Analysis of Time and Beam Synchronization Errors for Distributed Spaceborne SAR System
-
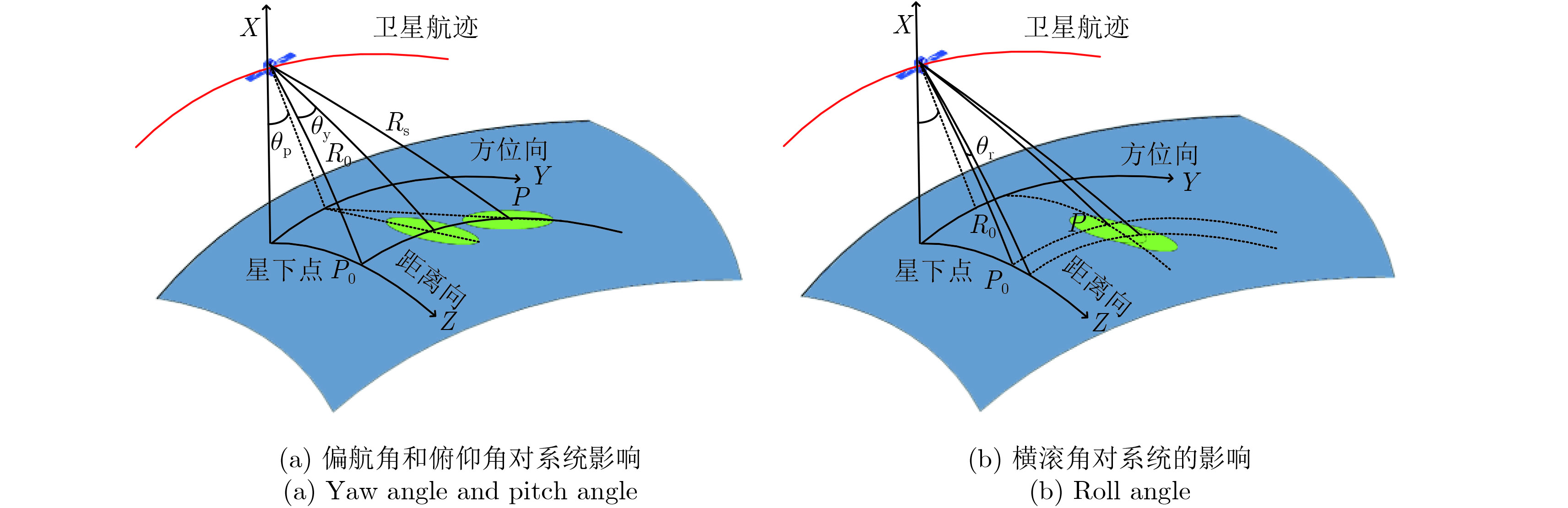
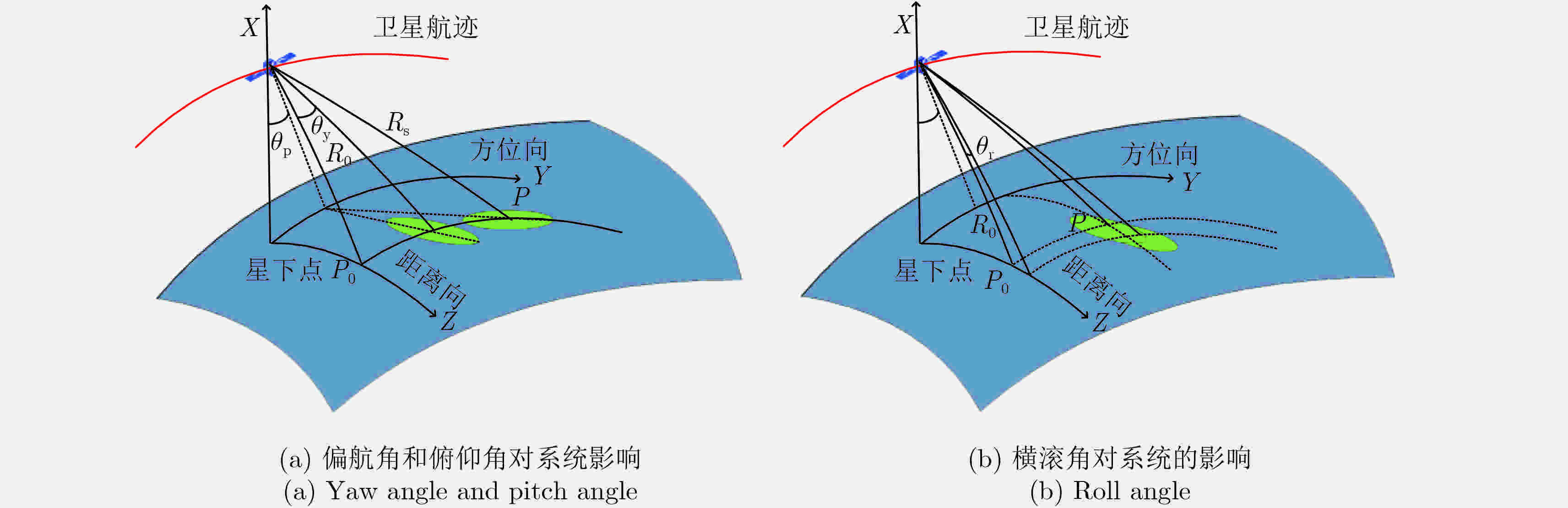
摘要: 三大同步是分布式星载SAR系统需要解决的关键问题之一。该文系统分析了时间同步和波束同步误差对分布式星载SAR系统的影响,时间同步部分首先推导了时间同步误差对成像的影响,其次基于时间同步误差模型和脉冲对传相位同步模型,分析时间同步和相位同步导致的相位误差之间的关系,波束同步部分基于星载双基SAR系统的不同姿态导引方式,分析波束指向误差和卫星姿态误差对合成天线方向图的影响,以及对多普勒去相干的影响,最后分析波束同步误差对距离向重叠幅宽的影响。仿真结果验证了本文理论分析的正确性,分析结果可以为分布式星载SAR的系统设计提供重要指导。Abstract: Synchronization is a key problem in distributed Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) systems. In this paper, we perform a complex mathematical deduction and then analyze the influences of time synchronization on the SAR imaging and interferometric process. We discuss the relationship between time and phase synchronization, considering that different oscillators in separated transmitters and receivers lead to both time and phase synchronization errors. With respect to beam synchronization, we present the effects of the accuracies of beam pointing and satellite attitude on the antenna gain, based on the attitude-steering strategy, which involves azimuth weighting of the Doppler spectra for independent zero-Doppler beam steering. We also analyze the influences of beam synchronization on Doppler decorrelation, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and overlapping swath error. We conduct simulations to validate the analysis results. Our findings provide guidance for system design.
-
表 1 仿真参数表
Table 1. Simulation parameters
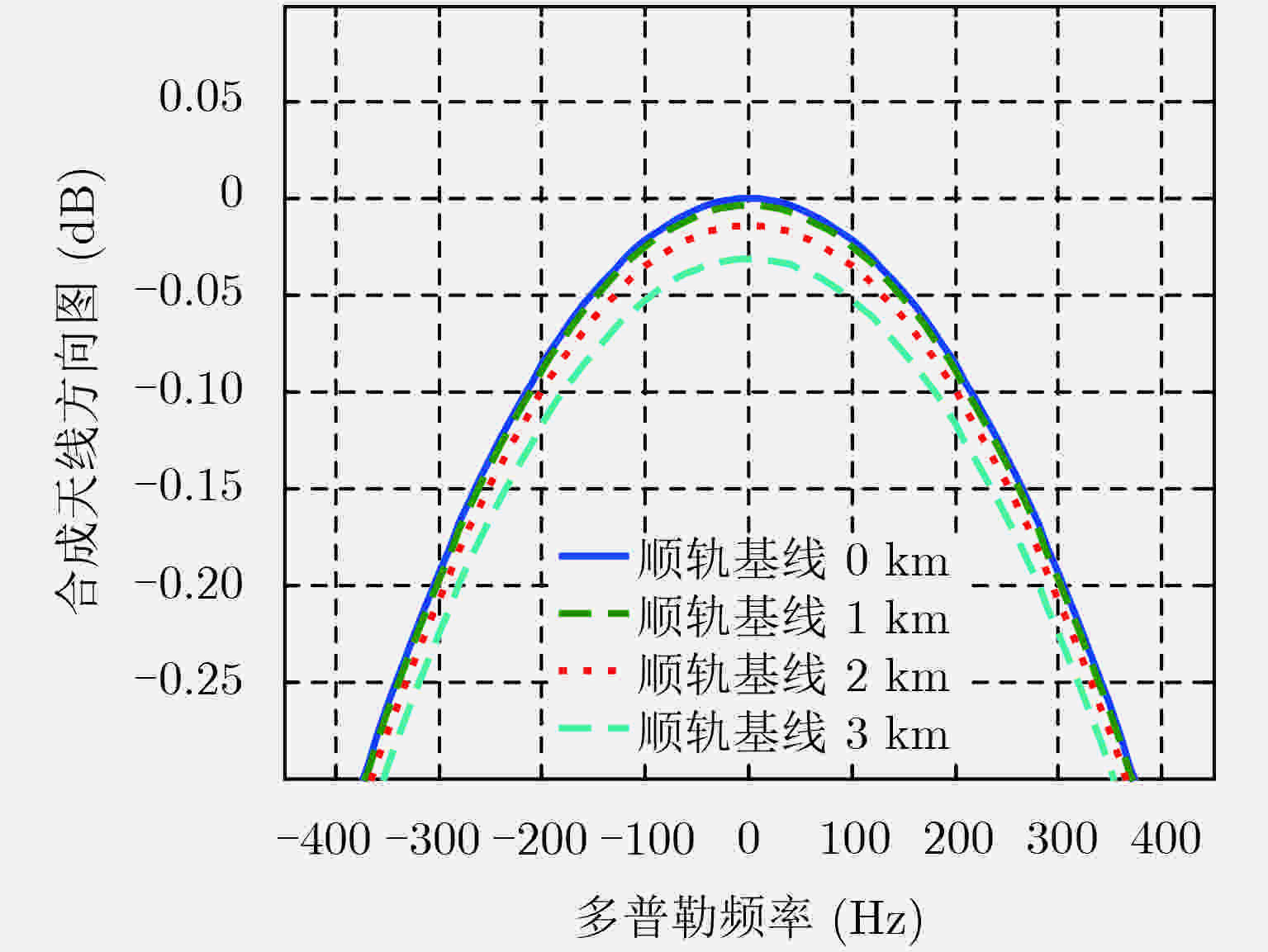
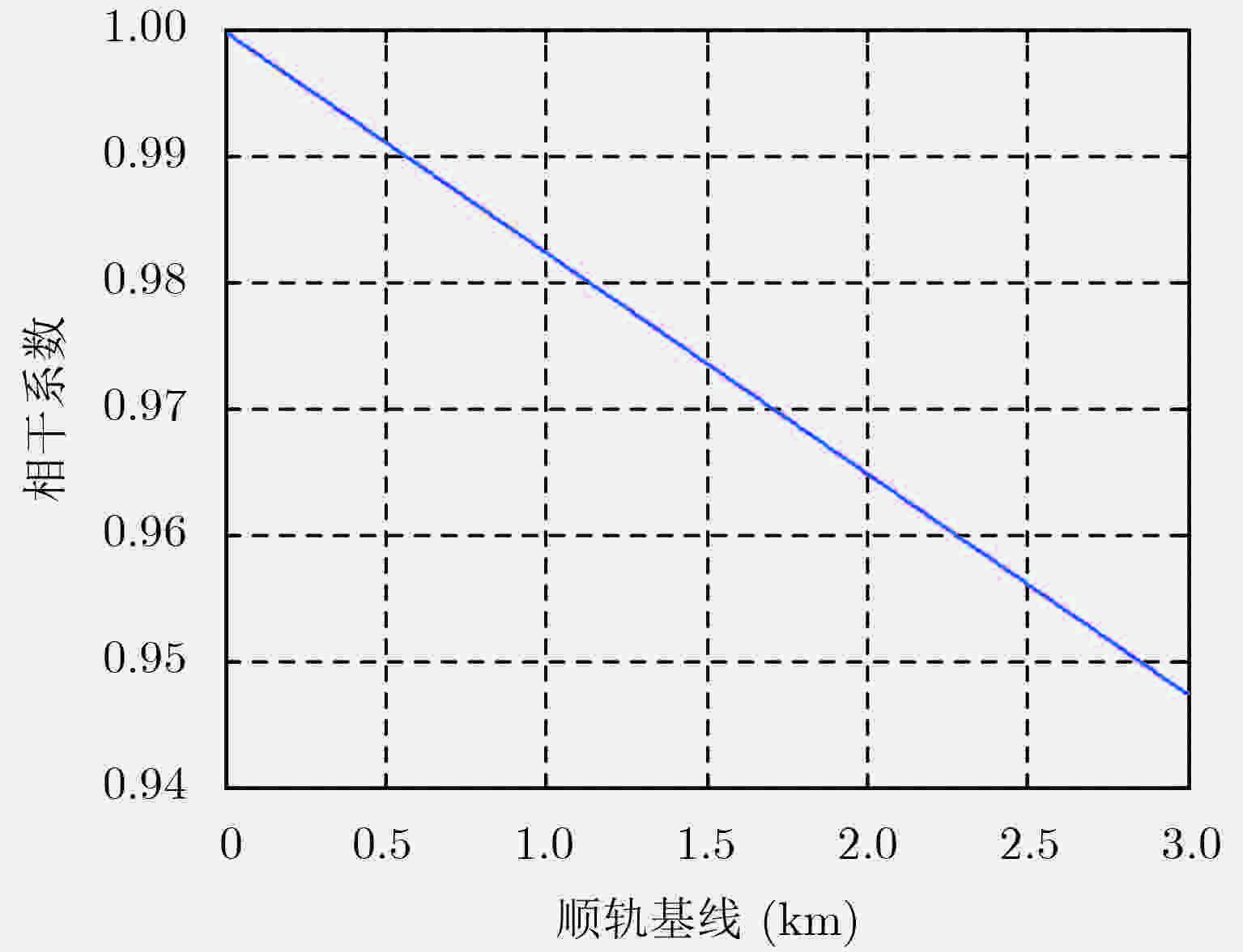
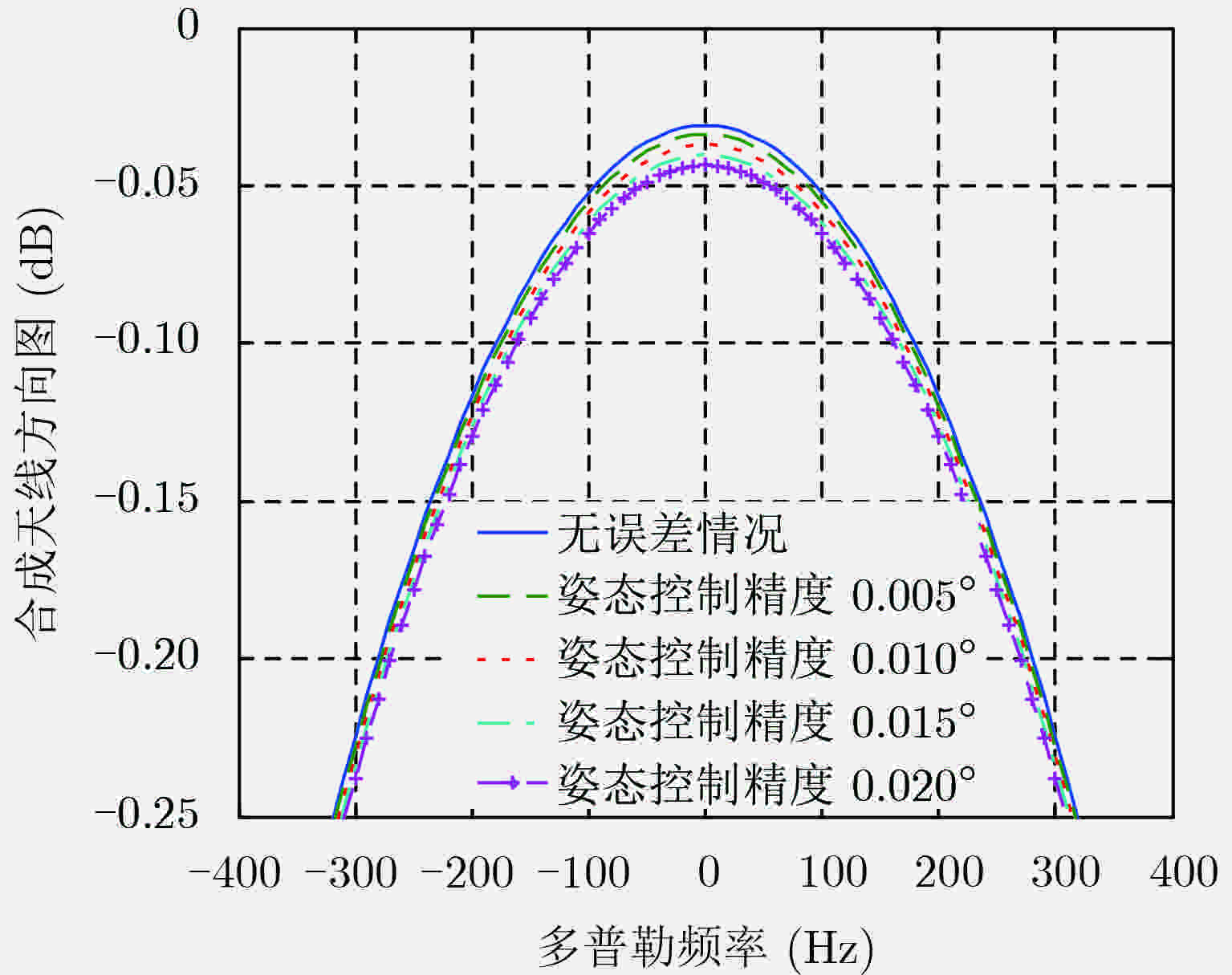
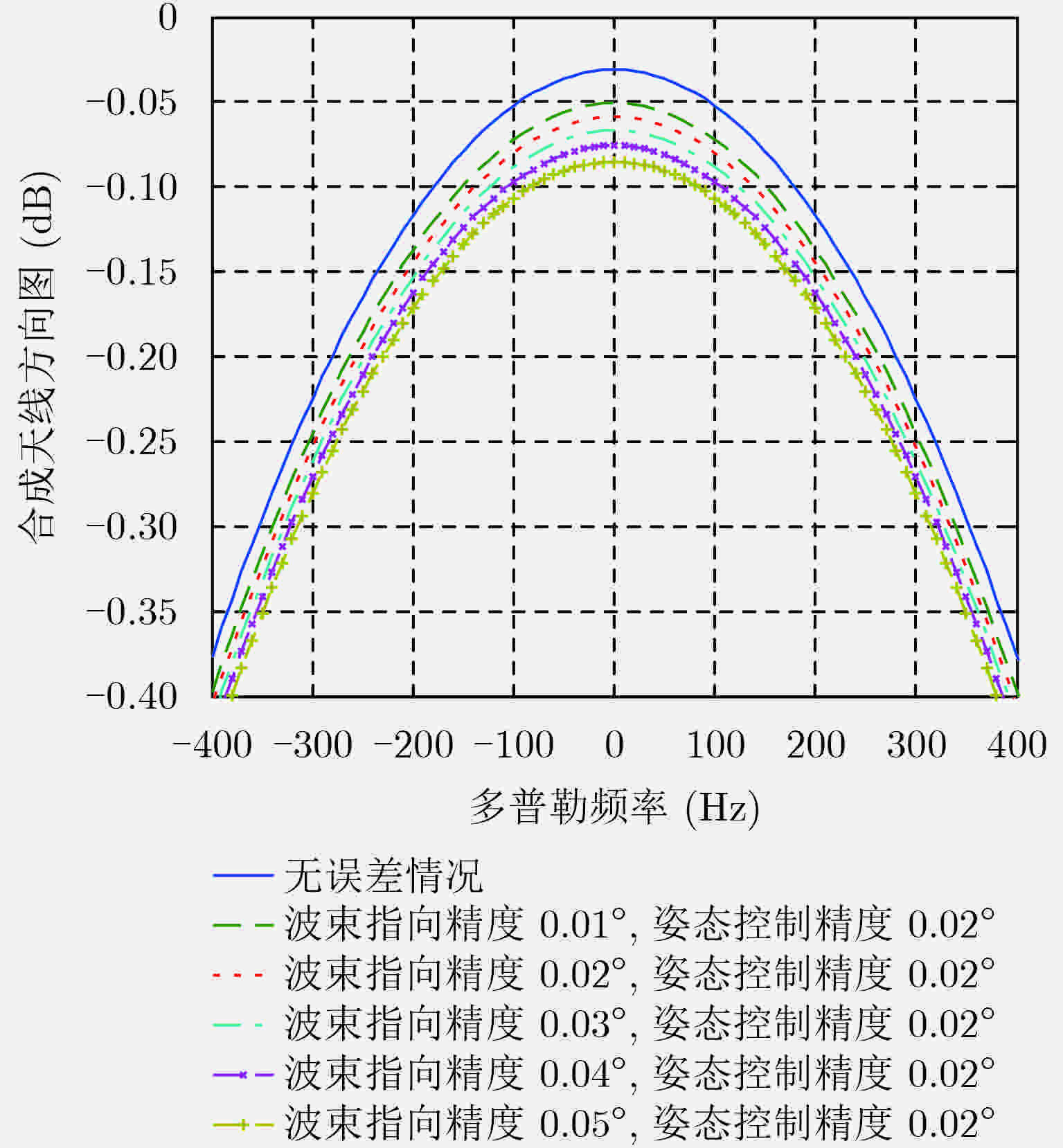
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 1.30 卫星高度(km) 700 方位向天线长度(m) 6 脉冲宽度(μs) 80 距离向带宽(MHz) 100 PRF(Hz) 1600 卫星有效速度(m/s) 7500 距离向波束指向精度(°) 0.06 方位向波束指向精度(°) 0.05 姿态控制精度(°) 0.02 顺轨基线(km) 3 表 2 波束同步误差造成的辅星图像信噪比损失(dB)
Table 2. Influence of beam synchronization error on SNR (dB)
波束指向精度(°) 姿态控制精度(°) 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.021 0.025 0.02 0.028 0.032 0.03 0.036 0.039 0.04 0.046 0.048 0.05 0.055 0.057 表 3 波束同步误差对重叠幅宽的影响(m)
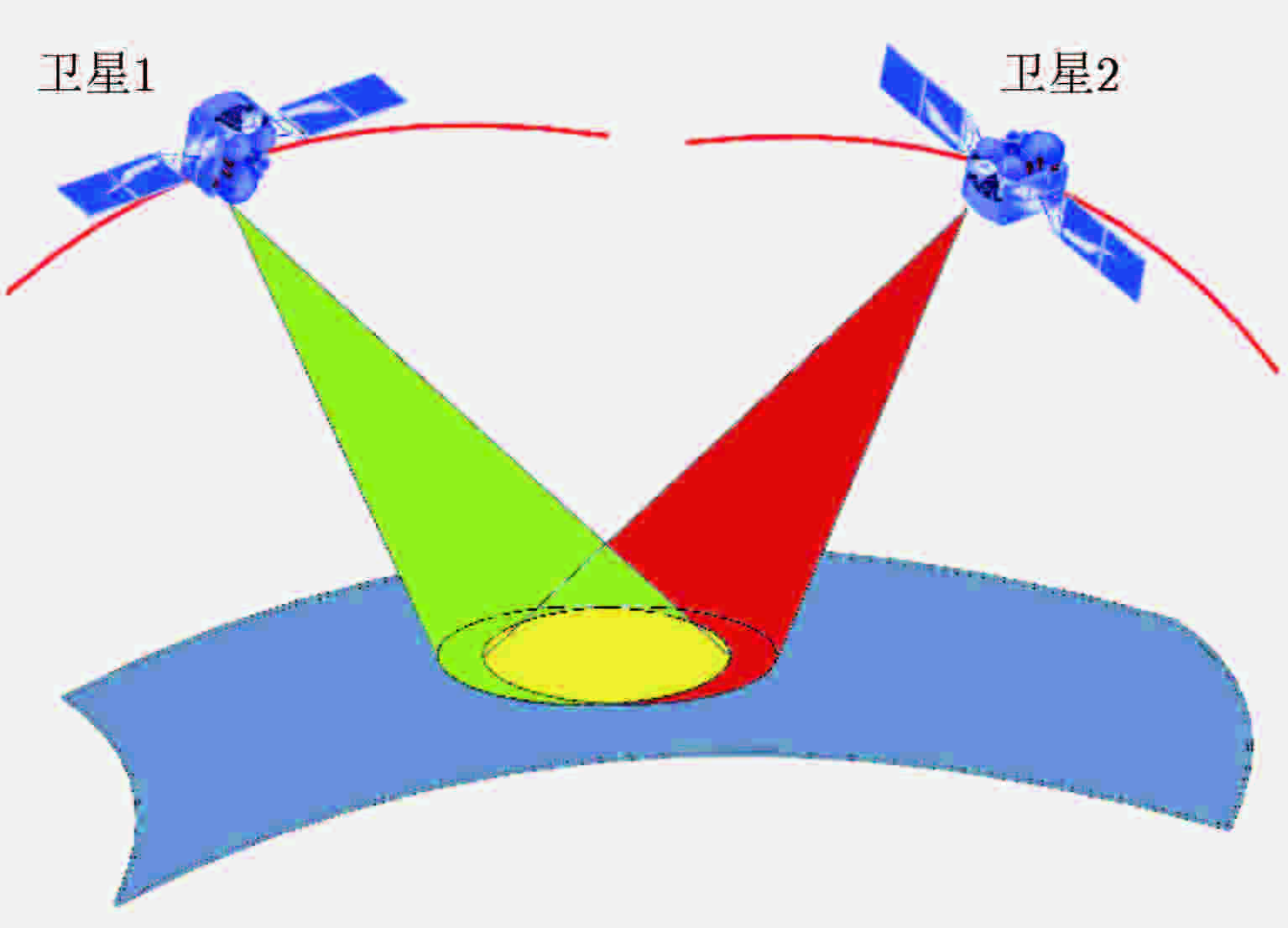
Table 3. Influence of beam synchronization error to overlapping area (m)
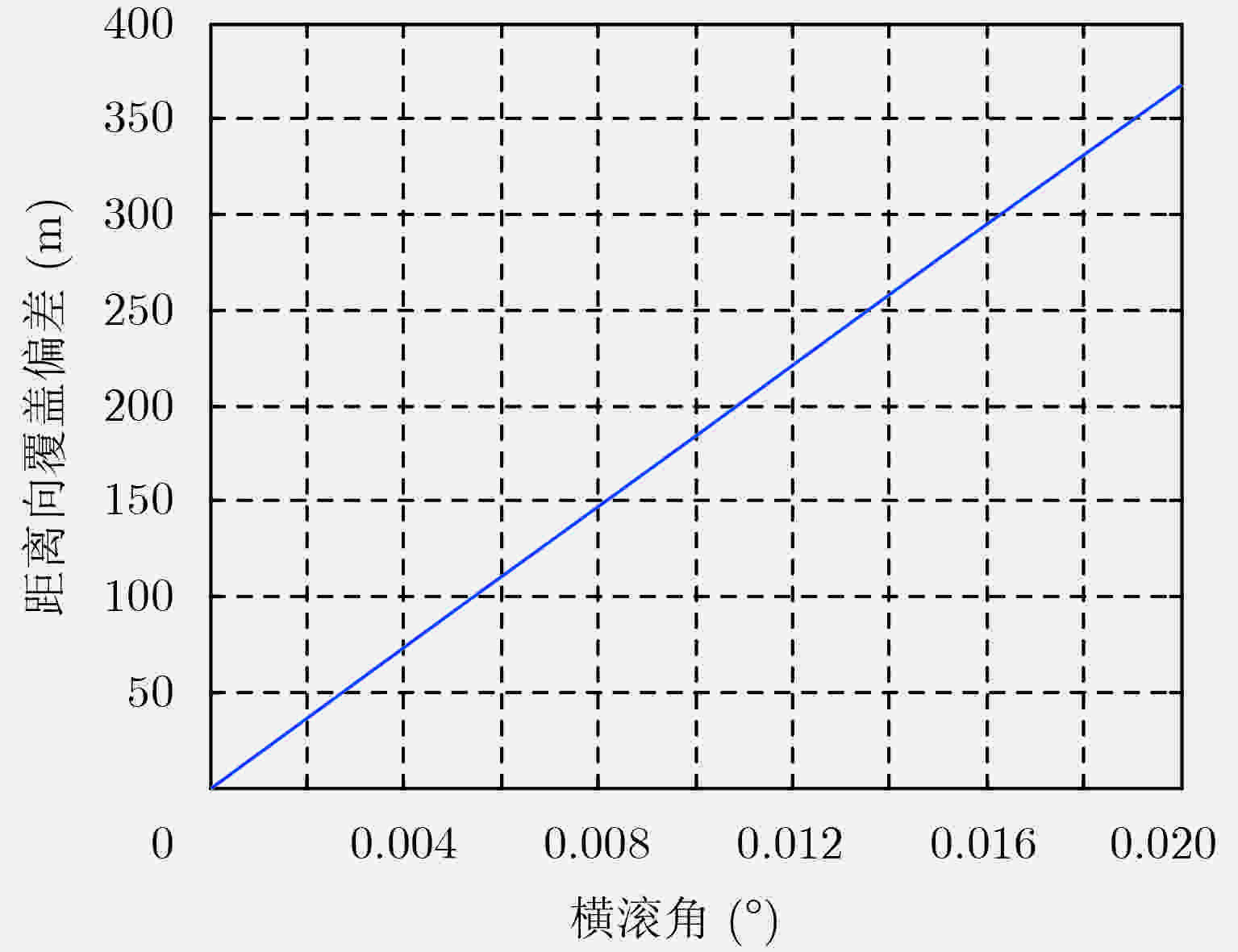
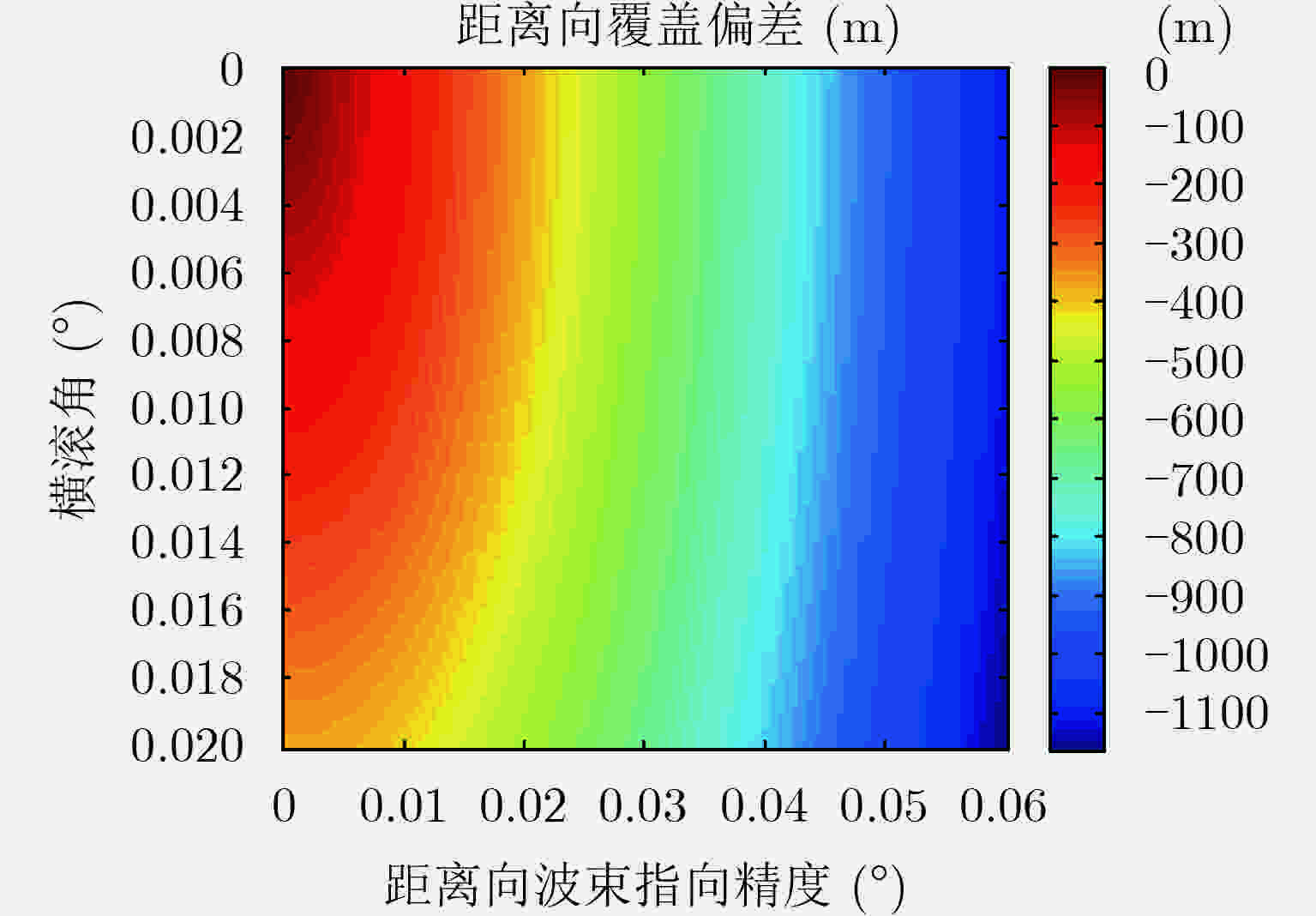
波束指向精度(°) 姿态控制精度(°) 0.01 0.02 0.01 260 411 0.02 411 520 0.03 582 663 0.04 759 823 0.05 938 991 0.06 1119 1164 -
[1] Curlander J C and Mcdonough R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991, 2077: 3–7. [2] Krieger G, Hajnsek I, Papathanassiou K P, et al. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) missions employing formation flying[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(5): 816–843. DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2038948 [3] Wang Wen-qin. GPS-based time & phase synchronization processing for distributed SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(3): 1040–1051. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5259181 [4] Krieger G and Younis M. Impact of oscillator noise in bistatic and multistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(3): 424–428. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.874164 [5] Rutman J. Characterization of phase and frequency instabilities in precision frequency sources: Fifteen years of progress[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1978, 66(9): 1048–1075. DOI: 10.1109/PROC.1978.11080 [6] Wang W Q, Cai J Y, and Yang Y W. Extracting phase noise of microwave and millimetre-wave signals by deconvolution[J]. IEE Proceedings-Science,Measurement and Technology, 2006, 153(1): 7–12. DOI: 10.1049/ip-smt:20050013 [7] Krieger G, Moreira A, Fiedler H, et al. TanDEM-X: A satellite formation for high-resolution SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3317–3341. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.900693 [8] Eineder M. Ocillator clock drift compensation in bistatic interferometric SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1449–1451. [9] Younis M, Metzig R, Krieger G, et al.. Performance prediction and verification for the synchronization link of TanDEM-X[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007: 5206–5209. [10] Younis M, Metzig R, and Krieger G. Performance prediction of a phase synchronization link for bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(3): 429–433. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.874163 [11] He Zhi-hua, Jin Guang-hu, Feng He, et al.. Phase synchronization method for distributed spaceborne fmcw SAR system[J]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium,Beijing,China, 2016: 1776–7379. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730924 [12] Marquez J, Mak K, Notter M, et al.. Design of passive non-cooperative spaceborne SAR payloads-challenges and strategies[C]. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1138–1143. [13] Zhang Yong-sheng, Liang Dian-nong, and Dong Zhen. Analysis of time and frequency synchronization errors in spaceborne parasitic InSAR system[C]. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 2006: 3047–3050. [14] Cherniakov M. Bistatic Radars: Emerging Technology[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. [15] Knedlik S, Loffeld O, and Gebhardt U. On position and attitude determination requirements for future bistatic SAR experiments[C]. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, Colorado, USA, 2006: 1216–1219. [16] D’Errico M and Moccia A. Attitude and antenna pointing design of bistatic radar formations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 949–960. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238748 [17] Wang Wen-qin. Clock timing jitter analysis and compensation for bistatic synthetic aperture radar systems[J]. Fluctuation and Noise Letters, 2007, 7(3): L341–L350. DOI: 10.1142/S0219477507003982 [18] 杨威, 李春升, 陈杰, 等. 时钟同步对星载多通道合成孔径雷达成像影响[J]. 电波科学学报, 2011, 26(4): 636–640. DOI: 10.13443/j.cjors.2011.04.012Yang Wei, Li Chun-sheng, Chen Jie, et al. Effects of time synchronization on image quality of spaceborne multi-channels SAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2011, 26(4): 636–640. DOI: 10.13443/j.cjors.2011.04.012 [19] 何志华. 分布式卫星SAR半实物仿真关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.He Zhi-hua. Study on key techniques of distributed spaceborne SAR hardware-in-the-loop simulation[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011. [20] 眭明. 星机双基地SAR同步技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2014.Sui Ming. Research on synchronization for spaceborne/ airborne bistatic hybrid SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronics Science and Technology of China, 2014. [21] 周鹏, 皮亦鸣, 戴永寿, 等. 星机双基地SAR的时间同步误差分析[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(6): 1467–1470Zhou Peng, Pi Yi-ming, Dai Yong-shou, et al. Analysis of time synchronization errors in spaceborne/airborne hybrid bistatic SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(6): 1467–1470 [22] Cumming I G and Wong F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005. [23] Wang Wen-qing. Inflight antenna pattern measurement for bistatic synthetic aperture radar systems[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2007, 6(11): 432–435. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2007.905013 [24] Geudtner D, Zink M, Gierull C, et al. Interferometric alignment of the X-SAR antenna system on the space shuttle radar topography mission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(5): 995–1006. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.1010887 [25] 张永俊, 黄海风, 张永胜, 等. 最大相干波束同步方法及其性能验证研究[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(8): 1564–1571. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.08.011Zhang Yong-jun, Huang Hai-feng, Zhang Yong-sheng, et al. Maximum coherenc illumination synchronization method and its performance verification[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(8): 1564–1571. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.08.011 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: