Matrix Inversion Method for Azimuth Reconstruction in Bistatic Spaceborne High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR System
-
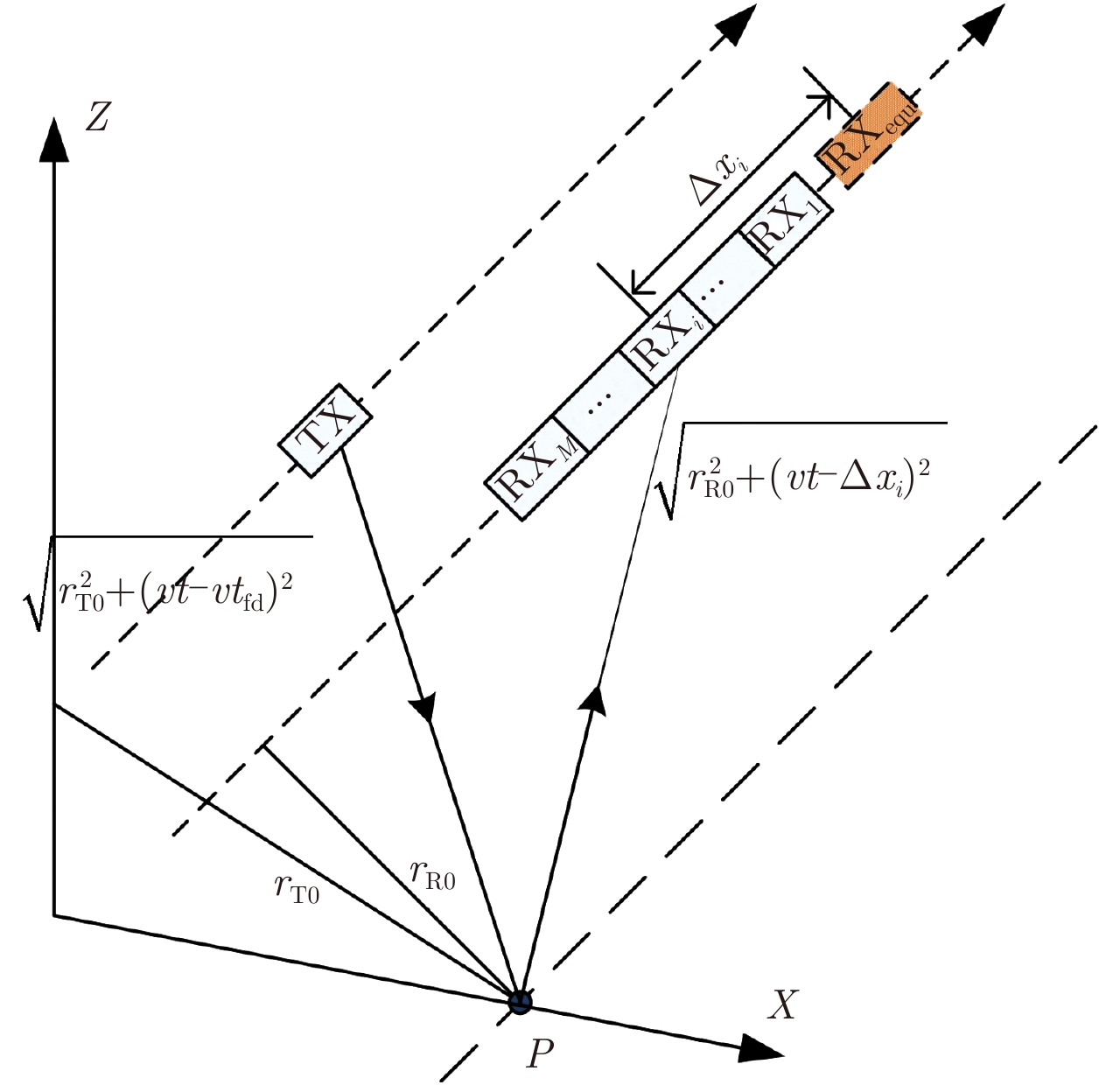
摘要: 双基星载高分辨率宽测绘带SAR系统(HRWS-SAR)的方位向信号普遍为非均匀采样,重构其均匀采样信号或多普勒频谱是成像处理的关键步骤。该文将方位照射时间内时变的发射接收距离比近似为常数,利用双基系统与单基系统方位向通道间传递函数的等效关系,建立了一般双基构型星载HRWS-SAR系统的方位向信号模型,进而给出了方位向信号重构的矩阵求逆算法及重构性能指标信噪比缩放因子和方位模糊比的计算公式。该文对几种典型双基构型的星载HRWS-SAR系统进行方位向信号重构仿真,结果表明在非重叠采样条件下矩阵求逆算法能较好地重构出方位向信号的多普勒频谱。Abstract: In bistatic spaceborne High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR systems (HRWS-SAR), the azimuth reconstruction to obtain a uniform sampling signal or Doppler spectrum is a crucial step in image processing because azimuth signals are generally of non-uniform sampling type. In this study, the variant transmitting distance to receiving distance radio is approximated to be a constant, the equivalence between the bistatic and monostatic SAR azimuth interchannel transfer functions is deduced, and the azimuth signal model in spaceborne HRWS-SAR with general bistatic configuration is established. Furthermore, the matrix inversion algorithm to reconstruct the azimuth signal is proposed; in addition, to measure the reconstruction performance, the formulae for the signal noise ratio scaling factor and the azimuth ambiguity signal ratio are provided. The azimuth reconstruction is simulated in several spaceborne HRWS-SAR systems with typical bistatic configuration, and the results show that the azimuth Doppler spectrum can be correctly reconstructed via the matrix inversion algorithm when the azimuth sampling is conducted without coinciding samples.
-
表 1 双基星载HRWS-SAR系统的方位向系统参数
Table 1. Azimuth parameters in bistatic spaceborne HRWS-SAR
参数 数值 发射天线方位尺寸(m) 2.4 接收通道方位尺寸(m) 2.4 接收通道数目 5 轨道高度(km) 600 接收天线最短距离(km) 700 方位向速度(m/s) 7600 载波波长(cm) 3.1 表 2 双基星载HRWS-SAR系统的7种双基构型
Table 2. Seven configurations for bistatic spaceborne HRWS-SAR
构型编号 tfd (s) L (km) Ⅰ 0 0 Ⅱ 1 0 Ⅲ 10 0 Ⅳ 0 10 Ⅴ 0 100 Ⅵ 0 –10 Ⅶ 0 –100 表 3 C0及典型PRF值
Table 3. C0 and typical PRF
构型编号 C0 PRFuni (kHz) PRFrep1 (kHz) PRFrep2 (kHz) Ⅰ 1.0000 2.533 1.583 2.111 Ⅱ 1.0001 2.533 1.583 2.111 Ⅲ 1.0059 2.540 1.588 2.117 Ⅳ 0.9927 2.524 1.577 2.103 Ⅴ 0.9345 2.450 1.531 2.041 Ⅵ 1.0074 2.542 1.589 2.118 Ⅶ 1.0805 2.635 1.647 2.196 -
[1] Zink M, Bachmann M, Brautigam B, et al. TanDEM-X: The new global DEM takes shape[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2014, 2(2): 8–23. DOI: 10.1109/MGRS.2014.2318895 [2] Bueso-Bello J L, Prats-Iraola P, Martone M, et al.. Performance evaluation of the TanDEM-X quad polarization acquisitions in the science phase[C]. Proceedings of EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, 2016: 627–632. [3] Moreira A, Krieger G, Hajnsek I, et al. Tandem-L: A highly innovative bistatic SAR mission for global observation of dynamic processes on the earth’s surface[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2015, 3(2): 8–23. DOI: 10.1109/MGRS.2015.2437353 [4] Huber S, Villano M, Younis M, et al.. Tandem-L: Design concepts for a next-generation spaceborne SAR system[C]. Proceedings of EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, 2016: 1–5. [5] 范强, 吕晓德, 张平, 等. 星载SAR DPCMAB技术的方位向非均匀采样研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2006, 28(1): 31–35Fan Qiang, Lü Xiao-de, Zhang Ping, et al. Study of nonuniform azimuth sampling of DPCMAB technique in spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2006, 28(1): 31–35 [6] Currie A and Brown M A. Wide-swath SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1992, 139(2): 122–135. DOI: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0016 [7] Yen J. On nonuniform sampling of bandwidth-limited signals[J]. IRE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 1956, 3(4): 251–257. DOI: 10.1109/TCT.1956.1086325 [8] Gebert N, Krieger G, and Moreira A. Digital beamforming on receive: Techniques and optimization strategies for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 564–592. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089542 [9] Krieger G, Gebert N, and Moreira A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 260–264. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.832700 [10] Cheng Pu, Wan Jian-wei, Xin Qin, et al. An improved azimuth reconstruction method for multichannel SAR using vandermonde matrix[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 67–71. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2626309 [11] Liu Bao-chang and He Yi-jun. Improved DBF algorithm for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 1209–1225. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2476496 [12] Liu Na, Wang R, Deng Yun-kai, et al. Modified multichannel reconstruction method of SAR with highly nonuniform spatial sampling[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(2): 617–627. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2630048 [13] Wang Ming-jian, Yu Wei-dong, Wang R, et al. Improved azimuth multichannel SAR imaging for configurations with redundant measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1610–1614. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2415511 [14] Cerutti-Maori D, Sikaneta I, Klare J, et al. MIMO SAR processing for multichannel high-resolution wide-swath radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 5034–5055. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2286520 [15] Sikaneta I, Gierull C H, and Cerutti-Maori D. Optimum signal processing for multichannel SAR: With application to high-resolution wide-swath imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6095–6109. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2294940 [16] Sikaneta I, Cerutti-Maori D, Klare J, et al.. Comparison of multi-channel high-resolution wide-swath SAR processing methods[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS) 2014, Quebec, 2014: 3834–3837. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6947320. [17] Zhao Shuo, Wang R, Deng Yun-kai, et al. Modifications on multichannel reconstruction algorithm for SAR processing based on periodic nonuniform sampling theory and nonuniform fast Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 4998–5006. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2421303 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: