- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | ZHOU Zheng, ZHAO Lingjun, HE Qishan, et al. Research progress and prospects of SAR image target detection based on multi-source information cross-domain learning[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25205 |
Research Progress and Prospects of SAR Image Target Detection Based on Multi-source Information Cross-domain Learning
DOI: 10.12000/JR25205 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25205
More Information-
Abstract
Deep learning is primarily used for target detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images; however, its performance heavily relies on large-scale labeled datasets. The detection performance of deep learning models degrades when applied to SAR data with varying distributions, hindering their real-world applicability. In addition, manual labeling of SAR data is costly. Hence, cross-domain learning strategies based on multisource information are being explored to address these challenges. These strategies can assist detection models in realizing cross-domain knowledge migration by integrating prior information from optical remote sensing images or heterogeneous SAR images acquired from different sensors. This paper focuses on cross-domain learning technologies within the deep learning framework. In addition, it provides a systematic overview of the latest research progress in this field and analyzes the core issues, advantages, and applicable scenarios of existing technologies from a methodological perspective. It outlines future research directions based on the law of technological evolution, aiming to offer theoretical support and methodological references to enhance the generalizability of target detection in SAR images. -

-
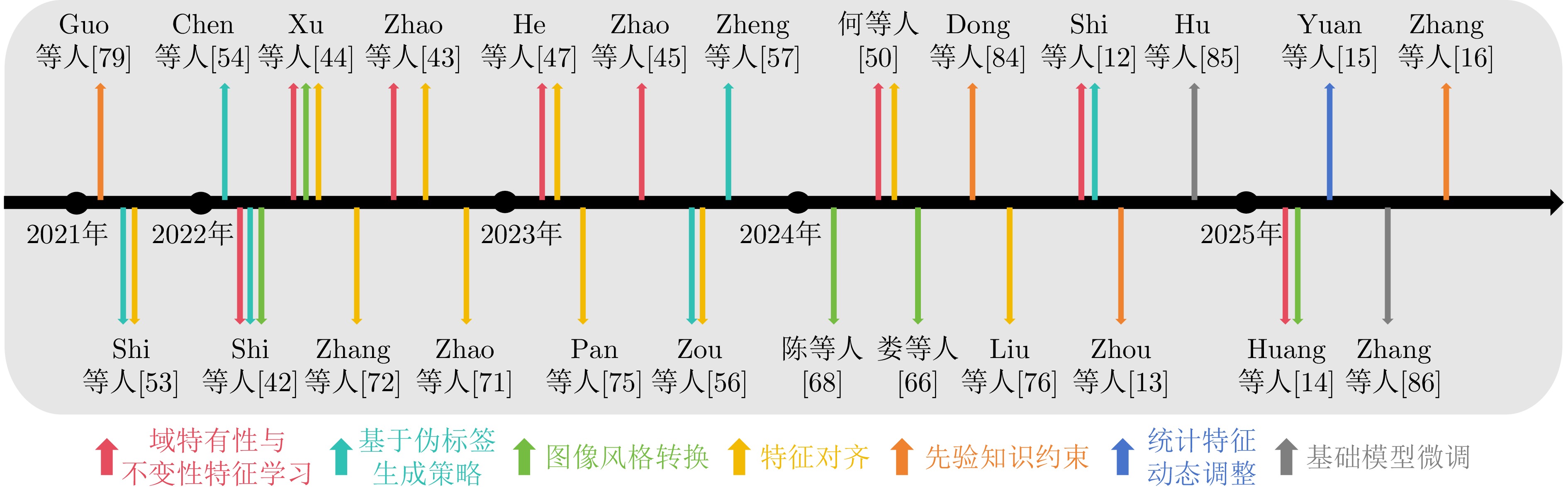
References
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301.[2] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 从物理智能到微波视觉[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004.XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004.[3] 江碧涛. 我国空间对地观测技术的发展与展望[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1153–1159. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220199.JIANG Bitao. The development and prospect of China’s space earth observation technology[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1153–1159. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220199.[4] 关键. 雷达海上目标特性综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114.GUAN Jian. Summary of marine radar target characteristics[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114.[5] TANG Gang, ZHUGE Yichao, CLARAMUNT C, et al. N-YOLO: A SAR ship detection using noise-classifying and complete-target extraction[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(5): 871. doi: 10.3390/rs13050871.[6] PELICH R, CHINI M, HOSTACHE R, et al. Large-scale automatic vessel monitoring based on dual-polarization Sentinel-1 and AIS data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1078. doi: 10.3390/rs11091078.[7] 赵琰, 赵凌君, 匡纲要. 基于注意力机制特征融合网络的SAR图像飞机目标快速检测[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(9): 1665–1674. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200486.ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, and KUANG Gangyao. Attention feature fusion network for rapid aircraft detection in SAR images[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(9): 1665–1674. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200486.[8] LI Weijie, YANG Wei, HOU Yuenan, et al. SARATR-X: Toward building a foundation model for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2025, 34: 869–884. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2025.3531988.[9] ZHOU Jie, LIU Yongxiang, PENG Bowen, et al. MaDiNet: Mamba diffusion network for SAR target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(11): 10787–10800. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3574657.[10] FRANCESCHETTI G, IODICE A, RICCIO D, et al. SAR raw signal simulation for urban structures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(9): 1986–1995. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.814626.[11] FORNARO G. Trajectory deviations in airborne SAR: Analysis and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(3): 997–1009. doi: 10.1109/7.784069.[12] SHI Yu, LI Yi, DU Lan, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptative SAR target detection based on feature decomposition and uncertainty-guided self-training[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 20265–20283. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3486922.[13] ZHOU Zheng, ZHAO Lingjun, JI Kefeng, et al. A domain-adaptive few-shot SAR ship detection algorithm driven by the latent similarity between optical and SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5216318. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3421512.[14] HUANG Hailiang, GUO Jingchao, LIN Huangxing, et al. Domain adaptive oriented object detection from optical to SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5200314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3515161.[15] YUAN Yuxuan, TANG Luyao, XU Ying, et al. Filling and disentanglement: Toward low- and high-order parallel single-domain generalization for SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 3668–3682. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3489572.[16] ZHANG Xianghui, ZHANG Siqian, SUN Zhongzhen, et al. Cross-sensor SAR image target detection based on dynamic feature discrimination and center-aware calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5209417. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3559618.[17] ZHAO Siyuan, KANG Yong, YUAN Hang, et al. FsDAOD: Few-shot domain adaptation object detection for heterogeneous SAR image[J]. Science of Remote Sensing, 2025, 11: 100202. doi: 10.1016/j.srs.2025.100202.[18] PATEL V M, GOPALAN R, LI Ruonan, et al. Visual domain adaptation: A survey of recent advances[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2015, 32(3): 53–69. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2347059.[19] WANG Mei and DENG Weihong. Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 312: 135–153. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.083.[20] ZHUANG Fuzhen, QI Zhiyuan, DUAN Keyu, et al. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(1): 43–76. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.3004555.[21] TOLDO M, MARACANI A, MICHIELI U, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation in semantic segmentation: A review[J]. Technologies, 2020, 8(2): 35. doi: 10.3390/technologies8020035.[22] ZHAO Sicheng, YUE Xiangyu, ZHANG Shanghang, et al. A review of single-source deep unsupervised visual domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(2): 473–493. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3028503.[23] OZA P, SINDAGI V A, VS V, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation of object detectors: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(6): 4018–4040. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3217046.[24] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91.[25] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.[26] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826.[27] SUN Zhongzhen, LENG Xiangguang, LEI Yu, et al. BiFA-YOLO: A novel YOLO-based method for arbitrary-oriented ship detection in high-resolution SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(21): 4209. doi: 10.3390/rs13214209.[28] ZHOU Zheng, CHEN Jie, HUANG Zhixiang, et al. HRLE-SARDet: A lightweight SAR target detection algorithm based on hybrid representation learning enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5203922. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3251694.[29] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. The 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.81.[30] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. The 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169.[31] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031.[32] LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. The 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934.[33] LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, LENG Xiangguang, et al. Squeeze and excitation rank Faster R-CNN for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(5): 751–755. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2882551.[34] JIAO Jiao, ZHANG Yue, SUN Hao, et al. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20881–20892. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2825376.[35] CHEN Shiqi, ZHAN Ronghui, and ZHANG Jun. Robust single stage detector based on two-stage regression for SAR ship detection[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Innovation in Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 2018: 169–174. doi: 10.1145/3194206.3194223.[36] WEI Shunjun, SU Hao, MING Jing, et al. Precise and robust ship detection for high-resolution SAR imagery based on HR-SDNet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 167. doi: 10.3390/rs12010167.[37] CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988.[38] ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, XIONG Boli, et al. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2738–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997081.[39] WANG Shiyu, CAI Zhanchuan, and YUAN Jieyu. Automatic SAR ship detection based on multifeature fusion network in spatial and frequency domains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4102111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3267495.[40] PAN Dece, GAO Xin, DAI Wei, et al. SRT-Net: Scattering region topology network for oriented ship detection in large-scale SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5202318. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3351366.[41] ZHANG Chongqi, DENG Yao, CHONG Mingzhe, et al. Entropy-based re-sampling method on SAR class imbalance target detection[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 209: 432–447. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.02.019.[42] SHI Yu, DU Lan, GUO Yuchen, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation based on progressive transfer for ship detection: From optical to SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5230317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3185298.[43] ZHAO Siyuan, LUO Ying, ZHANG Tao, et al. A feature decomposition-based method for automatic ship detection crossing different satellite SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5234015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3201628.[44] XU Chujie, ZHENG Xiangtao, and LU Xiaoqiang. Multi-level alignment network for cross-domain ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(10): 2389. doi: 10.3390/rs14102389.[45] ZHAO Siyuan, LUO Ying, ZHANG Tao, et al. A domain specific knowledge extraction transformer method for multisource satellite-borne SAR images ship detection[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 198: 16–29. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.02.011.[46] YUAN Yuxuan, RAO Zhijie, LIN Chuyang, et al. Adaptive ship detection from optical to SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3508205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3317321.[47] HE Jiayue, SU Nan, XU Congan, et al. A cross-modality feature transfer method for target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5213615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3300536.[48] SHI Yu, DU Lan, GUO Yuchen, et al. Optical knowledge assisted unsupervised cross-domain SAR target detection[J]. IET Conference Proceedings, 2024, 2023(47): 1474–1480. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1303.[49] ZHANG Ruixiang, WANG Yuxuan, LI Haoyuan, et al. Decoupled multi-teacher: Cross-modal learning enhanced object detection in SAR imagery[C]. IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 7858–7862. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10641529.[50] 何佳月, 宿南, 徐从安, 等. 从光学到SAR: 基于多级跨模态对齐的SAR图像舰船检测算法[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(7): 1789–1801. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20243249.HE Jiayue, SU Nan, XU Congan, et al. From optical to SAR: A SAR ship detection algorithm based on multi-level cross-modality alignment[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(7): 1789–1801. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20243249.[51] ZHAO Xiaolin, ZHAO Siyuan, LUO Ying, et al. Generalizing SAR object detection: A unified framework for cross-source scenarios[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2025, 22: 4009105. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2025.3575173.[52] SHI Yu, DU Lan, and GUO Yuchen. Unsupervised domain adaptation for SAR target detection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6372–6385. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3089238.[53] SHI Yu, DU Lan, GUO Yuchen, et al. Cross sensor transfer learning for unsupervised SAR target detection[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 2082–2086. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028188.[54] CHEN Shiqi, ZHAN Ronghui, WANG Wei, et al. Domain adaptation for semi-supervised ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4507405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3171789.[55] ZHANG Tingting, LOU Xin, WANG Han, et al. Context-preserving region-based contrastive learning framework for ship detection in SAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2023, 95(1): 3–12. doi: 10.1007/s11265-022-01799-8.[56] ZOU Bin, QIN Jiang, and ZHANG Lamei. Cross-scene target detection based on feature adaptation and uncertainty-aware pseudo-label learning for high resolution SAR images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 200: 173–190. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.05.009.[57] ZHENG Xiangtao, CUI Haowen, XU Chujie, et al. Dual teacher: A semisupervised cotraining framework for cross-domain ship detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5613312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3287863.[58] ZHANG Xin and ZHAO Siyuan. A domain adaptation detector for heterogenous SAR image object detection[J]. IET Conference Proceedings, 2024, 2023(47): 3215–3218. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1613.[59] CHEN Xi, WANG Zhirui, WANG Wenhao, et al. CroMoDa: Unsupervised oriented SAR ship detection via cross-modality distribution alignment[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 11899–11914. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3420901.[60] LOU Xin and WANG Han. Object detection in SAR via generative knowledge transfer[C]. 2021 IEEE 31st International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Gold Coast, Australia, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/MLSP52302.2021.9596254.[61] PU Xinyang, JIA Hecheng, XIN Yu, et al. Ship detection in low-quality SAR images via an unsupervised domain adaption method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(13): 3326. doi: 10.3390/rs15133326.[62] PU Xinyang, JIA Hecheng, and XU Feng. Cross-domain SAR ship detection in strong interference environment based on image-to-image translation[C]. IGARSS 2023 - 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 1798–1801. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282746.[63] YU Wenbo, WANG Zijian, LI Jiamu, et al. Unsupervised aircraft detection in SAR images with image-level domain adaption from optical images[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Analysis (ICCPA 2023), Hangzhou, China, 2023. doi: 10.1117/12.2684516.[64] YU Wenbo, LI Jiamu, WANG Zijian, et al. Boosting SAR aircraft detection performance with multi-stage domain adaptation training[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(18): 4614. doi: 10.3390/rs15184614.[65] YANG Yanrui, CHEN Jie, SUN Long, et al. Unsupervised domain-adaptive SAR ship detection based on cross-domain feature interaction and data contribution balance[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(2): 420. doi: 10.3390/rs16020420.[66] 娄欣, 王晗, 卢昊, 等. 生成式知识迁移的SAR舰船检测[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(2): 470–480. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211354.LOU Xin, WANG Han, LU Hao, et al. SAR ship detection through generative knowledge transfer[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(2): 470–480. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20211354.[67] WU Baolong, WANG Haonan, ZHANG Cunle, et al. Optical-to-SAR translation based on CDA-GAN for high-quality training sample generation for ship detection in SAR amplitude images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(16): 3001. doi: 10.3390/rs16163001.[68] 陈亮, 李健昊, 何成, 等. 多域特征引导的无监督SAR图像舰船检测方法[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2024, 41(3): 121–129. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096-8655.2024.03.013.CHEN Liang, LI Jianhao, HE Cheng, et al. A multi-domain feature-guided method for unsupervised ship detection in SAR images[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 2024, 41(3): 121–129. doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096-8655.2024.03.013.[69] LUO Cheng, ZHANG Yueting, GUO Jiayi, et al. SAR-CDSS: A semi-supervised cross-domain object detection from optical to SAR domain[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(6): 940. doi: 10.3390/rs16060940.[70] ZHU Ya’nan, AI Jiaqiu, XUE Weibao, et al. Cross-modal ship detection from optical to SAR images based on pixel- and feature-level progressive transfer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(8): 13344–13356. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3543520.[71] ZHAO Siyuan, ZHANG Zenghui, GUO Weiwei, et al. An automatic ship detection method adapting to different satellites SAR images with feature alignment and compensation loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3160727.[72] ZHANG Jun, LI Simin, DONG Yongfeng, et al. Hierarchical similarity alignment for domain adaptive ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5240611. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3227626.[73] 宋玉成, 李景润, 田甜, 等. 跨模态域自适应SAR图像舰船检测与识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 50(11): 107–113. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.221113.SONG Yucheng, LI Jingrun, TIAN Tian, et al. Ship detection and recognition in SAR images with cross-modality domain adaption[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2022, 50(11): 107–113. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.221113.[74] JEONG S, KIM Y, KIM S, et al. Enriching SAR ship detection via multistage domain alignment[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4018905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3115498.[75] PAN Bin, XU Zhehao, SHI Tianyang, et al. An imbalanced discriminant alignment approach for domain adaptive SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5108111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3303507.[76] LIU Shuang, LI Dong, WAN Jun, et al. Source-assisted hierarchical semantic calibration method for ship detection across different satellite SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5215221. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3419025.[77] HU Kaiou, WAN Hongjie, and MA Fei. Cross-domain SAR detection method based on salient object alignment[J]. IET Conference Proceedings, 2024, 2023(47): 3347–3351. doi: 10.1049/icp.2024.1638.[78] LIAO Leiyao, DU Lan, and GUO Yuchen. Semi-supervised SAR target detection based on an improved Faster R-CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 14(1): 143. doi: 10.3390/rs14010143.[79] GUO Yuchen, DU Lan, and LYU Guoxin. SAR target detection based on domain adaptive Faster R-CNN with small training data size[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(21): 4202. doi: 10.3390/rs13214202.[80] WANG Xu, ZHOU Huaji, CHEN Zheng, et al. Few-shot SAR ship image detection using two-stage cross-domain transfer learning[C]. IGARSS 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2195–2198. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883172.[81] QIN Jiang, ZOU Bin, ZHANG Lamei, et al. Domain adaptive target detection with optimal transportation for different satellite SAR images[C]. EUSAR 2024; 15th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Munich, Germany, 2024: 498–502.[82] CHAN Haopeng, QIU Xiaolan, GAO Xin, et al. A complex background SAR ship target detection method based on fusion tensor and cross-domain adversarial learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(18): 3492. doi: 10.3390/rs16183492.[83] LIAO Leiyao. Semi-supervised SAR target detection with cross-domain transfer learning based on YOLOv5[C]. IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 7401–7404. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10641642.[84] DONG Jun, FENG Jiewen, and TANG Xiaoyu. OptiSAR-Net: A cross-domain ship detection method for multisource remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4709311. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3502447.[85] HU Kaiou, WAN Hongjie, MA Fei, et al. Cross-domain SAR object detection by efficiently fine-tuning SAM[C]. 2024 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Chengdu, China, 2024: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/PIERS62282.2024.10618373.[86] ZHANG Chaochen, CHEN Jie, HUANG Zhongling, et al. SAR image target segmentation guided by the scattering mechanism-based visual foundation model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(7): 1209. doi: 10.3390/rs17071209.[87] ZOU Zhengxia and SHI Zhenwei. Random access memories: A new paradigm for target detection in high resolution aerial remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(3): 1100–1111. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2773199.[88] ZHANG Yuanlin, YUAN Yuan, FENG Yachuang, et al. Hierarchical and robust convolutional neural network for very high-resolution remote sensing object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5535–5548. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2900302.[89] CHEN Ziyi, WANG Cheng, LUO Huan, et al. Vehicle detection in high-resolution aerial images based on fast sparse representation classification and multiorder feature[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(8): 2296–2309. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2016.2517826.[90] LI Ke, WAN Gang, CHENG Gong, et al. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296–307. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.023.[91] LIU Zikun, YUAN Liu, WENG Lubin, et al. A high resolution optical satellite image dataset for ship recognition and some new baselines[C]. The 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods, Porto, Portugal, 2017: 324–331. doi: 10.5220/0006120603240331.[92] XIA Guisong, BAI Xiang, DING Jian, et al. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3974–3983. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00418.[93] ZHANG Zhengning, ZHANG Lin, WANG Yue, et al. ShipRSImageNet: A large-scale fine-grained dataset for ship detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 8458–8472. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3104230.[94] SHERMEYER J, HOGAN D, BROWN J, et al. SpaceNet 6: Multi-sensor all weather mapping dataset[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 768–777. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW50498.2020.00106.[95] SHIN C, KIM S, and KIM Y. From planetscope to worldview: Micro-satellite image super-resolution with optimal transport distance[C]. The 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020: 898–902. doi: 10.1109/ICIP40778.2020.9190810.[96] INVERSION, FAUDI J, and MARTIN. Airbus ship detection challenge[EB/OL]. https://www.kaggle.com/c/airbus-ship-detection, 2018.[97] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, LI Jianwei, et al. SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD): Official release and comprehensive data analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3690. doi: 10.3390/rs13183690.[98] WEI Shunjun, ZENG Xiangfeng, QU Qizhe, et al. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234–120254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005861.[99] SANDIA mini SAR complex imagery[EB/OL]. http://www.sandia.gov/radar/complex-data/index.Html, 2005. Accessed: Apr. 15, 2021.[100] FARADSAR public release data[EB/OL]. 2015. https://www.sandia.gov/radar/complex_data/FARAD_KA_BAND.zip.[101] LEI Songlin, LU Dongdong, QIU Xiaolan, et al. SRSDD-v1.0: A high-resolution SAR rotation ship detection dataset[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5104. doi: 10.3390/rs13245104.[102] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097.SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097.[103] WANG Yuanyuan, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, et al. A SAR dataset of ship detection for deep learning under complex backgrounds[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 765. doi: 10.3390/rs11070765.[104] 陈杰, 黄志祥, 夏润繁, 等. 大规模多类SAR目标检测数据集-1.0[J/OL]. 雷达学报, https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=MSAR, 2022.CHEN Jie, HUANG Zhixiang, XIA Runfan, et al. Large-scale multi-class SAR image target detection dataset-1.0[J/OL]. Journal of Radars, https://radars.ac.cn/web/data/getData?dataType=MSAR, 2022.[105] 徐从安, 苏航, 李健伟, 等. RSDD-SAR: SAR舰船斜框检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 581–599. doi: 10.12000/JR22007.XU Congan, SU Hang, LI Jianwei, et al. RSDD-SAR: Rotated ship detection dataset in SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 581–599. doi: 10.12000/JR22007. -
Proportional views

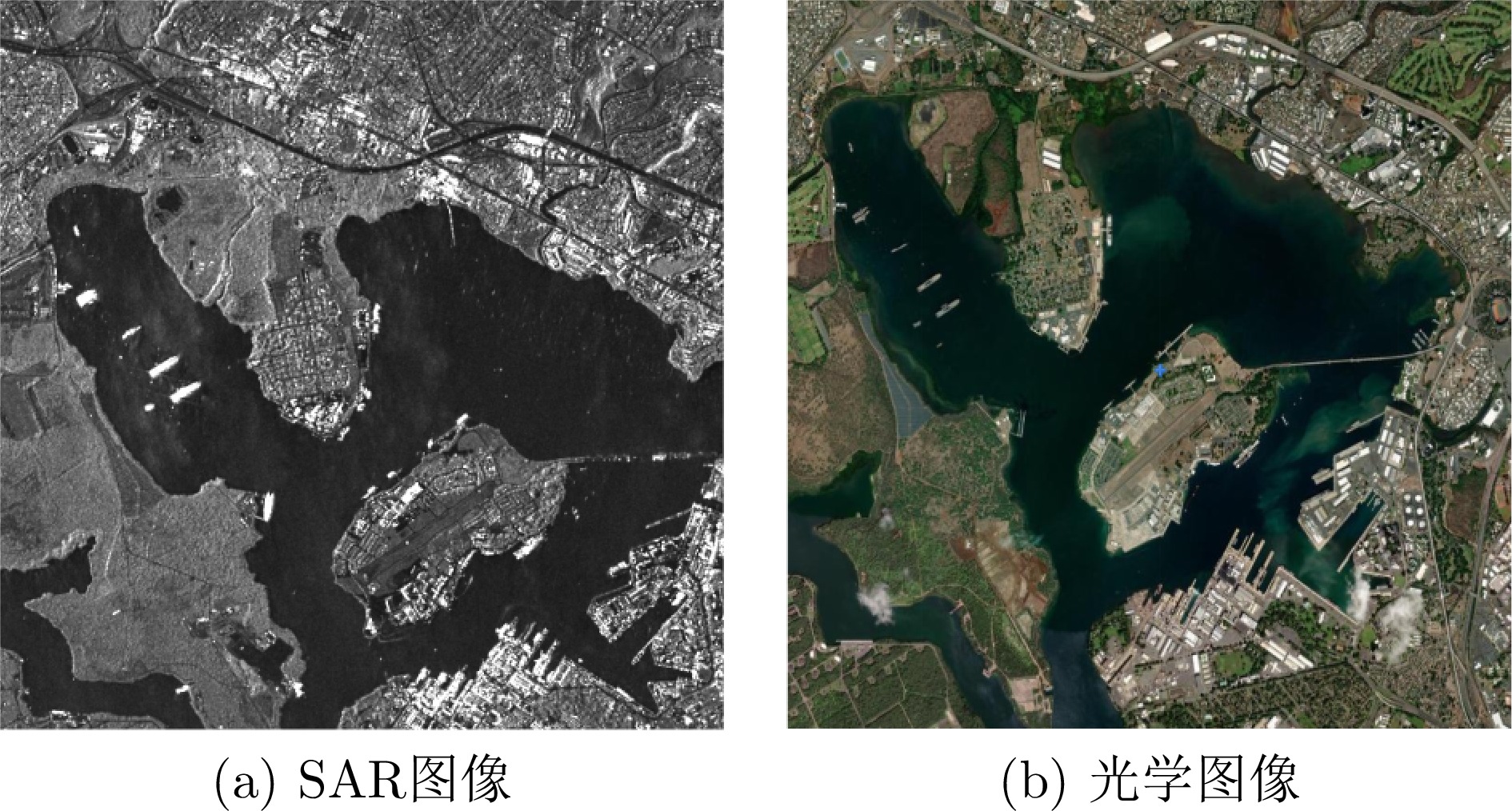
- Figure 1. Comparison between high-resolution SAR images and corresponding optical remote sensing images of a certain port
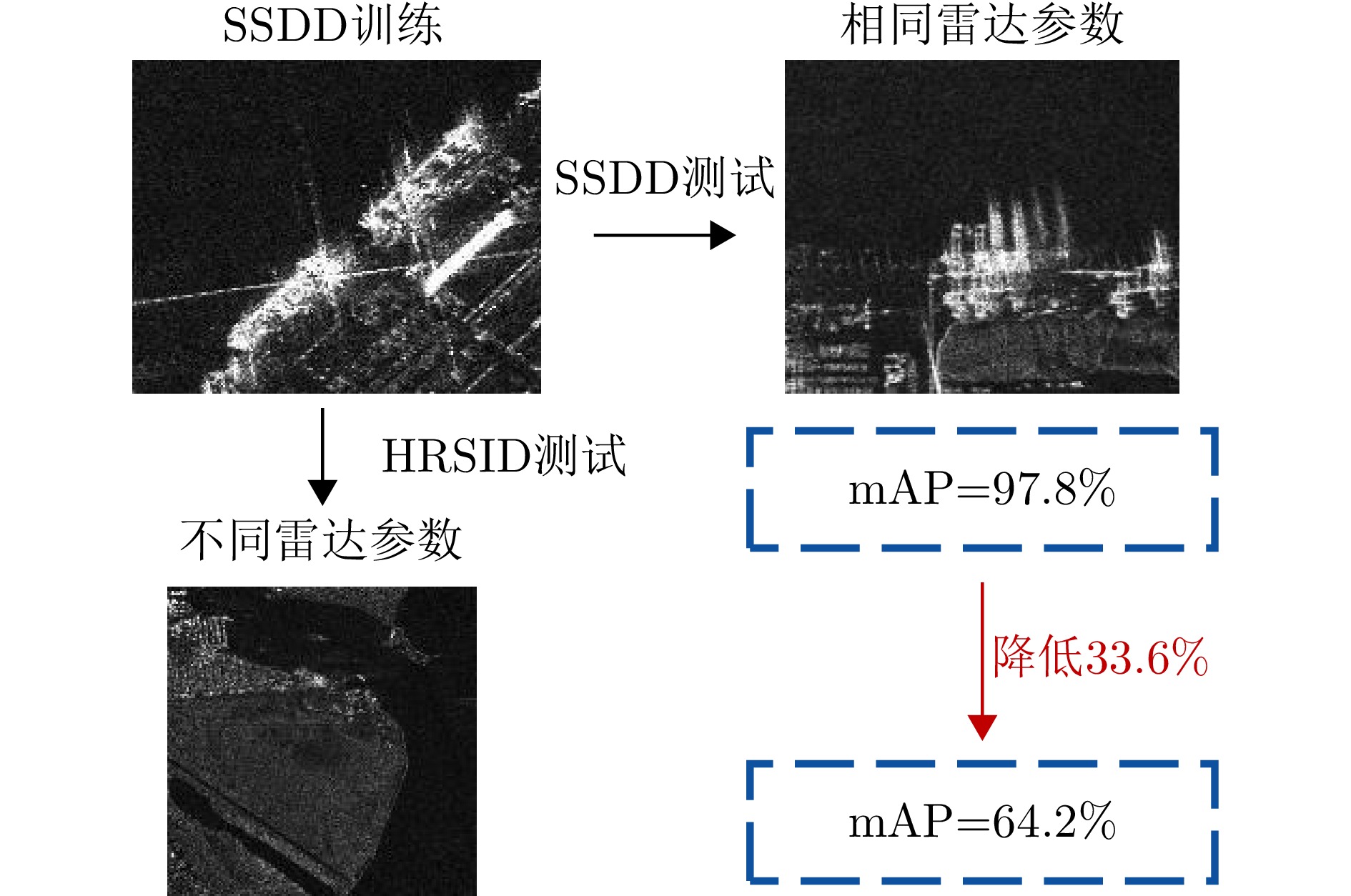
- Figure 2. The influence of different radar parameters on the detection model (YOLOv5n)
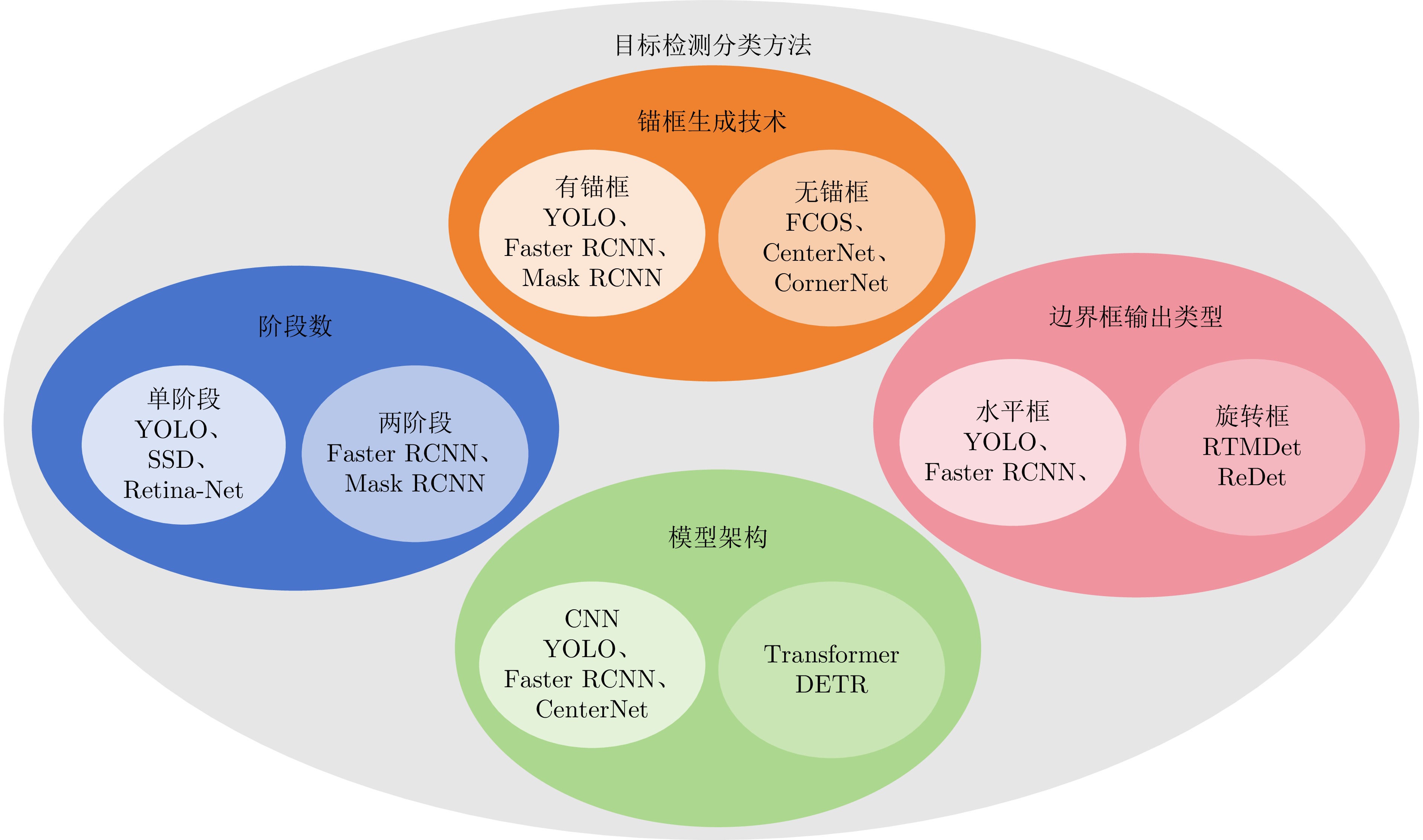
- Figure 3. Different classification methods for target detection
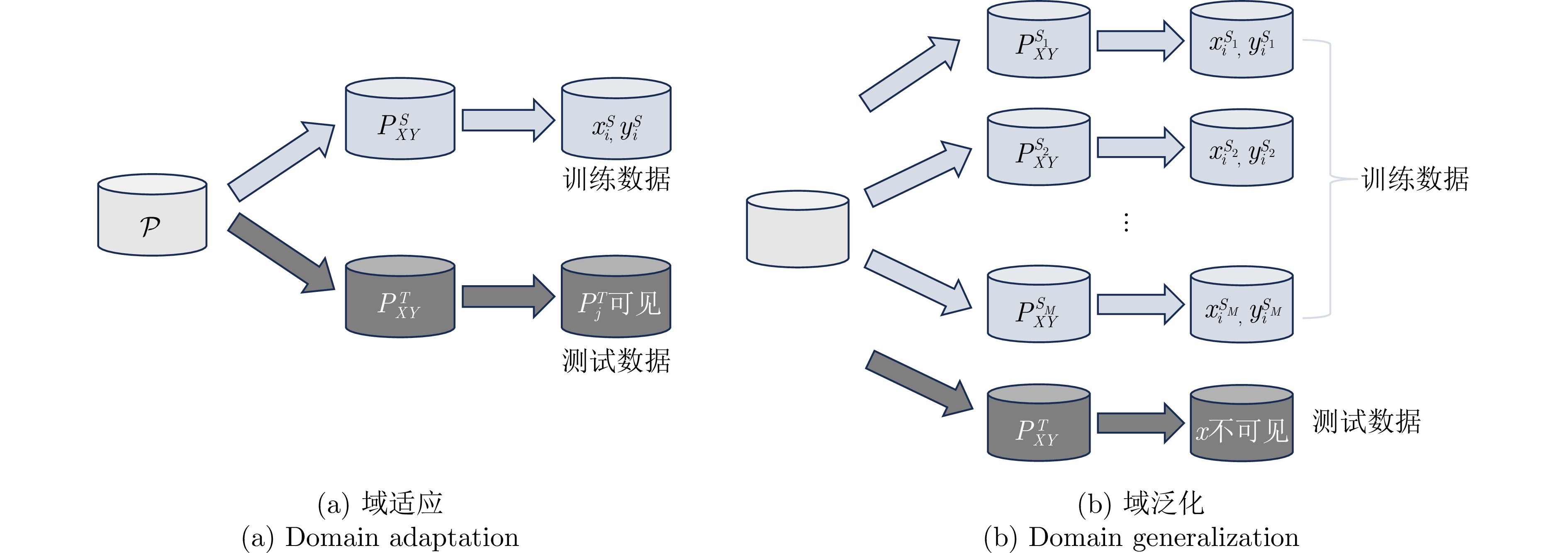
- Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the training and testing process for domain adaptation and domain generalization
- Figure 5. The t-SNE distribution map of SAR ship dataset under different imaging
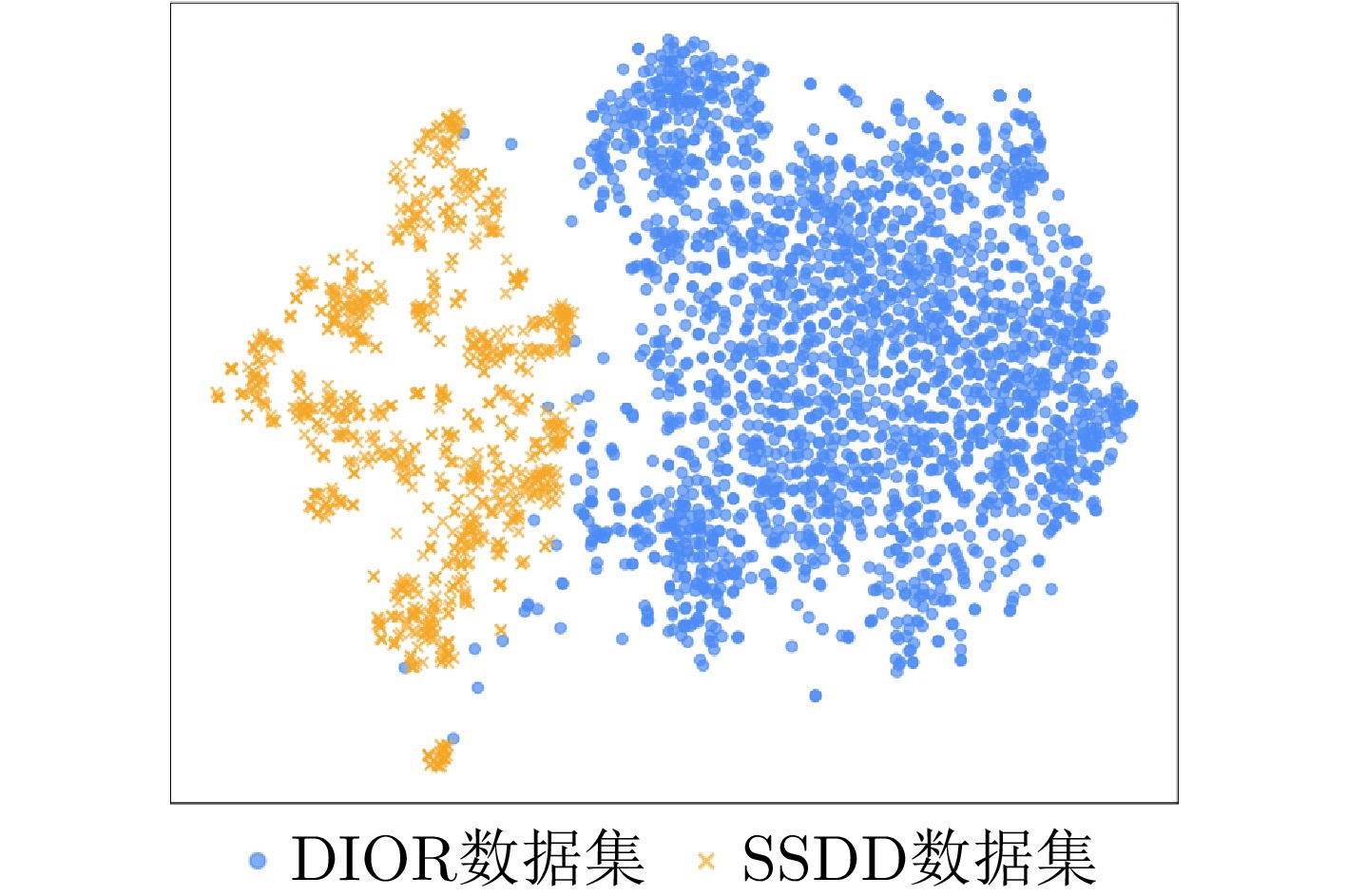
- Figure 6. The t-SNE distribution map of optical and SAR ship datasets
- Figure 7. Schematic diagram of domain specific and invariant feature learning process
- Figure 8. Schematic diagram of pseudo label generation process
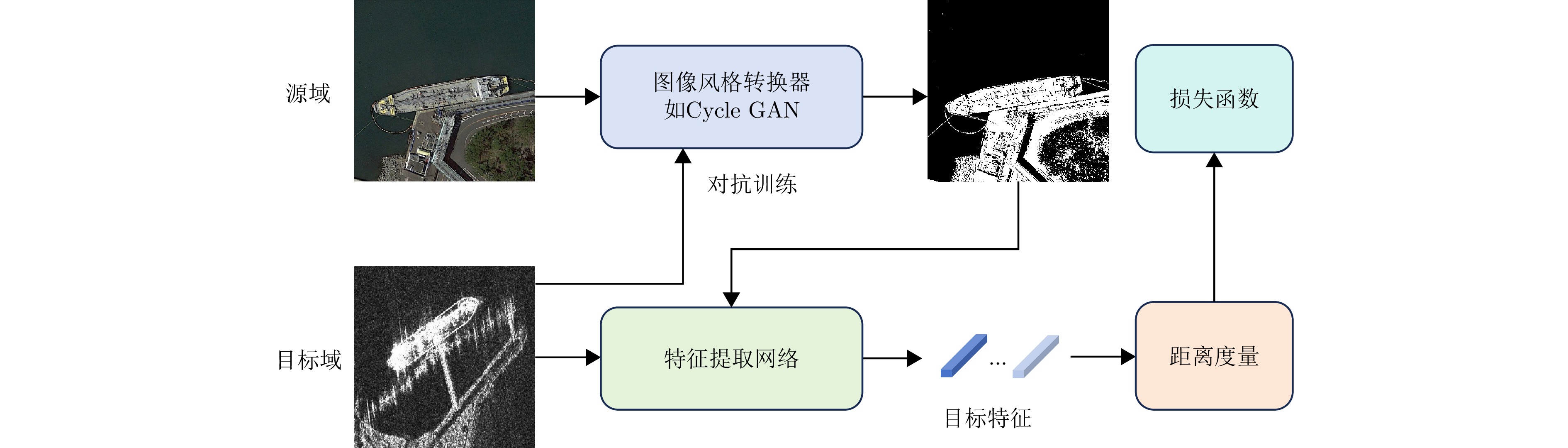
- Figure 9. Schematic diagram of image style conversion process
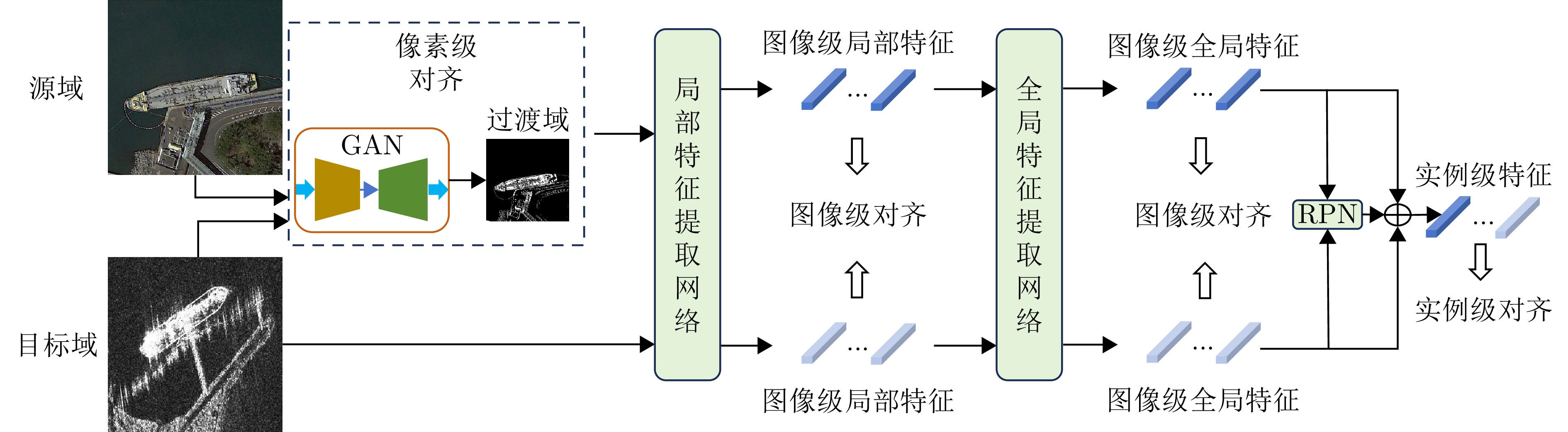
- Figure 10. Schematic diagram of feature alignment process
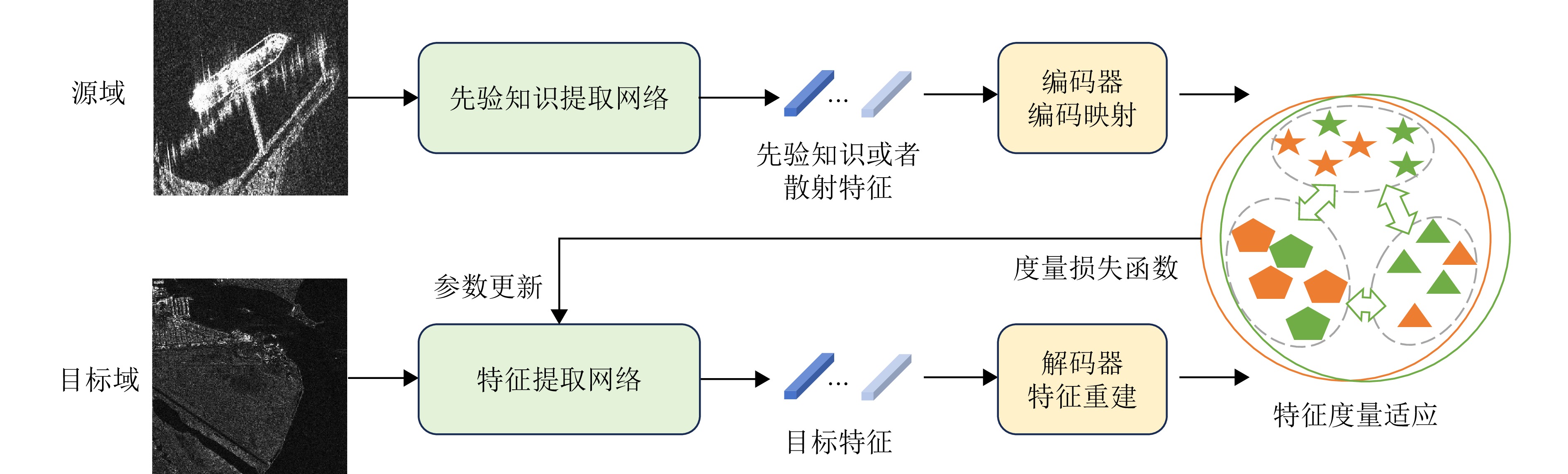
- Figure 11. Schematic diagram of prior knowledge constraint process
- Figure 12. Schematic diagram of dynamic adjustment of statistical features process
- Figure 13. Schematic diagram of the fine-tuning process for large visual foundation models


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: