- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Proofreading [3rd]
| Citation: | CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Jia, WANG Xinghai, et al. Digital array radar lss-target detection dataset (LSS-DAUR-1.0) and graph network-based target classification[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25240 |
Digital Array Radar LSS-target Detection Dataset (LSS-DAUR-1.0) and Graph Network-based Target Classification
DOI: 10.12000/JR25240 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25240
More Information-
Abstract
To address issues such as insufficient feature extraction, limited spatiotemporal correlation modeling, and poor classification performance in radar classification of low, slow, and small targets, this paper investigates on graph network-based feature extraction and classification methods. First, focusing on digital array ubiquitous radar, a radar detection dataset for LSS targets, named LSS-DAUR-1.0, is constructed; it contains Doppler and track data for six types of targets: passenger ships, speedboats, helicopters, rotor drones, birds, and fixed-wing drones. Second, based on this dataset, the multidomain and multidimensional characteristics of the targets are analyzed, and the complementarity between Doppler and physical motion features is verified through correlation and cosine similarity analyses. On this basis, a Graph Convolutional Network with Dynamic Graph Construction (DG-GCN) classification method fusing dual features is proposed. An adaptive window adjustment, a hybrid attenuation function, and a dynamic threshold mechanism are designed to construct an adaptive dynamic graph based on spatiotemporal correlation. Combined with graph convolution–based feature learning and classification modules, this approach achieves refined classification of low, slow, and small targets. Validation on the LSS-DAUR-1.0 dataset shows that the DG-GCN achieves 99.66% classification accuracy, which is 6.78% and 17.97% higher than that of ResNet and Transformer models, respectively. The total processing time is only 4.98 ms, which is more than 80% lower than that of the aforementioned comparison models. Hence, the DG-GCN achieves both high accuracy and efficiency. In addition, noise environment tests show good robustness. Ablation experiments verify that the dynamic edge weight mechanism compensates for the lack of spatial feature correlation in purely temporal connections and improves the model’s generalizability. -

-
References
[1] 陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068.CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068.[2] 郭瑞, 张月, 田彪, 等. 全息凝视雷达系统技术与发展应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Review of the technology, development and applications of holographic staring radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.[3] JAHANGIR M and BAKER C J. L-band staring radar performance against micro-drones[C]. 2018 19th International Radar Symposium, Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2018.8448107.[4] BENNETT C, JAHANGIR M, FIORANELLI F, et al. Use of symmetrical peak extraction in drone micro-Doppler classification for staring radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266702.[5] JAHANGIR M, ATKINSON G M, ANTONIOU M, et al. Measurements of birds and drones with L-band staring radar[C]. 2021 21st International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS51887.2021.9466224.[6] GRIFFIN B, BALLERI A, BAKER C, et al. Prototyping a dual-channel receiver for use in a staring cooperative radar network for the detection of drones[C]. 2021 21st International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2021: 1–7. doi: 10.23919/IRS51887.2021.9466221.[7] 徐世友, 戴婷, 陈曾平. 基于多维特征的全息雷达“低慢小”目标识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(11): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.11.001.XU Shiyou, DAI Ting, and CHEN Zengping. LSS target recognition in holographic radar based on multi-dimensional features[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(11): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.11.001.[8] 陈小龙, 黄勇, 关键, 等. MIMO雷达微弱目标长时积累技术综述[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001.CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Review of long-time integration techniques for weak targets using MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1947–1964. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.001.[9] 贺治华, 段佳, 芦达. 雷达海面目标识别技术研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 61–68. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.006.HE Zhihua, DUAN Jia, and LU Da. A review of radar sea target recognition technology[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 61–68. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.006.[10] 田凯祥, 于恒力, 王中训, 等. 基于雷达目标特征可分性的一维特征选择方法[J]. 海军航空大学学报, 2024, 39(4): 453–460,500. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2024.04.007.TIAN Kaixiang, YU Hengli, WANG Zhongxun, et al. One-dimensional feature selection method based on radar target feature divisibility[J]. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2024, 39(4): 453–460,500. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.2097-1427.2024.04.007.[11] KUMAWAT H C, CHAKRABORTY M, RAJ A A B, et al. DIAT-μSAT: Small aerial targets’ micro-Doppler signatures and their classification using CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 6004005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3102039.[12] PARK D, LEE S, PARK S, et al. Radar-spectrogram-based UAV classification using convolutional neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(1): 210. doi: 10.3390/s21010210.[13] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077.[14] WANG Jinhao, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. A time-frequency representation method based on ETF-MDNet for radar target micro-motion features[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2025, 34(4): 1199–1208. doi: 10.23919/cje.2024.00.233.[15] YU Xiaojie, WEI Song, FANG Yuyuan, et al. Low-altitude slow small target threat assessment algorithm by exploiting sequential multifeature with long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(18): 21524–21533. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3301090.[16] ZHU J, CHEN H and YE W. A hybrid CNN–LSTM network for the classification of human activities based on micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24713–24720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971064.[17] SONG Qiang, HUANG Shilin, ZHANG Yue, et al. Radar target classification using enhanced Doppler spectrograms with ResNet34_CA in ubiquitous radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(15): 2860. doi: 10.3390/rs16152860.[18] WU Qi, CHEN Jie, LU Yue, et al. A complete automatic target recognition system of low altitude, small RCS and slow speed (LSS) targets based on multi-dimensional feature fusion[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(22): 5048. doi: 10.3390/s19225048.[19] YUAN Wang, CHEN Xiaolong, DU Xiaolin, et al. A low slow small target classification network model based on K-band radar dynamic multifeature data fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(1): 1656–1668. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3496493.[20] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段多角度FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-2.0)及特征融合分类方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multi-band multi-angle FMCW radar low-slow-small target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-2.0) and feature fusion classification methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1276–1293. doi: 10.12000/JR25004.[21] 赵子健, 许述文, 水鹏朗. 基于多域雷达回波数据融合的海面小目标分类网络模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(3): 696–706. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240818.ZHAO Zijian, XU Shuwen, and SHUI Penglang. A network model for sea surface small targets classification based on multidomain radar echo data fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(3): 696–706. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240818.[22] 何肖阳, 陈小龙, 杜晓林, 等. 基于CBAM-Swin-Transformer迁移学习的海上微动目标分类方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(4): 1155–1167. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.12.HE Xiaoyang, CHEN Xiaolong, DU Xiaolin, et al. Classification of maritime micromotion target based on transfer learning in CBAM-Swin-Transformer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1155–1167. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.12.[23] SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61–80. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005605.[24] KHEMANI B, PATIL S, KOTECHA K, et al. A review of graph neural networks: Concepts, architectures, techniques, challenges, datasets, applications, and future directions[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2024, 11(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s40537-023-00876-4.[25] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Maritime target detection based on radar graph data and graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133473.[26] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Radar Maritime Target detection via spatial–temporal feature attention graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5102615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358862.[27] Meng Han, Peng Yuexing, Wang Wenbo, et al. Spatio-temporal-frequency graph attention convolutional network for aircraft recognition based on heterogeneous radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(6): 5548–5559. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2204.07360.[28] MENG Han, PENG Yuexing, XIANG Wei, et al. Semantic feature-enhanced graph attention network for radar target recognition in heterogeneous radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(7): 6369–6377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3250708.[29] CHEN Lingfeng, PAN Zhiliang, LIU Qi, et al. HRRPGraphNet++: Dynamic graph neural network with meta-learning for few-shot HRRP radar target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(12): 2108. doi: 10.3390/rs17122108.[30] MENG Han, PENG Yuexing, and WANG Wenbo. Dynamic graph network augmented by contrastive learning for radar target classification[C]. 2024 IEEE Radar Conference, Denver, USA, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2458775.2024.10548626.[31] LIN Huiping, XIE Zixuan, ZENG Liang, et al. Multi-scale time-frequency representation fusion network for target recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(16): 2786. doi: 10.3390/rs17162786.[32] CHEN Lingfeng, SUN Xiao, PAN Zhiliang, et al. HRRPGraphNet: Make HRRPs to be graphs for efficient target recognition[J]. Electronics Letters, 2024, 60(22): e70088. doi: 10.1049/ell2.70088.[33] WANG Ruiqiu, SU Tao, XU Dan, et al. MIGA-Net: Multi-view image information learning based on graph attention network for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(11): 10779–10792. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3418979.[34] 陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1.0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142.[35] 陈小龙, 饶桂林, 关键, 等. 被动雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-PR-1.0)及多域特征提取和分析方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145.CHEN Xiaolong, RAO Guilin, GUAN Jian, et al. Passive radar low slow small detection dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) and multi-domain feature extraction and analysis methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145.[36] 邓振华, 陈小龙, 薛伟, 等. 海空背景下低慢小目标泛探雷达多域多维特征建模与分析[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001.DENG Zhenhua, CHEN Xiaolong, XUE Wei, et al. Multi-domain and multi-dimensional feature modeling and analysis of low, slow, and small targets via ubiquitous radar under sea and air background[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(5): 801–814. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.05.001.[37] LIU Huaiyuan, YANG Donghua, LIU Xianzhang, et al. TodyNet: Temporal dynamic graph neural network for multivariate time series classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2024, 677: 120914. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2024.120914.[38] DUAN Ziheng, XU Haoyan, WANG Yueyang, et al. Multivariate time-series classification with hierarchical variational graph pooling[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 154: 481–490. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.07.032.[39] YIN Yongqiang, ZHENG Xiangwei, HU Bin, et al. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 100: 106954. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106954.[40] FENG Lin, CHENG Cheng, ZHAO Mingyan, et al. EEG-based emotion recognition using spatial-temporal graph convolutional LSTM with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2022, 26(11): 5406–5417. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2022.3198688. -
Proportional views

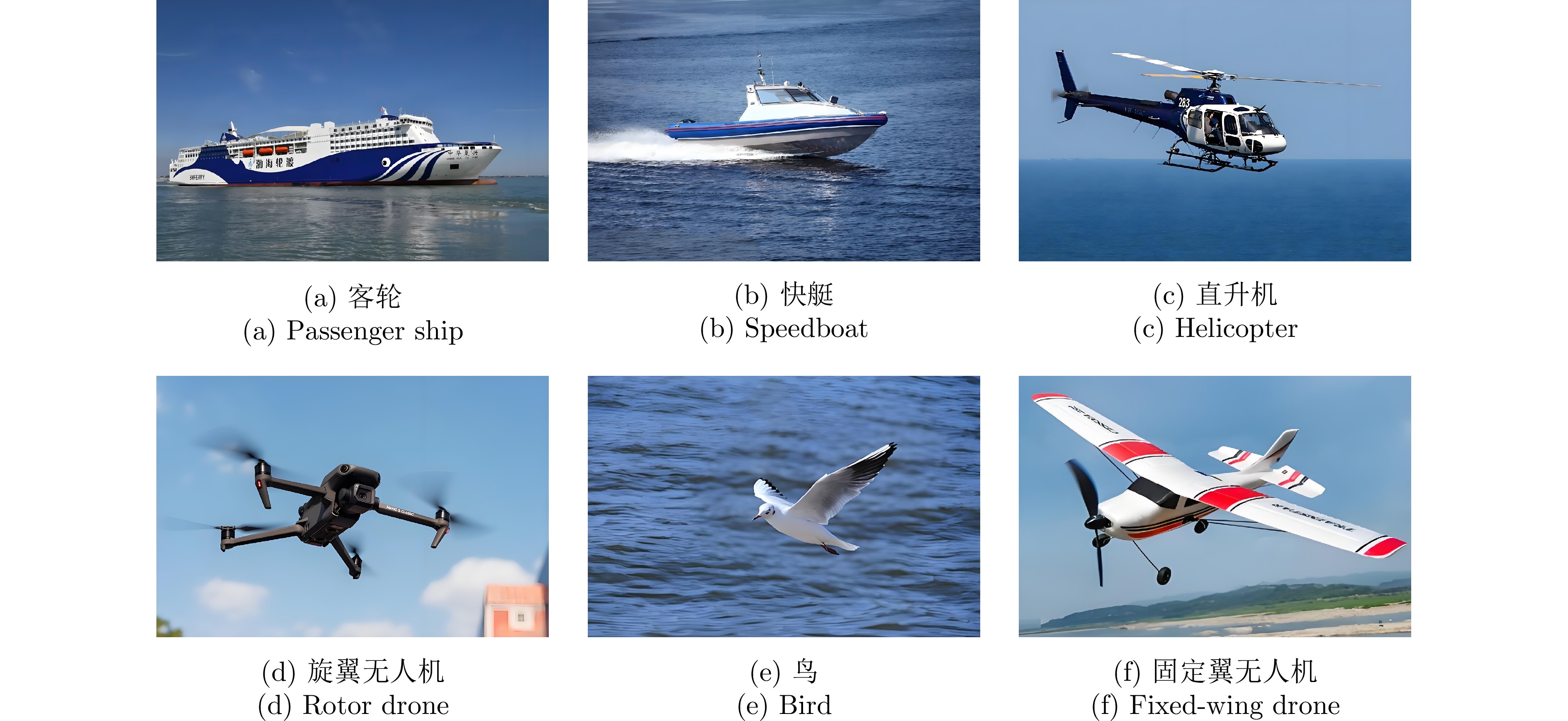
- Figure 1. Target photos in the LSS-DAUR-1.0 dataset
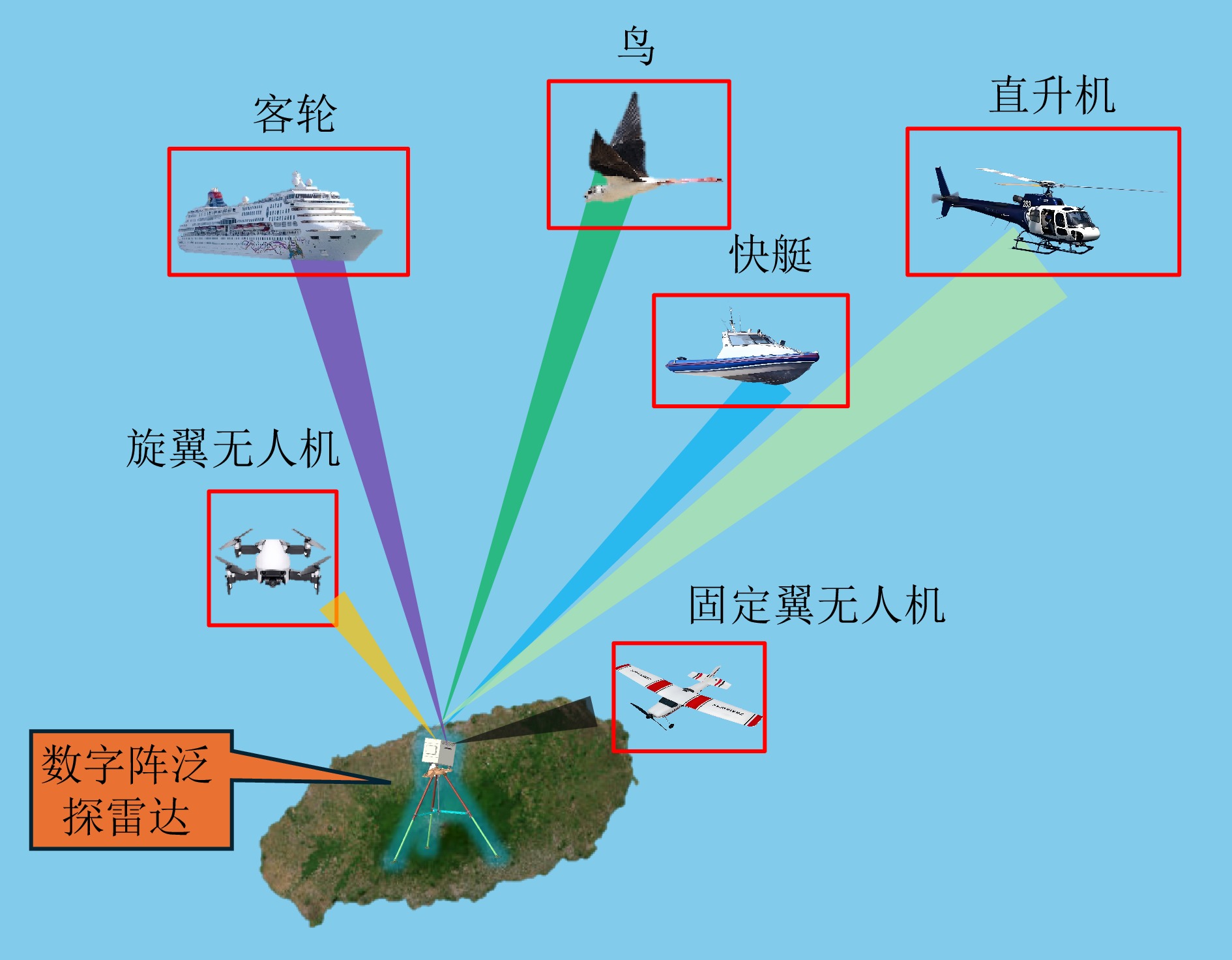
- Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the data acquisition scenario
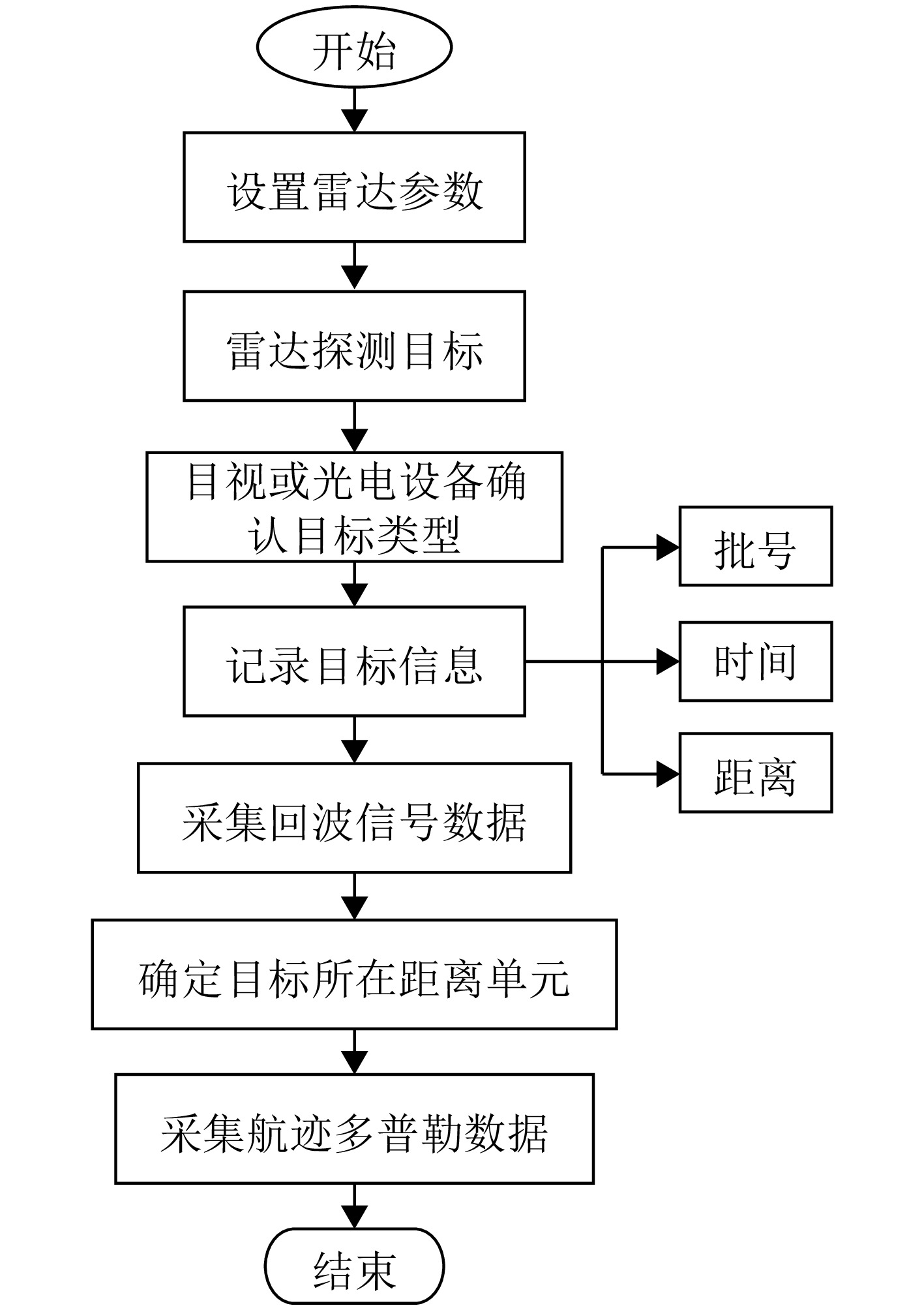
- Figure 3. Flowchart of target data collection
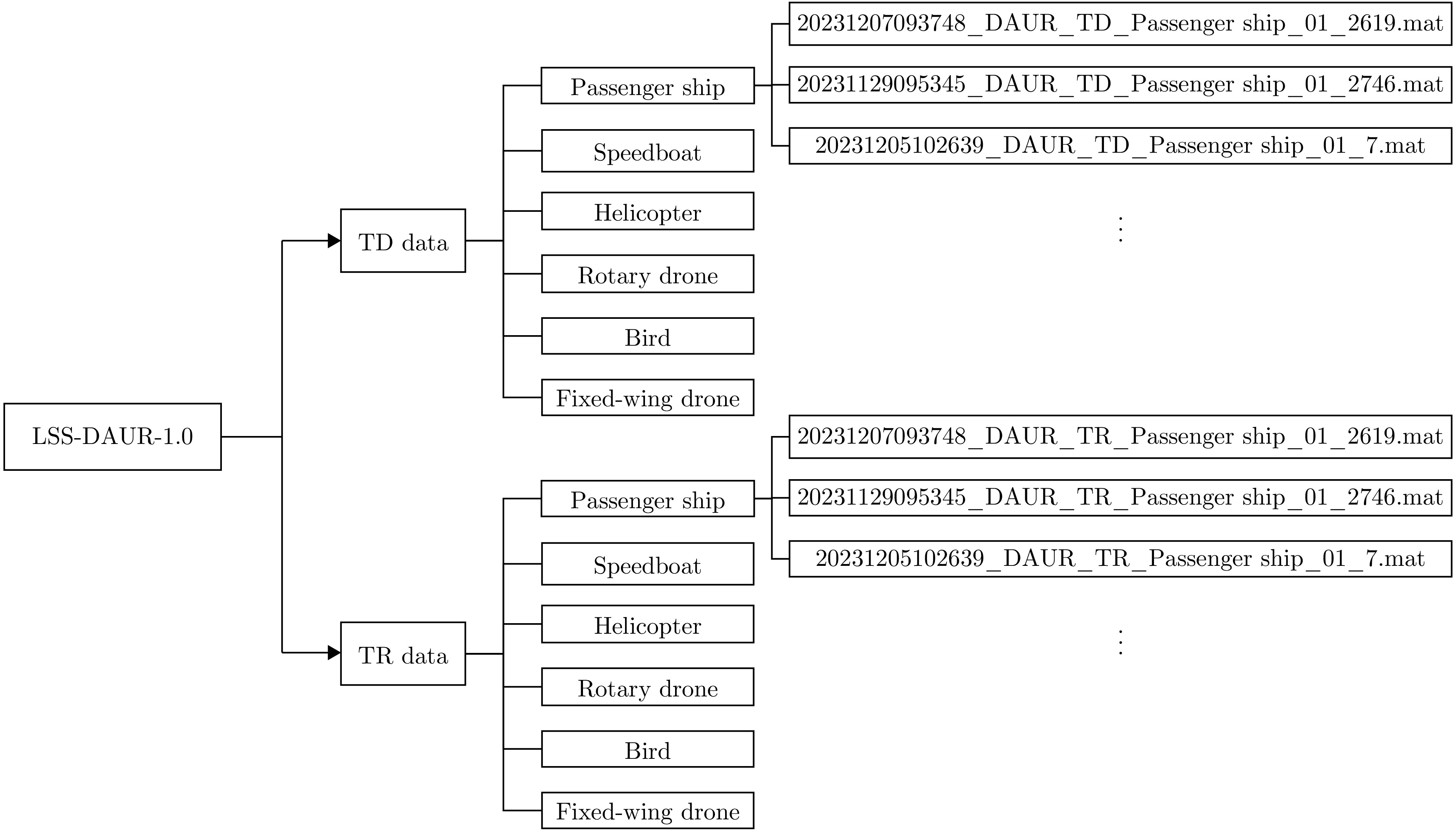
- Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the structure of the LSS-DAUR-1.0 dataset
- Figure 5. Comparison of Doppler waterfall diagrams of various targets
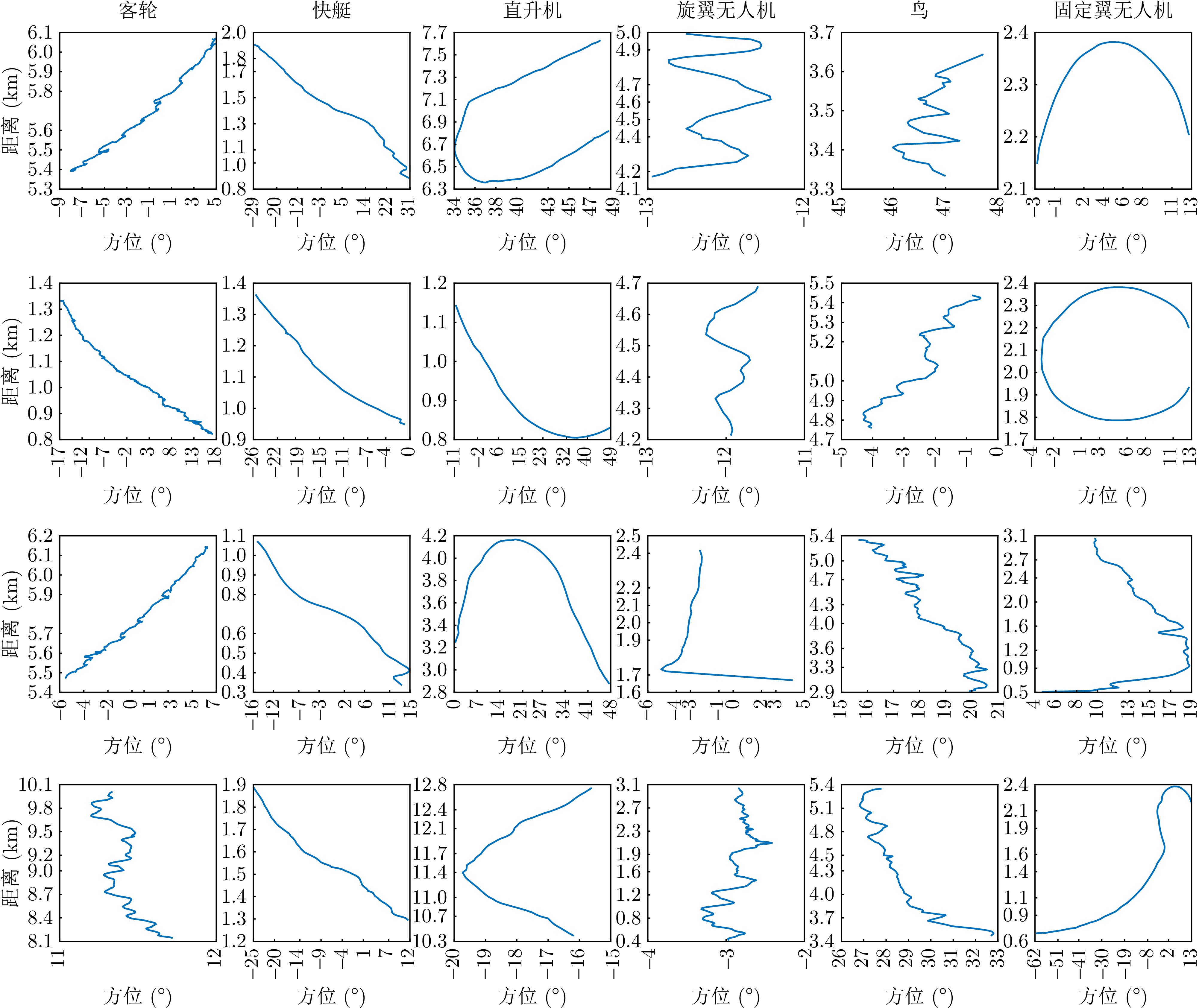
- Figure 6. Two-dimensional trajectory maps of various targets
- Figure 7. Kinematic statistical graphs of various targets
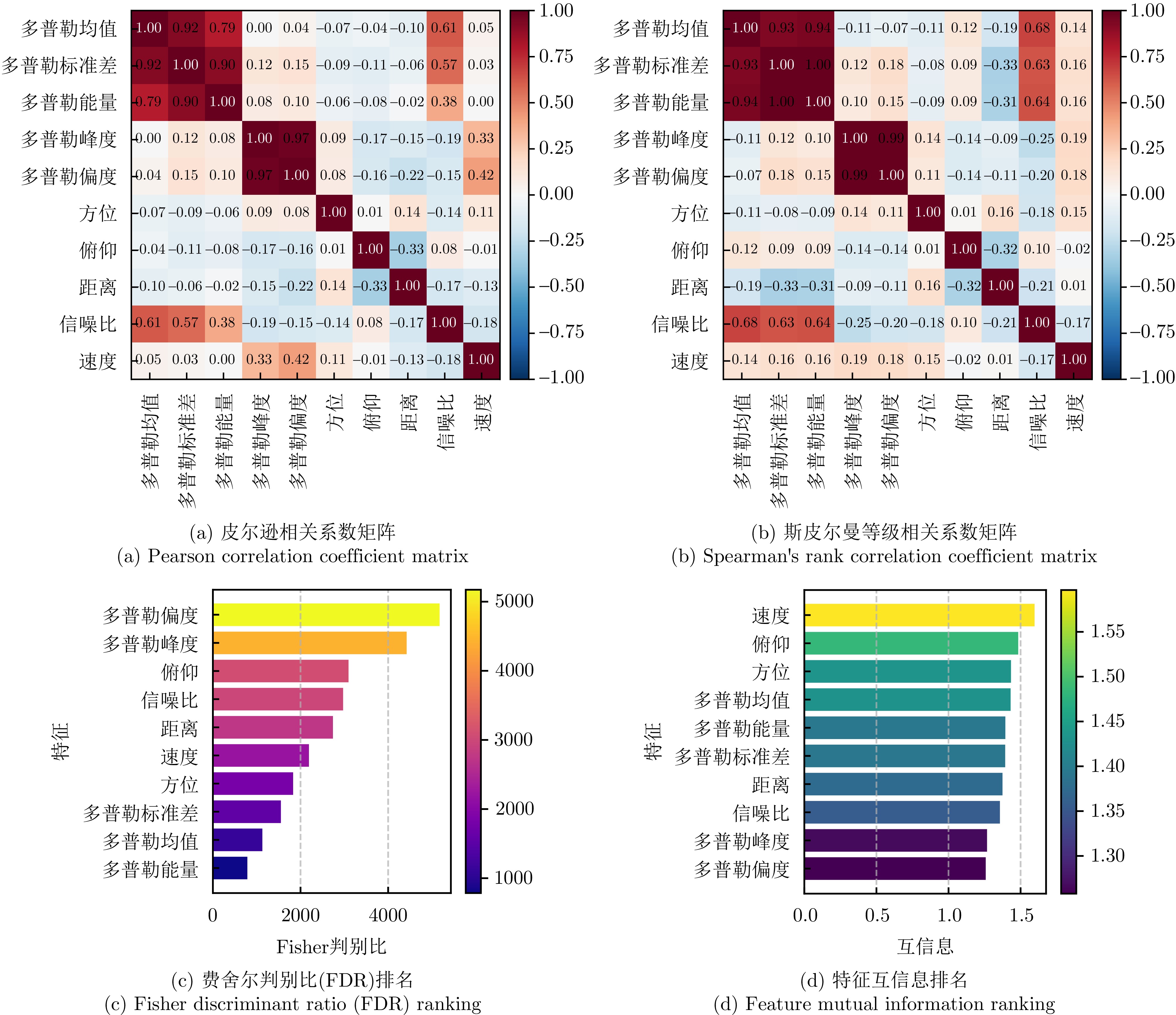
- Figure 8. Analysis of the correlation between doppler characteristics and radar observation characteristics
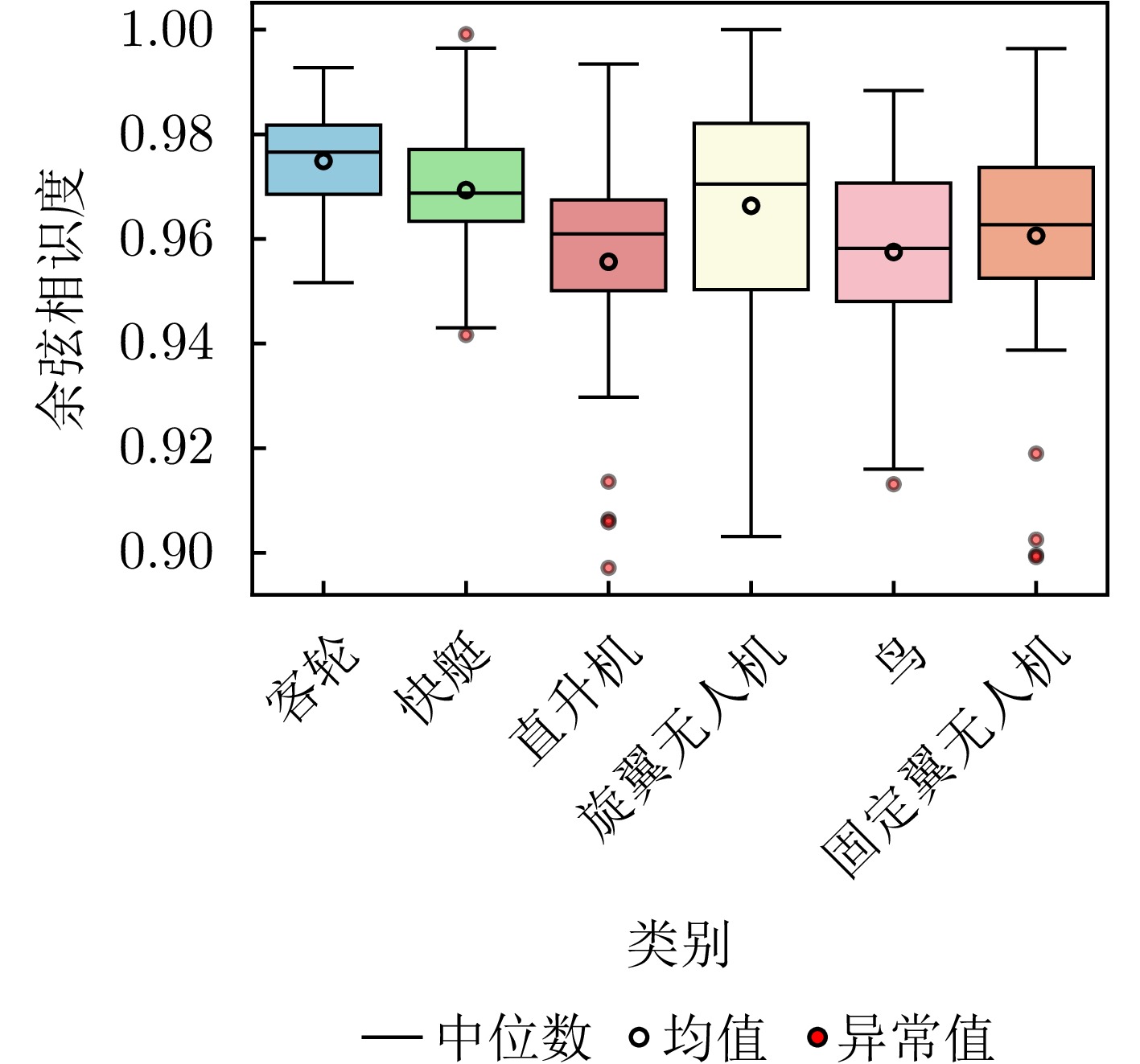
- Figure 9. Box plot of similarity distribution of samples within various target classes
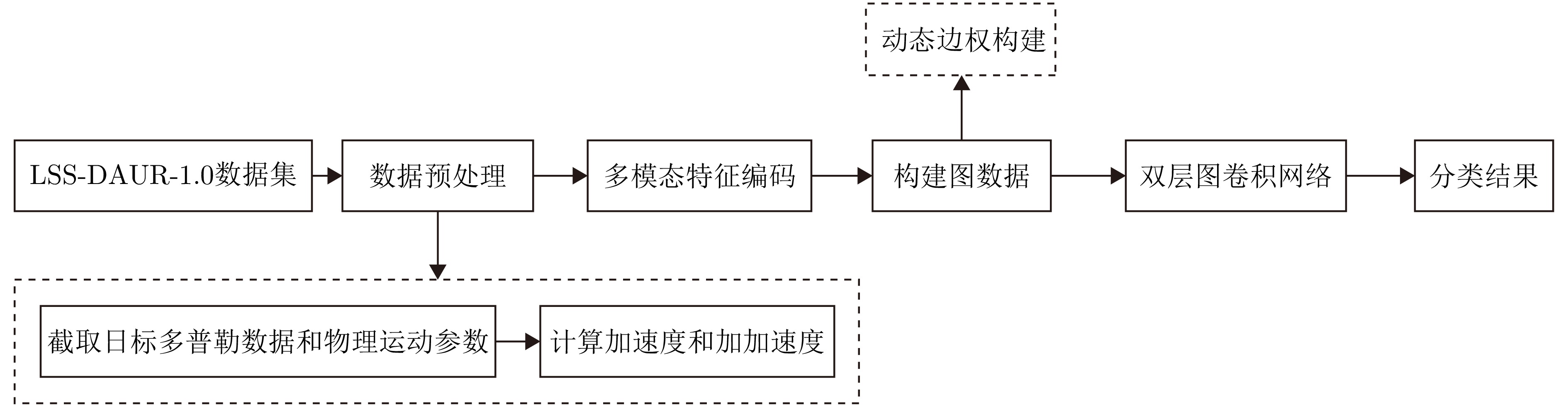
- Figure 10. Target classification method process based on DG-GCN
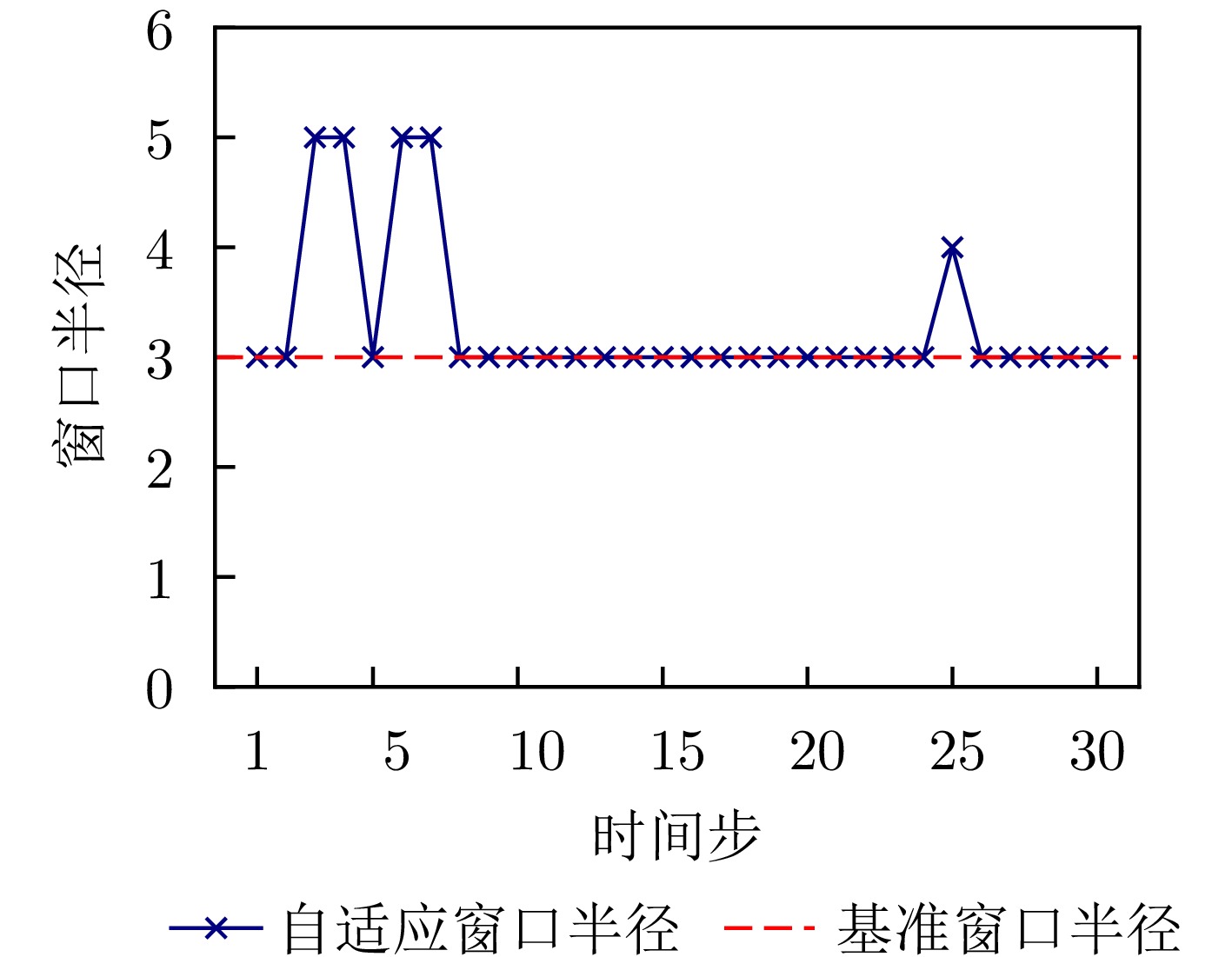
- Figure 11. Variation of window radius of temporal adjacency edges for the 25th Helicopter sample
- Figure 12. Curve of time series attenuation weight varying with distance
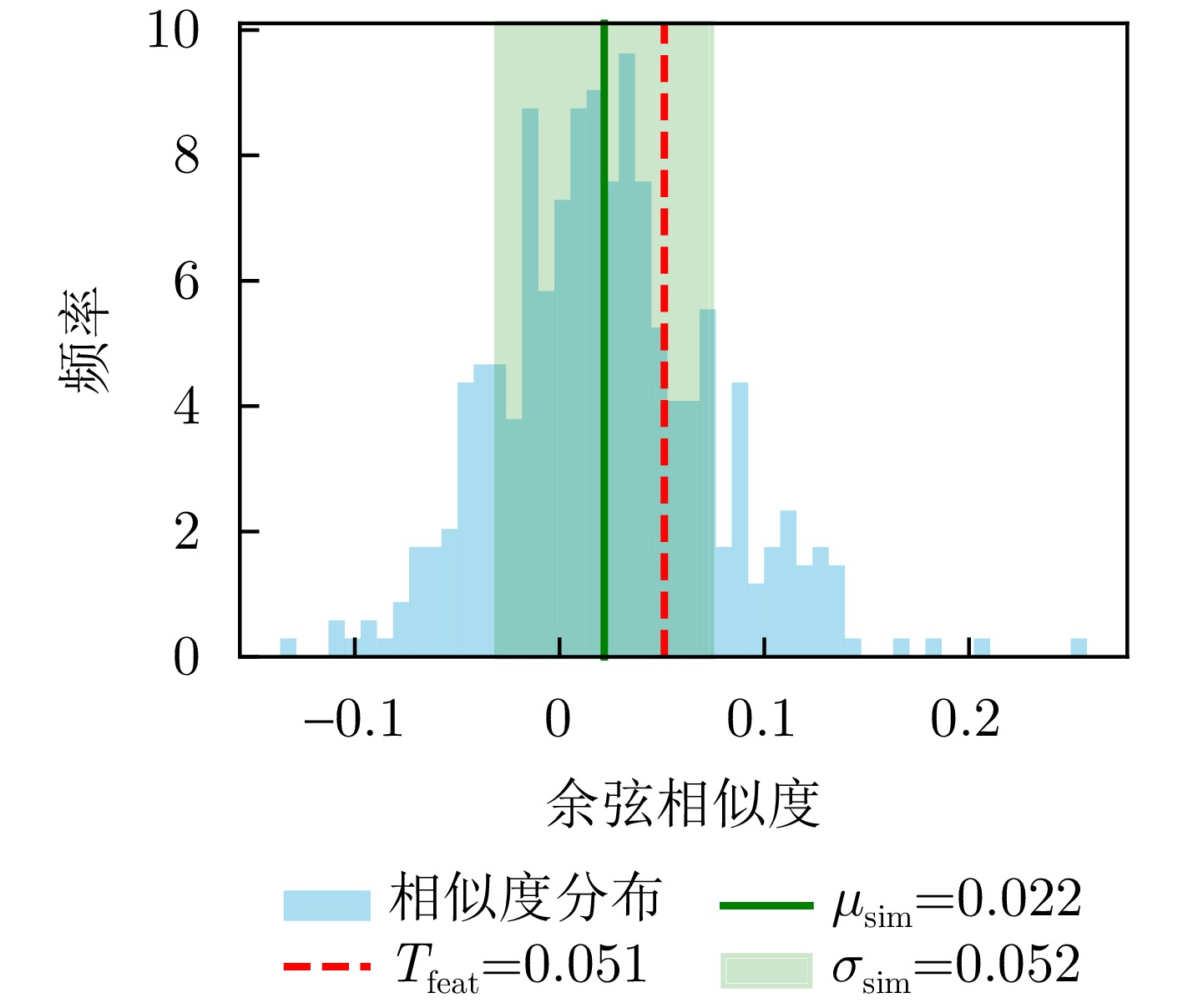
- Figure 13. Schematic diagram of threshold generation for feature similar edges of the 25th Helicopter sample
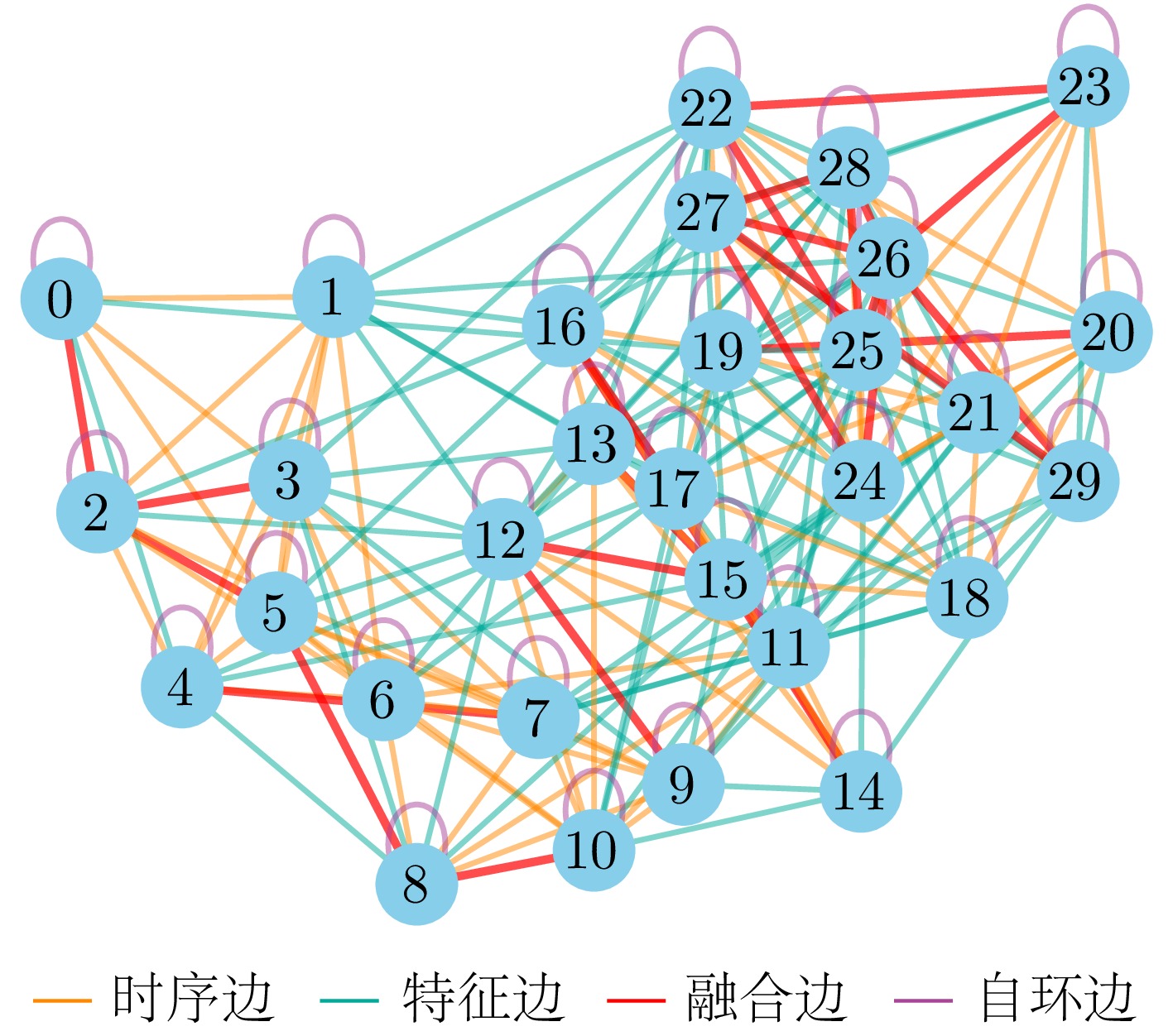
- Figure 14. Graph structure constructed from the 25th sample of the helicopter
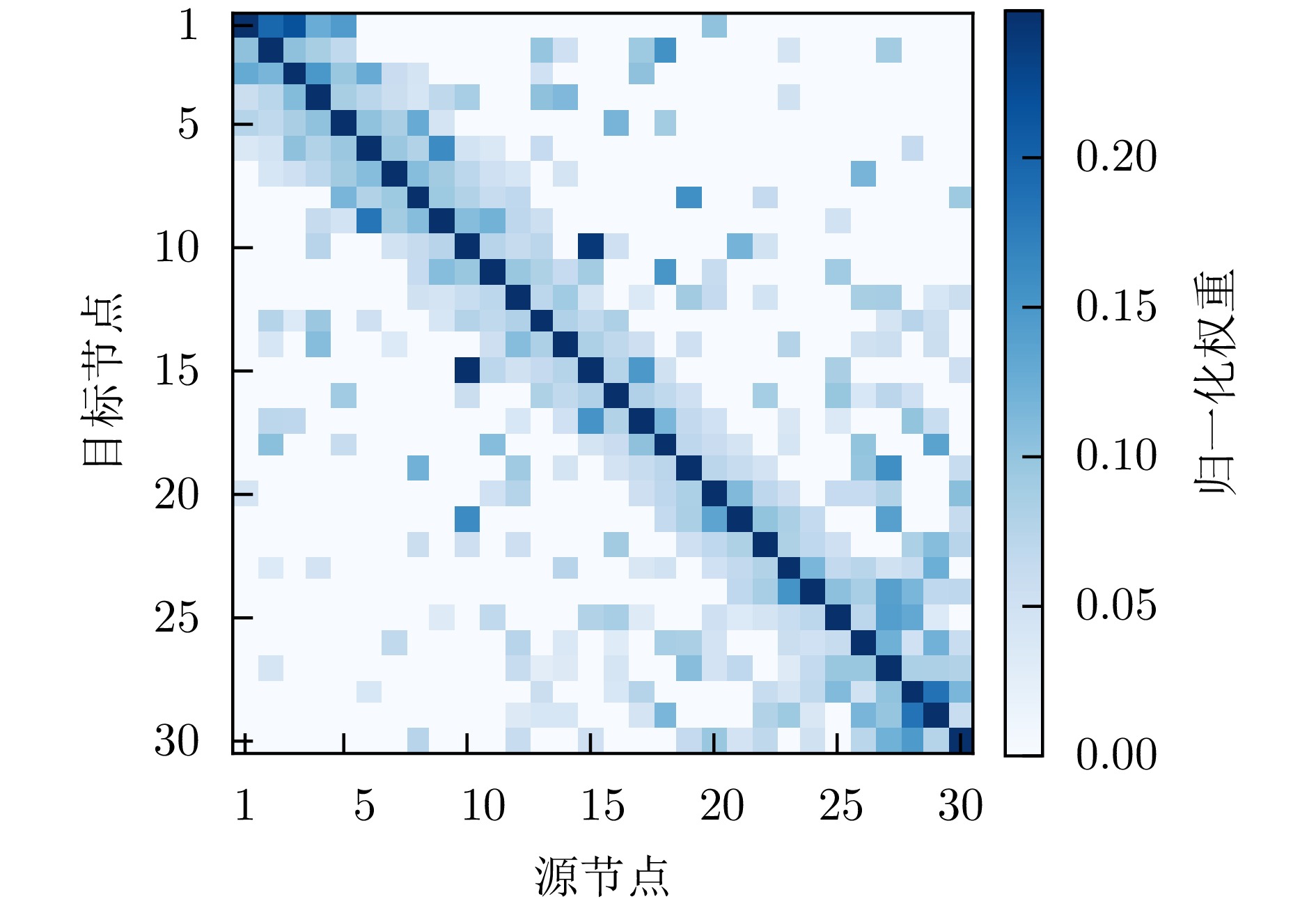
- Figure 15. Distribution of the normalized edge weight matrix for helicopter sample 25
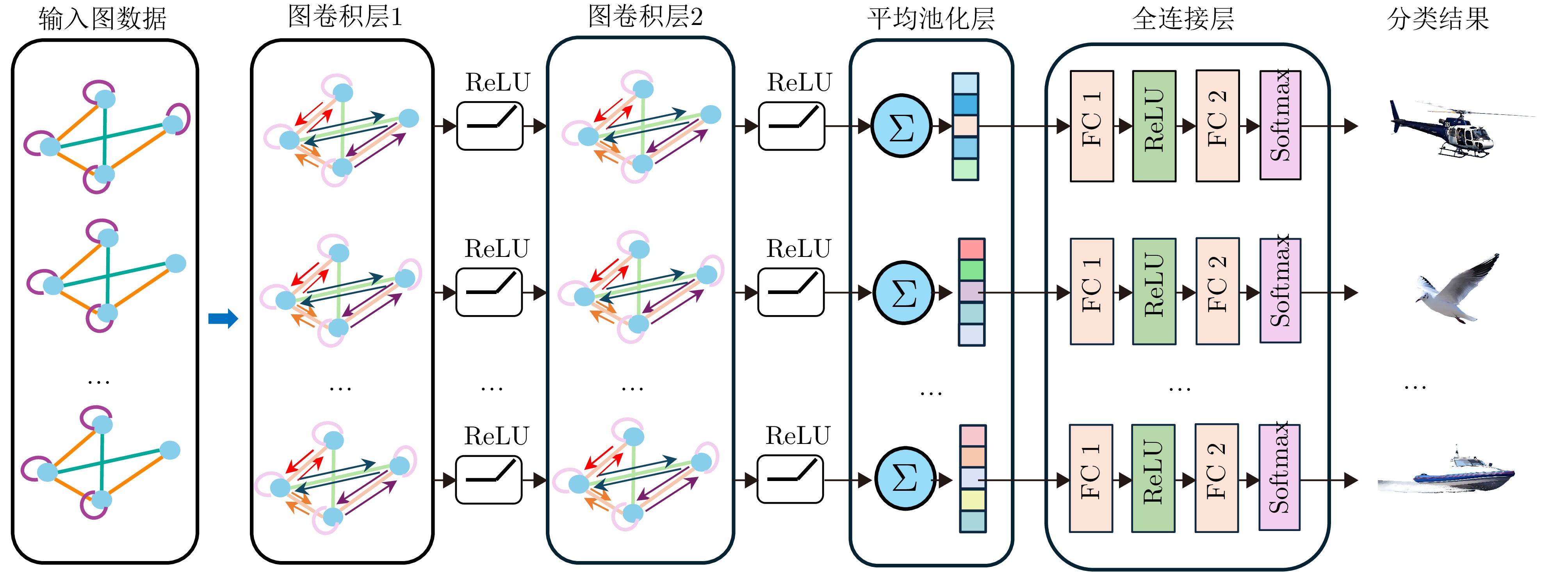
- Figure 16. Double-layer graph convolutional network with dynamic graph construction structure
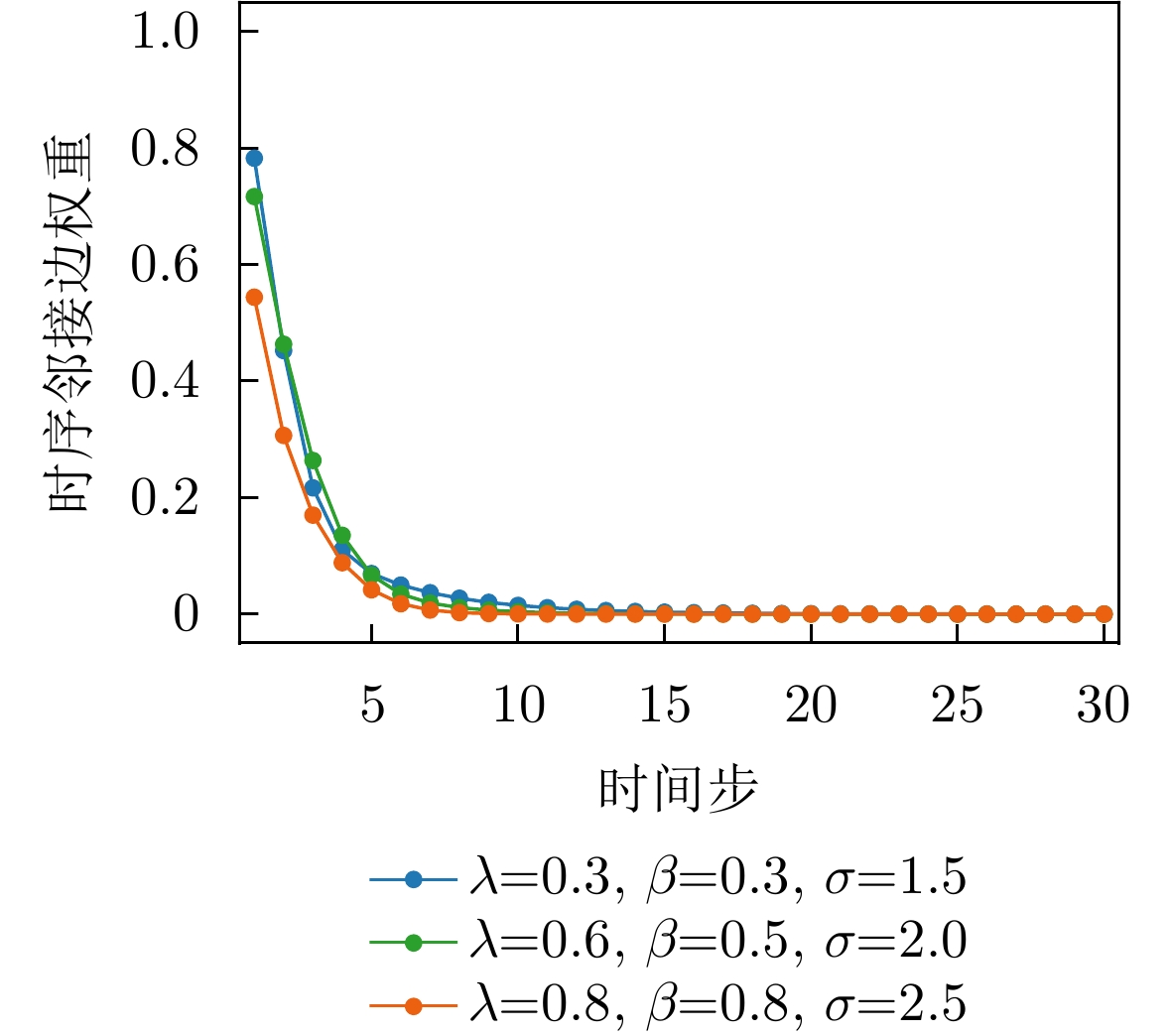
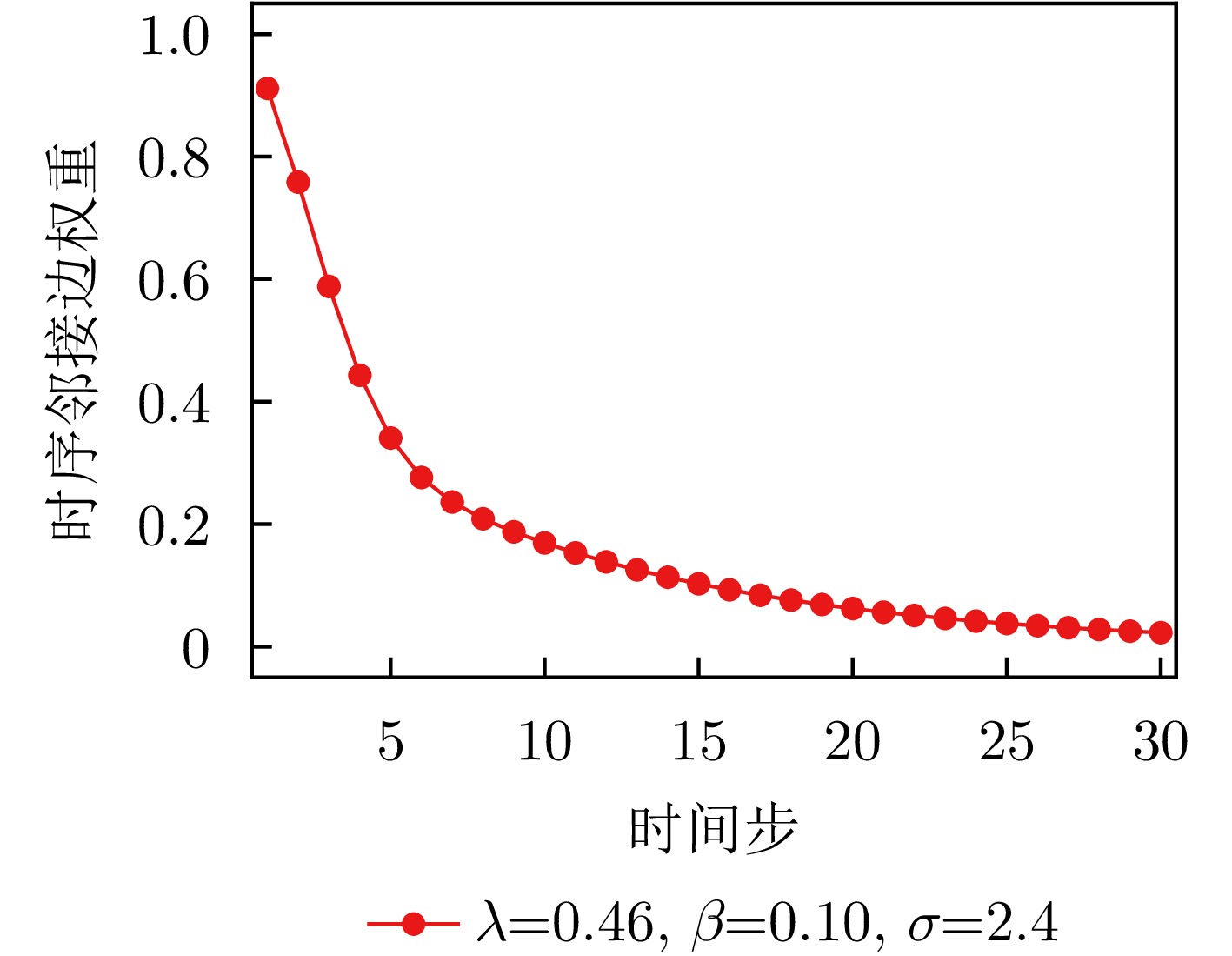
- Figure 17. Changes in time-series decay weights under the optimal parameter combination
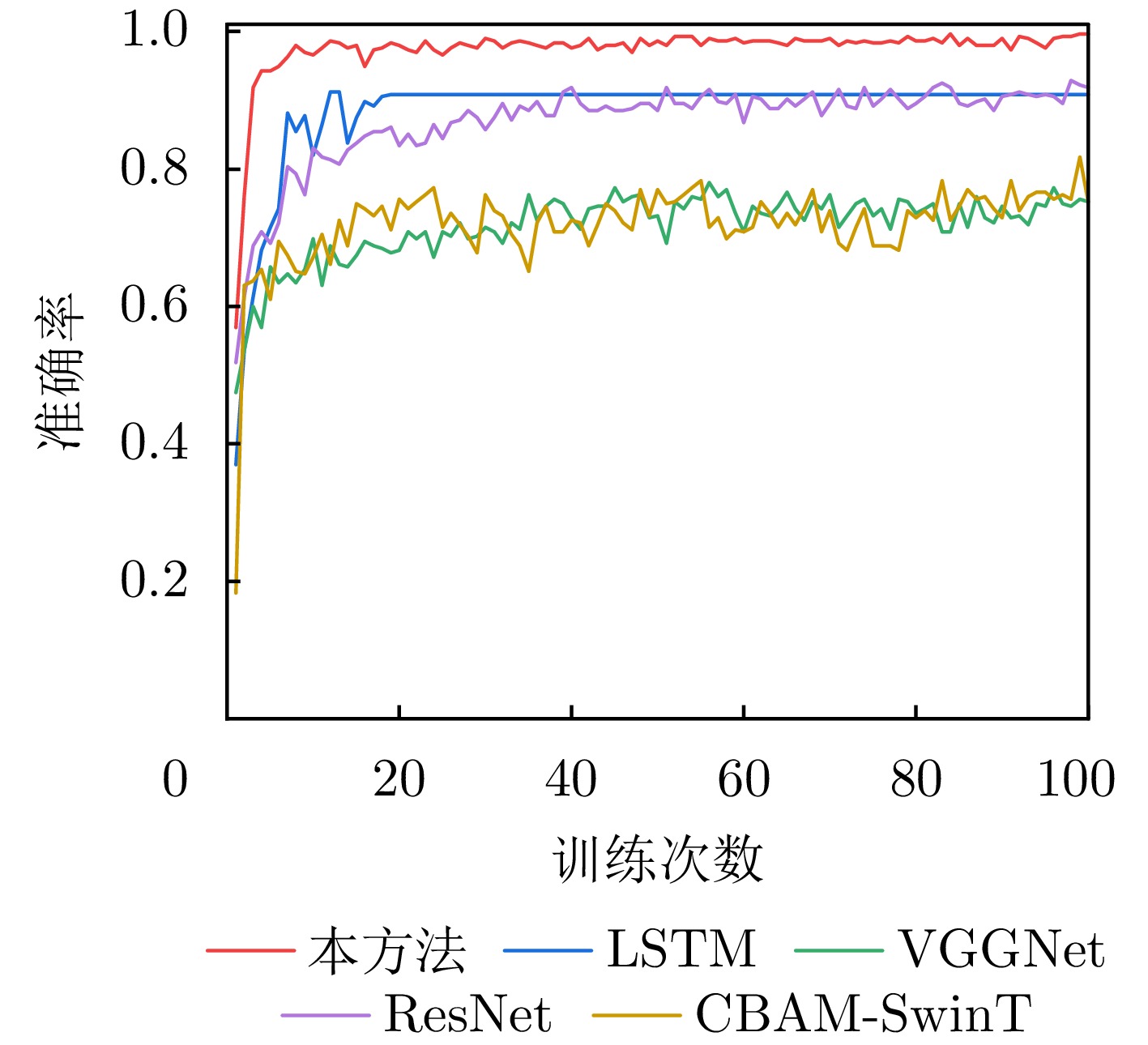
- Figure 18. Accuracy curves of each model during training
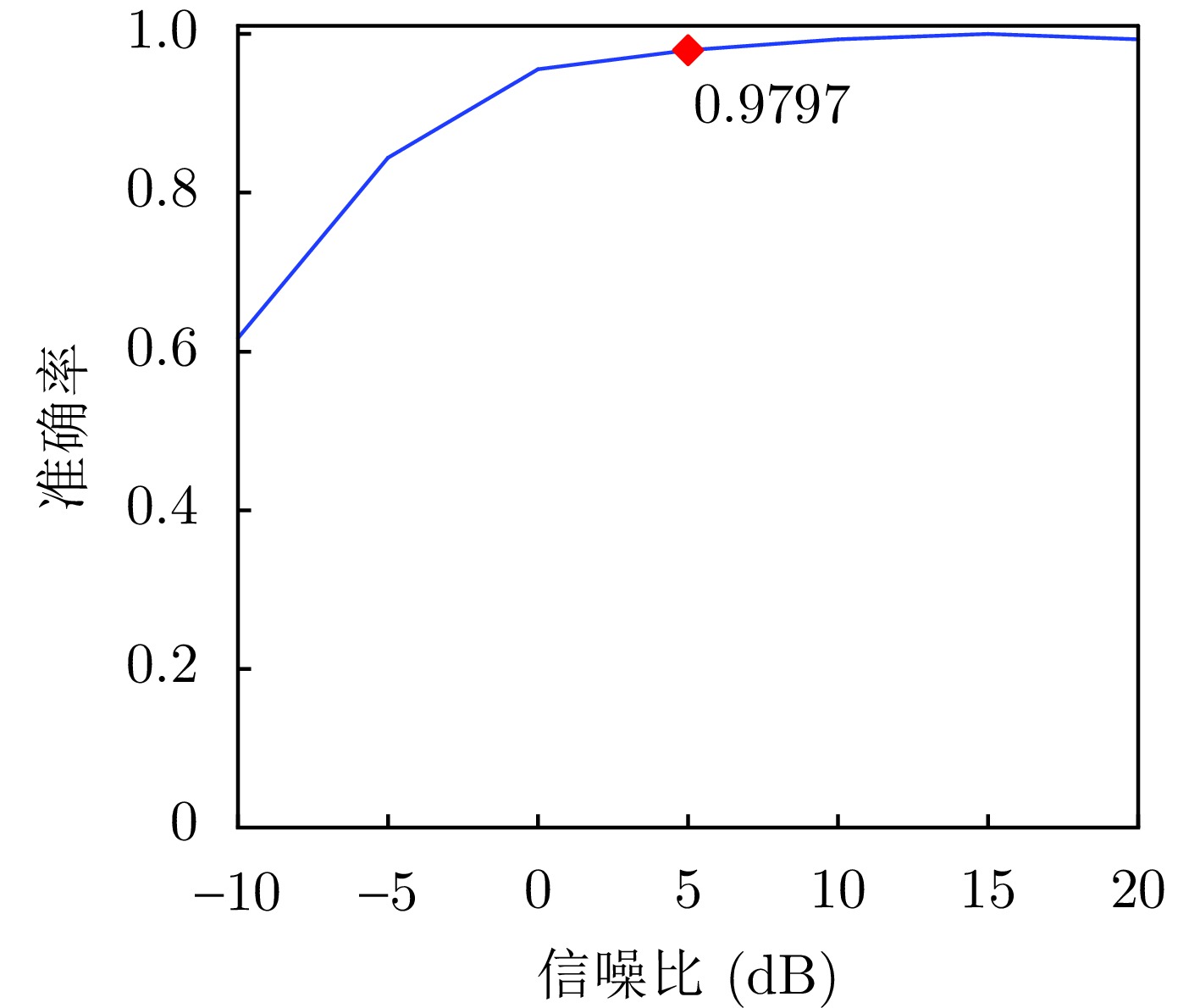
- Figure 19. Classification accuracy of the proposed method under different signal-to-noise ratios
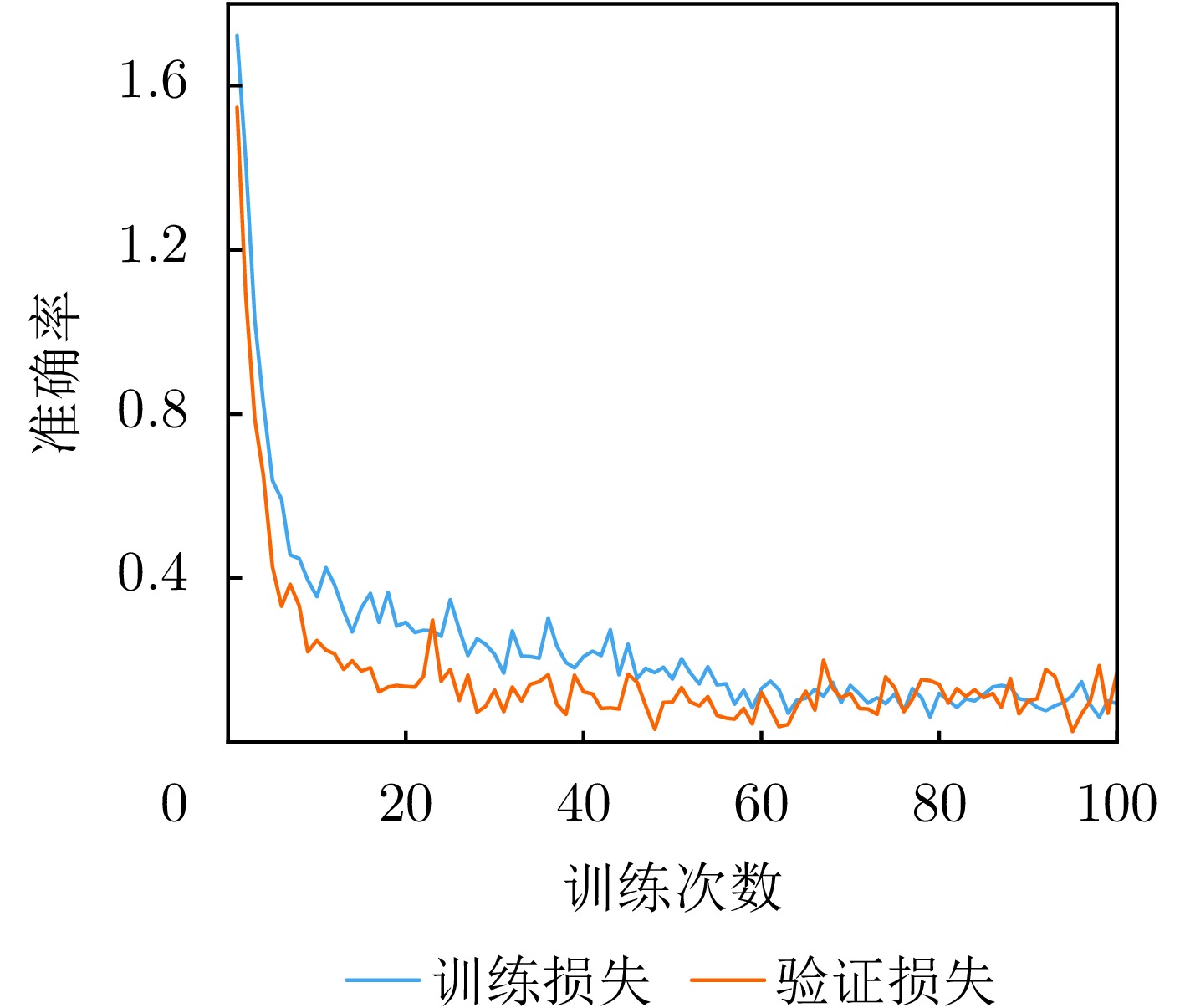
- Figure 20. 20 Training and validation loss curves under SNR = 5 dB noise
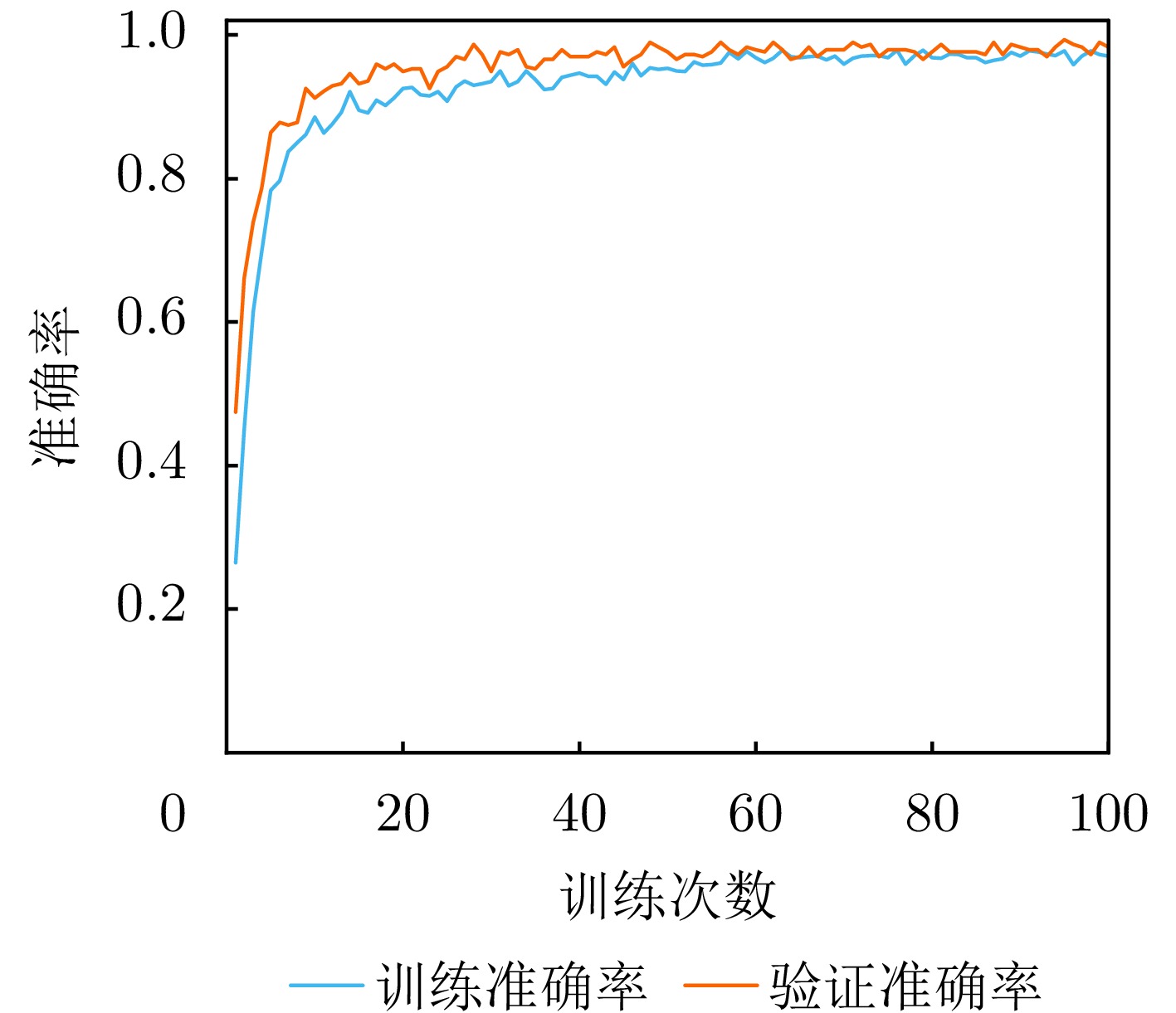
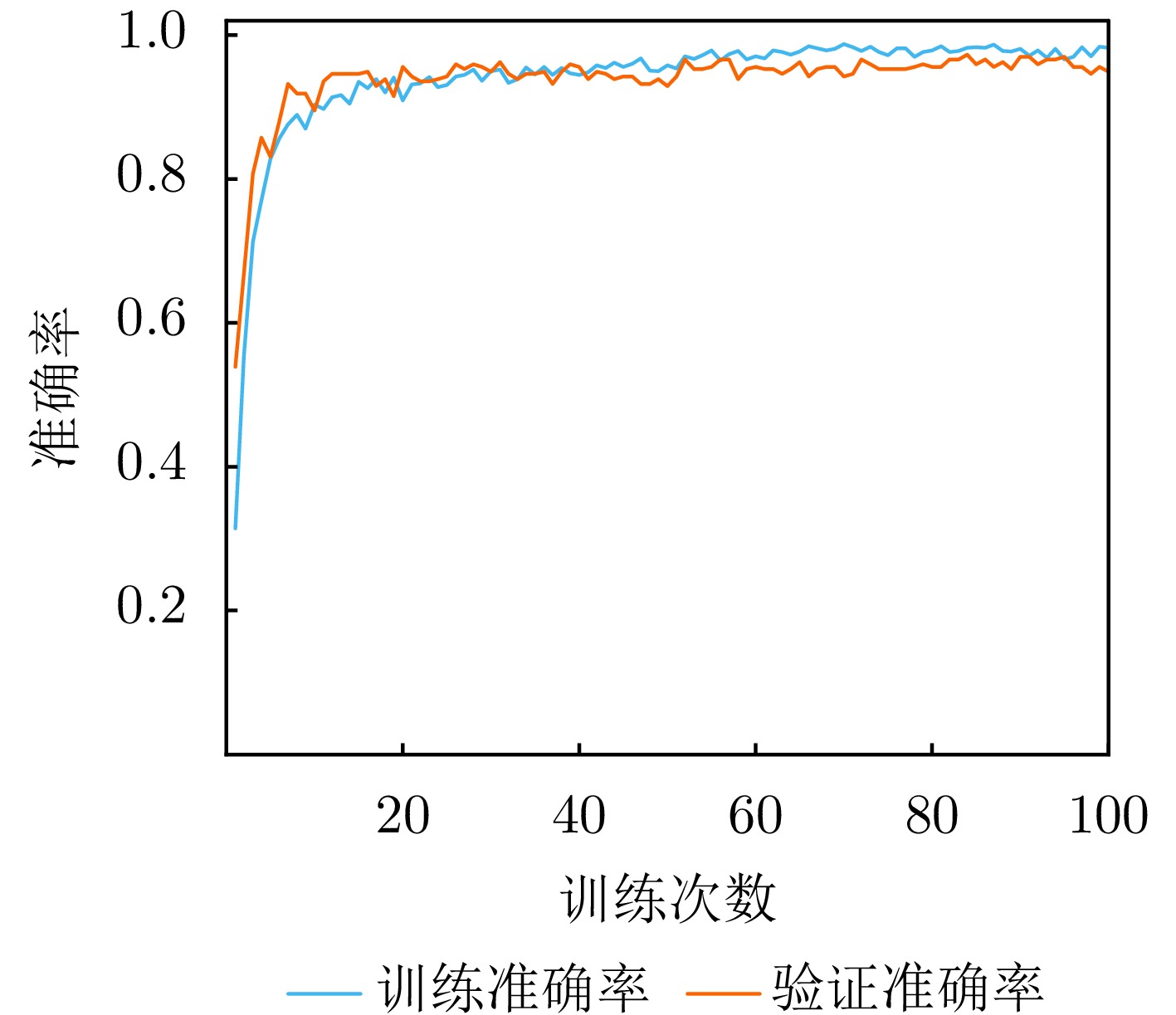
- Figure 21. Training and validation accuracy curves under SNR = 5 dB noise
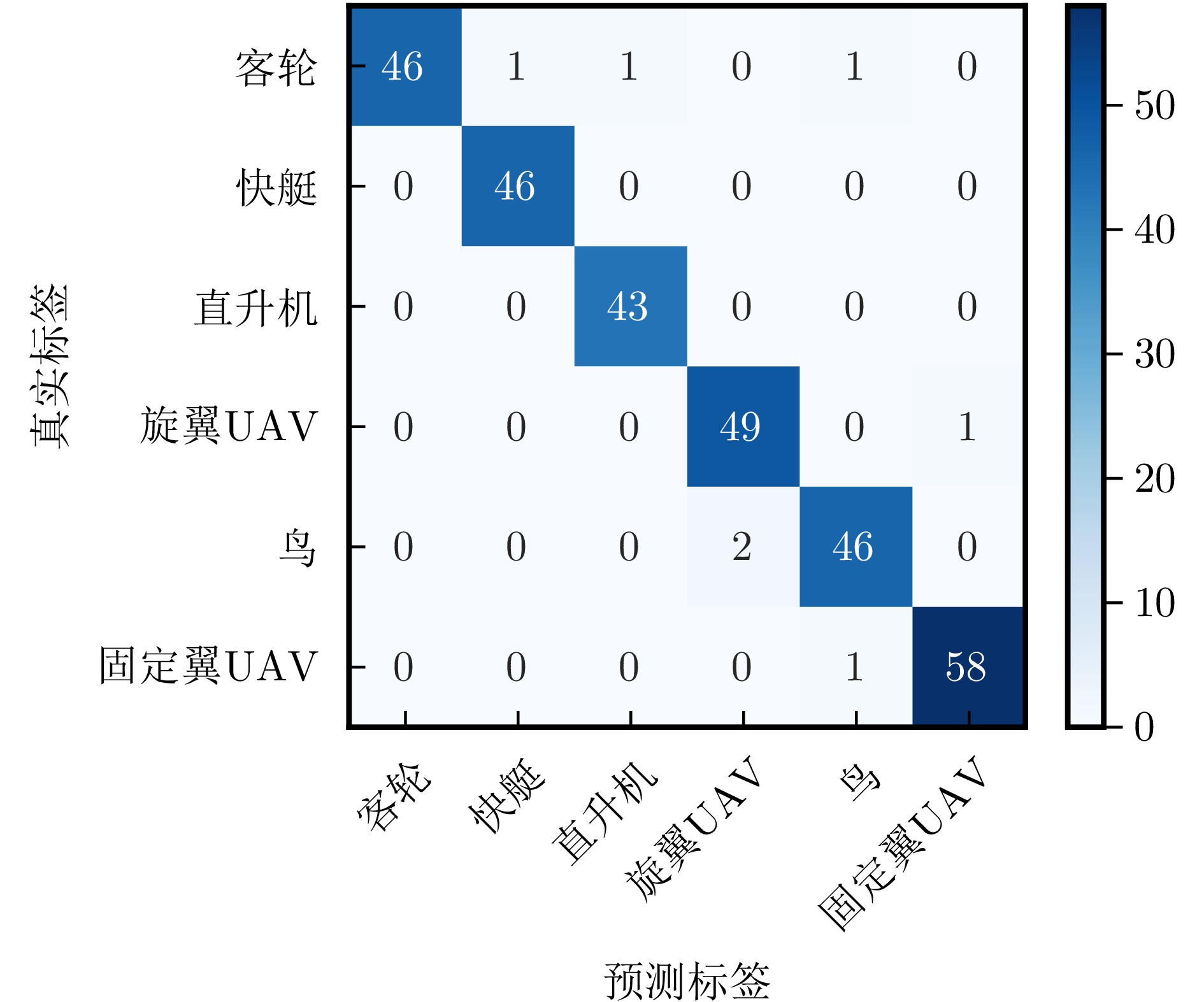
- Figure 22. Classification confusion matrix under SNR = 5 dB noise
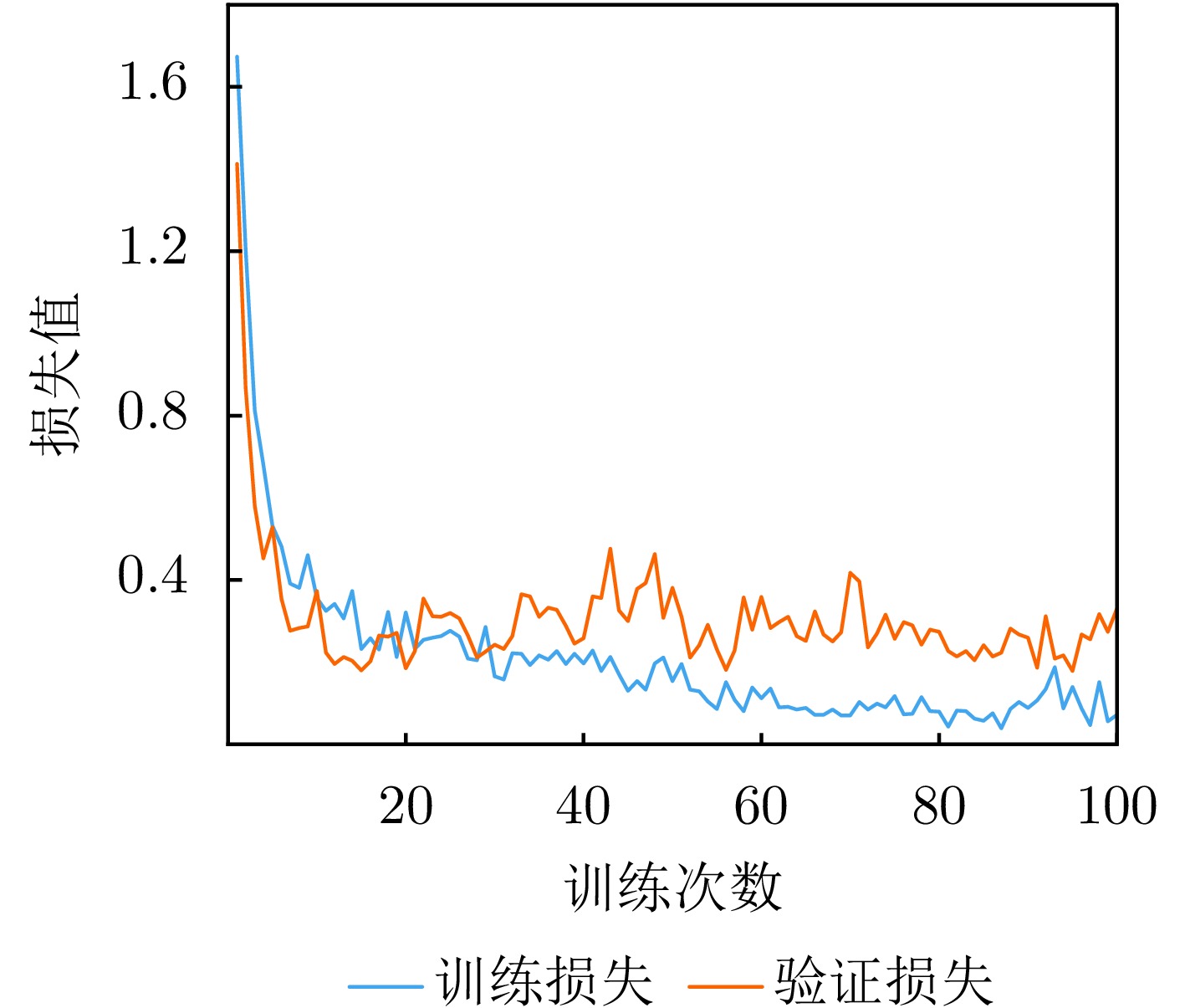
- Figure 23. 23 Training and validation loss curves of the 3-layer GCN model
- Figure 24. Training and validation accuracy curves of the 3-layer GCN model


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: