Convolutional Neural Network-based SAR Image Classification with Noisy Labels
-
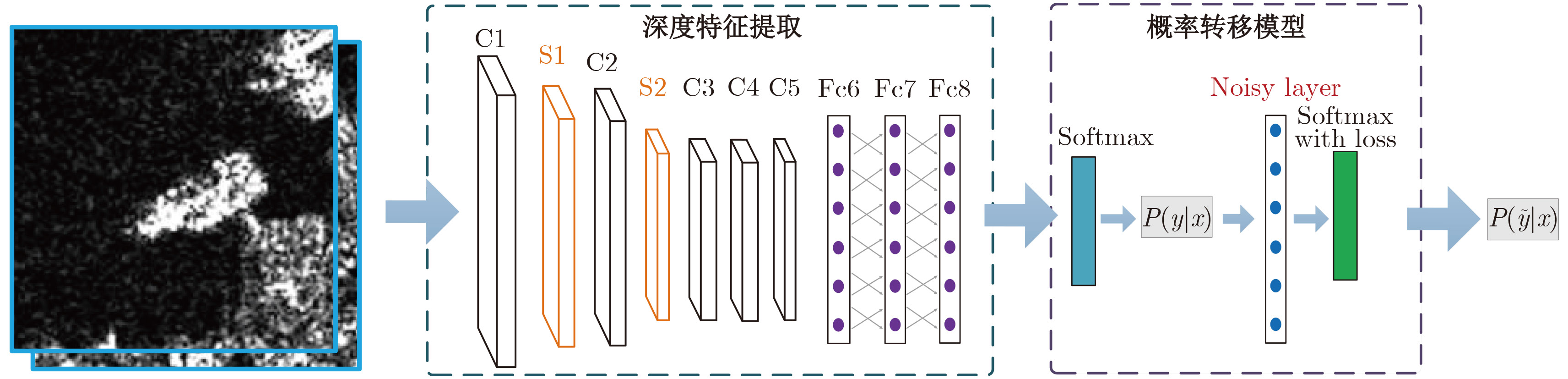
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Radar, SAR)图像分类是SAR图像解译的重要任务。以卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks, CNN)为代表的监督学习方法需要大量已标注的训练样本。然而对于SAR图像真值标注而言,由于SAR特殊的成像机理,图像受相干斑噪声、几何畸变和结构缺失等因素影响较为严重,非直观性较强,使得SAR图像人工标注非常困难,极易出错,从而导致CNN等模型学习和泛化性能急剧降低。针对这种含噪标记条件下的SAR图像分类问题,该文提出了一种基于概率转移模型的卷积神经网络(Probability Transition CNN, PTCNN)方法,该方法在传统CNN模型基础上,基于含噪标记与正确标记之间的概率转移模型,建立噪声标记转移层,这种新的卷积网络模型可潜在地校正错误标记,增强了含噪标记下分类模型的鲁棒性。与经典CNN等模型相比,在构建的16类SAR图像地物数据集和MSTAR数据集上的实验结果表明该文方法相比于经典CNN等模型,在保持SAR图像分类性能的同时具有较好的抗噪性,能够有效校正训练样本中的标注错误,从而降低了SAR图像有监督分类任务对样本标注质量的要求,具有一定的研究价值与应用前景。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像分类 /
- 监督学习 /
- 含噪标记 /
- 概率转移卷积神经网络(PTCNN) /
- 深度特征
Abstract: SAR image classification is an important task in SAR image interpretation. Supervised learning methods, such as the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), demand samples that are accurately labeled. However, this presents a major challenge in SAR image labeling. Due to their unique imaging mechanism, SAR images are seriously affected by speckle, geometric distortion, and incomplete structural information. Thus, SAR images have a strong non-intuitive property, which causes difficulties in SAR image labeling, and which results in the weakened learning and generalization performance of many classifiers (including CNN). In this paper, we propose a Probability Transition CNN (PTCNN) for patch-level SAR image classification with noisy labels. Based on the classical CNN, PTCNN builds a bridge between noise-free labels and their noisy versions via a noisy-label transition layer. As such, we derive a new CNN model trained with a noisily labeled training dataset that can potentially revise noisy labels and improve learning capacity with noisily labeled data. We use a 16-class land cover dataset and the MSTAR dataset to demonstrate the effectiveness of our model. Our experimental results show the PTCNN model to be robust with respect to label noise and demonstrate its promising classification performance compared with the classical CNN model. Therefore, the proposed PTCNN model could lower the standards required regarding the quality of image labels and have a variety of practical applications. -
表 1 TerraSAR-X卫星成像参数
Table 1. TerraSAR-X satellite imaging parameters
参数 武汉地区 上海交大闵行校区 产品类型 MGD Level 1b SSC Level 1b 成像模式 Spotlight Staring spotlight 图像尺寸/地距向(pixel)×方位向(pixel) 7500×8000 18299×7880 像元大小/地距向(m)×方位向(m) 1.60×1.27 0.71×0.17 表 2 SAR图像地物分类训练与测试数据集
Table 2. Training and testing set for SAR image land cover classification
地物分类数据集 训练集 测试集 港口 112 76 稀疏建筑区 247 169 池塘 168 112 桥梁 180 120 湿地 233 155 舰船 146 98 小溪 264 176 公路 91 61 运动场 127 85 沙滩 247 165 密集建筑区 274 182 河流 101 67 森林 62 42 道路 192 128 绿化带 461 307 水体 293 195 总计 3198 2138 表 3 用于训练和测试的MSTAR数据集
Table 3. Training and testing set of MSTAR database
MSTAR数据集 训练集 测试集 2S1 299 274 BMP2_C21 233 196 BRDM_2 298 274 BTR_60 256 195 BTR_70 233 196 D7 299 274 T62 299 273 T72_132 232 196 ZIL131 299 274 ZSU_23_4 299 274 总计 2747 2426 表 4 不同标记噪声比例下的地物分类准确率(%)
Table 4. Land cover classification accuracies of different label noise fraction (%)
噪声比例 PTCNN CNN Gabor+SVM 0 98.94 96.62 94.05 10 98.61 93.14 84.35 20 98.80 86.23 78.07 30 98.79 85.22 71.93 40 98.89 76.99 62.93 50 98.61 69.85 52.86 表 5 不同标记噪声比例下MSTAR车辆目标分类准确率(%)
Table 5. Classification accuracies of MSTAR vehicle target with different noise fractions (%)
噪声比例 PTCNN CNN PCA+SVM 0 97.76 96.92 84.67 10 97.00 93.48 71.39 20 96.76 89.48 63.07 30 96.00 84.40 56.80 40 95.43 80.36 51.90 50 95.30 68.68 41.92 -
[1] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, and Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012: 1097–1105. [2] He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al.. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [3] Chan T H, Jia K, Gao S, et al.. PCANet: A simple deep learning baseline for image classification?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5017–5032. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2475625 [4] Chen X, Xiang S, Liu C L, et al.. Vehicle detection in satellite images by hybrid deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1797–1801. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2309695 [5] Kalchbrenner N, Grefenstette E, and Blunsom P. A convolutional neural network for modelling sentences[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1404. 2188, 2014. [6] Kim Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1408. 5882, 2014. [7] Chen S and Wang H. SAR target recognition based on deep learning[C]. 2014 International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Shanghai, 2014: 541–547. [8] Wagner S. Combination of convolutional feature extraction and support vector machines for radar ATR[C]. 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, 2014: 1–6. [9] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract351.shtmlTian Zhuangzhuang, Zhan Ronghui, Hu Jiemin, et al.. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract351.shtml [10] Li X, Li C, Wang P, et al.. SAR ATR based on dividing CNN into CAE and SNN[C]. 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 2015: 676–679. [11] Ding J, Chen B, Liu H, et al.. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. [12] Zhao J, Guo W, Cui S, et al.. Convolutional neural network for SAR image classification at patch level[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, 2016: 945–948. [13] Chen S, Wang H, Xu F, et al.. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 [14] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, et al.. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami Beach, Florida, 2009: 248–255. [15] Zhu X and Wu X. Class noise vs. attribute noise: A quantitative study[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2004, 22(3): 177–210. doi: 10.1007/s10462-004-0751-8 [16] Chang C C and Lin C J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2011, 2(3): 27. [17] Jia Y, Shelhamer E, Donahue J, et al.. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, 2014: 675–678. [18] Hecht-Nielsen R. Theory of the backpropagation neural network[C]. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 1989: 593–605. [19] Bottou L. Stochastic gradient learning in neural networks[J]. Proceedings of Neuro-Nımes, 1991, 91(8). [20] Cui S, Dumitru C O, and Datcu M. Semantic annotation in earth observation based on active learning[J]. International Journal of Image and Data Fusion, 2014, 5(2): 152–174. doi: 10.1080/19479832.2013.858778 [21] Popescu A A, Gavat I, and Datcu M. Contextual descriptors for scene classes in very high resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 80–84. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2160838 [22] Singh J, Cui S, Datcu M, et al.. A survey of density estimation for SAR images[C]. 20th European of Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), 2012: 2526–2530. [23] Ross T D, Worrell S W, Velten V J, et al.. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set[C]. Aerospace/Defense Sensing and Controls. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1998: 566–573. [24] Wu T, Chen X, Ruang X W, et al.. Study on SAR target recognition based on support vector machine[C]. 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, 2009: 856–859. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: