SAR ATR Based on 3D Parametric Electromagnetic Scattering Model
-
摘要: 合成孔径雷达目标识别是雷达数据解译中一个长期研究的难点问题。近年来,基于模型的SAR目标识别方法由于在扩展条件下的识别性能表现良好而备受关注。在联合国内多家研究单位进行攻关的基础上,该文简要阐述了对该问题的初步研究成果及思考。首先从3个方面出发梳理了散射部件模型发展的技术脉络并对其进行了补充完善;然后从正向推算和逆向反演两条技术途径提出了复杂目标电磁散射参数化建模方法;最后提出了基于复杂目标电磁散射参数化模型的目标识别新框架。论文最后对基于模型的SAR目标识别下一步研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) is one of the most difficult problems in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data interpretation. In recent years, the model-based SAR target recognition method has attracted much attention because of its good performance in the extended operation condition. Based on the research of a few domestic research institutes, this paper briefly introduces the preliminary research results and gives some thoughts about SAR ATR problem. First of all, the development of parametric scattering model are discussed from three aspects. Next, two ways to model the parametric electromagnetic scattering for complex target are put forward. Finally, we propose a new framework for a Three-Dimensional (3D) parametric scattering model based SAR ATR. In the end, the future research direction of model-based SAR target recognition is prospected.
-
表 1 几种不同散射中心的 ${α}_{i}$取值
Table 1. The ${α}_{i}$ for different scattering centers
ai 取值 散射中心 –1 角绕射,尖顶绕射 –1/2 边缘绕射 0 点散射,双曲面反射,直边镜面反射 1/2 单曲面反射 1 平板法向发射,二面角反射,三面角反射 表 2 我们研究的耦合散射中心模型的频率依赖因子
Table 2. The ${α}$ in the proposed model by our team
电磁散射中心类型 电磁散射中心名称 a取值 镜面-镜面耦合 平面-平面耦合 1 单弯曲-平面耦合 0.5 双弯曲-平面耦合 0 单弯曲-单弯曲耦合 0.5 双弯曲-单弯曲耦合 0 双弯曲-双弯曲耦合 0 镜面-边缘耦合 平面-直边耦合 0 单弯曲-直边耦合 0 双弯曲-直边耦合 –0.5 曲边-平面耦合 –0.5 曲边-单弯曲耦合 –0.5 曲边-双弯曲耦合 –0.5 边缘-边缘耦合 直边-直边耦合 –0.5 直边-曲边耦合 –1 曲边-曲边耦合 –1 表 3 简易坦克的部件级3维电磁散射模型
Table 3. The 3D parametric electromagnetic part model for the simplified tank target
编号 形成原因 可见 范围(°) 参数化 模型形式 RCS峰值 (dB) 1 车身 俯仰: [19, 39] 方位: [75, 105] 平板 1 2 车身平板 与立方体 俯仰: [9, 30] 方位: [75, 105] 方形顶帽 32 … … … … … 28 右履带与车身 前斜平板 俯仰: [2, 30] 方位: [75, 105] 二面角 33 29 车身平板与炮筒 俯仰: [11, 30] 方位: [75, 105] 平板上 倒圆柱 10 表 4 基于部件级3维电磁散射模型的识别结果
Table 4. The recognition results
操作条件 数据描述 基于目标3维参数化电磁散射模型 方法的识别率(%) 基于模板方法的识别率(%) 标准 500幅电磁计算数据和75幅暗室测量数据 99.13 91.2 扩展 62幅电磁计算数据和106幅暗室测量数据 90.48 58.2 1 10种典型体参数化模型表达式列表
1. The parametric models for ten scatterers
典型散射部件名称 图形 参数化模型 模型适用角度范围 各参数排列顺序和含义的解释 长方体 
$\begin{array}{l}S_{\rm vv,hh}^{\rm cuboid} = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3} + {S_{\rm 4vv,hh}} + {S_{\rm 5vv,hh}} + {S_{\rm 6vv,hh}}\\{S_1} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kbc}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_x}{\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_2} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kca}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_y}{\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {b{l_y} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_3} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kab}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_z}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{ \rm j}2kc{l_z}}}\\{S_{4{\rm vv,hh}}} = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{9}\frac{c}{{\sqrt {π} }}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left[ { \mp 1 - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \phi } \right)}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{\phi }{3}\sin \displaystyle\frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} - \phi } \right)}}} \right]\\ \cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} - b{l_y} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\ + \left[ { \mp 1 + \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}\frac{1}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \phi } \right)\cos \displaystyle\frac{\phi }{3}}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} + b{l_y} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\ + \left[ { \mp 1 - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{\phi }{3}}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \phi } \right)\sin \displaystyle\frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} /2 + \phi } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} - b{l_y} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\end{array} \right\}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ 0^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ 0^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\end{array}$ a, b, c:长方体边长 ${S_{5{\rm vv,hh}}} = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{9}\frac{a}{{\sqrt {π} }}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left[ { \pm 1 - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)\sin \displaystyle\frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} /2 + \theta } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kb{l_y}}}\\ + \left[ { \pm 1 + \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}\frac{1}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}\cos\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {b{l_y} + 2c{l_z}} \right)}}\\ + \left[ { \pm 1 - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}\sin \displaystyle\frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} - \theta } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( { - b{l_y} + 2c{l_z}} \right)}}\end{array} \right\}\\{S_{6{\rm vv,hh}}} = \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{9}\frac{b}{{\sqrt {π} }}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}\left[ { \pm 1 - \displaystyle\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}\sin \frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} - \theta } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( { - a{l_x} + 2c{l_z}} \right)}}\\ + \left[ { \pm 1 + \displaystyle\frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}\frac{1}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)\cos \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} + 2c{l_z}} \right)}}\\ + \left[ { \pm 1 - \frac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\frac{{\sin \displaystyle\frac{\theta }{3}}}{{\cos \displaystyle\frac{1}{3}\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)\sin \displaystyle\frac{2}{3}\left( {{π} /2 + \theta } \right)}}} \right]\\\cdot {\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka{l_x}}}\end{array} \right\}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ 0^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ 0^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\end{array}$ a, b, c:长方体边长 圆柱体 
$S_{\rm vv,hh}^{\rm cylinder} = {S_{1{\rm vv,hh}}} + {S_{2{\rm vv,hh}}} + {S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}}$ 当 $2kr\sin \theta > 2.44$且 $kh\cos \theta > 2.25$ $\begin{array}{l}{S_{1{\rm vv,hh}}} = \sqrt {\frac{{{\rm j}r}}{{3k\sin \theta }}} \left[ { \mp \frac{2}{3} - {{\left( {\frac{1}{2} + \cos \frac{{4\theta }}{3}} \right)}^{ - 1}}} \right]{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2kr\sin \theta }}\\{S_{2{\rm vv,hh}}} = \sqrt {\frac{{{\rm j}r}}{{3k\sin \theta }}} \left[ { \mp \frac{2}{3} - {{\left( {\frac{1}{2} + \cos \frac{{4\left( {{π} - \theta } \right)}}{3}} \right)}^{ - 1}}} \right]{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2k\left( {r\sin \theta + h\cos \theta } \right)}}\\{S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}} = {\rm j}\sqrt {\frac{{{\rm j}r}}{{3k\sin \theta }}} \left[ { \mp \frac{2}{3} - {{\left( {\frac{1}{2} + \cos \frac{{4\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)}}{3}} \right)}^{ - 1}}} \right]{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2k\left( { - r\sin \theta + h\cos \theta } \right)}}\end{array}$ 当 $kh\cos \theta \le 2.25$ ${\left( {{S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3}} \right)_{\theta \to \displaystyle\textstyle\frac{{π} }{2}}} = - \sqrt {{\rm j}kr{h^2}\sin \theta } {\rm sinc}\left( {kh\cos \theta } \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {h\cos \theta + 2r\sin \theta } \right)}}$ 当 $2kr\sin \theta \le 2.44$ ${\left( {{S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3}} \right)_{\theta \to 0}} = - {\rm j}2\sqrt {π} k{r^2}\left| {\cos \theta } \right|\frac{{{J_1}\left( {2kr\sin \theta } \right)}}{{2kr\sin \theta }}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kh\left( {\cos \theta + \left| {\cos \theta } \right|} \right)}}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ r:圆柱半径
h:圆柱的长方形顶帽 
$\begin{array}{l}S_{{\rm vv,hh}}^{{\rm cuboid - hat}} = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3} + {S_{4{\rm vv,hh}}} + {S_{5{\rm vv,hh}}}\\{S_1} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kbc}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_x}{\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_2} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kca}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_y}{\rm sinc}\left( {kc{l_z}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {b{l_y} + c{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_3} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kab}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_z}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2kc{l_z}}}\\{S_{4{\rm vv,hh}}} =\!\! \mp \frac{1}{{\sqrt {π} }}\!\! \frac{{\min \left\{ {c{l_x},{d_1}{l_z}} \right\}}}{{{l_y}}}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{\!\!\! {\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {b - {\delta _1}} \right){l_y}}} {\rm sinc}\left( {k{\delta _1}{l_y}} \right)\! - \!{{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}kb{l_y}}},{\delta _1} \! \le \! b\\\frac{b}{{{\delta _1}}}\left[ {{\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right) - {{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}kb{l_y}}}} \right],\quad{\delta _1} > b\end{array} \right\}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka{l_x}}}\\{S_{5{\rm vv,hh}}} = \mp \frac{1}{{\sqrt {π} }}\frac{{\min \left\{ {c{l_y},{d_2}{l_z}} \right\}}}{{{l_x}}}\left\{ \begin{array}{l}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a - {\delta _2}} \right){l_x}}}{\rm sinc}\left( {k{\delta _2}{l_x}} \right) - {{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}ka{l_x}}},{\delta _2} \le a\\\frac{a}{{{\delta _2}}}\left[ {{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right) - {{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}ka{l_x}}}} \right],\quad\ \ {\delta _2} > a\end{array} \right\}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kb{l_y}}}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}\theta \in \left[ {{{20}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\!\!\!\!\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{15}^{°}}} \right]\\\quad \cup \left[ {{{75}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ a, b, c:长方体边长 d1:x方向“帽沿” 宽度 d2:y方向“帽沿” 宽度 圆形顶帽 
$\begin{array}{l}S_{{\rm vv,hh}}^{{\rm top - hat}} = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}}\\{S_1} = - \sqrt {{\rm j}kr{h^2}\sin \theta } {\rm sinc}\left( {kh\cos \theta } \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {h\cos \theta + 2r\sin \theta } \right)}}\\{S_2} = - {\rm j}2\sqrt {π} k{r^2}\left| {\cos \theta } \right|\frac{{{J_1}\left( {2kr\sin \theta } \right)}}{{2kr\sin \theta }}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kh\left( {\cos \theta + \left| {\cos \theta } \right|} \right)}}\\{S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}} = \mp 2\sqrt {{\rm j}kr\sin \theta } \min \left\{ {h,\frac{d}{{\tan \theta }}} \right\}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2kr\sin \theta }}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{{0.1}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ r:圆柱半径 h:圆柱的长d:“帽沿”宽度 平板上倒圆柱 
$\begin{array}{c}\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\! S_{{\rm vv,hh}}^{{\rm cyl - plane}} = {S_1} + {S_{2{{\rm vv,hh}}}} + {S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}}\\\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!{S_1} = - \sqrt {{\rm j}kr\sqrt {1 - l_y^2} } L{\rm sinc}\left( {kL{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2k\left( {r + h} \right){l_z}}}\\{S_{2{\rm vv,hh}}} = \pm \sqrt { - {\rm j}kr{L^2}\sin \theta } \sin \! {\rm c}\left( {kL{l_y}} \right)U\left( {\arctan \left( {\frac{d}{{r + h}}} \right) - \theta } \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2kr\sin \theta }}\\\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!{S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}} = \frac{{2{b_0}}}{{\sqrt {3{π} } }}\left[ { \pm \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{{1 + 2\cos \displaystyle\frac{{4\theta }}{3}}}} \right]{\rm sinc}\left( {k{b_0}{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k{a_0}{l_x}}}\\ \quad\quad+ \frac{{2{b_0}}}{{\sqrt {3{π} } }}\left[ { \pm \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{{1 + 2\cos \displaystyle\frac{{4\left( {{π} - \theta } \right)}}{3}}}} \right]{\rm sinc}\left( {k{b_0}{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {{a_0}{l_x} + 2{d_0}{l_z}} \right)}}\\ \quad\quad \quad\ + \frac{{2{b_0}}}{{\sqrt {3{π} } }}\left[ { \pm \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{{1 + 2\cos \displaystyle\frac{{4\left( {{π} /2 - \theta } \right)}}{3}}}} \right]{\rm sinc}\left( {k{b_0}{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( { - {a_0}{l_x} + 2{d_0}{l_z}} \right)}}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{10}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ r:圆柱半径 L:圆柱的长h:圆柱面到平面距离 a0:平板边长 b0:平板边长 d0:平板厚度 直二面角 
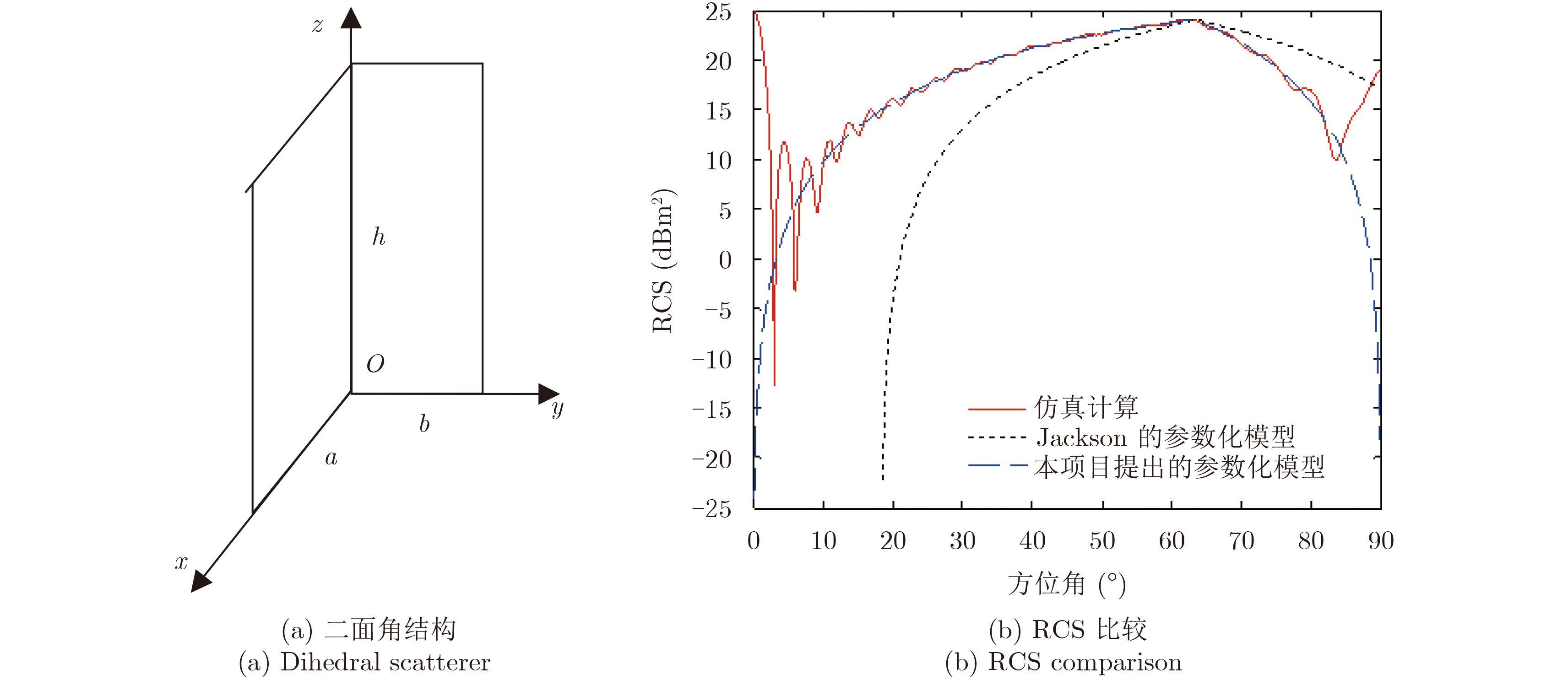
$\begin{array}{l}S_{{\rm vv,hh}}^{{\rm dihedral}} = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_{3{\rm vv,hh}}}\\{S_1} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kah}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_y}{\rm sinc}\left( {kh{l_z}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {a{l_x} + h{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_2} = - {\rm j}\frac{{kbh}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_x}{\rm sinc}\left( {kh{l_z}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {kb{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {b{l_y} + h{l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_{\rm 3vv,hh}} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ \pm \frac{1}{{\sqrt {π} }}\frac{{\min \{ b{l_x},a{l_y}\} }}{{{l_z}}}\left\{ {{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}k\left( {h - \delta } \right){l_z}}}{\rm sinc}\left( {k\delta {l_z}} \right) - {{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}kh{l_z}}}} \right\}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kh{l_z}}}},&\!\!{\delta \le h}\\\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\! { \pm \frac{1}{{\sqrt {π} }}\frac{{\min \{ b{l_x},a{l_y}\} }}{{{l_z}}}\left\{ {\frac{h}{\delta }{\rm sinc}\left( {kh{l_z}} \right) - {{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}kh{l_z}}}} \right\}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}kh{l_z}}}},&\!\!{\delta > h}\end{array}} \right.\\\quad\quad\ \delta = \min \left\{ {b{l_z}/{l_y},a{l_z}/{l_x}} \right\}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{{40}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ a, b:二面角两面宽度h:二面角的长度 直三面角 
$\begin{array}{l}S_{{\rm vv,hh}}^{\rm trihedral} = {S_1} + {S_2} + {S_3} + {S_{12{\rm vv,hh}}} + {S_{\rm 23vv,hh}} + {S_{\rm 31vv,hh}} + {S_{123}}\\{S_1} = - {\rm j}\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_x}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_y}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka\left( {{l_y} + {l_z}} \right)}}\\{S_2} = - {\rm j}\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_y}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_z}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka\left( {{l_z} + {l_x}} \right)}}\\{S_3} = - {\rm j}\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}{l_z}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka\left( {{l_x} + {l_y}} \right)}}\\{S_{\rm 12vv,hh}} = \mp {\rm j}2\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}\min \left\{ {{l_x},{l_y}} \right\}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_z}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka{l_z}}}\\{S_{\rm 23vv,hh}} = \pm {\rm j}2\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}\min \left\{ {{l_y},{l_z}} \right\}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_x}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka{l_x}}}\\{S_{\rm 31vv,hh}} = \pm {\rm j}2\frac{{k{a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}\min \left\{ {{l_z},{l_x}} \right\}{\rm sinc}\left( {ka{l_y}} \right){{\rm e}^{{\rm j}ka{l_y}}}\\\begin{aligned}{S_{123}} = & - {\rm j}\frac{{k\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{{\sqrt {π} }}\min \left\{ {\sin \left( {\theta + {π} /4 - \alpha } \right),\cos \left( {\theta + {π} /4 - \alpha } \right)} \right\} \\ &\cdot \min \left\{ {\sin \phi ,\cos \phi } \right\}\end{aligned}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{{10}^{°}},{{80}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{{10}^{°}},{{80}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ a:三面角边长 圆边浅凹体 
$\begin{array}{l}\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\ S_{\rm vv,hh}^{\rm pan} = \pm {10^{{p_{\rm vv,hh}}\left( \theta \right)/20}}{{\rm e}^{ - {\rm j}2ka\sin \theta }}\\\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\ {p_{\rm vv}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm vv}}} {c_i^{\rm vv}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}} \\\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\ {p_{\rm hh}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm hh}}} {c_i^{\rm hh}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}} \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {20}^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ 0^{°},{{90}^{°}} \right]\end{array}$ ${N_{\rm vv,hh}}$:拟合函数阶数 $c_j^{\rm vv,hh}$:拟合系数 a:圆盘半径 kc:中心波数 矮顶帽 
$\begin{array}{l}S_{\rm vv,hh}^{\rm short - tophat} = \pm {10^{{p_{\rm vv,hh}}\left( \theta \right)/20}}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2ka\sin \theta }}\\{p_{\rm vv}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm vv}}} {c_i^{\rm vv}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}} \\{p_{\rm hh}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm hh}}} {c_i^{\rm hh}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{{20}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ ${N_{\rm vv,hh}}$:拟合函数阶数 $c_j^{\rm vv,hh}$:拟合系数a:顶部半径kc:中心波数 狭长二面角 
$\begin{array}{l}\quad\quad\quad S_{\rm vv,hh}^{\rm dihedral\_smallsurf}\\\quad\quad\quad\quad = \pm {{\rm e}^{ - \frac{2}{3}{{\left( {{π} fL\sin \theta /{\rm c}} \right)}^2}{{\left( {\phi - {π} } \right)}^2}}}{10^{{p_{\rm vv,hh}}\left( \theta \right)/20}}{{\rm e}^{{\rm j}2ka\sin \theta }}\\\quad\quad\quad{p_{\rm vv}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm vv}}} {c_i^{\rm vv}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}} \\\quad\quad\quad{p_{\rm hh}}\left( \theta \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{{N_{\rm hh}}} {c_i^{\rm hh}{{\left( {90 - \theta } \right)}^i}} \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{l}\theta \in \left[ {{{20}^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\\\phi \in \left[ {{0^{°}},{{90}^{°}}} \right]\end{array}$ ${N_{\rm vv,hh}}$:拟合函数阶数 $c_j^{\rm vv,hh}$:拟合系数 d:狭长立板偏置距离 L:狭长立板长度kc:中心波数 说明: ${l_x} = \sin \theta \cos \phi, \;{l_y} = \sin \theta \sin \phi, \;{l_z} = \cos \theta $ ${J_1}\left( \cdot \right)$为一阶贝塞尔函数;min{a,b}指取a,b中的较小值;U(x)为单位阶跃函数,即x大于等于0时取1,小于0时取0; $k = \frac{{2{π} f}}{\rm c}$为波数。 -
[1] 张澄波. 综合孔径雷达—原理、系统分析与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.Zhang Cheng-bo. Synthetic Aperture Radar Emdash the Principle, System Analysis and Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. [2] 黄培康, 殷红成, 许小剑. 雷达目标特性[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.Huang Pei-kang, Yin Hong-cheng, and Xu Xiao-jian. Radar Target Characteristics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006. [3] Wehner D R. High-Resolution Radar[M]. Norwood, MA: Artech House Inc., 1987. [4] Oliver C, Quegan S, Ding Chi-biao, et al. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009. [5] El-Darymli K, Gill E W, McGuire P, et al. Automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art review[J].IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 6014–6058. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2611492 [6] Novak L M, Owirka G J, Brower W S, et al. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP[J].The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 187–202. [7] Kreithen D E, Halversen S D, and Owirka G J. Discriminating targets from clutter[J].The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1993, 6(1): 25–52. [8] Meth R and Chellappa R. Feature matching and target recognition in synthetic aperture radar imagery[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, AZ, March 1999: 3333–3336. [9] Nicoli L P and Anagnostopoulos G C. Shape-based recognition of targets in synthetic aperture radar images using elliptical Fourier descriptors[C]. Proc. SPIE 6967, Automatic Target Recognition XVIII, Orlando, FL, April 2008. [10] Liu Xian, Huang Yu-lin, Pei Ji-fang, et al. Sample discriminant analysis for SAR ATR[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2120–2124. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2321164 [11] Park J I, Park S H, and Kim K T. New discrimination features for SAR automatic target recognition[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 476–480. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2210385 [12] Huang Yu-lin, Pei Ji-fang, Yang Jian-yu, et al. Neighborhood geometric center scaling embedding for SAR ATR[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(1): 180–192. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.110769 [13] Mishra A K. Validation of PCA and LDA for SAR ATR[C]. TENCON 2008-2008 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Hyderabad, Nov. 2008: 1–6. [14] 宦若虹, 杨汝良. 基于小波域NMF特征提取的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(3): 588–591. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX200903019.htmHuan Ruo-hong and Yang Ru-liang. Synthetic aperture radar images target recognition based on wavelet domain NMF feature extraction[J].Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(3): 588–591. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX200903019.htm [15] Dong Gang-gang and Kuang Gang-yao. Classification on the monogenic scale space: Application to target recognition in SAR image[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(8): 2527–2539. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2421440 [16] Jones G and Bhanu B. Recognition of articulated and occluded objects[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1999, 21(7): 603–613. doi: 10.1109/34.777371 [17] Liu Jun. Model learning with probabilistic networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], George Mason University, 1997. [18] Kottke D P, Fwu J K, and Brown K. Hidden Markov modeling for automatic target recognition[C]. Conference Record of the 31st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, Nov. 1997: 859–863. [19] Sun Yi-jun, Liu Zhi-peng, Todorovic S, et al. Adaptive boosting for SAR automatic target recognition[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(1): 112–125. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.357120 [20] Zhao Zhi-qiang, Jiao Li-cheng, Zhao Jia-qi, et al. Discriminant deep belief network for high-resolution SAR image classification[J].Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 686–701. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.028 [21] El-Dawlatly S, Osman H, and Shahein H I. Enhanced SVM versus several approaches in SAR target recognition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems, Cairo, Nov. 2006: 266–270. [22] Thiagarajan J J, Ramamurthy K N, Knee P, et al. Sparse representations for automatic target classification in SAR images[C]. 4th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing, Limassol, Mar. 2010: 1–4. [23] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, and Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA., Dec. 2012: 1097–1105. [24] Ding Jun, Chen Bo, Liu Hong-wei, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. [25] Du Kang-ning, Deng Yun-kai, Wang R, et al. SAR ATR based on displacement-and rotation-insensitive CNN[J].Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(9): 895–904. [26] Li Xuan, Li Chun-sheng, Wang Peng-bo, et al. SAR ATR based on dividing CNN into CAE and SNN[C]. 2015 IEEE 5th-Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, Sep. 2015: 676–679. [27] Morgan D A E. Deep convolutional neural networks for ATR from SAR imagery[C]. Proc. SPIE 9475, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXII, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, Apr. 2015. [28] Chen Si-zhe, Wang Hai-peng, Xu Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 [29] Keydel E R, Lee S W, and Moore J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. Proc. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, FL, April 1996: 228–242. [30] Diemunsch J R and Wissinger J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. Proc. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V. Orlando, Florida, 1998: 481–492. [31] Ross T D, Bradley J J, Hudson L J, et al. SAR ATR: So what’s the problem? An MSTAR perspective[C]. Proc. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, FL, Apr. 1999: 662–672. [32] Chew W C, Michielssen E, Song J M, et al. Fast and Efficient Algorithms in Computational Electromagnetics[M]. Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House, Inc., 2001: 94–96. [33] Hurst M and Mittra R. Scattering center analysis via Prony’s method[J].IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1987, 35(8): 986–988. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1987.1144210 [34] Potter L C, Chiang D M, Carriere R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J].IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641 [35] Sacchini J J, Steedly W M, and Moses R L. Two-dimensional Prony modeling and parameter estimation[J].IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(11): 3127–3137. doi: 10.1109/78.257242 [36] Potter L C and Moses R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 [37] Gerry M J, Potter L C, Gupta I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J].IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750 [38] Li Jian, Wu Ren-biao, Bi Zhao-qiang, et al. Robust semiparametric method for feature extraction and SAR image formation of targets consisting of trihedrals and dihedrals[C]. Proc. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, FL, April 1999: 92–103. [39] Ai Fa-zhi, Zhou Jian-xiong, Hu Lei, et al. The parametric model of non-uniformly distributed scattering centers[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems (Radar 2012), Glasgow, UK, Oct. 2012: 1–5. [40] 周剑雄. 光学区雷达目标三维散射中心重构理论与技术[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2006.Zhou Jian-xiong. Theory and technology on reconstructing 3D scattering centers of radar targets in optical region[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2006. [41] Zhou Jian-xiong, Shi Zhi-guang, Xiao Cheng, et al. Automatic target recognition of SAR images based on global scattering center model[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3713–3729. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2162526 [42] Zhou Jian-xiong, Shi Zhi-guang, and Fu Qiang. Three-dimensional scattering center extraction based on wide aperture data at a single elevation[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1638–1655. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346509 [43] He Yang, He Si-yuan, Zhang Yun-hua, et al. A forward approach to establish parametric scattering center models for known complex radar targets applied to SAR ATR[J].IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(12): 6192–6205. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2360700 [44] Richards J A. Target model generation from multiple synthetic aperture radar images[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], MIT, 1996. [45] Rigling B D. Signal processing strategies for bistatic synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], The Ohio State University, 2003. [46] Jackson J A and Moses R L. An algorithm for 3D target scatterer feature estimation from sparse SAR apertures[C]. Proc. SPIE 7337, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVI, Orlando, Florida, USA, Apr. 2009. [47] Jackson J A and Moses R L. Feature extraction algorithm for 3D scene modeling and visualization using monostatic SAR[C]. Proc. SPIE 6237, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIII, Orlando (Kissimmee), FL, Apr. 2006. [48] Jackson J A. Three-dimensional feature models for synthetic aperture radar and experiments in feature extraction[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], The Ohio State University, 2009. [49] 吴敏, 张磊, 段佳, 等. 基于属性散射中心模型的SAR超分辨成像算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(9): 1058–1064. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB201409012.htmWu Min, Zhang Lei, Duan Jia, et al. Super resolution SAR imaging algorithm based on attribute scattering center model[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(9): 1058–1064. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHXB201409012.htm [50] 吴敏, 张磊, 邢孟道, 等. 基于分布式压缩感知的全极化雷达超分辨成像[J]. 电波科学学报, 2015, 30(1): 29–36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201501005.htmWu Min, Zhang Lei, Xing Meng-dao, et al. Full polarization super-resolution radar imaging algorithm based on distributed compressive sensing[J].Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2015, 30(1): 29–36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201501005.htm [51] 黄大荣, 张磊, 郭新荣, 等. 全极化频谱外推的合成孔径雷达成像分辨率增强方法[J]. 电波科学学报, 2014, 29(5): 799–806. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201405002.htmHuang Da-rong, Zhang Lei, Guo Xin-rong, et al. Enhanced resolution in fully polarimetric synthetic aperture radar imaging using bandwidth extrapolation[J].Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2014, 29(5): 799–806. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBKX201405002.htm [52] Mittra R, Lee S W, and Chuang C A. Analytic radar target modeling[R]. AD755854, 1972. [53] Shirman Y D. Computer Simulation of Aerial Target Radar Scattering, Recognition, Detection, and Tracking[M]. Boston: Artech House Publisher, 2002. [54] 罗宏, 许小剑, 黄培康, 等. 目标宽带雷达特征信号的建模与预测[J]. 电子学报, 1999, 27(9): 41–44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU199909012.htmLuo Hong, Xu Xiao-jian, Huang Pei-kang, et al. On the modeling and prediction of wideband radar signals[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 1999, 27(9): 41–44. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXU199909012.htm [55] 钟金荣. 目标三维电磁散射参数化模型反演方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2016.Zhong Jin-rong. Inverse methods for three dimensional parametric scattering model of target[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2016. [56] Chiang H-C, Moses R L, and Potter L C. Model-based classification of radar images[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2000, 46(5): 1842–1854. doi: 10.1109/18.857795 [57] Wissinger J, Ristroph R, Diemunsch J R, et al. MSTAR’s extensible search engine and model-based inferencing toolkit[C]. Proc. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, FL, Aug. 1999: 554–570. [58] 丁柏圆, 文贡坚, 钟金荣, 等. 匹配滤波在SAR目标单个散射部件检测中的应用[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2015, 20(3): 357–365. doi: 10.11834/jig.20150307Ding Bai-yuan, Wen Gong-jian, Zhong Jin-rong, et al. The application of matched filter in detecting single scattering parts of SAR targets[J].Journal of Image and Graphics, 2015, 20(3): 357–365. doi: 10.11834/jig.20150307 [59] Ma Cong-hui, Wen Gong-jian, Ding Bo-yuan, et al. Three-dimensional electromagnetic model-based scattering center matching method for synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition by combining spatial and attributed information[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(1): 016025. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.016025 [60] Ma Cong-hui, Wen Gong-jian, Huang Xiao-hong, et al. Scatterer-based approach to evaluate similarity between 3D em-model and 2D SAR data for ATR[J].IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2017, 11(2): 254–259. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0123 [61] Ding Bai-yuan, Wen Gong-jian, Zhong Jin-rong, et al. Robust method for the matching of attributed scattering centers with application to synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(1): 016010. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.016010 [62] Ding Bai-yuan, Wen Gong-jian, Zhong Jin-rong, et al. A robust similarity measure for attributed scattering center sets with application to SAR ATR[J].Neurocomputing, 2017, 219: 130–143. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.007 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: