- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Proofreading [3rd]
| Citation: | JIANG Meiqiu, LUO Haolan, GUO Shisheng, et al. Indoor target tracking method for millimeter-wave radar based on multipath extension mapping[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25245 |
Indoor Target Tracking Method for Millimeter-wave Radar Based on Multipath Extension Mapping
DOI: 10.12000/JR25245 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25245
More Information-
Abstract
With the widespread use of millimeter-wave radar technology in indoor target detection and tracking, multipath effects have become a key factor affecting tracking accuracy. Indoor millimeter-wave radar target tracking is highly susceptible to multipath interference, and conventional point-target tracking methods, which ignore the extended characteristics of targets and the multipath propagation mechanism, struggle to effectively suppress ghost targets caused by multipath reflections. To address this issue, this paper proposes an extension mapping-based extended target tracking (EM-ETT) method for indoor target tracking using millimeter-wave radar. First, a random matrix model is used to characterize the target’s geometric shape, with the extension modeled as an inverse Wishart distribution. Next, an extended projection framework is constructed by integrating a Monte Carlo-based statistical propagation mechanism. Through nonlinear multipath mapping of scattering points from the true target, ghost point clouds are generated, and their extended state priors are estimated. Furthermore, a target–path association method is introduced to establish path associations in multipath propagation based on geometric consistency and likelihood evaluation, enhancing state discrimination capability. Experimental results demonstrate that in multitarget scenarios with multipath interference, the proposed method significantly improves state estimation accuracy and effectively prevents the generation of false trajectories. Compared with conventional point-target tracking algorithms, the proposed method exhibits significant advantages in both tracking accuracy and robustness. -

-
References
[1] ZHANG Jia, XI Rui, HE Yuan, et al. A survey of mmWave-based human sensing: Technology, platforms and applications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(4): 2052–2087. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3298300.[2] SOUMYA A, KRISHNA MOHAN C, and CENKERAMADDI L R. Recent advances in mmWave-radar-based sensing, its applications, and machine learning techniques: A review[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(21): 8901. doi: 10.3390/s23218901.[3] CUI Han and DAHNOUN N. High precision human detection and tracking using millimeter-wave radars[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2021, 36(1): 22–32. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2020.3021322.[4] GRANSTRÖM K, BAUM M, and REUTER S. Extended object tracking: Introduction, overview and applications[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1604.00970, 2016.[5] JIANG Meiqiu, GUO Shisheng, LUO Haolan, et al. A robust target tracking method for crowded indoor environments using mmWave radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(9): 2425. doi: 10.3390/rs15092425.[6] SHAMSFAKHR F, MACII D, PALOPOLI L, et al. A multi-target detection and position tracking algorithm based on mmWave-FMCW radar data[J]. Measurement, 2024, 234: 114797. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114797.[7] HUANG Xu, CHEENA H, THOMAS A, et al. Indoor detection and tracking of people using mmWave sensor[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 2021(1): 6657709. doi: 10.1155/2021/6657709.[8] LI Shenglei and HISHIYAMA R. An indoor people counting and tracking system using mmWave sensor and sub-sensors[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023, 56(2): 7096–7101. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.577.[9] SVENSSON L, SVENSSON D, GUERRIERO M, et al. Set JPDA filter for multitarget tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(10): 4677–4691. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2161294.[10] TEXAS Instruments Inc. Tracking radar targets with multiple reflection points[EB/OL]. https://dev.ti.com/tirex/explore/node?isTheia=false&node=A__AObLJnMJzRrRFRE5nTbQ1g__radar_toolbox__1AslXXD__2.20.00.05&placeholder=true, 2023.[11] LAN Jian. Extended object tracking using random matrix with extension-dependent measurement numbers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4464–4477. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3241888.[12] HAAG S, DURAISAMY B, GOVAERS F, et al. Extended object tracking assisted adaptive clustering for radar in autonomous driving applications[C]. 2019 Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications (SDF), Bonn, Germany, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/SDF.2019.8916658.[13] BAUM M and HANEBECK U D. Extended object tracking with random hypersurface models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(1): 149–159. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120107.[14] BAUM M, NOACK B, and HANECK U D. Extended object and group tracking with elliptic random hypersurface models[C]. 2010 13th International Conference on Information Fusion, Edinburgh, UK, 2010: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ICIF.2010.5711854.[15] CAO Xiaomeng, LAN Jian, LI X R, et al. Automotive radar-based vehicle tracking using data-region association[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 8997–9010. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3089676.[16] CAO Xiaomeng, LAN Jian, LIU Yushuang, et al. Tracking of rectangular object using key points with regionally concentrated measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(6): 5312–5327. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3332606.[17] HAO Zhanjun, YAN Hao, DANG Xiaochao, et al. Millimeter-wave radar localization using indoor multipath effect[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(15): 5671. doi: 10.3390/s22155671.[18] COPA E I P, AZIZ K, RYKUNOV M, et al. Radar fusion for multipath mitigation in indoor environments[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266697.[19] LIU Chenwen, LIU Shengheng, ZHANG Cheng, et al. Multipath propagation analysis and ghost target removal for FMCW automotive radars[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IET IRC 2020), Chongqing, China, 2020: 330–334. doi: 10.1049/icp.2021.0554.[20] FENG Ruoyu, DE GREEF E, RYKUNOV M, et al. Multipath ghost recognition for indoor MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5104610. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3109381.[21] PARK J K, PARK J H, and KIM K T. Multipath signal mitigation for indoor localization based on MIMO FMCW radar system[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(2): 2618–2629. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3292349.[22] LUO Haolan, ZHU Zhihao, JIANG Meiqiu, et al. An effective multipath ghost recognition method for sparse MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5111611. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3335454.[23] LI Yunda and SHANG Xiaolei. Multipath ghost target identification for automotive MIMO radar[C]. 2022 IEEE 96th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2022-Fall), London, United Kingdom, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2022-Fall57202.2022.10012904.[24] GARCIA J M, PROPHET R, MICHEL J C F, et al. Identification of ghost moving detections in automotive scenarios with deep learning[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Detroit, USA, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2019.8726704.[25] FENG Ruoyu, DE GREEF E, RYKUNOV M, et al. Multipath ghost classification for MIMO radar using deep neural networks[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764274.[26] PULFORD G W and EVANS R J. A multipath data association tracker for over-the-horizon radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(4): 1165–1183. doi: 10.1109/7.722704.[27] PULFORD G W and LA SCALA B F. Multihypothesis Viterbi data association: Algorithm development and assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 583–609. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461643.[28] HABTEMARIAM B, THARMARASA R, THAYAPARAN T, et al. A multiple-detection joint probabilistic data association filter[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 461–471. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2256772.[29] CHEN Weiyan, YANG Hongliu, BI Xiaoyang, et al. Environment-aware multi-person tracking in indoor environments with mmWave radars[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2023, 7(3): 89. doi: 10.1145/3610902.[30] FENG Ruoyu, DE GREEF E, RYKUNOV M, et al. Multipath ghost recognition and joint target tracking with wall estimation for indoor MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2024, 2: 154–164. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2024.3354509.[31] CHENG Qiaoling, YANG Zhaocheng, CHU Ping, et al. Space boundary-aware people tracking and counting method using MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(14): 27209–27220. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3577228.[32] LIAN Tongsheng, CHU Ping, YANG Zhaocheng, et al. Indoor multi-target tracking exploiting target motion characteristics and prior boundary knowledge using multiple-input multiple-output radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2025, 34(6): 1767–1777. doi: 10.23919/cje.2024.00.165.[33] TUNCER B and ÖZKAN E. Random matrix based extended target tracking with orientation: A new model and inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1910–1923. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3065136.[34] JIANG Meiqiu, LUO Haolan, GUO Shisheng, et al. Indoor human tracking with 3-D expansion estimation based on mmWave radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(6): 16647–16665. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3595827.[35] TAO Ding, ANFINSEN S N, and BREKKE C. Robust CFAR detector based on truncated statistics in multiple-target situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 117–134. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2451311.[36] WOLFEL M and MCDONOUGH J. Minimum variance distortionless response spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2005, 22(5): 117–126. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2005.1511829.[37] SCHUBERT E, SANDER J, ESTER M, et al. DBSCAN revisited, revisited: Why and how you should (still) use DBSCAN[J]. ACM Transactions on Database Systems, 2017, 42(3): 19. doi: 10.1145/3068335.[38] FELDMANN M, FRÄNKEN D, and KOCH W. Tracking of extended objects and group targets using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2101064.[39] SEDEHI M, LOMBARDO P, and FARINA A. A modified M/N logic for track initiation of low observable targets using amplitude information[C]. 2006 International Radar Symposium (IRS), Kraków, Poland, 2006: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/IRS.2006.4338080.[40] Texas Instruments Inc. 60GHz mmWave sensor EVMs[EB/OL]. https://www.ti.com/lit/ug/swru546e/swru546e.pdf, 2022.[41] Texas Instruments Inc. DCA1000EVM data capture card[EB/OL]. https://www.ti.com.cn/cn/lit/pdf/spruij4, 2019. -
Proportional views

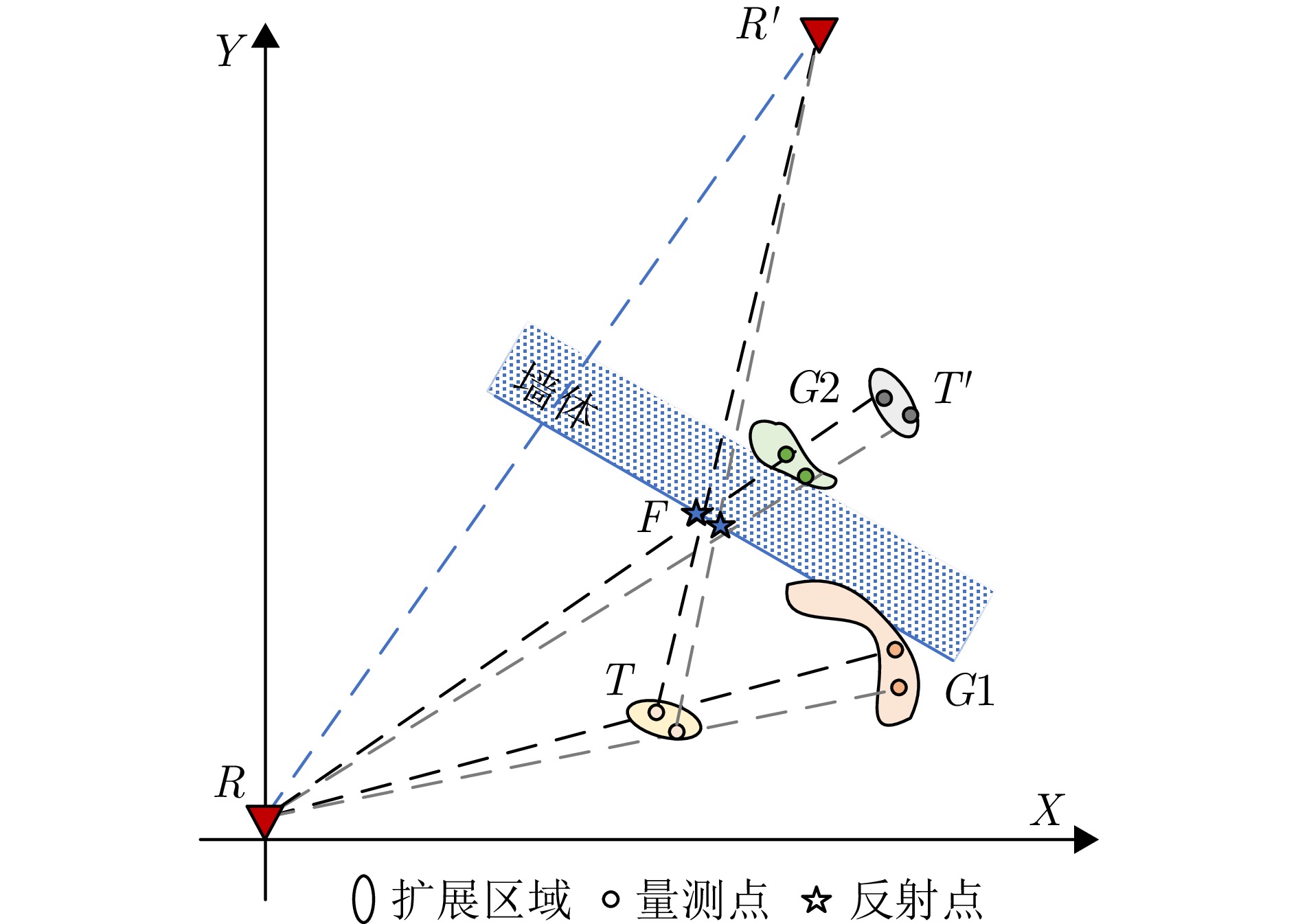
- Figure 1. Illustration of the indoor multipath propagation model
- Figure 2. Three-dimensional indoor scene
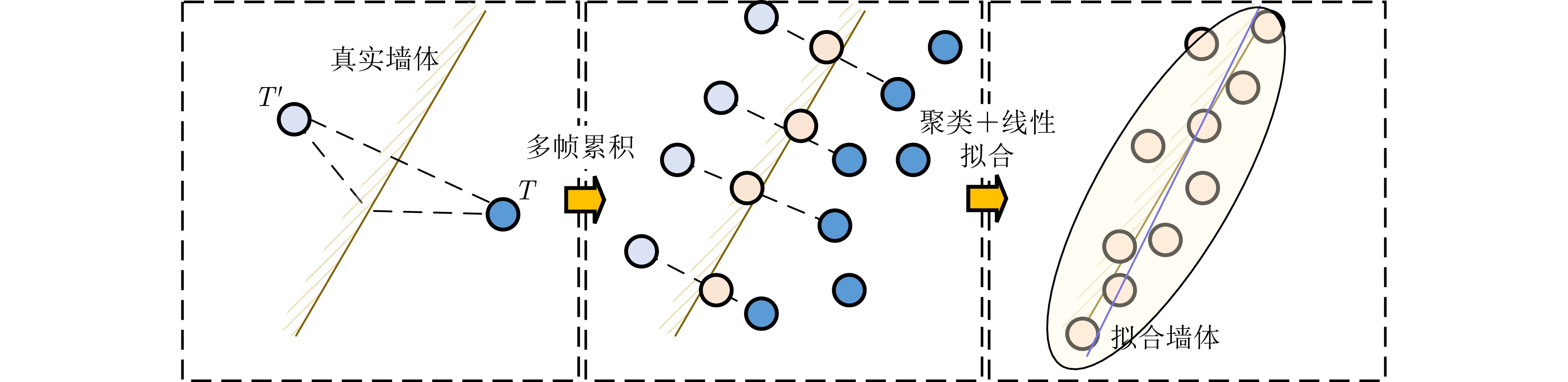
- Figure 3. Flowchart of the wall estimation process
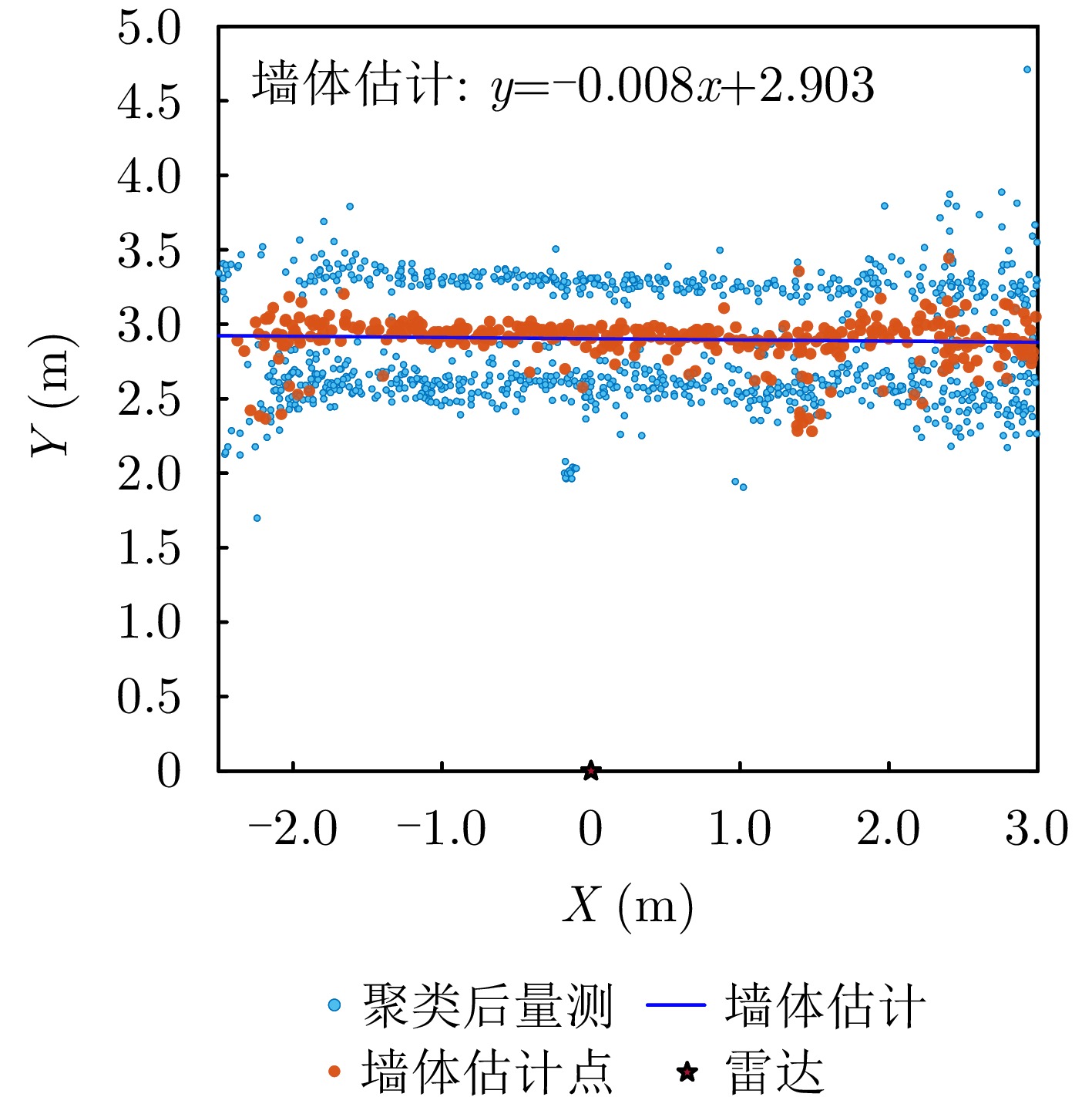
- Figure 4. Experimental results of wall estimation
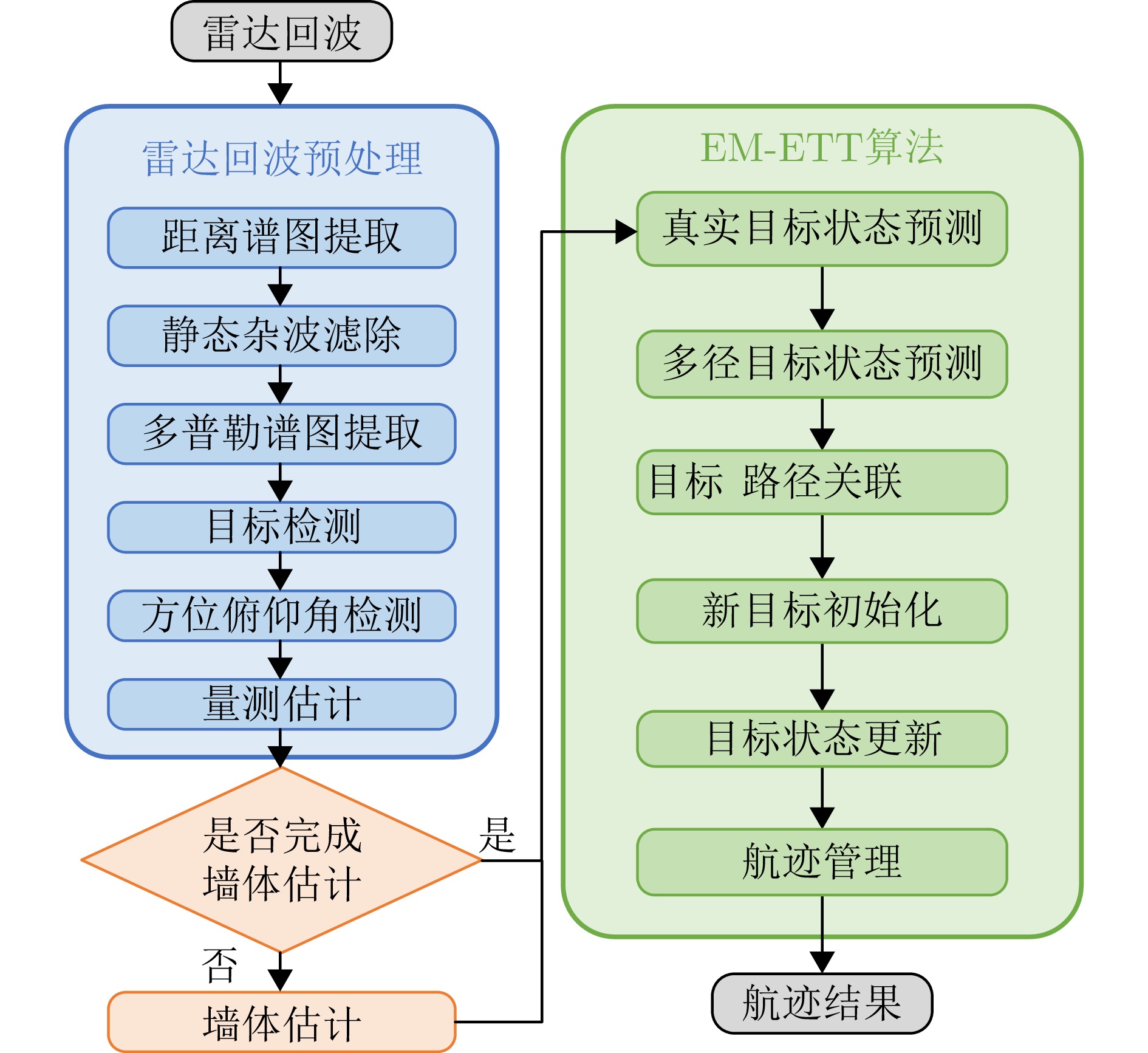
- Figure 5. Flowchart of the extended target tracking algorithm in multipath scenarios
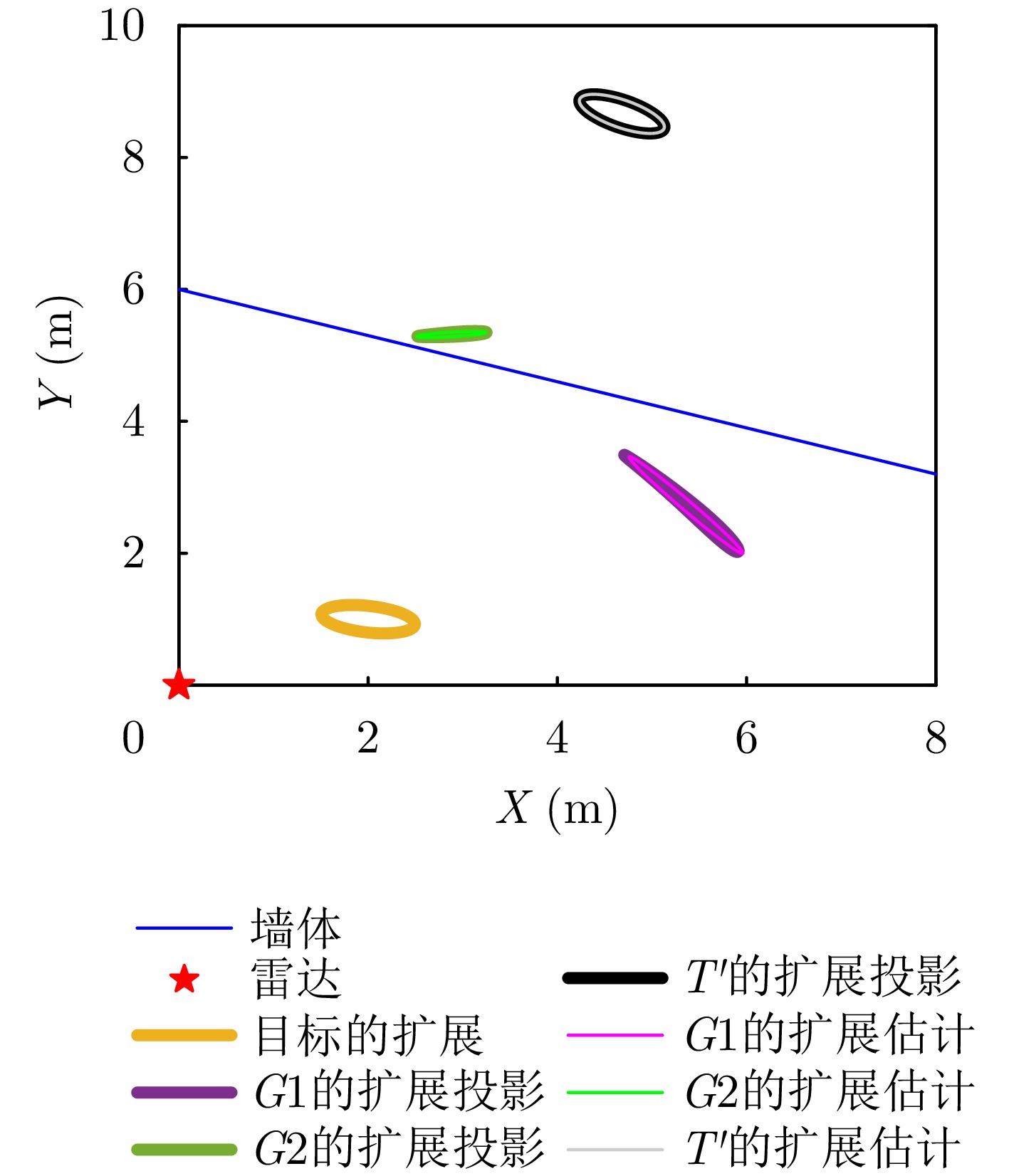
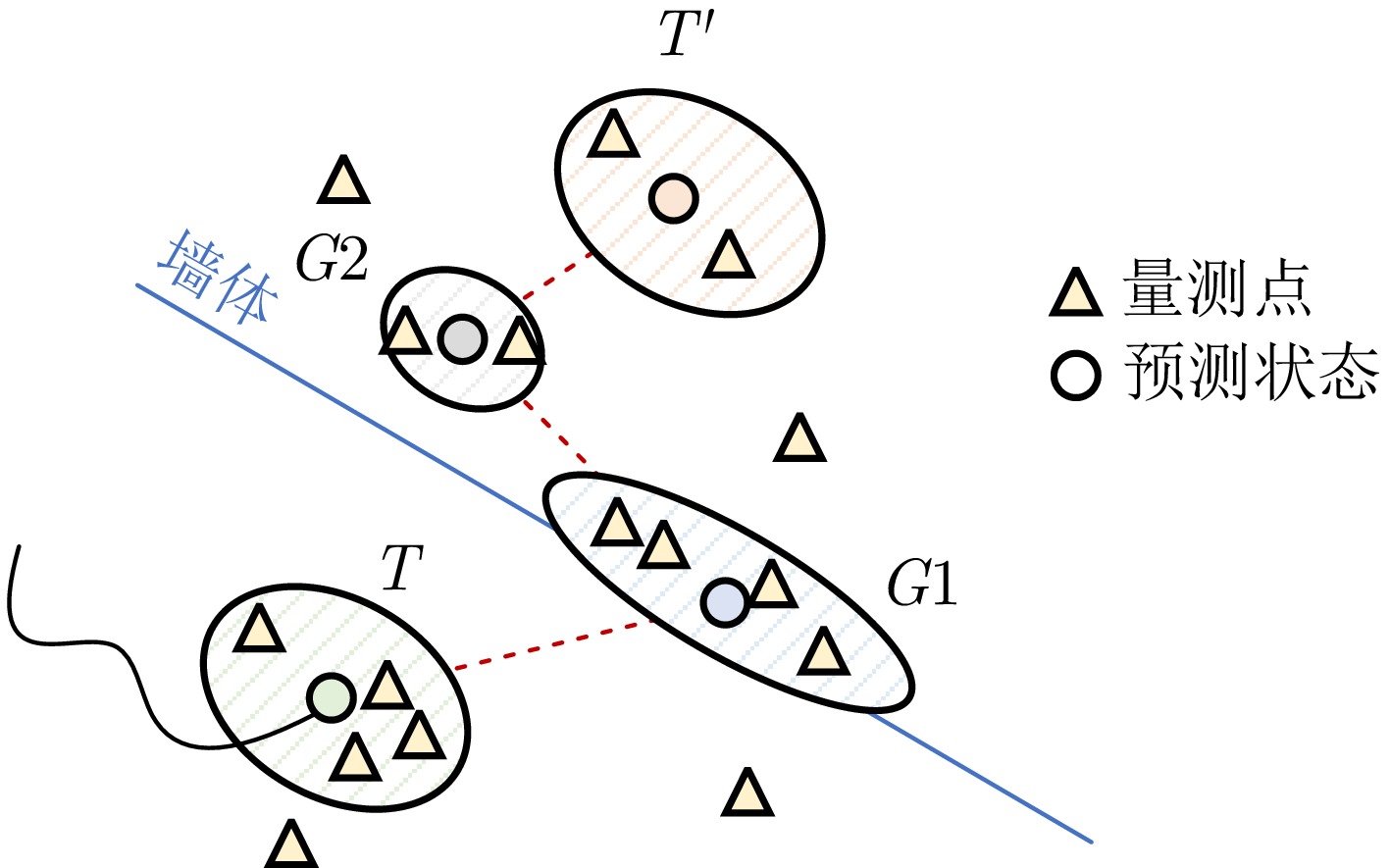
- Figure 6. Illustration of the predicted results of extended multipath target states
- Figure 7. Illustration of the target association model
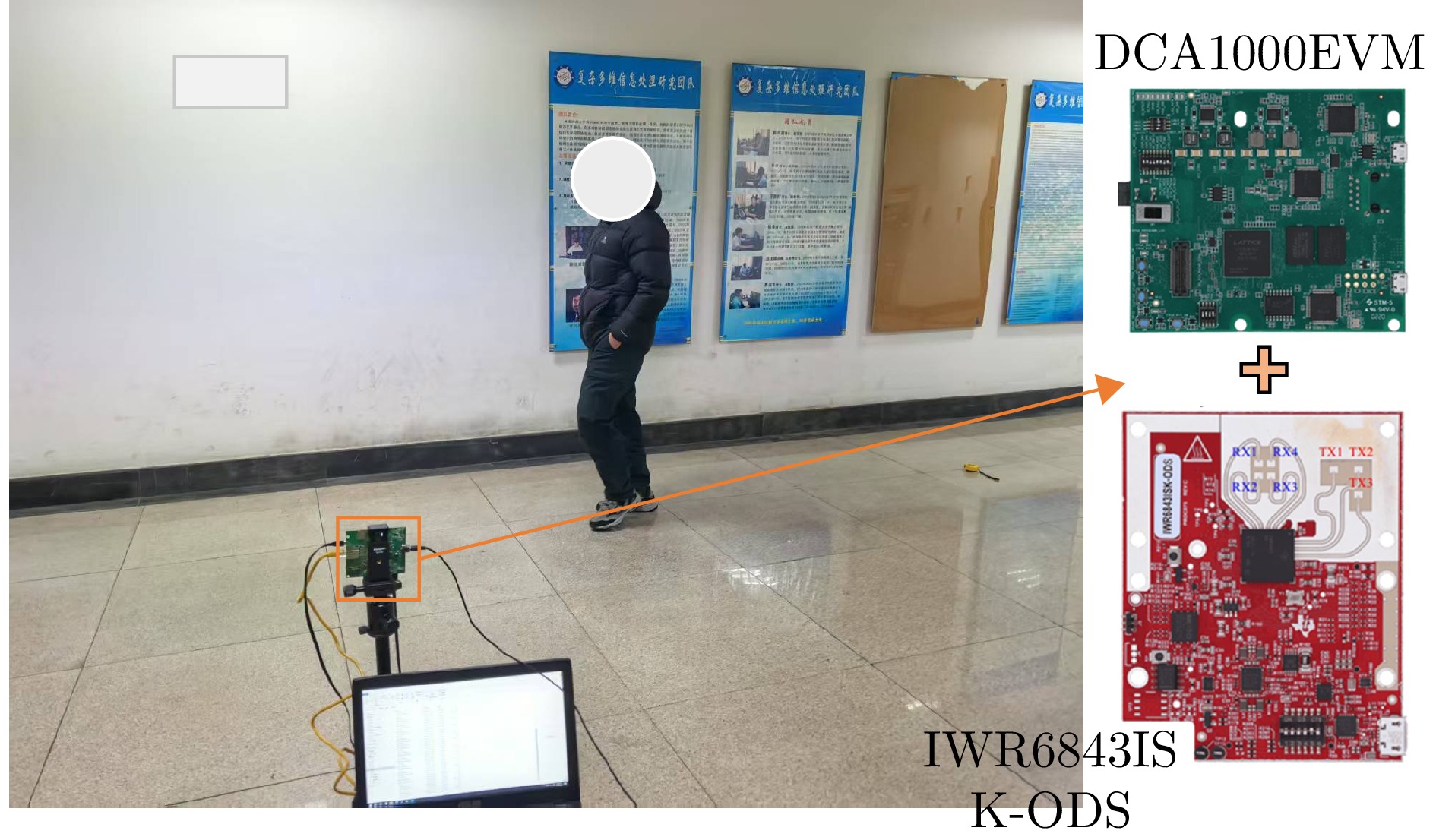
- Figure 8. Illustration of the experimental setup
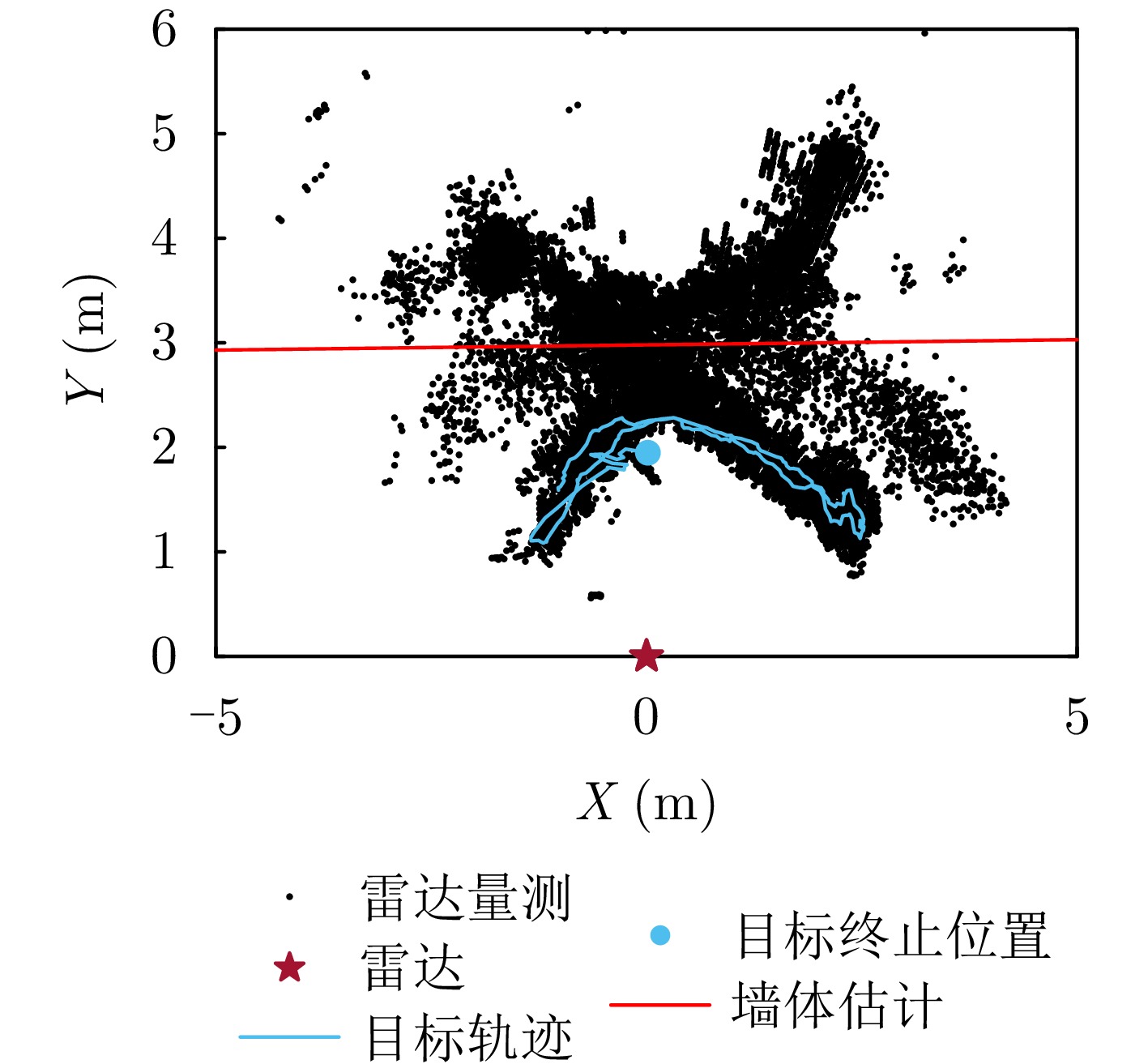
- Figure 9. Single-target tracking results
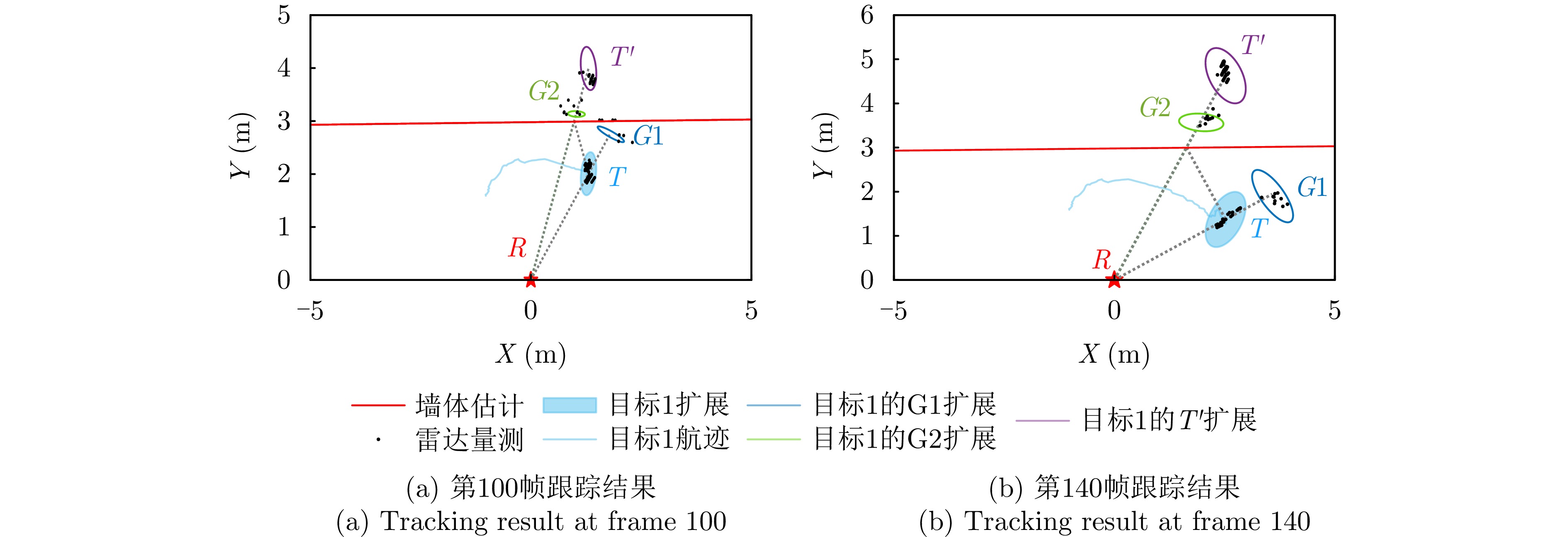
- Figure 10. Tracking results for the single-target scenario
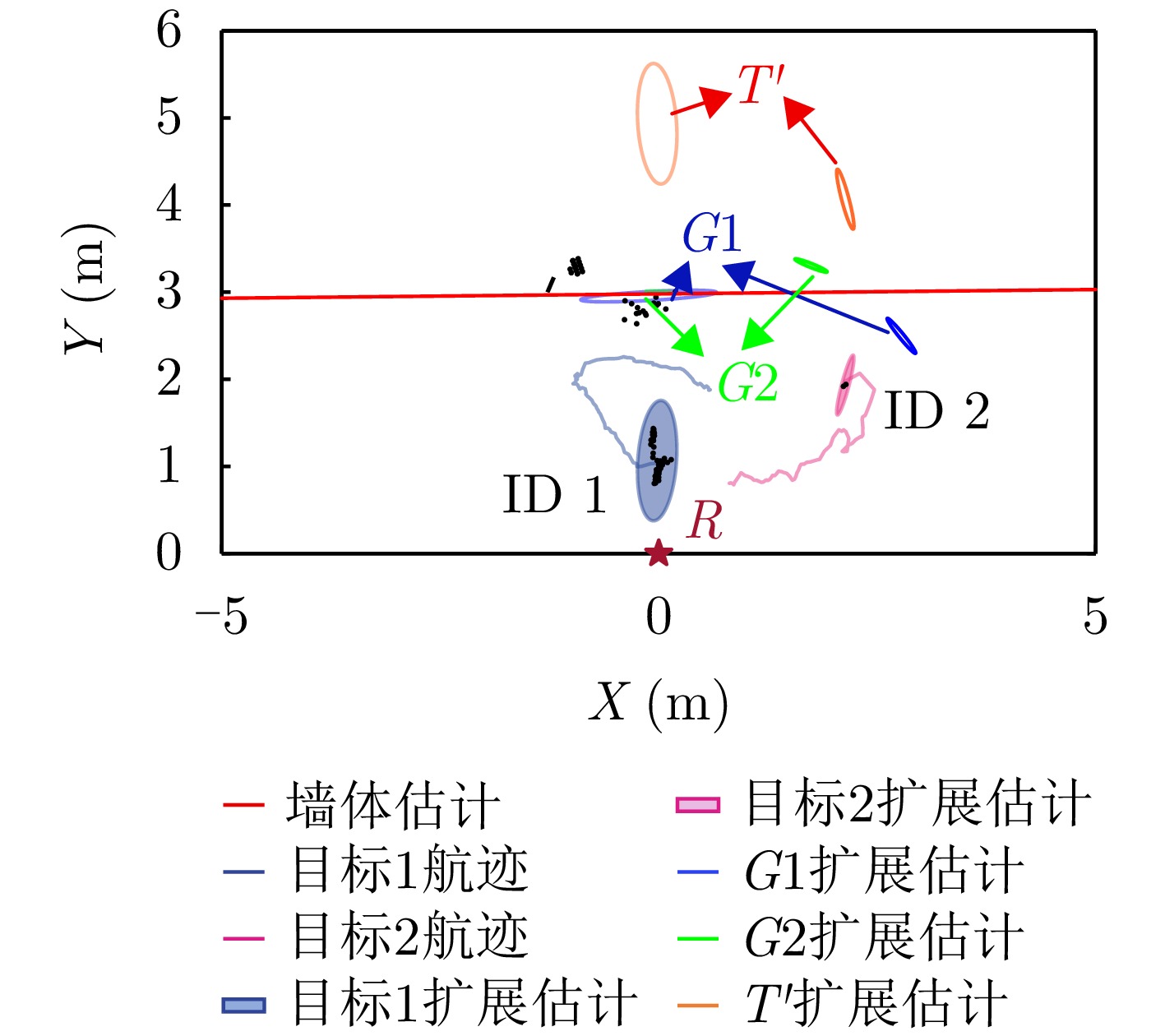
- Figure 11. Tracking results of two targets at frame 60
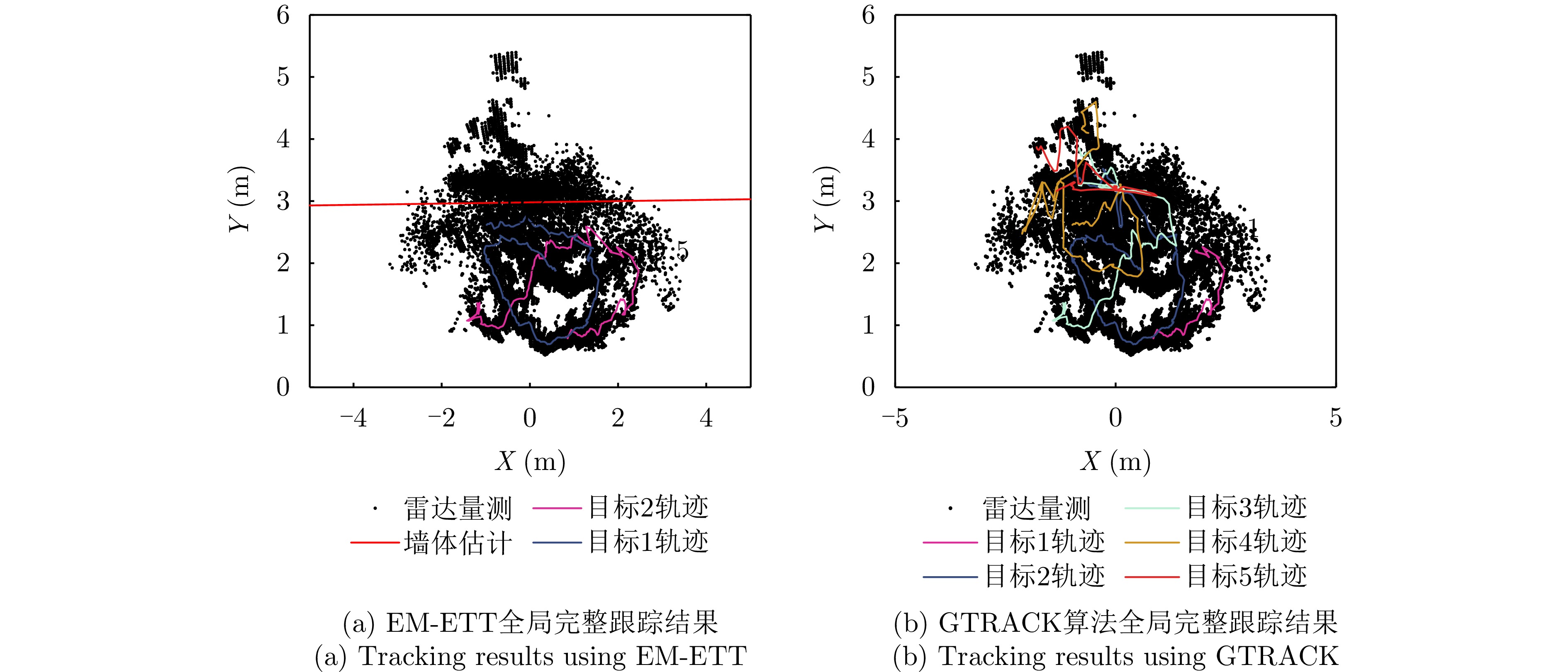
- Figure 12. Comparison of multi-target tracking results using EM-ETT and GTRACK
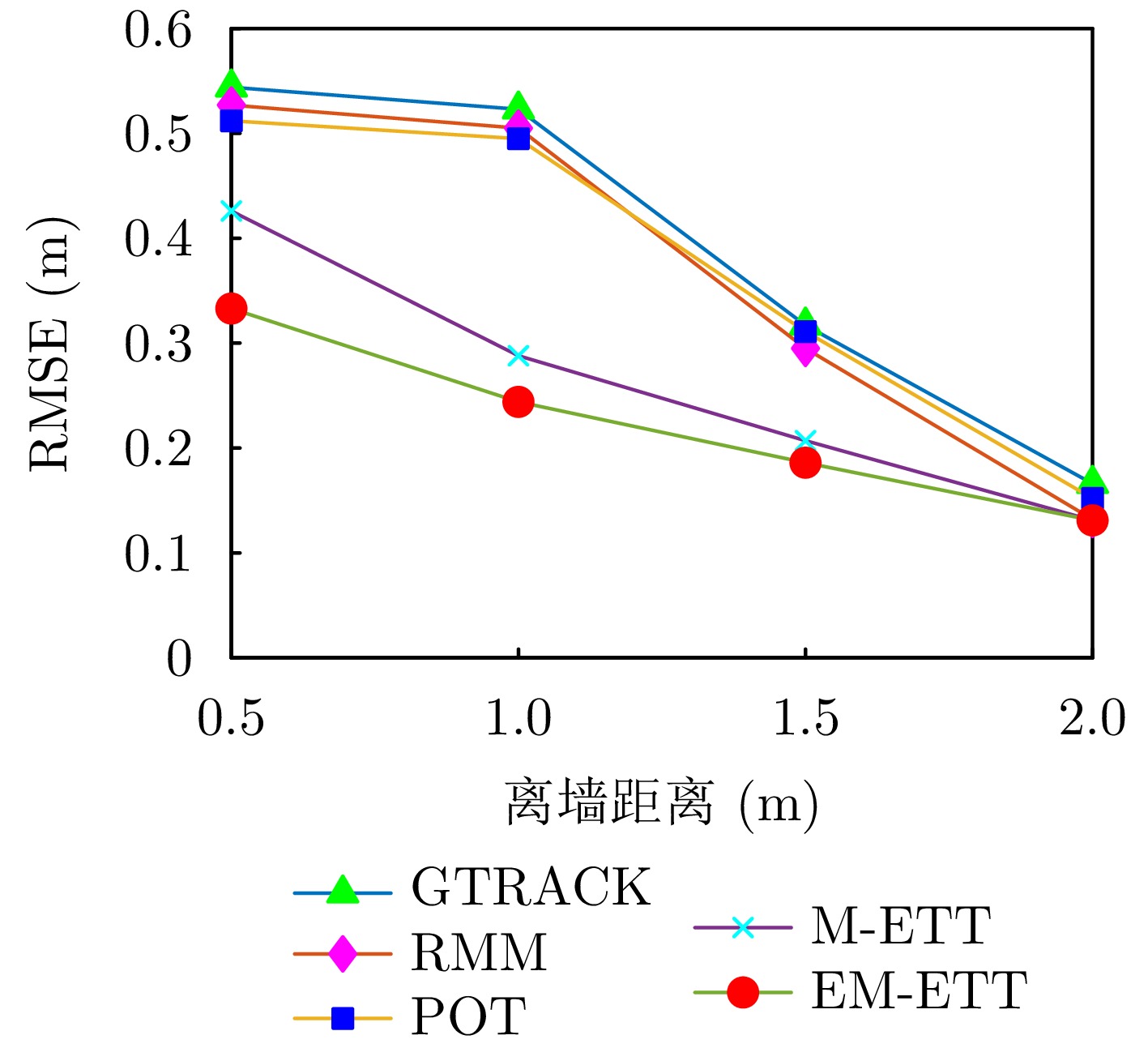
- Figure 13. RMSE comparison under different distances to the wall
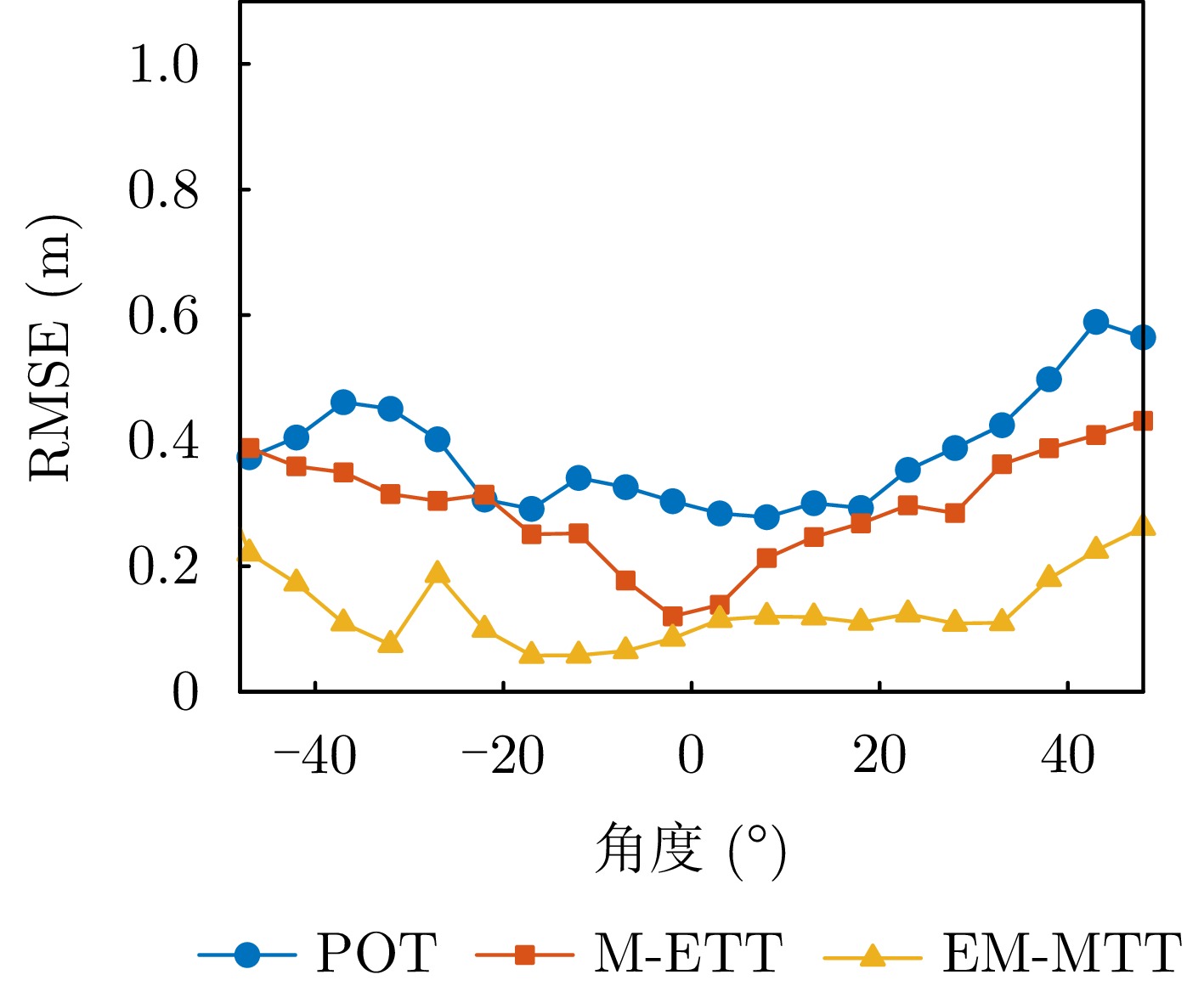
- Figure 14. RMSE comparison under different azimuth
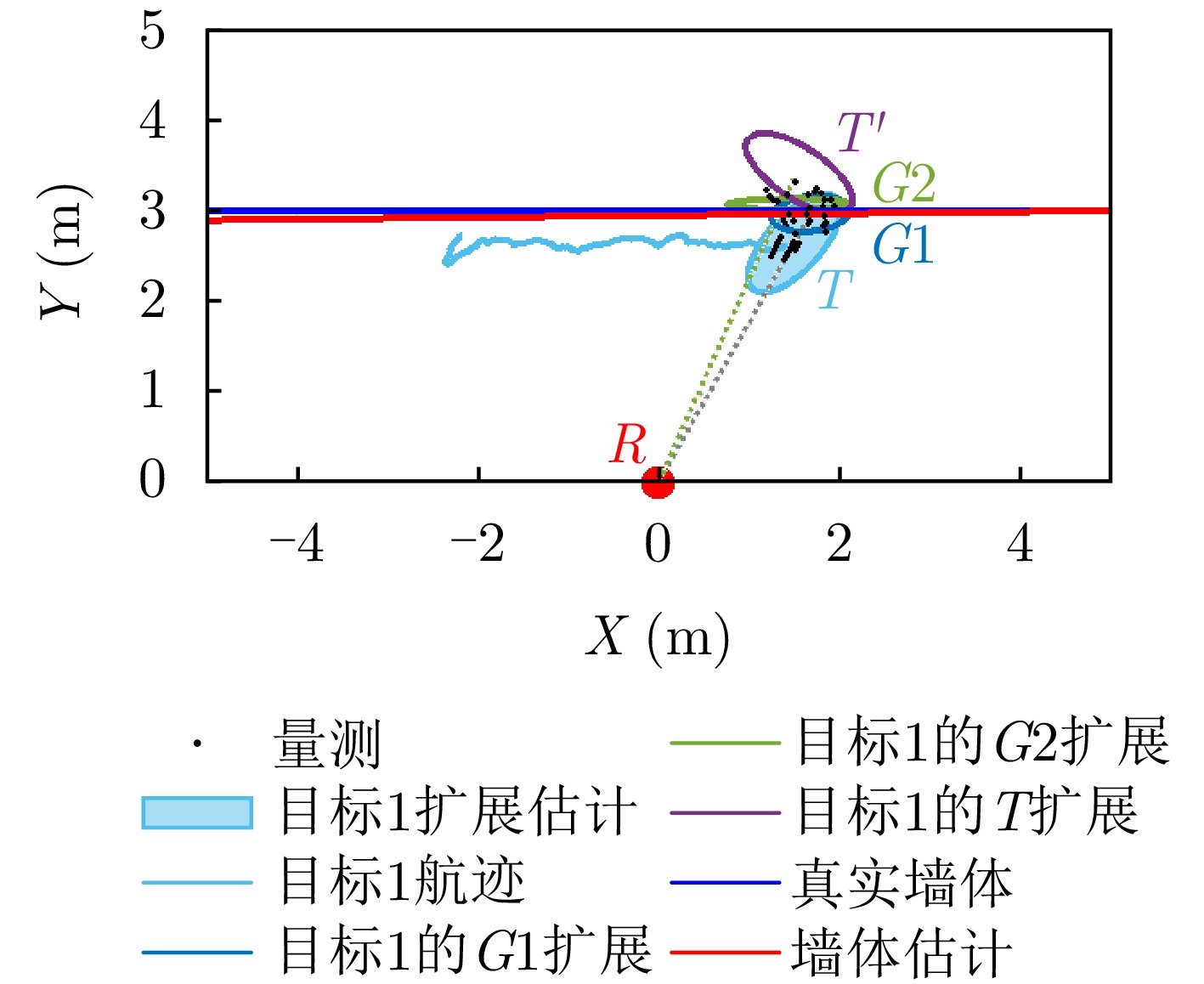
- Figure 15. Tracking results of a single target walking along the wall
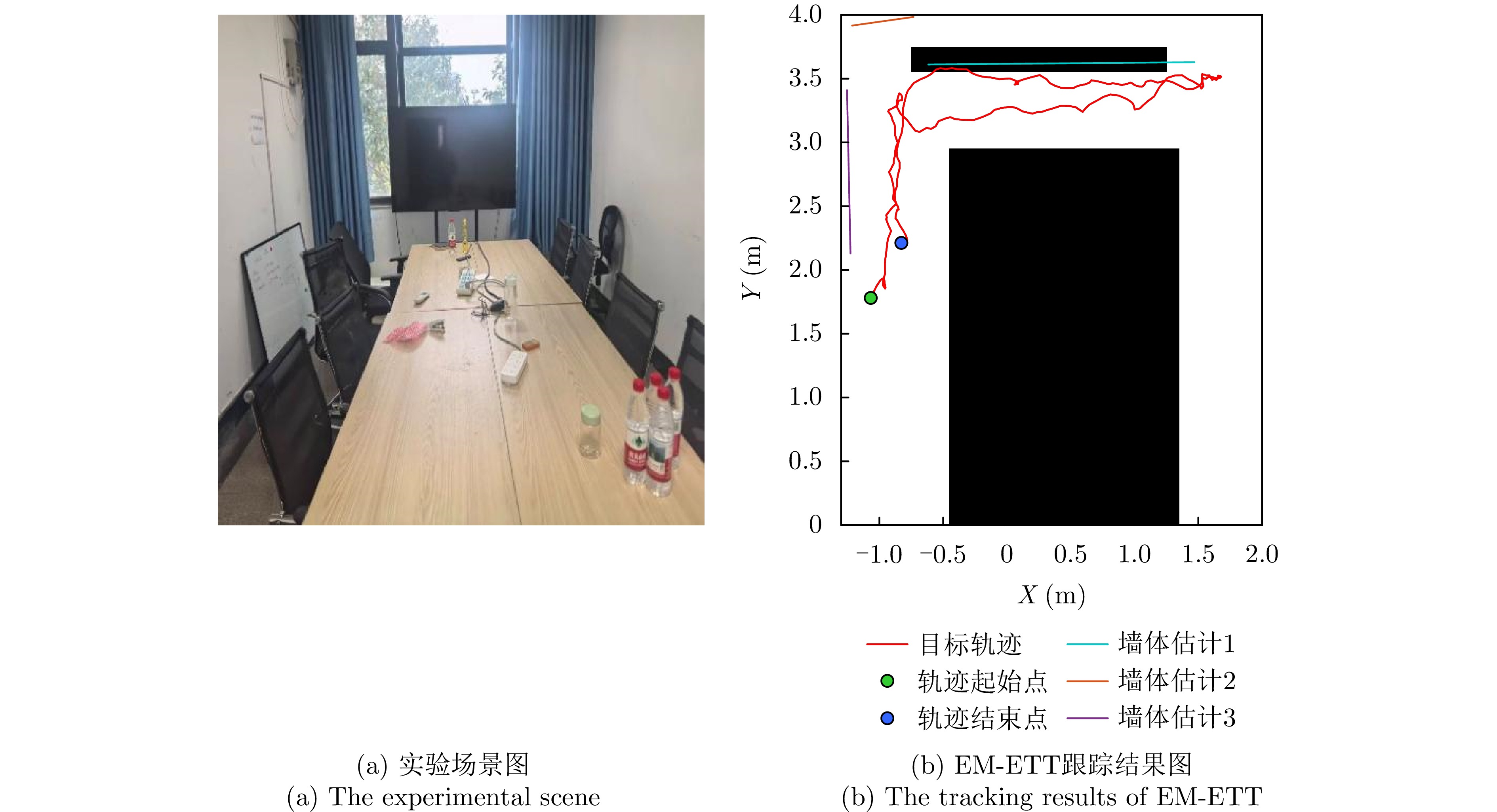
- Figure 16. Tracking results in the conference room
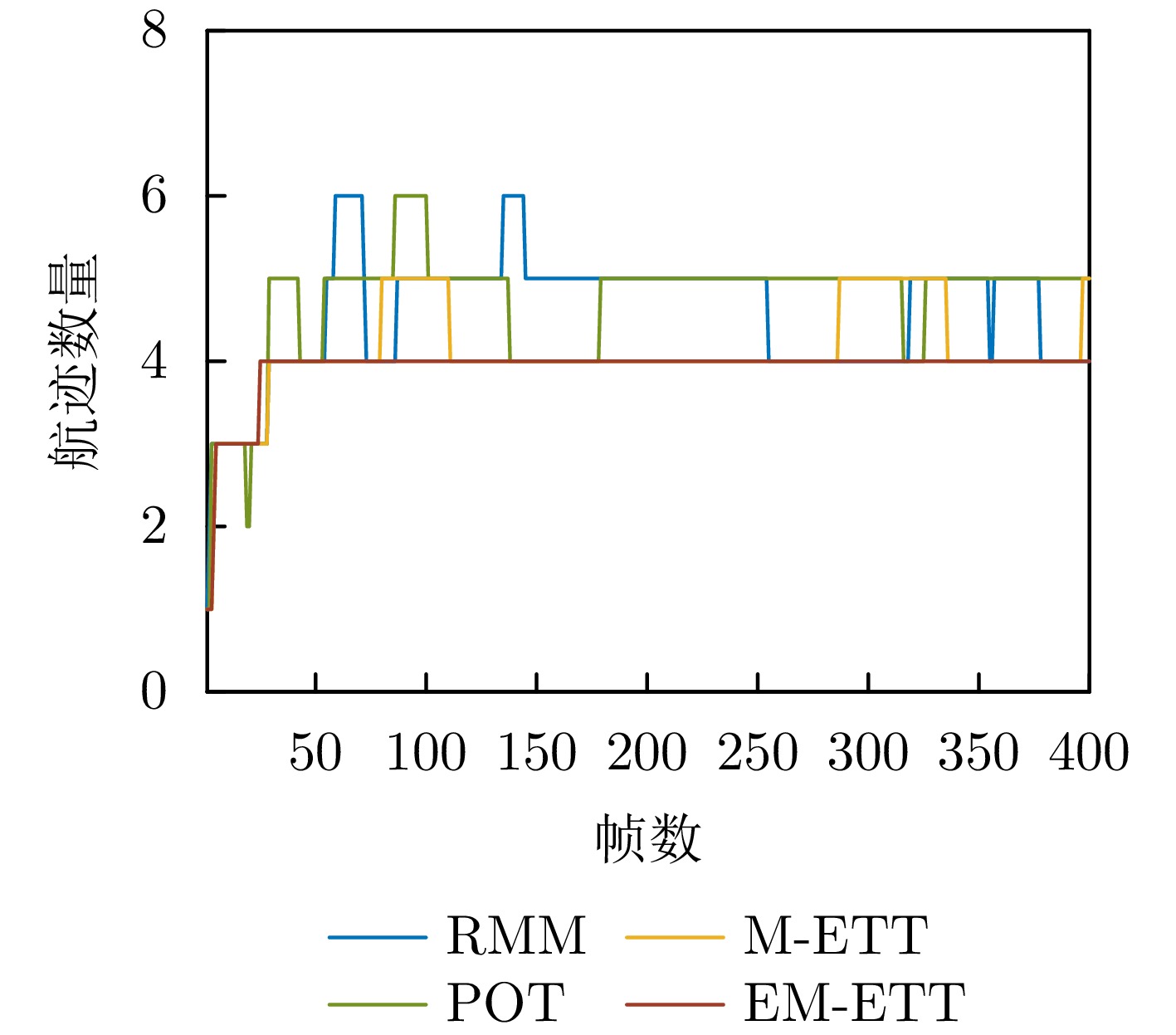
- Figure 17. Variation of the estimated number of tracks in the four-target scenario


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: