SAR Target Recognition with Feature Fusion Based on Stacked Autoencoder
-
摘要: 该文提出了一种基于栈式自编码器(Stacked AutoEncoder, SAE)特征融合的合成孔径雷达(Synthetic Aperture Rader, SAR)图像车辆目标识别算法。首先,该算法提取了SAR图像的25种基线特征(baseline features)和局部纹理特征(Three-Patch Local Binary Patterns, TPLBP)。然后将特征串联输入SAE网络中进行融合,采用逐层贪婪训练法对网络进行预训练。最后利用softmax分类器微调网络,提高网络融合性能。另外,该文提取了SAR图像的Gabor纹理特征,进行了不同特征之间的融合实验。结果表明基线特征与TPLBP特征冗余性小,互补性好,融合后的特征区分性大。与直接利用SAE, CNN (Convolutional Neural Network)进行目标识别的算法相比,基于SAE的特征融合算法简化了网络结构,提高了识别精度与识别效率。基于MSTAR数据集的10类目标分类精度达95.88%,验证了算法的有效性。Abstract: A feature fusion algorithm based on a Stacked AutoEncoder (SAE) for Synthetic Aperture Rader (SAR) imagery is proposed in this paper. Firstly, 25 baseline features and Three-Patch Local Binary Patterns (TPLBP) features are extracted. Then, the features are combined in series and fed into the SAE network, which is trained by a greedy layer-wise method. Finally, the softmax classifier is employed to fine tune the SAE network for better fusion performance. Additionally, the Gabor texture features of SAR images are extracted, and the fusion experiments between different features are carried out. The results show that the baseline features and TPLBP features have low redundancy and high complementarity, which makes the fused feature more discriminative. Compared with the SAR target recognition algorithm based on SAE or CNN (Convolutional Neural Network), the proposed method simplifies the network structure and increases the recognition accuracy and efficiency. 10-classes SAR targets based on an MSTAR dataset got a classification accuracy up to 95.88%, which verifies the effectiveness of the presented algorithm.
-
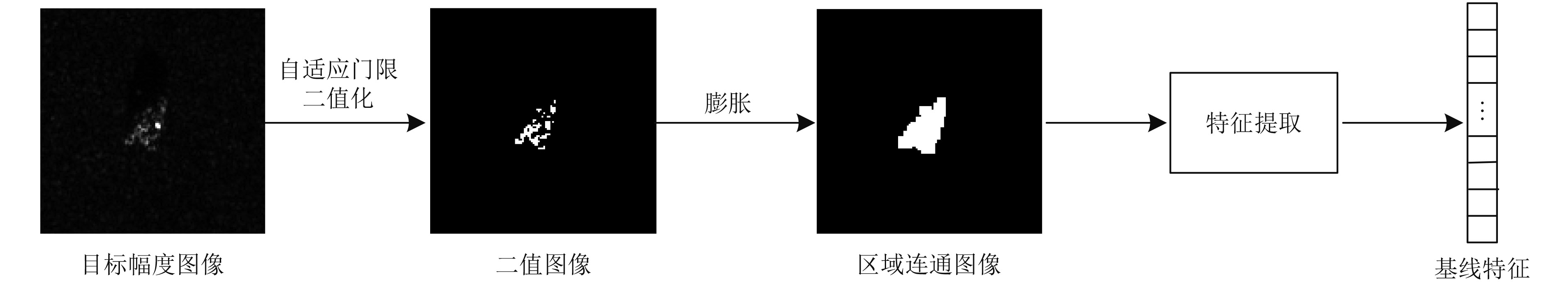
表 1 基线特征
Table 1. The selected baseline features
序号 特征 序号 特征 1 连通区域数 14 极值 2 面积 15 等圆直径 3 质心 16 充实度 4 边界矩形 17 扩展度 5 主轴长 18 周长 6 短轴长 19 重心 7 离心率 20 平均密度 8 方向 21 最小密度 9 凸多边形 22 最大密度 10 凸多边形数 23 子阵列索引 11 凸多边形面积 24 像素索引 12 填充面积 25 像素坐标 13 欧拉数 表 2 10类目标训练、测试样本数
Table 2. Number of training samples and test samples
Targets 17° 15° BMP2 233 196 BTR70 233 196 T72 232 196 BTR60 256 195 2S1 299 274 BRDM2 298 274 D7 299 274 T62 299 273 ZIL131 299 274 ZSU234 299 274 总计 2747 2426 表 3 特征分类结果
Table 3. Classification accuracy of features
目标类别 基线特征 TPLBP特征 融合后特征 BMP2 69.90 72.96 89.80 BTR70 82.14 73.98 91.33 T72 87.76 81.63 93.37 BTR60 83.59 71.79 91.79 2S1 98.54 97.08 98.54 BRDM2 83.58 99.27 96.72 D7 94.89 97.08 99.27 T62 94.87 96.70 97.07 ZIL131 98.91 99.27 99.64 ZSU234 97.08 96.72 96.35 平均精度(%) 90.19 90.40 95.88 表 4 不同特征融合分类结果
Table 4. Classification accuracy of different features
目标类别 基线+Gabor Gabor+TPLBP 基线+TPLBP BMP2 85.20 83.16 89.80 BTR70 89.29 92.35 91.33 T72 96.94 96.43 93.37 BTR60 92.82 94.36 91.79 2S1 86.13 70.44 98.54 BRDM2 97.81 98.91 96.72 D7 90.11 93.43 99.27 T62 98.91 91.94 97.07 ZIL131 98.91 98.91 99.64 ZSU234 98.54 99.64 96.35 平均精度(%) 93.65 92.00 95.88 表 5 不同算法识别精度对比
Table 5. Classification accuracy comparison of different algorithms
表 6 不同算法训练时间与测试时间对比
Table 6. Training time and testing time of different methods
算法 训练时间(s) 测试时间(s) SAE 907.5 0.154 本文算法 114.1 0.017 -
[1] Jiang Y, Chen J, and Wang R. Fusing local and global information for scene classification[J].Optical Engineering, 2010, 49(4): 047001–047001-10. doi: 10.1117/1.3366666 [2] Liu Z and Liu C. Fusion of color, local spatial and global frequency information for face recognition[J].Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(8): 2882–2890. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2010.03.003 [3] Mohamed R and Mohamed M. A Hybrid feature extraction for satellite image segmentation using statistical global and local feature[C]. Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference on Information & Communication Technologies 2015. Springer International Publishing, 2016: 247–255. [4] Zou J, Li W, Chen C, et al. Scene classification using local and global features with collaborative representation fusion[J].Information Sciences, 2016, 348: 209–226. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.02.021 [5] 王大伟, 陈定荣, 何亦征. 面向目标识别的多特征图像融合技术综述[J]. 航空电子技术, 2011, 42(2): 6–12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDZ201102003.htmWang Dawei, Chen Dingrong, and He Yizheng. A survey of feature-level image fusion based on target recognition[J].Avionics Technology, 2011, 42(2): 6–12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDZ201102003.htm [6] 王璐, 张帆, 李伟, 等. 基于Gabor滤波器和局部纹理特征提取的SAR目标识别算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 658–665. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract308.shtmlWang Lu, Zhang Fan, Li Wei, et al. A method of SAR target recognition based on Gabor filter and local texture feature extraction[J].Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 658–665. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract308.shtml [7] Lin C, Peng F, Wang B H, et al. Research on PCA and KPCA self-fusion based MSTAR SAR automatic target recognition algorithm[J].Journal of Electronic Science Technology, 2012, 10(4): 352–357. [8] Huan R, Liang R, and Pan Y. SAR target recognition with the fusion of LDA and ICA[C]. 2009 International Conference on Information Engineering and Computer Science, IEEE, Wuhan, China, 2009: 1–5. [9] Chaudhary M D and Upadhyay A B. Fusion of local and global features using stationary wavelet transform for efficient content based image retrieval[C]. 2014 IEEE Students' Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), IEEE, Bhopal, India, 2014: 1–6. [10] Hinton G E and Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J].Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504–507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [11] Geng J, Fan J, Wang H, et al. High-Resolution SAR image classification via deep convolutional autoencoders[J].IEEE Geoscience &Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(11): 1–5. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2015IGRSL.12.2351G [12] Chen Y, Lin Z, Zhao X, et al. Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations &Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(6): 2094–2107. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264564342_Deep_Learning-Based_Classification_of_Hyperspectral_Data [13] Sun Z, Xue L, and Xu Y. Recognition of SAR target based on multilayer auto-encoder and SNN[J].International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, 2013, 9(11): 4331–4341. http://www.ijicic.org/ijicic-12-11029.pdf [14] Chen Y W and Lin C J. Combining SVMs with Various Feature Selection[M]. In Feature Extraction: Foundations and Applications, Guyon I, Gunn S, Nikravesh M, and Zadeh L A Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2006: 315–324. [15] Chen Y W. Combining SVMs with various feature selection strategies[D]. [Master. dissertation], National Taiwan University, 2005. [16] El Darymli K, Mcguire P, Gill E W, et al. Characterization and statistical modeling of phase in single-channel synthetic aperture radar imagery[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 2071–2092. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140711 [17] Kapur J N, Sahoo P K, and Wong A K C. A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram[J].Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1985, 29(3): 273–285. doi: 10.1016/0734-189X(85)90125-2 [18] Mathworks. Morphology Fundamentals: Dilation and Erosion[OL]. http://tinyurl.com/q6zf. [19] Wolf L, Hassner T, and Taigman Y. Descriptor based methods in the wild[C]. Workshop on Faces in Real-Life Images: Detection, Alignment, and Recognition, 2008. [20] 施彦, 韩力群, 廉小亲. 神经网络设计方法与实例分析[M]. 北京: 北京邮电大学出版社, 2009: 32–108.Shi Yan, Han Liqun, and Lian Xiao qin. Neural Network Design and Case Analysis[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2009: 32–108. [21] Maaten L and Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2579–2605. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.457.7213 [22] Hu F, Zhang P, Yang R, et al. SAR target recognition based on Gabor filter and sub-block statistical feature[C]. 2009 IET International Radar Conference, 2009: 1–4. [23] Song H, Ji K, Zhang Y, et al. Sparse Representation-based SAR image target classification on the 10-class MSTAR data set[J].Applied Sciences, 2016, 6(1): 26. doi: 10.3390/app6010026 [24] Morgan D A. Deep convolutional neural networks for ATR from SAR imagery[C]. SPIE Defense Security. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2015: 94750F-94750F-13. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: