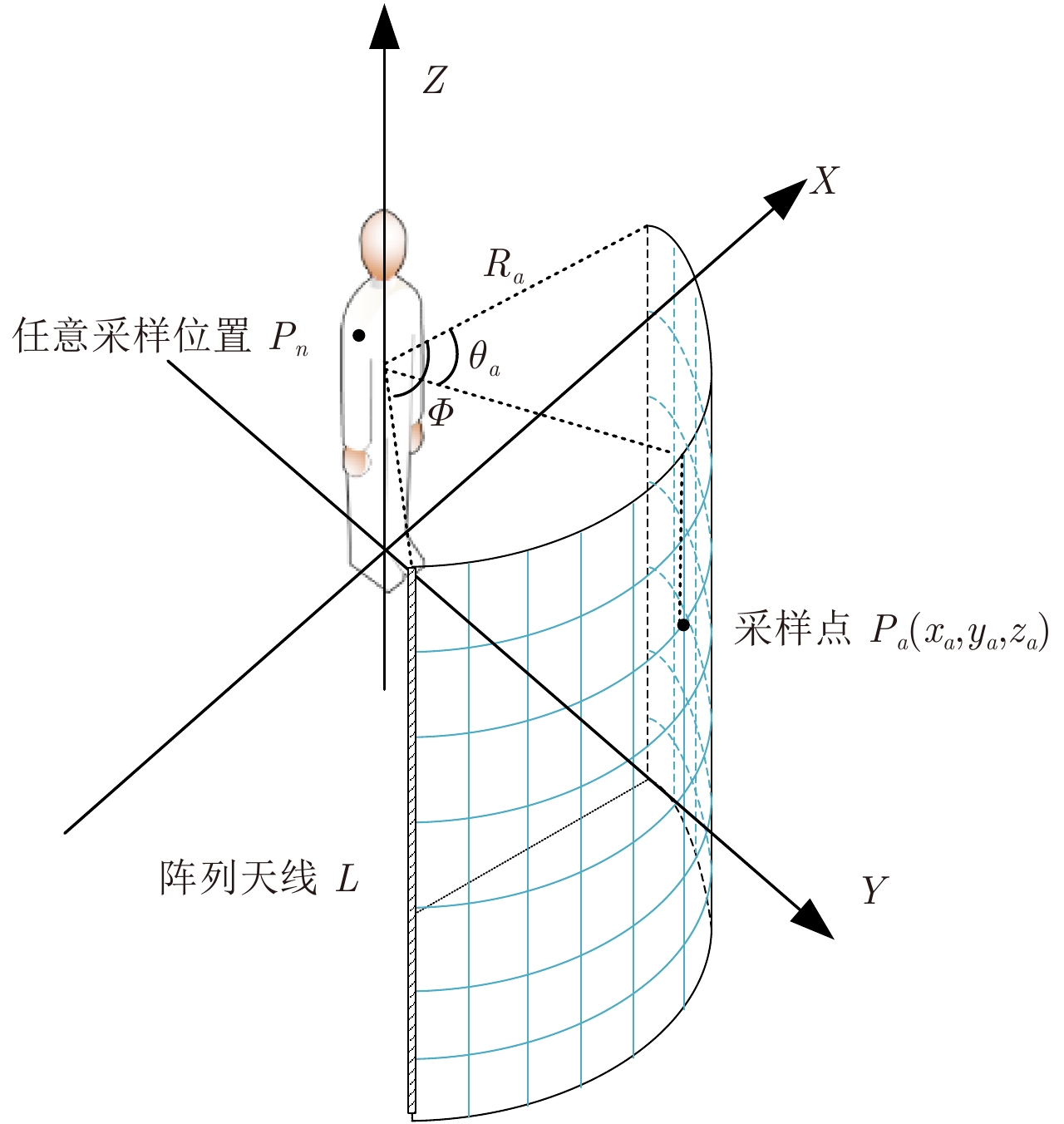
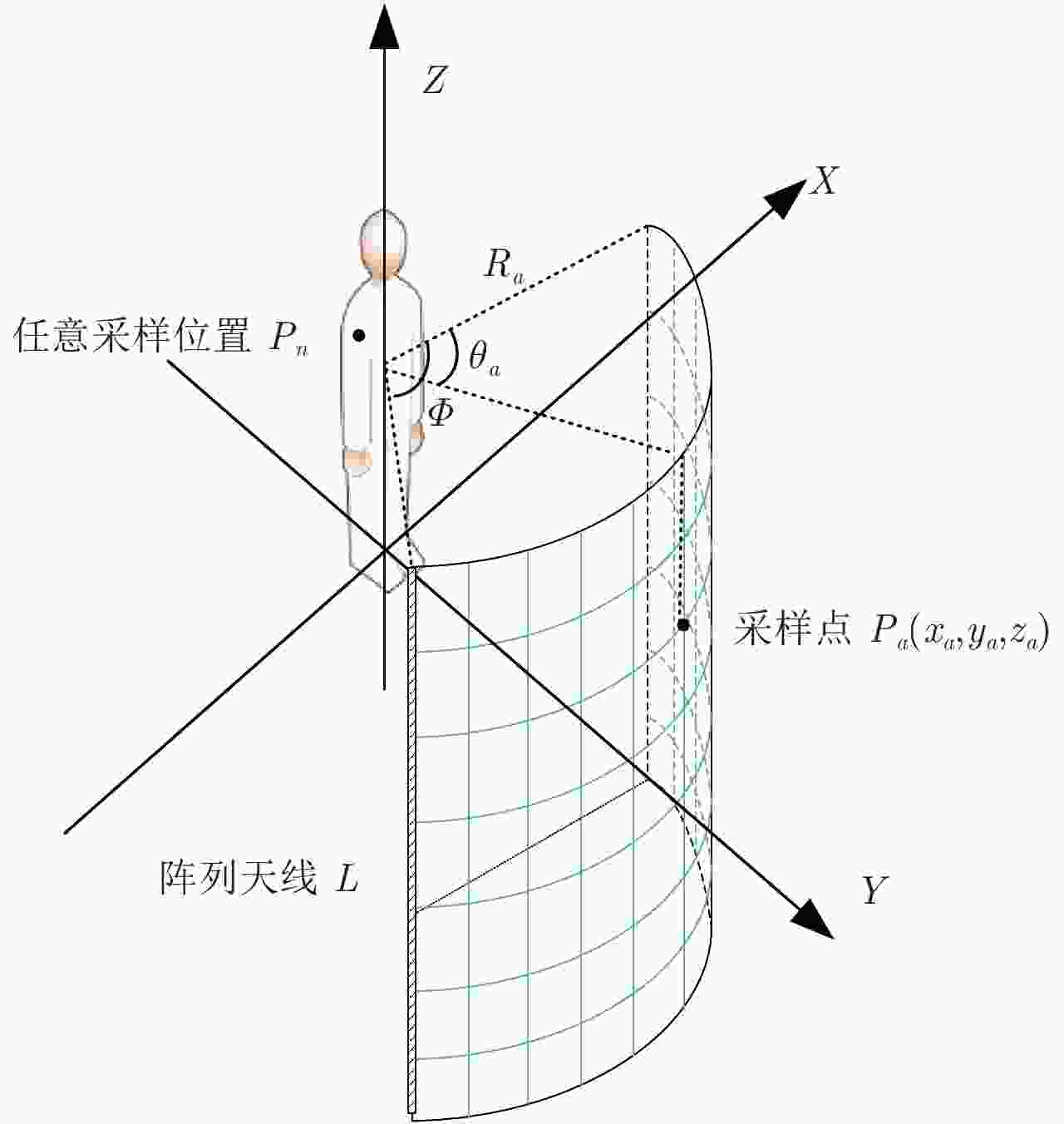
摘要: 该文研究工作包括频域稀疏毫米波人体安检成像数据处理和用于快速安检成像的稀疏阵列设计两部分。首先基于柱面扫描成像模型,采用巴克码随机稀疏采样方式减少成像所需数据量;提出一种基于干涉处理和频域压缩感知的3维成像算法,利用干涉处理使人体复图像在频域具备稀疏性,建立频域压缩感知测量模型并重建图像频谱,进而实现稀疏采样下人体安检图像3维重建。实际数据处理结果表明,该方法在数据采集量减少约50%条件下,可获得接近满采样对应的图像分辨率和成像效果,稀疏采样前后的图像相关系数优于0.9。其次基于频域稀疏成像方法、巴克码稀疏采样方式和收发分置工作模式,设计了用于快速安检成像的稀疏阵列布局,在保证人体成像质量前提下,稀疏率高达94.6%。该方法用于实际安检成像系统中可大幅增加安检通过速率、减少辐射单元数量和系统复杂度,在大人流量、高安检要求场所安全检测中具有重要应用价值和市场前景。Abstract: This paper examines the processing of millimeter-wave imaging data based on sparse sampling and sparse array design for the rapid imaging of human security data. First, based on the cylindrical scanning imaging model, the Barker code-based randomly sparse sampling method is employed to reduce the scanning time. Then, a three-dimensional imaging algorithm based on interferometry and compressed sensing in the frequency domain is proposed, with sparse representation of the image in the frequency domain after interferometry and Compressed Sensing measurement model, to recover the image frequency spectrum, thereby implementing human security image reconstruction via sparse sampling. Real data processing results indicated that the proposed method could obtain image resolution and performance similar to those of complete samples and that the image correlation coefficients before and after sparse sampling were better than 0.9, with 50% time/data reduction. Furthermore, based on the Barker codes and multistatic work mode, a sparse array architecture for rapid imaging was designed with a sparse rate of 94.6% and the guarantee of imaging quality. The proposed method was found to considerably increase the passage rate and reduce the amount of radiation unit and system complexity, marking its application significance and market prospect in security clearance.
-
Key words:
- Millimeter wave imaging /
- 3D imaging /
- Sparse sampling /
- Sparse array /
- Interferometry /
- Human security
-
表 1 系统参数
Table 1. System parameters
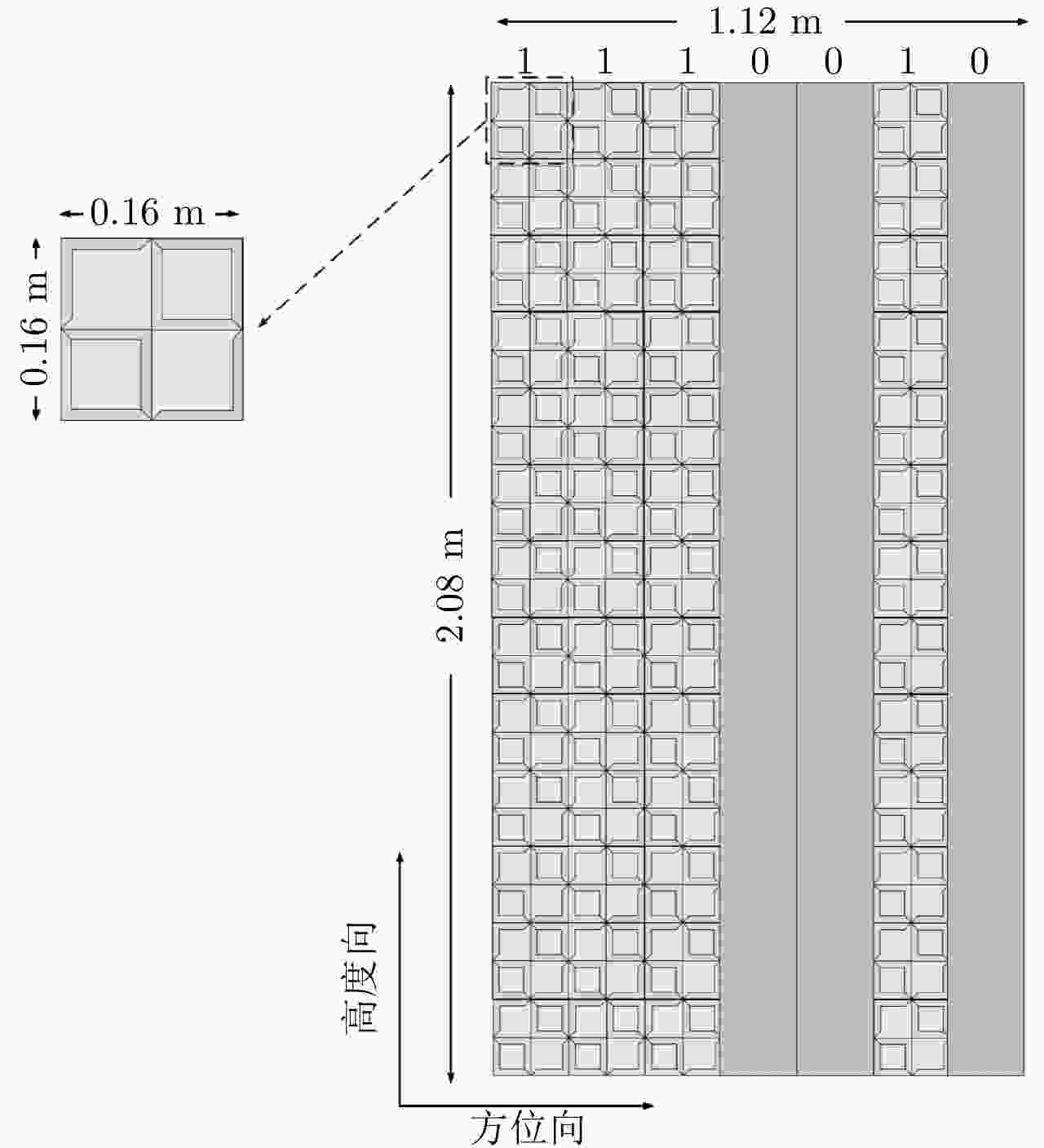
参数 数值 测试距离Ra (m) 0.675 发射信号带宽Bs (GHz) 9.50 雷达中心频率f0 (GHz) 33.87 雷达工作波长 $\lambda $ (mm) 8.90 距离向采样率fs (GHz) 9.50 距离向采样间隔dr (cm) 1.58 方位向扫描角 ${{Φ}}$ (°) 66 方位向采样间隔da (°) 0.32 阵列长度L (m) 2 高度向采样间隔dz (mm) 4.80 距离向分辨率 (cm) 1.58 方位向分辨率 (mm) 4.50 高度向分辨率 (mm) 4.50 表 2 3种巴克码序列
Table 2. The 3 kinds of Barker sequences
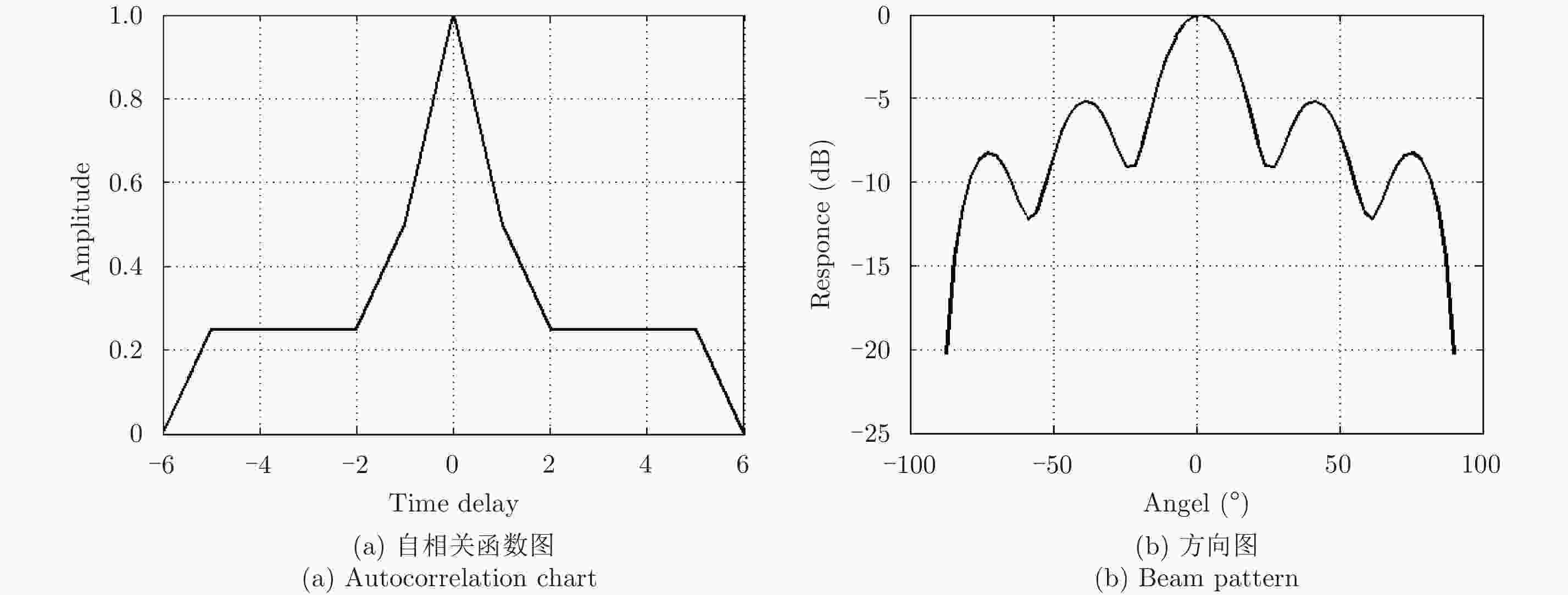
巴克码长度 码型 稀疏率(%) 7 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 42.86 11 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 54.55 13 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 30.77 表 3 7位巴克码稀疏采样方式对应的图像质量评价
Table 3. The image quality assessment corresponding to Barker code with length of 7
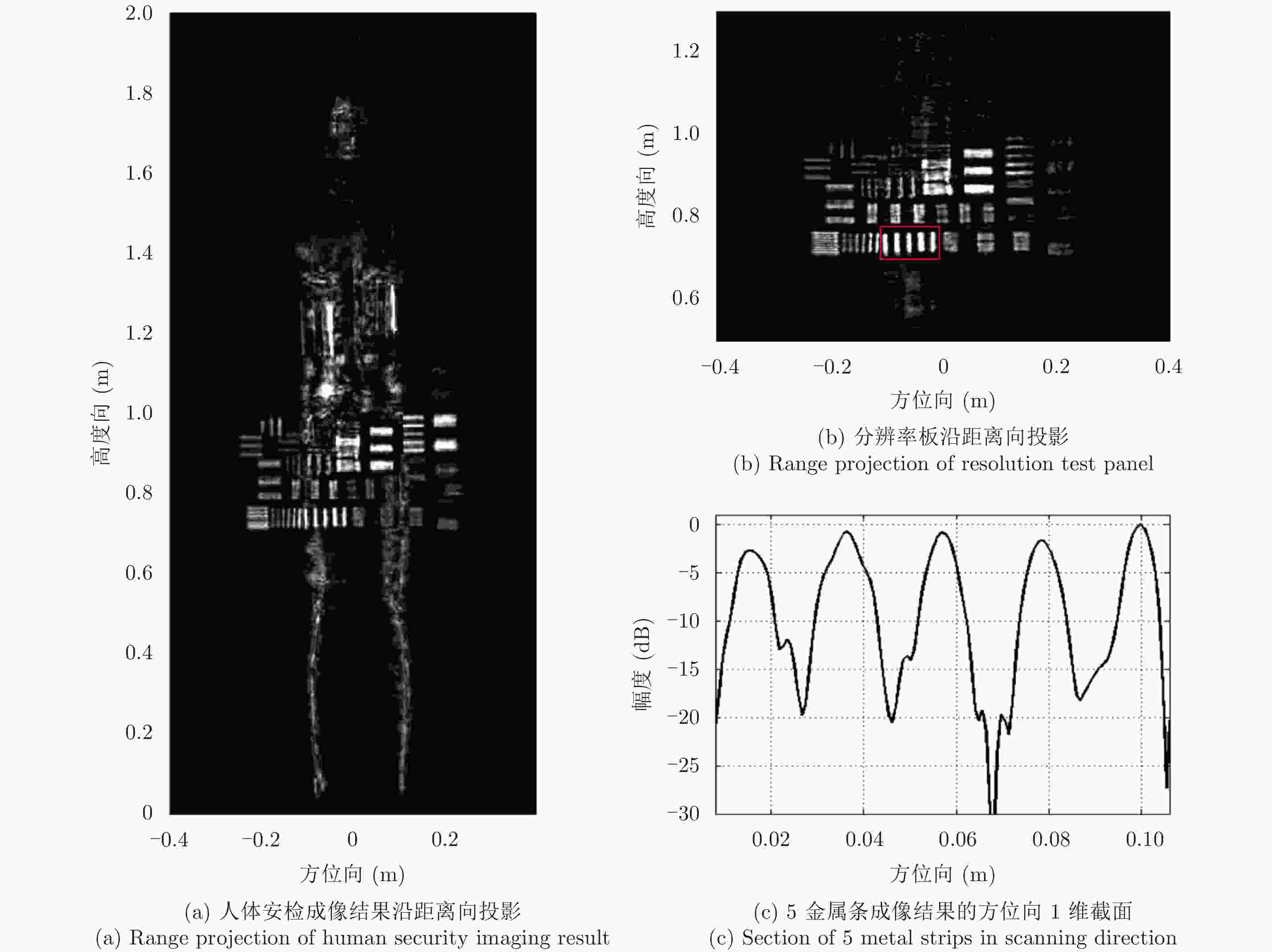
成像方法 相关系数 SSIM MSE 等间隔稀疏采样直接成像 0.8698 0.8169 0.0431 7 位Barker码稀疏采样直接成像 0.8991 0.8973 0.0388 7 位Barker码稀疏采样干涉处理频域CS成像 0.9118 0.9036 0.0359 表 4 11位巴克码稀疏采样方式对应的图像质量评价
Table 4. The image quality assessment corresponding to Barker code with length of 11
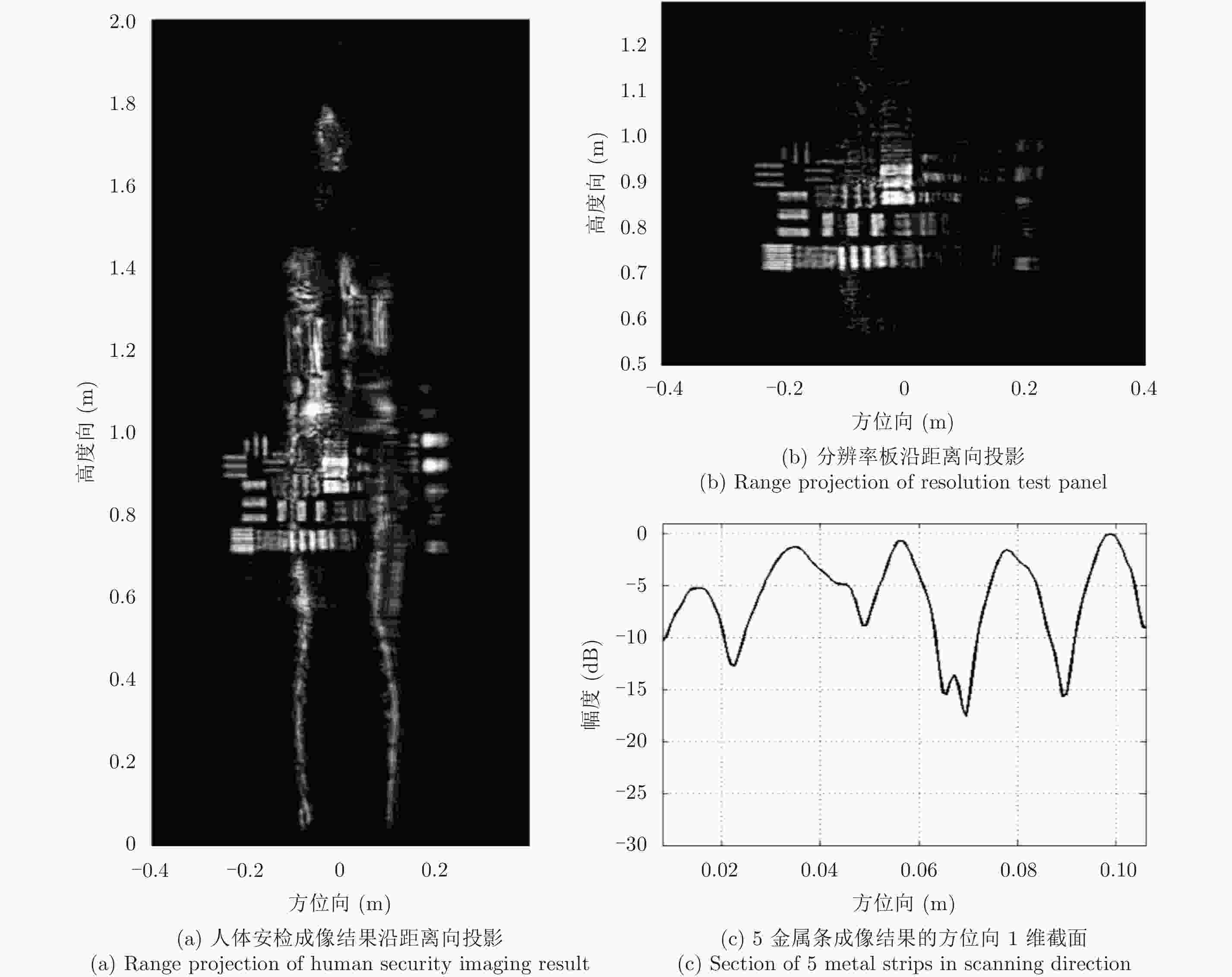
成像方法 相关系数 SSIM MSE 11位Barker码稀疏采样直接成像 0.8768 0.8552 0.0491 11位Barker码稀疏采样干涉处理频域CS成像 0.9028 0.8676 0.0418 表 5 13位巴克码稀疏采样方式对应的图像质量评价
Table 5. The image quality assessment corresponding to Barker code with length of 13
成像方法 相关系数 SSIM MSE 13位Barker码稀疏采样直接成像 0.9159 0.8892 0.0343 13位Barker码稀疏采样干涉处理频域CS成像 0.9321 0.9052 0.0324 -
[1] McMillan R W, Currie N C, Ferris D D, et al.. Concealed weapon detection using microwave and millimeter wave sensors[C]. Proceedings of 1998 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology Proceedings, Beijing, 1998: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/ICMMT.1998.768213. [2] 温鑫, 黄培康, 年丰, 等. 主动式毫米波近距离圆柱扫描三维成像系统[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(6): 1044–1049. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.06.05Wen Xin, Huang Pei-kang, Nian Feng, et al. Active millimeter-wave near-field cylindrical scanning three-dimensional imaging system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(6): 1044–1049. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.06.05 [3] Farhat N H and Guard W R. Millimeter wave holographic imaging of concealed weapons[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1971, 59(9): 1383–1384. DOI: 10.1109/PROC.1971.8441 [4] Gomez-Maqueda I, Almorox-Gonzalez P, Callejero-Andres C, et al. A millimeter-wave imager using an illuminating source[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2013, 14(4): 132–138. DOI: 10.1109/MMM.2013.2248652 [5] Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, Schiessl A, et al. Fully electronic E-band personnel imager of 2 m2 aperture based on a multistatic architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(1): 651–657. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2228221 [6] Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, Schiessl A, et al.. Fully electronic active E-band personnel imager with 2 m2 aperture[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012: 1–3. DOI: 10.1109/MWSYM.2012.6259549. [7] Li L C, Li D J, and Pan Z H. Compressed sensing application in interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(10): 102305. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9017-6 [8] Tian H, Li D J, and Li L C. Simulation of signal reconstruction based sparse flight downward-looking 3D imaging SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, 2015: 3762–3765. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326642. [9] Holubnychyi A. Generalized binary barker sequences and their application to radar technology[C]. Proceedings of 2013 Signal Processing Symposium (SPS), Serock, 2013: 1–9. DOI: 10.1109/SPS.2013.6623610. [10] Detlefsen J, Dallinger A, and Schelkshorn S. Approaches to millimeter-wave imaging of humans[C]. Proceedings of the First European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2004: 279–282. [11] Rosen P A, Hensley S, Joughin I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. DOI: 10.1109/5.838084 [12] Tian H and Li D J. Sparse flight array SAR downward-looking 3-D imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1395–1399. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2560238 [13] 张清娟, 李道京, 李烈辰. 连续场景的稀疏阵列SAR侧视三维成像研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136Zhang Qing-juan, Li Dao-jing, and Li Lie-chen. Research on continuous scene side-looking 3D imaging based on sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136 [14] 田鹤, 李道京, 潘洁, 等. 基于修正均匀冗余阵列正反编码的稀疏阵列SAR下视三维成像处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209Tian He, Li Dao-jing, Pan Jie, et al. Downward-looking 3D imaging processing of sparse array SAR based on modified uniformly redundant arrays positive and negative coding[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209 [15] 李烈辰, 李道京. 基于压缩感知的连续场景稀疏阵列SAR三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645Li Lie-chen and Li Dao-jing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 [16] Candès E and Romberg J. Sparsity and incoherence in compressive sampling[J]. Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(3): 969–985. DOI: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/3/008 [17] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [18] Baraniuk R and Steeghs P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, Mass, USA, 2007: 128–133. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2007.374203. [19] Patel V M, Easley G R, Healy jr D M, et al. Compressed synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 244–254. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2039181 [20] Tian H and Li D J. Sparse sampling-based microwave 3D imaging using interferometry and frequency-domain principal component analysis[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(12): 1886–1891. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0087 [21] Schiessl A, Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, et al.. A technology demonstrator for a 0.5 m x 0.5 m fully electronic digital beamforming mm-Wave imaging system[C]. Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Rome, 2011: 2606–2609. [22] Tian H, Li D J, and Hu X. Microwave three-dimensional imaging under sparse sampling based on MURA code[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, 2016: 7411–7414. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730933. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: