Orthogonal Polyphase Coded Waveform Design Method for Simultaneous Fully Polarimetric Radar
-
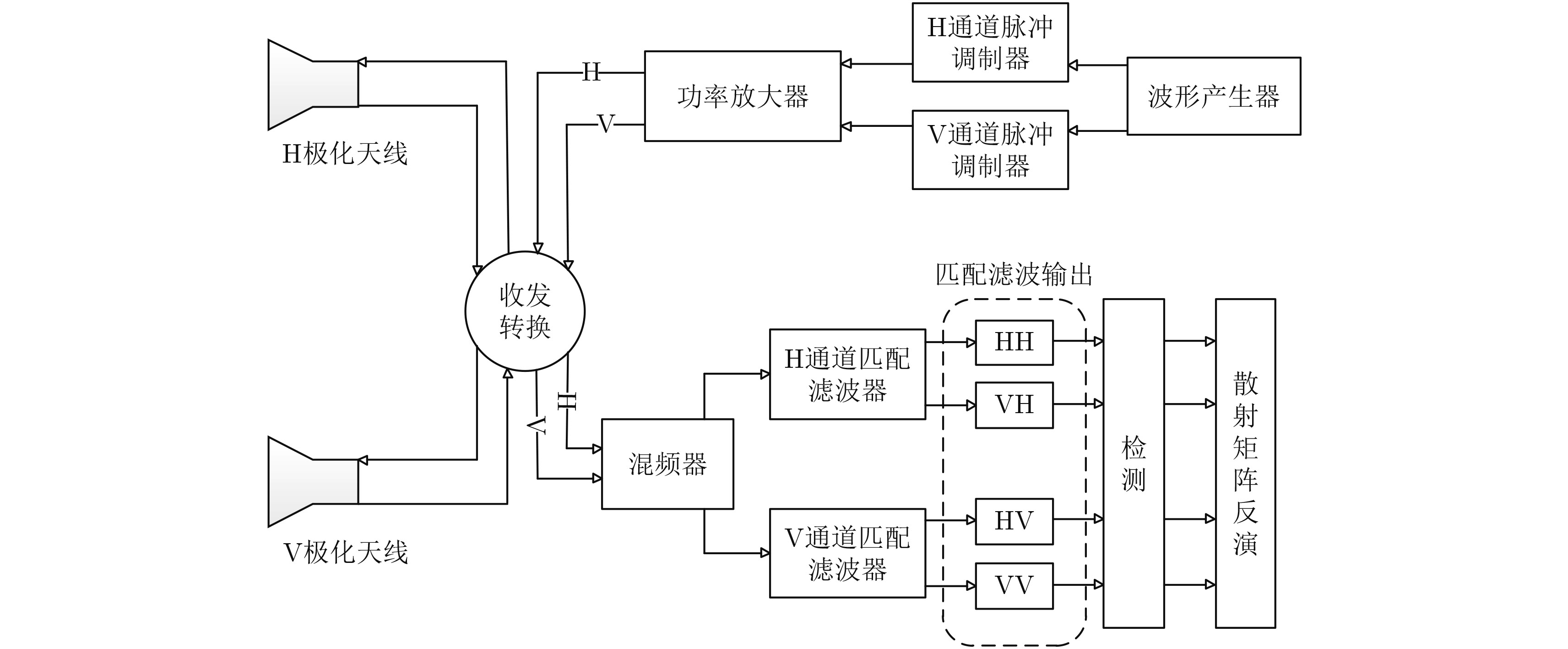
摘要: 为了获得精确的极化散射矩阵测量结果,同时全极化测量体制雷达对发射信号的正交性能提出了很高要求。传统的设计方法得到的正交多相编码波形正交性能受码长的限制,同时对多普勒频移比较敏感。该文提出一种具有较好多普勒容限的正交多相编码波形优化设计方法,针对目标匀速和匀加速运动状态,考虑波形的峰值旁瓣比和波形隔离度等指标,将波形设计问题转化为非线性优化问题,利用遗传算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,相比于Deng, Khan等人提出的编码,该文设计的正交多相编码波形具有更好的多普勒容限,同时峰值旁瓣比和正交性能提升约为1.5~2 dB,能够提高同时全极化测量体制雷达的测量精度。Abstract: To obtain an accurate polarization scattering matrix, simultaneous full polarization radar systems must transmit two signals. The performance of orthogonal polyphase codes designed by the traditional method is limited by the code length and is sensitive to Doppler frequency. In this paper, we propose a design method for orthogonal polyphase codes that have good Doppler tolerance. We consider the peak sidelobe level and isolation and transform the signal design problem into a nonlinear optimization problem, which we solve using a genetic algorithm. Our simulation results show that our proposed orthogonal polyphase codes have better Doppler tolerance and their peak sidelobe levels and orthogonal performances are 1.5~2 dB better than the codes designed by Deng or Khan. As such, the new design can improve the measurement accuracy of simultaneous full polarization radar systems.
-
Key words:
- Radar /
- Simultaneous full polarization /
- Orthogonal poly-phase codes /
- Doppler tolerance
-
表 2 N=40时算法仿真结果(dB)
Table 2. Simulation results of N=40 (dB)
表 3 N=512时算法仿真结果(dB)
Table 3. Simulation results of N=512 (dB)
算法 ${v_0} = 0$, α = 0 ${v_0}T = 0.8$, α = 0 ${v_0} = 0$, αT 2 = 0.9 PSL I PSL I PSL I 本文编码(G=64) –23.8 –22.9 –17.4 –17.1 –15.8 –15.7 Deng编码[5] –22.5 –21.7 –15.9 –15.5 –14.3 –14.0 表 1 编码波形优化设计主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters for optimization of poly-phase codes
参数 数值 载波频率f0 (MHz) 100 信号时宽T (ms) 0.128 信号带宽B (MHz) 1 相位编码数M 4 子序列数G 32 交叉概率 0.7 变异概率 0.1 种群数量 100 最大遗传代数 300 -
[1] Melvin L S and Banner G P. Radars for the detection and tracking of ballistic missiles, satellites, and planets[J]. Lincoln laboratory Journal, 2000, 12(2): 217–244. [2] Giuli D, Fossi M, and Facheris L. Radar target scattering matrix measurement through orthogonal signals[J]. Radar and Signal Processing,IEE Proceeding F, 1993, 140(4): 233–242. [3] 李永祯, 王雪松, 曾永虎, 等. 宽带雷达目标的瞬态极化时频分布表征[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2004, 2(6): 321–326Li Yong-zhen, Wang Xue-song, Zeng Yong-hu, et al. Time-Frequency Distribution Characterization of Radar Targets’ Instantaneous Polarization Scattering[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2004, 2(6): 321–326 [4] Babur G, Krasnov O, Yarovoy A, et al. Nearly Orthogonal Waveforms for MIMO FMCW Radar[J]. IEEE Transactions onAerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(3): 1426–1437. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6557996 [5] Deng H. Polyphase code design for orthogonal netted radar systems[J]. IEEE Trans on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(11): 3126–3135. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2004.836530 [6] Liu B. Orthogonal Discrete Frequency-Coding Waveform Set Design with Minimized Autocorrelation Sidelobes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(4): 1650–1657. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5310326 [7] Gao C, Teh K C, and Liu A. Orthogonal Frequency Diversity Waveform with Range-Doppler Optimization for MIMO Radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(10): 1201–1205. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2329944 [8] Wang Z, Tigrek F, Krasnov O, et al. Interleaved OFDM Radar for Simultaneous Polarimetric Measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(3): 2085–2099. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6237580 [9] Brunkow D A, George J, Bring V N, et al.. Recent data system and antenna upgrades to the CSU-CHILL radar[C]. AMS 32nd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA, 2005. [10] Xiao Jin-jun and Arye Nehorai. Joint Transmitter and Receiver Polarization Optimization for Scattering Estimation in Clutter[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(10): 4142–4147. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2022887 [11] Nadav Levanon and Eli Mozeson. Radar Signals[M]. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2004: 101–103. [12] Khan H A and Edwards D J. Doppler problems in orthogonal MIMO radar[C]. IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, NY, USA, April 24–27, 2006, Vol. 1: 24–27. [13] Frank R L. Polyphase Complementary-Codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1980, 26: 641–647. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.1980.1056272 [14] Lei Y J, Zhang S W, Li X W, et al.. MATLAB GA Algorithm Toolbox and It’s Applications[M]. Xi’an: Xidian Press, 2005: 66–70. [15] 刘波. MIMO雷达正交波形设计及信号处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2008.Liu Bo. Study on orthogonal waveform design and signal processing for MIMO radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2008. [16] 王璐璐, 王宏强, 王满喜, 等. 雷达目标检测的最优波形设计综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 487–498Wang Lulu, Wang Hongqiang, Wang Manxi, et al. An Overview of Radar Waveform Optimization for Target Detection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 487–498 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: