Modified Eigensubspace-based Approach for Radio-frequency Interference Suppression of SAR Image
-
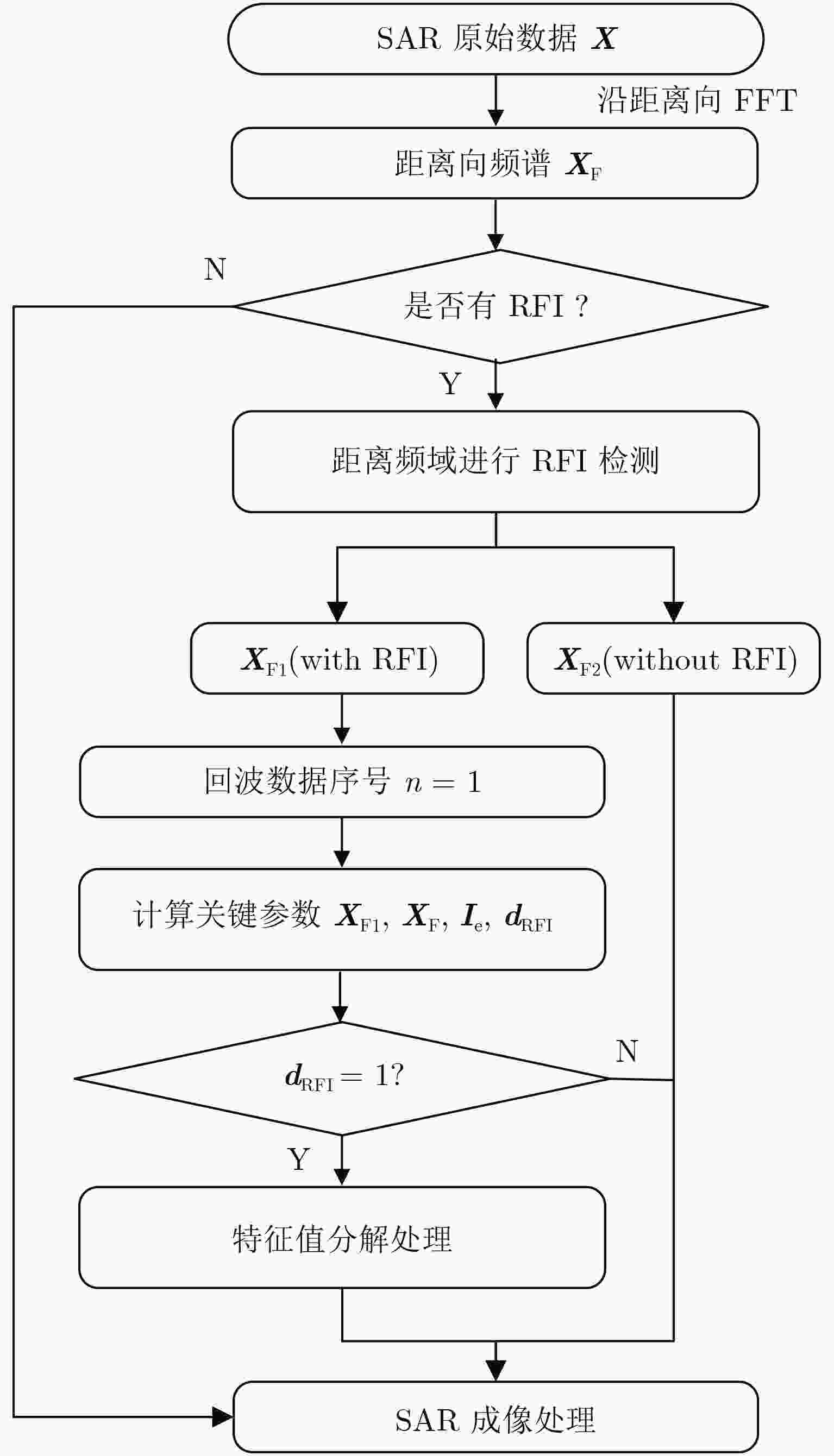
摘要: 射频干扰(the Radio Frequency Interference, RFI)会对有用信号产生不利影响,进而严重影响成像质量。该文提出了一种改进的基于特征子空间的合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)图像射频干扰抑制算法。相比传统算法,所提算法增加了专门用于射频干扰检测的预处理模块。在预处理阶段,分别在频域和时域对干扰所在的数据区域进行检测。在后处理阶段,只对检测到干扰的数据区域进行基于特征子空间的干扰抑制。相比传统算法,所提算法在保持图像细部结构方面效果更好,且避免了时域逐脉冲干扰抑制带来的巨大运算量,运算效率大幅提高。Abstract: Radio-Frequency Interference (RFI) adversely affects useful signals, thereby seriously affecting image quality. In this study, a modified eigensubspace-based approach for radio-frequency interference suppression of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is proposed. In the preprocessing stage of our proposed algorithm, RFI detection is conducted in both the frequency and time domains. Subsequently, we can only deal with the data containing the RFI via the traditional eigensubspace-based approach. Compared with the traditional eigensubspace-based approach, our proposed algorithm can function more efficiently and effectively.
-
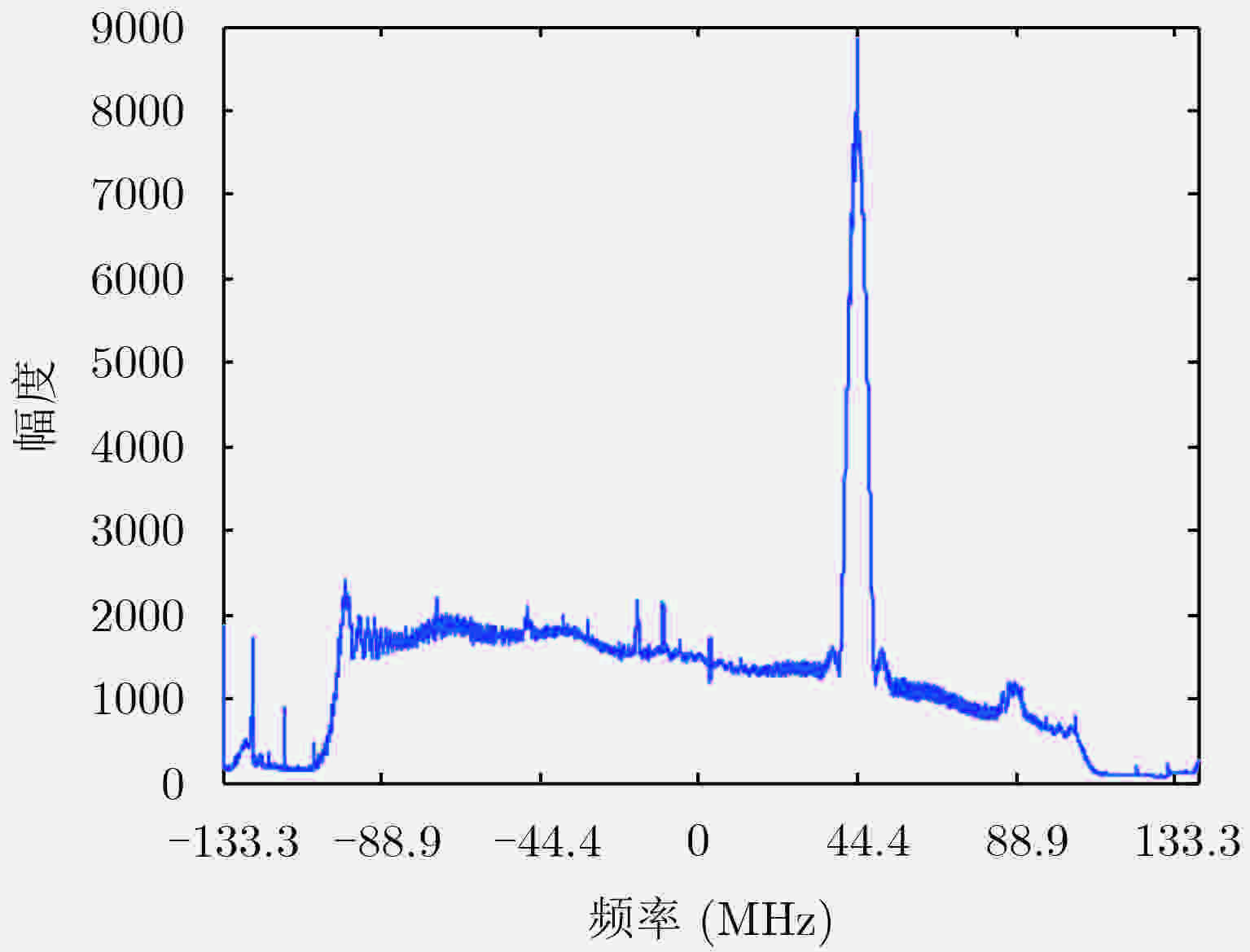
图 2 距离向频谱图
Figure 2. Average range direction spectrum of Fig. 1
表 1 仿真实验的主要系统参数
Table 1. Main system parameters for experiment
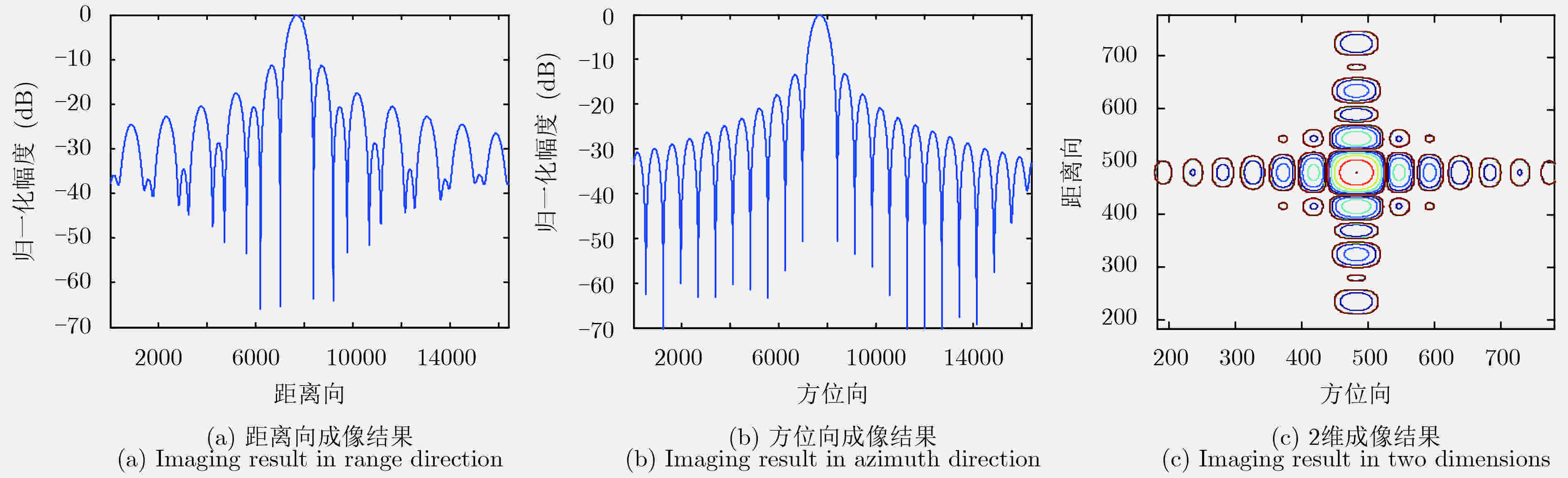
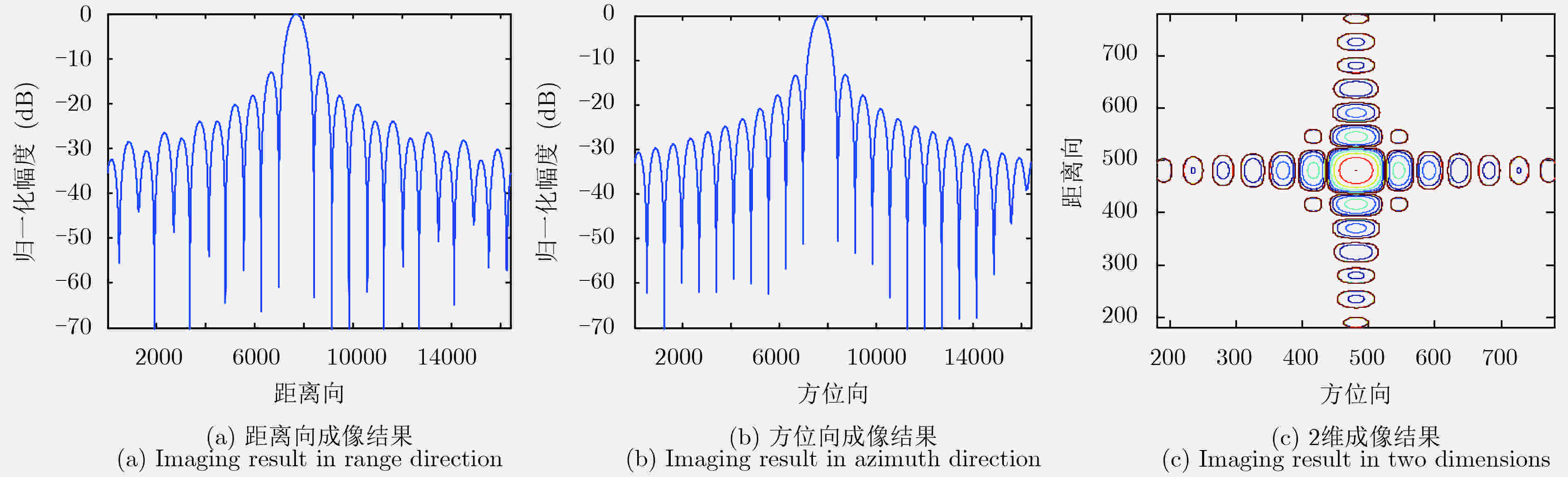
参数 数值 雷达工作频率(GHz) 1.3 景中心斜距(km) 20 雷达有效速度(m/s) 150 波束斜视角 正侧视 发射脉冲时宽(μs) 2.5 距离向带宽(MHz) 50 距离向采样频率(MHz) 70 天线长度(孔径)(m) 3.75 方位向采样率(PRF)(Hz) 112 表 2 距离向/方位向关键指标的仿真实验结果(dB)
Table 2. Simulation results of key indicators in range /azimuth direction (dB)
方法 PSLR(峰值旁瓣比) ISLR(积分旁瓣比) 传统方法 –11.3740/–13.2009 –8.2197/–10.0441 改进方法 –12.9144/–13.2255 –9.9132/–10.1378 表 3 机载实验系统的主要系统参数
Table 3. Main system parameters for experiment
参数 数值 雷达工作频率(GHz) 1.3 景中心斜距(km) 15.883 雷达有效速度(m/s) 130.099 波束斜视角 正侧视 发射脉冲时宽(μs) 10.4 距离向带宽(MHz) 210 距离向采样频率(MHz) 266.667 天线长度(孔径)(m) 1.36 方位向采样率(PRF)(Hz) 899.5393 -
[1] Goriachkin O V. Azimuth resolution of spaceborne P, VHF-band SAR[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 251–254. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.833777 [2] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015Deng Yun-kai, Zhao Feng-jun, and Wang Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [3] Meyer F J, Nicoll J B, and Doulgeris A P. Correction and characterization of radio frequency interference signatures in L-band synthetic aperture radar data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(10): 4961–24972. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2252469 [4] Nguyen L and Soumekh M. Suppression of radio frequency inteference (RFI) for synchronous impulse reconstruction ultra-wideband radar[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 5808, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XII, Orlando, Florida, USA, 2005: 178–184. [5] Ojowu Jr O O and Li Jian. RFI suppression for synchronous impulse reconstruction UWB radar using RELAX[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing Applications, 2013, 3(1): 33–46. [6] Lord R T and Inggs M R. Efficient RFI suppression in SAR using LMS adaptive filter integrated with range/Doppler algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 1999, 35(8): 629–630. DOI: 10.1049/el:19990437 [7] Luo X, Ulander L M H, Askne J, et al. RFI suppression in ultra-wideband SAR systems using LMS filters in frequency domain[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(4): 241–243. DOI: 10.1049/el:20010153 [8] Ulug B. An Algorithm for Sinusoidal Interference Reduction Using Iterative Maximum Likelihood Estimation Techniques[M]. 1992. [9] Buckreuss S. Filtering interferences from p-band SAR data[C]. Proceedings of EUSAR’98 Conference, Frie- drichshafen, Germany, 1998. [10] Ruan Hang, Ye Wei, Yin Can-bin, et al.. Wide band noise interference suppression for SAR with dechirping and eigensubspace filtering[C]. Proceedings of 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing, Dalian, China, 2010: 39–42. [11] Feng Jin, Zheng Hui-fang, Deng Yun-kai, et al. Application of subband spectral cancellation for SAR narrow-band interference suppression[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(2): 190–193. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2163150 [12] Zhou Feng, Tao Ming-liang, Bai Xue-ru, et al. Narrow-band interference suppression for SAR based on independent component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(10): 4952–4960. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2244605 [13] Zhou Feng and Tao Ming-liang. Research on methods for narrow-band interference suppression in synthetic aperture radar data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3476–3485. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2431916 [14] 郑慧芳, 杨淋, 冯锦. SAR窄带干扰抑制的子带子空间滤波技术研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(12): 2836–2842. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00201Zheng Hui-fang, Yang Lin, and Feng Jin. Research on the subband subspace filtering for narrow band interference suppression in SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2013, 35(12): 2836–2842. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00201 [15] Smola A J and Schölkopf B. A tutorial on support vector regression[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3): 199–222. DOI: 10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88 [16] Huang Guang-bin, Zhou Hong-ming, Ding Xiao-jian, et al. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,Part B(Cybernetics) , 2012, 42(2): 513–529. DOI: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2168604 [17] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 128–139.Zhou Zhi-hua. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 128–139. [18] Zhou Feng, Wu Ren-biao, Xing Meng-dao, et al. Eigensubspace-based filtering with application in narrow-band interference suppression for SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(1): 75–79. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.887033 [19] Li Ning, Wang R, Deng Yun-kai, et al. Autofocus correction of residual RCM for VHR SAR sensors with light-small aircraft[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 441–452. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2608423 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: