- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Online First
| Citation: | LIU Ziyuan, WANG Shaoping, HE Yiting, et al. A multitask motion information extraction method based on range-Doppler maps for near-vertical scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25259 |
A MultiTask Motion Information Extraction Method Based on Range-Doppler Maps for Near-vertical Scenarios
DOI: 10.12000/JR25259 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25259
More Information-
Abstract
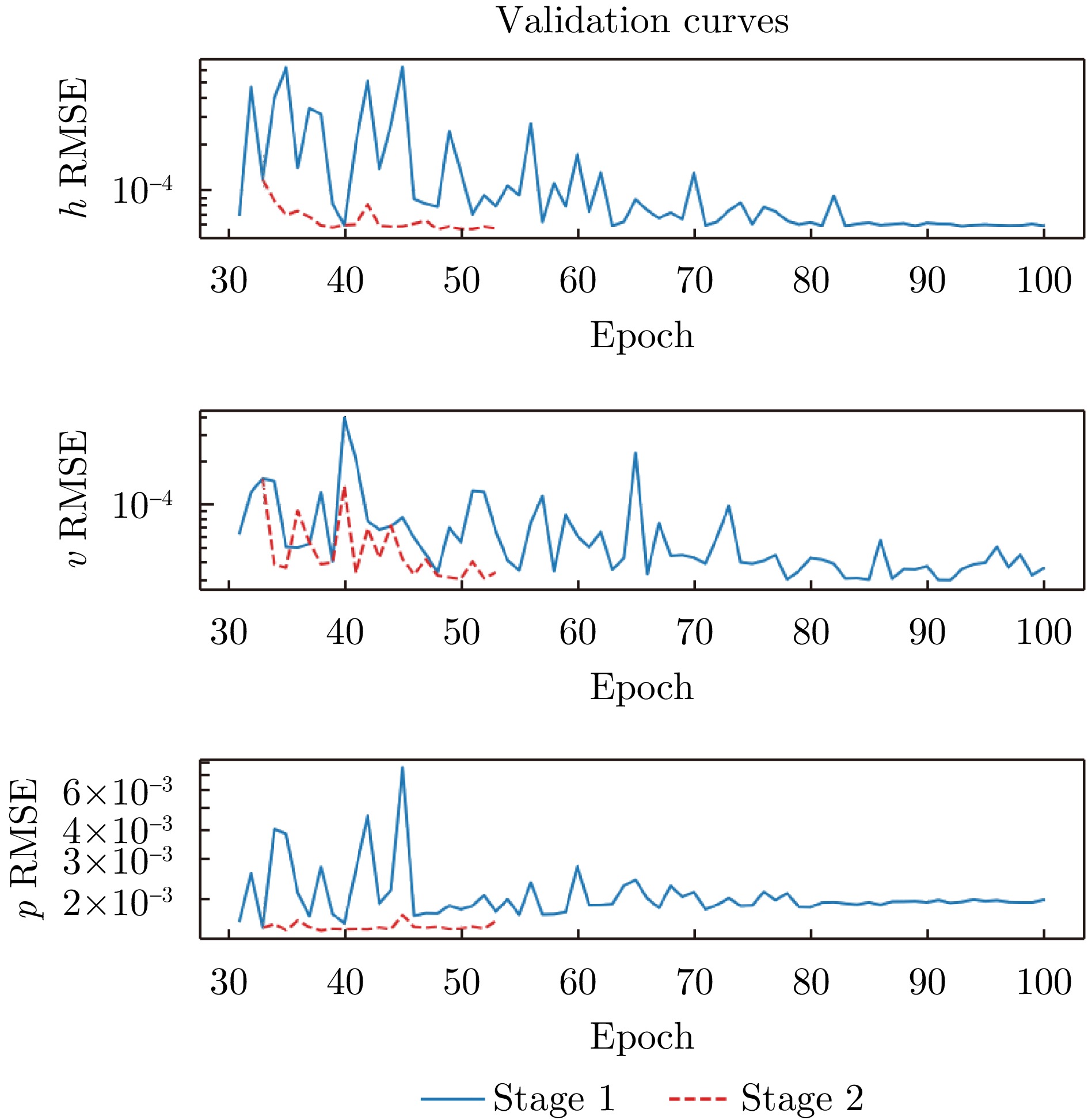
Pulse Doppler radar provides all-weather operational capability and enables simultaneous acquisition of target range and velocity through Range-Doppler (RD) maps. In near-vertical flight scenarios, the geometric structure of RD maps implicitly encodes key platform motion parameters, including altitude, velocity, and pitch angle. However, these parameters are strongly coupled in the RD domain, making effective decoupling difficult for traditional signal-processing-based inversion methods, particularly under complex terrain and near-vertical incidence conditions. Although recent advances in deep learning have shown strong potential for motion information sensing, multitask learning in this context still faces challenges in achieving both real-time performance and high estimation accuracy. To address these issues, this study proposes a novel network architecture, termed Range-Doppler Map Fusion Network (RDMFNet), that performs multirepresentation information fusion via shared encoders and parallel decoders, along with a two-stage progressive training strategy to enhance parameter estimation accuracy. Experimental results show that RDMFNet achieves estimation errors of 14.447 m for altitude, 4.635 m/s for velocity, and 0.755° for pitch angle, demonstrating its effectiveness for high-precision, real-time perception. -

-
References
[1] MILLER S D, MWAFFO V, and COSTELLO III D H. Deep learning-based relative bearing estimation between naval surface vessels and uas in challenging maritime environments[C]. 2025 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Charlotte, USA, 2025: 742–748. doi: 10.1109/ICUAS65942.2025.11007882.[2] 毛军, 付浩, 褚超群, 等. 惯性/视觉/激光雷达SLAM技术综述[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2022, 9(4): 17–30. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.04.003.MAO Jun, FU Hao, CHU Chaoqun, et al. A review of simultaneous localization and mapping based on inertial-visual-Lidar fusion[J]. Navigation Positioning and Timing, 2022, 9(4): 17–30. doi: 10.19306/j.cnki.2095-8110.2022.04.003.[3] NARASIMHAPPA M, MAHINDRAKAR A D, GUIZILINI V C, et al. MEMS-based IMU drift minimization: Sage Husa adaptive robust Kalman filtering[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(1): 250–260. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2941273.[4] 李道京, 朱宇, 胡烜, 等. 衍射光学系统的激光应用和稀疏成像分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR19081.LI Daojing, ZHU Yu, HU Xuan, et al. Laser application and sparse imaging analysis of diffractive optical system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR19081.[5] 王超, 王岩飞, 刘畅, 等. 基于参数估计的高分辨率SAR运动目标距离徙动校正方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 64–72. doi: 10.12000/JR18054.WANG Chao, WANG Yanfei, LIU Chang, et al. A new approach to range cell migration correction for ground moving targets in high-resolution SAR system based on parameter estimation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 64–72. doi: 10.12000/JR18054.[6] 许京新. 基于深度学习的SAR图像舰船目标检测[D]. [硕士论文], 烟台大学, 2025. doi: 10.27437/d.cnki.gytdu.2025.000610.XU Jingxin. Deep learning-based ship target detection in SAR images[D]. [Master dissertation], Yantai University, 2025. doi: 10.27437/d.cnki.gytdu.2025.000610.[7] DE HOOP M V, LASSAS M, and WONG C A. Deep learning architectures for nonlinear operator functions and nonlinear inverse problems[J]. Mathematical Statistics and Learning, 2022, 4(1/2): 1–86. doi: 10.4171/MSL/28.[8] DARA S and TUMMA P. Feature extraction by using deep learning: A survey[C]. 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 2018: 1795–1801. doi: 10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474912.[9] KWON H Y, YOON H G, LEE C, et al. Magnetic Hamiltonian parameter estimation using deep learning techniques[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(39): eabb0872. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb0872.[10] KOLLIAS D. ABAW: Learning from synthetic data & multi-task learning challenges[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2023: 157–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-25075-0_12.[11] CIPOLLA R, GAL Y, and KENDALL A. Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7482–7491. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00781.[12] RICHARDS M A and MELVIN W L. Principles of Modern Radar: Basic Principles[M]. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2022: 360.[13] WANG Aiguo, ZHANG Wei, and CAO Jianshu. Terrain clutter modeling for airborne radar system using digital elevation model[C]. The 2012 International Workshop on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Circuits and System Technology, Chengdu, China, 2012: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MMWCST.2012.6238182.[14] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456.[15] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.123.[16] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.[17] ABDULATIF S, CAO Ruizhe, and YANG Bin. CMGAN: Conformer-based metric-GAN for monaural speech enhancement[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2024, 32: 2477–2493. doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2024.3393718.[18] RUDER S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.05098, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1706.05098. -
Proportional views

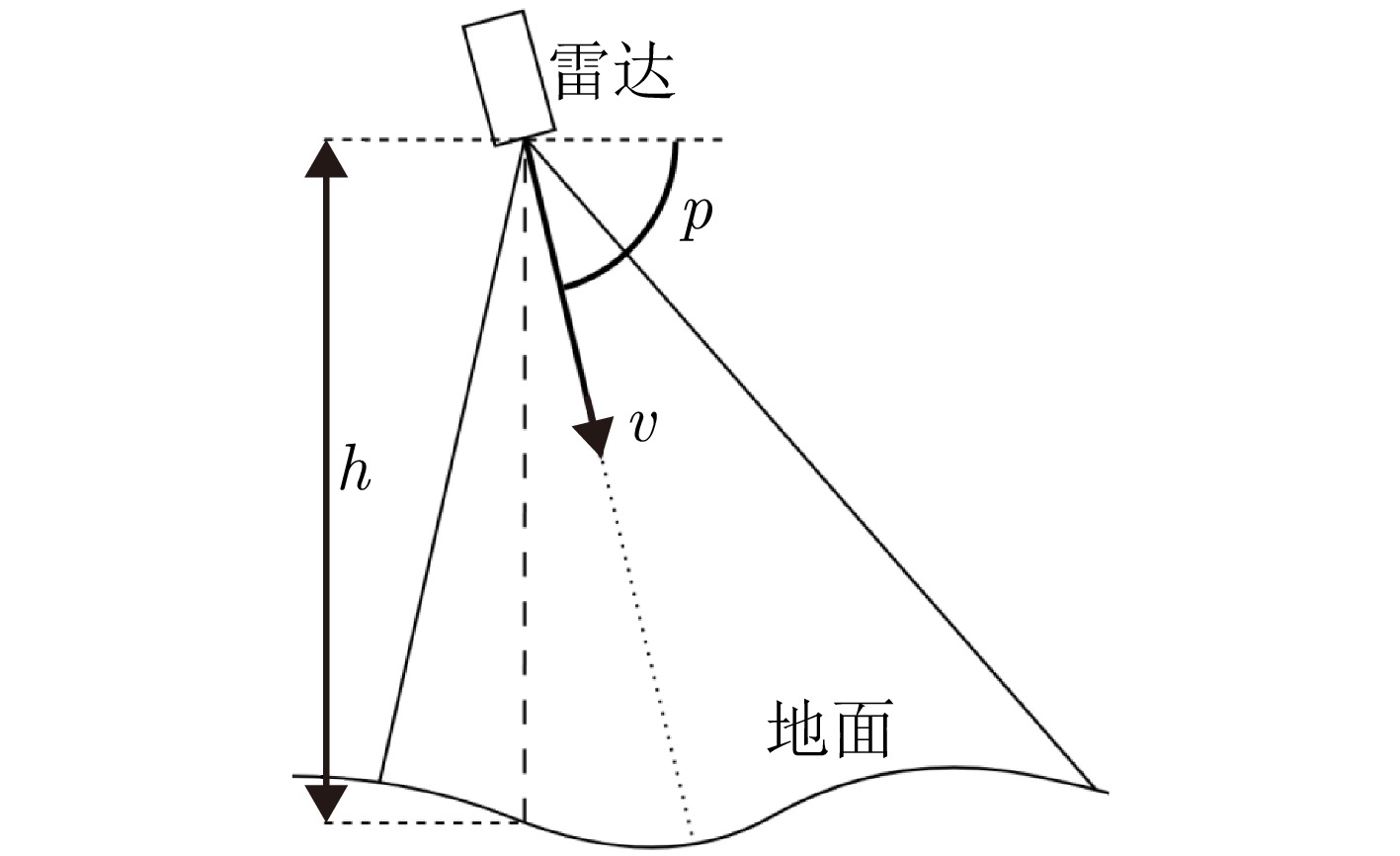
- Figure 1. An illustration of a near-vertical radar scenario
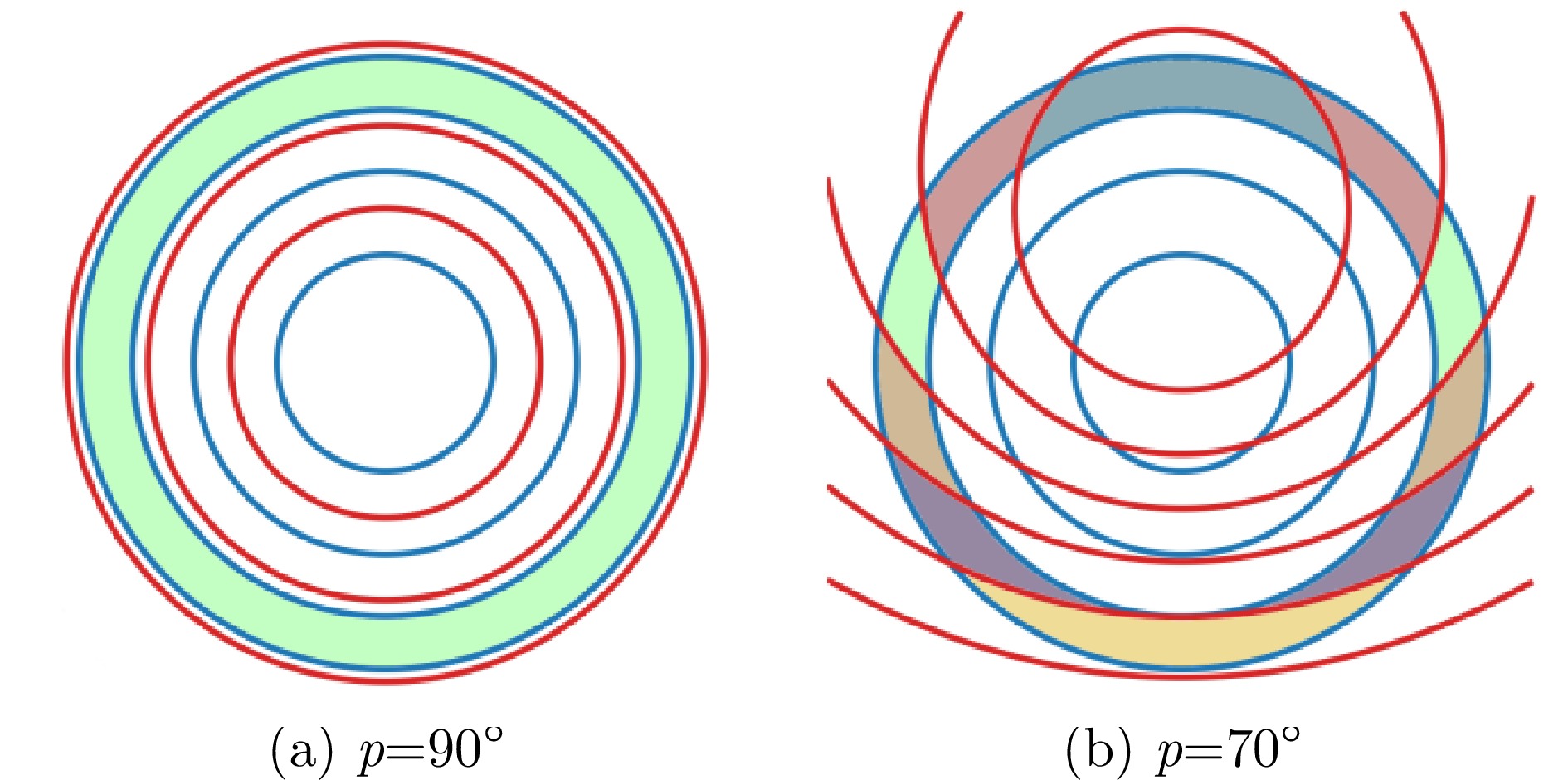
- Figure 2. A schematic illustration depicting isorange contours (in blue) and isovelocity contours (in red) in a near-vertical scenario
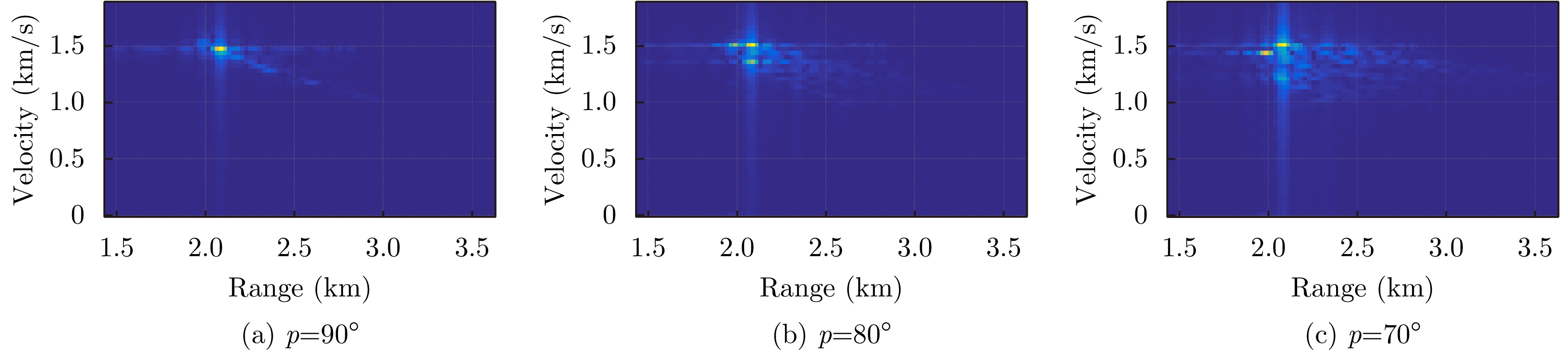
- Figure 3. Simulated RD maps of the same altitude and velocity with different pitch angles
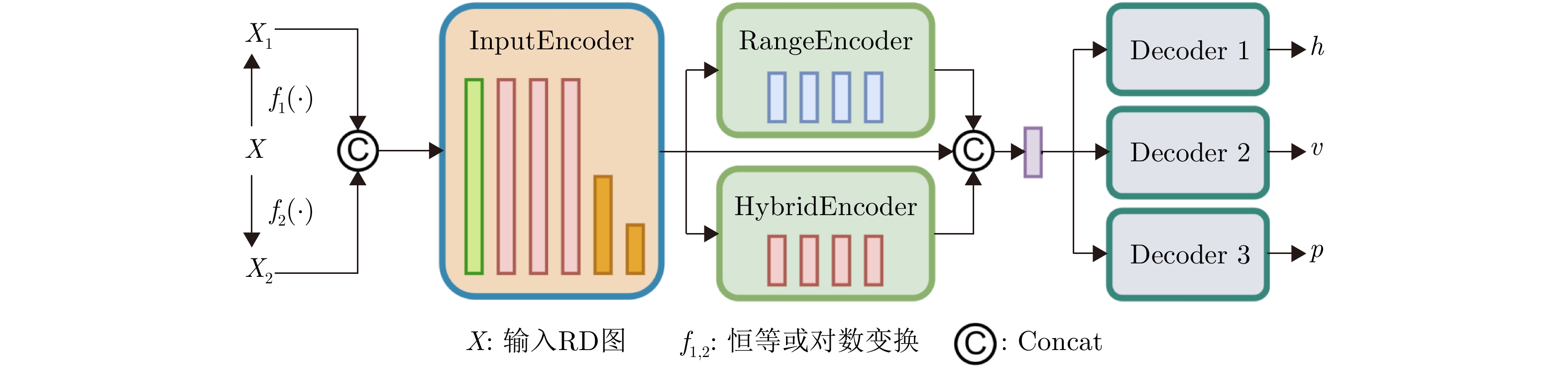
- Figure 4. Network architecture of RDMFNet
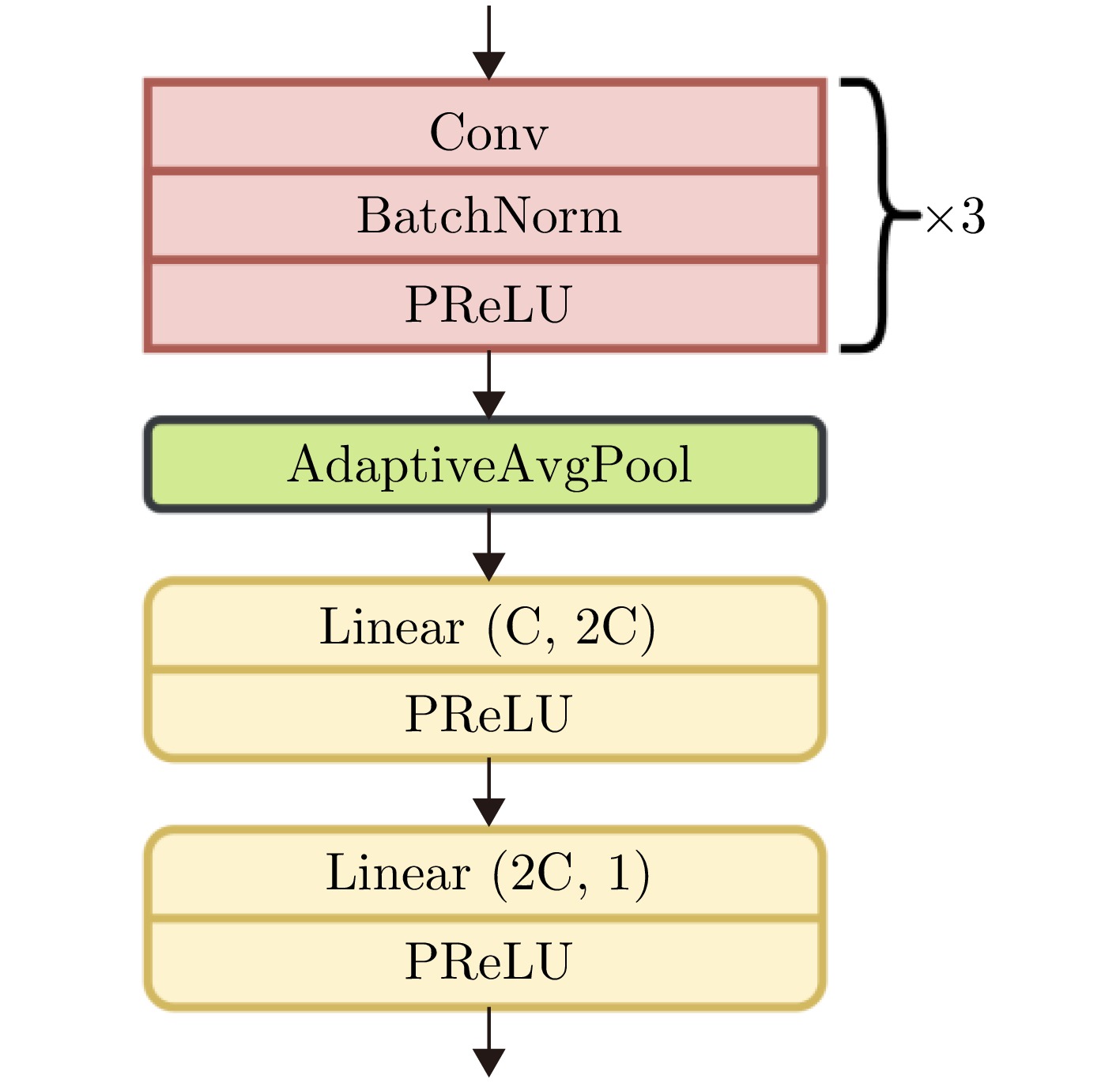
- Figure 5. The architecture of the decoders
- Figure 6. RMSE curves on the validation set during the two-stage training process
- Figure 7. Comparison of RMSE under different SNR settings


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: