A Classification Method Based on Polarimetric Entropy and GEV Mixture Model for Intertidal Area of PolSAR Image
-
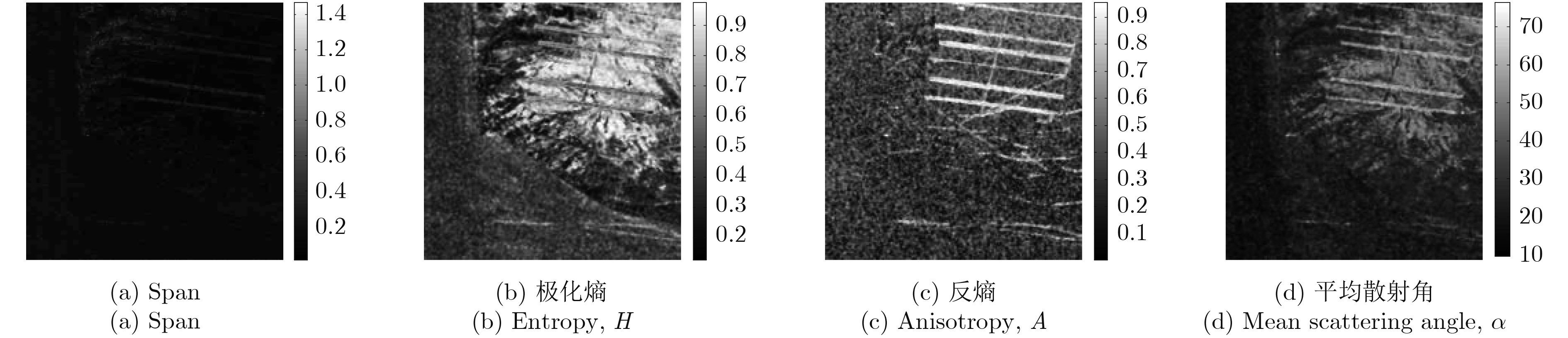
摘要: 该文提出了一种可用于全极化SAR的潮间带区域地物分类的方法。首先针对潮间带的特点对4种典型极化特征进行分析和筛选,得到一组最适合描述潮间带区域的多极化特征:极化熵(Polarimetric entropy)和反熵(Anisotropy)。然后基于对潮间带区域极化熵图像的散射特性分析和极值理论,利用广义极值分布(Generalized Extreme Value, GEV)描述其统计特性。在此基础上,提出了一种基于GEV混合模型的EM算法实现对潮间带地物分类的方法。最后,基于上海崇明东滩潮间带的Radarsat-2全极化数据进行了实验,实验结果证明了方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 多极化特征 /
- 广义极值分布(GEV) /
- 有限混合模型 /
- 潮间带地物分类
Abstract: This paper proposes a classification method for the intertidal area using quad-polarimetric synthetic aperture radar data. In this paper, a systematic comparison of four well-known multipolarization features is provided so that appropriate features can be selected based on the characteristics of the intertidal area. Analysis result shows that the two most powerful multipolarization features are polarimetric entropy and anisotropy. Furthermore, through our detailed analysis of the scattering mechanisms of the polarimetric entropy, the Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) distribution is employed to describe the statistical characteristics of the intertidal area based on the extreme value theory. Consequently, a new classification method is proposed by combining the GEV Mixture Models and the EM algorithm. Finally, experiments are performed on the Radarsat-2 quad-polarization data of the Dongtan intertidal area, Shanghai, to validate our method. -
图 6 GEVMM及其各分量与Gamma分布和log-normal分布的对比:(a)–(e)分别为5个分量与Gamma分布,log-normal分布以及对应标记区域的直方图的对比,其中蓝色区域为归一化直方图,绿线是GEV拟合结果,黑线是Gamma拟合结果,红线是log-normal拟合结果,(f)给出了GEVMM及其各个分量与研究区域直方图的对比结果,其中蓝线为归一化直方图,红线为GEVMM,绿线为GEVMM的各个分量
Figure 6. Fitness comparison among GEV distribution and Gamma distribution and Log-normal distribution of each component in GEVMM: (a)–(e) represent the five components of the GEVMM and the fitting results by the Gamma distribution and log-normal distribution for the histograms, which are marked as blue, the green lines represent the GEV fitting results, the black lines represent the most fitted Gamma distribution and the red lines represent the most fitted log-normal distribution, (f) shows the five components of GEVMN as green lines and the respective histograms as blue lines, the red line represents the final model
表 1 各极化特征的Michelson类间对比度
Table 1. Michelson between-region contrast of different features
极化特征 类间对比度 Span 0.4092 Entropy 0.7703 Anisotropy 0.9959 α 0.6757 表 2 GEV分布,Gamma分布和log-normal分布在每种类别中的拟合结果的AIC值
Table 2. The AIC values of the fitting results between the GEV distribution, the Gamma distribution and log-normal distribution
AIC 1 2 3 4 5 GEV 6.3988 4.0095 4.1105 4.7009 6.2093 Gamma 11.3878 9.3573 7.6928 9.0210 8.3989 log-normal 11.3878 9.3573 7.6928 9.0213 8.3997 -
[1] Lee Hoonyol, Chae Heesam, and Cho Seong-Jun. Radar backscattering of intertidal mudflats observed by Radarsat-1 SAR images and ground-based scatterometer experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1701–1711. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2084094 [2] Li Xiaofeng, Li Chunyan, Xu Qing, et al.. Sea surface manifestation of along-tidal-channel underwater ridges imaged by SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(8): 2467–2477. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2014154 [3] Won Eun-Sung, Ouchi Kazuo, and Yang Chan-Su. Extraction of underwater laver cultivation nets by SAR polarimetric entropy[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 231–235. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2199077 [4] Inglada J and Garello R. Underwater bottom topography estimation from SAR images by regulariziation of the inverse imaging mechanism[C]. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2000, 5: 1848–1850. [5] Kim Ji-Eun, Park Sang-Eun, Kim Duk-Jin, et al.. Recent advances in POL(in)SAR remote sensing & stress-change monitoring of wetlands with applications to the Sunchon Bay Tidal Flats[C]. Synthetic Aperture Radar European Conference (EUSAR), Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–3. [6] Park S E, Moon W M, and Kim D J. Estimation of surface roughness parameter in intertidal mudflat using airborne polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(4): 1022–1031. [7] Zhen Li, Heygster G, and Notholt J. Intertidal topographic maps and morphological changes in the German Wadden Sea between 1996–1999 and 2006–2009 from the Waterline method and SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(8): 3210–3224. [8] Kim Duk-Jin, Park Sang-Eun, Lee Hyo-Sung, et al.. Investigation of multiple frequency polarimetric SAR signal backscattering from tidal flats[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2009: 896–899. [9] Sine Skrunes, Camilla Brekke, and Torbjorn Eltoft. Characterization of marine surface slicks by Radarsat-2 multi-polarization features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5302–5319. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2287916 [10] Cloude S R and Pottier E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 [11] 邢艳肖, 张毅, 李宁, 等. 一种联合特征值信息的全极化SAR图像监督分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 217–227. doi: 10.12000/JR16019Xing Yanxiao, Zhang Yi, Li Ning, et al.. Polarimetric SAR image supervised classification method integrating eigenvalues[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 217–227. doi: 10.12000/JR16019 [12] 孙勋, 黄平平, 涂尚坦, 等. 利用多特征融合和集成学习的极化SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 692–700. doi: 10.12000/JR15132Sun Xun, Huang Pingping, Tu Shangtan, et al.. Polarimetric SAR image classification using multiple-feature fusion and ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 692–700. doi: 10.12000/JR15132 [13] 邵璐熠, 洪文. 基于二维极化特征的POLSAR图像决策分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 681–691. doi: 10.12000/JR16002Shao Luyi and Hong Wen. Dicision tree classification of POLSAR image based on two-dimensional polarimetric features[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 681–691. doi: 10.12000/JR16002 [14] Fukuda S. Relating polarimetric SAR image texture to the scattering entropy[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004: 2475–2478. [15] Cloude S R and Papathanassiou K P. Surface roughness and polarimetric entropy[C]. IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 1999: 2443–2445. [16] Cloude S R and Pottier E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [17] Won E S and Ouchi K. A novel method to estimate underwater marine cultivation area by using SAR polarimetric entropy[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2011: 2097–2100. [18] 滑文强, 王爽, 侯彪. 基于半监督学习的SVM-Wishart极化SAR图像分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138Hua Wen-qiang, Wang Shuang, and Hou Biao. Semi-supervised Learning for Classifcation of polarimetric SAR images based on SVM-Wishart[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138 [19] Doulgeris A P, Akbari V, and Eltoft T. Automatic PolSAR segmentation with the u-distribution and Markov random fields[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, 2012: 183–186. [20] Li Zhen, Heygester Georg, and Notholt J. The topography comparsion between the year 1999 and 2006 of German tidal flat wadden sea analyzing SAR images with waterline method[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2013: 2443–2446. [21] Li Zhen, Heygester G, and Notholt J. Topographic mapping of Wadden Sea with SAR images and waterlevel model data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2012: 2645–2648. [22] Li Zhen, Heygester Georg, and Notholt J. Topographic mapping of Wadden Sea, with SAR images and waterlevel model data[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2012: 2645–2648. [23] Wal D V D, Herman P M J, and Dool W V D. Characterisation of surface roughness and sediment texture of intertidal flats using ERS SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 98(1): 96–109. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.06.004 [24] Geng X M, Li X M, Velotto D, et al.. Study of the polarimetric characteristics of mud flats in an intertidal zone using C-and X-band spaceborne SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 176: 56–68. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.01.009 [25] Ding Hao, Huang Yong, and Liu Ningbo. Modeling of sea spike events with generalized extreme value distribution[C]. 2015 European Radar Conference, 2015: 113–116. [26] 李恒超. 合成孔径雷达图像统计特性分析及滤波算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2007.Li Heng-chao. Research on statistical analysis and despeckling algorithm of synthetic aperture radar images[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2007. [27] Embrechts P. Quantitative Risk Management[M]. Quantitative Risk Management, Princeton University Press, 2005: 67–73. [28] 熊太松. 基于统计混合模型的图像分割方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.Xiong Taisong. The study of image segmentation based on statistical mixture models[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013. [29] Prescott P and Walden A T. Maximum iikelihood estimation of the parameters of the generalized extreme-value distribution[J]. Biometrika, 1980, 67(3): 723–724. doi: 10.1093/biomet/67.3.723 [30] Peli E. Contrast in complex images[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(10): 2032–2040. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.7.002032 [31] Sine Skrunes, Camilla Brekke, and Torbjorn Eltoft. Characterization of marine surface slicks by Radarsat-2 multipolarization features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5302–5319. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2287916 [32] Akaike H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle[C]. 2nd International Symposium on Information Theory, Budapest, 1973: 267–281. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: