- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Proofreading [3rd]
| Citation: | LI Hang, GUO Qichang, BU Xiangxi, et al. Time-varying baseline estimation algorithm for small UAVs-borne distributed tomosar[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25268 |
Time-varying Baseline Estimation Algorithm for Small UAVs-borne Distributed TomoSAR
DOI: 10.12000/JR25268 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25268
More Information-
Abstract
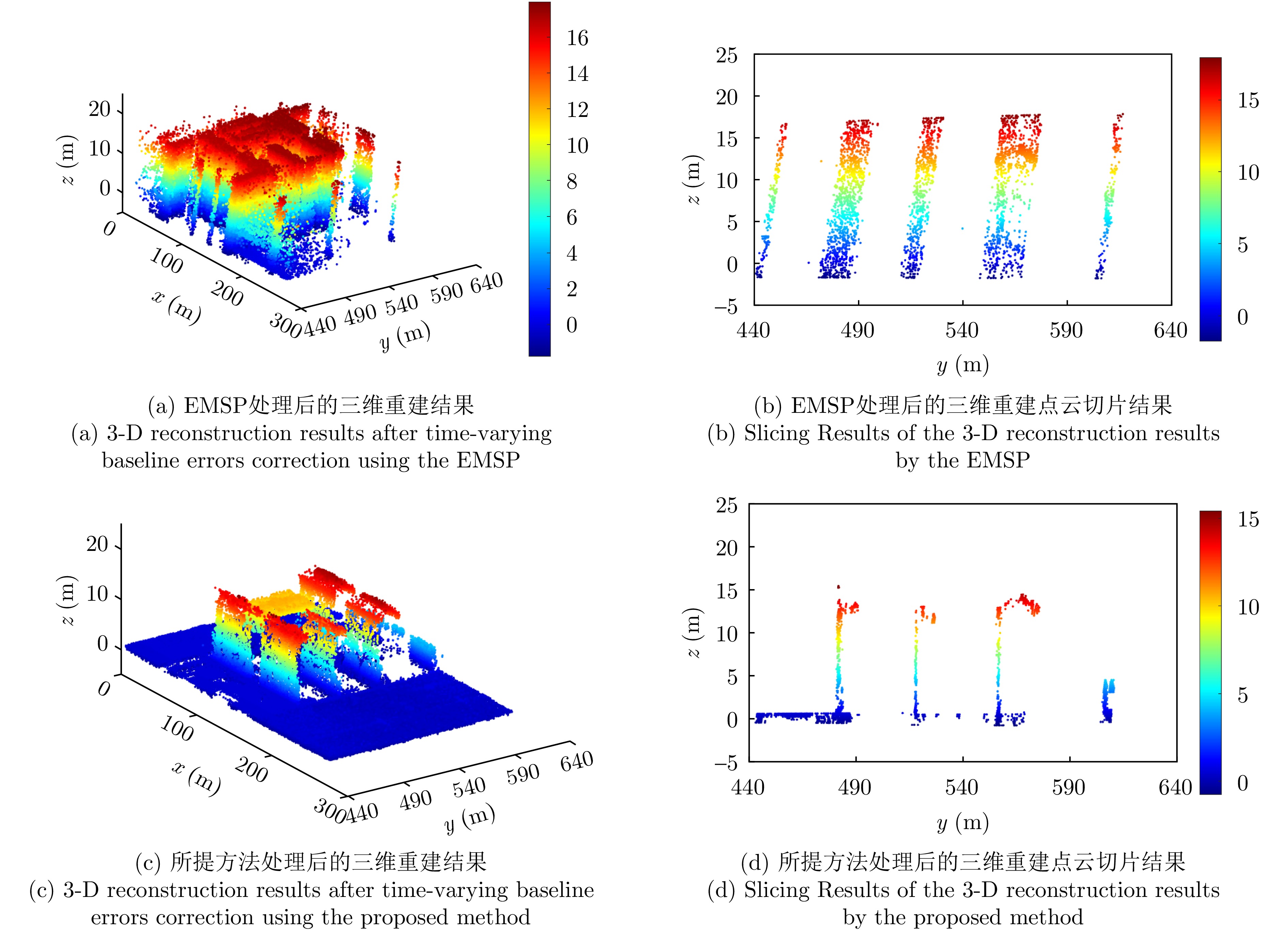
Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-borne distributed tomographic synthetic aperture radar (TomoSAR) systems exhibit remarkable residual time-varying baseline errors due to the limited precision of the position and orientation system on small UAV platforms. These errors critically degrade the performance of three-Dimensional (3D) target reconstruction. Compared with airborne repeat-pass 3D Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), distributed TomoSAR mounted on small UAVs imposes stricter compensation accuracy requirements for time-varying baseline errors because of the altitude constraints of the carrying platform. Under the conditions of low signal-to-noise ratio and substantial time-varying baseline errors, existing estimation methods often fail to provide stable and reliable results. In this paper, a two-step time-varying baseline error estimation method based on image azimuth displacement is proposed. The method sequentially estimates the low-frequency component through the co-registration of the master and slave images and the high-frequency component using a multisquint algorithm. Iterative refinement is applied to enhance estimation accuracy. The experimental results obtained from real C-band small UAV-borne distributed TomoSAR data demonstrate that, compared with the enhanced multisquint processing method, the proposed method considerably reduces the root mean square of differential interferometric phases across most channels, thereby effectively improving interchannel coherence. In addition, the elevation-direction standard deviation of the reconstructed point cloud is reduced from 5.16 to 1.33 m, and the height reconstruction error of building targets is less than 0.5 m, validating the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method. -

-
References
[1] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098.[2] LIN Yuqing, QIU Xiaolan, and DING Chibiao. TomoSAR three-dimensional image restoration in urban area by multipath exploitation[C]. IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 2031–2035. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10642195.[3] WANG Yan, DING Zegang, LI Linghao, et al. First demonstration of single-pass distributed SAR tomographic imaging with a P-band UAV SAR prototype[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5238618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3221859.[4] BUDILLON A, FERRAIOLI G, JOHNSY A C, et al. TomoSAR application for early warning in infrastructure health monitoring[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 3621–3624. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898674.[5] YANG Wenyu, VITALE S, AGHABABAEI H, et al. A deep learning solution for height inversion on forested areas using single and dual polarimetric TomoSAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 2505605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3322782.[6] PARDINI M, CAZCARRA-BES V, and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. TomoSAR mapping of 3D forest structure: Contributions of L-band configurations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(12): 2255. doi: 10.3390/rs13122255.[7] SHAHZAD M, MAURER M, FRAUNDORFER F, et al. Buildings detection in VHR SAR images using fully convolution neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1100–1116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864716.[8] SHAKHATREH H, SAWALMEH A H, AL-FUQAHA A, et al. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs): A survey on civil applications and key research challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 48572–48634. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909530.[9] WANG Huan, LIU Yunlong, LI Yanlei, et al. Improved real-time SPGA algorithm and hardware processing architecture for small UAVs[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(13): 2232. doi: 10.3390/rs17132232.[10] BRANCATO V, JÄGER M, SCHEIBER R, et al. A motion compensation strategy for airborne repeat-pass SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1580–1584. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2848596.[11] REIGBER A. Correction of residual motion errors in airborne SAR interferometry[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(17): 1083–1084. doi: 10.1049/el:20010724.[12] REIGBER A and SCHEIBER R. Airborne differential SAR interferometry: First results at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(6): 1516–1520. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.814610.[13] REIGBER A, PRATS P, and MALLORQUI J J. Refined estimation of time-varying baseline errors in airborne SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(1): 145–149. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.860482.[14] ZHONG Xuelian, XIANG Maosheng, YUE Huanyin, et al. Algorithm on the estimation of residual motion errors in airborne SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1311–1323. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2249665.[15] CAO Ning, LEE H, ZAUGG E, et al. Estimation of residual motion errors in airborne SAR interferometry based on time-domain backprojection and multisquint techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2397–2407. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2779852.[16] WANG Huiqiang, FU Haiqiang, ZHU Jianjun, et al. Correction of time-varying baseline errors based on multibaseline airborne interferometric data without high-precision DEMs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9307–9318. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3041056.[17] DE MACEDO K A C, SCHEIBER R, and MOREIRA A. An autofocus approach for residual motion errors with application to airborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3151–3162. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.924004.[18] LUOMEI Yixiang and XU Feng. Real-time implementation of segmental aperture imaging algorithm for multirotor-borne minisar[C]. IGARSS 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 4529–4532. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883374.[19] FU Haiqiang, ZHU Jianjun, WANG Changcheng, et al. A wavelet decomposition and polynomial fitting-based method for the estimation of time-varying residual motion error in airborne interferometric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 49–59. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2727076.[20] TEBALDINI S, ROCCA F, MARIOTTI D’ALESSANDRO M, et al. Phase calibration of airborne tomographic SAR data via phase center double localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1775–1792. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2488358.[21] ZENG Guobing, XU Huaping, WANG Yuan, et al. A novel method for airborne SAR tomography baseline error correction driven by small baseline interferometric phase[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5225013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3478055.[22] IMPERATORE P and FORNARO G. Joint phase-screen estimation in airborne multibaseline SAR tomography data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4412614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3446186.[23] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Demonstration of super-resolution for tomographic SAR imaging in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3150–3157. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2177843.[24] BUCKREUSS S. Motion compensation for airborne SAR based on inertial data, RDM and GPS[C]. IGARSS '94 - 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 1994: 1971–1973. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1994.399626.[25] CHEN Jianlai, XING Mengdao, YU Hanwen, et al. Motion compensation/autofocus in airborne synthetic aperture radar: A review[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(1): 185–206. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2021.3113982.[26] 张福博. 阵列干涉SAR三维重建信号处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015: 34–37.ZHANG Fubo. Research on Signal Processing of 3-D reconstruction in Linear Array Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015: 34-37.[27] REIGBER A and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Correction of residual motion errors in airborne repeat-pass interferometry[C]. IGARSS 2001. Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future. Proceedings. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (Cat. No.01CH37217), Sydney, Australia, 2001: 3077–3079. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2001.978260.[28] CHENG Kexin and DONG Youqiang. An image compensation-based range-Doppler model for SAR high-precision positioning[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(19): 8829. doi: 10.3390/app14198829.[29] XU Bing, LI Zhiwei, WANG Qijie, et al. A refined strategy for removing composite errors of SAR interferogram[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 143–147. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2250903.[30] 邓袁. 机载重轨干涉SAR高精度配准算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2014: 5–7.DENG Yuan. Research on Highly Precise Registration Algorithm of Airborne Repeat-Pass Interferometric SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014: 5–7.[31] PRATS P, SCHEIBER R, REIGBER A, et al. Estimation of the surface velocity field of the Aletsch glacier using multibaseline airborne SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 419–430. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2004277.[32] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1 -norm regularization—the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117. -
Proportional views

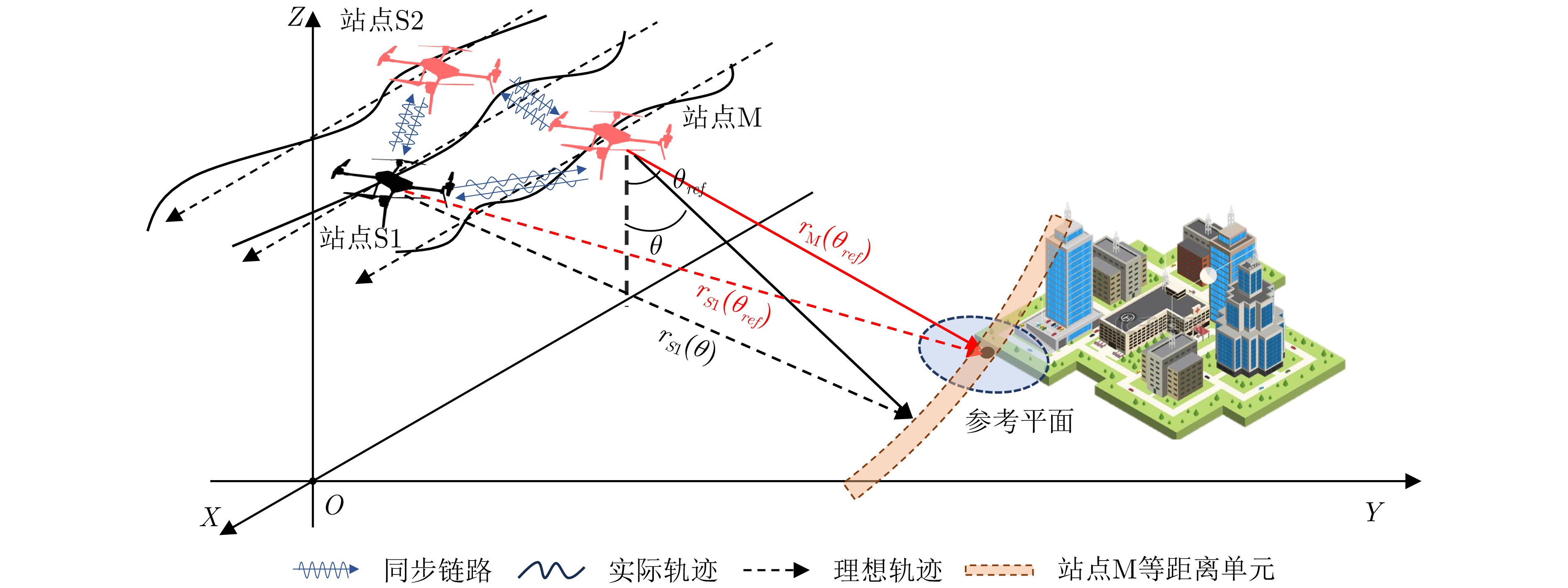
- Figure 1. Distributed TomoSAR imaging geometry
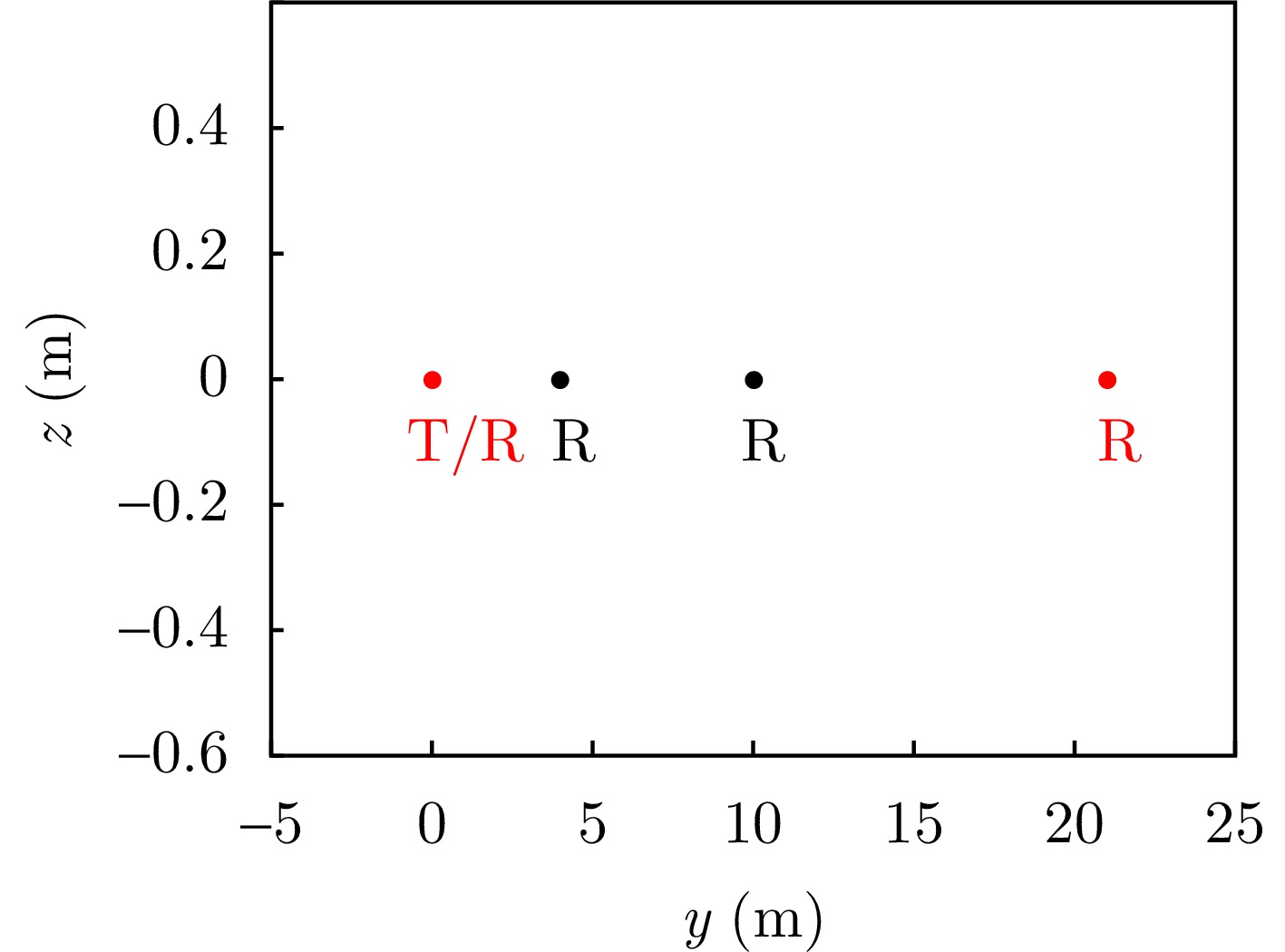
- Figure 2. Relative positions of transceiver sites in the simulation
- Figure 3. Probability of correct reconstruction vs. site location measurement errors
- Figure 4. Processing results of the EMSP method under different sub-aperture bandwidth
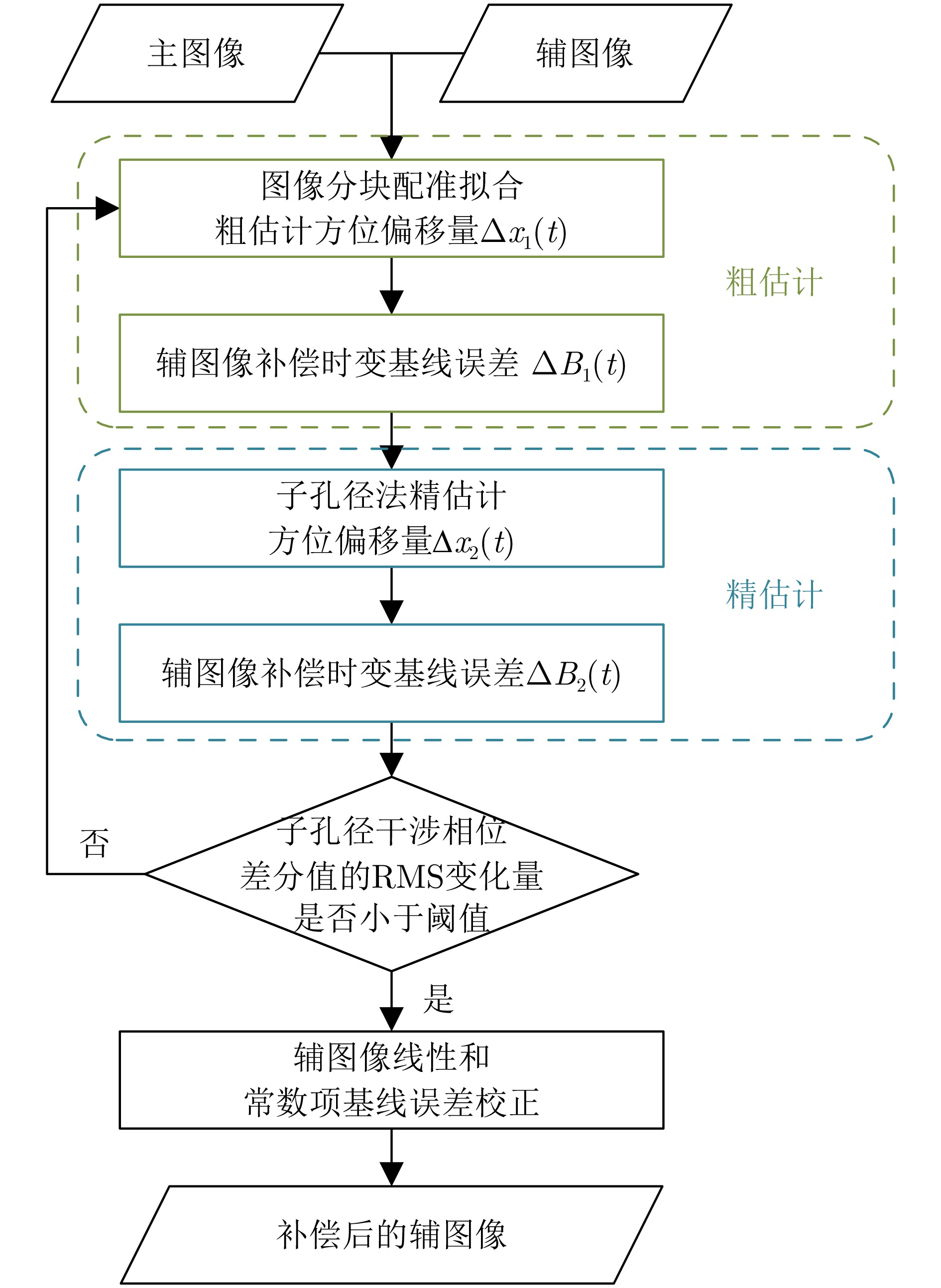
- Figure 5. Flowchart of the proposed method
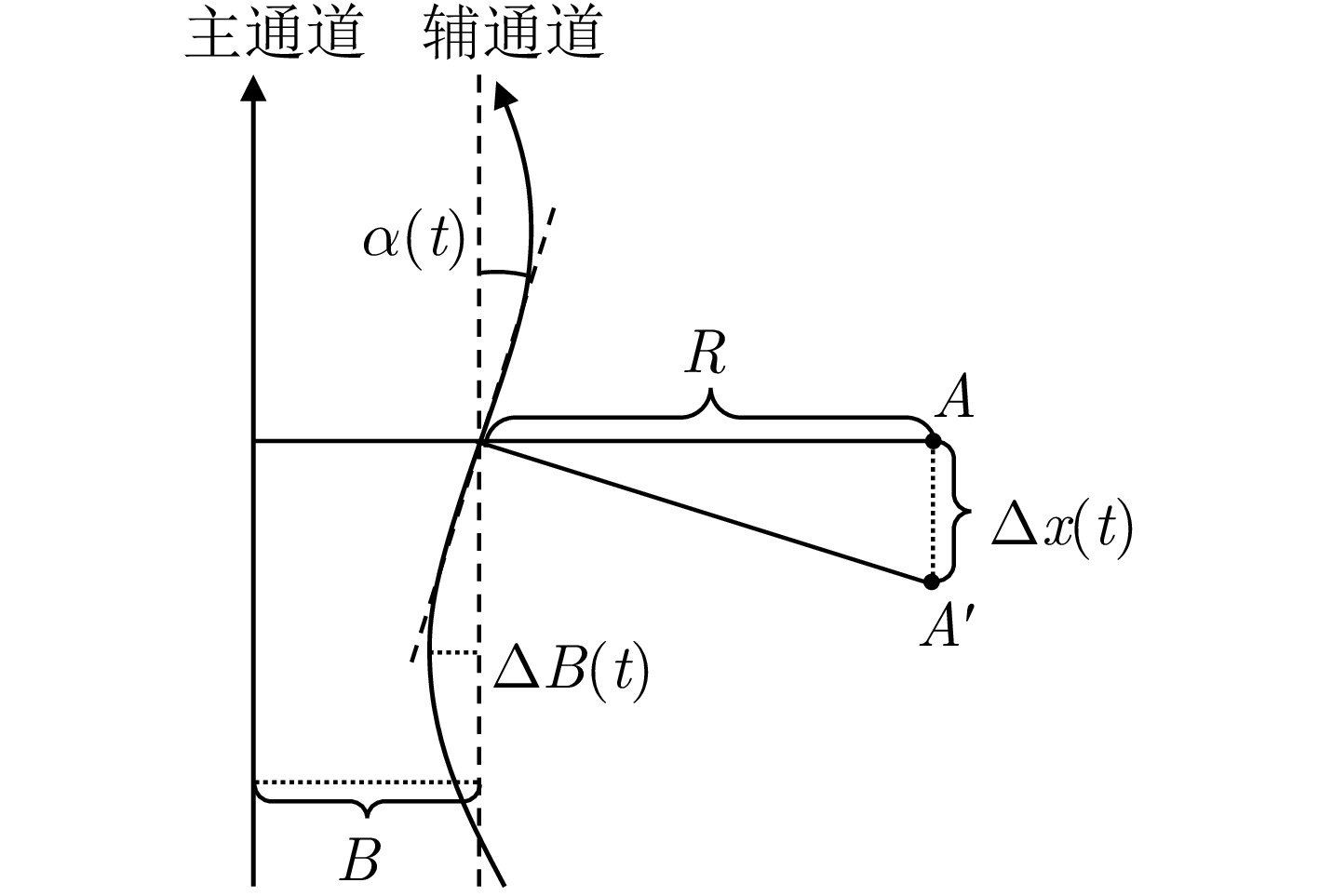
- Figure 6. Geometric relationship between azimuth displacement and the time-varying baseline-errors
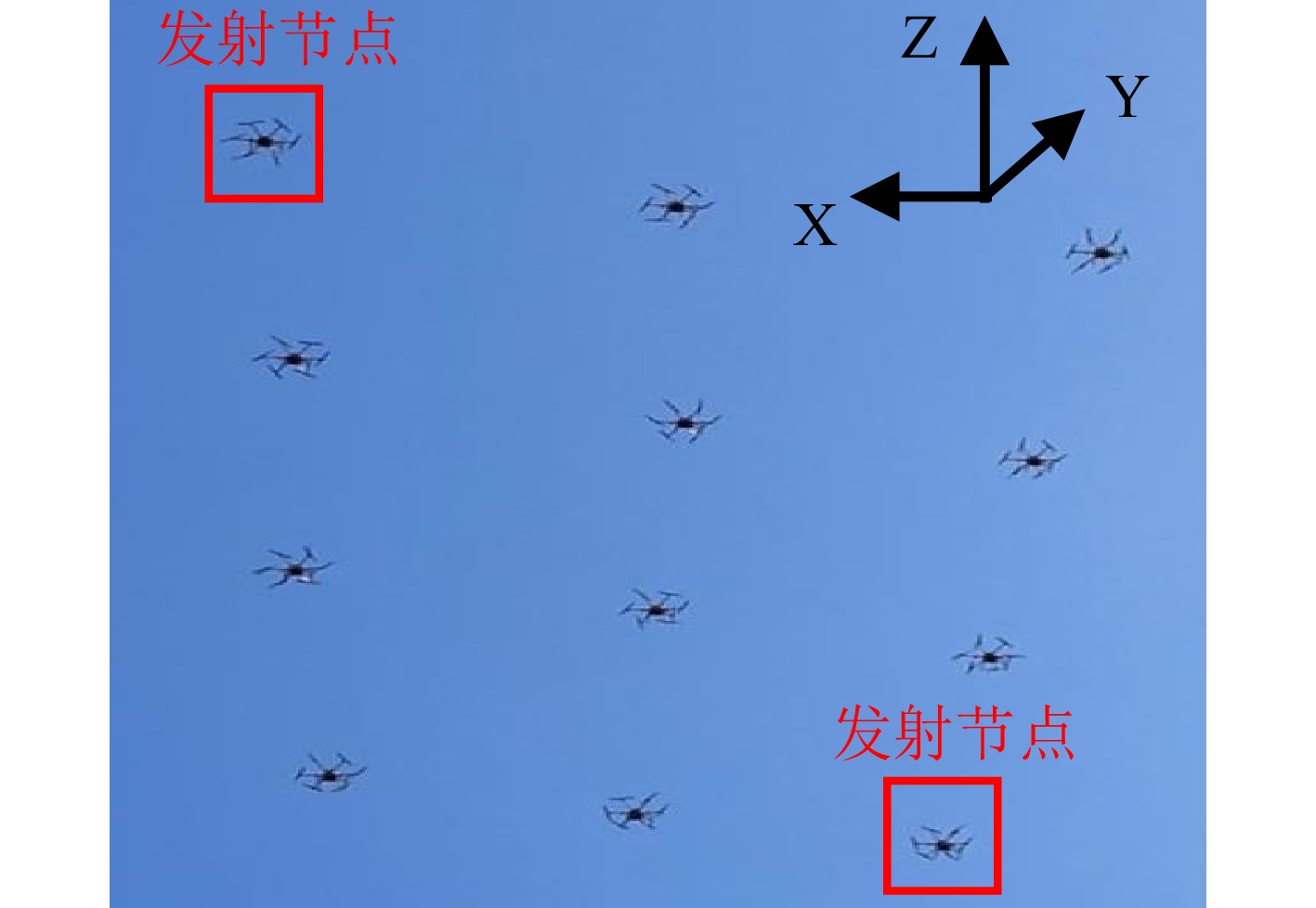
- Figure 7. Experimental formation geometry for distributed TomoSAR
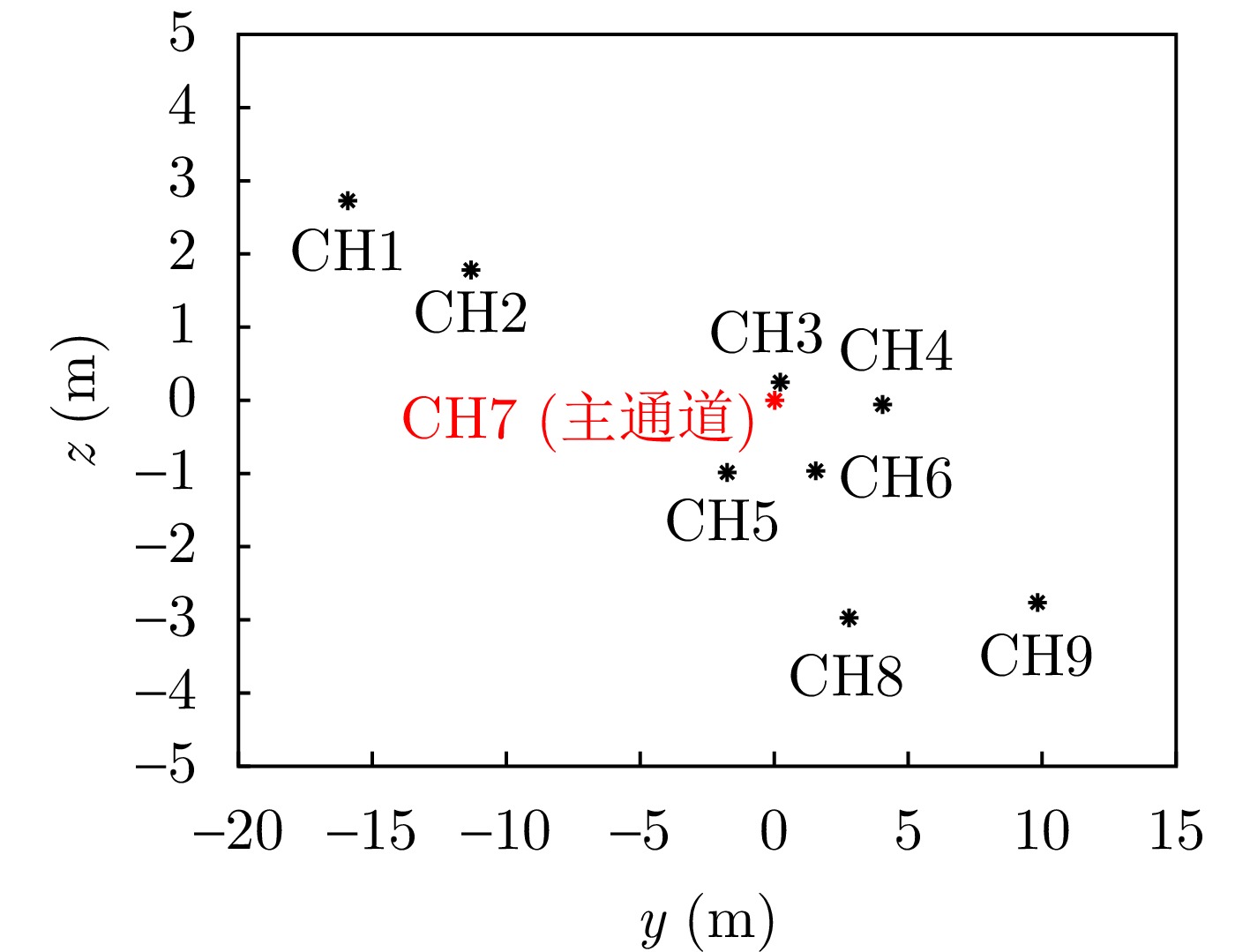
- Figure 8. Relative position diagram of equivalent phase centers
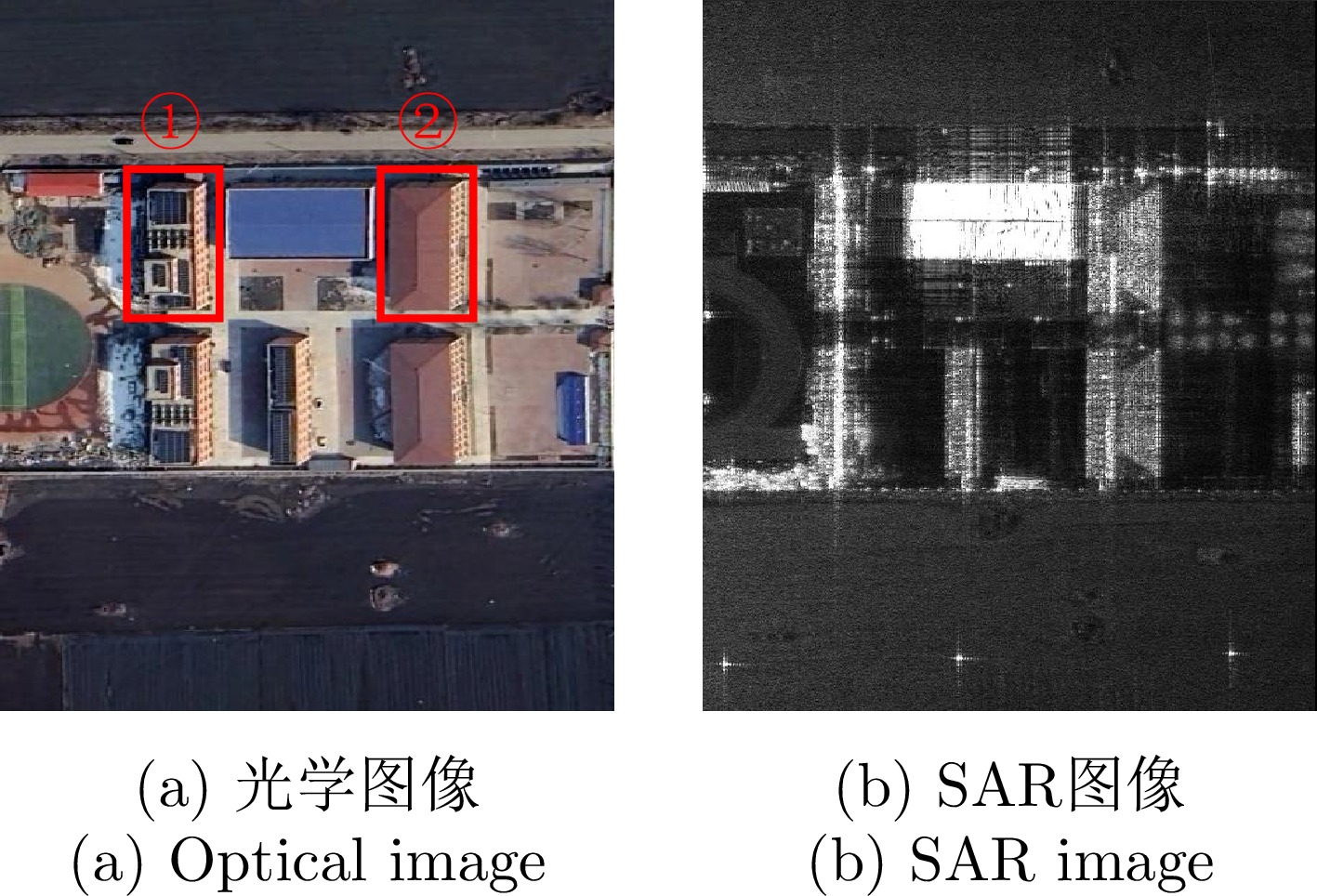
- Figure 9. SAR image and optical image of the test area
- Figure 10. Interferometric phase between the master (CH7) and other slave images before and after time-varying baseline error compensation
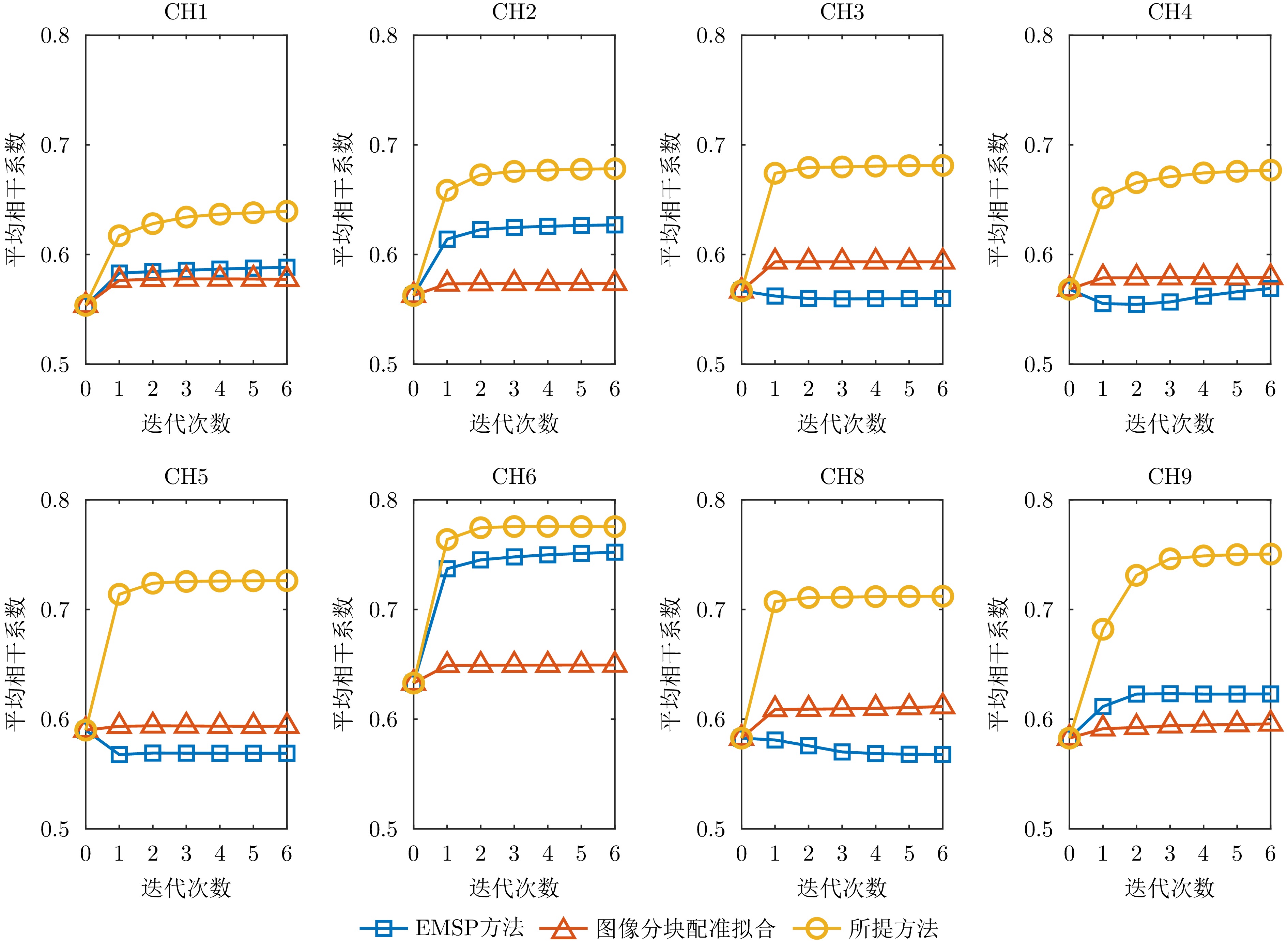
- Figure 11. Coherence coefficient variation curves after estimating the time-varying baseline error using different methods
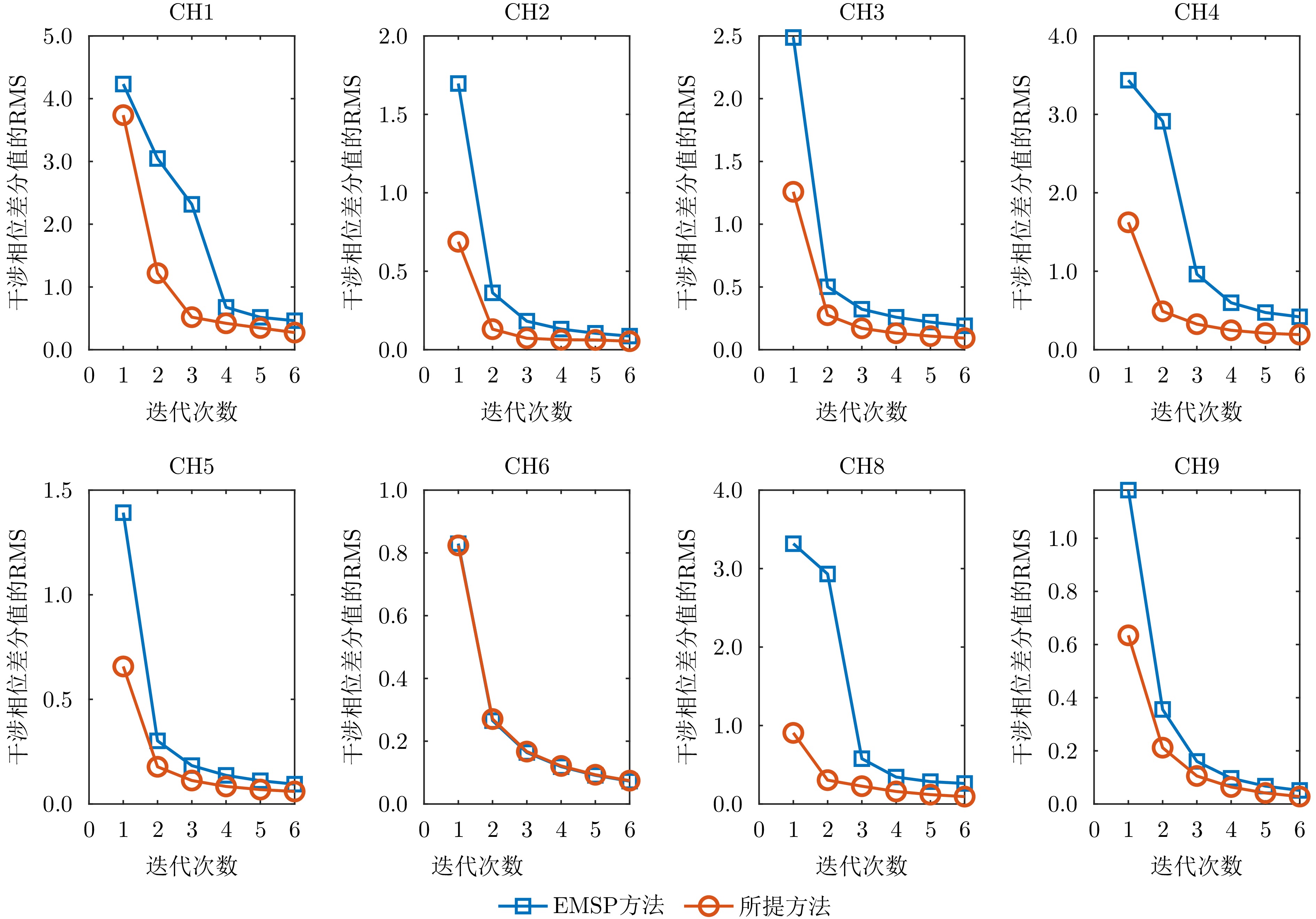
- Figure 12. RMS variation curves of interferometric phase differences during time-varying baseline error estimation using different methods
- Figure 13. Interferometric phase map after linear and constant baseline error correction
- Figure 14. Comparison of 3-D reconstruction Results


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: