- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Proofreading [3rd]
| Citation: | SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Research advances and applications of microwave photonic broadband vortex electromagnetic wave radar[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25263 |
Research Advances and Applications of Microwave Photonic Broadband Vortex Electromagnetic Wave Radar
DOI: 10.12000/JR25263 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25263
More Information-
Abstract
Vortex Electromagnetic (EM) wave radars utilize EM waves carrying orbital angular momentum to enrich target scattering information, thereby providing intrinsic in-beam azimuth resolution. Hence, this technology holds significant potential for advanced target detection and imaging. However, as sensing scenarios become more complex, conventional electronic vortex EM wave radars are increasingly limited by device bandwidth. Specifically, they encounter substantial challenges in broadband signal generation and control, making it difficult to achieve high range and azimuth resolutions simultaneously. Microwave photonics technology, with its inherent advantages of wide bandwidth, low transmission loss, and robustness against electromagnetic interference, is an effectivesolution to overcome these limitations. This paper reviews recent progress in microwave photonic broadband vortex EM wave radars, addressing the requirements for forward-looking imaging. The fundamental system architectures and imaging mechanisms are elucidated, followed by a critical analysis of the frequency-dependent characteristics of broadband vortex waves and their implications for imaging performance. Key microwave photonic enabling technologies, including broadband phase shifting, optical beamforming, and broadband signal generation, are summarized, and their advantages over traditional electronic schemes in terms of performance are highlighted. Based on these insights, typical system implementation schemes are described, and their high-resolution forward-looking imaging capabilities are demonstrated through proof-of-concept experiments. Finally, future development trends and research directions are discussed. -

-
References
[1] AUSHERMAN D A, KOZMA A, WALKER J L, et al. Developments in radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1984, AES-20(4): 363–400. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1984.4502060.[2] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099.[3] 刘永坦. 雷达成像技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2014: 169–170.LIU Yongtan. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 169–170.[4] 许会, 陈艳玲. 微波成像技术及其算法综述[J]. 无损检测, 2012, 34(10): 67–71,82.XU Hui and CHEN Yanling. Overview of the technology and algorithm of microwave imaging[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2012, 34(10): 67–71,82.[5] 程永强, 王宏强, 曹凯程, 等. 微波关联成像研究进展及展望(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(12): 20210790. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210790.CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, CAO Kaicheng, et al. Progress and prospect of microwave coincidence imaging (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(12): 20210790. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210790.[6] CHEN C C and ANDREWS H C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1980, AES-16(1): 2–14. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1980.308873.[7] WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752.[8] STEINBERG B D. Microwave imaging of aircraft[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1988, 76(12): 1578–1592. doi: 10.1109/5.16351.[9] STEINBERG B D. Radar imaging from a distorted array: The radio camera algorithm and experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1981, 29(5): 740–748. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1981.1142652.[10] 刘克成, 宋学诚. 天线原理[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 1989:178.LIU Kecheng and SONG Xuecheng. Principles of Antennas[M]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology Press, 1989:178.[11] MOHAMMADI S M, DALDORFF L K S, BERGMAN J E S, et al. Orbital angular momentum in radio—A system study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(2): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2037701.[12] WILLNER A E, HUANG Hao, YAN Yan, et al. Optical communications using orbital angular momentum beams[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2015, 7(1): 66–106. doi: 10.1364/AOP.7.000066.[13] TRINDER J R. Parabolic reflector[P]. WO, 2005069443A1, 2005.[14] THIDÉ B, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701.[15] 郭桂蓉, 胡卫东, 杜小勇. 基于电磁涡旋的雷达目标成像[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013.GUO Guirong, HU Weidong, and DU Xiaoyong. Electromagnetic vortex based radar target imaging[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013.[16] LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, YANG Zhaocheng, et al. Orbital-angular-momentum-based electromagnetic vortex imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 711–714. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2376970.[17] QU Haiyou, LI Shiyuan, CHEN Chang, et al. High-resolution orbital angular momentum imaging with the removal of Bessel function modulation effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2024, 72(4): 2577–2590. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3314107.[18] GHELFI P, LAGHEZZA F, SCOTTI F, et al. A fully photonics-based coherent radar system[J]. Nature, 2014, 507(7492): 341–345. doi: 10.1038/nature13078.[19] XU Shaofu, ZOU Weiwen, YANG Guang, et al. Ultra-high range resolution demonstration of a photonics-based microwave radar using a high-repetition-rate mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(6): 062801. doi: 10.3788/COL201816.062801.[20] ZHANG Siteng, ZOU Weiwen, QIAN Na, et al. Enlarged range and filter-tuned reception in photonic time-stretched microwave radar[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(11): 1028–1031. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2828459.[21] MA Cong, YANG Yue, CAO Fengting, et al. High-resolution microwave photonic radar with sparse stepped frequency chirp signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2007010. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3208112.[22] SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Millimeter-level resolution through-the-wall radar imaging enabled by an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(22): 5659–5662. doi: 10.1364/OL.441803.[23] BERLAND F, FROMENTEZE T, BOUDESCOQUE D, et al. Microwave photonic MIMO radar for short-range 3D imaging[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 107326–107334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000801.[24] DONG Jingwen, ZHANG Fubo, JIAO Zekun, et al. Microwave photonic radar with a fiber-distributed antenna array for three-dimensional imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(13): 19113–19125. doi: 10.1364/OE.393502.[25] SERAFINO G, MARESCA S, DI MAURO L, et al. A photonics-assisted multi-band MIMO radar network for the port of the future[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2021, 27(6): 6000413. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2021.3092880.[26] MARESCA S, SERAFINO G, NOVIELLO C, et al. Field trial of a coherent, widely distributed, dual-band photonics-based MIMO radar with ISAR imaging capabilities[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(20): 6626–6635. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3182421.[27] SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHAO Keyi, et al. Photonics-based broadband vortex electromagnetic wave generation for high-resolution imaging[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(6): 1894–1900. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3329424.[28] SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Frequency-dependent vortex electromagnetic wave imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2025, 24(1): 23–27. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2024.3481634.[29] SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, YU Xiaoyue, et al. Photonics-based broadband single-input-multiple- output-OAM coincidence imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2024, 2: 690–698. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2024.3418461.[30] WANG Xudong, CHAN E H W, and MINASIAN R A. All-optical photonic microwave phase shifter based on an optical filter with a nonlinear phase response[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2013, 31(20): 3323–3330. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2013.2281833.[31] BUI L A, MITCHELL A, GHORBANI K, et al. Wideband RF photonic vector sum phase-shifter[J]. Electronics Letters, 2003, 39(6): 536–537. doi: 10.1049/el:20030332.[32] SUN Xiaoqiang, FU Songnian, XU Kun, et al. Photonic RF phase shifter based on a vector-sum technique using stimulated Brillouin scattering in dispersion shifted fiber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(11): 3206–3212. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2010.2074811.[33] PAGANI M, MARPAUNG D, CHOI D Y, et al. Tunable wideband microwave photonic phase shifter using on-chip stimulated Brillouin scattering[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(23): 28810–28818. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.028810.[34] THÉVENAZ L. Slow and fast light in optical fibres[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(8): 474–481. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.147.[35] HERRÁEZ M G, SONG K Y, and THÉVENAZ L. Arbitrary-bandwidth Brillouin slow light in optical fibers[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(4): 1395–1400. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.001395.[36] LOAYSSA A, GALECH S, and LAHOZ F. Broadband microwave photonic phase-shifter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering[C]. The IEEE LEOS Annual Meeting, Sydney, Australia, 2005: 839–840. doi: 10.1109/LEOS.2005.1548269.[37] XUE Weiqi, SALES S, CAPMANY J, et al. Wideband 360° microwave photonic phase shifter based on slow light in semiconductor optical amplifiers[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(6): 6156–6163. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.006156.[38] DONG Yi, HE Hao, HU Weisheng, et al. Photonic microwave phase shifter/modulator based on a nonlinear optical loop mirror incorporating a Mach–Zehnder interferometer[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(7): 745–747. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.000745.[39] PU Minhao, LIU Liu, XUE Weiqi, et al. Tunable microwave phase shifter based on silicon-on-insulator microring resonator[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2010, 22(12): 869–871. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2010.2046725.[40] JIANG Hengyun, YAN Lianshan, YE Jia, et al. Photonic generation of phase-coded microwave signals with tunable carrier frequency[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(8): 1361–1363. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.001361.[41] LI Ze, LI Wangzhe, CHI Hao, et al. Photonic generation of phase-coded microwave signal with large frequency tunability[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2011, 23(11): 712–714. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2132121.[42] WEI Kai and DARYOUSH A S. Self-forced opto-electronic oscillators using Sagnac-loop PM-IM convertor[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(19): 5278–5285. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.2997652.[43] LI Wei, SUN Wenhui, WANG Wenting, et al. Photonic-assisted microwave phase shifter using a DMZM and an optical bandpass filter[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 5522–5527. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.005522.[44] ZHANG Yamei and PAN Shilong. Broadband microwave signal processing enabled by polarization-based photonic microwave phase shifters[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2018, 54(4): 0700112. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2018.2847398.[45] SHIN J D, LEE B S, and KIM B G. Optical true time-delay feeder for X-band phased array antennas composed of 2×2 optical MEMS switches and fiber delay lines[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2004, 16(5): 1364–1366. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.826083.[46] MOREIRA R L, GARCIA J, LI Wenzao, et al. Integrated ultra-low-loss 4-bit tunable delay for broadband phased array antenna applications[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2013, 25(12): 1165–1168. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2013.2261807.[47] LIU Yang, CHOUDHARY A, MARPAUNG D, et al. Gigahertz optical tuning of an on-chip radio frequency photonic delay line[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(4): 418–423. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000418.[48] YI Xiaoke, LI Liwei, HUANG T X H, et al. Programmable multiple true-time-delay elements based on a Fourier-domain optical processor[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(4): 608–610. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.000608.[49] LIU Yunqi, YANG Jianliang, and YAO Jianping. Continuous true-time-delay beamforming for phased array antenna using a tunable chirped fiber grating delay line[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2002, 14(8): 1172–1174. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2002.1022008.[50] CARDENAS J, FOSTER M A, SHERWOOD-DROZ N, et al. Wide-bandwidth continuously tunable optical delay line using silicon microring resonators[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(25): 26525–26534. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.026525.[51] CRUZ J L, ORTEGA B, ANDRES M V, et al. Chirped fibre Bragg gratings for phased-array antennas[J]. Electronics Letters, 1997, 33(7): 545–546. doi: 10.1049/el:19970407.[52] MATTHEWS P J, LIU P L, MEDBERRY J B, et al. Demonstration of a wide-band fiber-optic nulling system for array antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1999, 47(7): 1327–1331. doi: 10.1109/22.775474.[53] SHI Nuannuan, LI Wei, ZHU Ninghua, et al. Optically controlled phase array antenna [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(5): 052301. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.052301.[54] WANG Chao and YAO Jianping. Photonic generation of chirped microwave pulses using superimposed chirped fiber Bragg gratings[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2008, 20(11): 882–884. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2008.922333.[55] WANG Chao and YAO Jianping. Chirped microwave pulse generation based on optical spectral shaping and wavelength-to-time mapping using a Sagnac loop mirror incorporating a chirped fiber Bragg grating[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(16): 3336–3341. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.2010561.[56] LI Ming, SHAO Liyang, ALBERT J, et al. Tilted fiber Bragg grating for chirped microwave waveform generation[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2011, 23(5): 314–316. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2010.2102013.[57] RASHIDINEJAD A and WEINER A M. Photonic radio-frequency arbitrary waveform generation with maximal time-bandwidth product capability[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(20): 3383–3393. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2331491.[58] GUO Qingshui, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHOU Pei, et al. Dual-band LFM signal generation by optical frequency quadrupling and polarization multiplexing[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(16): 1320–1323. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2722004.[59] YAO Yao, ZHANG Fangzheng, ZHANG Ying, et al. Demonstration of ultra-high-resolution photonics-based Ka-band inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging[C]. Optical Fiber Communication Conference, San Diego, USA, 2018: Th3G.5. doi: 10.1364/OFC.2018.Th3G.5.[60] YACOUBIAN A and DAS P K. Digital-to-analog conversion using electrooptic modulators[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2003, 15(1): 117–119. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2002.805844.[61] NISHITANI T, KONISHI T, FURUKAWA H, et al. All-optical digital-to-analog conversion using pulse pattern recognition based on optical correlation processing[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(25): 10310–10315. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.010310.[62] GAO Bindong, ZHANG Fangzheng, and PAN Shilong. Experimental demonstration of arbitrary waveform generation by a 4-bit photonic digital-to-analog converter[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 383: 191–196. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.08.083.[63] LI Jiading, XUE Xiaoxiao, ZHA Yu, et al. A segmented photonic digital-to-analog converter with a high effective number of bits[C]. 2019 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics, Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/MWP.2019.8892090.[64] ZHANG Bowen, ZHU Dan, ZHOU Pei, et al. Tunable triangular frequency modulated microwave waveform generation with improved linearity using an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(20): 5479–5485. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.005479.[65] ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, GUO Qingshui, et al. Linearly chirped microwave waveform generation with large time-bandwidth product by optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(16): 18460–18467. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.018460.[66] ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, GUO Qingshui, et al. Reconfigurable radar waveform generation based on an optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(6): 1801109. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2017.2699659.[67] ZHOU Pei, ZHANG Fangzheng, YE Xingwei, et al. Flexible frequency-hopping microwave generation by dynamic control of optically injected semiconductor laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2016, 8(6): 5501909. doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2016.2629082.[68] YUAN Tiezhu, WANG Hongqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, et al. Electromagnetic vortex-based radar imaging using a single receiving antenna: Theory and experimental results[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 630. doi: 10.3390/s17030630.[69] LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. High-resolution electromagnetic vortex imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(21): 6918–6927. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2754554.[70] LIU Da, SHI Hongyin, YANG Ting, et al. Autofocusing and imaging algorithm for moving target by vortex electromagnetic wave radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2023, 134: 103903. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103903. -
Proportional views

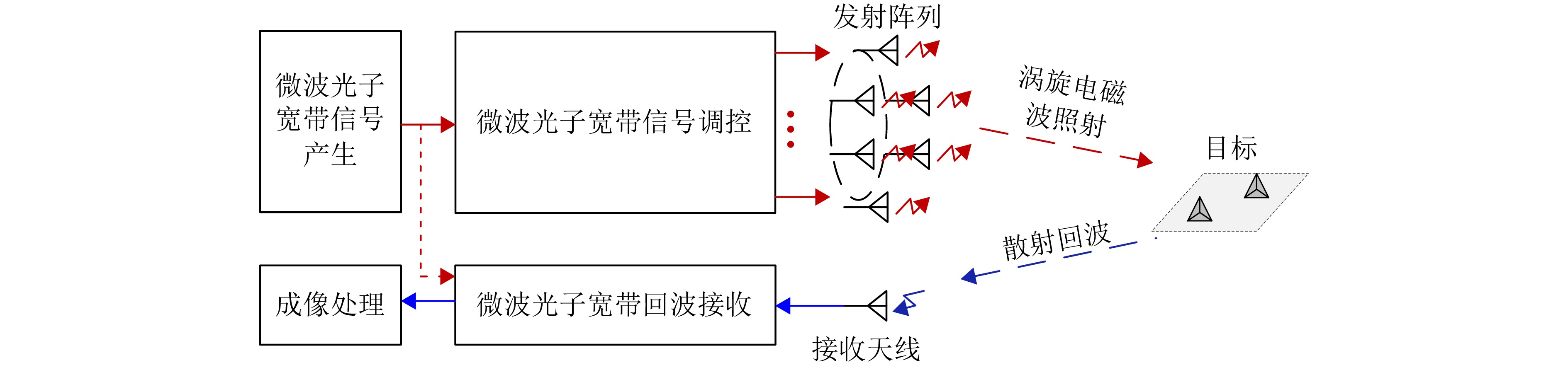
- Figure 1. Schematic diagram of microwave photonic vortex electromagnetic wave radar
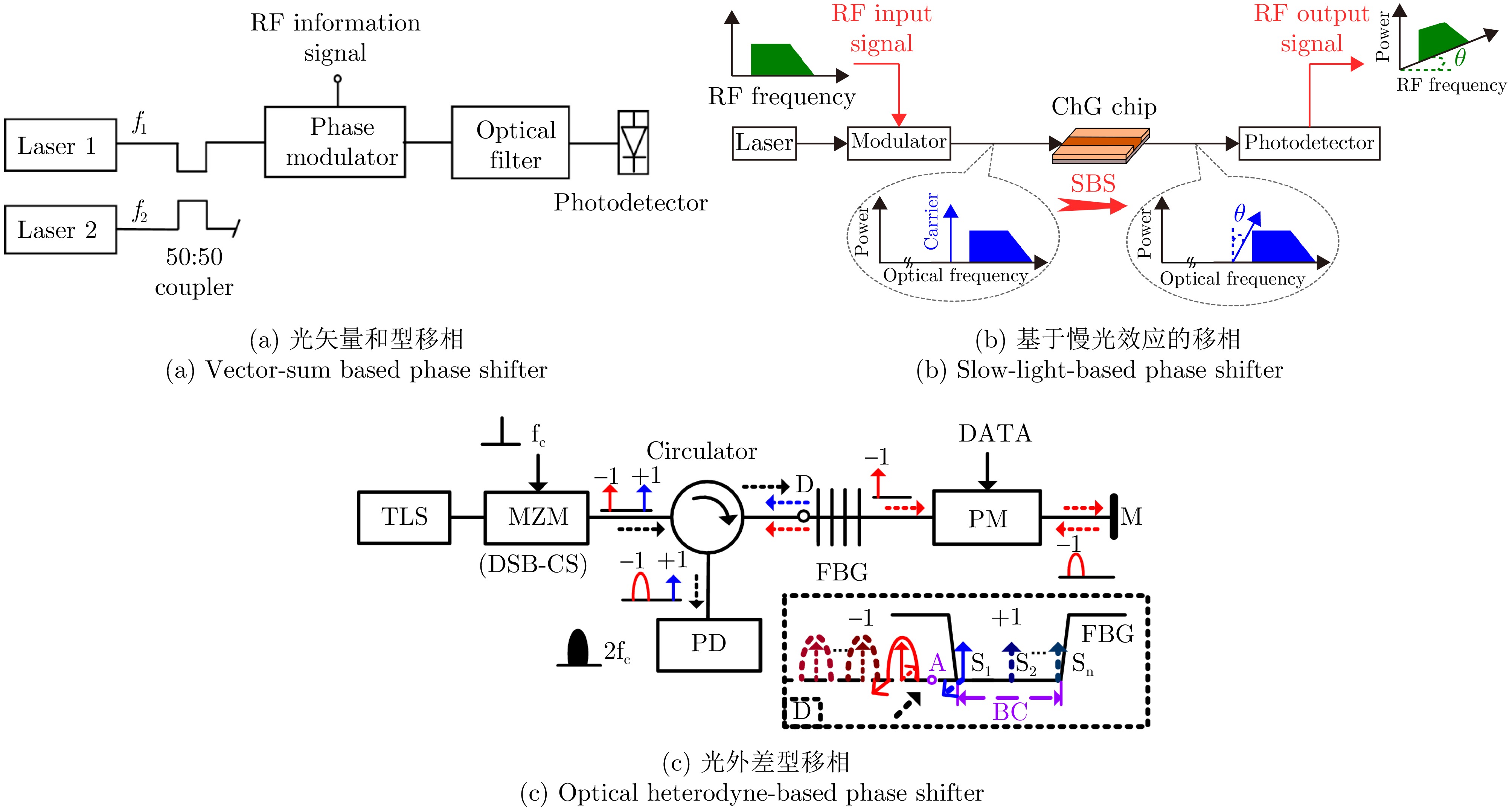
- Figure 2. Diagrams of typical microwave photonic broadband phase shifters [30, 33, 40]
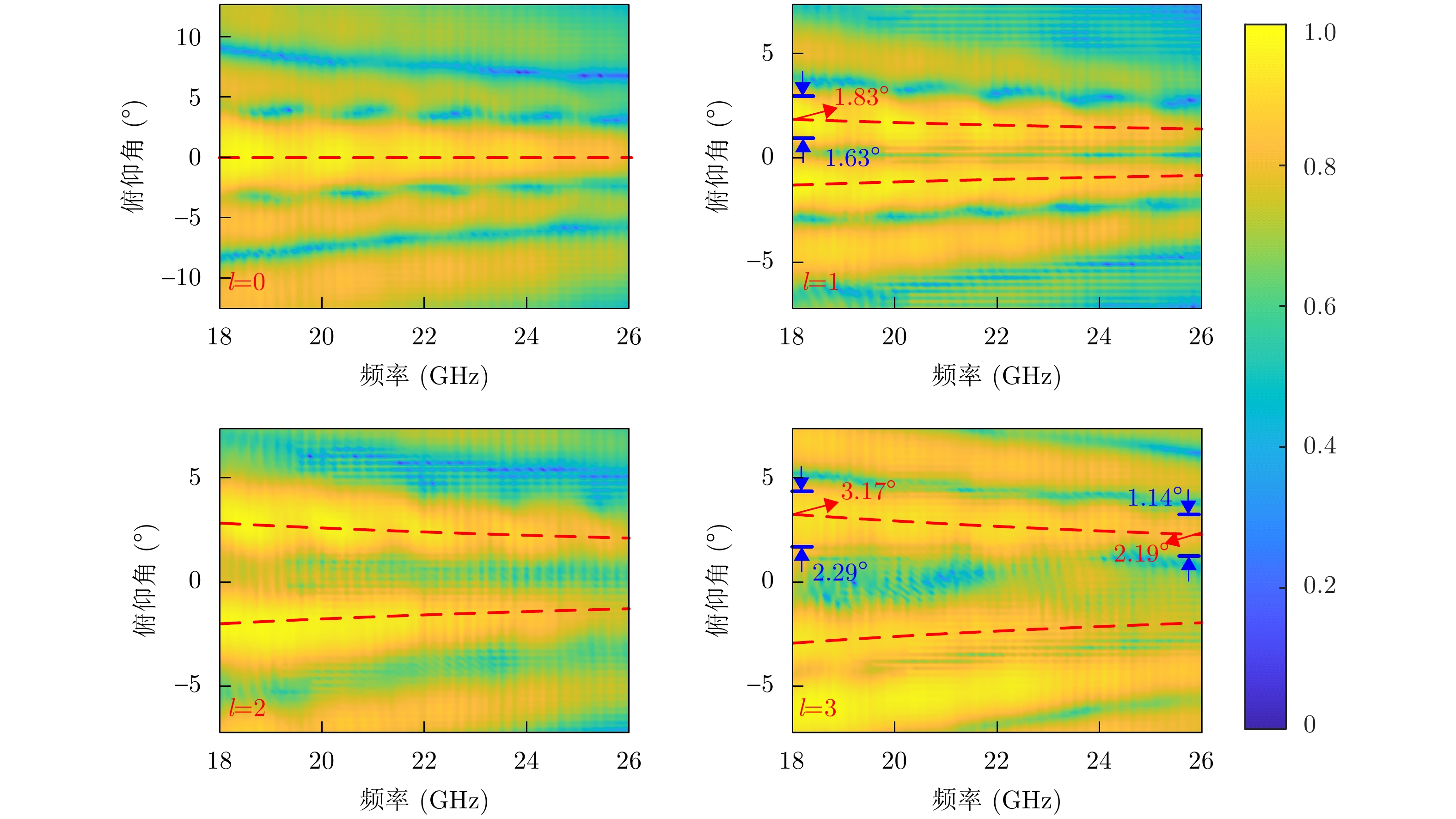
- Figure 3. Measured field patterns along elevation direction [27]
- Figure 4. The radiation fields of vortex EM waves with different bandwidths for l = 15 [27]
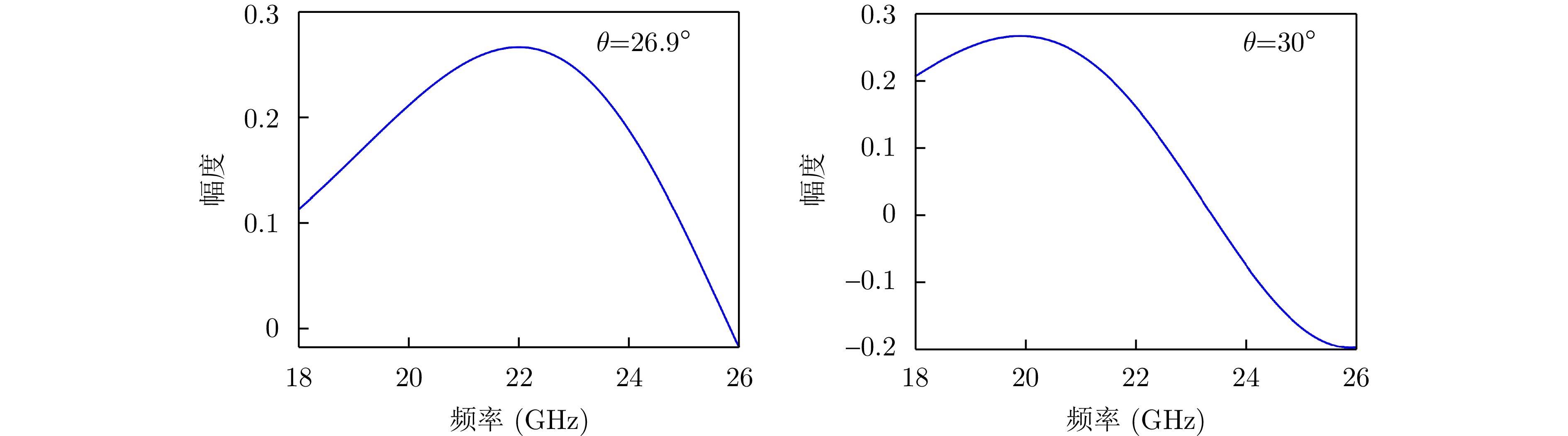
- Figure 5. Amplitude-frequency curve of modulation coefficient Jl(kasinθ) with different elevation angles [27]
- Figure 6. Detection model and imaging processing workflow of the microwave photonic broadband vortex EM wave radar
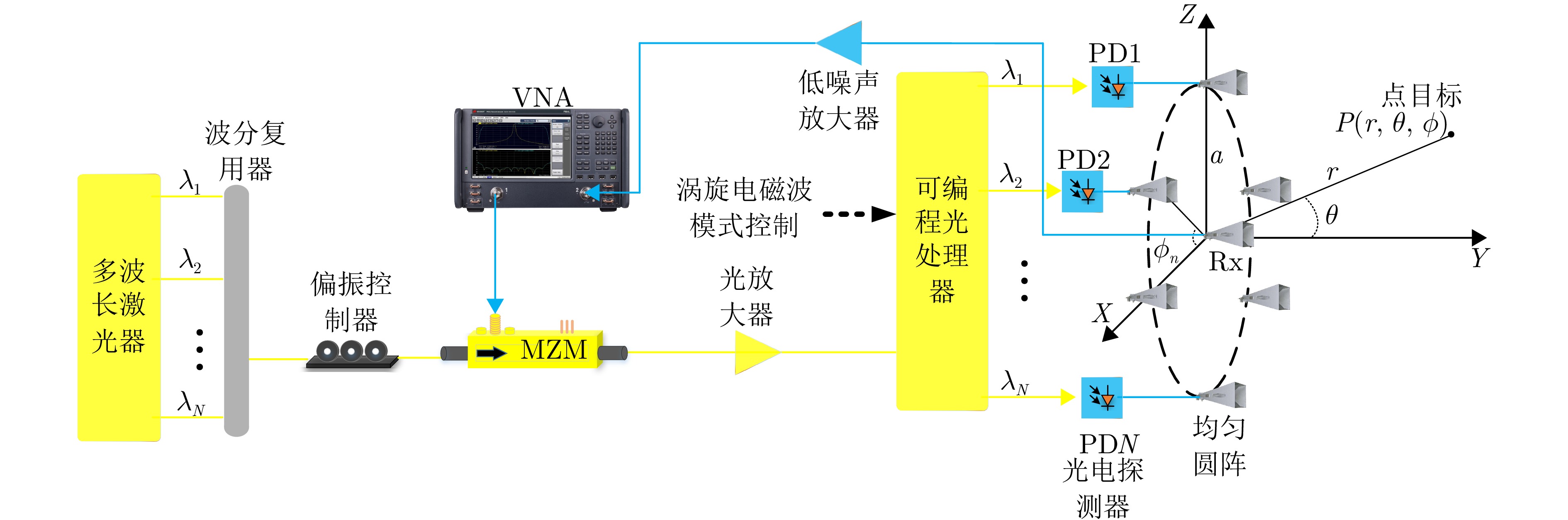
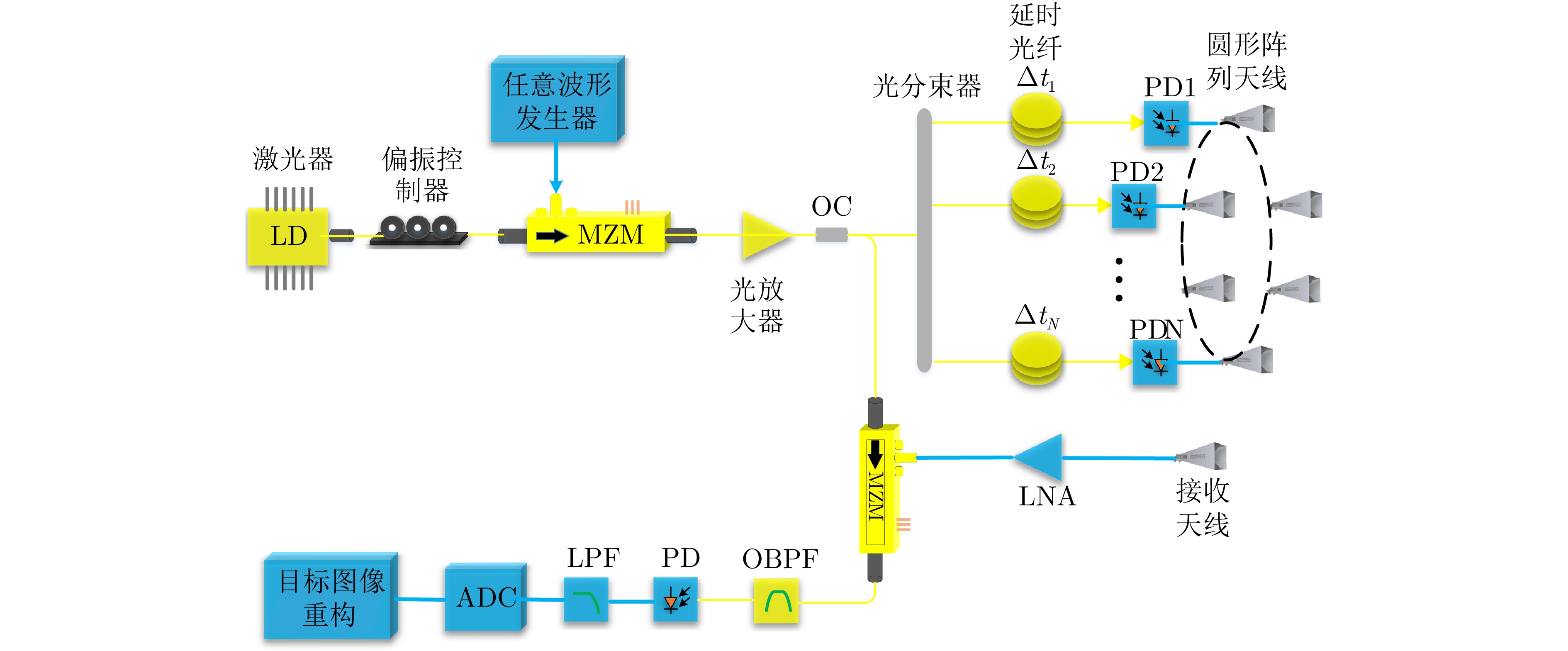
- Figure 7. Broadband vortex EM wave radar system based on microwave photonic phase shifting [27]
- Figure 8. Principle schematic of broadband vortex EM wave generation based on microwave photonic phase shifting[27]
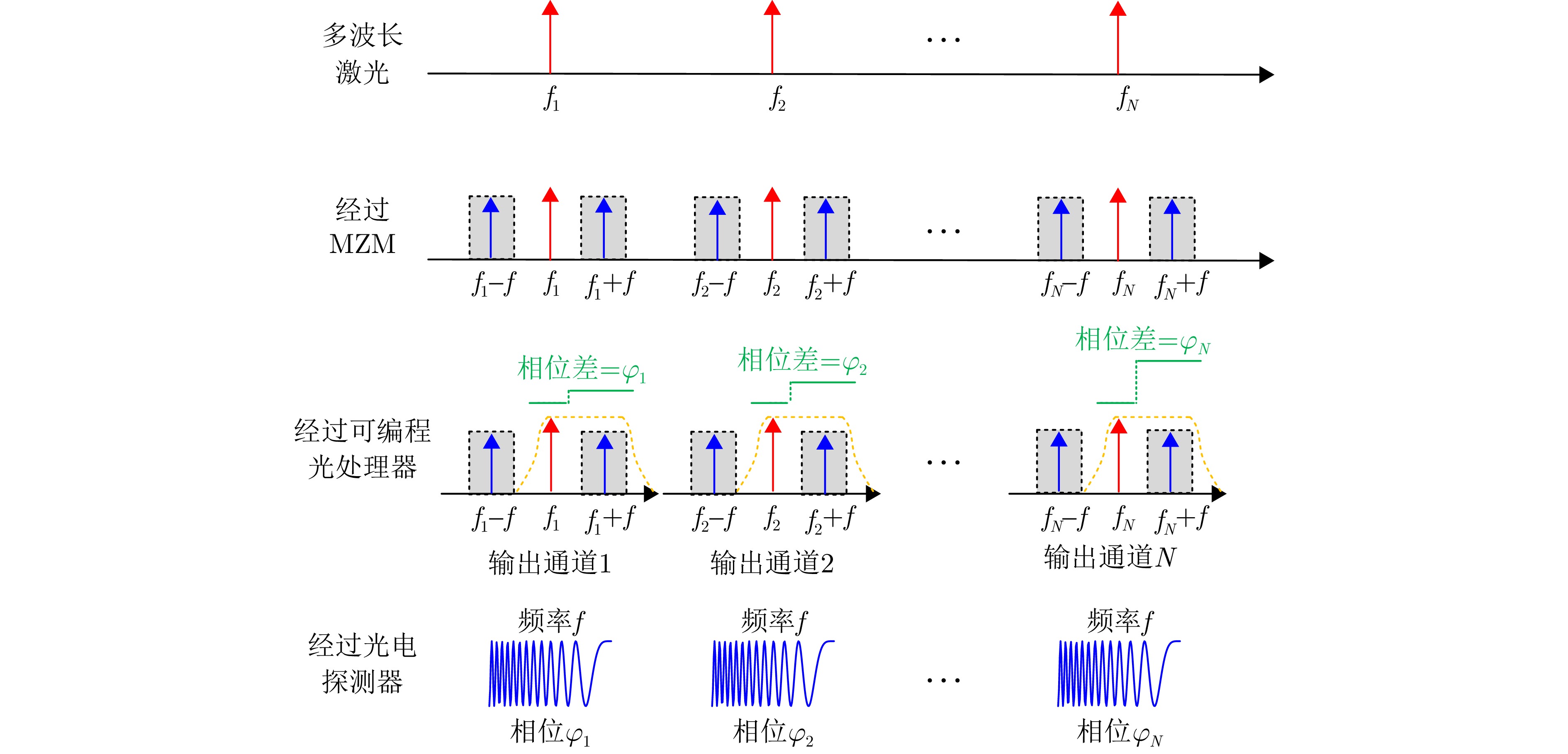
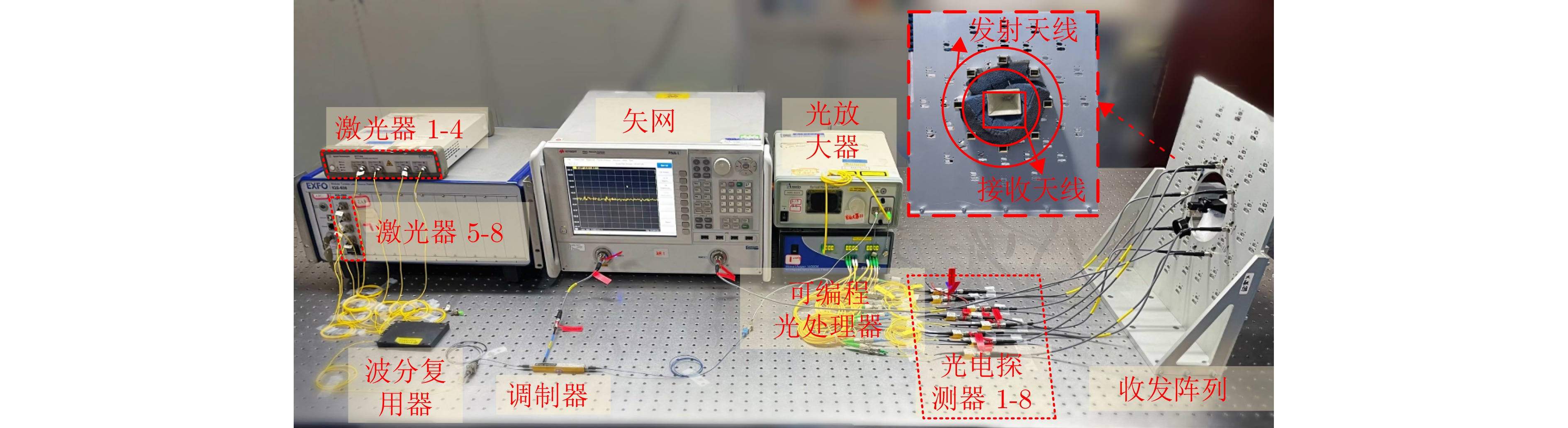
- Figure 9. 8-channel broadband vortex EM wave radar system based on microwave photonic phase shifting [27]
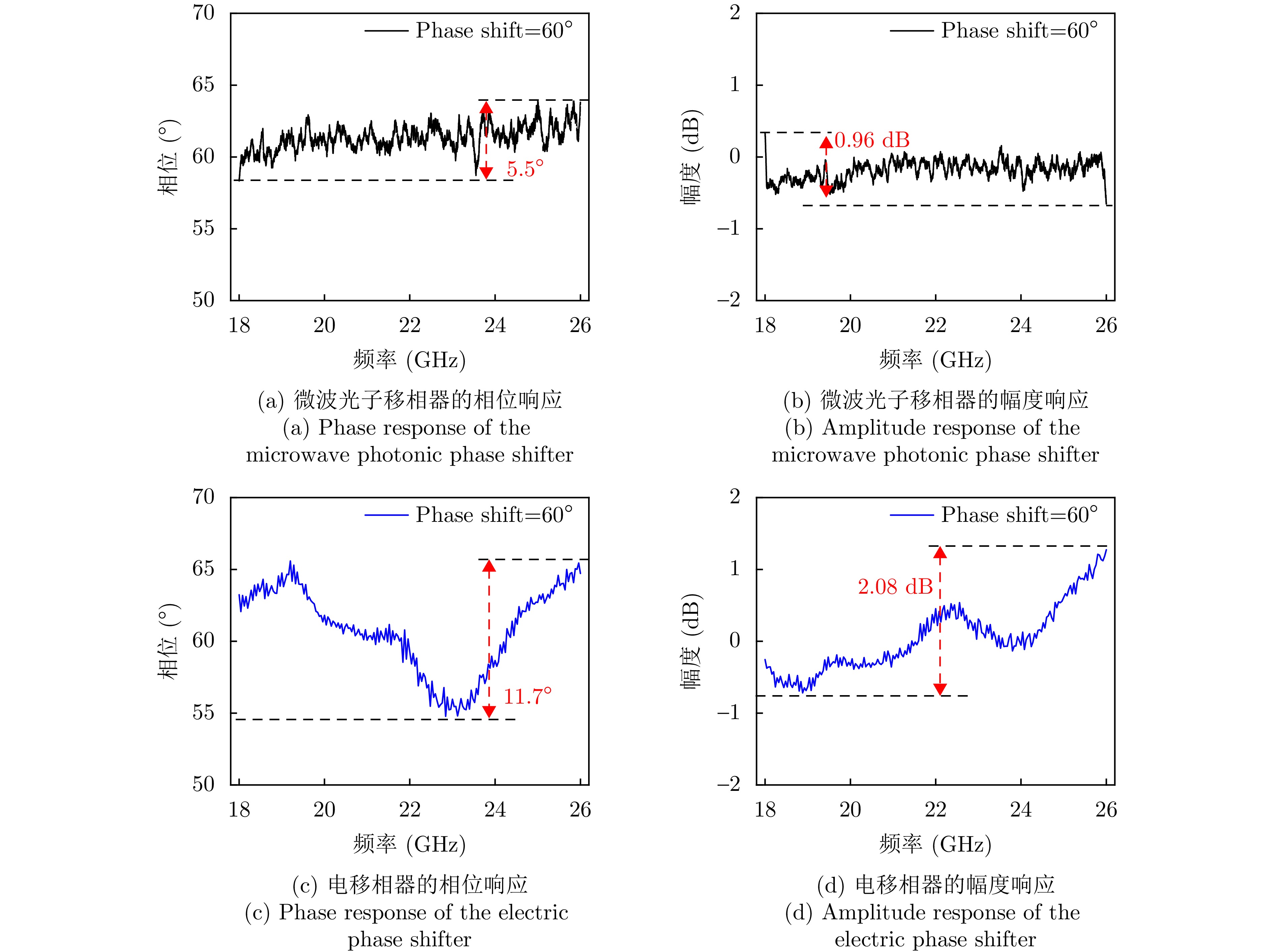
- Figure 10. Broadband performance validation of the microwave photonic phase shifter [27]
- Figure 11. Measured amplitude and phase patterns of the vortex EM waves under different OAM modes and frequencies[27]
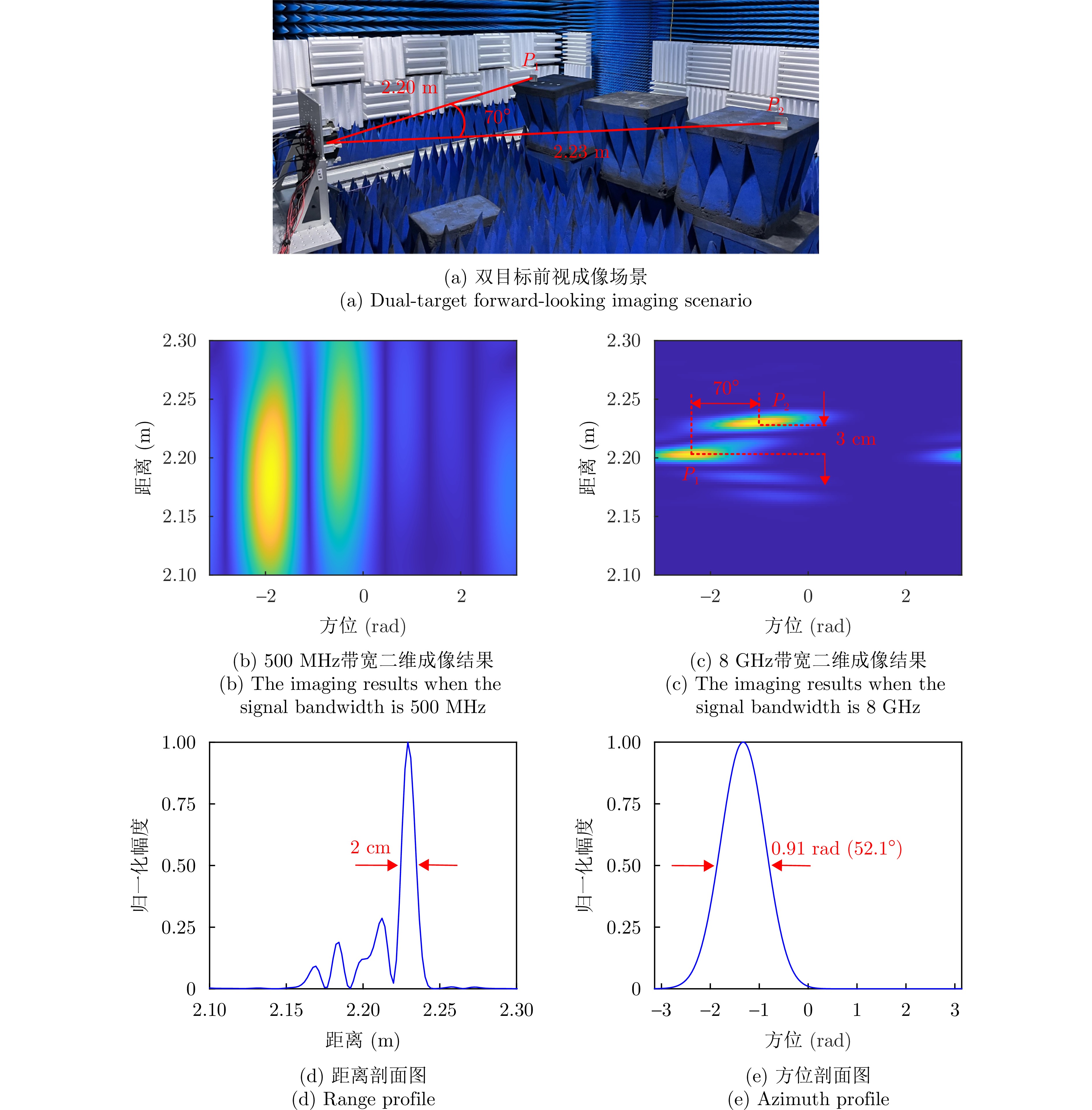
- Figure 12. Verification of high-resolution imaging performance for photonics-based broadband vortex EM wave radar [27]
- Figure 13. Schematic diagram of the broadband vortex EM fast imaging radar based on a single-loop optical delay network[28]
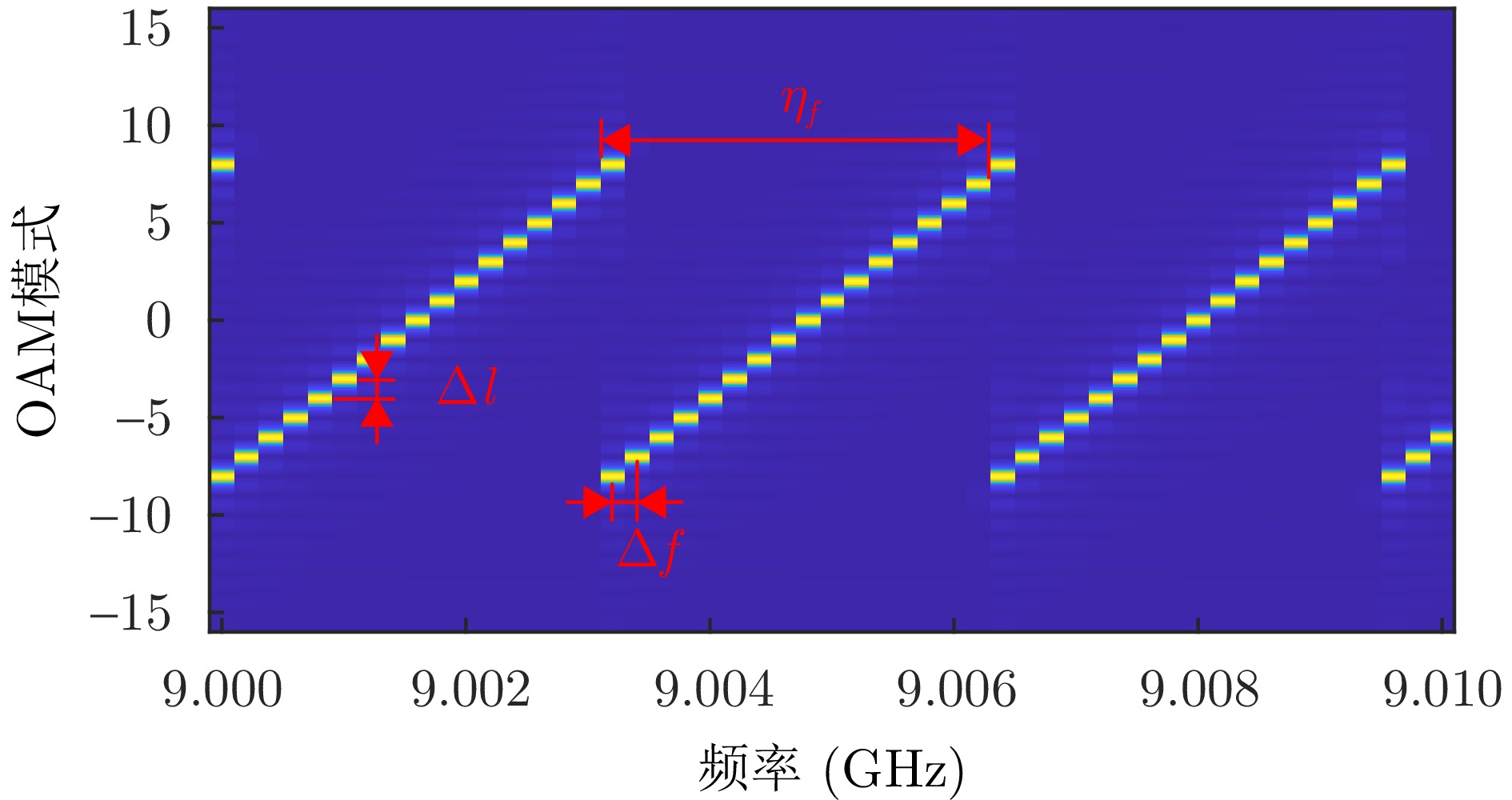
- Figure 14. Frequency versus OAM mode relationship for vortex EM waves [28]
- Figure 15. Phase distributions for 16 sub-pulses at different frequencies [28]
- Figure 16. Flowchart of the image reconstruction method based on information decoupling [28]
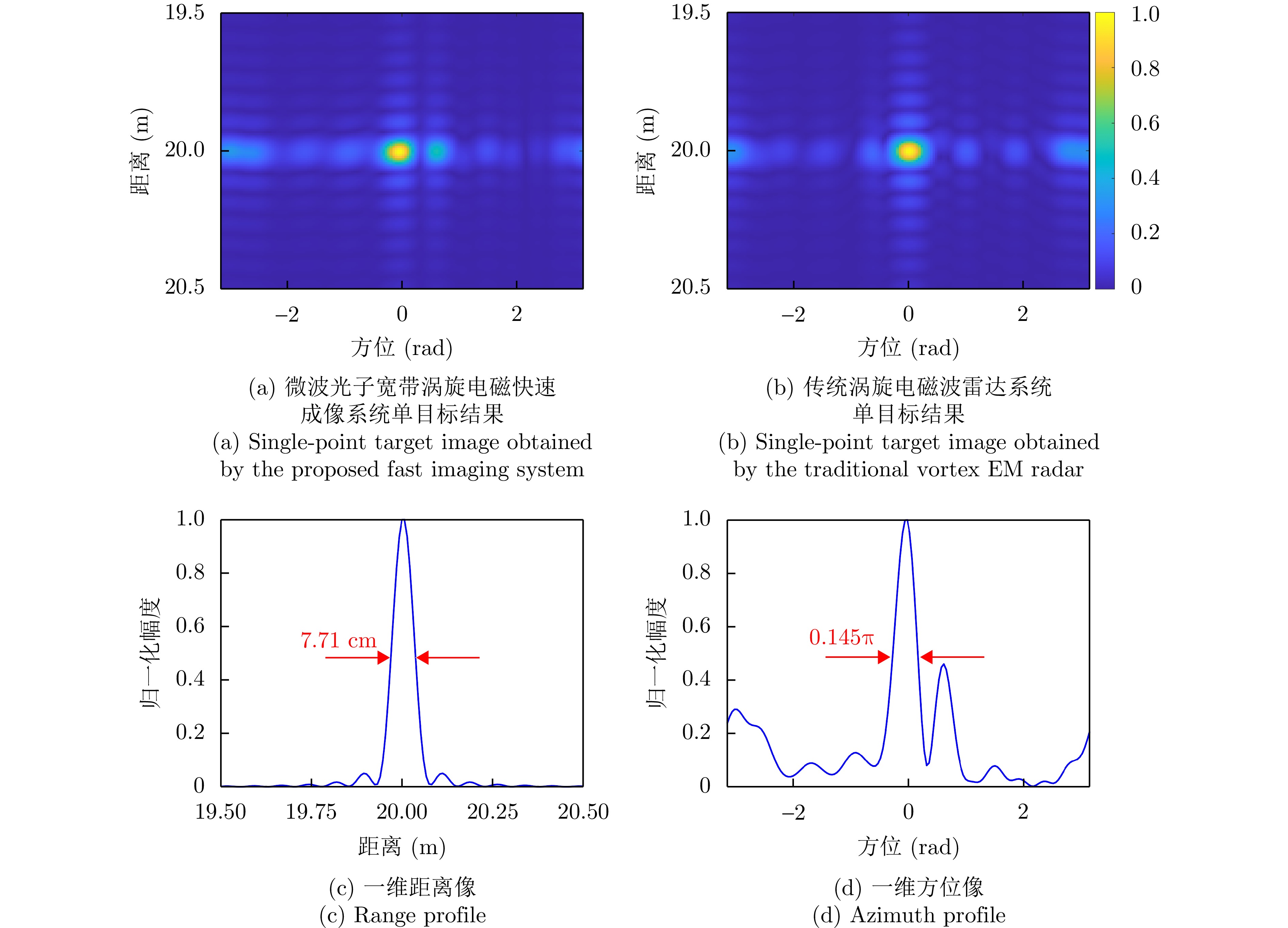
- Figure 17. Comparison of imaging results for single-point target[28]
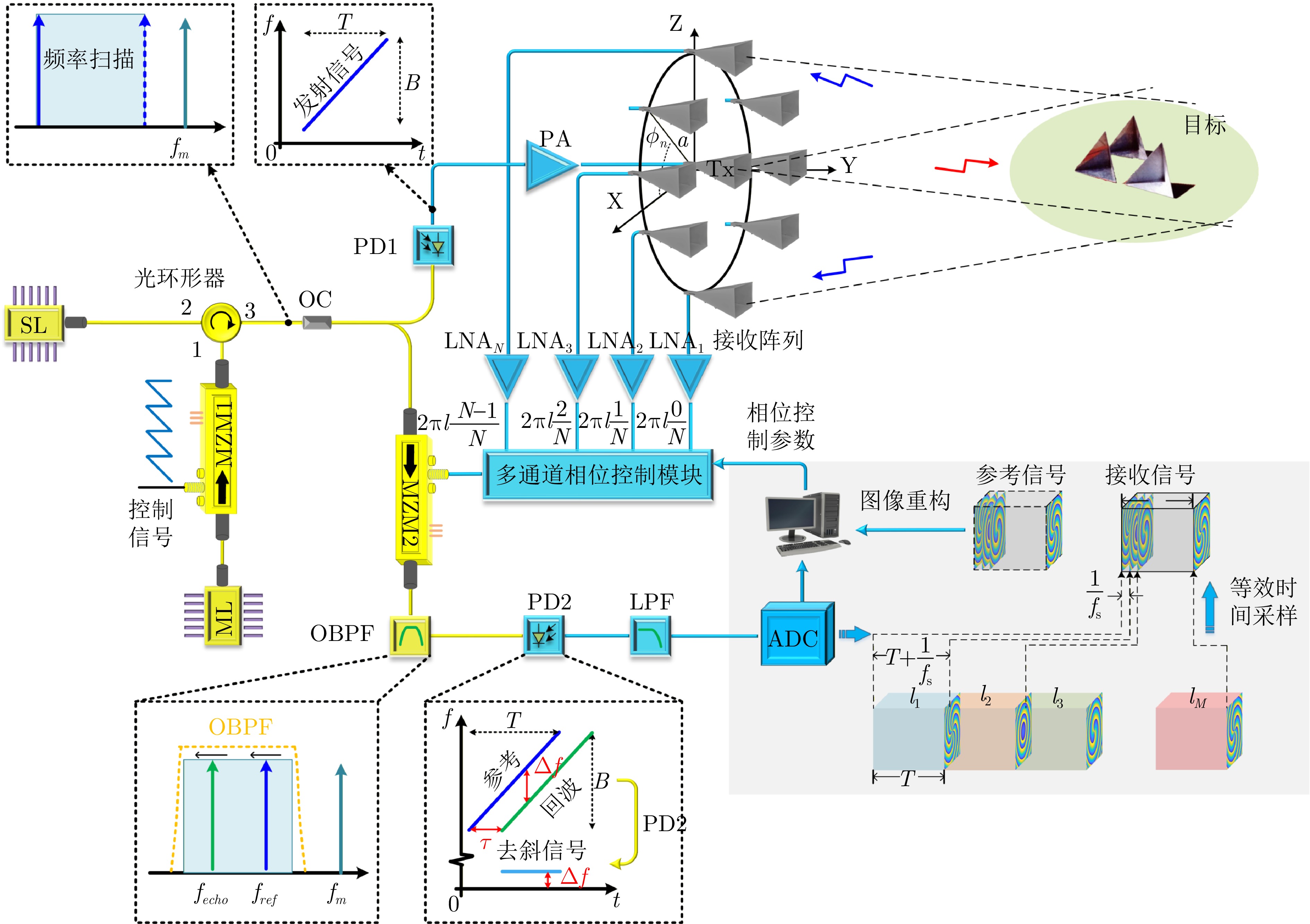
- Figure 18. Schematic diagram of the broadband vortex EM super-resolution imaging radar system based on an optical injection semiconductor laser[29]
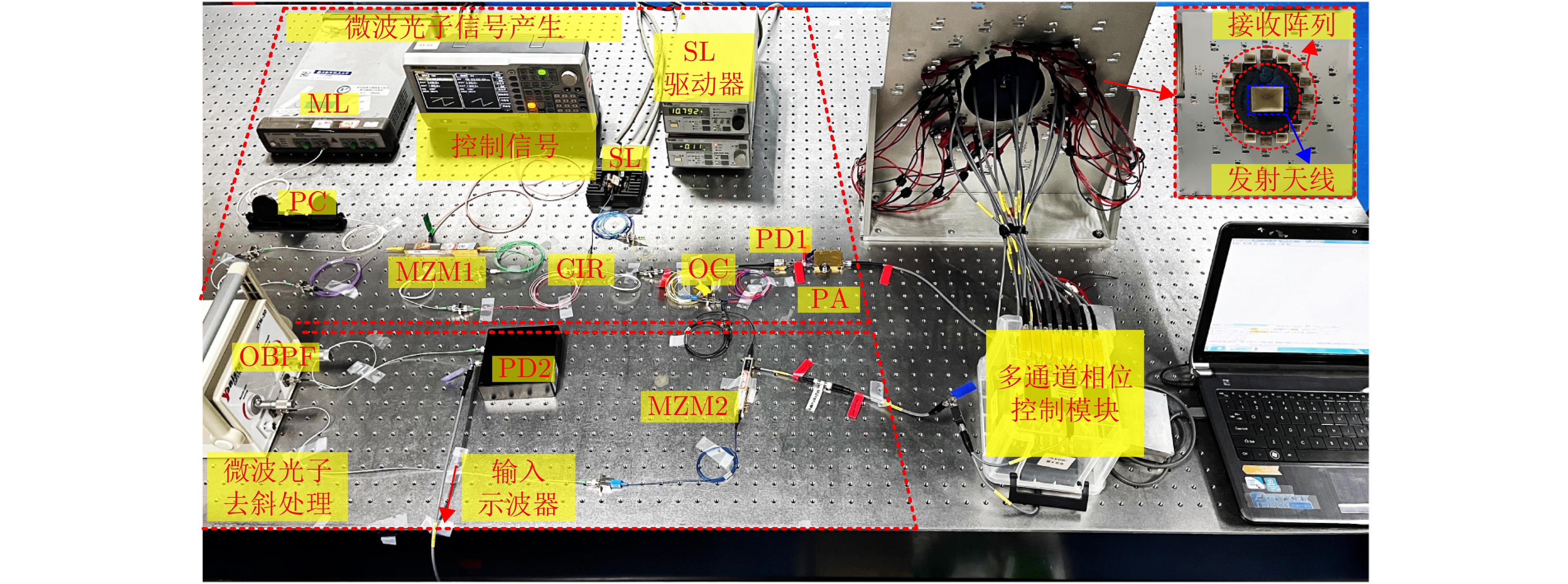
- Figure 19. Diagram of the proof-of-concept system for super-resolution vortex EM imaging based on an optical injection semiconductor laser[29]
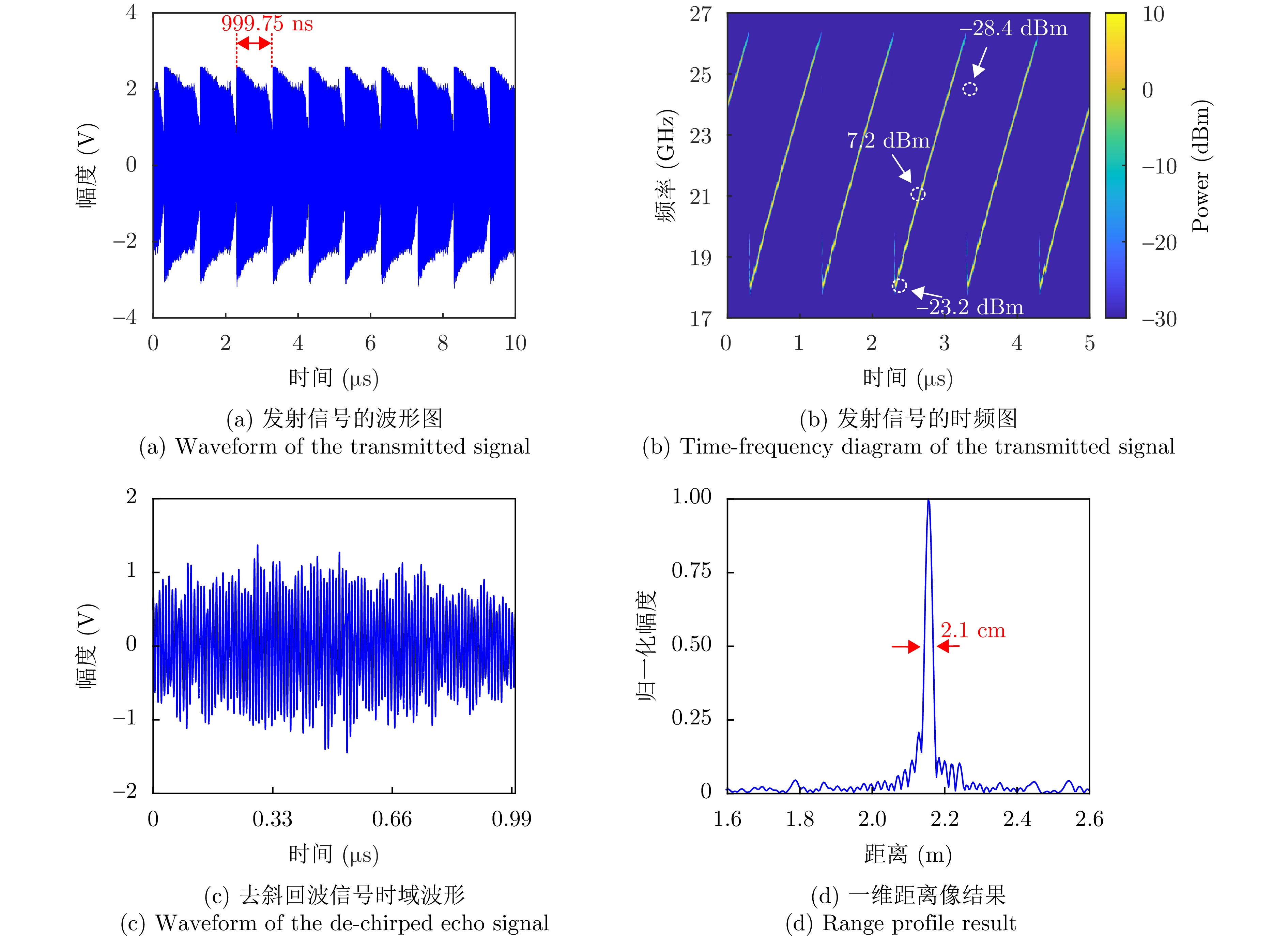
- Figure 20. Verification of radar transceiver performance[29]
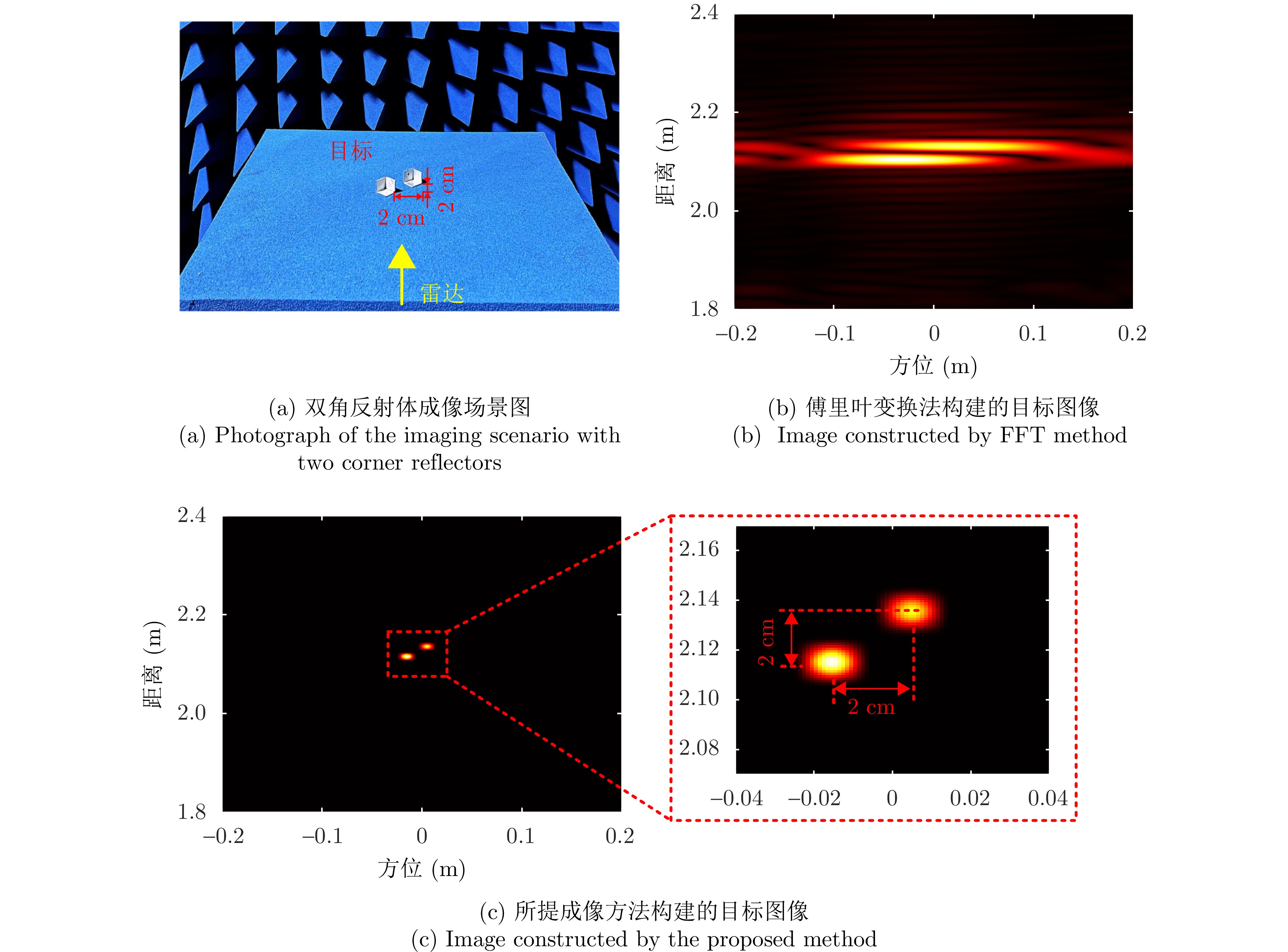
- Figure 21. Super-resolution performance verification [29]
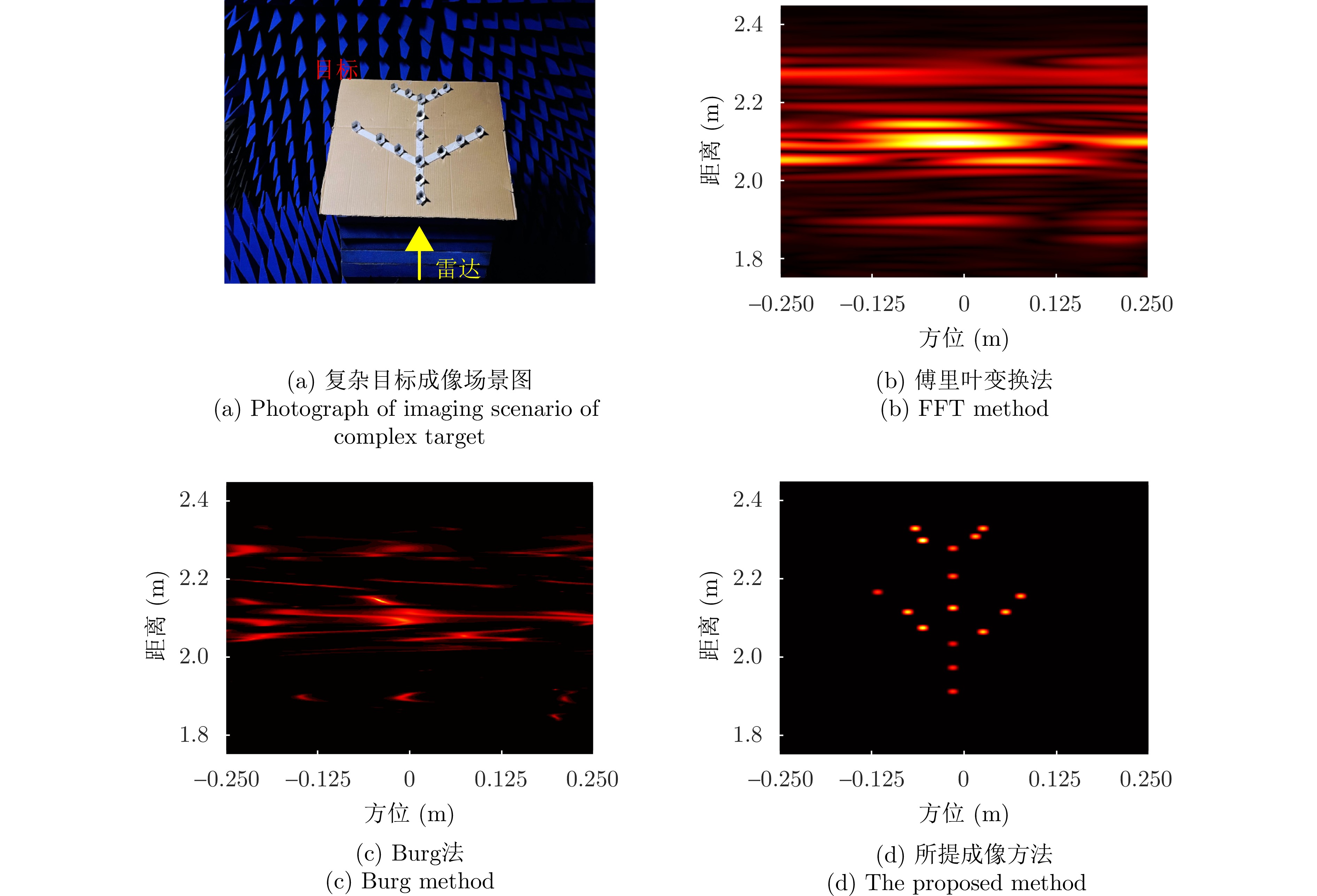
- Figure 22. Comparison of complex target imaging performance[29]


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: