- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2026
> Online First
| Citation: | WU Xijie, LIU Tianpeng, LIU Yongxiang, et al. A multi-target detection method for distributed MIMO radar based on reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25219 |
A Multi-target Detection Method for Distributed MIMO Radar Based on Reinforcement Learning
DOI: 10.12000/JR25219 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25219
More Information-
Abstract
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a critical approach for enabling cognitive radar target detection. Existing studies primarily focus on detection methods for centralized Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar, which are limited to a single observation perspective. To address this issue, this paper proposes an RL-based multi-target detection method for a distributed MIMO radar system that possesses waveform and spatial diversity. The proposed method exploits spatial diversity to ensure robust target detection, while waveform diversity is used to construct a Markov decision process. Specifically, the radar first perceives target attributes through statistical signal detection techniques, then optimizes the transmit waveform accordingly, and iteratively updates its understanding of the environmental context using accumulated experience. This cyclic process gradually converges, yielding radar waveforms focused on target directions and achieving improved detection performance. To facilitate target localization, a maximization grid-based generalized likelihood ratio test detector for multi-antenna configurations is derived, using regularly shaped grids as the cell under test. For waveform optimization, two types of optimization problems, namely conventional and strong-target-limited formulations, are developed, and their solutions are obtained using continuous convex approximation. Simulation results across static and dynamic scenarios demonstrate that the proposed method can autonomously perceive environmental context and achieve superior detection performance compared with benchmark methods, particularly in weak target detection. -

-
References
[1] BERGIN J and GUERCI J R. Book review of “MIMO radar: Theory and application”[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2018, 33(10): 51–53. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2018.180062.[2] 何子述, 程子扬, 李军, 等. 集中式MIMO雷达研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128.HE Zishu, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. A survey of collocated MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128.[3] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812.[4] STOICA P, LI Jian, and XIE Yao. On probing signal design for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(8): 4151–4161. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894398.[5] GUO Lilin, DENG Hai, HIMED B, et al. Waveform optimization for transmit beamforming with MIMO radar antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(2): 543–552. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2382637.[6] 程子扬, 何子述, 王智磊, 等. 分布式MIMO雷达目标检测性能分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 81–89. doi: 10.12000/JR16147.CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, WANG Zhilei, et al. Detection performance analysis for distributed MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 81–89. doi: 10.12000/JR16147.[7] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMINI L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448.[8] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8.[9] FORTUNATI S, SANGUINETTI L, GINI F, et al. Massive MIMO radar for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 859–871. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2967181.[10] YANG Shixing, JAKOBSSON A, and YI Wei. Moving target detection using a distributed MIMO radar system with synchronization errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5107417. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3299233.[11] GUAN Jian, MU Xiaoqian, HUANG Yong, et al. Space-time-waveform joint adaptive detection for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 1807–1811. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3327872.[12] SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018.[13] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Playing Atari with deep reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv: 1312.5602. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1312.5602.[14] 杜兰, 王梓霖, 郭昱辰, 等. 结合强化学习自适应候选框挑选的SAR目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121.DU Lan, WANG Zilin, GUO Yuchen, et al. Adaptive region proposal selection for SAR target detection using reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121.[15] WANG Li, FORTUNATI S, GRECO M S, et al. Reinforcement learning-based waveform optimization for MIMO multi-target detection[C]. 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2018: 1329–1333. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2018.8645304.[16] AHMED A M, AHMAD A A, FORTUNATI S, et al. A reinforcement learning based approach for multitarget detection in massive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 2622–2636. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3061809.[17] LISI F, FORTUNATI S, GRECO M S, et al. Enhancement of a state-of-the-art RL-based detection algorithm for massive MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(6): 5925–5931. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3168033.[18] ZHAI Weitong, WANG Xiangrong, GRECO M S, et al. Weak target detection in massive MIMO radar via an improved reinforcement learning approach[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 4993–4997. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746472.[19] ZHAI Weitong, WANG Xiangrong, CAO Xianbin, et al. Reinforcement learning based dual-functional massive MIMO systems for multi-target detection and communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 741–755. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2023.3252885.[20] WANG Zicheng, XIE Wei, ZHOU Zhengchun, et al. Reinforcement learning-based MIMO radar multitarget detection assisted by Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4463–4478. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3380581.[21] WU Xijie, LIU Tianpeng, LIU Yongxiang, et al. Reinforcement learning-based multitarget detection method for MIMO radar via multirank beamformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(3): 7686–7709. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3540803.[22] FRIEDLANDER B. On transmit beamforming for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3376–3388. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324717.[23] DE MAIO A and LOPS M. Design principles of MIMO radar detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 886–898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383581.[24] FISHLER E, HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R S, et al. Spatial diversity in radars—models and detection performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 823–838. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862813.[25] HE Qian and BLUM R S. Diversity gain for MIMO Neyman-Pearson signal detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(3): 869–881. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2094611.[26] MAGAZ B, BENCHEIKH M L, WANG Yide, et al. Numerical analysis of MIMO radar detection performance under Weibull-distributed clutter[C]. 11-th International Radar Symposium, Vilnius, Lithuania, 2010: 1–4.[27] CHONG C Y, PASCAL F, OVARLEZ J P, et al. MIMO radar detection in non-Gaussian and heterogeneous clutter[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(1): 115–126. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2038980.[28] HASSANIEN A and VOROBYOV S A. Phased-MIMO radar: A tradeoff between phased-array and MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(6): 3137–3151. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2043976.[29] XU Luzhou and LI Jian. Iterative generalized-likelihood ratio test for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(6): 2375–2385. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.893937.[30] XU Jia, DAI Xizeng, XIA Xianggan, et al. Optimizations of multisite radar system with MIMO radars for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2329–2343. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034636.[31] XU Jia, DAI Xizeng, XIA Xianggan, et al. Optimal transmitting diversity degree-of-freedom for statistical MIMO radar[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2010: 437–440. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2010.5494582.[32] CHEN Peng, ZHENG Le, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Moving target detection using colocated MIMO radar on multiple distributed moving platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4670–4683. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2714999.[33] ZHOU Dingsen, YANG Minglei, LIAN Hao, et al. Hybrid signal fusion for target detection in distributed PA-MIMO radar systems on moving platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(4): 10378–10393. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3562169.[34] YANG Shixing, YI Wei, and JAKOBSSON A. Multitarget detection strategy for distributed MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5113516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3175046.[35] HE Lifeng, CHAO Yuyan, SUZUKI K, et al. Fast connected-component labeling[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2009, 42(9): 1977–1987. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.10.013.[36] GRANT M and BOYD S. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming[EB/OL]. http://cvxr.com/cvx, 2020.[37] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. The schematic diagram of the distributed MIMO radar adopted in this paper
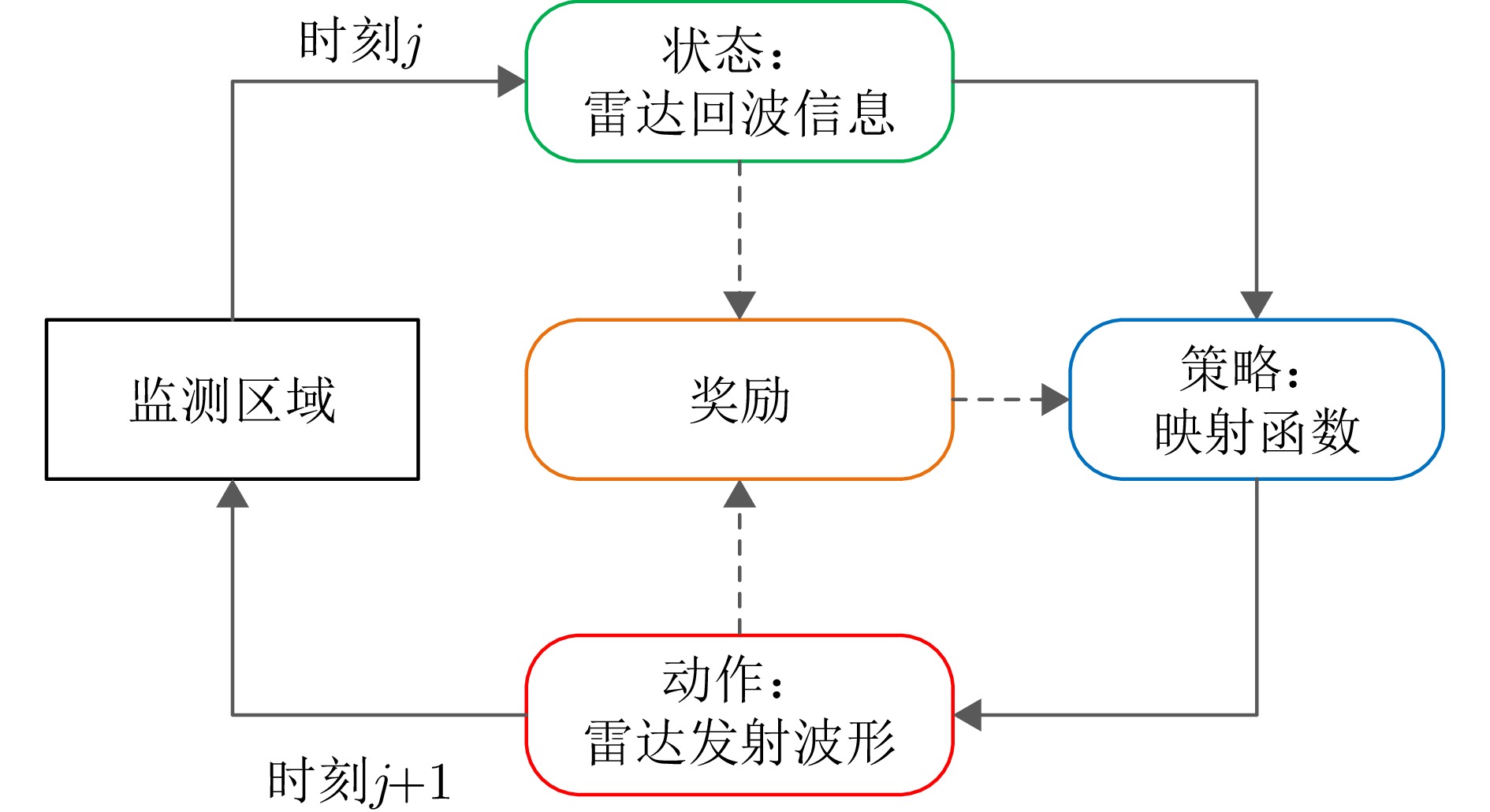
- Figure 2. The cognitive radar modeling mode based on reinforcement learning
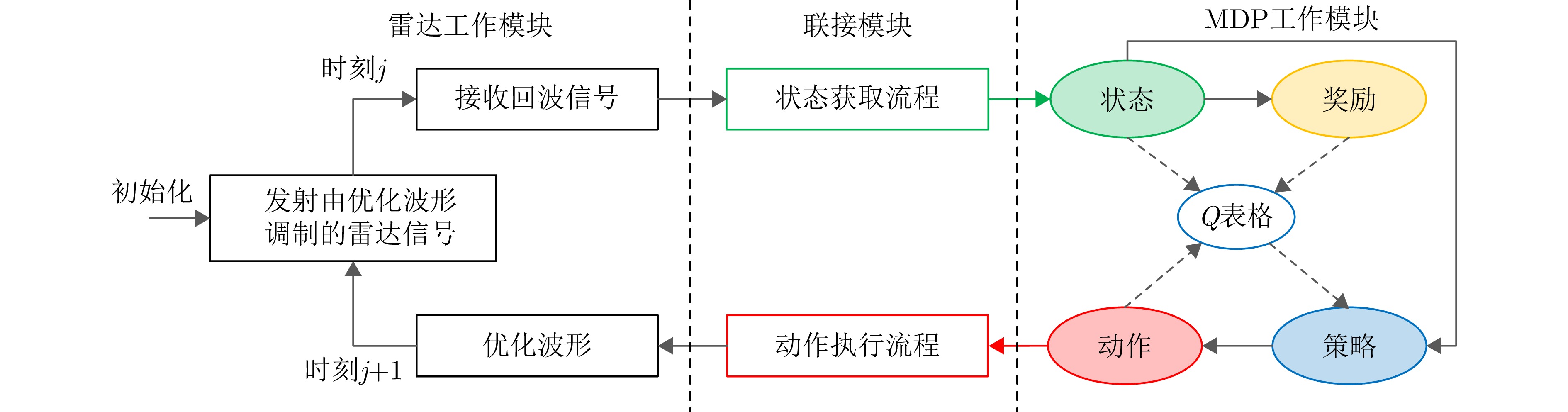
- Figure 3. The cognitive radar detection process in this paper
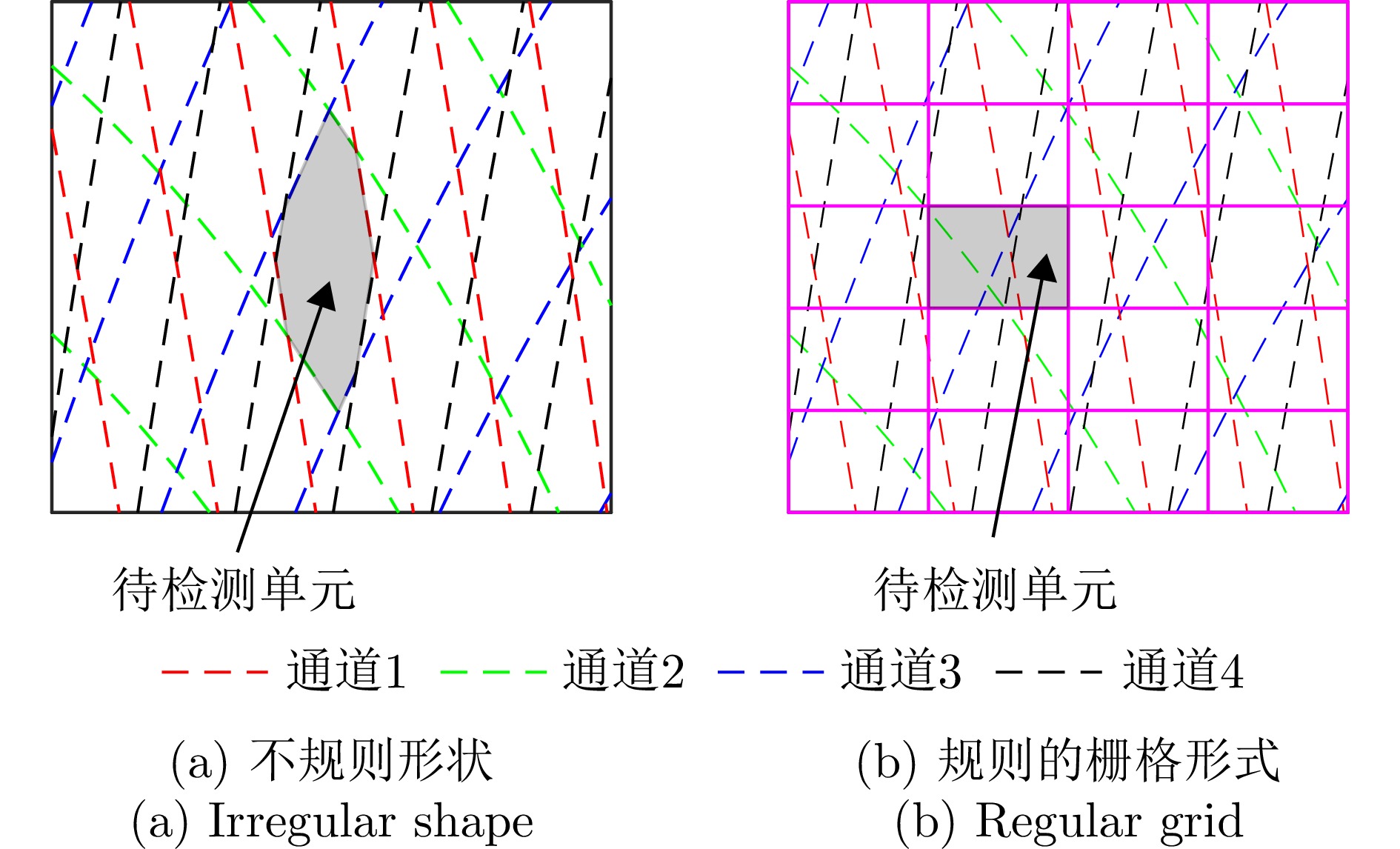
- Figure 4. Different forms of CUT
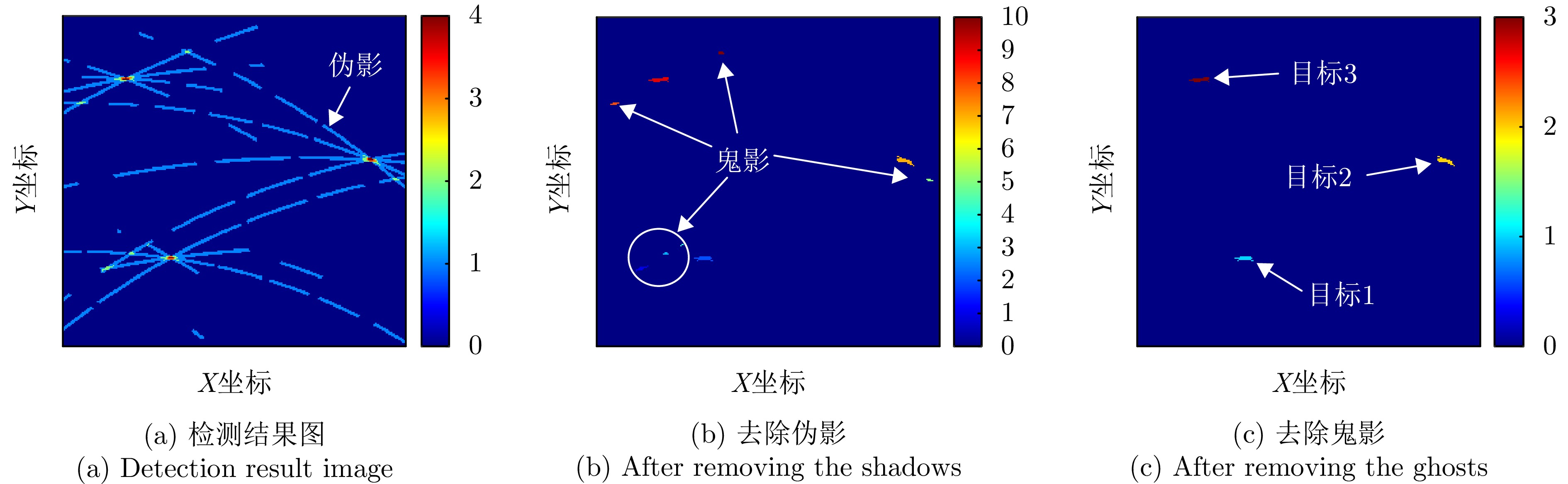
- Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the false target removal approach
- Figure 6. Schematic diagram of simulation scenario
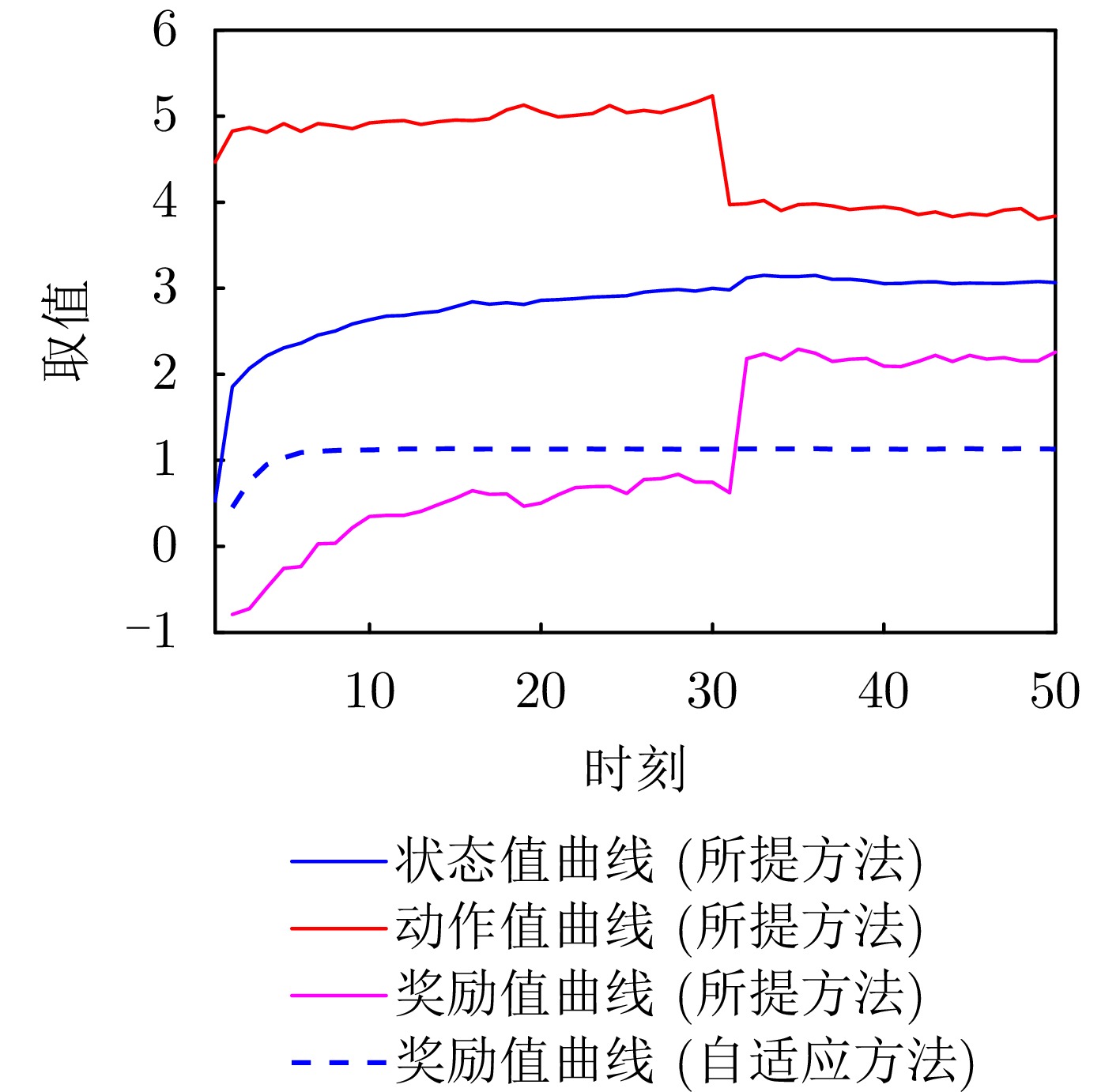
- Figure 7. Variation curves of RL elements
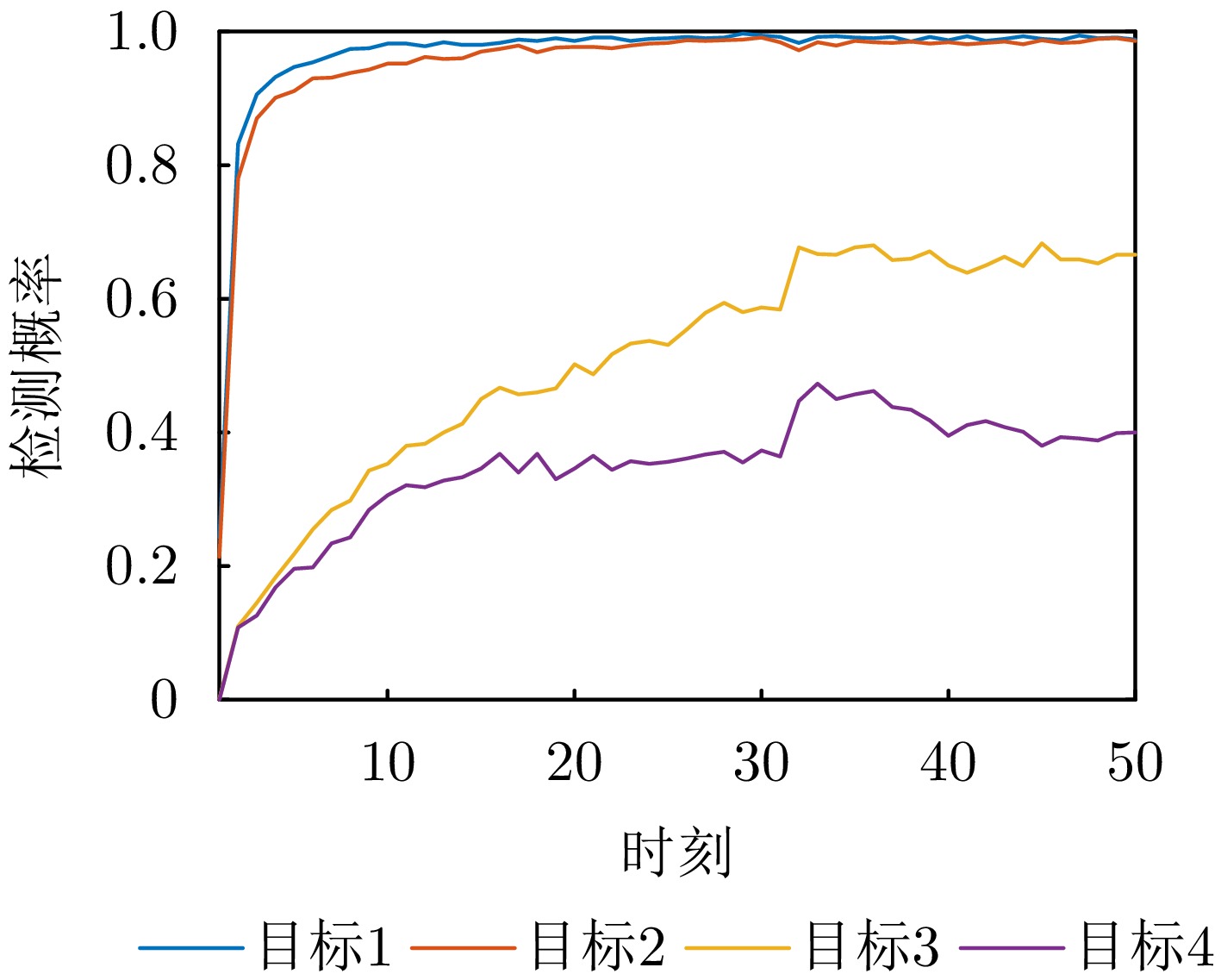
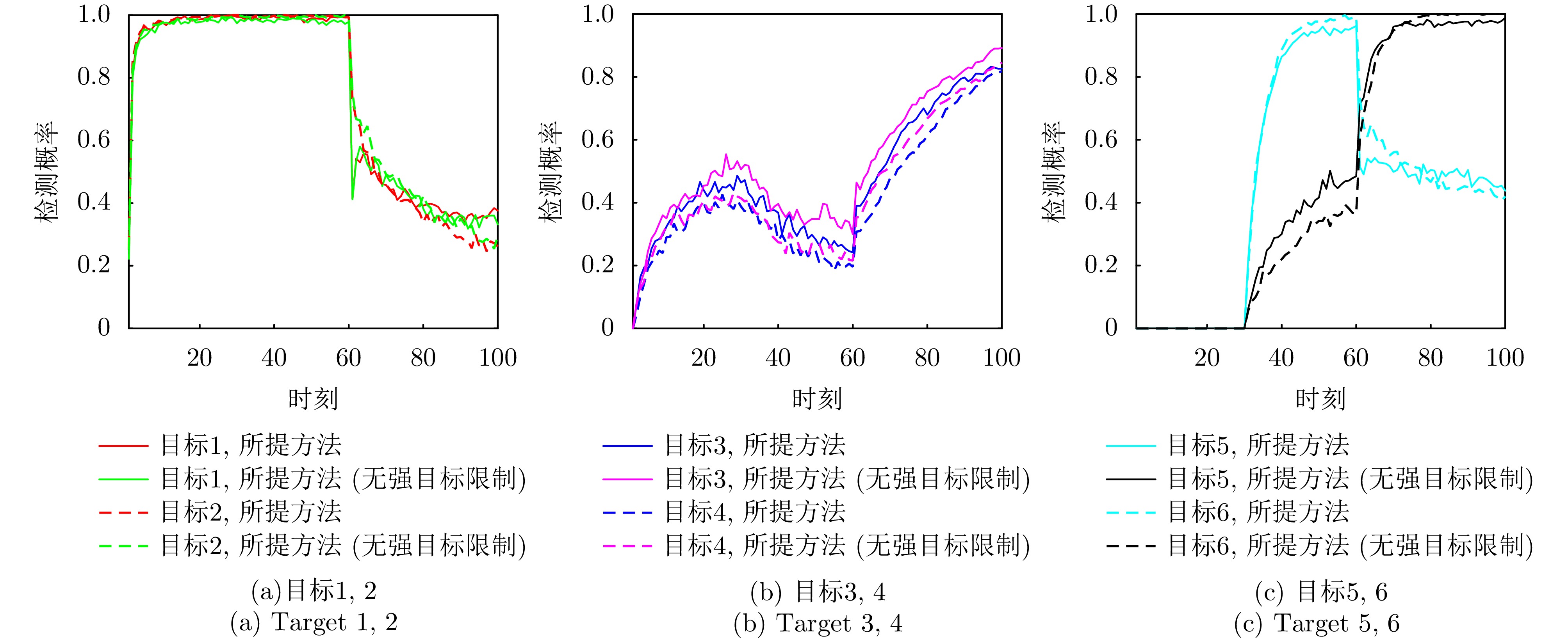
- Figure 8. The detection probability variation of the proposed method in static scenario
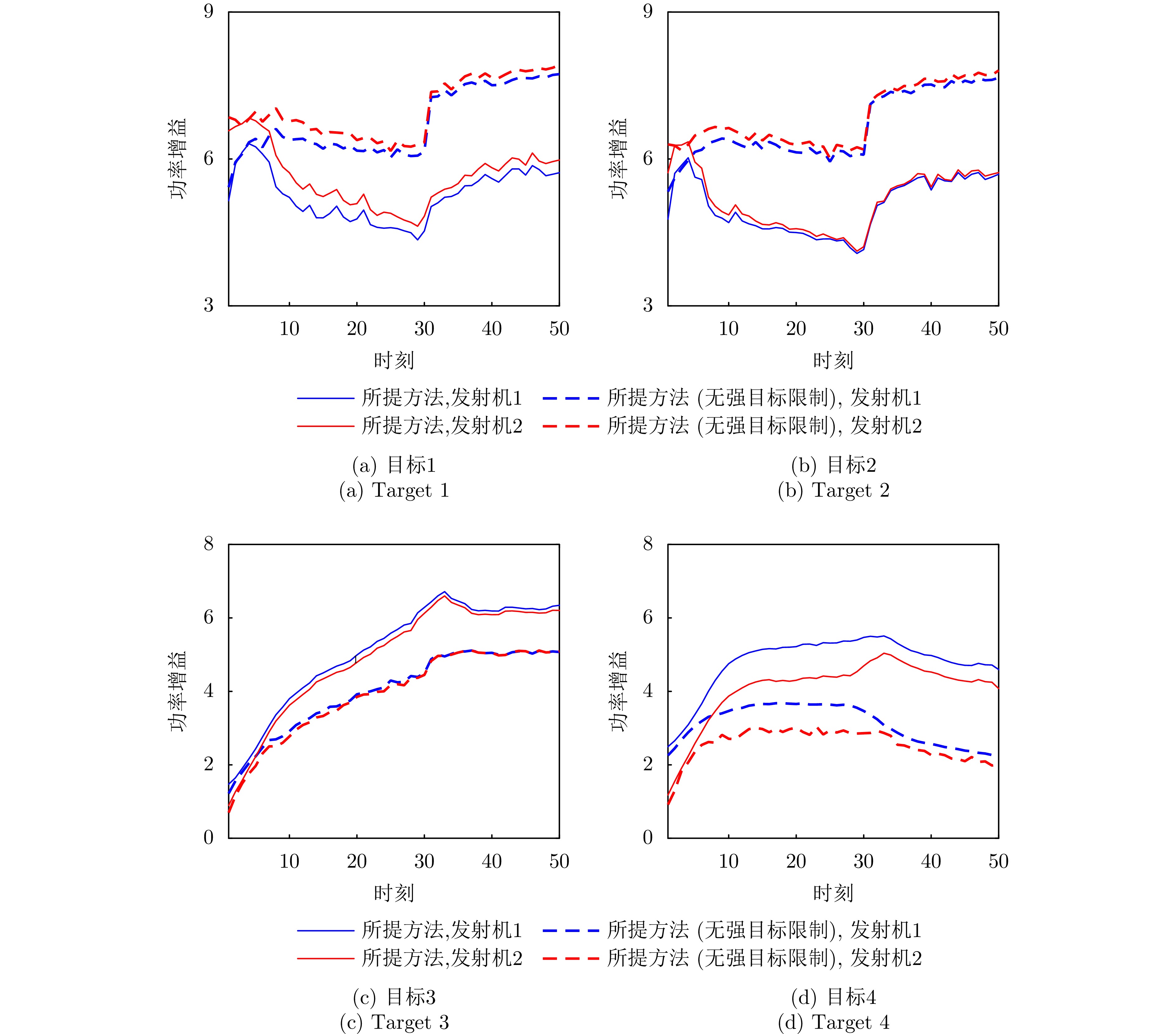
- Figure 9. Comparison of the power gain variations on the four targets
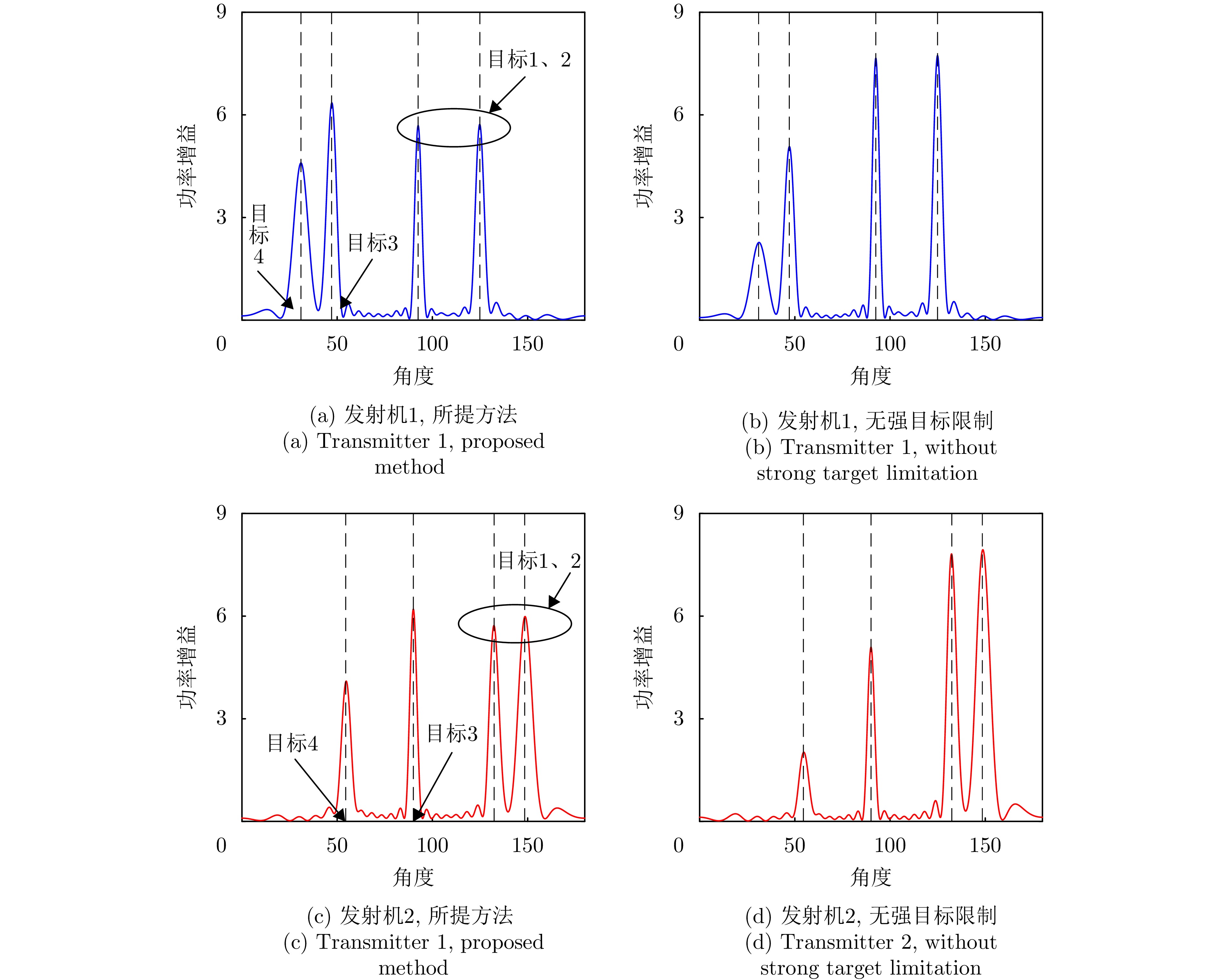
- Figure 10. Comparison of beampatterns at the final time
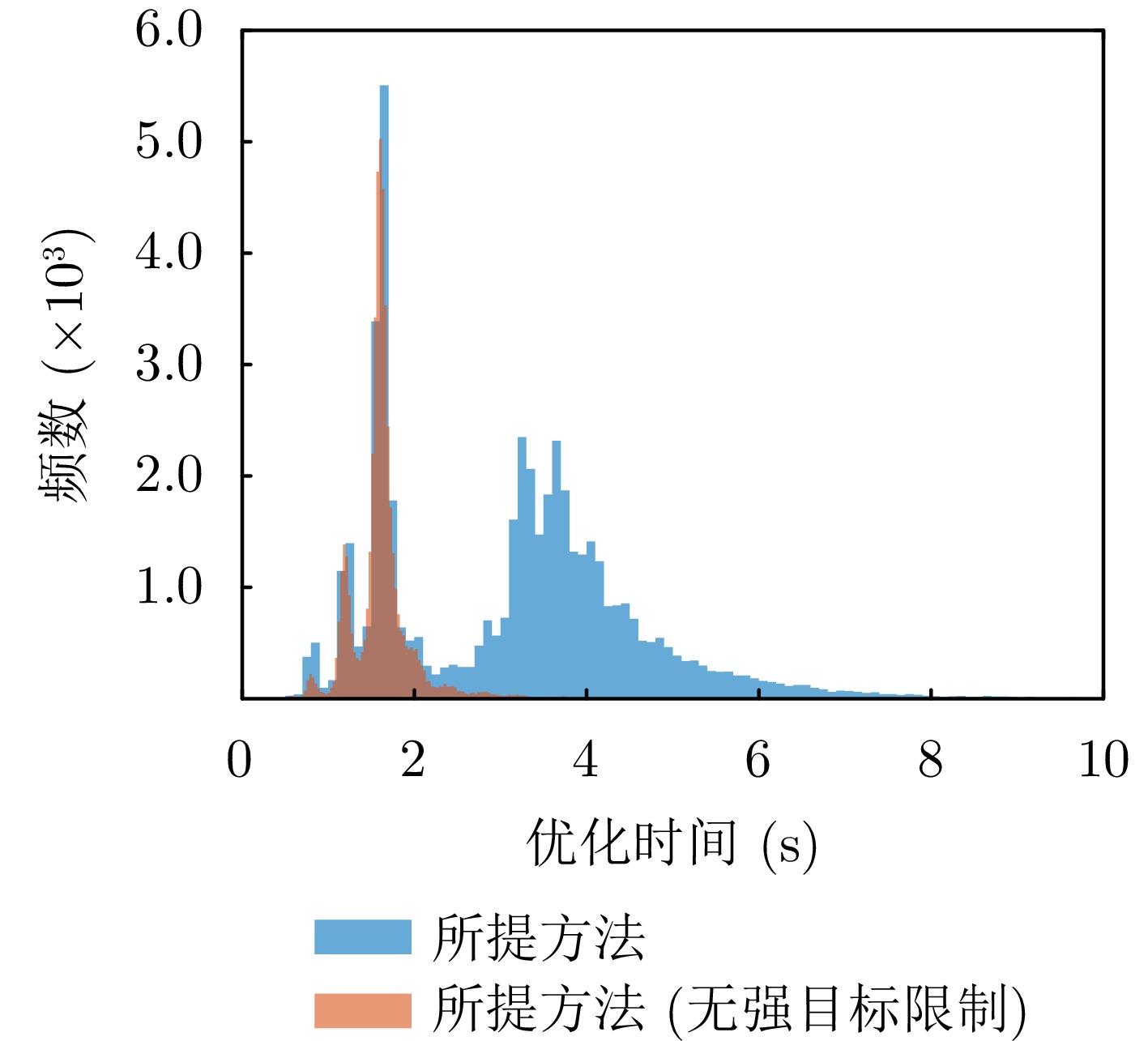
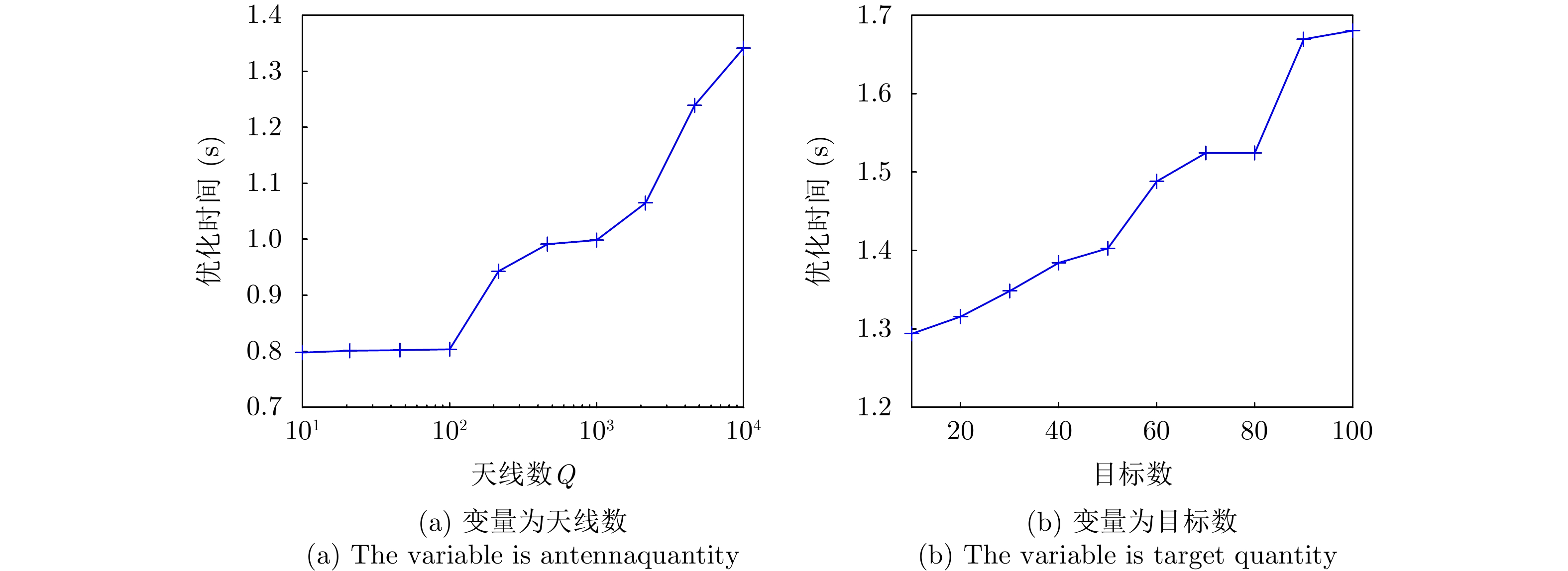
- Figure 11. Comparison of optimization time
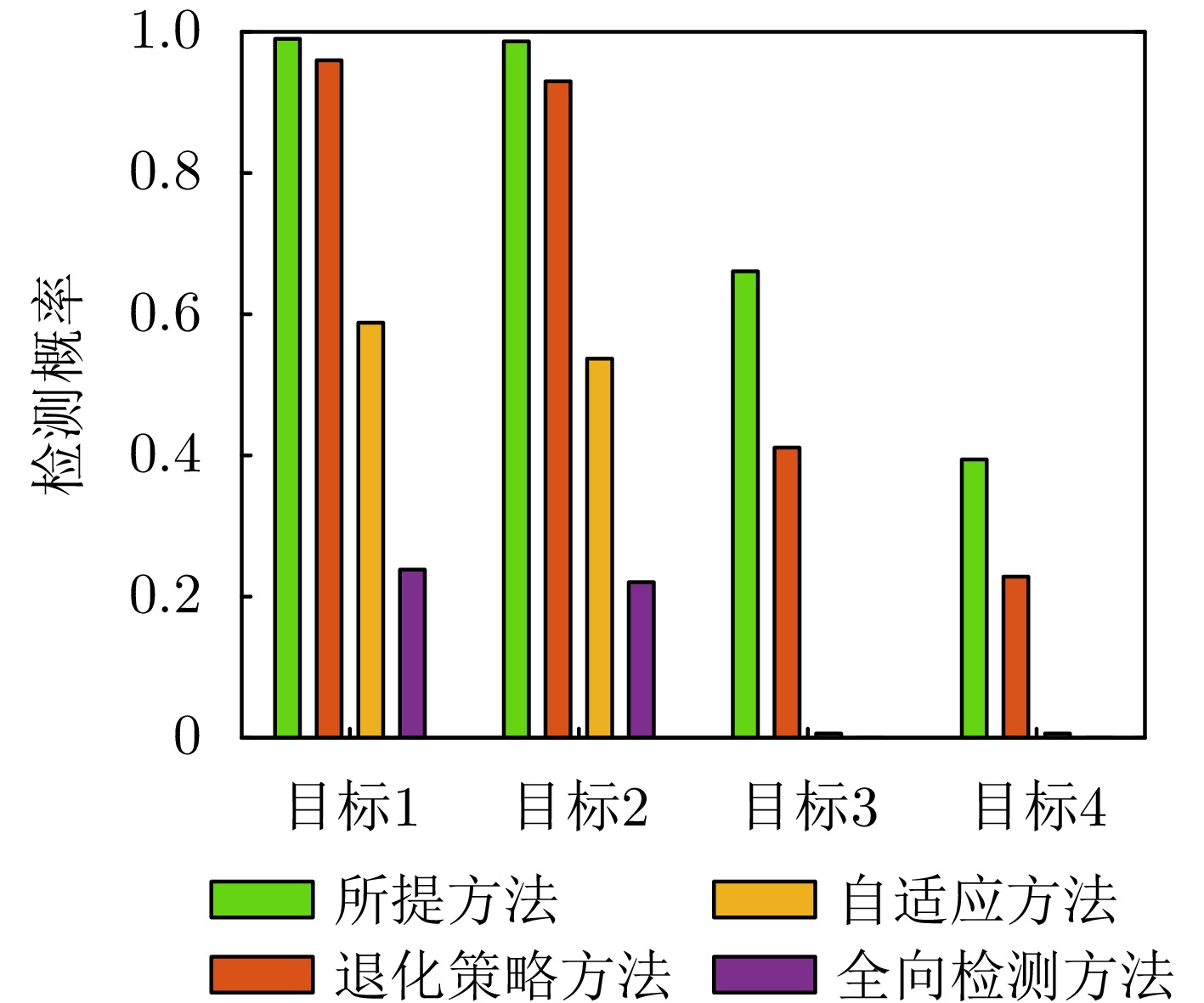
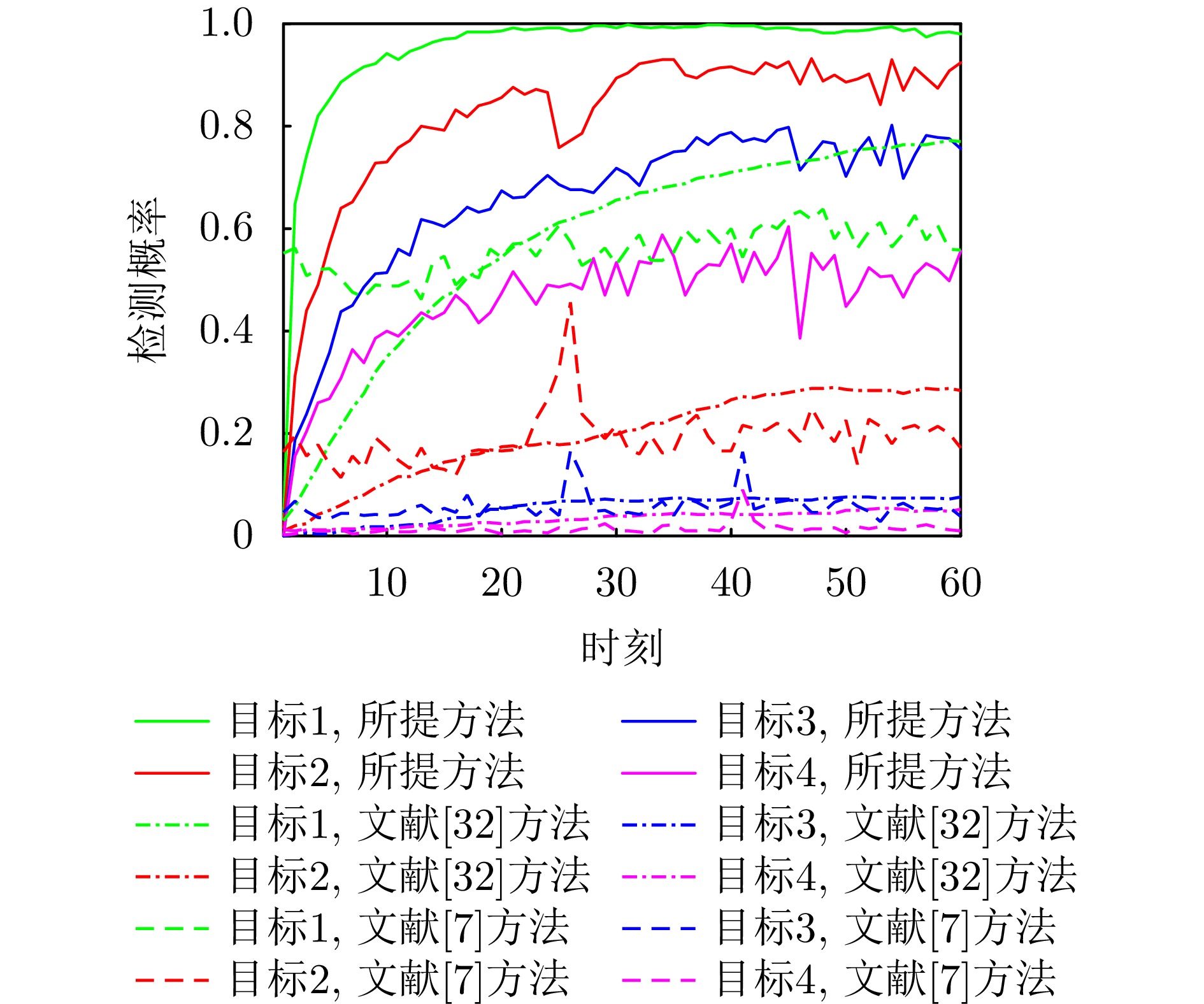
- Figure 12. Comparison of detection probabilities between the proposed method and the compared methods
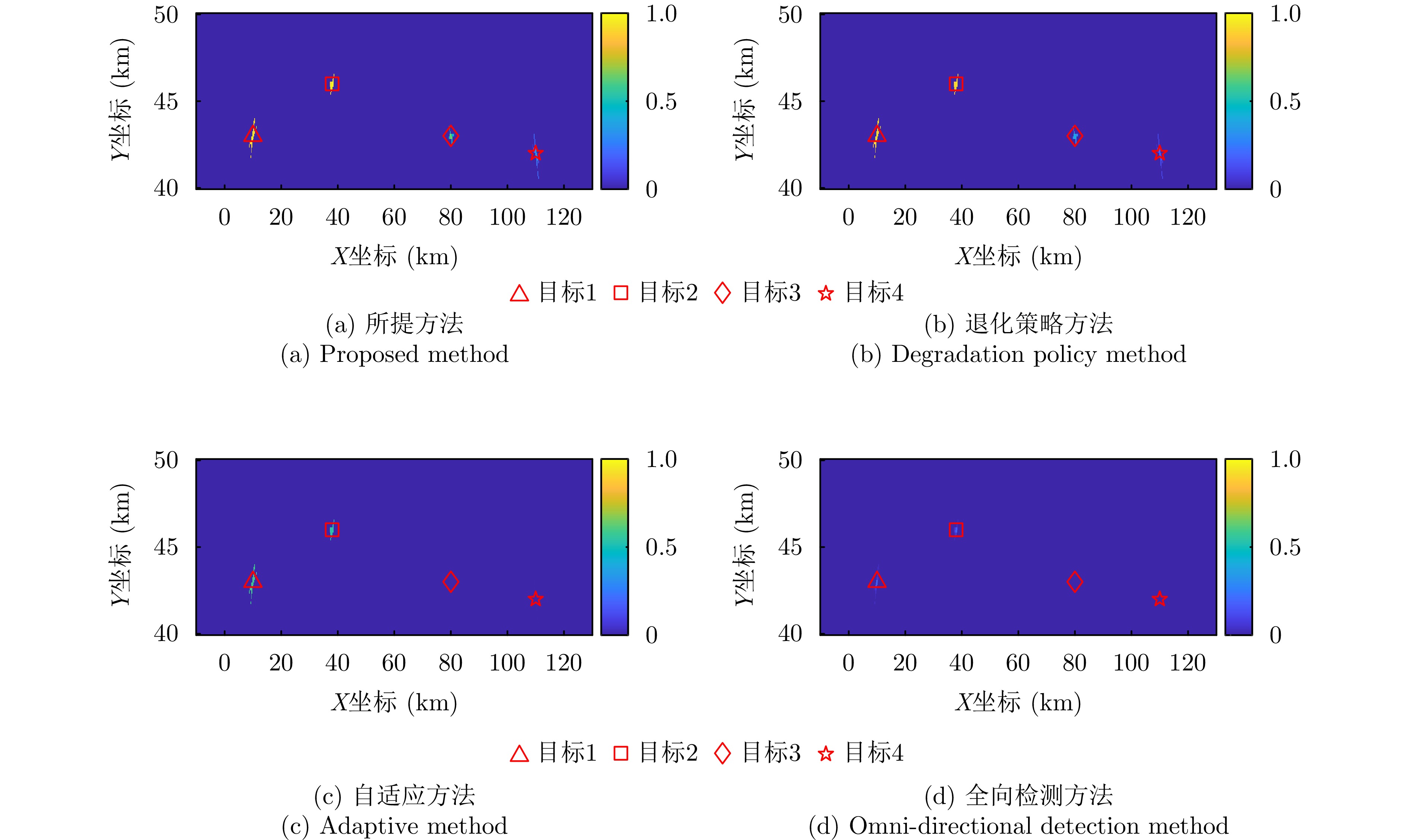
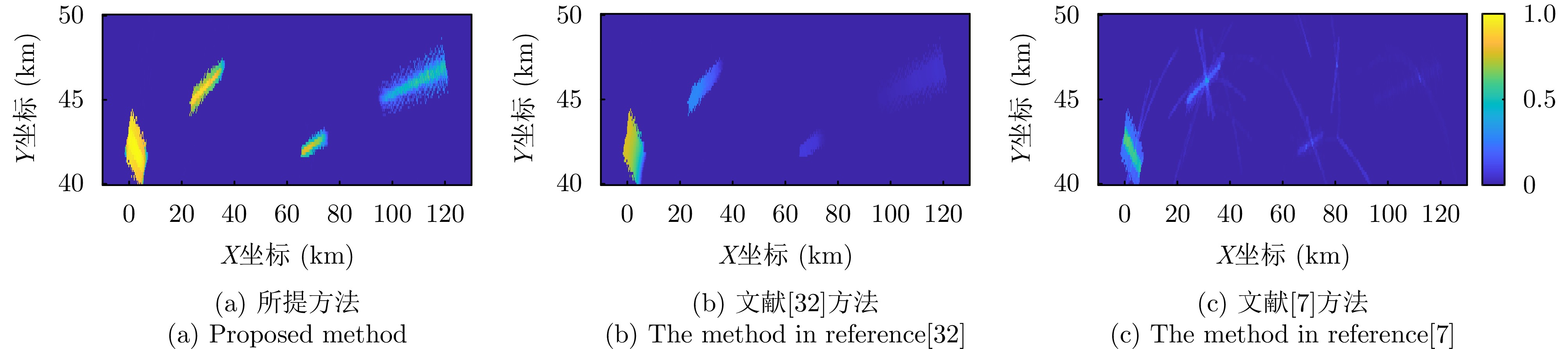
- Figure 13. Comparison of detection result images at the final time
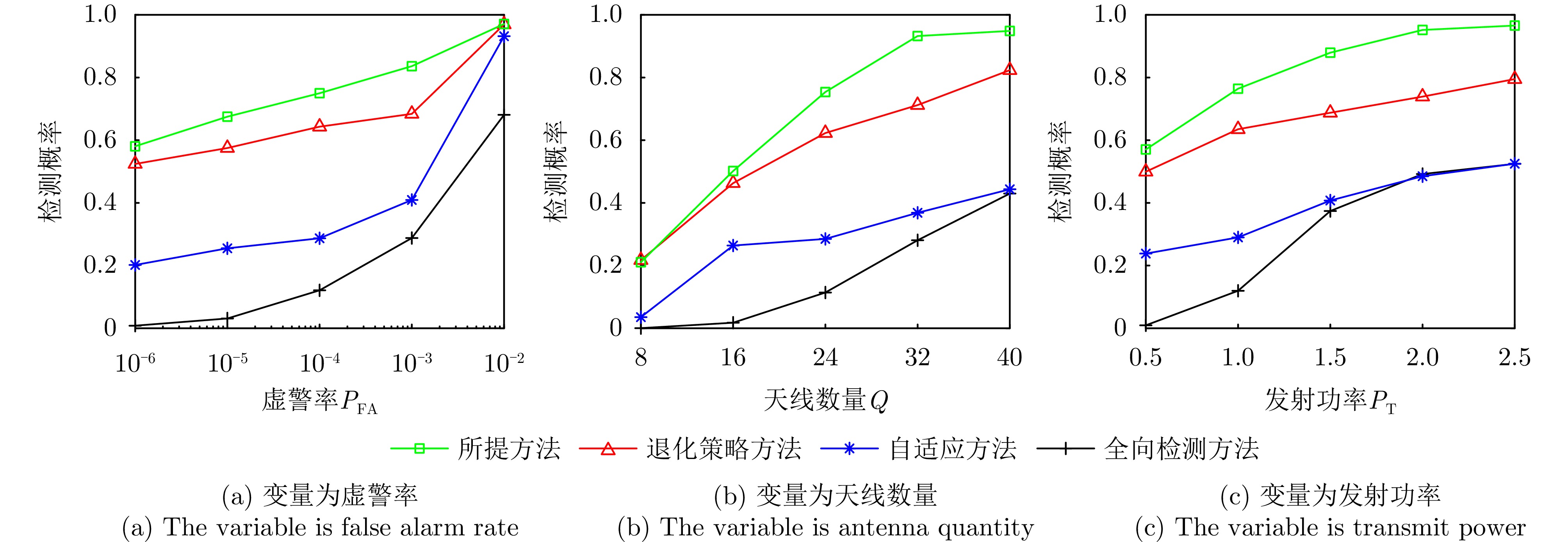
- Figure 14. Comparison of performance change curves
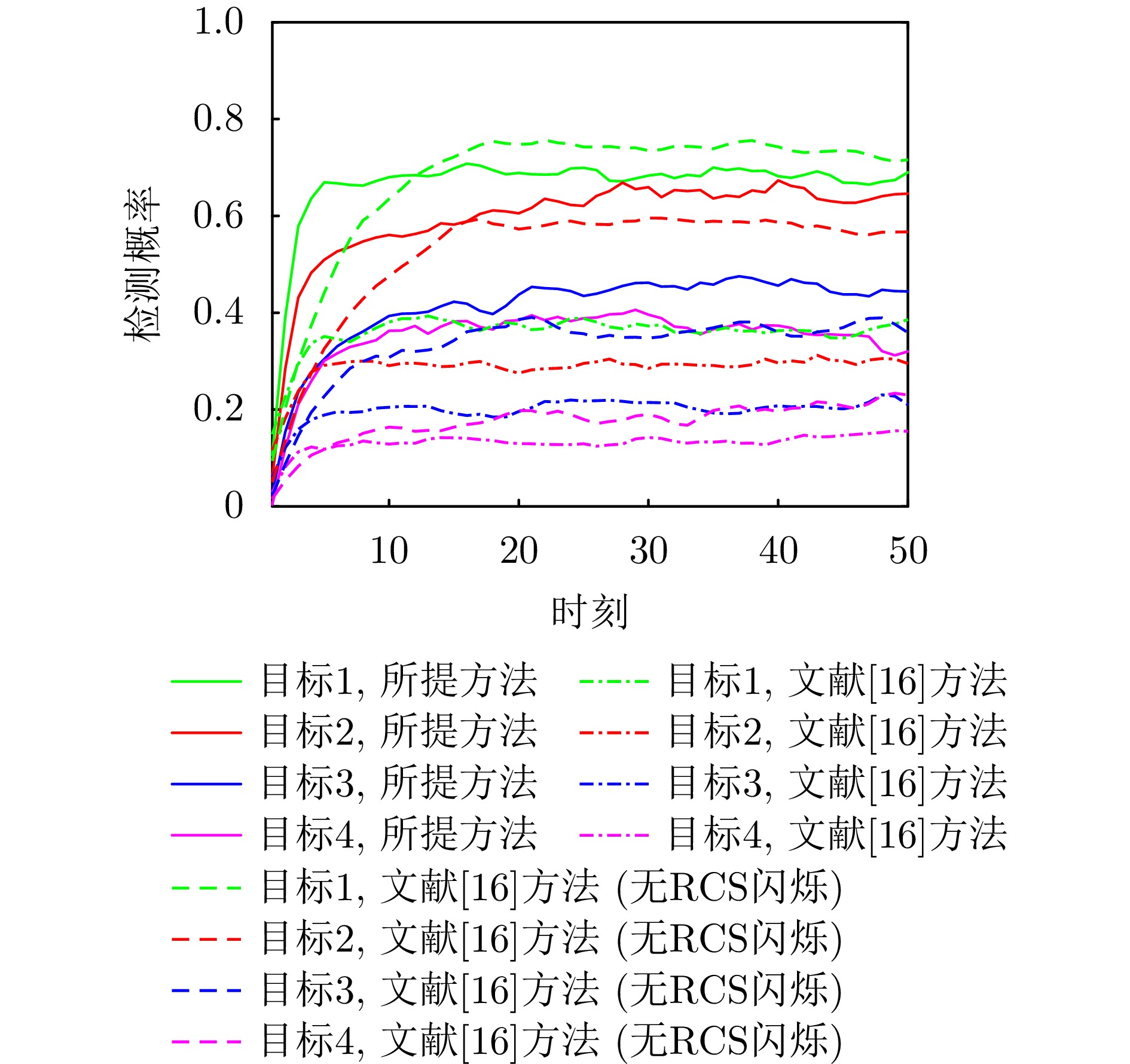
- Figure 15. Comparison of detection probability variation curves under dynamic scenario 1
- Figure 16. Schematic diagram of dynamic scenario 2
- Figure 17. Comparison of detection probability variation curves under dynamic scenario 2
- Figure 18. Comparison of full-time detection result images
- Figure 19. Comparison of detection probability variation curves under dynamic scenario 3
- Figure 1. The solution time curve of the CCA method


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: